Abstract
In this paper, an adaptive neural network approach is developed based on the integral nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method, with the aim of fixed-time position tracking control of a wheelchair upper-limb exoskeleton robot system under external disturbance. The dynamical equation of the upper-limb exoskeleton robot system is obtained using a free and typical model of the robotic manipulator. Afterward, the position tracking error between the actual and desired values of the upper-limb exoskeleton robot system is defined. Then, the integral nonsingular terminal sliding surface based on tracking error is proposed for fixed-time convergence of the tracking error. Furthermore, the adaptive neural network procedure is proposed to compensate for the external disturbance which exists in the upper-limb exoskeleton robotic system. Finally, to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, simulation results using MATLAB/Simulink are provided.
Keywords:
adaptive control; neural network; fixed-time convergence; disabilities robot; wheelchair exoskeleton robot; sliding mode control MSC:
68T07; 68Txx; 93D09; 92B20; 93Dxx; 62F35; 70E60; 93C10
1. Introduction
Usage of a wheelchair by people with disabilities is one of the best ways in which they can compensate for their disability and accomplish some of required tasks in their daily life [1,2]. However, some problems such as opening or closing a door, picking up objects placed on the floor or high shelves and climbing steps persist when disabled people work with a wheelchair [3,4]. Hence, some technologies need to be expanded to improve the wheelchair system [5]. With respect to the advancement of robotic technology, the exoskeleton has been recommended to assist human motion [6,7]. Among different types of exoskeleton, wheelchair upper-limb exoskeleton robots have attracted consideration due to its significant features. The chief role of the wheelchair upper-limb exoskeleton is to provide physical assistance for people with disabilities to accomplish the activities of daily living; hence, some efficient controllers need to be employed to improve the power-assist of the wheelchair upper-limb exoskeleton [8,9,10].
The main purpose in the design of the control of the wheelchair upper-limb exoskeleton robot is the position tracking control of each of its joints. Hence, various control schemes can be implemented to accomplish position tracking control of the wheelchair upper-limb exoskeleton robot using the position tracking control of each of its joints [11]. Where wheelchair upper-limb exoskeleton systems possess nonlinear dynamics, model uncertainty and external disturbance, control methods based on the Lyapunov concept can be implemented for their control [12,13]. One of the best control methods is the sliding mode control approach, which is considered a robust control method against uncertainties and external disturbances. In [14], a sliding mode controller using reaching laws is recommended for exoskeleton robots. Moreover, experimental results have demonstrated the effectiveness of the designed control technique. However, the fast convergence rate of the closed-loop system is not offered using this control method. Among different control strategies, the non-singular sliding mode control technique has been preferred due to the fast convergence rate and removal of the non-singularity, which damages the performance of the system [15,16]. In [17], the integral terminal sliding mode tracker for control of the exoskeleton robot system is proposed. In [18], fast convergence rate tracking control of the exoskeleton robot system is suggested using a terminal sliding mode control approach. In [19], a fractional sliding mode control method is recommended with the target of tracking control of the exoskeleton robot system. In [20,21], the fractional-order terminal sliding control for tracking control of the exoskeleton robot system is suggested. However, the effect of external disturbances is not considered in [17,18,19,20,21]. Unknown dynamics such as model uncertainties, external disturbances and unmodeled dynamics always exist which can deteriorate closed-loop performance and lead to the instability of physical systems; hence, they need to be compensated for. Therefore, intelligent approximation based on the adaptive neural network technique has been proposed to learn unknown dynamics without any knowledge of model information. The main advantage of an intelligent approximation method like a neural network is that these methods contain a lot of adaptive weight parameters to learn the uncertainties and external disturbances, which enhances the performance of the system during practical applications [22,23]. In [24], a non-parametric adaptive approximate model according to the differential neural network is proposed for non-negative environmental systems in the presence of parametric uncertainties. A neural network approximation-based robust optimal feedback control method is proposed in [25] for uncertain systems, where a min–max approach is employed to obtain a robust-like solution for the optimal control problem. In [26], the backstepping sliding mode control method based on an adaptive neural network has been proposed for trajectory tracking control of an exoskeleton robot system. In [27], the sliding mode control based on an adaptive neural network is proposed for tracking control of the exoskeleton robot system. However, in these studies, the fast convergence rate of tracking error has not been investigated. In [28], with the aim of saving energy in nodes in clustered networks, an adaptive duty cycle medium access control protocol is proposed to obtain a low duty cycle for a cluster and a lower number of collisions in a network. In addition, an adaptive power control is adopted to broaden the lifetime of nodes. In [29], two data-driven-based sliding mode control and fuzzy control methods are offered for the stability of the error dynamics of the nonlinear system. Moreover, the validity of this approach is proved by three-dimensional crane system laboratory equipment. In [30], the reinforcement learning control is investigated using both a Deep Q-Learning (DQL) algorithm and a metaheuristic Gravitational Search Algorithm (GSA). The GSA is applied to initialize the weights and the biases of the neural network used in DQL for prevention of instability and achieving optimal control.
For easy understanding of the disadvantages of the existing methods compared with the designed control scheme in this paper, Table 1 is provided as follows:

Table 1.
Disadvantages of the existing methods.
According to the review and investigation of the articles which examine the position tracking control of the upper-limb exoskeleton robot system, fixed-time position tracking control of the upper-limb exoskeleton robot system based on the integral nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method mixed with an adaptive neural network has been a little considered, and remains an open question in the literature. Hence, in this paper, the integral nonsingular terminal sliding mode control technique is combined with an adaptive neural network procedure to accomplish the fixed-time convergence control of the upper-limb exoskeleton robot system. Therefore, the chief contributions of this article are as listed below:
- -
- Recommendation of the integral nonsingular terminal sliding mode control scheme, with the aim of fixed-time convergence of position tracking error of the upper-limb exoskeleton robot system;
- -
- Demonstration of fixed-time convergence of the proposed switching surface using the Lyapunov stability concept;
- -
- Compensation for the external disturbance existing in the upper-limb exoskeleton robot system by adopting the adaptive neural network procedure.
The remainder of this article can be summarized as follows. In Section 2, the dynamical equations of the upper-limb exoskeleton robot system are described. In Section 3, some required preliminaries are presented. In Section 4, the main results related to the proposed method using an adaptive neural network based on integral nonsingular terminal sliding mode control scheme are expressed. Simulation results and conclusion are given in Section 5 and Section 6, respectively.
2. Wheelchair Upper-Limb Exoskeleton Robot System
Two major parts of the wheelchair upper-limb exoskeleton robot system, as displayed in Figure 1, are the glove which is designed to allow users to use necessary abilities, and the upper-limb exoskeleton. The main parts of the upper limb exoskeleton system are: Joint 1, which is used for adduction and abduction action; joint 2, which is used for accomplishment of internal and external rotation; joint 3, which is applied for achieving flexion and extension actions; and joint 4, which is used for the accomplishment of elbow flexion and extension.
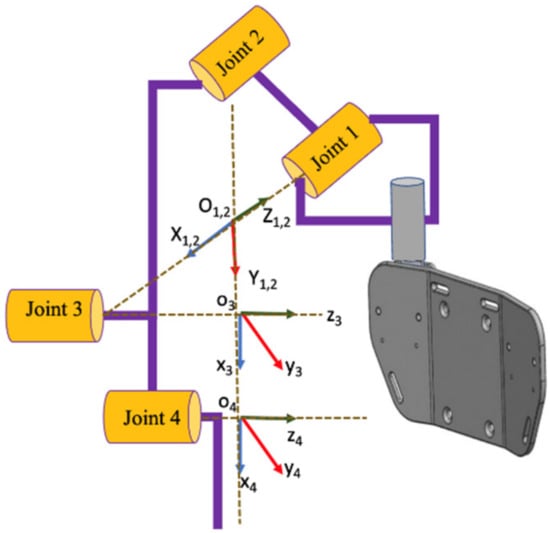
Figure 1.
Schematic of wheelchair upper-limb exoskeleton robotic system.
As noted in [11], with the aim of position tracking control of exoskeleton robot system, free and typical dynamical model of the robot system is considered as
where , and signify the position, velocity and accelerations of the robot system, respectively. The terms of indicate the inertia matrix as
with , , . The term denote the Coriolis and centrifugal forces matrix as
with . The term indicates the gravitational forces matrices as
Moreover, implies the control input. Additionally, the essential parameters and their units and quantities are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Constant parameters of the upper-limb exoskeleton robot system.
Equation (1) is rewritten as the following after doing some simplification:
The above dynamical equation is considered under external disturbance as follows:
3. Preliminaries
In this part, some assumptions and Lemmas are presented to be used in the design of the control strategy.
Assumption 1.
for the external disturbance, the following conditions are satisfied as
whereandare the positive constants.
Lemma 1 ([31]).
For the dynamical system , with and as a continuous nonlinear function, the origin of the system is globally fixed-time stable, if it is finite-time with time function and its convergence time is globally bounded, i.e., .
4. Main Results
In this section, firstly, position tracking control of the upper-limb exoskeleton robot system is suggested using the integral nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method. Secondly, for the rejection of the external disturbance, an adaptive neural network is proposed.
4.1. Integral Nonsingular Fixed-Time Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control
The position tracking error between the actual (q) and desired value () of the upper-limb exoskeleton robot system is defined as
Previously, the integral sliding mode control has been investigated in various studies [32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41]. In this paper, the integral nonsingular terminal sliding mode control is proposed for an upper-limb exoskeleton robot system. The integral fixed-time nonsingular terminal sliding surface is proposed as following:
where and are given as
where is a constant coefficient. Taking time-derivative form (9) yields to
Substitution from Equations (5) and (8), one con gain
Therefore, the integral nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller is designed as
with
where , . Moreover, in order to realize the finite-stability of the position tracking error, the condition of holds.
Theorem 1.
Presume that an upper-limb exoskeleton robot system in the existence of the external disturbance satisfying Assumption 1 be as (5), tracking error and sliding surface be as (8) and (9), respectively. Hence, the fixed-time convergence of the tracking error is realized using integral nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller (13).
Proof.
Consider the candidate Lyapunov function as . With taking time-derivative of the considered Lyapunov function, we have; . Now, with substitution from Equation (12), one can gain
With substation of the control law (13) in the above equation, we have
With considering and substation in (16), one can result
whereas , it can result
Therefore, the fixed-time convergence of the position tracking error of the upper-limb exoskeleton robot system is realized. □
4.2. Adaptive Neural Network Control Technique
4.2.1. Description of the Neural Network
In this part, the wavelet neural network is applied to compensate for the external disturbance in the upper-limb exoskeleton robot system. In fact, wavelets are mathematical functions with finite continuity and variable frequency contrary to sinusoidal waves. The optimal vectors of dilation , translation , and weight matrix based on Wavelet neural networks exist as
where is the wavelet transformation, indicates the neural network input vector and is the minimum approximation error vector. In fact, is the unknown; hence, the estimation vector is defined as [42]
where , and are the estimation of the , , and , respectively. Then, the estimation error of neural network is defined as . So, with substitution from Equations (19) and (20), we have
where and , one can obtain
With the use of the Taylor expansion linearization method, non-linear function is written as below [43]:
where is the higher-order expression from the Taylor series. Moreover,
where indicates the number of neurons in the hidden layer of the wavelet neural network. Substitution (23) into (22) results in
where . In addition, the structure of the neural network is displayed in Figure 2.
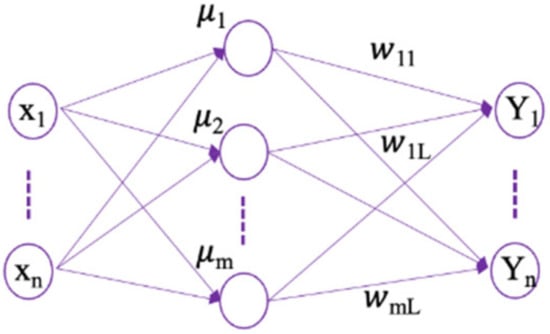
Figure 2.
Structure of the neural network.
4.2.2. Adaptive Neural-Based Nonsingular Terminal Sliding Mode Control Method
Adaptive laws for regulation of the wavelet neural network parameters are gained as follows:
where . Now, the adaptation law for estimator error is designed as
where . The adaptive neural network-based integral nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller is obtained as
with
Theorem 2.
Suppose an upper-limb exoskeleton robot system with dynamic (5). If the tracking error and sliding surface are selected as (8) and (9), respectively, the control law is defined as (28) and adaptive laws are selected as (26) and (27), then the stability and fixed-time convergence of position tracking error of the upper-limb exoskeleton robot system to zero is guaranteed.
Proof.
Construct the candidate Lyapunov function as
Taking the time-derivative of the considered Lyapunov function leads to
with substitution (12) and (28)
Considering external disturbance , it can gain
where , the Equation (25) is substituted in (23), so we have
Substituting (26) into (34) results in
Considering , and and substitution of (27), it can gain
Therefore, fixed-time convergence of the tracking error of the upper-limb exoskeleton robot system is proved. □
Remark 1.
[44]: Whereasis a positive diagonal matrix, from Equations (18) and (36) it can be observed that the sliding surface converges to zero in the finite time globally. Under this condition, we have
The above equation has a fixed-time stable equilibrium point at such that the position tracking error is converged to zero in the bounded finite time. Thus, fixed-time convergence of the position tracking error based on Lemma 1 is demonstrated.
The block diagram of the proposed method based on the adaptive neural network using an integral nonsingular terminal sliding mode approach with the fixed-time convergence rate is depicted in Figure 3.
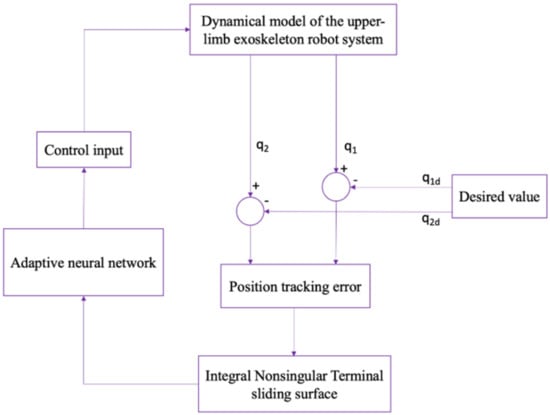
Figure 3.
Block diagram of the proposed method.
5. Simulation Results
In this part, with the use of the MATLAB/Simulink software, simulation results are prepared using an adaptive neural network technique based on the integral nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method, with the aim of demonstrating the accuracy of the above-designed method with presentation of various examples. Moreover, simulation outcomes, which are presented in each example, are obtained using various initial conditions as given in Table 3. In addition, the desired values are presented in Table 4, and designed parameters, which are obtained based on trial and error, are shown in Table 5. With the aim of the proficiency of the adaptive neural network, the external disturbances are presented in Table 6. Therefore, the adaptive neural network based integral nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller is considered as
with

Table 3.
Considered initial conditions.

Table 4.
Desired values.

Table 5.
Design parameters.

Table 6.
External disturbances.
The above-designed controller is entered into the system and the following results are obtained:
Simulation results using information and data given in the above tables are provided to show the efficiency of the proposed method based on an adaptive neural network mixed with the integral nonsingular terminal sliding mode technique on an upper limb exoskeleton robot system. The desired tracking of the upper limb exoskeleton robot system is shown in Figure 4. One can observe that the desired tracking has been accomplished using the suggested method. Additionally, time histories of the tracking errors are illustrated in Figure 5, which demonstrates the accuracy of the desired tracking. Moreover, time responses of sliding surfaces are depicted in Figure 6. It can be found that sliding surfaces are converged to zero with fixed-time convergence rate. The control inputs are displayed in Figure 7, in which can be seen that control signals own appropriate amplitude without any chattering phenomenon. The approximation of the upper bounds of external disturbances based on the adaptive neural network has been done and shown in Figure 8. Thus, it can be observed that the adaptive neural network presents an effective and productive technique for estimation of the uncertainties. The tracking performance of the upper limb exoskeleton robot system, with different initial conditions and various desired values, is shown in Figure 9. Time responses of the tracking errors under different initial conditions are illustrated in Figure 10. Moreover, sliding surfaces with different initial conditions and diverse desired values and external disturbances are depicted in Figure 11. Time histories of the control inputs under different initial conditions are shown in Figure 12. Moreover, the trajectories of adaptation laws based on neural network in example 2 are demonstrated in Figure 13. All of the simulation figures prove the suitability and efficiency of the proposed method.
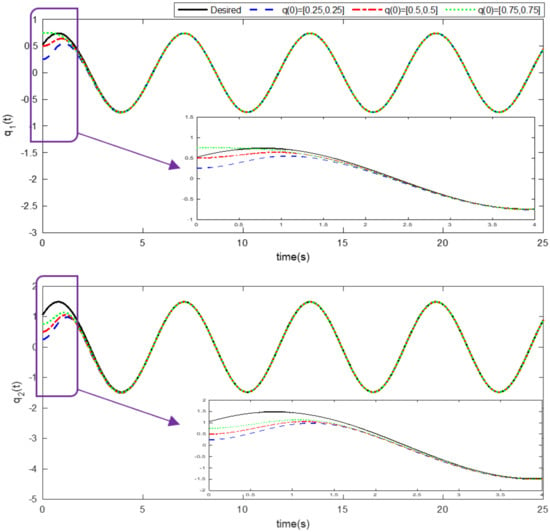
Figure 4.
Desired tracking of the exoskeleton robot system (Example 1).
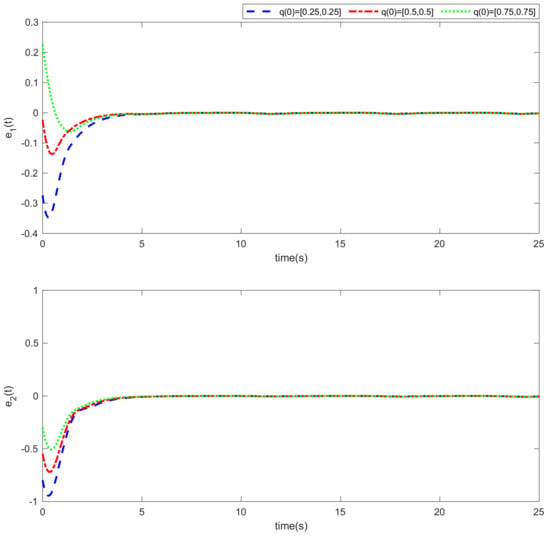
Figure 5.
Time responses of the tracking error (Example 1).
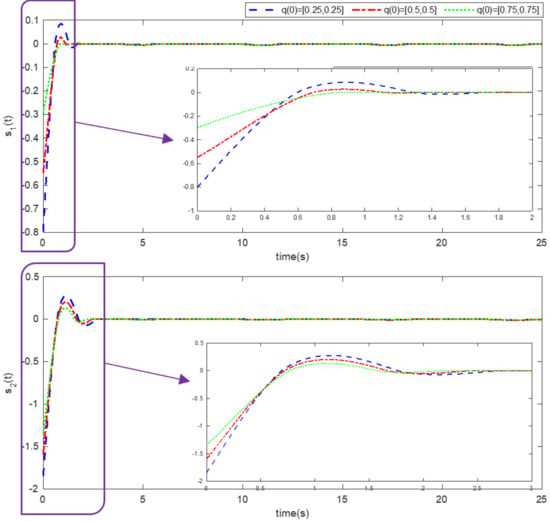
Figure 6.
Time history of the sliding surface (Example 1).
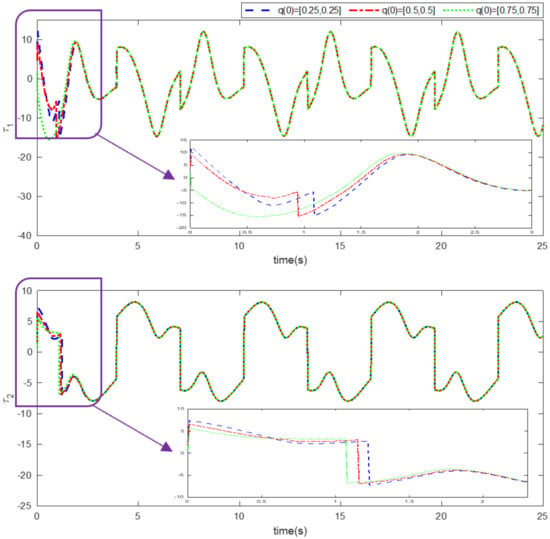
Figure 7.
Control inputs (Example 1).
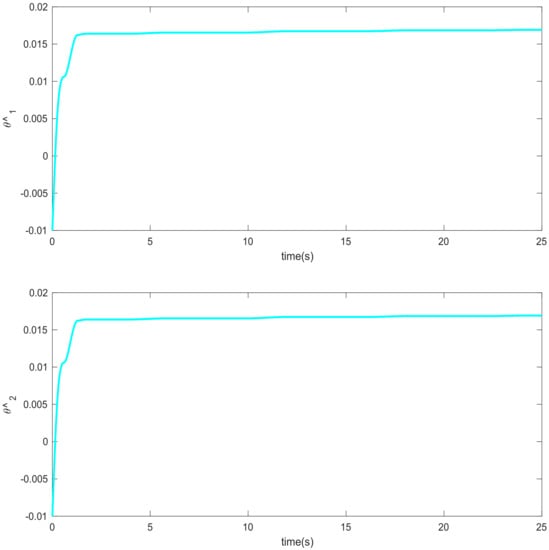
Figure 8.
Adaptation law based on neural network (Example 1).
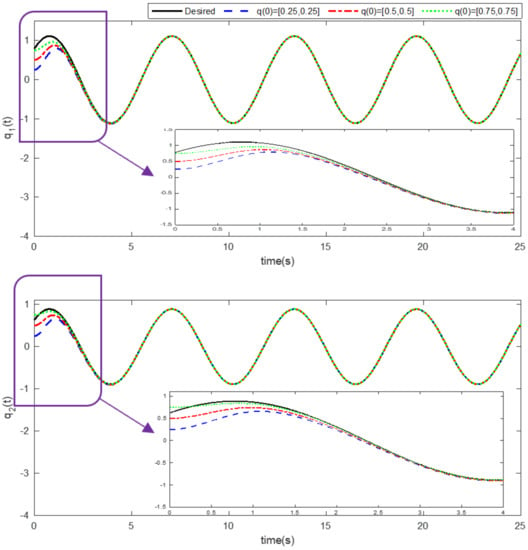
Figure 9.
Desired tracking of the exoskeleton robot system under different initial conditions. (Example 2).

Figure 10.
Time responses of the tracking error under different initial conditions (Example 2).
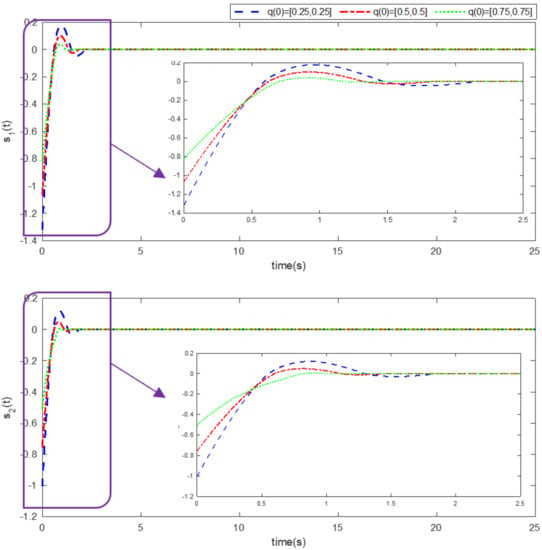
Figure 11.
Time history of the sliding surface under different initial conditions. (Example 2).
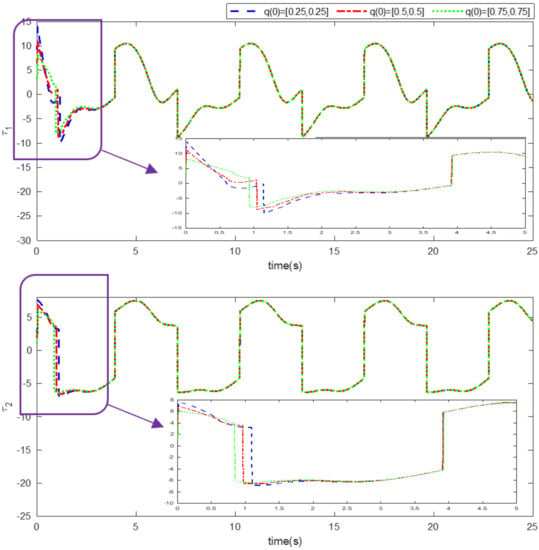
Figure 12.
Control input under different initial conditions. (Example 2).
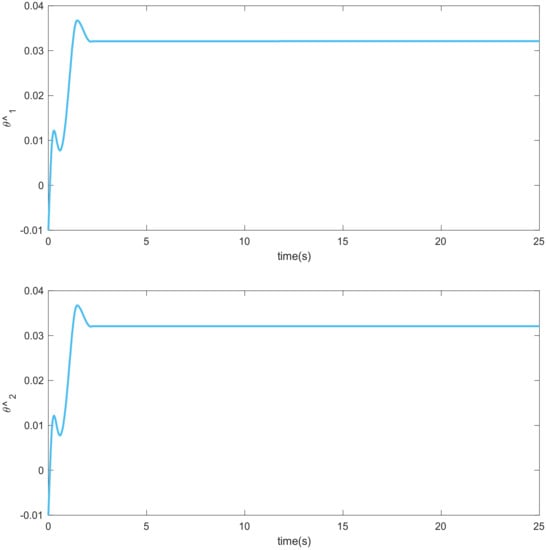
Figure 13.
Adaptation laws based on neural network. (Example 2).
Remark 2.
The design parameters of the proposed adaptive neural network fixed-time tracking control approach are assigned by trial-and-error tactic as a trade-off among the amplitude of control input, convergence rate, control precision and chattering problem. If the parametersandare increased, the amplitude of control signal is increased, the convergence speed and control precision are improved, but a chattering problem occurs. The increase in the parametersandleads to the increase of the control input amplitude, decrease of the convergence speed, and reduction in the control accuracy. If the parametersandare increased, the control signal amplitude will be decreased and the convergence speed will be reduced. Increase ofresults in a decrease in the convergence speed, reduction in control amplitude and control precision improvement.
6. Conclusions
As mentioned in this paper, applications of the wheelchair upper-limb exoskeleton robot system have been developed in recent decades. For this reason, control, especially position control, has been investigated by many researchers. In this paper, an adaptive neural network is combined with an integral nonsingular terminal sliding mode control scheme, with the aim of position tracking control of the upper-limb exoskeleton robot system during the appearance of an external disturbance. Then, an integral nonsingular terminal sliding surface is proposed based on position tracking error control of the upper-limb exoskeleton robot system. Afterward, rejection of the external disturbance is accomplished by applying an adaptive neural network procedure. Finally, simulation results are prepared to prove the efficiency of the designed method.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.A., M.T.V., K.-H.H. and F.F.M.E.-S.; formal analysis, S.M., A.A., G.M. and D.-N.L.; funding acquisition, M.T.V.; investigation, S.M., M.T.V., G.M., K.-H.H. and A.A.A.; methodology, F.F.M.E.-S. and S.M.; writing—original draft, M.T.V., G.M., K.-H.H. and A.A.; writing—review and editing, and supervision, S.M., D.-N.L., A.A.A. and M.T.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by King Salman Center for Disability Research through Research Group no KSRG-2022-021.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the King Salman Center for Disability Research for funding this work through Research Group no KSRG-2022-021.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ikeda, H.; Tohyama, T.; Maki, D.; Sato, K.; Nakano, E. Autonomous Step Climbing Strategy Using a Wheelchair and Care Robot. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th International Conference on Control, Robotics and Cybernetics (CRC), Tokyo, Japan, 27–30 September 2019; pp. 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Aly, A.A.; Vu, M.T.; El-Sousy, F.F.M.; Alotaibi, A.; Mousa, G.; Le, D.-N.; Mobayen, S. Fuzzy-Based Fixed-Time Nonsingular Tracker of Exoskeleton Robots for Disabilities Using Sliding Mode State Observer. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinderer, M.; Friedrich, P.; Wolf, B. An autonomous stair-climbing wheelchair. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2017, 94, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglia, G.; Nisi, M. Design of a self-leveling cam mechanism for a stair climbing wheelchair. Mech. Mach. Theory 2017, 112, 84–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo, A.; Spalanzani, A.; Laugier, C. Multimodal control of a robotic wheelchair: Using contextual information for usability improvement. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 4262–4267. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Tian, C.; Dai, J.S. Mechanism design and analysis of a proposed wheelchair-exoskeleton hybrid robot for assisting human movement. Mech. Sci. 2019, 10, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghian, A. A fuzzy neural network-based fractional-order Lyapunov-based robust control strategy for exoskeleton robots: Application in upper-limb rehabilitation. Math. Comput. Simul. 2022, 193, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Xie, Q.; Shao, H.; Cao, W.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Yu, H.; Li, S. Pilot study of a powered exoskeleton for upper limb rehabilitation based on the wheelchair. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 9627438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schabron, B.; Desai, J.; Yihun, Y. Wheelchair-mounted upper limb robotic exoskeleton with adaptive controller for activities of daily living. Sensors 2021, 21, 5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gull, M.; Thoegersen, M.; Bengtson, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Struijk, L.A.; Moeslund, T.; Bak, T.; Bai, S. A 4-dof upper limb exoskeleton for physical assistance: Design, modeling, control and performance evaluation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.; Gull, M.A.; Bai, S. PD-based fuzzy sliding mode control of a wheelchair exoskeleton robot. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2020, 25, 2546–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.S.; Ramli, R.; Ibrahim, M.F. Initialized model reference adaptive control for lower limb exoskeleton. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 167210–167220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Li, Z.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, T. Design and adaptive control for an upper limb robotic exoskeleton in presence of input saturation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 30, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.H.; Saad, M.; Kenné, J.-P.; Archambault, P.S. Control of an exoskeleton robot arm with sliding mode exponential reaching law. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2013, 11, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofid, O.; Amirkhani, S.; Din, S.u.; Mobayen, S.; Vu, M.T.; Assawinchaichote, W. Finite-time convergence of perturbed nonlinear systems using adaptive barrier-function nonsingular sliding mode control with experimental validation. J. Vib. Control 2022, 10775463221094889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alattas, K.A.; Mofid, O.; Alanazi, A.K.; Abo-Dief, H.M.; Bartoszewicz, A.; Bakouri, M.; Mobayen, S. Barrier Function Adaptive Nonsingular Terminal Sliding Mode Control Approach for Quad-Rotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Sensors 2022, 22, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riani, A.; Madani, T.; Benallegue, A.; Djouani, K. Adaptive integral terminal sliding mode control for upper-limb rehabilitation exoskeleton. Control Eng. Pract. 2018, 75, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-F.; Du, Z.-J.; He, L.; Wang, J.-Q.; Wu, D.-M.; Dong, W. Active disturbance rejection with fast terminal sliding mode control for a lower limb exoskeleton in swing phase. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 72343–72357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Rahmani, M.; Rahman, M.H. A novel exoskeleton with fractional sliding mode control for upper limb rehabilitation. Robotica 2020, 38, 2099–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Wang, H.; Tian, Y. Model-free control using time delay estimation and fractional-order nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode for uncertain lower-limb exoskeleton. J. Vib. Control 2018, 24, 5273–5290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Wang, H.; Tian, Y. Robust adaptive fractional-order terminal sliding mode control for lower-limb exoskeleton. Asian J. Control 2019, 21, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Huo, W. Robust adaptive backstepping neural networks control for spacecraft rendezvous and docking with uncertainties. Nonlinear Dyn. 2016, 84, 1683–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; He, W.; Sun, C. Adaptive fuzzy relative pose control of spacecraft during rendezvous and proximity maneuvers. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 26, 3440–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chairez, I.; Andrianova, O.; Poznyak, T.; Poznyak, A. Adaptive modeling of nonnegative environmental systems based on projectional Differential Neural Networks observer. Neural Netw. 2022, 151, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, M.; Chairez, I.; Poznyak, A. Robust optimal feedback control design for uncertain systems based on artificial neural network approximation of the Bellman’s value function. Neurocomputing 2020, 413, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, B.; Wu, H. Rbfn-based adaptive backstepping sliding mode control of an upper-limb exoskeleton with dynamic uncertainties. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 134635–134646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, D.; Wang, P.; Yang, X.; Li, H. Model-free adaptive sliding mode robust control with neural network estimator for the multi-degree-of-freedom robotic exoskeleton. Complexity 2020, 2020, 8327456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, B.; Manohar, S.S. Adaptive Power Control and Duty Cycle based Medium Access Control Protocol for Cluster based Wireless Sensor Network. Sci. Technol. 2020, 23, 38–54. [Google Scholar]
- Precup, R.-E.; Roman, R.-C.; Hedrea, E.-L.; Petriu, E.M.; Bojan-Dragos, C.-A. Data-Driven Model-Free Sliding Mode and Fuzzy Control with Experimental Validation. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Control 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamfirache, I.A.; Precup, R.-E.; Roman, R.-C.; Petriu, E.M. Reinforcement Learning-based control using Q-learning and gravitational search algorithm with experimental validation on a nonlinear servo system. Inf. Sci. 2021, 583, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, V.I.; Poznyak, A.S. Adaptive sliding mode control with application to super-twist algorithm: Equivalent control method. Automatica 2013, 49, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznyak, A.; Fridman, L.; Bejarano, F. Mini-max integral sliding-mode control for multimodel linear uncertain systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2004, 49, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, V.; Shi, J. Integral sliding mode in systems operating under uncertainty conditions. In Proceedings of the 35th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Kobe, Japan, 11–13 December 1996; pp. 4591–4596. [Google Scholar]
- Laghrouche, S.; Plestan, F.; Glumineau, A. Higher order sliding mode control based on integral sliding mode. Automatica 2007, 43, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidi, K.; Xu, J.-X.; Xinghuo, Y. On the discrete-time integral sliding-mode control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2007, 52, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Yang, C.; Pan, L.; Yu, H. Integral sliding mode control: Performance, modification, and improvement. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 14, 3087–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.-C.; Lai, Y.M.; Tse, C.K. Indirect sliding mode control of power converters via double integral sliding surface. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2008, 23, 600–611. [Google Scholar]
- Castanos, F.; Fridman, L. Analysis and design of integral sliding manifolds for systems with unmatched perturbations. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2006, 51, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.H. LMI-based sliding surface design for integral sliding mode control of mismatched uncertain systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2007, 52, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobayen, S. Chaos synchronization of uncertain chaotic systems using composite nonlinear feedback based integral sliding mode control. ISA Trans. 2018, 77, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobayen, S.; Vargas, A.N.; Acho, L.; Pujol-Vázquez, G.; Caruntu, C.F. Stabilization of two-dimensional nonlinear systems through barrier-function-based integral sliding-mode control: Application to a magnetic levitation system. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussar, Y.; Rivals, I.; Personnaz, L.; Dreyfus, G. Training wavelet networks for nonlinear dynamic input–output modeling. Neurocomputing 1998, 20, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-M.; Hsu, C.-F. Neural-network hybrid control for antilock braking systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2003, 14, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Zhang, G.; Ouyang, H.; Mei, L. Novel fixed-time nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode control for second-order uncertain systems based on adaptive disturbance observer. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 126615–126627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).