Multitask Image Splicing Tampering Detection Based on Attention Mechanism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fundamentals and Related Work
2.1. Convolutional Neural Network
2.2. Attention Mechanism
2.3. Residual Noise Extraction
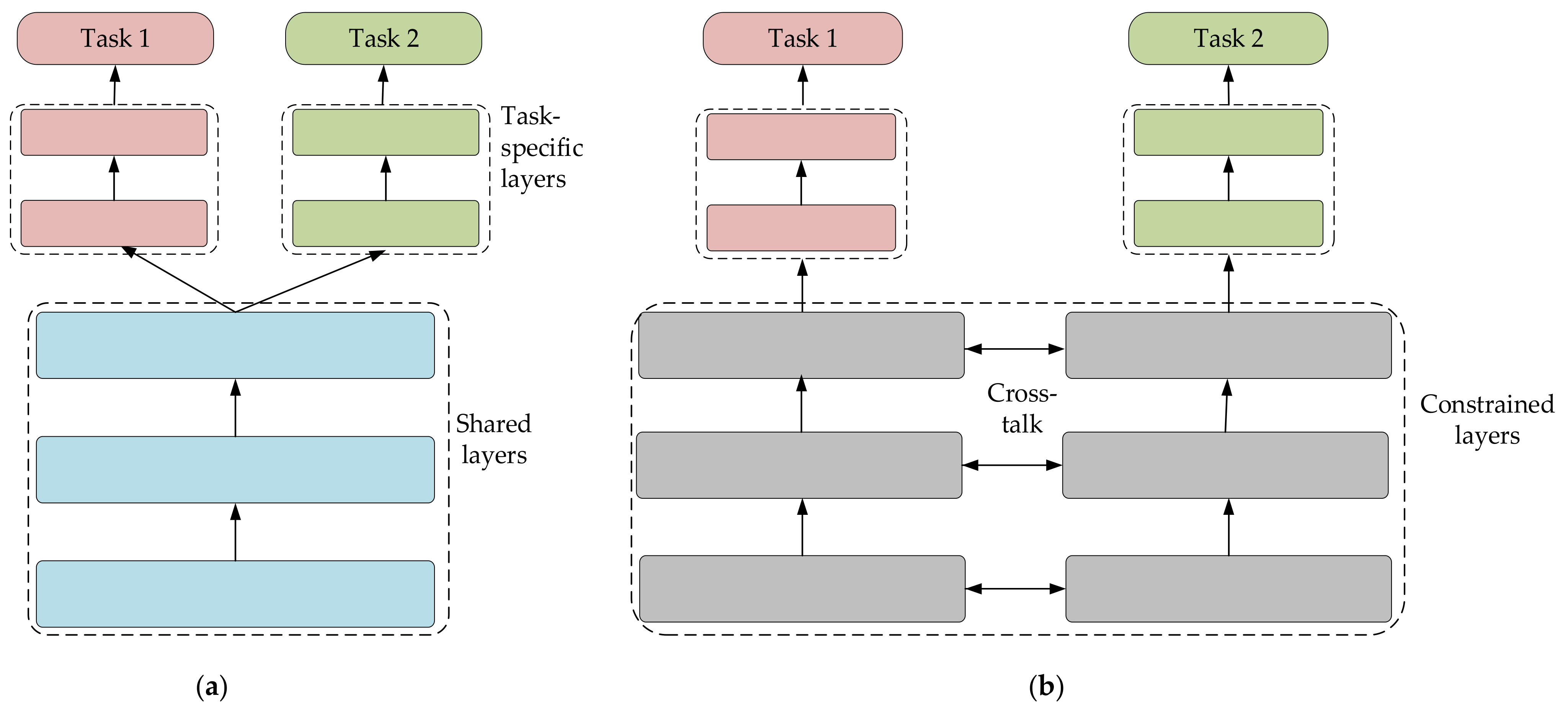
2.4. Multitask Learning
3. AttDAU-Net—Proposed Multitask Splicing Tampering Detection Model
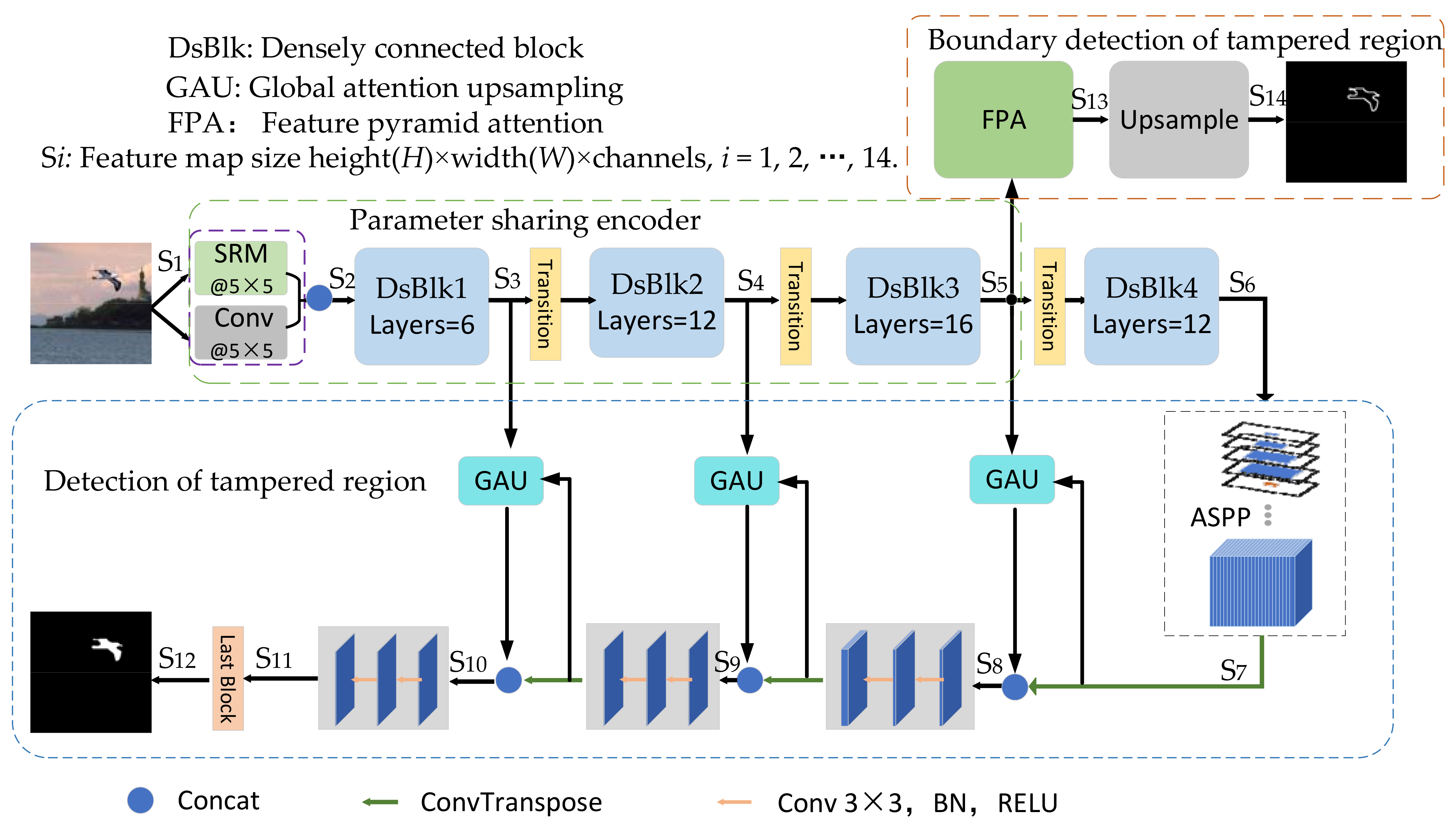
3.1. The Model
3.2. Loss Functions
4. Results and Discussion
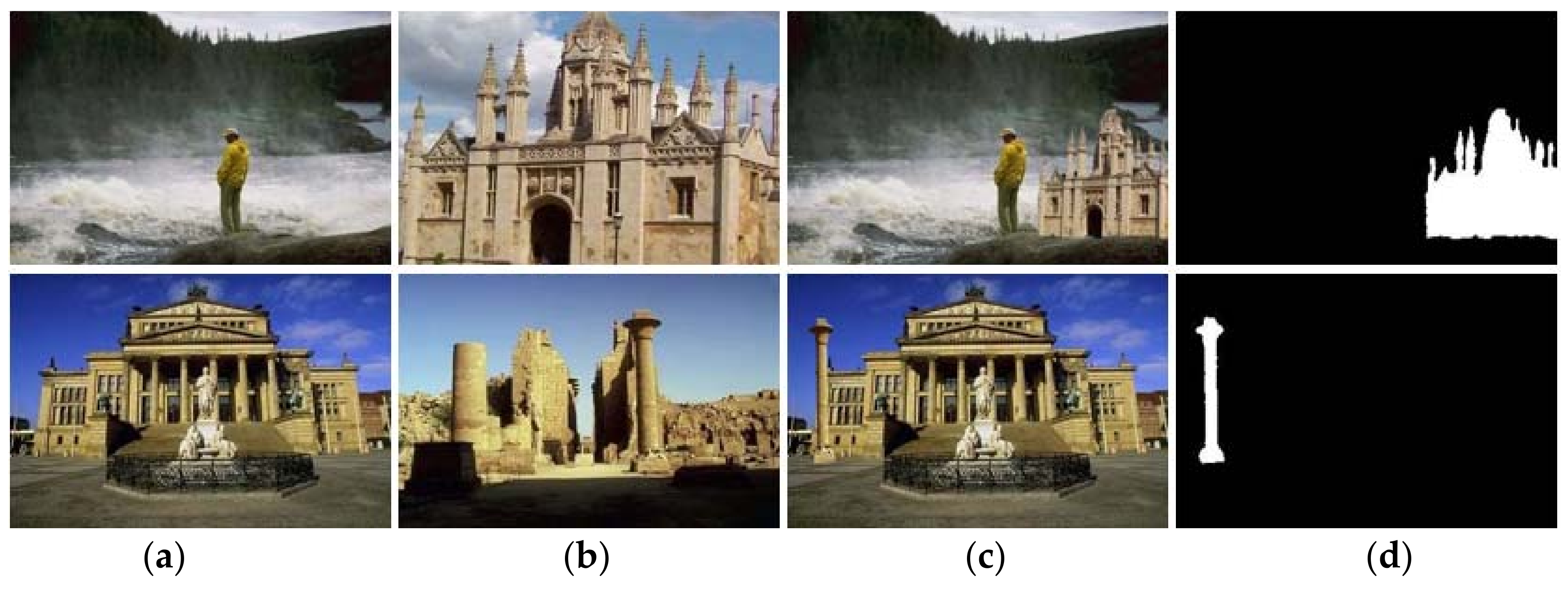
4.1. Development Environment, Experimental Settings and Datasets
4.2. Performance Evaluation Metrics
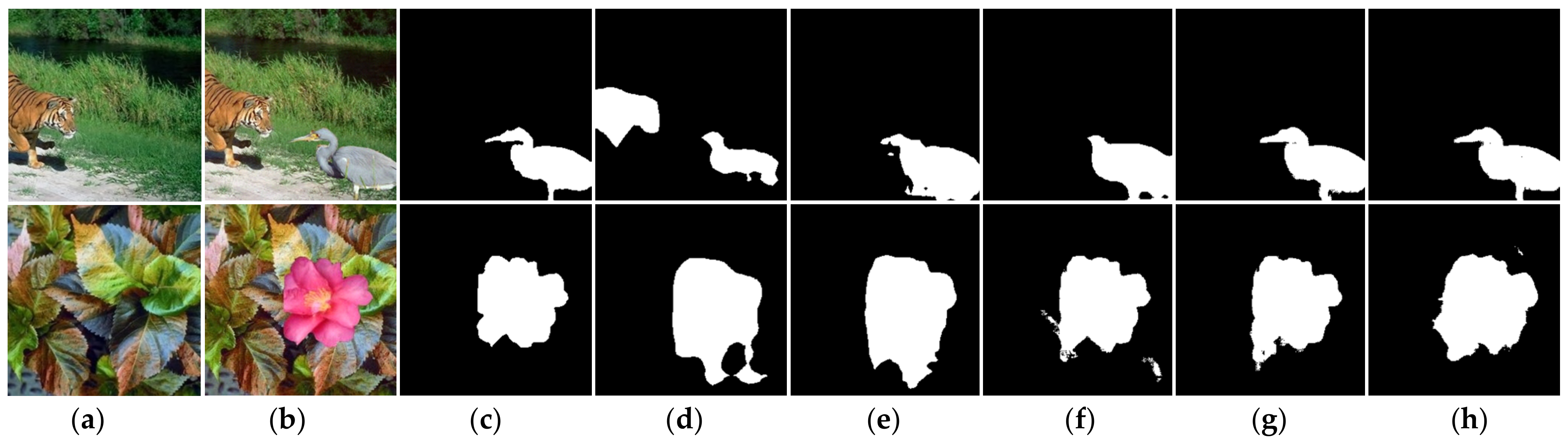
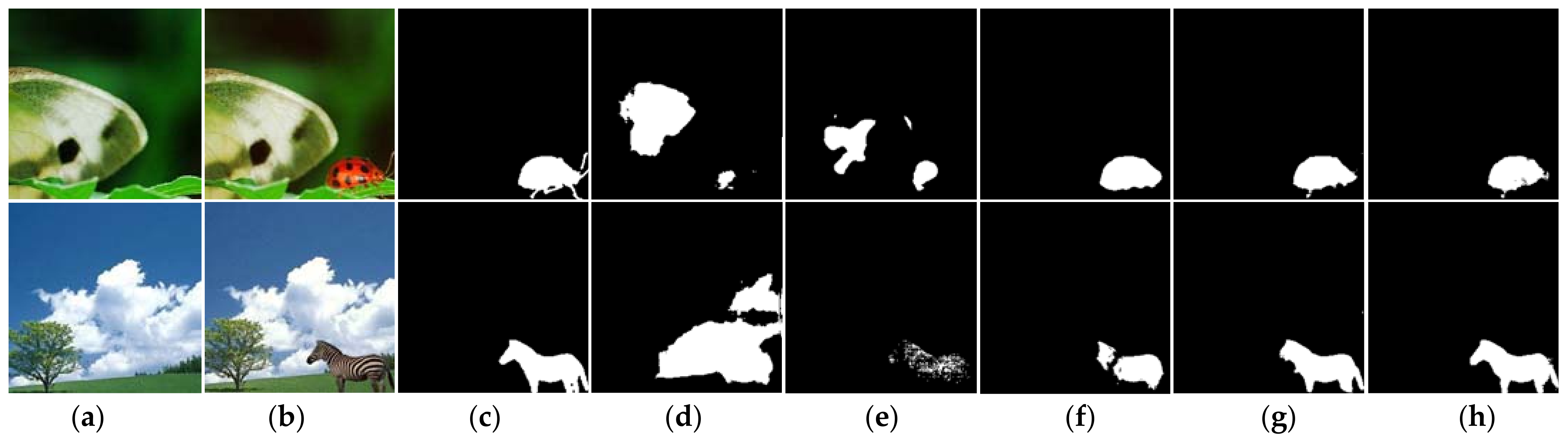
4.3. Comparative Results
4.4. Ablation Study
4.5. Robustness to Compression and Blurring Attacks
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barad, Z.J.; Goswami, M.M. Image forgery detection using deep learning: A survey. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems, Tamil Nadu, India, 6–7 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, R.; Rohilla, R. Recent advances in digital image manipulation detection techniques: A brief review. Forensic Sci. Int. 2020, 312, 110311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, S.J.; Ruan, G.Q.; Li, H.; He, J. Robust watermarking of databases in order-preserving encrypted domain. Front. Comput. Sci. 2021, 16, 162804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehab, A.; Elhoseny, M.; Muhammad, K.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Yang, P.; Huang, H.; Hou, G. Secure and robust fragile watermarking scheme for medical images. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 10269–10278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Chen, W.; Zhang, W.; Pei, J.; Gao, W.; Wang, G. Digital signature scheme for information non-repudiation in blockchain: A state-of the art review. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2020, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Pun, C.M. Locating splicing forgery by adaptive-SVD noise estimation and vicinity noise descriptor. Neurocomputing 2020, 387, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Zhan, Y.; Kang, X.; Lin, X. Image splicing localization using PCA-based noise level estimation. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 4783–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, T.; Piva, A. Image forgery localization via block-grained analysis of JPEG artifacts. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2012, 7, 1003–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, W.; Wu, F.; Han, H.; Zhang, L. Revealing the traces of nonaligned double JPEG compression in digital Images. Optik 2020, 204, 164196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Lei, J.; Li, B.; Wang, Q.; Xue, J. Coarse-to-fine-grained method for image splicing region detection. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 122, 108347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G.E. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Razmjooy, N. Brain tumor diagnosis based on metaheuristics and deep learning. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2021, 31, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Diwakar, M.; Choudhary, S. Application of edge detection for brain tumor detection. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2012, 58, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabahmadi, M.; Farahbakhsh, R.; Rezazadeh, J. 12-Deep learning for smart healthcare—A survey on brain tumor detection from medical imaging. Sensors 2022, 22, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Wu, Y.; Ren, X.; Razmjooy, N. A new optimized sequential method for lung tumor diagnosis based on deep learning and converged search and rescue algorithm. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 68, 102761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, T.A.; Zheng, L.; Afifi, A.J.; Ali, A.; Soomro, S.; Yin, M.; Gao, J. Image segmentation for MR brain tumor detection using machine learning: A Review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2022. early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 39, 640–651. [Google Scholar]
- Bayar, B.; Stamm, M.C. A deep learning approach to universal image manipulation detection using a new convolutional layer. In Proceedings of the 4th ACM Workshop on Information Hiding and Multimedia Security, New York, NY, USA, 20–22 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Y.; Ni, J. A deep learning approach to detection of splicing and copy-move forgeries in images. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 4–7 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fridrich, J.; Kodovsky, J. Rich models for steganalysis of digital images. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2012, 7, 868–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Abdalmageed, W.; Natarajan, P. ManTra-Net: Manipulation tracing network for detection and localization of image forgeries with anomalous features. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, B.; Wei, Y.; Bi, X.; Li, W.; Ma, J. Image splicing forgery detection combining coarse to refined convolutional neural network and adaptive clustering. Inf. Sci. 2020, 511, 172–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A ConvNet for the 2020s. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11976–11986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W., Frangi, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9351, pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 20–24 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Maaten, L.V.D. Densely connected convolutional networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1608.06993v5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.H.; Park, J.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, Q.; Ge, Y.; Duan, S. GAU-Net, U-Net based on global attention mechanism for brain tumor segmentation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1861, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xiong, P.; An, J.; Wang, L. Pyramid attention network for semantic segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.10180. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Han, X.; Morariu, V.I.; Davis, L.S. Learning rich features for image manipulation detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q. An overview of multitask learning. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caruana, R. Multitask learning. Mach. Learn. 1997, 28, 41–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomerleau, D.A. ALVINN, an Autonomous Land Vehicle in a Neural Network; School of Computer Science at Research Showcase @ CMU, Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Vandenhende, S.; Georgoulis, S.; Van Gansbeke, W.; Proesmans, M.; Dai, D.; Van Gool, L. Multitask learning for dense prediction tasks: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 3614–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Wang, W.; Tan, T. Casia image tampering detection evaluation database. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE China Summit and International Conference on Signal and Information Processing, Beijing, China, 1–5 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Krawetz, N. A Picture’s Worth: Digital Image Analysis and Forensics. Available online: https://www.hackerfactor.com/papers/bh-usa-07-krawetz-wp.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2016).
- Ye, S.; Sun, Q.; Chang, E. Detecting digital image forgeries by measuring inconsistencies of blocking artifacts. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Beijing, China, 2–5 July 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 16–20 July 2017. [Google Scholar]



| Methods | CASIA1.0 | CASIA2.0 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | Recall | -Score | Precision | Recall | -Score | |
| ELA | 0.1242 | 0.9147 | 0.2188 | 0.0971 | 0.8864 | 0.1751 |
| Ye’s method | 0.2305 | 0.8272 | 0.3605 | 0.1784 | 0.7798 | 0.2904 |
| FCNS | 0.7763 | 0.4610 | 0.5785 | 0.6482 | 0.4251 | 0.5135 |
| PSPNet | 0.7119 | 0.4953 | 0.5842 | 0.4372 | 0.3775 | 0.4052 |
| DeepLabV3 | 0.7487 | 0.3738 | 0.4987 | 0.5525 | 0.3760 | 0.4475 |
| U-Net | 0.7607 | 0.5337 | 0.6273 | 0.7404 | 0.4654 | 0.5716 |
| DAU-Net | 0.8365 | 0.6765 | 0.7481 | 0.7707 | 0.6114 | 0.6819 |
| AttDAU-Net | 0.7876 | 0.7601 | 0.7736 | 0.7582 | 0.6393 | 0.6937 |
| Method | CASIA1.0 | CASIA2.0 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | Recall | -Score | Precision | Recall | -Score | |
| Basic model | 0.7159 | 0.6539 | 0.6834 | 0.7673 | 0.5393 | 0.6334 |
| Basic model + SRM | 0.7868 | 0.6472 | 0.7102 | 0.8311 | 0.5501 | 0.6620 |
| Basic model + GAU | 0.7316 | 0.6672 | 0.6979 | 0.7680 | 0.5675 | 0.6527 |
| Basic model + SRM + GAU | 0.7954 | 0.7081 | 0.7492 | 0.7381 | 0.6141 | 0.6704 |
| AttDAU-Net | 0.7876 | 0.7601 | 0.7736 | 0.7582 | 0.6393 | 0.6937 |
| Attack | Compression (Quality Factor) | Gaussian Blurring (Standard Deviation) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metrics | 95% | 90% | 80% | 70% | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | |
| Precision | 0.7795 | 0.7699 | 0.6143 | 0.5667 | 0.7742 | 0.7548 | 0.7362 | 0.7265 | |
| Recall | 0.6827 | 0.5765 | 0.4830 | 0.4962 | 0.7554 | 0.7618 | 0.7571 | 0.7563 | |
| -score | 0.7279 | 0.6593 | 0.5408 | 0.5291 | 0.7647 | 0.7583 | 0.7465 | 0.7411 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, P.; Tong, L.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, N.; Wu, J. Multitask Image Splicing Tampering Detection Based on Attention Mechanism. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3852. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10203852
Zeng P, Tong L, Liang Y, Zhou N, Wu J. Multitask Image Splicing Tampering Detection Based on Attention Mechanism. Mathematics. 2022; 10(20):3852. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10203852
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Pingping, Lianhui Tong, Yaru Liang, Nanrun Zhou, and Jianhua Wu. 2022. "Multitask Image Splicing Tampering Detection Based on Attention Mechanism" Mathematics 10, no. 20: 3852. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10203852
APA StyleZeng, P., Tong, L., Liang, Y., Zhou, N., & Wu, J. (2022). Multitask Image Splicing Tampering Detection Based on Attention Mechanism. Mathematics, 10(20), 3852. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10203852









