Parameter Estimation for a Fractional Black–Scholes Model with Jumps from Discrete Time Observations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
- The processes , and are independent;
- ;
- For any , the random variables are independent and identically distributed.
- The expectation of is
- The variance of is
- (i)
- Equation (6) leads to the expectation of conditionally to :Since condition is verified, thenThe independence of and implies that and then
- (ii)
- Similarly, we getso that . □
- If and , then converges in mean square to zero.
- If and then converges in mean square to zero.
- If , there is no mean-square convergence.
3. Parameter Estimation
3.1. Maximum Likelihood Estimator of
3.2. Estimation of
3.3. Quadratic Variation Method for Estimating
3.4. Asymptotic Properties of MLEs
- The estimator of μ is unbiased.
- If for with and , then converges in mean square to μ as .
- follows a Gaussian distribution with expectation μ and variance .
- From Equation (35), we obtain the variance of :Since , we obtainis symmetric positive definite which implies thatwhere denotes the largest eigenvalue of .
- follows a noncentral chi-square distribution.
- ;
- , ;
- for with and .
- The estimator of is asymptotically unbiased.
- converges in mean square to as .
- (i)
- (ii)
- From Equation (24), we haveSincethenSimilarly to Inequality (37), we getWhen conditions and are verified, we obtainwhich leads toso that the bias of for converges to zero when n tends to infinity.Due to the preservation of the convergence in probability and the distribution by continuous mappings (see Lemmas 3.3 and 3.7 in [22]), we obtain the final result.
- From Equation (24), we haveand sincewe get□
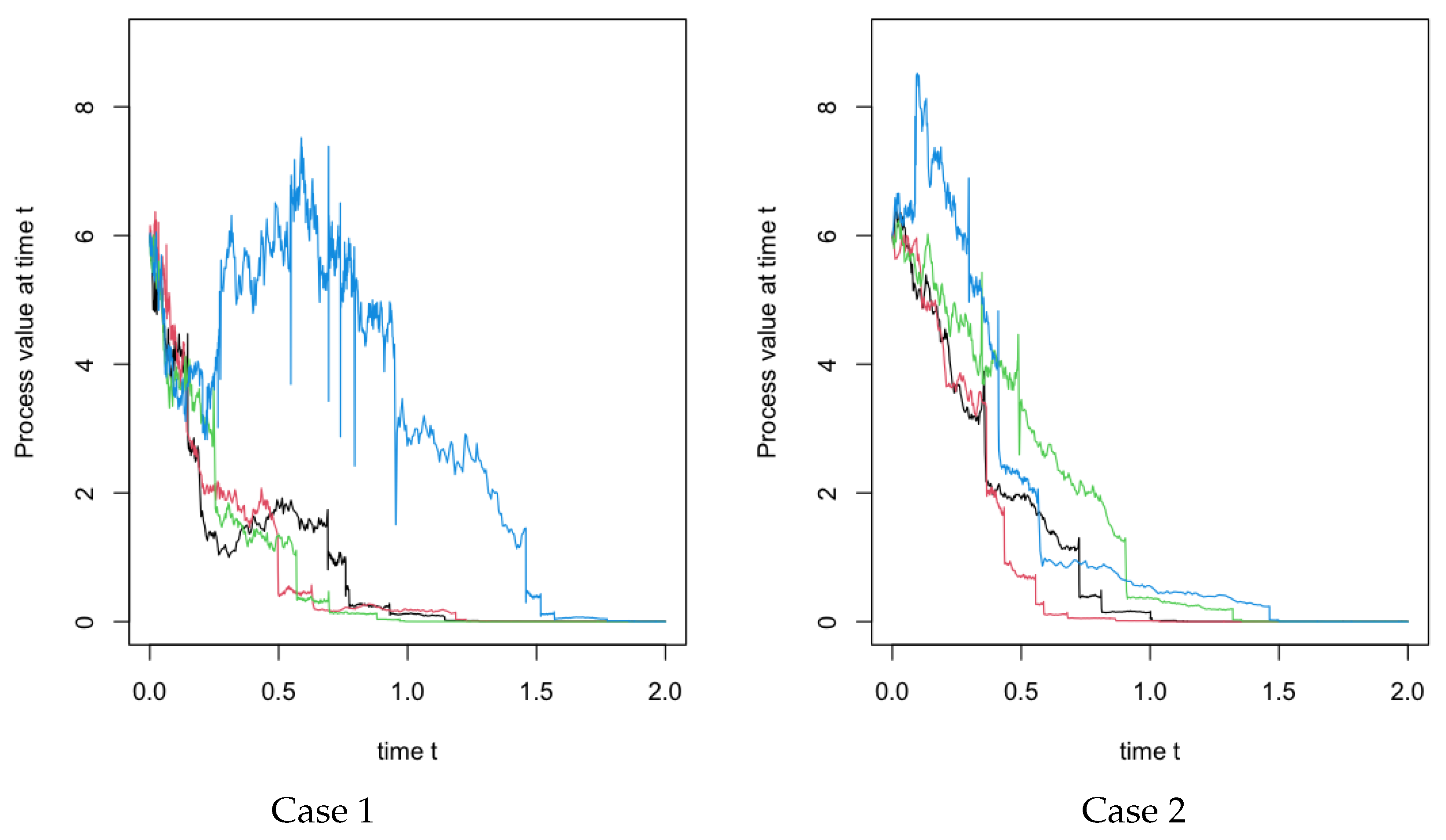
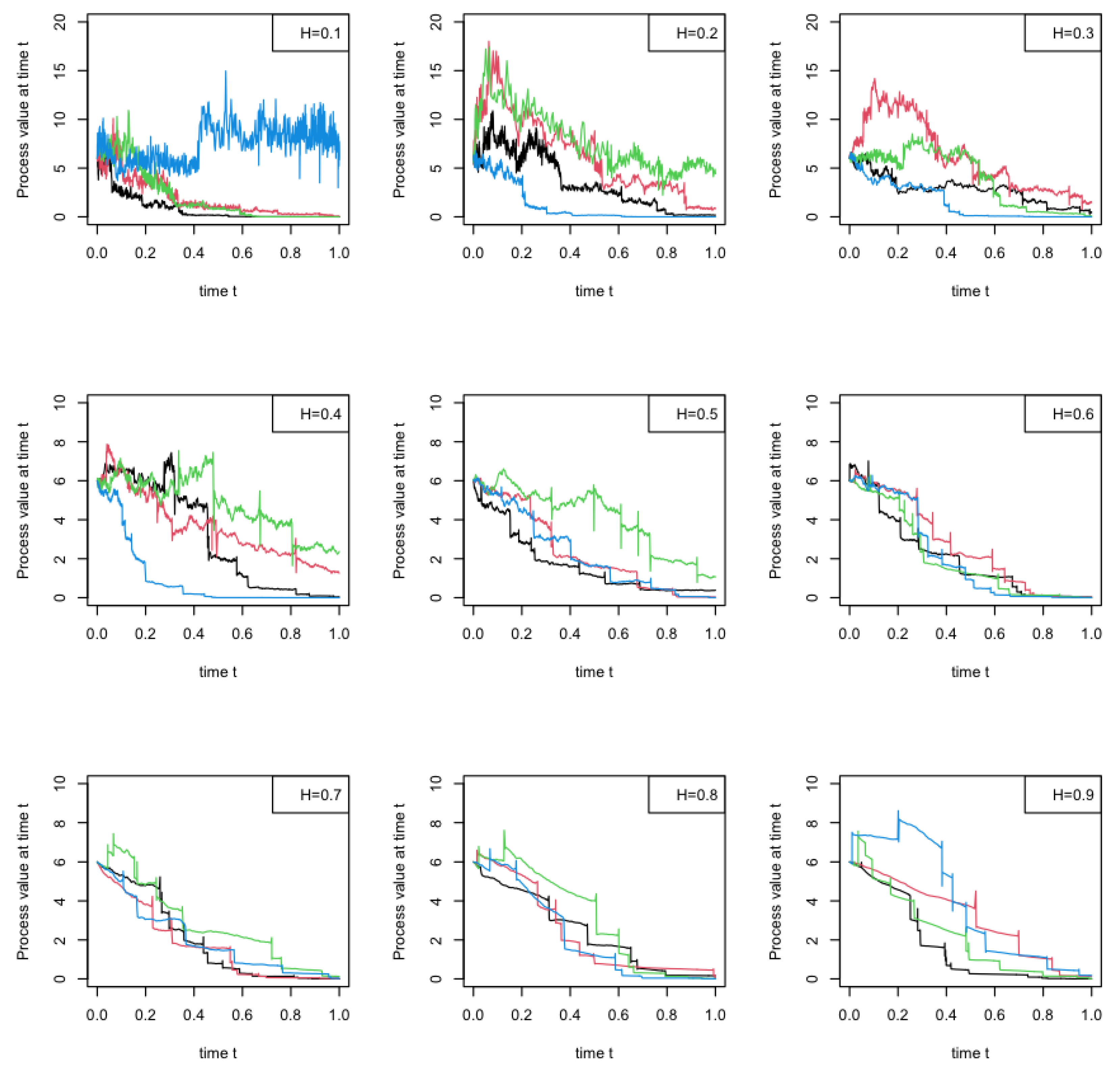
4. Numerical Simulations
 [25]. With function of , we can simulation a standard fBm on .
[25]. With function of , we can simulation a standard fBm on .5. Conclusions
 programming environment.
programming environment.Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Codes with R Programming Language
|
References
- Black, F.; Scholes, M.S. The Pricing of Options and Corporate Liabilities. J. Political Econ. 1973, 81, 637–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagini, F.; Hu, Y.; Øksendal, B.; Zhang, T. Stochastic Calculus for Fractional Brownian Motion and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X. Parameter identification for the discretely observed geometric fractional Brownian motion. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2015, 85, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, G. Mixed fractional stochastic differential equations with jumps. Stochastics Int. J. Probab. Stoch. Process. 2014, 86, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, K.; Torres, S.; Tudor, C.A. Maximum-likelihood estimators and random walks in long memory models. Statistics 2011, 45, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubilius, K.; Melichov, D. Quadratic variations and estimation of the Hurst index of the solution of SDE driven by a fractional Brownian motion. Lith. Math. J. 2010, 50, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzin, C.; León, J.R. Estimation in models driven by fractional Brownian motion. Ann. Inst. H. Poincaré Probab. Statist. 2008, 44, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Nualart, D. Parameter estimation for fractional Ornstein–Uhlenbeck processes. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2010, 80, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishura, Y.; Ralchenko, K.; Shklyar, S. Maximum likelihood estimation for Gaussian process with nonlinear drift. Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control. 2018, 23, 120–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haress, E.M.; Hu, Y. Estimation of all parameters in the fractional Ornstein–Uhlenbeck model under discrete observations. Stat. Inference Stoch. Process. 2021, 24, 327–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesars, J.; Nuiro, S.; Vaillant, J. Statistical Inference on a Black-Scholes Model with Jumps. Application in Hydrology. J. Math. Stat. 2019, 15, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishura, Y. Stochastic Calculus for Fractional Brownian Motion and Related Processes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nualart, D. The Malliavin Calculus and Related Topics, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Mandelbrot, B.B.; Van Ness, J.W. Fractional Brownian motions, fractional noises and applications. SIAM Rev. 1968, 10, 422–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, G.; Dinler, A. Exact linearization of one dimensional Itô equations driven by fBm: Analytical and numerical solutions. Nonlinear Dyn. 2008, 53, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishura, Y.; Ralchenko, K.; Shklyar, S. Maximum likelihood drift estimation for Gaussian process with stationary increments. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.00160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaozhong, H.; David, N.; Weilin, X.; Weiguo, Z. Exact maximum likelihood estimator for drift fractional Brownian motion at discrete observation. Acta Math. Sci. 2011, 31, 1851–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, G.; Berger, R.L. Statistical Inference; Cengage Learning: Belmont, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Henningsen, A.; Toomet, O. maxLik: A package for maximum likelihood estimation in R. Comput. Stat. 2011, 26, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, G.H.; Van Loan, C.F. Matrix Computations; JHU Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rencher, A.C.; Schaalje, G.B. Linear Models in Statistics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kallenberg, O. Foundations of Modern Probability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Coeurjolly, J.F. Simulation and identification of the fractional Brownian motion: A bibliographical and comparative study. J. Stat. Softw. 2000, 5, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beran, J.; Whitcher, B.; Maechler, M. Longmemo: Statistics for Long-Memory Processes. 2009. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=longmemo (accessed on 2 June 2020).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thony, J.-F.; Vaillant, J. Parameter Estimation for a Fractional Black–Scholes Model with Jumps from Discrete Time Observations. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4190. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10224190
Thony J-F, Vaillant J. Parameter Estimation for a Fractional Black–Scholes Model with Jumps from Discrete Time Observations. Mathematics. 2022; 10(22):4190. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10224190
Chicago/Turabian StyleThony, John-Fritz, and Jean Vaillant. 2022. "Parameter Estimation for a Fractional Black–Scholes Model with Jumps from Discrete Time Observations" Mathematics 10, no. 22: 4190. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10224190
APA StyleThony, J.-F., & Vaillant, J. (2022). Parameter Estimation for a Fractional Black–Scholes Model with Jumps from Discrete Time Observations. Mathematics, 10(22), 4190. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10224190






