Abstract
In this paper, a hybrid SEIAM model for infectious disease with a continuous age structure is established, where combined dynamic effects of media coverage and multi-staged infected progression on threshold dynamics are discussed. Sufficient conditions for uniform persistence of the solution are studied by using the basic reproduction number. By constructing appropriate Lyapunov functions, the global stability analysis of endemic equilibrium is investigated based on Lyapunov–LaSalle’s stability theorem. In order to minimize costs incurred due to applied controls and infectious disease burden, an optimal cost-effective control strategy associated with disease treatment and media coverage is discussed. Numerical simulations are carried out to show consistency with theoretical analysis.
Keywords:
media coverage; multi-staged infected progression; uniform persistence; global stability analysis; optimal control strategy MSC:
34K34; 92D25
1. Introduction
According to some recent epidemiological data collected in medical observations, it is found that parasite levels in vectors or viral loads in an infected population have a great influence on disease infectivity [1], and not all of the infected population behave in a homogeneous way during the entire infectivity period [2,3,4]. Some infectious diseases with a comparatively long infectivity period, such as HIV [1], bilharzia [2], HBV and HCV [3,4], usually exhibit various infecting forces at successive discrete stages of infection. Some staged progression models are proposed to depict disease progression with typical varying characters in infectivity transmission [5,6,7]. For epidemic models with multiple infectious stages and general distributions for the stage durations (exponential distribution [5] and Gamma distribution [6] as special cases), it is shown that disease dynamics are determined by the derived basic reproduction number. The global threshold dynamics and uniform persistence of stage-processed disease models are discussed based on the basic reproduction number in [7].
In recent decades, many research efforts have been made to discuss the potential impact of age on disease progression, and some age-structured models have also been established to depict the vaccination or latency phenomena in the studied epidemiology [8,9]. Although these mathematical models are usually composed of partial differential equations and corresponding dynamical analysis is particularly challenging, global stability for some type of age-structured models have been investigated by constructing Lyapunov functionals in [10,11,12] and the references therein. Complex bifurcation phenomenon stability analyses are discussed in some multi-group epidemic models with age structure [13,14,15,16] and the references therein. A novel multi-group SVEIAR epidemic model with ages of vaccination and latency is formulated in [17], where the sufficient conditions for the occurrence of backward bifurcation in epidemic models are investigated. In order to discuss the possible effects of the variable infected population in each stage of disease dynamics, some epidemic model multi-age structures are proposed in [18,19,20], and the uniform persistence of the models and global stability analysis around the epidemic equilibrium are investigated. In [21], the authors propose a reaction-diffusion SIR epidemic model with multi-group and the nonlinear infectious force function is investigated, and global asymptotic stability for disease-free and endemic equilibria is discussed by using the Lyapunov functions method.
It is well known that media coverage reduces the prevalence of infectious disease and shortens the duration of infection [22]; public health alerts through social media and TV advertisements play an important role in effectively communicating with people regarding the spread of any infectious disease during a short period of time [23]. The impact of public awareness and local behavioral response is studied in [24], and the awareness among the infected population reduces the infectivity due to pharmaceutical interventions. Since human behavior is usually changed toward the diseases through mass media, it is constructive to prevent the spread of infectious diseases as the public relies on what mass media projects to them [25,26]. By assuming the public health alert programs are implemented proportional to the infected population, there has been recent progress on cost-effective analysis for the social media coverage to promote vaccination against infectious disease [27,28], and some recent studies were conducted to discuss the increment in vaccination coverage due to social media and TV advertisements, such as [29,30,31,32], by considering media alerts as a decreasing function of the infected population.
Recent theoretical research shows that vaccination and treatment are the most effective as well as applicable preventive and control strategies during the outbreak of infectious disease. In order to evaluate optimal strategies of social distancing and vaccination, an age-structured dynamic system is established to describe the transmission mechanism of seasonal influenza in [33]. By using Pontryagins’ maximum principle, the authors identify the best way of reducing morbidity and mortality at a minimal cost. By choosing the treatment (a pharmaceutical intervention) and constructive public health alerts (a non-pharmaceutical intervention) as control tools, an optimal control problem is formulated in [34], which is utilized to minimize the cost and disease fatality. In [35,36], the author discusses the optimal distribution strategies of an infectious disease with the mixing of two sub-groups under a resource-constrained environment. An optimal control strategy is formulated [37] to explore cost-effective intervention strategies associated with vaccination and water sanitation, which are designed for the prevention and intervention of cholera epidemics. By considering information-induced vaccination and treatment as controls, optimal control profiles for the applied controls are obtained in [38]. For some specific infectious diseases (foot-and-mouth disease model in [39] and liver cirrhotic disease model [40]), optimal vaccination and treatment measures are formulated.
To the author’s best knowledge, there are few results concerning mathematical modeling of the age-structured epidemic model with stage progression and media coverage. The combined dynamic effects of multi-staged infected progression and public health alerts on epidemiological dynamics have not been investigated before. The optimal control strategy associated with treatment and media coverage has not been discussed in the related references mentioned above.
2. Model Formulation
Based on the above analysis, some hypotheses are proposed as follows:
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
The total population at any time t is divided into the susceptible population , exposed population , time and age-dependent infected population and aware population . It is assumed that media campaigns induce behavioral changes among the susceptible population, which form an isolated aware class fully protected from the infectious disease. Λ denotes the constant recruitment rate of the susceptible population. , and denote the per capita death rate of , and , respectively. δ stands for per capita transfer rate from the exposed population to the infected population, c denotes the dissemination rate of awareness among the susceptible population, represents the transmission rate of the aware to the susceptible population.
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
In order to investigate the possible effects of multiple infectious stages and variable infectivities in each stage on the epidemiological dynamics, the infection age in the k-th stage is assumed to be characterized by its relationship to the corresponding adjacent stages. The entire infectious period in this paper is assumed to be partitioned into -th stages defined by infection age intervals () such that .
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
It is assumed that the susceptible population is vulnerable to the infectious disease as well as public health alerts regarding social media advertisements and TV. represents the age-dependent transmission coefficient in the k-th infectious stage, which describes the varying probability of infectiousness in the k-th stage. denotes the age-dependent recovery rate. stands for the per capita death rate of the infectious population at the k-th stage, denotes the transmission rate of the infectious population from the k-th stage to the next -th stage.
Hypothesis 4 (H4).
represents the cumulative number of social media and TV advertisements at time t. It is plausible to assume that the cumulative number of social media and TV advertisements proportionally increases with the number of infected individuals. It is also assumed that the growth rate of social media and TV advertisements is proportional to the number of the infected population with a decreasing function of the aware population. l represents the half-saturation point for the impact of social media and TV advertisements on the susceptible population. and η represent the baseline number and diminution rate of social media and TV advertisements, respectively. denotes the age-dependent growth rate of social media and TV advertisements. denotes the age-dependent decay rate in social media and TV advertisements due to an increase in the aware population. represents the half-saturation point as attains half of its maximum value .
Hypothesis 5 (H5).
All constant parameters are nonnegative, and the age-dependent functions are all nonnegative, bounded and integrable in their definition intervals.
Keeping all these Hypotheses (H1)–(H5) in mind, we formulate a multi-stage SEIAM model for infectious diseases with media coverage and multi-staged infection progression, which is governed by the following hybrid model with ODE and PDE,
for with and for any .
The boundary conditions are
For any , and initial conditions
such that
Remark 1.
Recently, some epidemic models with media-induced nonlinear incidence and age-dependent vaccination have been established in [41,42]. Uniform persistence and the sharp threshold dynamics are investigated, and the efficacy of vaccines is discussed due to the variation in vaccination reproduction number. However, the combined dynamic effects of multiple disease progressions and public health alerts on epidemiological dynamics have not been investigated. Compared with the work in [41,42], model (1) can not only describe infectious disease progression through multiple stages but also assess the dynamic impact of social media and TV advertisements on the spread of an infectious disease. The treatment measures generally minimize the serious consequences of infection, and efficient media coverage act as a constructive public health alert, which reduces the infection rate. With these proper control measures, the authorities may significantly reduce wealth loss and mortality due to disease burden. Compared with recent references [33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40] concerning the optimal control strategies for infectious disease, the treatment and diminution rate of media coverage are first adopted as control variables in this paper. An optimal cost-effective control strategy is discussed to minimize the costs incurred due to applied controls and infectious disease burden.
The rest of the sections of this paper are organized as follows. In the Section 2, nonnegativity and the uniform persistence of the solution are studied by using the basic reproduction number. By constructing the appropriate Lyapunov functions, the global stability analysis of endemic equilibrium is investigated. In the Section 3, an optimal cost-effective control strategy is discussed to minimize costs incurred due to applied controls and infectious disease burden. In the Section 4, numerical simulations are provided to support the theoretical analysis. Finally, this paper ends with a conclusion.
3. Qualitative Analysis of SEIAM Model
In this section, the combined dynamic effects of media coverage and multi-staged infected progression on infectious disease dynamics are discussed. Sufficient conditions for uniform persistence of the solution are studied by using the basic reproduction number. By constructing appropriate Lyapunov functions, global stability analysis of the endemic equilibrium is investigated based on the Lyapunov–LaSalle stability theorem.
3.1. Basic Reproduction Number and Endemic Equilibrium
In order to describe the age-specific survival probability of an infected person in the age interval , we define
and some mathematical notations are also defined for ,
Remark 2.
It should be noted that () represents the probability that an infected individual survives during the k-th infection age and proceeds to the -th infection age. denotes the expected new infectious individual generated by an infected individual during the k-th infection age from . Furthermore, is the fraction of individuals surviving through the exposed stage and reaching the first infection age. stands for the part of secondary infections generated from the k-th infection age, when a typical infected individual contacts a susceptible individual. Hence, the sum of terms denotes secondary infections from all infection ages.
By using Remark 2 and simple computations, it is easy to show the basic reproduction number is as follows:
Based on system (1), if , then it follows from simple computations that the endemic equilibrium is as follows,
3.2. Nonnegativity and Uniform Persistence of Solution
In order to facilitate the following proof, vector w is defined as follows,
it is a solution vector, which is endowed with the following norm,
Lemma 1.
Proof.
Based on the standard theory for age-structured models [43], boundary conditions (2) and initial conditions (3), by integrating on it yields,
According to the classical existence and uniqueness results for functional differential equations, by substituting (8) into system (1), it is easy to show that is nonnegative for any nonnegative initial value, and there exists a unique solution for system (1).
If there exists such that and holds for , then it implies that and holds for . By using similar arguments, the nonnegativity of other variables, , , and , can be shown for any nonnegative initial values. This completes the proof. □
In order to guarantee the existence of the semiflow solution for system (1), which admits a compact global attractor, system (1) can be rewritten as the following Cauchy problem defined on boundary condition (2),
where , take the following form,
with , , represents a Sobolev space and is defined as follows,
Furthermore, is defined as follows,
,
It follows from Theorem 2.1 and Theorem 2.2 in [44] that there exists a unique solution semiflow defined by system (9).
Let , it follows from simple computations and system (1) that
where ().
By using (13) and the comparison principle [45], it can be obtained that
which reveals that all solutions of system (1) and the corresponding system (9) are uniformly bounded. Hence, the solution semiflow is point dissipative. According to Theorem 3.6.1 [45], it can be obtained that is compact for all , and it is easy to show that has a compact global attractor in based on Theorem 1.1.3 [46]. Based on the above analysis, Lemma 2 can be concluded as follows.
Lemma 2.
System (9) has a unique solution semiflow . Furthermore, there exists a compact global attractor for .
Lemma 3.
The subset is positively invariant under the semiflow and . When t is large enough, holds for each , where , and are defined as follows,
Proof.
Based on (14), it is easy to show that , for any initial point in and , we consider the following auxiliary system
By using the comparison principle [46], it can be obtained that , , and (), where is a solution of system (15).
Based on (8) and system (15), the is obtained as follows,
where () can be obtained from the following expressions,
Since , it is easy to show holds for any , which implies that
It follows from (16) and (17) that is the unique solution of Volterra’s Equation (18),
which implies that holds for .
On the other hand, for , it yields that
where (). Hence, it can be concluded that for .
By utilizing the comparison theorem [46], it is easy to show that holds for each . This completes the proof. □
Theorem 1.
When , the semiflow is uniformly persistent with respect to , i.e., there is a such that solution of system (9) with initial value , and
Furthermore, there exists a compact subsect of , which is also a global attractor for in .
Proof.
According to Lemma 3, it is easy to show that is globally asymptotically stable in . In order to investigate the asymptotic behavior of the solution to system (15) from the neighborhood of , where is defined in Lemma 3.
In the following part, we will show that there exists such that , i.e., holds for and any .
If , then it yields that
holds for any .
For any , satisfies
Let , it follows from (19) that
holds for any and .
For the following auxiliary system (20) with and ,
By similar arguments in [18,47], the following notations are defined to facilitate discussing the characteristic equation of system (22),
where .
When and there is a sufficiently large , it follows from simple computations that the dominant eigenvalues of system (22) satisfy the following characteristic equation
It follows from (23) that and () are decreasing functions with respect to . Hence, it is easy to show that there exists a unique root provided that .
Let and , then system (22) can be linearized as follows:
where
and the closed linear operator is as follows,
where is the resolvent operator of with .
According to the Hille–Yosida theorem [48], a strongly continuous semigroup can be generated by the operator . For any from the neighborhood of , denotes the specific projector on the eigenspace with respect to the dominant eigenvalue , it follows from the similar arguments in [18,49], it yields
where represents the identity matrix.
By the similar arguments and computations in [8], it can be obtained that
According to the recurrence relationships of , it yields that
and
Hence, it follows from the above analysis that (31) contradicts (28). Based on Theorem 4.2 in [50], it is easy to show that the semiflow is uniformly persistent with respect to , i.e., there is a such that there is a solution of system (9) with an initial value , and
Furthermore, according to the above analysis, it is easy to show that there exists a compact subsect of , which is also a global attractor for in . □
3.3. Stability Analysis of Endemic Equilibrium
Theorem 2.
When , the endemic equilibrium is locally stable.
Proof.
According to (7), there exists an endemic equilibrium when , by defining some following new variables with exponential form,
and
By separating and solving Equation (34), and are obtained as follows,
where and are defined in (5), and is defined in (23).
According to , the characteristic equation is expressed as follows:
In order to investigate the possibility of a solution to Equation (37) having a nonnegative real part, i.e., , some discussions are provided as follows.
Furthermore, if , then it is easy to show
which also leads to a contradiction.
Hence, it can be concluded that Equation (37) only has eigenvalues with negative real parts and the endemic equilibrium is locally stable. □
Theorem 3.
When , if and , then the endemic equilibrium is globally asymptotically stable.
Proof.
First, we define the following () as follows:
where
By calculating the time derivatives of (), it yields that
According to (8), can be rewritten as follows,
Based on mathematical formulations of defined above and and defined in (5), it follows from simple computations that
By differentiating with respect to t, it yields that
According to (42), some expressions are obtained as follows,
- (i)
- when , it follows from and that
- (ii)
- when , it follows from (42) that
- (iii)
Since it is easy to show that
which follows that
According to (47), Lemma 1 and Theorem 1, it follows from simple computations that Equation (46) can be rewritten as follows,
If and , where () is defined in (39), then it is easy to show that .
Hence, it follows from the Lyapunov–LaSalle stability theorem [45] that the endemic equilibrium is globally asymptotically stable. □
4. Optimal Control Strategy
In this section, we formulate and analyze an optimal control strategy considering the diminution of media coverage and treatment to control the disease progression and balance the economic loss generated due to infectious disease and treatment measures. We will adopt time and age-dependent treatment on the infected population and a time-dependent diminution rate of media coverage on the cumulative number of social media and TV advertisements. Hence, the controlled system takes the following form,
where system (49) shares the same boundary and initial values with system (1), other parameters share the same mathematical forms and biological interpretations described in system (1).
The proper treatment measures and efficient media coverage significantly minimize the serious consequences of infection associated with wealth loss and mortality due to disease burden. Our aim is to optimize the use and minimize the cost of these two mentioned measures, and the optimal control problem is formulated as follows:
where and are defined as follows,
where and are positive upper constants of and , respectively, and where
where state variables are all subject to system (49), and are positive weights with respect to disease infection and the cumulative amount of media coverage. represents the positive unit cost of controls at different levels. and denote positive constants associated with two quadratic terms accounting for control costs of disease infection and media coverage.
In order to derive the optimal problem (50) with respect to time-dependent and age-dependent control functions, some derivations of the adjoint system (53) and the characterization of the optimal control functions are discussed as follows.
where denotes a scalar, is a constant balancing of the different units between time and age and and are arbitrary functions. and in system (49) are replaced with and in adjoint system (53), respectively.
Since the solutions of system (53) are associated with , we will differentiate system (53) with respect to at and the system for sensitivities are obtained as follows,
where , , , and denote the derivatives of S, E, , A and M with respect to and are evaluated at (), respectively.
In order to facilitate deriving adjoint system (54), we introduce the adjoint variable vectors . By projecting an adjoint operator on both sides of system (54), it yields that
where , and () are defined as follows,
and
and
which derives that
According to (), it yields
By differentiating the optimal objective functional H with respect to around , it can be obtained that
and
For adjoint variable vectors and optimal control variable , it follows from the above analysis of (56), (57) and (59) that the adjoint system is as follows,
where the transversality conditions are as follows:
which hold for and , and boundary condition holds for .
It is easy to show that adjoint system (60) has a mild solution with Lipschitz continuity, which takes the form
Theorem 4.
Proof.
By transferring the first part of on adjoint functions, it yields
Based on (62), the characterization of the optimal control is as follows,
Consequently, it follows from the above analysis that a pair of optimal controls can be obtained as follows: □
Remark 3.
Generally, it is difficult to solve the sequence of optimal controls and the associated state variables converging with the optimal controls due to a lack of compact characters in the age-structured first-order PDEs. Hence, Ekeland’s principle [51] will be utilized to minimize the sequences of the approximate functionals.
According to the corresponding analysis in Chapter 14 [52] that there exists a pair of controls , and the optimal control objective functional is defined as follows,
If is a pair of optimal control subjects to the optimal control problem minimizing , then it follows from the corresponding analysis in Chapter 14 [52], it is easy to show
where and () hold for all .
Theorem 5.
If () is sufficiently small, then there exists a pair of unique optimal controls subject to optimal control problem (50).
Proof.
First, two functions are defined as follows,
For two pairs of controls, and , according to Lipschitz estimations for the states and adjoint functions, it yields that
where () are positive Lipschitz constants associated with the essential boundedness of the state variables and adjoint functions.
Consequently, if () is sufficiently small, then it yields
which reveals that converges to the optimal control . It follows from Ekeland’s principle [51] that there exists a unique pair of optimal controls when the time period is sufficiently small, and as . □
5. Numerical Simulation
In this section, some numerical simulations are conducted to show the feasibility of our analysis in the previous section regarding global stability and optimal control strategy, where values of parameters in numerical simulations are partially taken from [18,31,37].
When progressing to the deterioration of diseases, it is well known that infectivity during the acute state is greater than that of the chronic one, and infection awareness among susceptible individuals increases due to obvious symptoms of chronic patients. In order to indicate varying degrees of transmissibility at the acute stage (from 0 to 2 months) and chronic stage (from 2 to 10 months), the age-dependent coefficients at different stages are as follows:
By using the set of parameter values, , , , , , , , the basic reproduction number due to variations of c and are plotted in Figure 1a,b, respectively. From this figure, it may be noted that decreases with the increasing dissemination rate of awareness (c), as well as the increasing baseline number of social media and TV advertisements (). becomes less than unity with the appropriate c and , which shows the importance of public health alerts in controlling the spread of infectious disease.
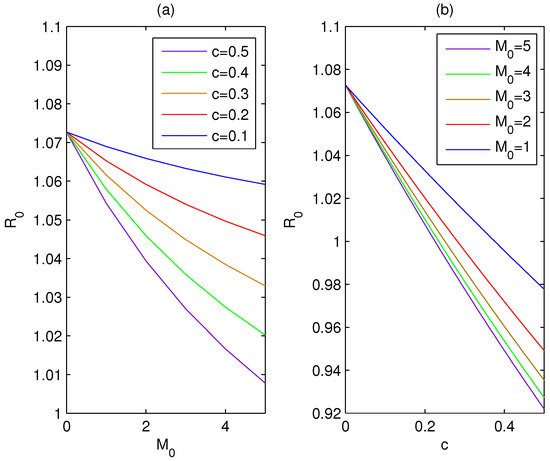
Figure 1.
(a) Description of basic reproduction number due to variations of for different values of c (). (b) Description of basic reproduction number due to variations of c for different values of ().
By adopting , , , , , , , , and other parameters given as follows
It is easy to show that and and , it follows from Theorem 3 that the endemic equilibrium is globally asymptotically stable. Figure 2 depicts the infectious disease becoming endemic and each population converges to the corresponding steady state.
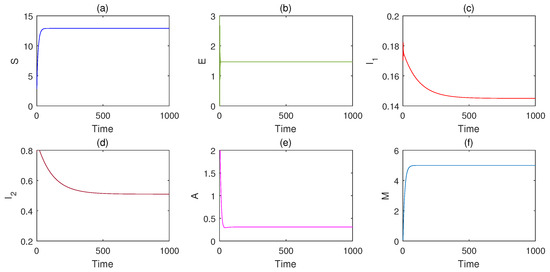
Figure 2.
Infectious disease becomes endemic, and each population converges to the corresponding steady state, which shows that endemic equilibrium is globally asymptotically stable. (a) The dynamical responses of S. (b) The dynamical responses of E. (c) The dynamical responses of . (d) The dynamical responses of . (e) The dynamical responses of A. (f) The dynamical responses of M.
Dynamic impacts of infection age on the two successive infectious states (acute stage from 0 to 2 months, chronic stage from 2 to 10 months) are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4. The distributions of the infected individuals with respect to both age and time are plotted in Figure 3, and the corresponding dynamical responses of and with respect to age are plotted in Figure 4, which reflects the transmission heterogeneity of the infected individuals in acute (Figure 4a) and chronic infectious stages (Figure 4b).
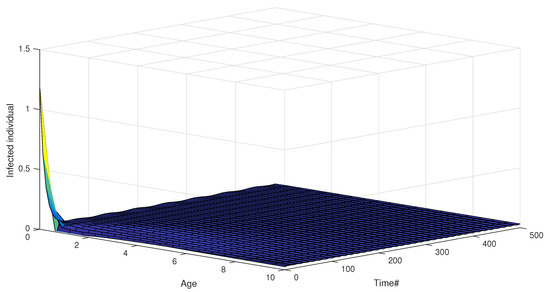
Figure 3.
Age distributions of infected individuals with respect to time and acute stage (from 0 to 2 months) and chronic stage (from 2 to 10 months).
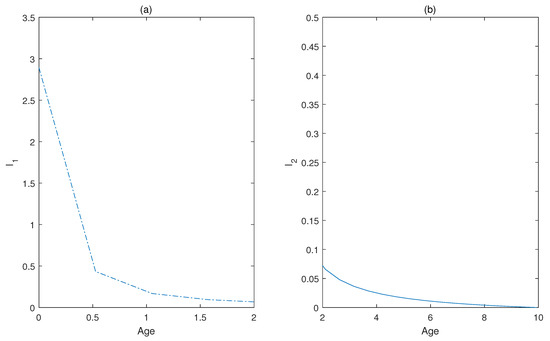
Figure 4.
(a) Age distributions of infected individuals at the acute stage. (b) Age distributions of infected individuals at the chronic stage.
In the following part, numerical simulations are carried out to show the effects of optimal controls on reducing infectious disease and minimizing the costs of control strategies, which are formulated and analyzed in the third section of this paper. By extending the forward-backward sweep method for ODE models, an iterative process is designed for numerical simulations of state and adjoint systems in the age-structured PDE model (60). In order to maintain relatively good numerical algorithm stability, a simple finite difference scheme is selected to facilitate the numerical implementations. By fixing the weight parameter values with respect to disease infection and cumulative number of media coverage as follows , and varying the control costs by discussing three scenarios as follows, (i) low optimal cost controls: ; (ii) moderate optimal cost controls: ; (iii) high optimal cost controls: . The total number of infected individuals with respect to time at the acute stage is plotted in Figure 5a, and at the chronic stage is plotted in Figure 5b. The total number of infected individuals with respect to age at the acute stage is plotted in Figure 6a, and at the chronic stage is plotted in Figure 6b. It follows from the curves of Figure 5 and Figure 6 that the infected individual with high control costs decreases quickly at the acute stage, which implies the spread of infectious disease can be significantly reduced with the increase in control costs. The infected individual with high control costs finally approaches a relatively steady state (approximately 0) at the chronic stage.
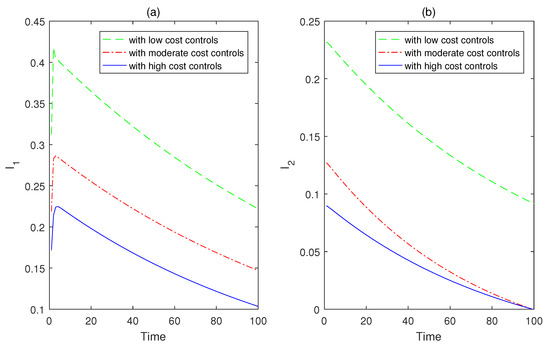
Figure 5.
The weight parameter values with respect to disease infection and the cumulative number of media coverage are set as , and three scenarios are as follows, (i) low optimal cost controls: ; (ii) moderate optimal cost controls: ; (iii) high optimal cost controls: . (a) The total number of infected individuals with respect to time at the acute stage. (b) The total number of infected individuals with respect to time at the chronic stage.
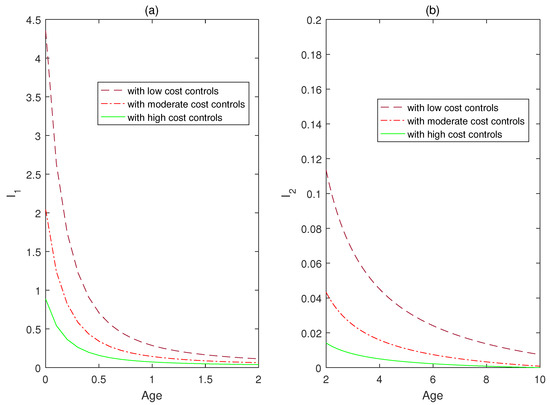
Figure 6.
The weight parameter values with respect to disease infection and cumulative number of media coverage are set as , and three scenarios are as follows, (i) low optimal cost controls: ; (ii) moderate optimal cost controls: ; (iii) high optimal cost controls: . (a) The total number of infected individuals with respect to age at the acute stage. (b) The total number of infected individuals with respect to age at the chronic stage.
6. Conclusions
It is observed that social media and TV advertisements regarding the spread of infectious diseases generally have potential effects on behavioral changes among susceptible people as well as to control the spread of diseases. The infected population usually shows different infecting forces during various stages of progress. Hence, it seems more reasonable for the specific purpose of disease modeling to introduce infection age structure. In this paper, we propose a mathematical model to discuss how media coverage impacts the global stability and threshold dynamics of an infectious disease. In order to depict varying degrees of transmissibility at different stages of infection, the continuous age structure for each successive infectious stage during a long infective period is taken into account. Sufficient conditions associated with the basic reproduction number are derived for uniform persistence of solution in Theorem 1. By constructing appropriate Lyapunov functions, it follows from the Lyapunov–LaSalle stability theorem that global stability analysis of endemic equilibrium is investigated in Theorem 3.
As public health alerts spread among the susceptible population, behavioral changes such as protective measures and vaccination will help healthy individuals to avoid contracting infection. Consequently, we quantify the information-induced vaccination function as a control measure to vaccinate susceptible individuals so that the maximum number of individuals get vaccinated with minimum cost involved. Since the treatment includes diagnosis, medication, hospitalization and other related hygienic efforts depending on limited medical resources, the treatment function is chosen as another control for optimal treatment. The total incurred cost is determined by taking a weighted sum of the cost of productivity loss due to disease and costs incurred in applying control interventions. Analytical characterization and the existence of optimal control paths is carried out in Theorems 4 and 5, respectively.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.L.; methodology, C.L. and P.C.; software, Q.J.; validation, C.L., P.C. and L.C.; investigation, C.L., P.C. and Q.J.; resources, Q.J.; writing—original draft preparation, C.L. and P.C.; writing—review and editing, Q.J. and L.C.; supervision, L.C.; funding acquisition, C.L. and P.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant No. 12171074. Hebei Natural Science Foundation, grant No. A2020501005. Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available in a publicly accessible repository.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the editor and anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions, and the time and effort they have spent on the review. Without the expert comments made by the editor and anonymous reviewers, the paper would not be of this quality.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hyman, J.M.; Li, J.; Stanley, E.A. The differential infectivity and staged progression models for the transmission of HIV. Math. Biosci. 1999, 155, 77–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, M. Global dynamics of a staged progression model for infectious diseases. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2006, 3, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, D.; Feng, Z. Analysis of a model with multiple infectious stages and arbitrarily distributed stage durations. Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. 2008, 3, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Li, M. Global dynamics of a staged progression model with amelioration for infectious diseases. J. Biol. Dyn. 2008, 2, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Zou, X. Global threshold property in an epidemic model for disease with latency spreading in a heterogeneous host population. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2010, 11, 3479–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, M.; Shuai, Z. Global dynamics of a general class of multistage models for infectious disseises. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2012, 72, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Liu, S.Q. The stability analysis of a general viral infection model with distributed delays and multi-staged infected progression. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2015, 20, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magal, P.; Clusky, C.C.M.; Webb, G. Lyapunov functional and global asymptotic stability for an infection age model. Appl. Anal. 2010, 89, 1109–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cluskey, C.C.M. Global stability for an SEI epidemiological model with continuous age structure in the exposed and infectious classes. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2012, 9, 819–841. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, X.; Takeuchi, Y. Lyapunov functions and global stability for age structured HIV infection model. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2012, 72, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Xiao, Y.; Rong, L. Global stability of an infection-age structured HIV-1 model linking within-host and between-host dynamics. Math. Biosci. 2015, 263, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cluskey, C.C.M. Global stability for an SEI model of infectious disease with age structure and immigration of infected. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2016, 13, 381–400. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.L.; Huang, W.Z.; Chavez, C.C. Global behavior of a multi-group SIS epidemic model with age structure. J. Differ. Equ. 2005, 218, 292–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuniya, T. Global stability analysis with a discretization approach for an age-structured multi-group SIR epidemic model. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2011, 12, 2640–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Xiao, Y. Global stability of a multi-group SVEIR epidemiological model with the vaccination age and infection age. Acta Appl. Math. 2016, 144, 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.J.; Hu, J.; Wang, L.W. Modelling and analysis of global resurgence of mumps: A multi-group epidemic model with asymptomatic infection, general vaccinated and exposed distributions. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2017, 37, 137–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif, A.; Dyson, J.; Maini, P.K.; Gupta, S. An age-structured multi-strain epidemic model for antigenically diverse infectious diseases: A multi-locus framework. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2017, 34, 275–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.X.; Guo, H.B. Global analysis of age-structured multi-stage epidemic models for infectious diseases. Appl. Math. Comput. 2018, 337, 214–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.X.; Guo, H.B.; Smith, R. Dynamical analysis for a hepatitis B transmission model with immigration and infection age. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2018, 15, 1291–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baiya, V.P.; Tripathi, J.P.; Kakkar, V.; Wang, J.S.; Sun, G.Q. Global dynamics of a multi-group SEIR epidemic model with infection age. Chin. Ann. Math. Ser. B 2021, 42, 833–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.T.; Tang, S.T.; Teng, Z.D.; Zhang, L. Global dynamics in a reaction diffusion multi-group SIR epidemic model with nonlinear incidence. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2019, 50, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wu, J.; Zhu, H. Media/psychological impact on multiple outbreaks of emerging infectious diseases. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2007, 8, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, J.; Tao, X.; Zhu, H. An SIS infection model incorporating media coverage. Rocky Mt. J. Math. 2008, 38, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, S.; Gilad, E.; Jansen, V.A.A. Endemic disease, awareness and local behavioural response. J. Theor. Biol. 2010, 264, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyabadza, F.; Chiyaka, C.; Mukandavire, Z.; Musekwa, S.D.H. Analysis of an HIV/AIDS model with public health information campaigns and individual withdrawal. J. Biol. Syst. 2010, 18, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, A.K.; Sharma, A.; Shukla, J.B. Modeling and analysis of effects of awareness programs by media on the spread of infectious diseases. Math. Comput. Model. 2011, 53, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Yoo, B.K. Cost-effectiveness analysis of a television campaign to promote seasonal influenza vaccination among the elderly. Value Health 2015, 18, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agaba, G.O.; Kyrychko, Y.N.; Blyuss, K.B. Mathematical model for the impact of awareness on the dynamics of infectious disease. Math. Biosci. 2017, 286, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Tang, S.; Wu, J. Media impact switching surface during an infectious disease outbreak. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharaon, J.; Bauch, C.T. The influence of social behaviour on competition between virulent pathogen strains. J. Theor. Biol. 2018, 455, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Misra, A.K.; Rai, R.K.; Takeuchi, Y. Modelling the control of infectious diseases: Effects of TV and social media advertisements. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2018, 15, 1315–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, A.J.; Song, B.J.; Yuan, S.L. Noise-induced transmitions in a non-smooth SIS epidemic model with media alert. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2021, 18, 745–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, E. Optimal strategies of social distancing and vaccination against seasonal influenza. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2013, 10, 1615–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Srivastava, P.K.; Takeuchi, Y. Modeling the role of information and limited optimal treatment on disease prevalence. J. Theor. Biol. 2017, 414, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.H.; Cao, D.Q.; Liu, S.Q. Epidemic model with group mixing: Stability and optimal control based on limited vaccination resources. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2018, 61, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.T.; Yang, Z.W.; Pawelek, K.A.; Liu, S.Q. Optimal control strategies for a two group epidemic model with vaccination resource constraints. Appl. Math. Comput. 2020, 371, 124956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Modnak, C.; Wang, J. Dynamical analysis and optimal control simulation for an age-structured cholera transmission model. J. Frankl. Inst. 2019, 356, 8438–8467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Srivastava, P.K.; Dong, Y.P.; Takeuchi, Y. Optimal control of infectious disease: Information-induced vaccination and limited treatment. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2020, 542, 123196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashirai, T.B.; Musekwa-Hove, S.D.; Lolika, P.O.; Mushayabasa, S. Global stability and optimal control analysis of a foot and mouth disease model with vaccine failure and environmental transmission. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 132, 109568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, M.S.; Biswas, M.H.A. Optimal control strateties for preventing hepatitis B infection and reducing chronic liver cirrhosis incidence. Infect. Dis. Model. 2020, 5, 91–110. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.W.; Liu, Z.J.; Zhang, X.A. Global dynamics for an age-structured epidemic model with media impact and incomplete vaccination. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2016, 32, 136–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.W.; Liu, Z.J.; Xu, D.S.; Zhang, X.A. Global dynamics and optimal control of an influenza model with vaccination, media coverage and treatment. Int. J. Biomath. 2017, 10, 1750068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, G.F. Theory of Nonlinear Age-Dependent Population Dynamics; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 101–134. [Google Scholar]
- Thieme, H.R. Semiflows generated by Lipschitz perturbation of non-densely defined operators. Differ. Integral Equ. 1990, 3, 1035–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Hale, J. Theory of Functional Differential Equations; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1977; pp. 25–76. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.Q. Dynamical Systems in Population Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 112–149. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, X. A mathematical model for hepatitis B with infection-age structure. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B 2016, 21, 1329–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brezis, H. Functional Analysis, Sobolev Spaces and Partial Differential Equations; Springer: London, UK, 2011; pp. 36–89. [Google Scholar]
- Inaba, H. A semigroup approach to the strong ergodic theorem of the multistate stable population process. Popul. Stud. 1988, 1, 49–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, J.; Waltman, P. Persistence in infinite dimensional systems. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 1989, 20, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DelValle, S.Y.; Hyman, J.M.; Chitnis, N. Mathematical models of contact patterns between age groups for predicting the spread of infectious diseases. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2013, 10, 1475–1497. [Google Scholar]
- Fister, K.R.; Gaff, H.; Lenhart, S.; Numfor, E.; Schaefer, E.; Wang, J. Optimal Control of Vaccination in An Age-Structured Cholera Model, Mathematical and Statistical Modeling for Emerging and Re-Emerging Infectious Diseases; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 221–248. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).