Mathematical Modelling of Harmful Algal Blooms on West Coast of Sabah
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
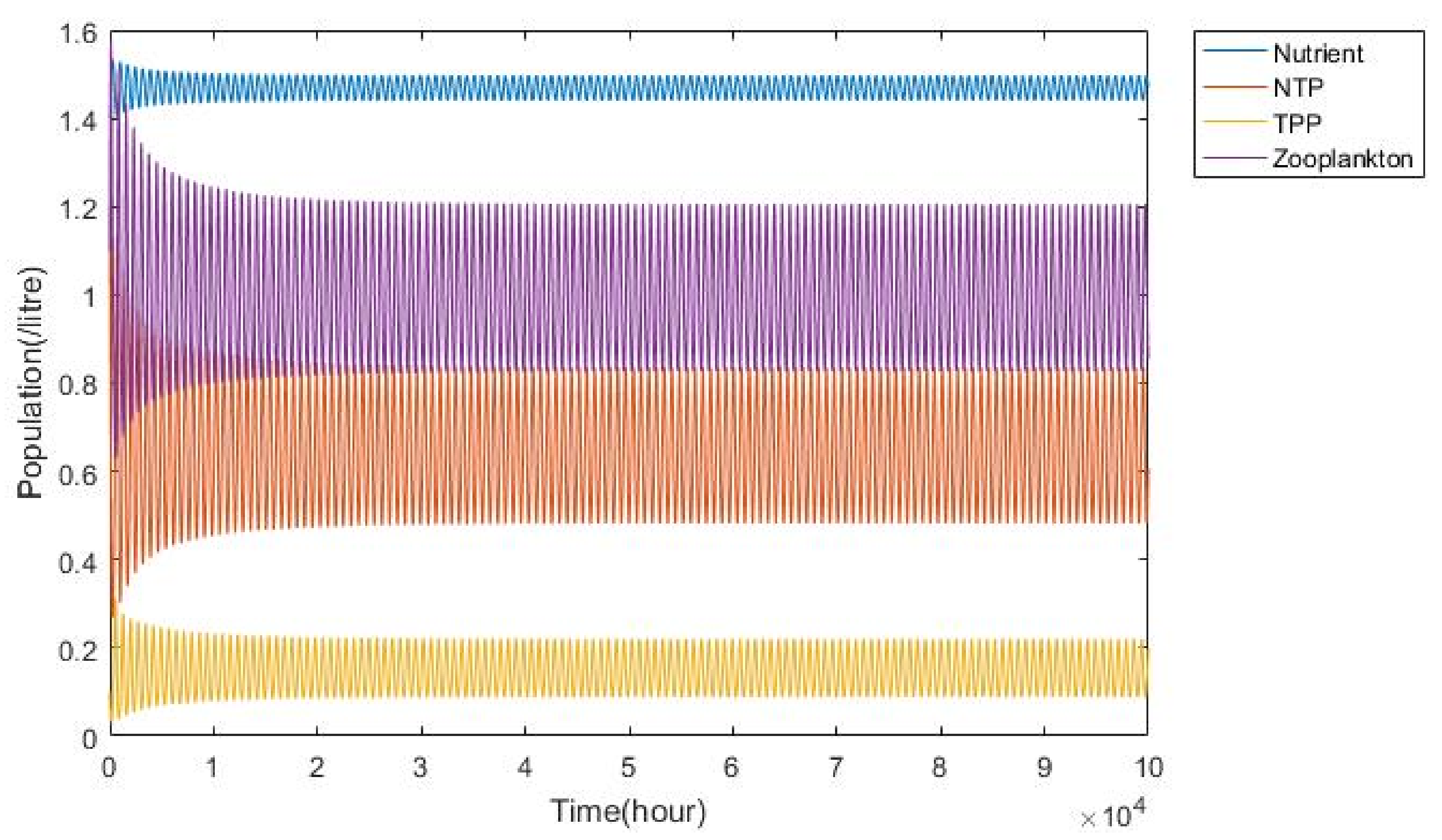
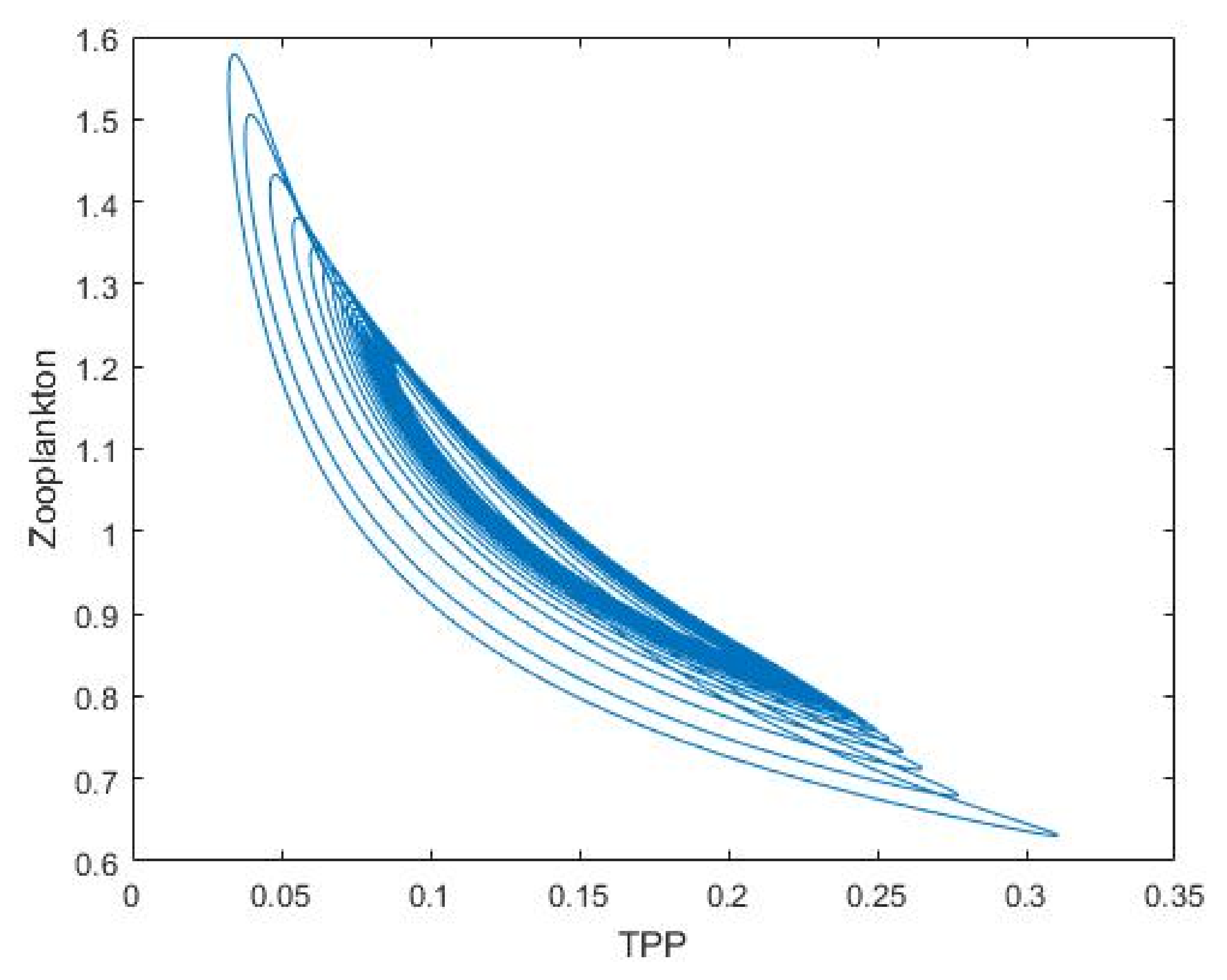
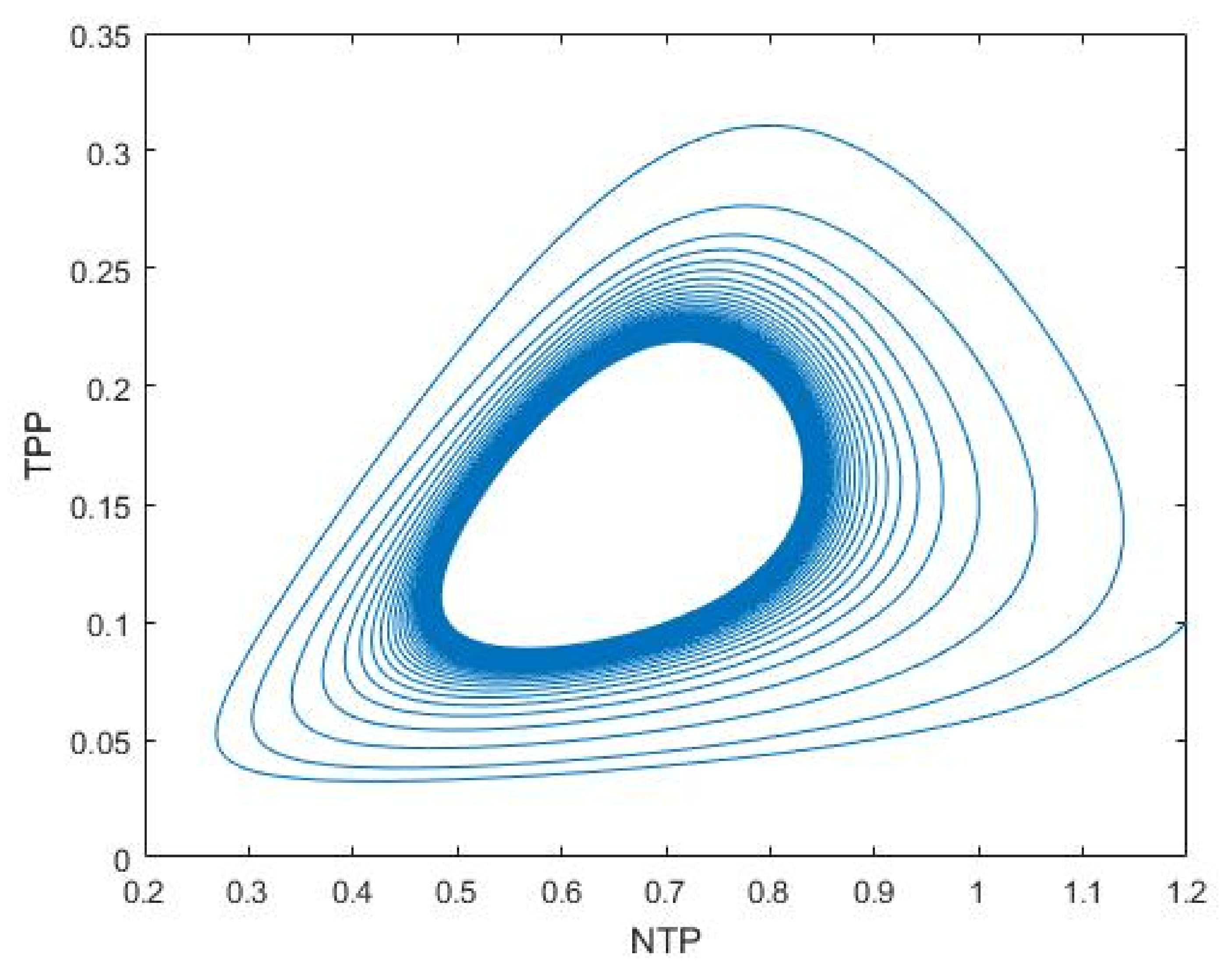
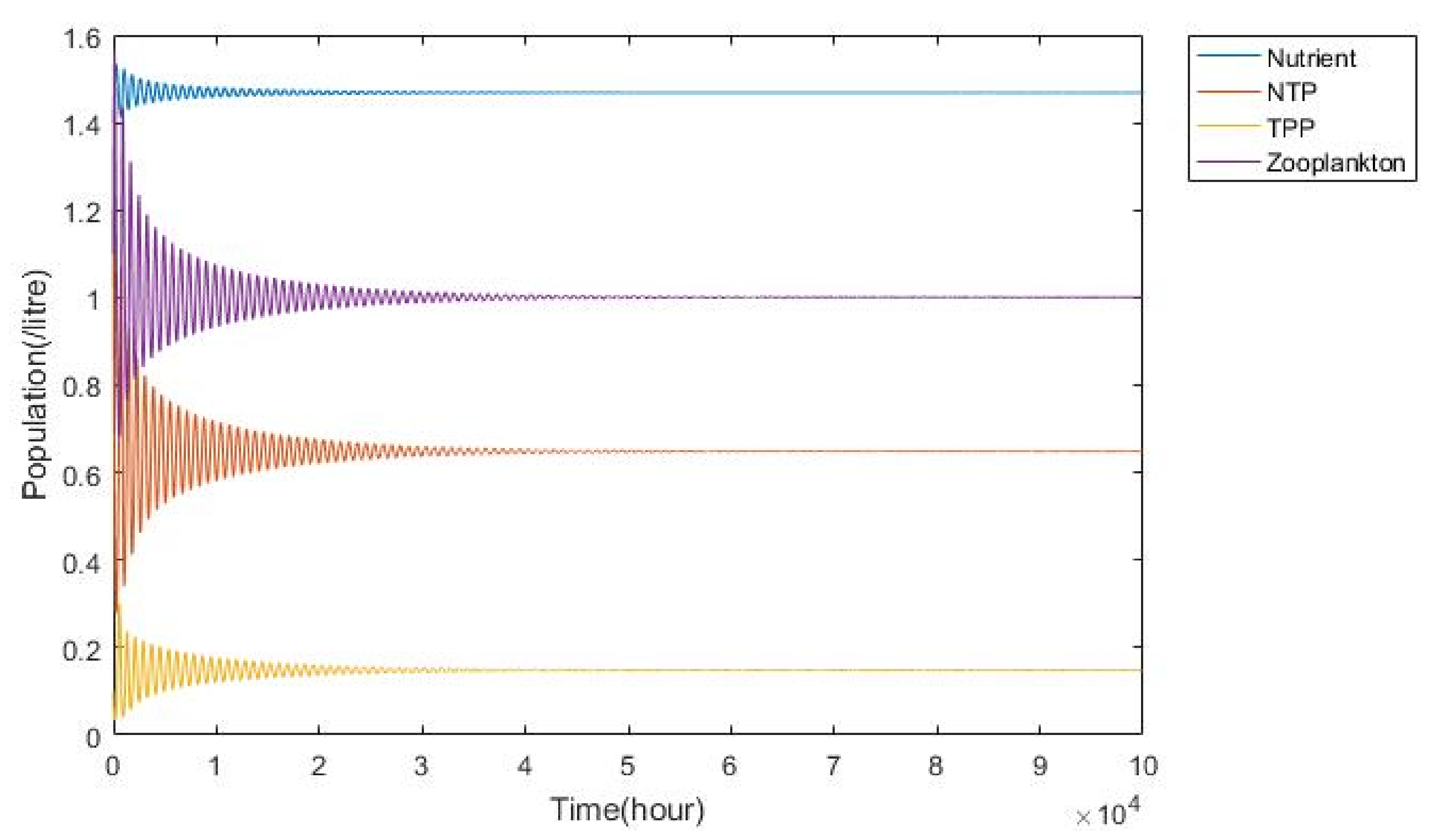
2.1. Nutrient-Phytoplankton-Zooplankton Interaction Model
- The linear mass action law is used for the maximal zooplankton predation rate for NTP and TPP [17].
- The model considered interspecies competition to obtain nutrients [17].
- TPP harm the zooplankton whenever they are consumed and the toxin content is produced at a high level [18].
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
2.2. Plankton–Zooplankton–Fish Interaction Model
- Let be the toxin production phytoplankton (TPP) which are being consumed by the zooplankton population which in turn serves as food for the fish population, .
- Let r be the intrinsic growth rate of phytoplankton; K be the environmental capacity of phytoplankton; and be the predation rate of zooplankton while is the predation rate of fish.
- is the birth rate of zooplankton while is the birth rate of fish, is the mortality rate of zooplankton and is mortality rate of fish, and f is coefficient of toxin substance from TPP.
- Let be the time delay for the fish to die when feeding on the infected zooplankton as this is not an instantaneous process. The infected zooplankton become harmful to the fish when eaten.
3. Results
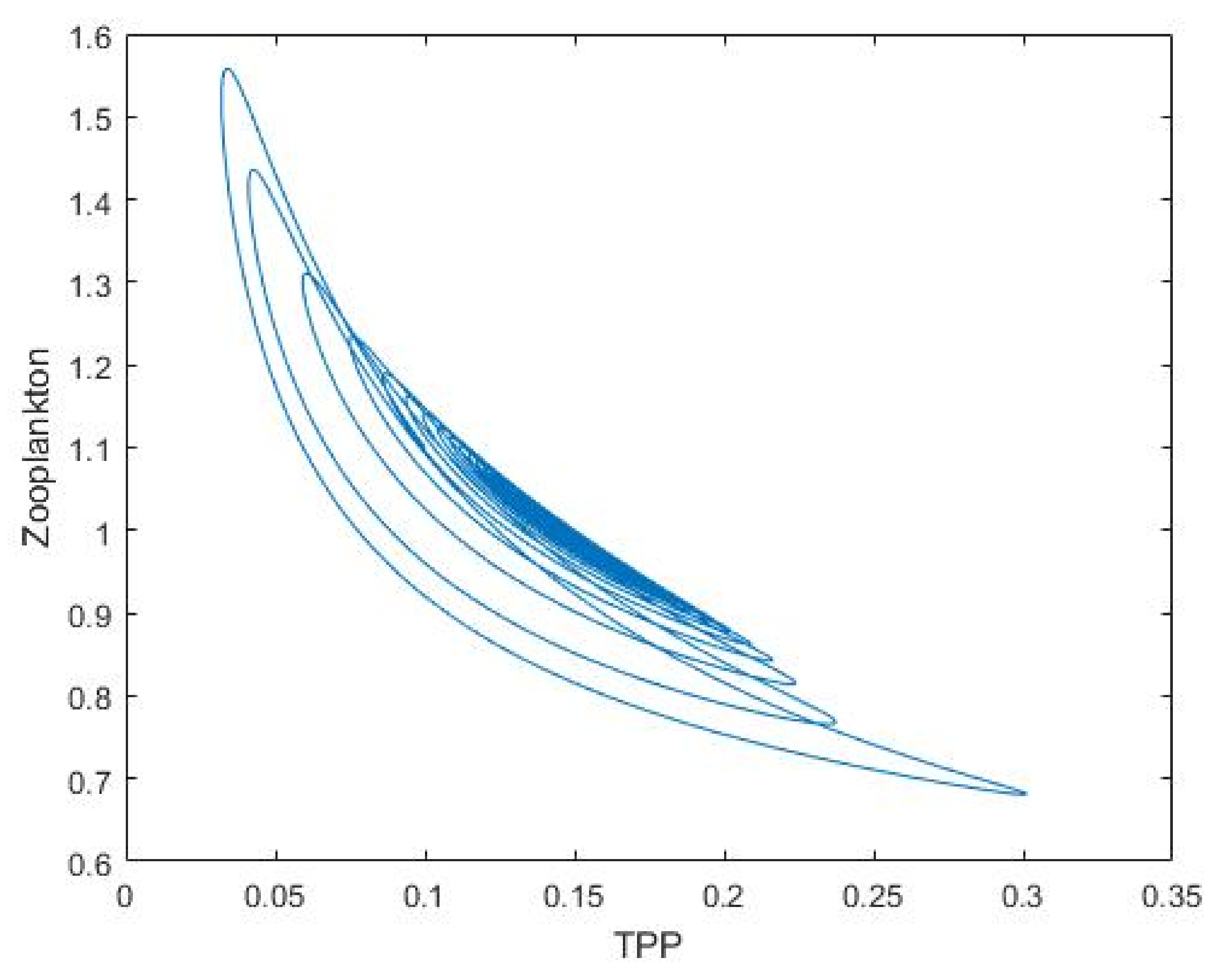
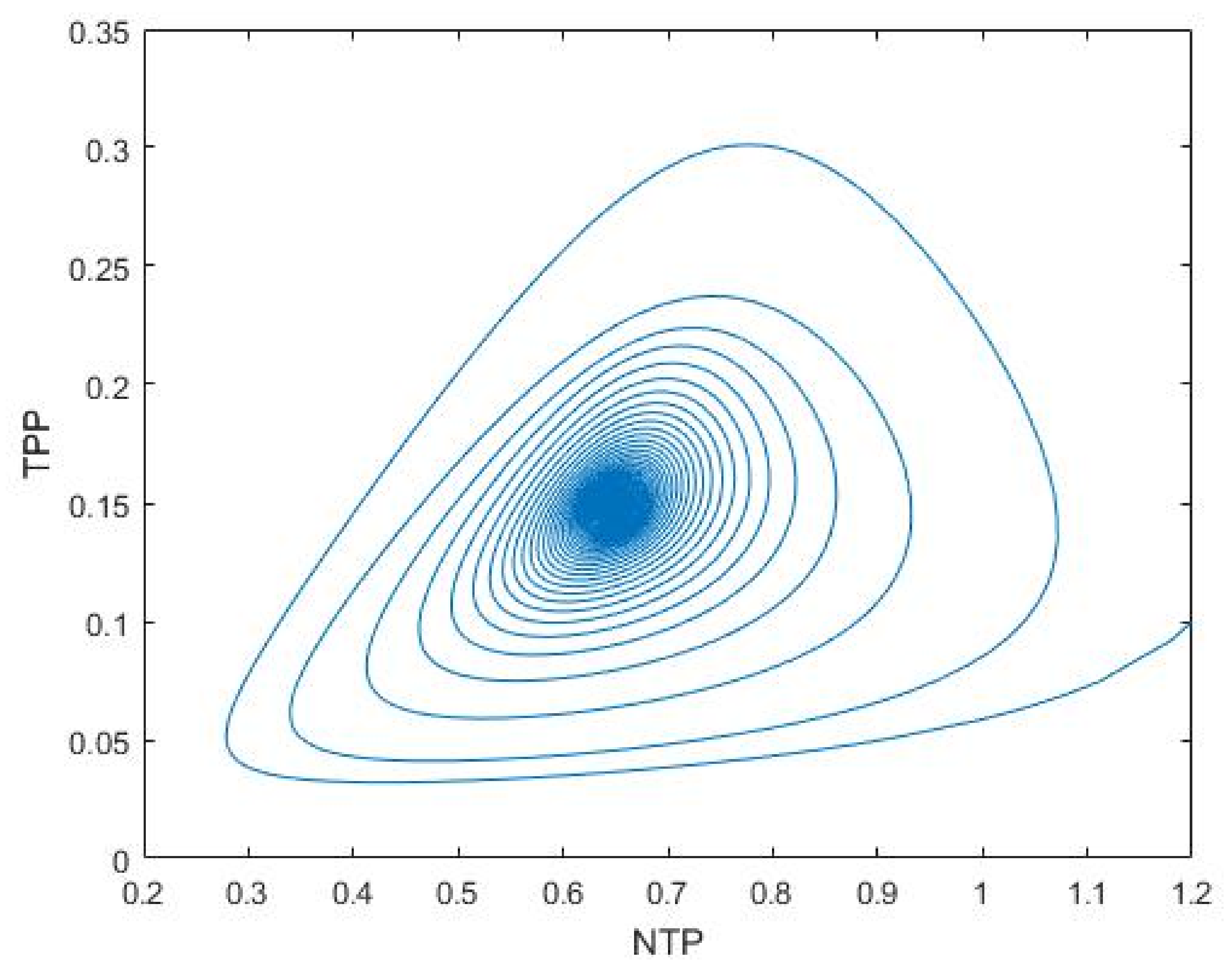
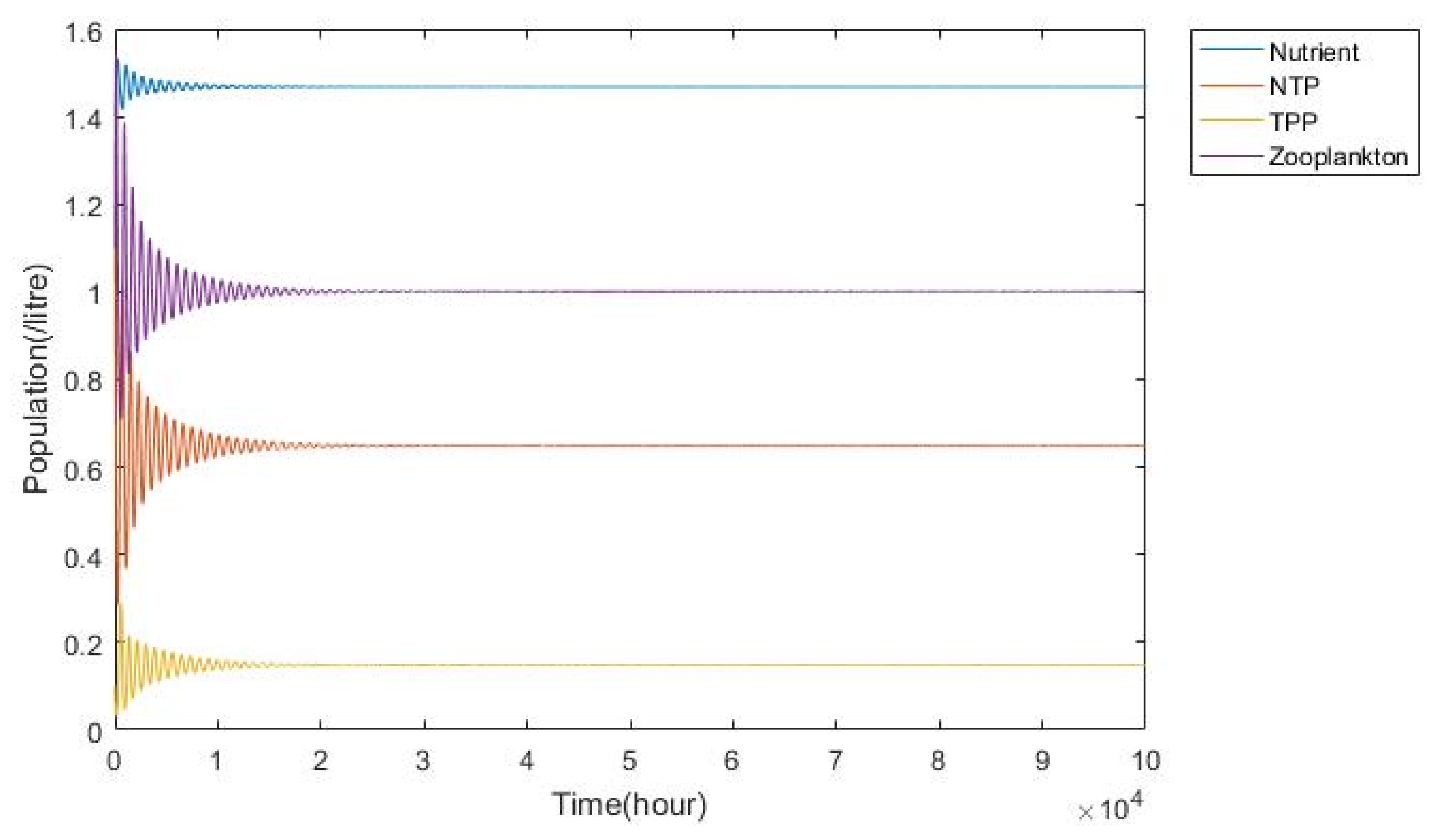
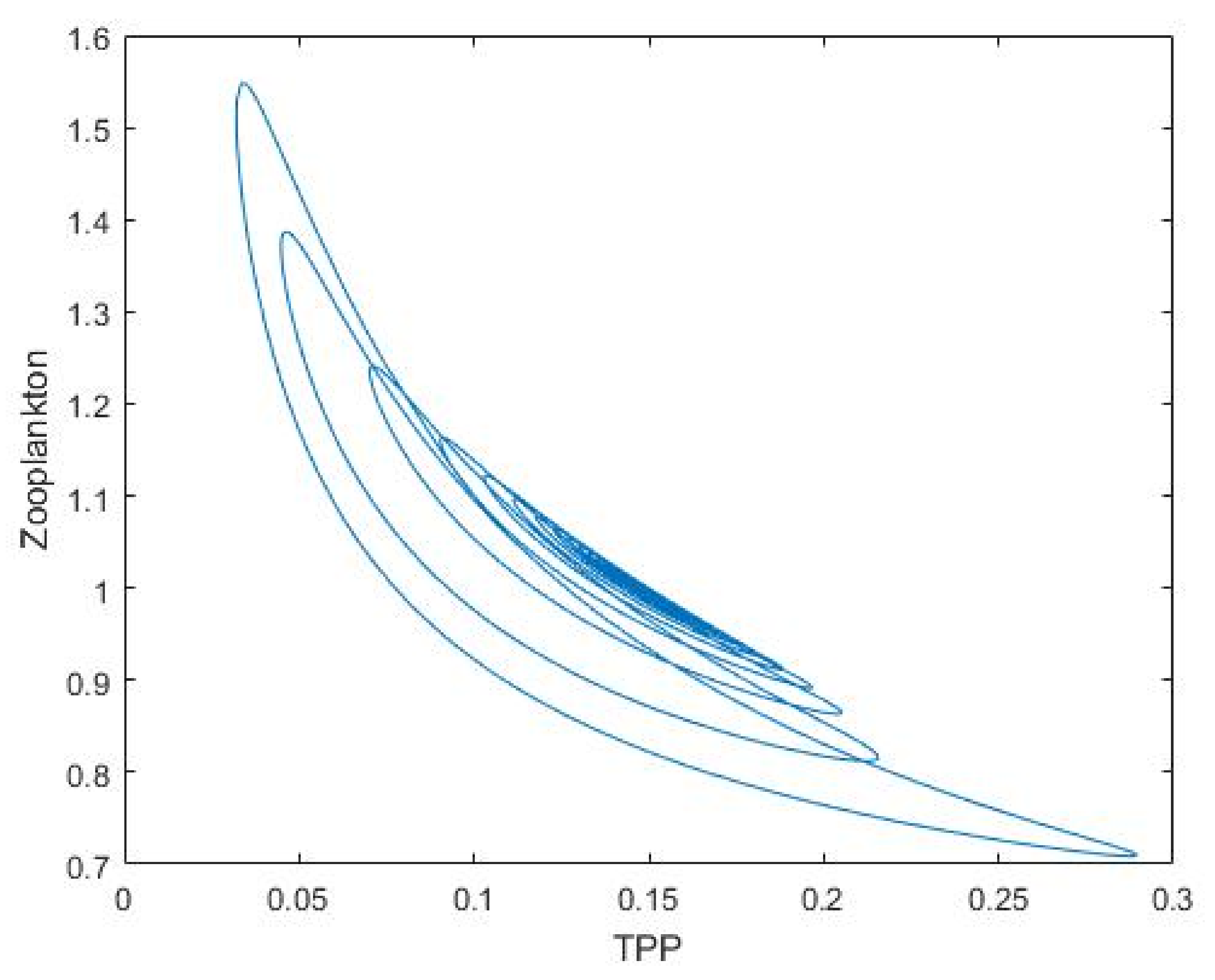
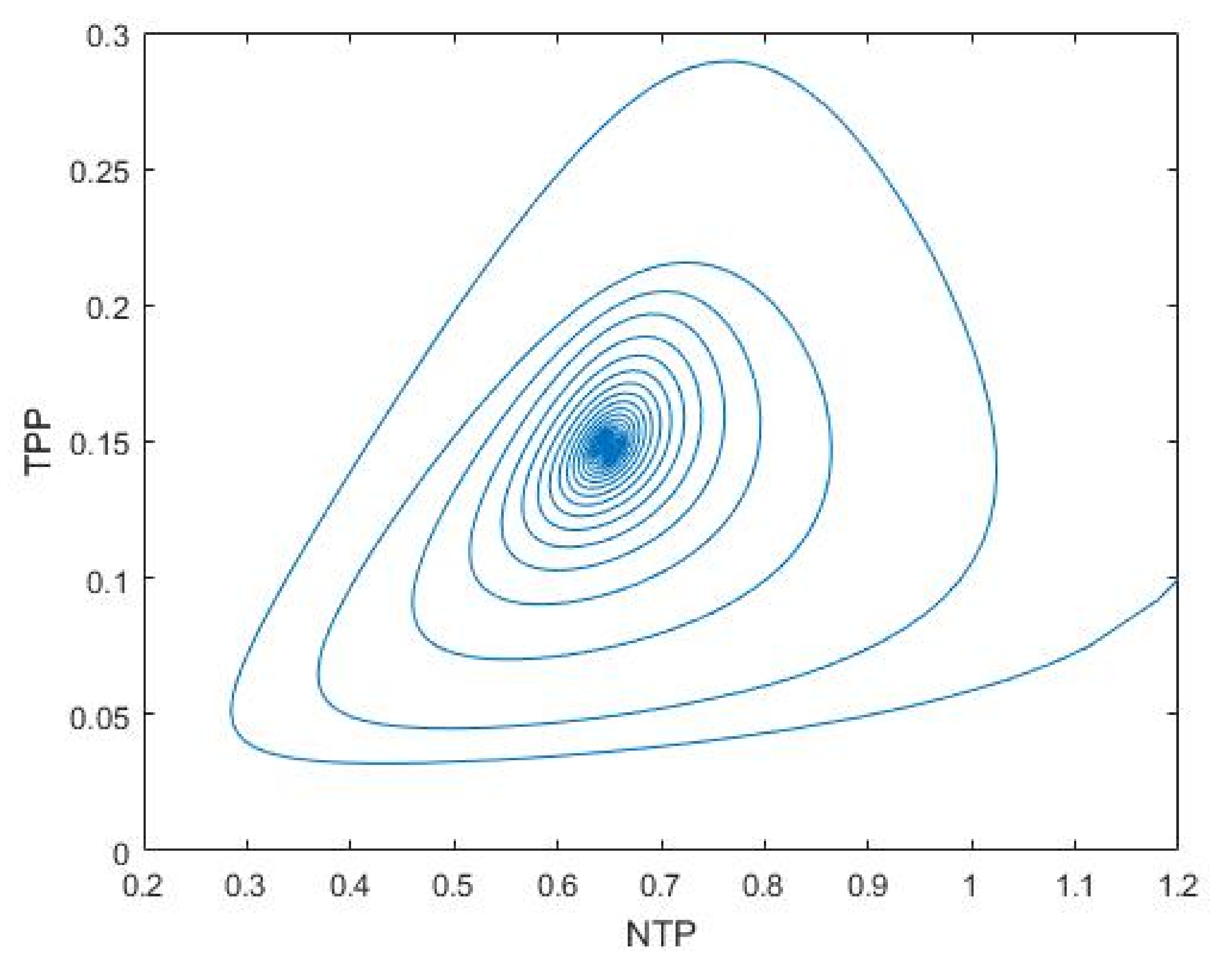
3.1. Nutrient–Phytoplankton–Zooplankton Interaction Model
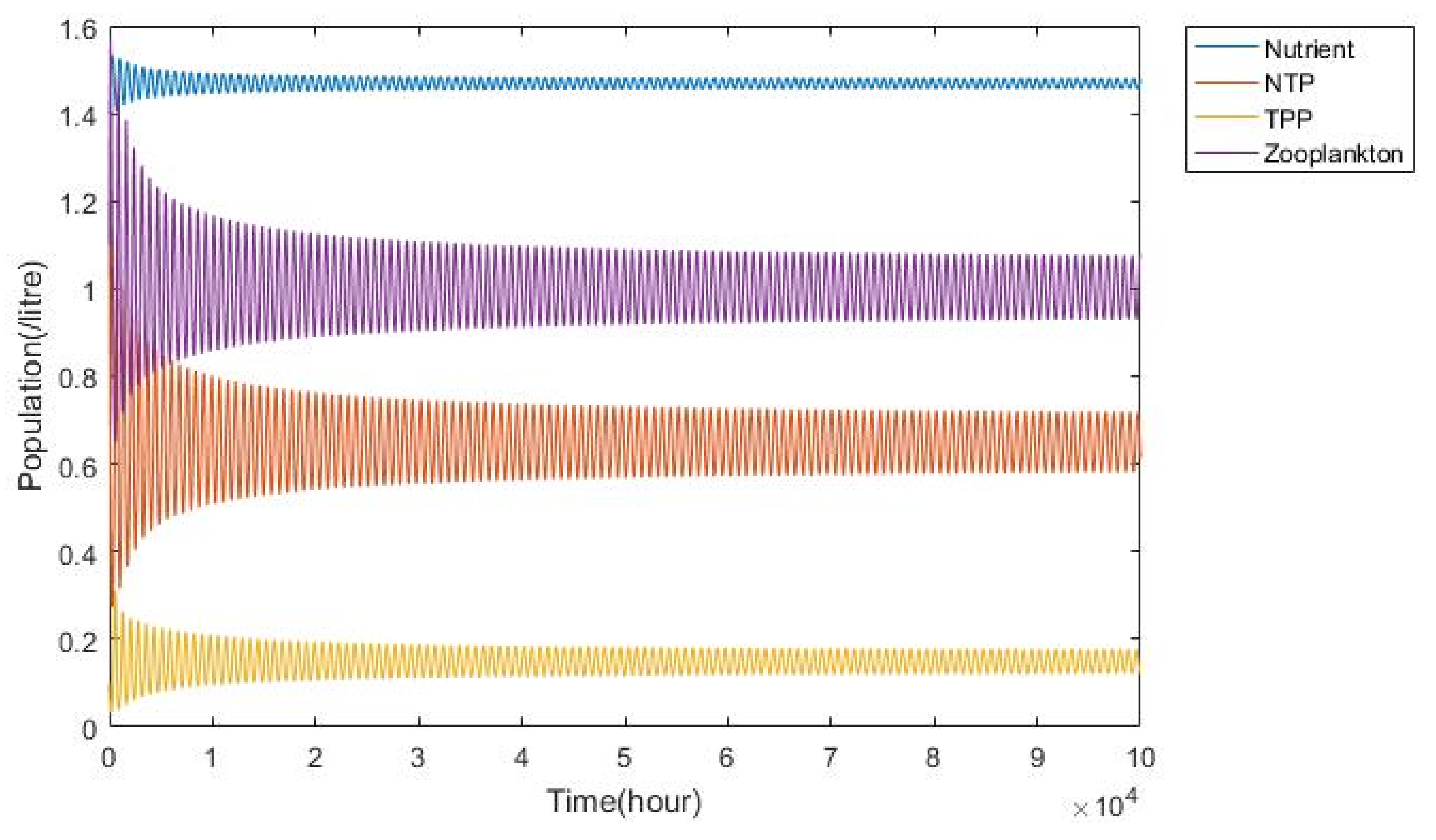
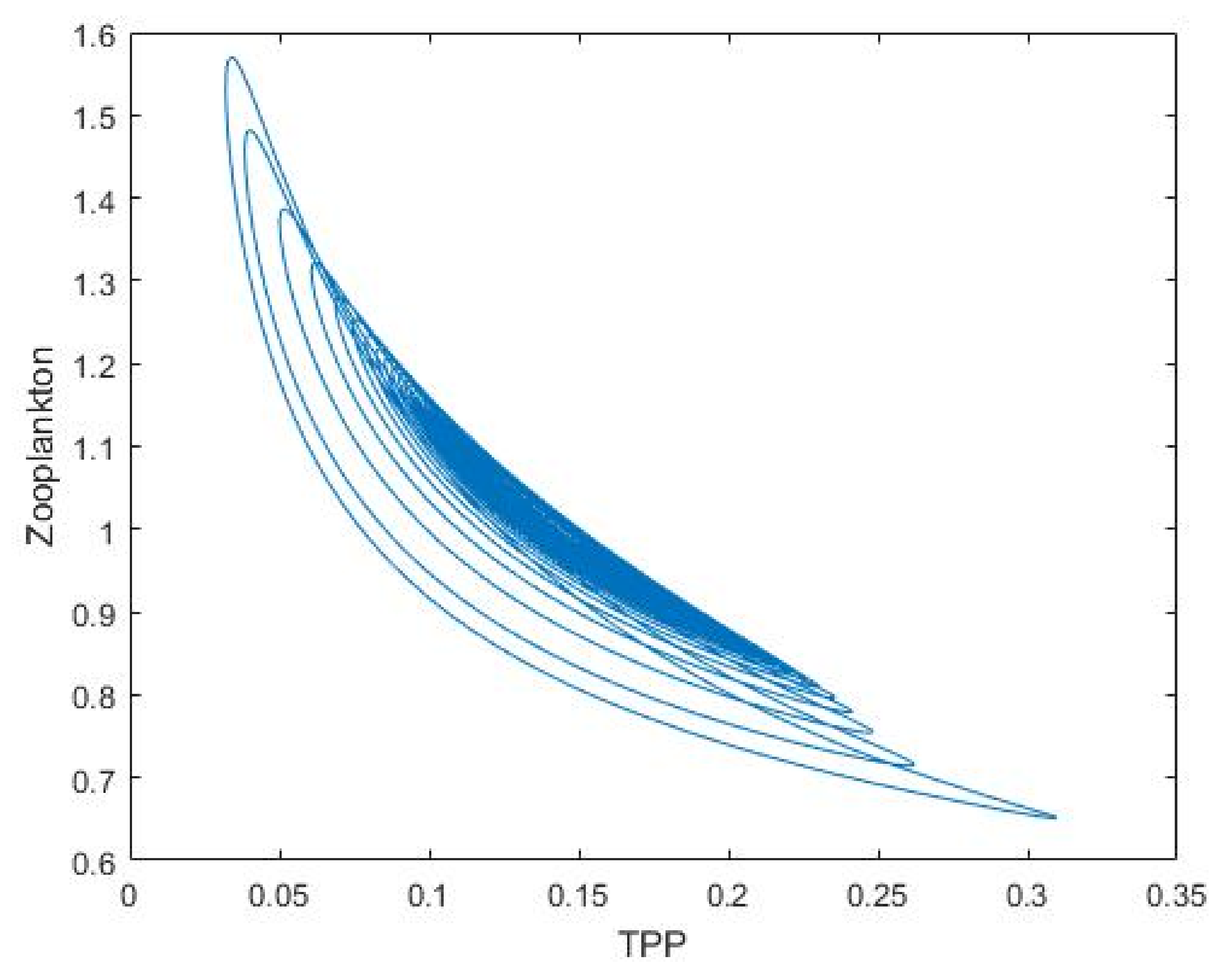
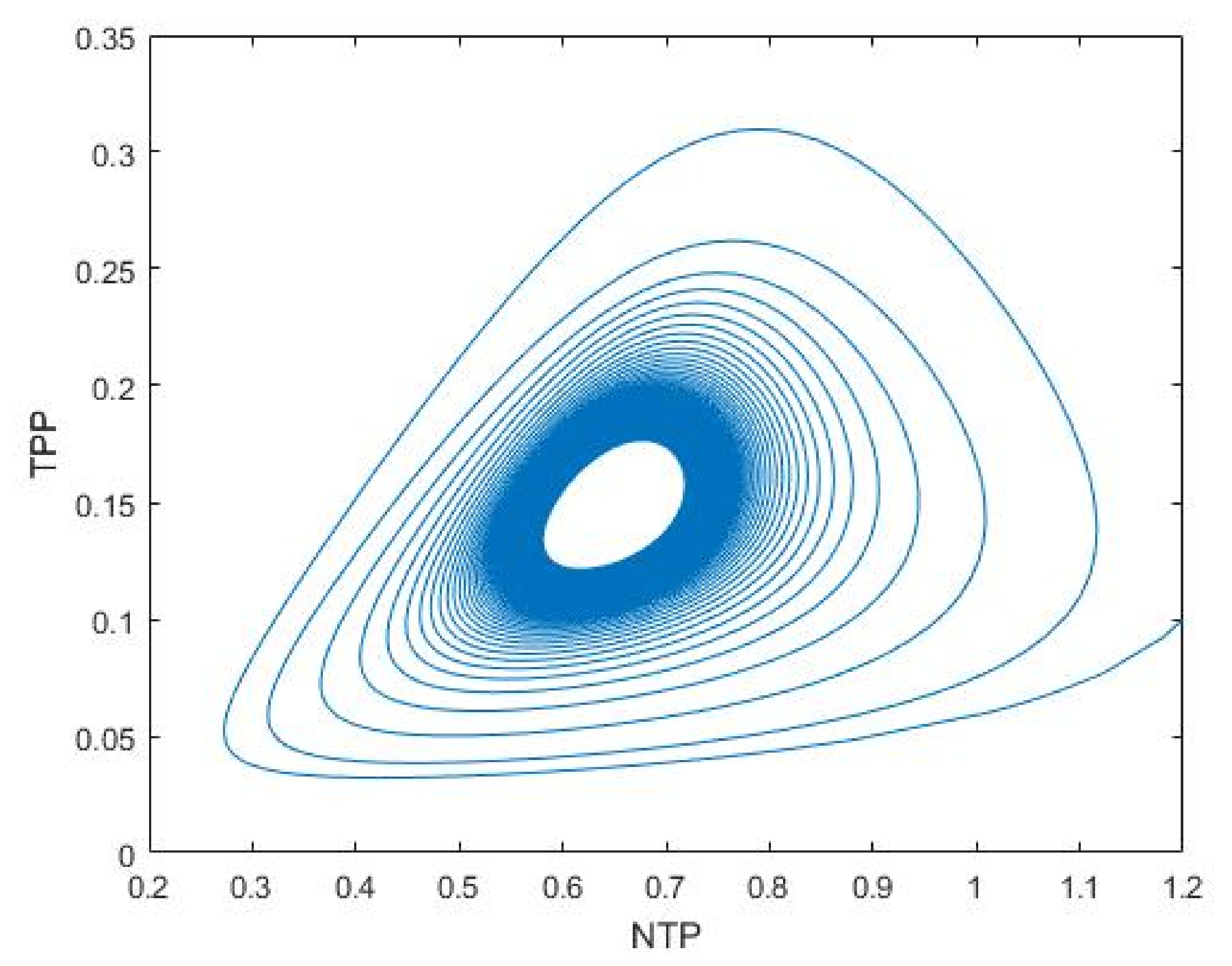
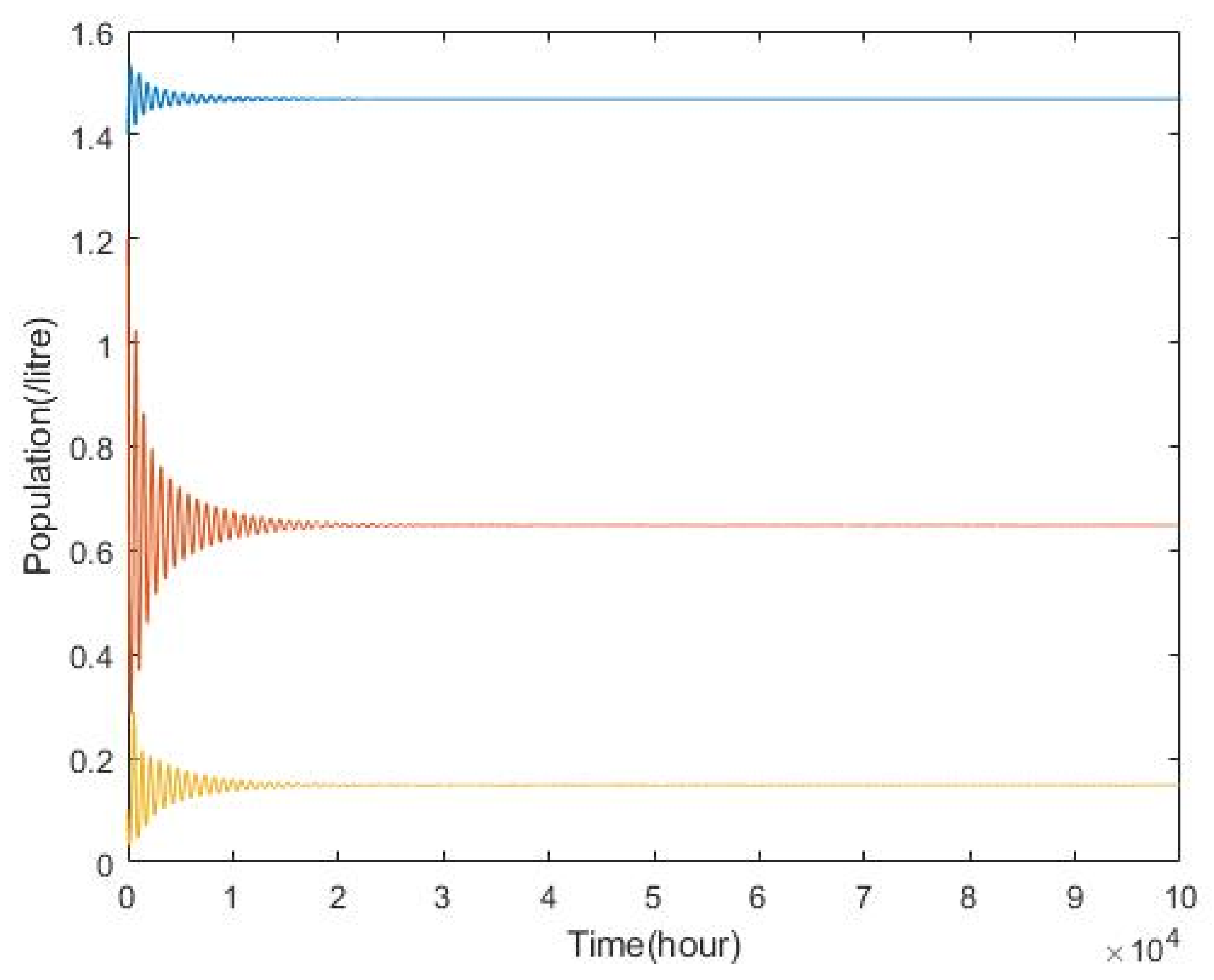
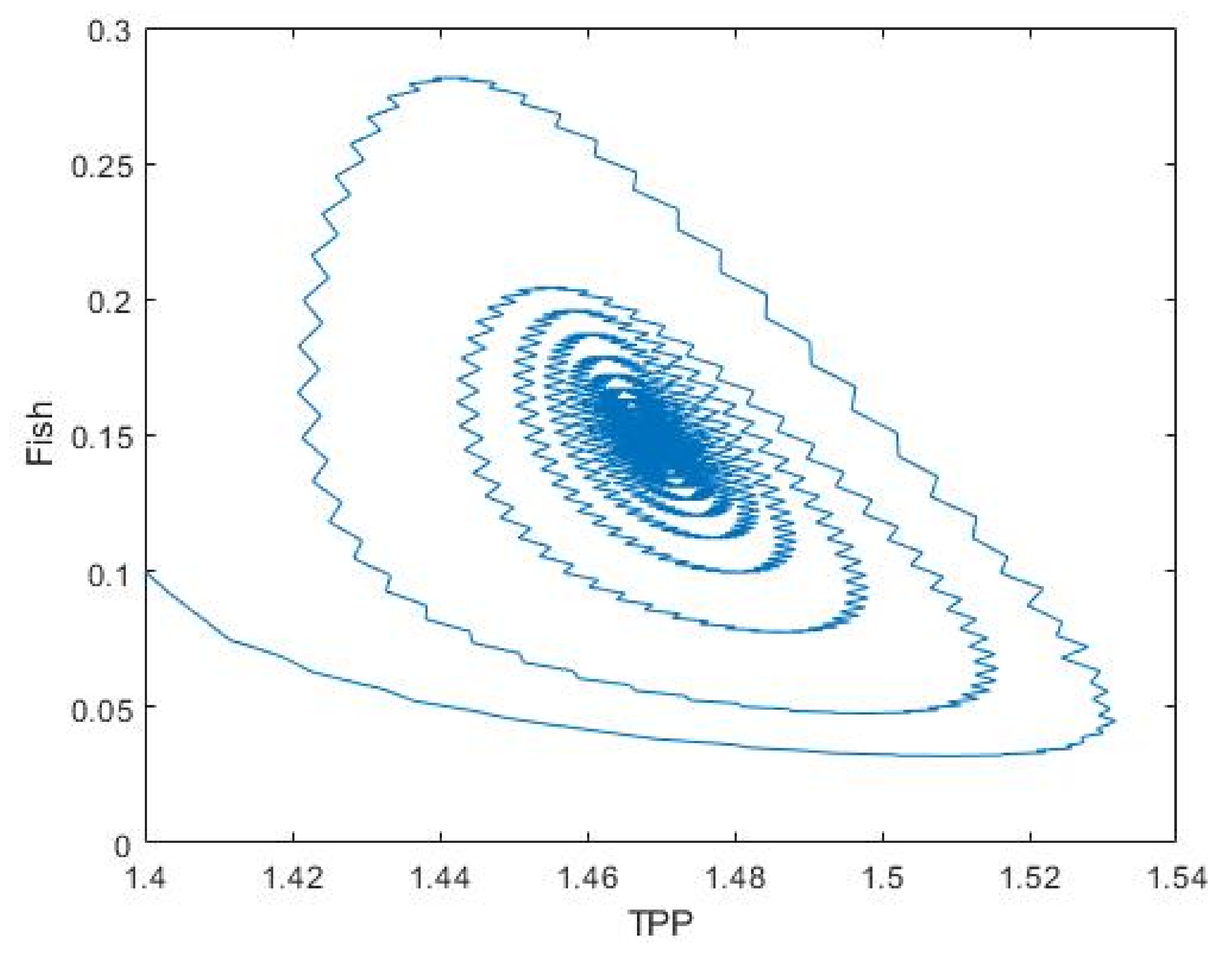
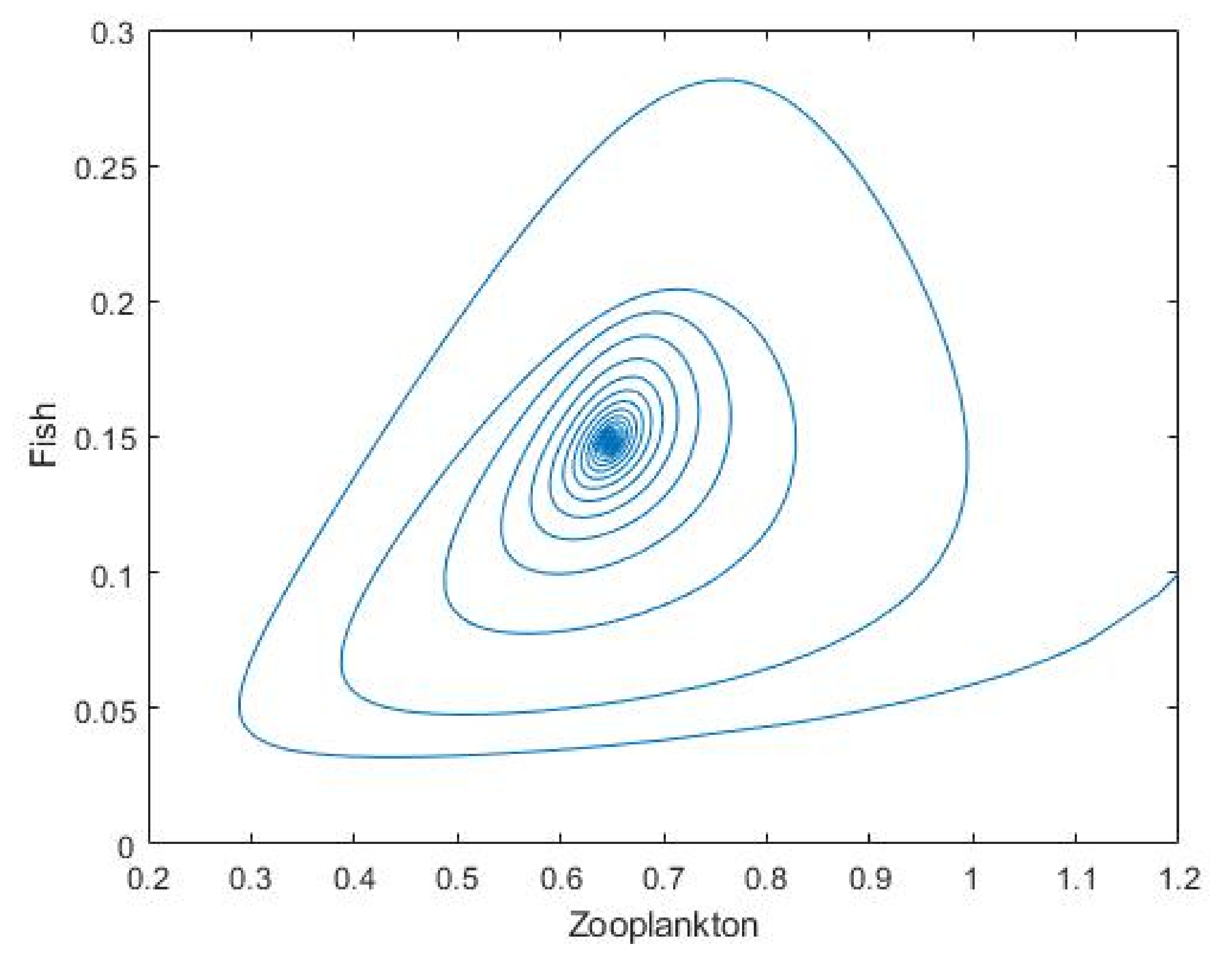
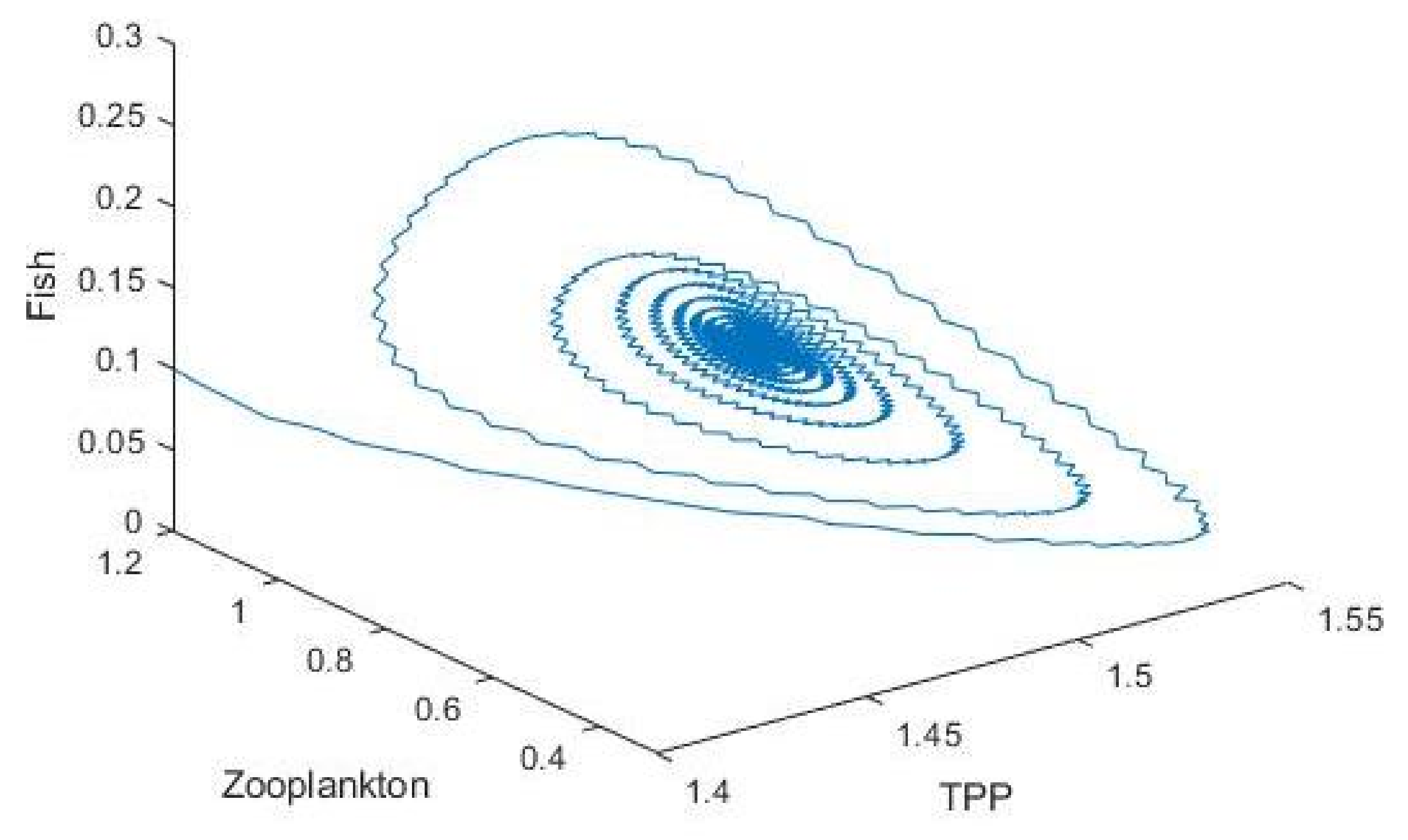
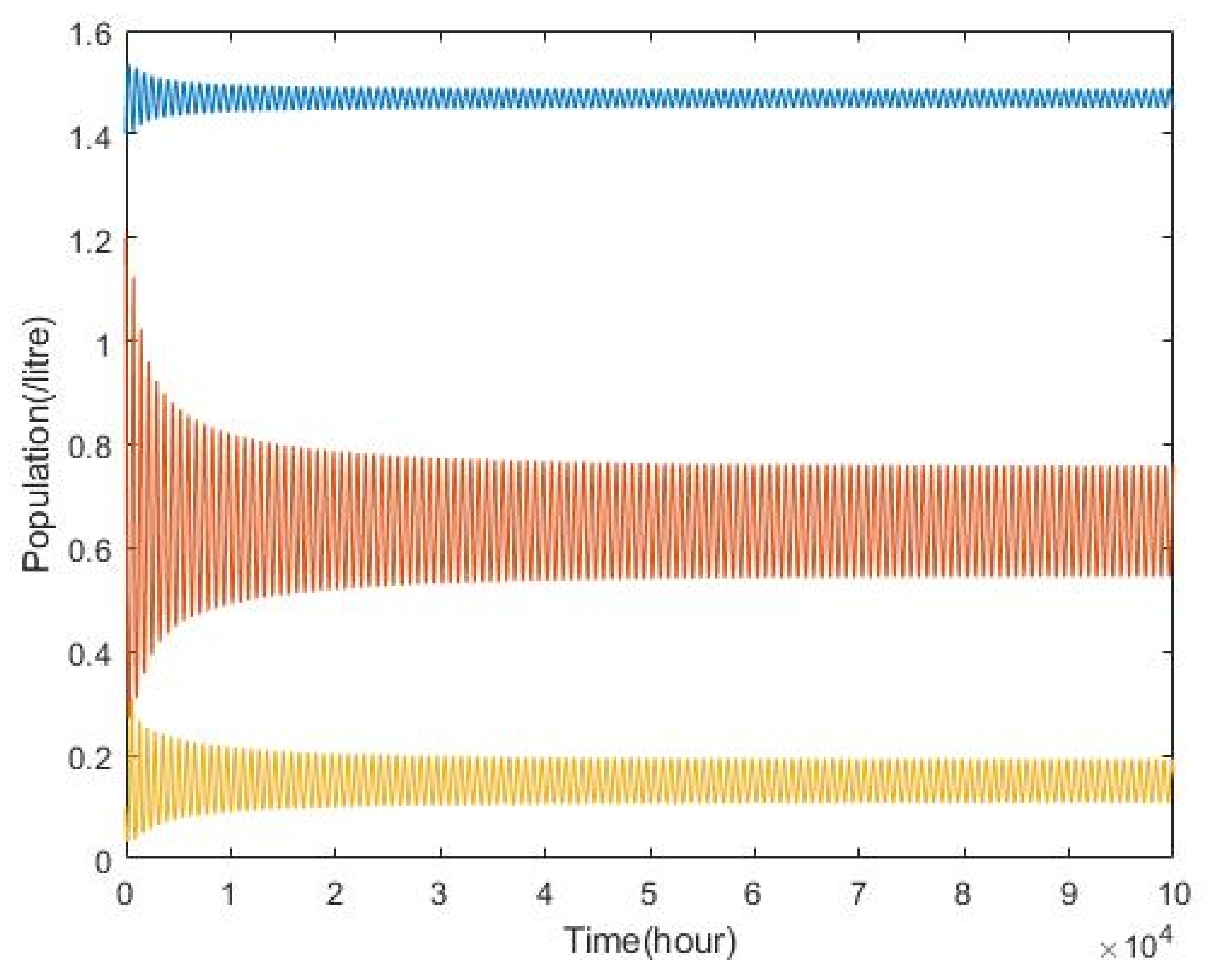
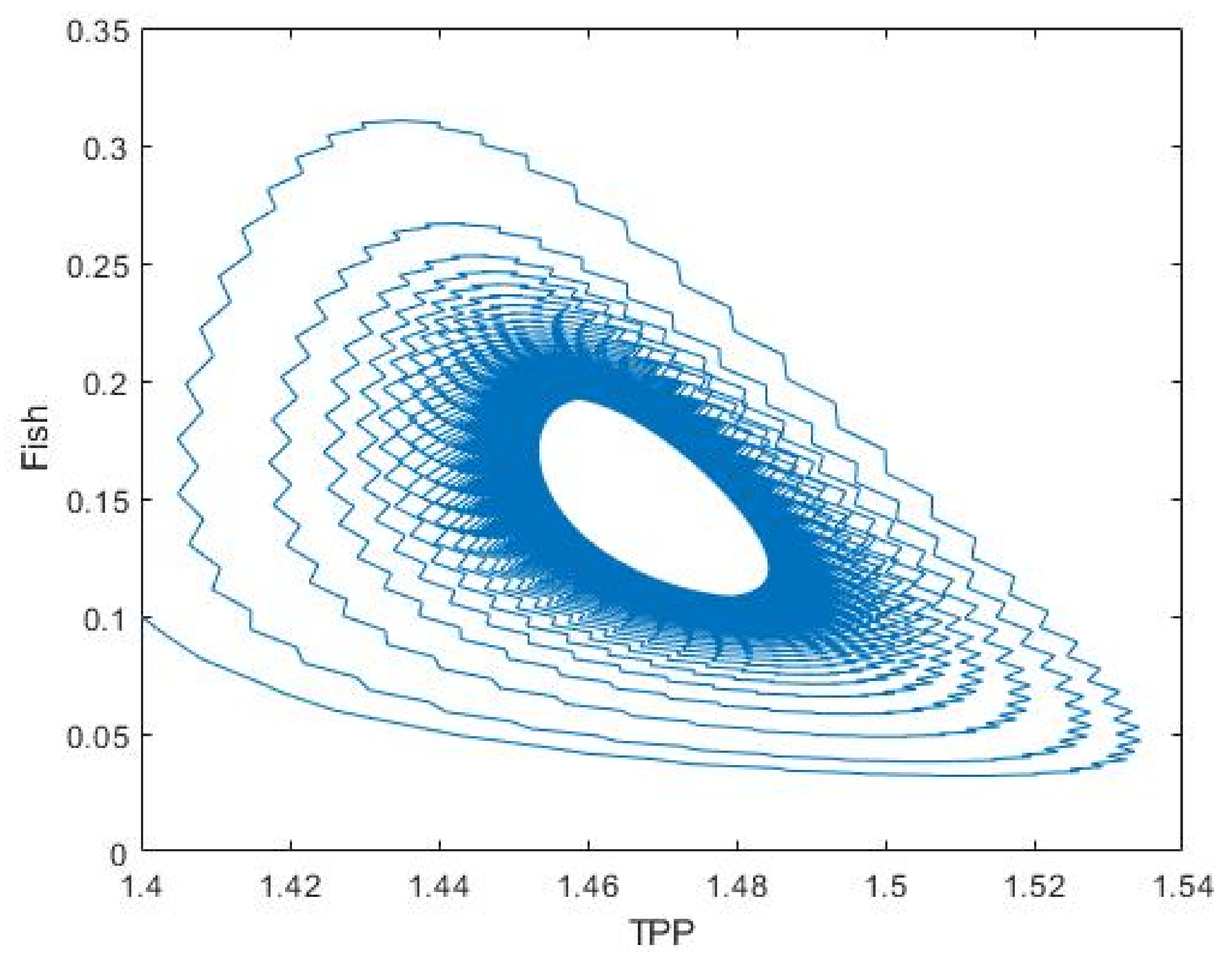
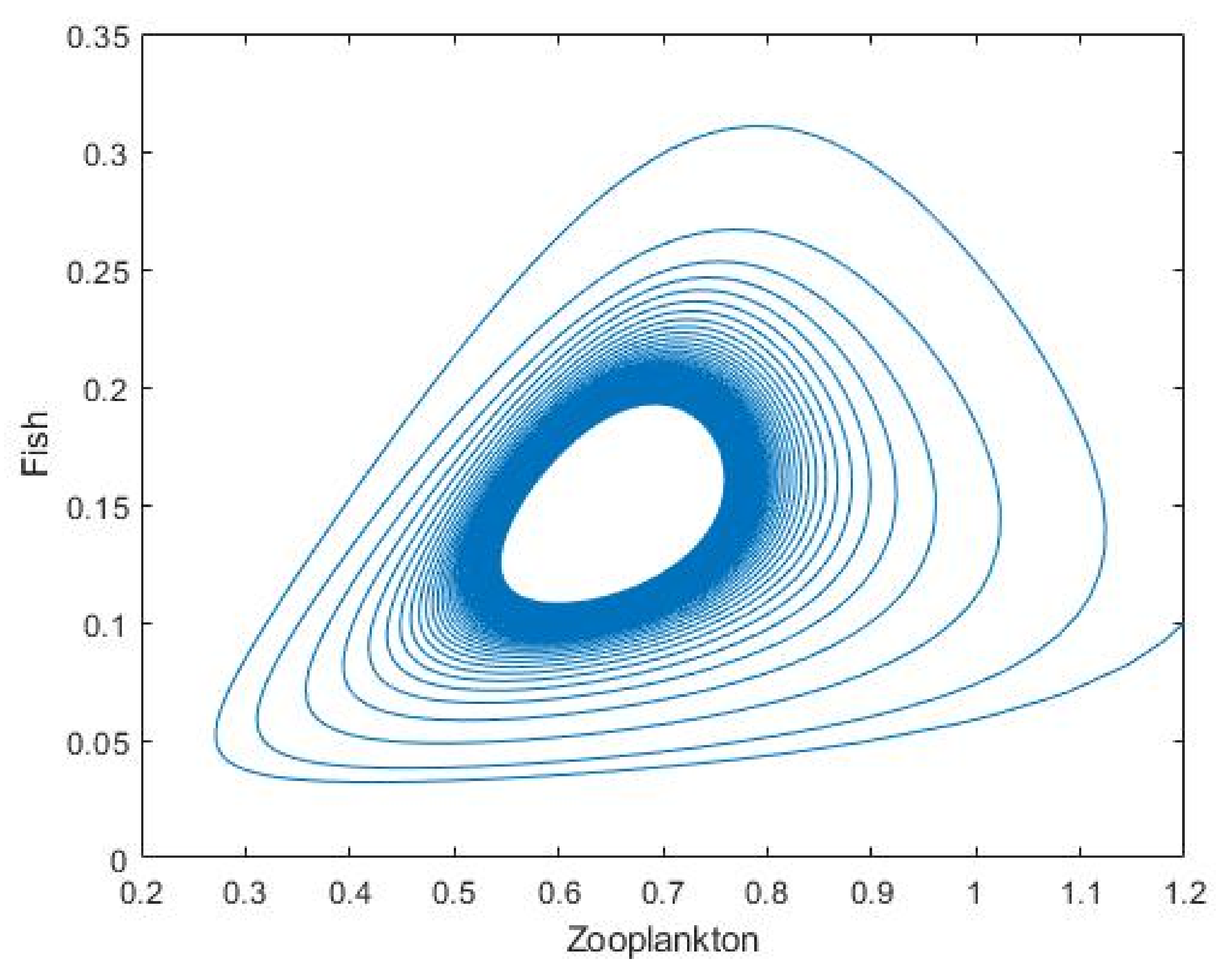
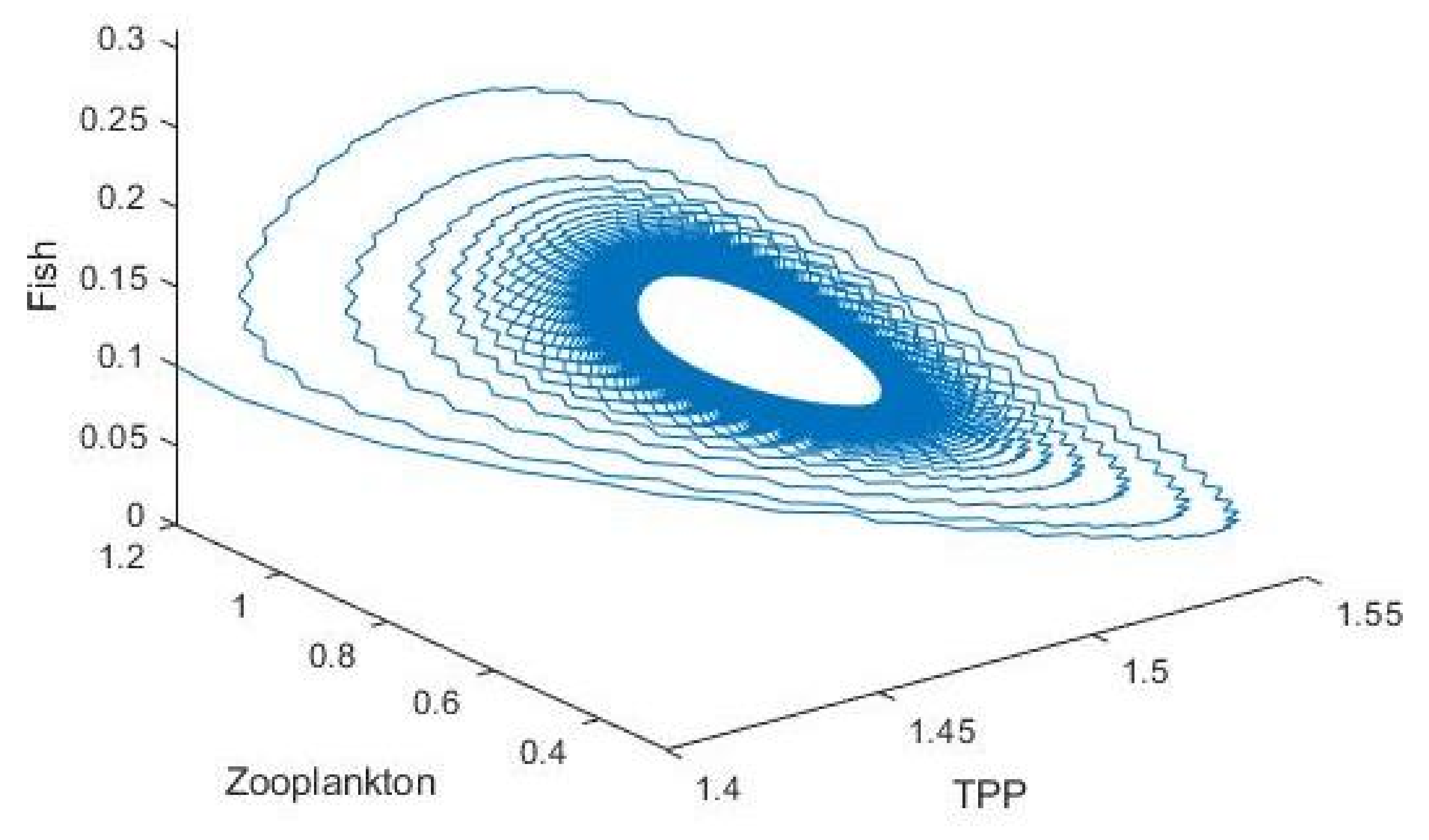
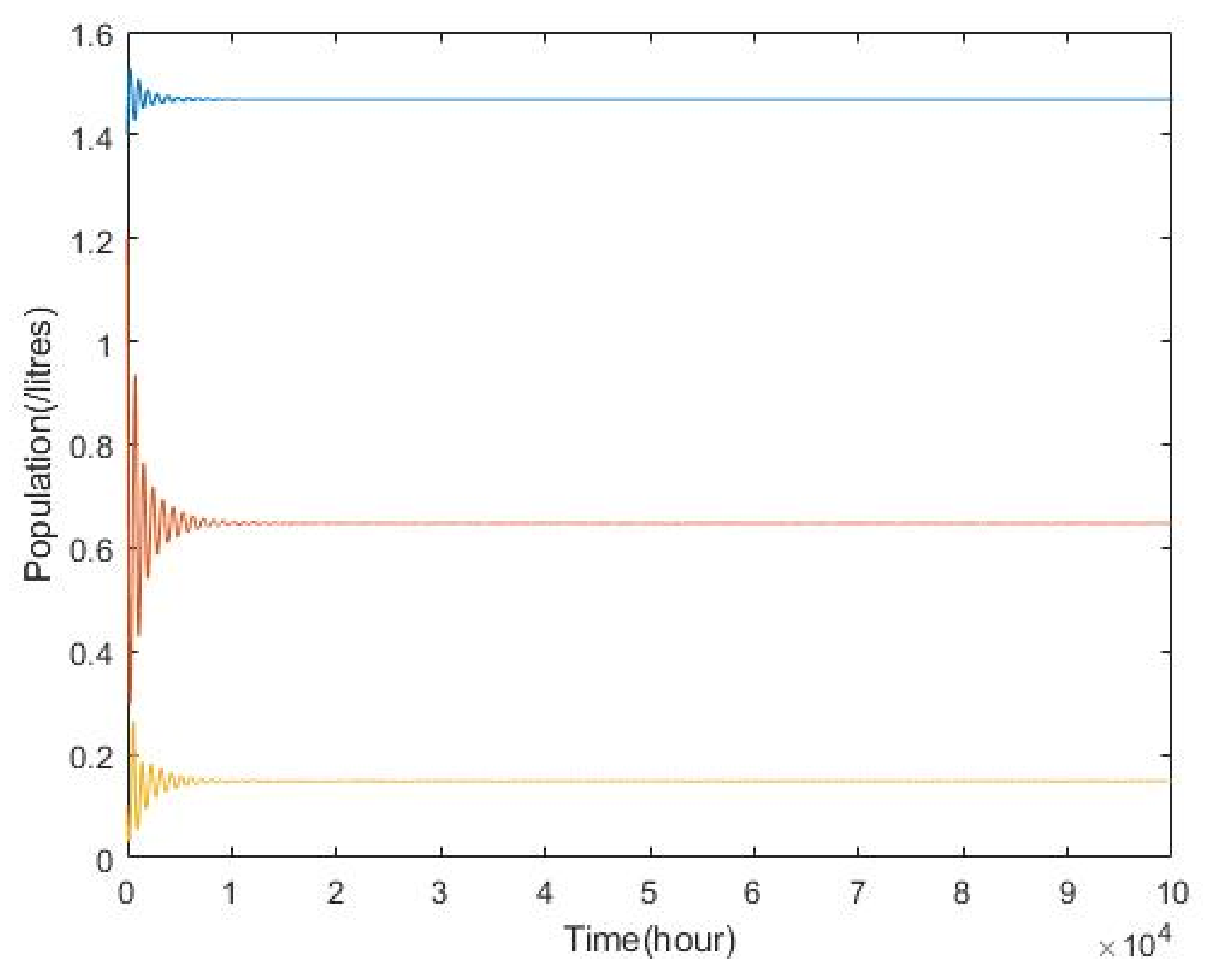
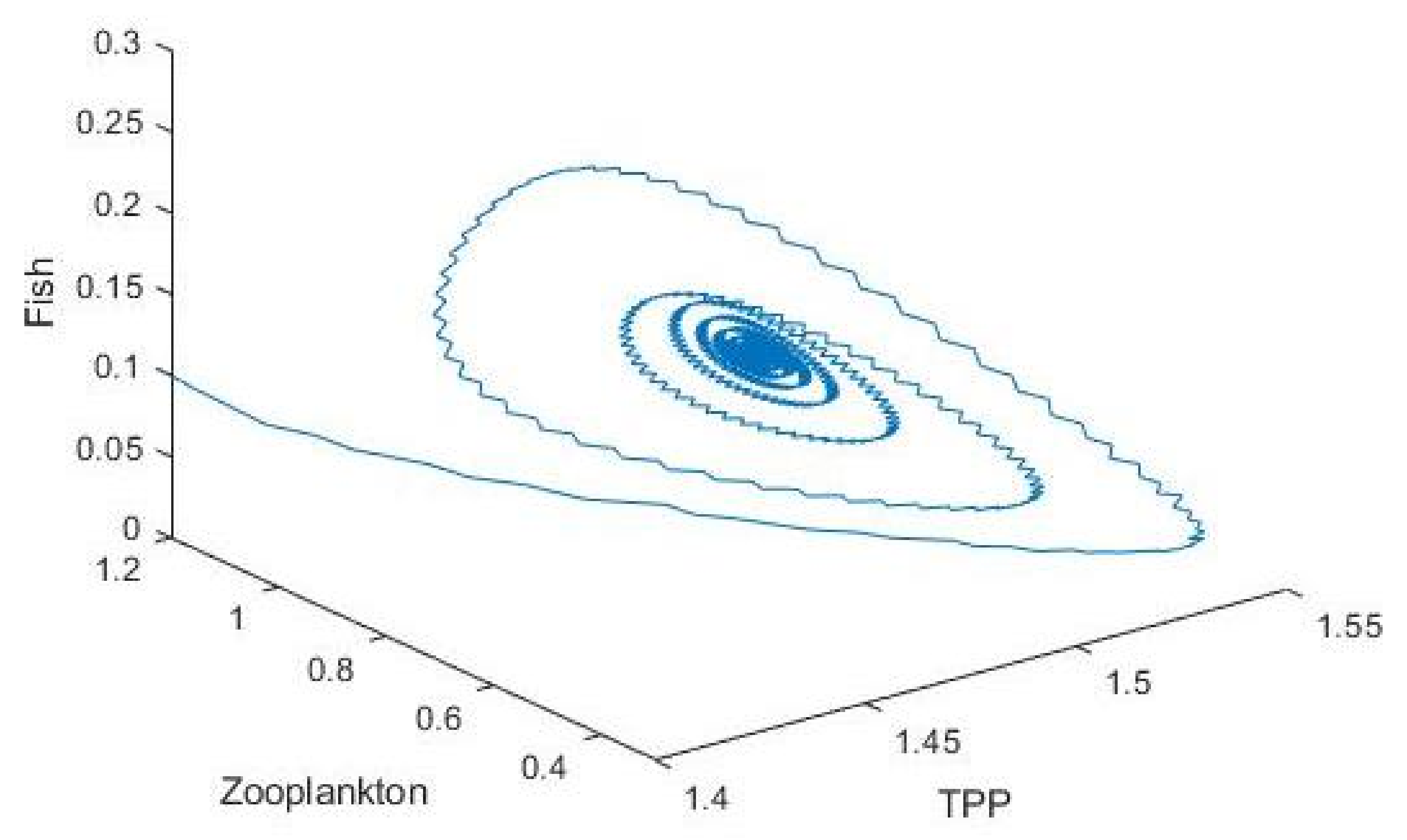
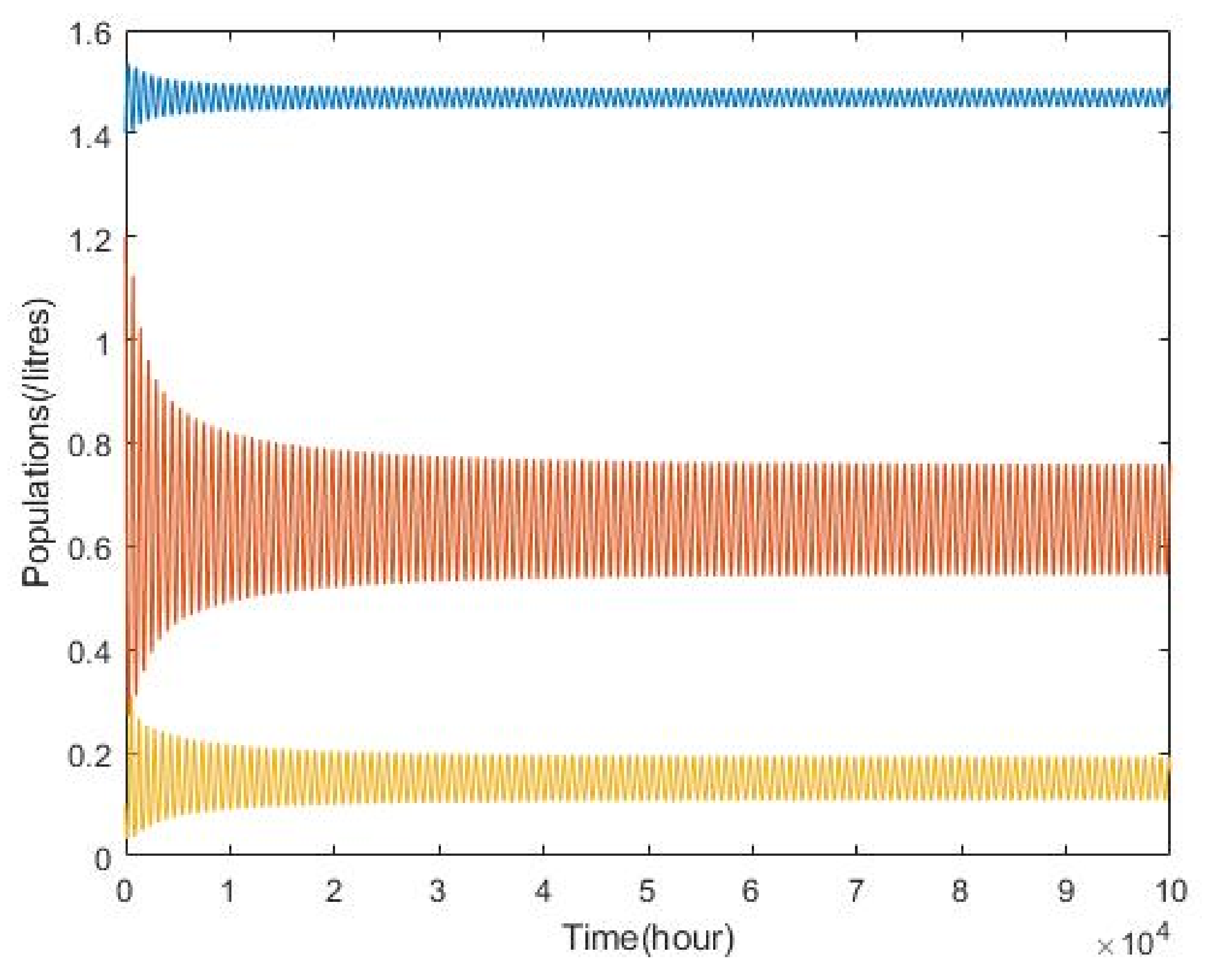
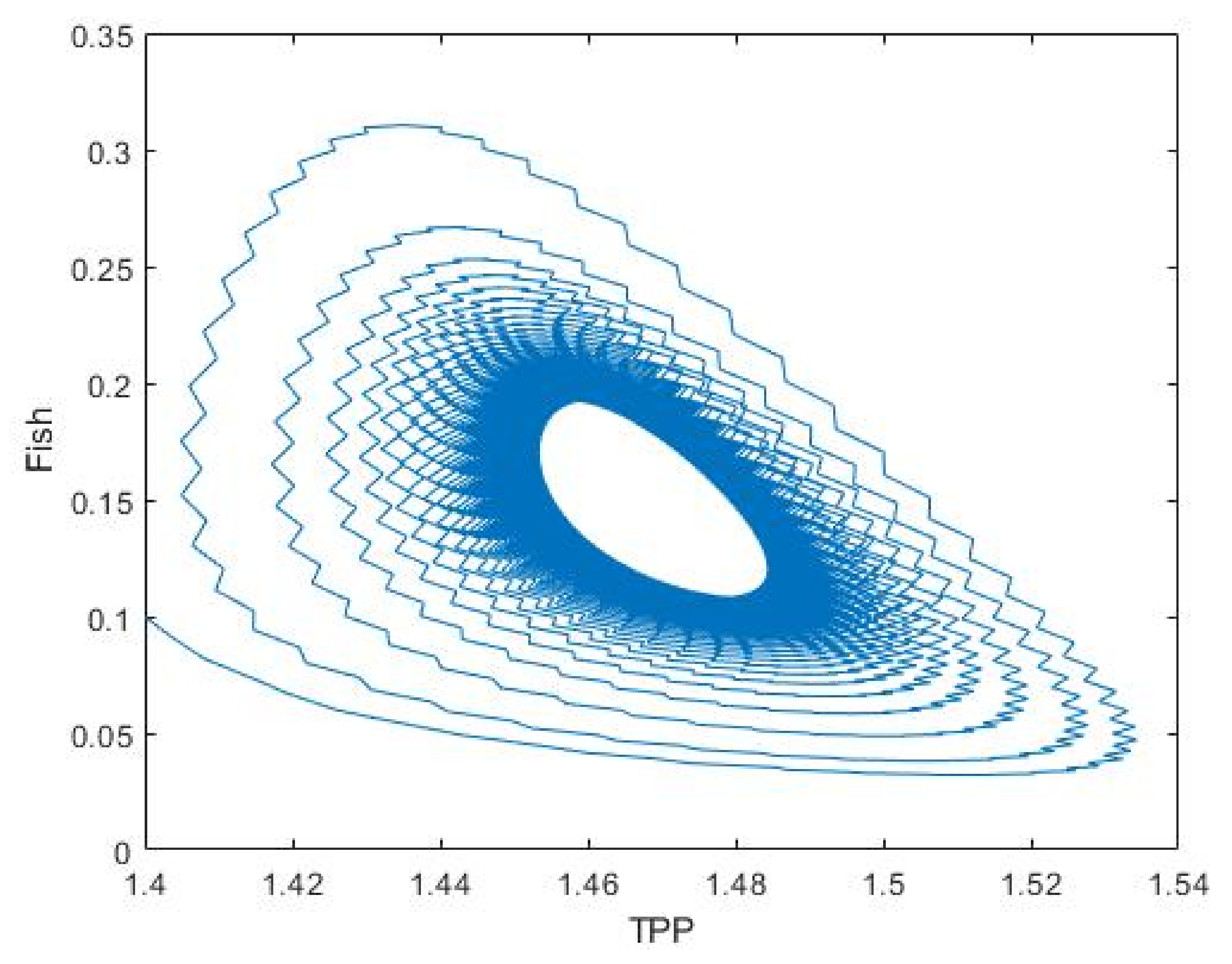
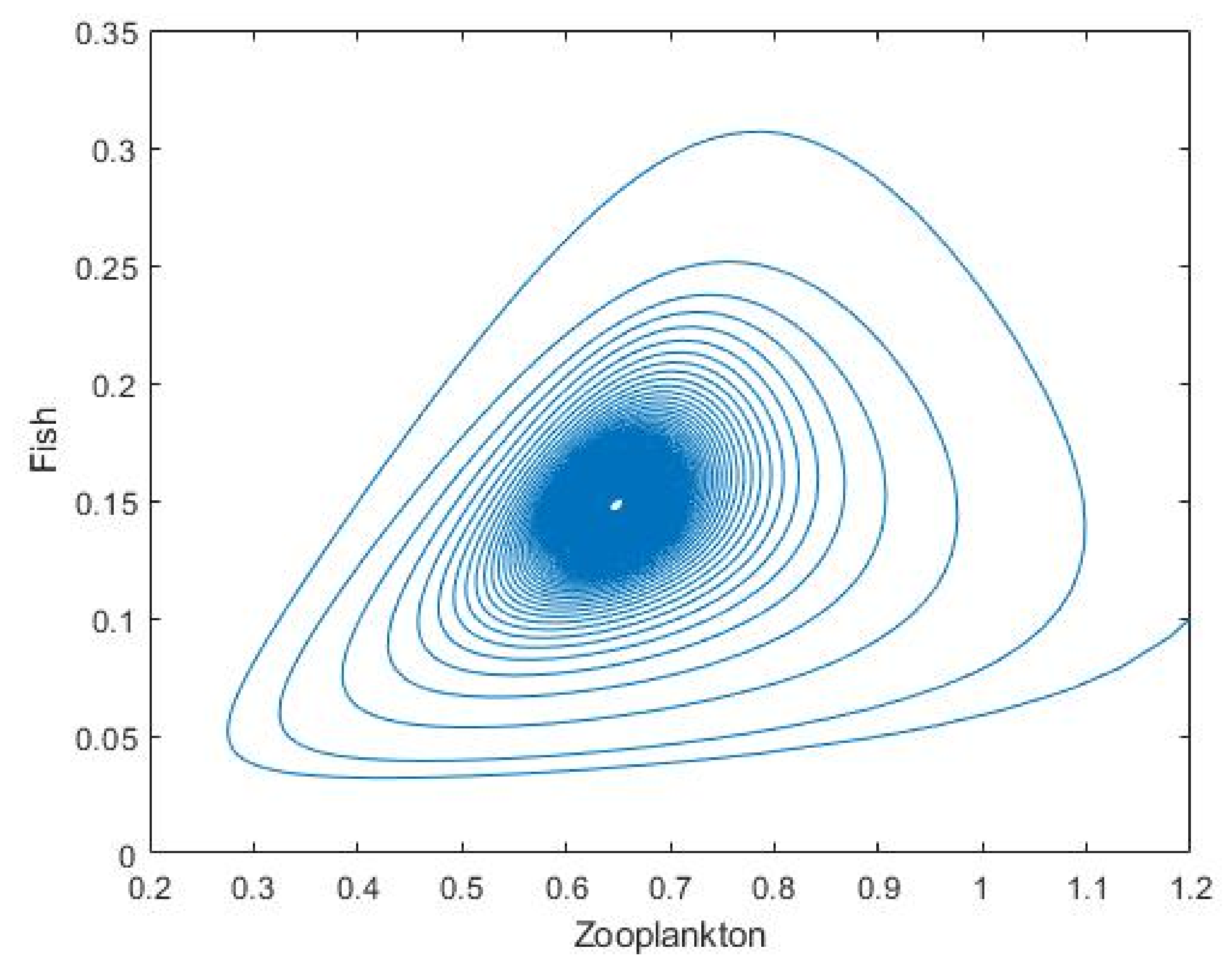
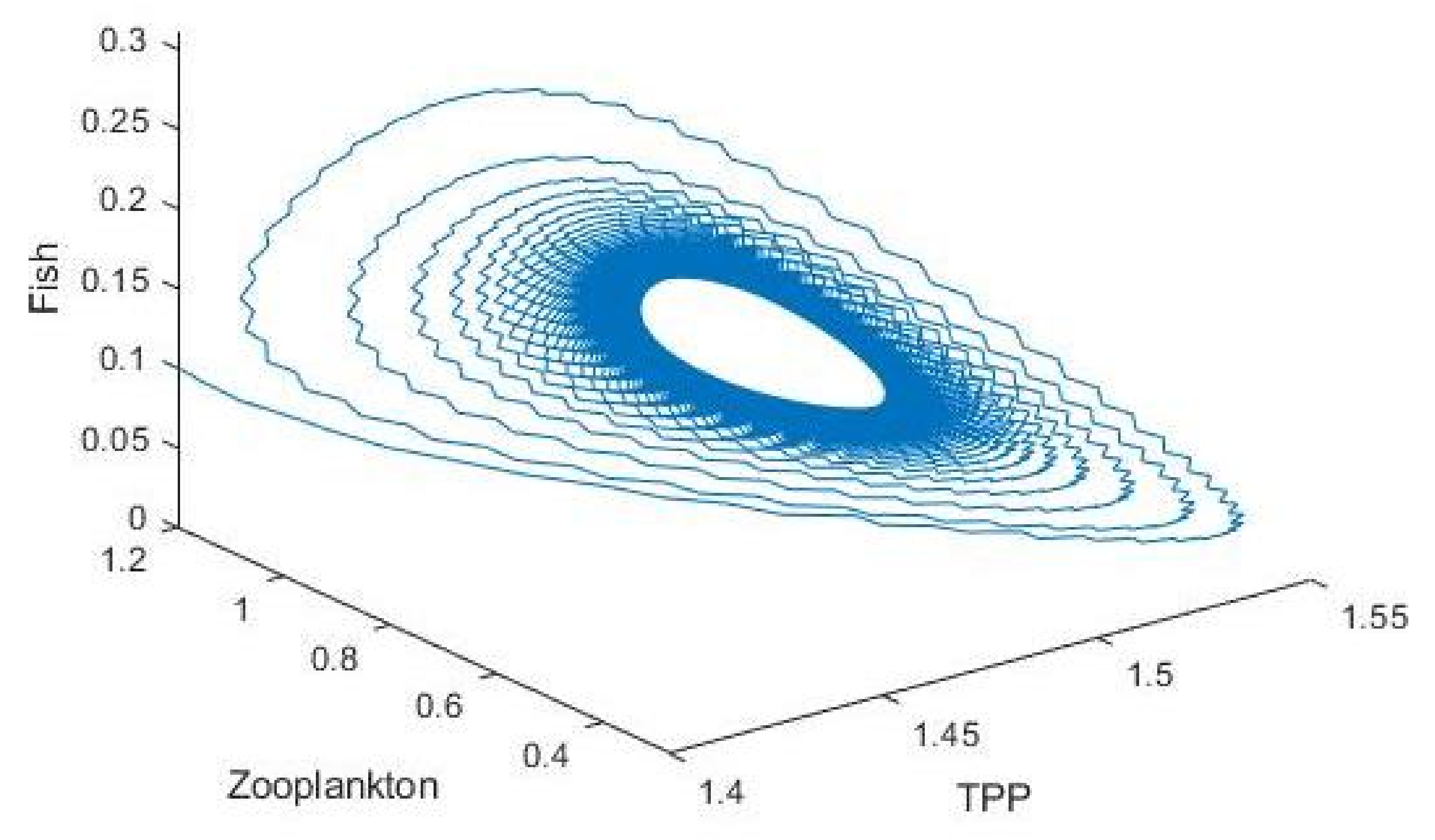
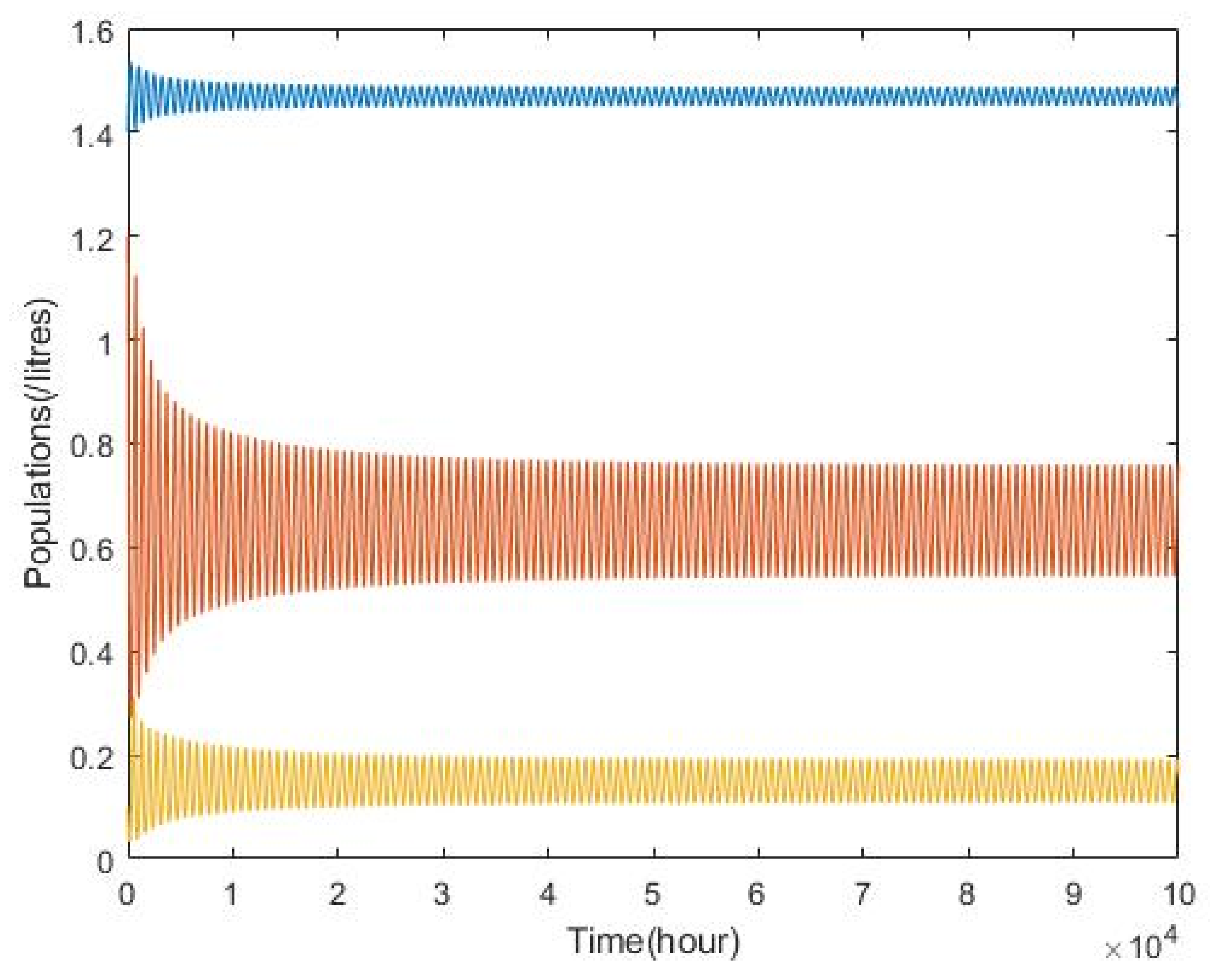
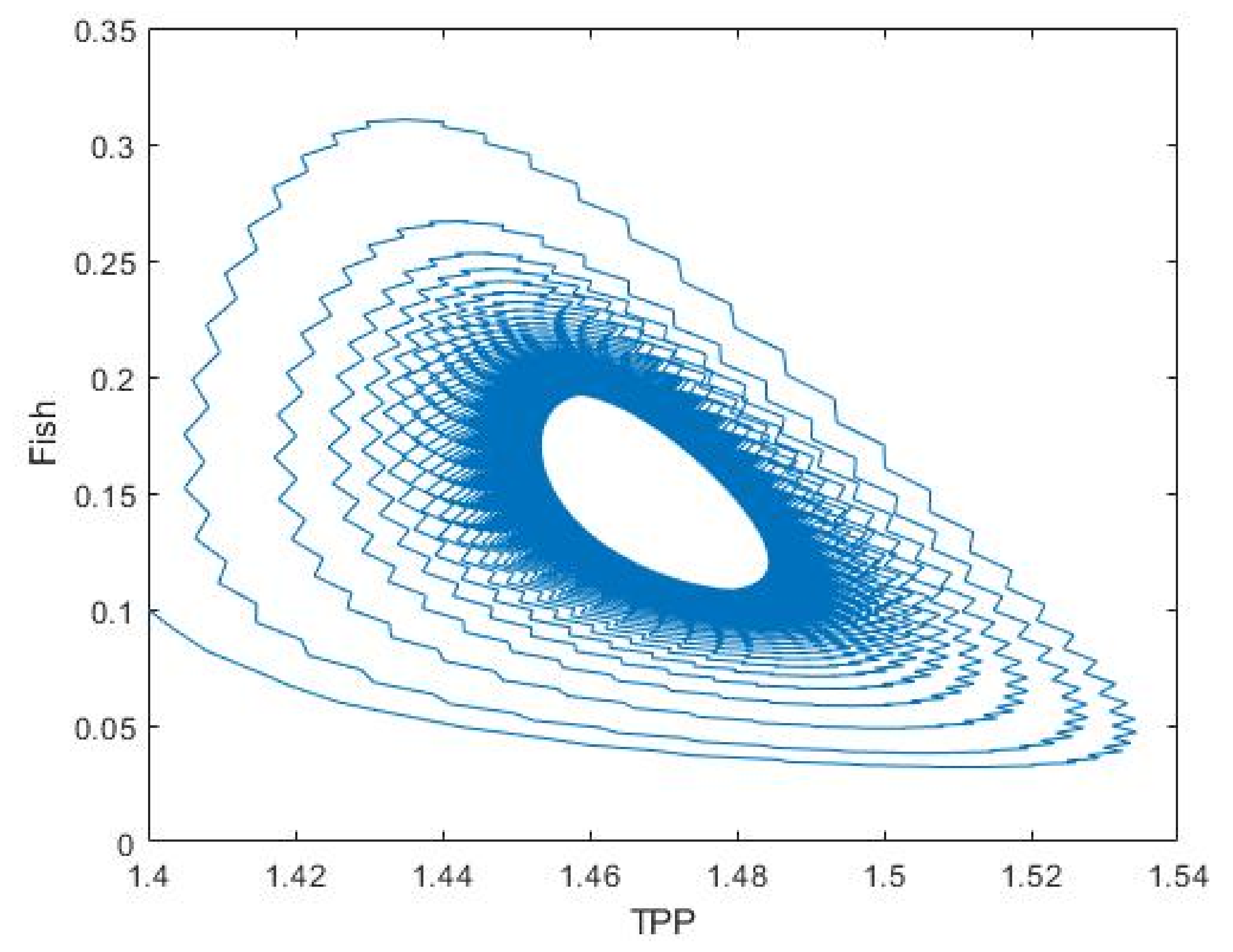
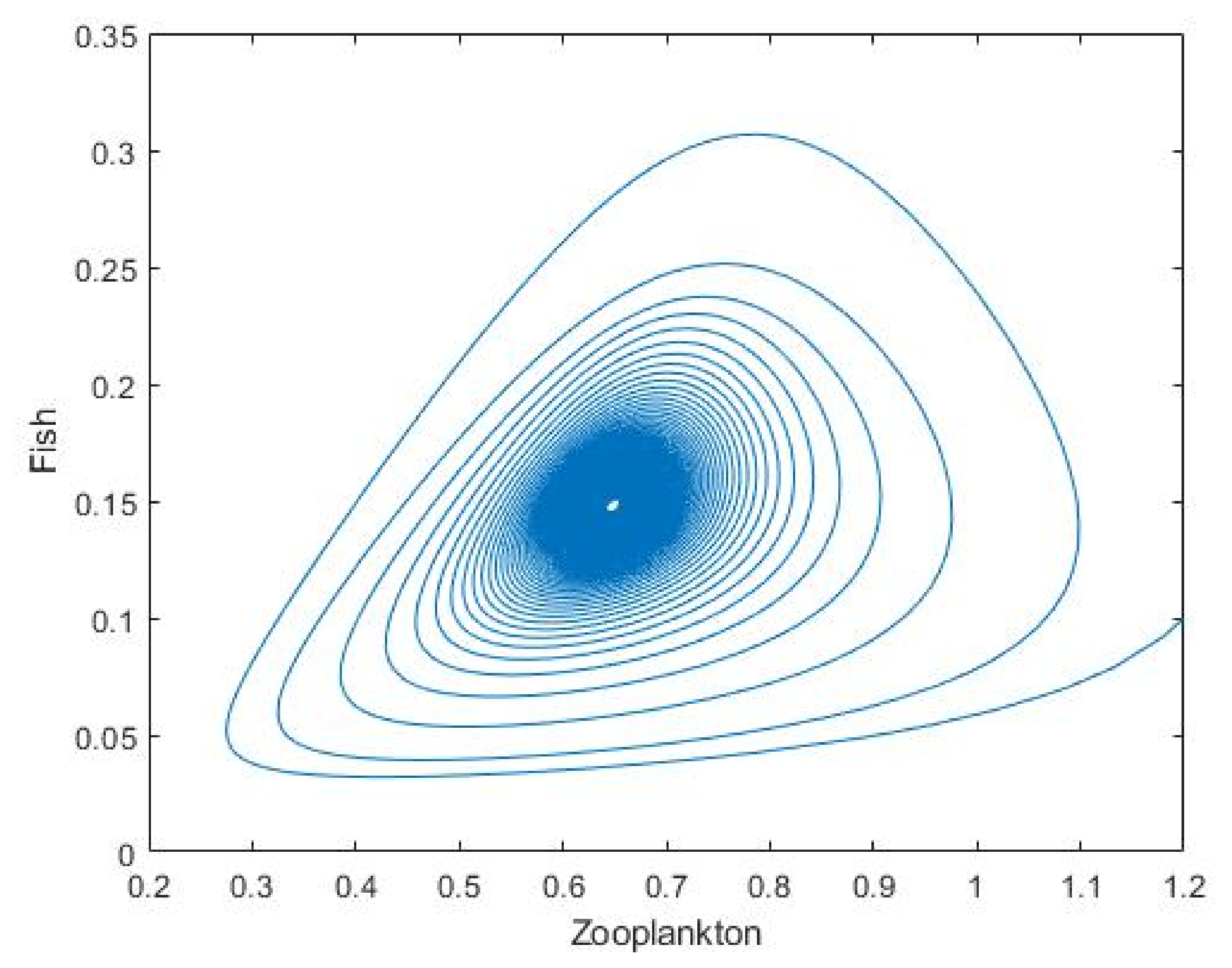
3.2. Plankton–Zooplankton–Fish Interaction Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HAB | Harmful Algal Bloom |
| TPP | Toxin-Producing Phytoplankton |
| NTP | Non-Toxic Phytoplankton |
| PSP | Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning |
| PST | Paralytic Shellfish Toxin |
References
- Daily, S.C. Available online: http://sinchew-i.com (accessed on 23 January 2005).
- Zingone, A.; Enevoldsen, O.H. The diversity of Harmful algal blooms: A challenge for science and management. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2000, 43, 725–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usup, G.; Ahmad, A.; Matsuoka, K.; Lim, P.T.; Leaw, C.P. Biology, ecology and bloom dynamics of the toxic marine dinoflagellate Pyrodinium bahamense. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.N. Red tide and outbreak of paralytic shellfish poisoning in Sabah. Med J. Malays. 1977, 31, 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- Suleiman, M.; Jelip, J.; Rundi, C.; Chua, T.H. Case report: Paralytic shellfish poisoning in Sabah, Malaysia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 1731–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jipanin, S.J.; Muhamad-Shaleh, S.R.; Lim, P.T.; Leaw, C.P.; Mustapha, S. The Monitoring of Harmful Algae Blooms in Sabah, Malaysia. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1358, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzul, G.; Seguel, M.; Guzman, L.; Denn, E.E. Comparison of allelopathic properties in threetoxic alexandrium species. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1999, 232, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallam, T.; Clark, C.; Jordan, G. Effects of toxicants on populations: A qualitative approach. II. First order kinetics. J. Theor. Biol. 1983, 18, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, K.; Das, K. Modeling and analysis of a two-zooplankton one-phytoplankton system in the presence of toxicity. Appl. Math. Model. 2015, 39, 1241–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teen, L.P.; Pin, L.C.; Gires, U. Harmful algal blooms in Malaysian waters. Sains Malays. 2012, 41, 1509–1515. [Google Scholar]
- Usup, G.; Ahmad, A.; Ismail, N. Pyrodinium bahamense var. compressum red tides studies in Sabah, Malaysia. In Biology, Epidemiology and Management of Pyrodinium Red Tides. Manila: ICLARM Conference Proceedings; Hallegraeff, G.M., Maclean, J.L., Eds.; ICLARM: Bandar Seri Begawan, Brunei, 1989; pp. 97–110. [Google Scholar]
- Rehim, M.; Zhang, Z.; Muhammadhaji, A. Mathematical Analysis of a Nutrient–Plankton System with Delay. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehim, M.; Imran, M. Dynamical analysis of a delay model of phytoplankton-zooplankton interaction. Appl. Math. Model. 2012, 36, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z. Mathematical Modelling and Study of Population Ecology; Anhui Education Publishing House: Hefei, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Holling, C.S. Some characteristics of simple types of predation and parasitism. Can. Entomol. 1959, 91, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Mukherjee, R.N.; Chaudhuri, K.S. Harvesting of a prey–predator fishery in the presence of toxicity. Appl. Math. Model. 2009, 33, 2282–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairagi, N.; Pal, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Chattopadhyay, J. Nutrient, non-toxic phytoplankton, toxic phytoplankton and zooplankton interaction in an open marine system. In Aspects of Mathematical Modelling; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 2008; pp. 41–63. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, M.J.; Teo, S.L. Toxic marine dinoflagellates in Singapore waters that cause seafood poisonings. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2002, 29, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, S.; Wei, J. On the zeros of transcendental functions with applications to stability of delay differential equations with two delays. Dyn. Contin. Discret. Impuls. Syst. Ser. A 2003, 10, 863–874. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.Y.; Shu, H. Multiple stable periodic oscillations in a mathematical model of CTL response to HTLV-I infection. Bull. Math. Biol. 2011, 73, 1774–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipahi, R.; Niculescu, S.I.; Abdallah, C.T.; Michiels, W.; Gu, K. Stability and stabilization of systems with time delay. IEEE Control Syst. 2011, 31, 38–65. [Google Scholar]




| Parameters | Symbols | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Dilution rate of nutrient | D | 0.3 (h) |
| Constant input of nutrient concentration | 1.58 (h) | |
| Nutrient uptake rate for the NTP | 0.03 (mL · h) | |
| Nutrient uptake rate for the TPP | 0.022 (mL·h) | |
| Conversion rate of NTP | 0.02 (mL·h) | |
| Conversion rate of TPP | 0.02 (mL·h) | |
| Natural death rate of NTP | 0.006 (h) | |
| Natural death rate of TPP | 0.006 (h) | |
| Natural death rate of zooplankton | 0.005 (h) | |
| Competition coefficient | 0.02 (mL·h) | |
| Competition coefficient | 0.02 (mL·h) | |
| Predation rate of NTP | 0.02 (mL·h) | |
| Predation rate of TPP | 0.01 (mL·h) | |
| Conversion rate for NTP | 0.01 (mL·h) | |
| Death rate due to consumption of TPP | 0.008 (mL·h) | |
| Dilution rate of NTP | 0.0004 (h) | |
| Dilution rate of TPP | 0.0004 (h) | |
| Dilution rate of zooplankton | 0.0003 (h) |
| Parameters | Symbols | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Intrinsic growth rate | r | 0.7 (mL·h) |
| Constant input of nutrient concentration | K | 28 (h) |
| Mortality rate of zooplankton | 0.23 (h) | |
| Mortality rate of fish | 0.15 (h) | |
| Predation rate of zooplankton | 0.65 (mL·h) | |
| Predation rate of fish | 0.45 (mL·h) | |
| Birth rate of zooplankton | 0.9 (mL·h) | |
| Birth rate of fish | 0.99 (mL·h) | |
| Coefficient of toxicity | f | 0.1 (h) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yussof, F.N.; Maan, N.; Md Reba, M.N.; Khan, F.A. Mathematical Modelling of Harmful Algal Blooms on West Coast of Sabah. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10162836
Yussof FN, Maan N, Md Reba MN, Khan FA. Mathematical Modelling of Harmful Algal Blooms on West Coast of Sabah. Mathematics. 2022; 10(16):2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10162836
Chicago/Turabian StyleYussof, Fatin Nadiah, Normah Maan, Mohd Nadzri Md Reba, and Faisal Ahmed Khan. 2022. "Mathematical Modelling of Harmful Algal Blooms on West Coast of Sabah" Mathematics 10, no. 16: 2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10162836
APA StyleYussof, F. N., Maan, N., Md Reba, M. N., & Khan, F. A. (2022). Mathematical Modelling of Harmful Algal Blooms on West Coast of Sabah. Mathematics, 10(16), 2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10162836






