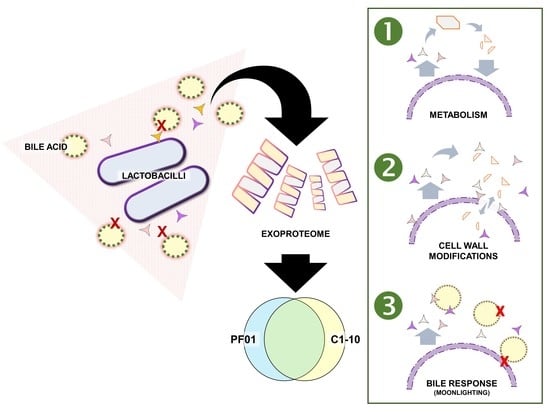
Exoproteome Perspective on the Bile Stress Response of Lactobacillus johnsonii
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
2.2. Bile Treatment and Extracellular Protein Collection
2.3. Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Heated Electrospray Ionization-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.4. MS Data Processing and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis of the Effects of Bile
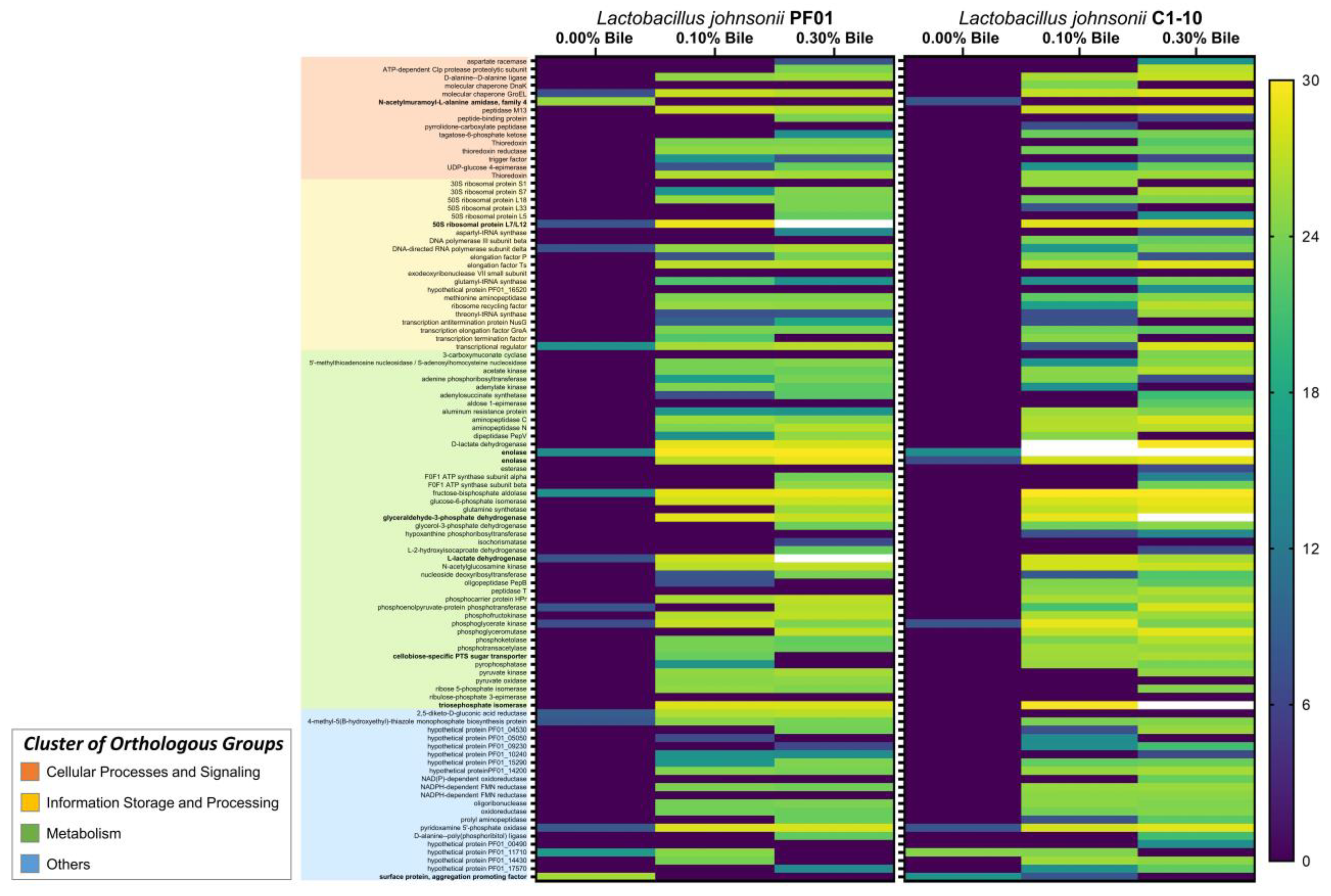
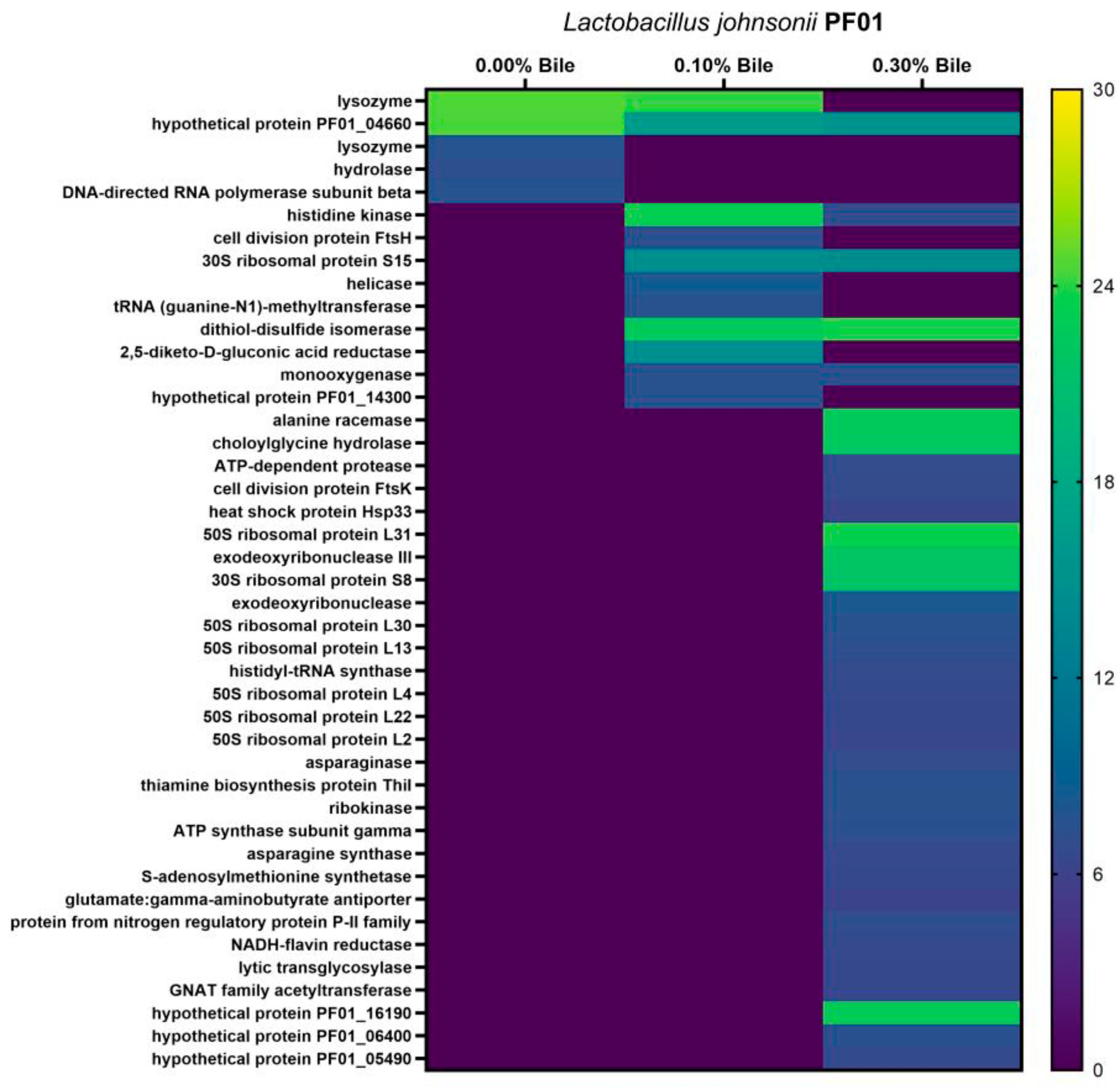
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Lactobacillus Johnsonii Bile Response Exoproteome
3.2. Species- and Strain-Specific Bile-Induced and Upregulated Proteins
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Bile Stress on L. johnsonii Exoproteome
4.2. Metabolic Adaptation to Support Protein Synthesis
4.3. Cell-Wall Modifications as a Dose-Dependent Bile Response
4.4. Cytoplasmic Proteins Function as a Bile-Stress Protective Matrix
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Acm | lysozyme |
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
| AnsB | asparaginase |
| ATP | adenosine triphosphate |
| BSH | bile salt hydrolase |
| CelA | cellobiose-specific PTS sugar transporter |
| COG | Cluster of Orthologous Groups |
| FlgJ | N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase |
| GapA | glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| GI | Gastrointestinal tract |
| GRAS | Generally Regarded As Safe |
| HESI | heated electrospray ionization |
| LFQ | label-free quantification |
| LtgG | lytic transglycosylase |
| Mdh | L-lactate dehydrogenase |
| MS | mass spectrometry |
| Pgk | phosphoglycerate kinase |
| PotE | glutamate:gamma-aminobutyrate antiporter |
| PTS | phosphotransferase system |
| Pyr | pyridoxamine 5′-phosphate oxidase |
| RplL | 50S ribosomal protein L7/L12 |
| SPapf | surface protein/aggregation promoting factor |
| Spr | hydrolase |
| TpiA | triosephosphate isomerase |
| UHPLC | ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography |
References
- FAO/WHO. Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations/World Health Organization: London, ON, Canada, 2002; Available online: https://www.who.int/foodsafety/fs_management/en/probiotic_guidelines.pdf (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- Lebeer, S.; Vanderleyden, J.; De Keersmaecker, S.C.J. Genes and Molecules of Lactobacilli Supporting Probiotic Action. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2008, 72, 728–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, G. The Scientific Basis for Probiotic Strains of Lactobacillus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 3763–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begley, M.; Gahan, C.G.M.; Hill, C. The Interaction between Bacteria and Bile. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 625–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waar, K.; van der Mei, H.C.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Degener, J.E.; Busscher, H.J. Adhesion to Bile Drain Materials and Physicochemical Surface Properties of Enterococcus Faecalis Strains Grown in the Presence of Bile. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 3855–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumbwe, L.; Skilbeck, C.A.; Nakano, V.; Avila-Campos, M.J.; Piazza, R.M.F.; Wexler, H.M. Bile Salts Enhance Bacterial Co-Aggregation, Bacterial-Intestinal Epithelial Cell Adhesion, Biofilm Formation and Antimicrobial Resistance of Bacteroides Fragilis. Microb. Pathog. 2007, 43, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaleghi, M.; Kermanshahi, R.K.; Yaghoobi, M.M.; Zarkesh-Esfahani, S.H.; Baghizadeh, A. Assessment of Bile Salt Effects on S-Layer Production, Slp Gene Expression and Some Physicochemical Properties of Lactobacillus Acidophilus ATCC 4356. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 20, 749–756. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, L.; Margolles, A.; Sánchez, B. Bile Resistance Mechanisms in Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, B.; Urdaci, M.C.; Margolles, A. Extracellular Proteins Secreted by Probiotic Bacteria as Mediators of Effects That Promote Mucosa-Bacteria Interactions. Microbiology 2010, 156 Pt 11, 3232–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, B.; Bressollier, P.; Urdaci, M.C. Exported Proteins in Probiotic Bacteria: Adhesion to Intestinal Surfaces, Host Immunomodulation and Molecular Cross-Talking with the Host. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 54, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Pajarillo, E.A.B.; Kim, M.J.; Chae, J.P.; Kang, D.-K. Proteomic and Transcriptional Analysis of Lactobacillus Johnsonii PF01 during Bile Salt Exposure by ITRAQ Shotgun Proteomics and Quantitative RT-PCR. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeriano, V.D.; Bagon, B.B.; Balolong, M.P.; Kang, D.-K. Carbohydrate-Binding Specificities of Potential Probiotic Lactobacillus Strains in Porcine Jejunal (IPEC-J2) Cells and Porcine Mucin. J. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, J.P.; Valeriano, V.D.; Kim, G.-B.; Kang, D.-K. Molecular Cloning, Characterization and Comparison of Bile Salt Hydrolases from Lactobacillus Johnsonii PF01. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagon, B.B.; Valeriano, V.D.V.; Oh, J.K.; Pajarillo, E.A.B.; Cho, C.-S.; Kang, D.-K. Comparative Exoproteome Analyses of Lactobacillus Spp. Reveals Species- and Strain-Specific Proteins Involved in Their Extracellular Interaction and Probiotic Potential. LWT 2018, 93, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskenniemi, K.; Laakso, K.; Koponen, J.; Kankainen, M.; Greco, D.; Auvinen, P.; Savijoki, K.; Nyman, T.A.; Surakka, A. Proteomics and Transcriptomics Characterization of Bile Stress Response in Probiotic Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2011, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiśniewski, J.R.; Zougman, A.; Nagaraj, N.; Mann, M. Universal Sample Preparation Method for Proteome Analysis. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. MaxQuant Enables High Peptide Identification Rates, Individualized p.p.b.-Range Mass Accuracies and Proteome-Wide Protein Quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Boekhorst, J.; Francke, C.; Siezen, R.J. LocateP: Genome-Scale Subcellular-Location Predictor for Bacterial Proteins. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, T.N.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 4.0: Discriminating Signal Peptides from Transmembrane Regions. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, M.L. Multiple Comparison Analysis Testing in ANOVA. Biochem. Med. 2011, 21, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bøhle, L.A.; Mathiesen, G. Identification of Proteins Related to the Stress Response in Enterococcus Faecalis V583 Caused by Bovine Bile. Proteome Sci. 2010, 8, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.-J.; Tang, H.-Y.; Chiang, M.-L. Effects of Heat, Cold, Acid and Bile Salt Adaptations on the Stress Tolerance and Protein Expression of Kefir-Isolated Probiotic Lactobacillus Kefiranofaciens M1. Food Microbiol. 2017, 66, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Douillard, F.P.; Wang, G.; Zhai, Z.; Yang, J.; Song, S.; Cui, J.; Ren, F.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, B.; et al. Integrated Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analysis of the Bile Stress Response in a Centenarian-Originated Probiotic Bifidobacterium Longum BBMN68. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 2558–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, B.; Champomier-Vergès, M.-C.; Anglade, P.; Baraige, F.; de Los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Margolles, A.; Zagorec, M. Proteomic Analysis of Global Changes in Protein Expression during Bile Salt Exposure of Bifidobacterium Longum NCIMB 8809. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 5799–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, L.; Zomer, A.; O’Connell-Motherway, M.; van Sinderen, D.; Margolles, A. Discovering Novel Bile Protection Systems in Bifidobacterium Breve UCC2003 through Functional Genomics. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, E.M.; Raftery, M.; Goodchild, A.; Mendz, G.L. Campylobacter Jejuni Response to Ox-Bile Stress. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 49, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, L.; Couté, Y.; Sánchez, B.; de los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Sanchez, J.-C.; Margolles, A. The Cell-Envelope Proteome of Bifidobacterium Longum in an in Vitro Bile Environment. Microbiology 2009, 155, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristoffersen, S.M.; Ravnum, S.; Tourasse, N.J.; Økstad, O.A.; Kolstø, A.-B.; Davies, W. Low Concentrations of Bile Salts Induce Stress Responses and Reduce Motility in Bacillus Cereus ATCC 14570. JB 2007, 189, 5302–5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Sun, Z.; Wu, J.; Meng, H.; Zhang, H. Effect of Bile Salts Stress on Protein Synthesis of Lactobacillus Casei Zhang Revealed by 2-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 3858–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, A.; Schmidt, T.B.; Nanduri, B.; Pendarvis, K.; Pittman, J.R.; Thornton, J.A.; Grissett, J.; Donaldson, J.R. Proteomic Analysis of the Response of Listeria Monocytogenes to Bile Salts under Anaerobic Conditions. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, Y.J.; Klaenhammer, T.R. Functional Roles of Aggregation-Promoting-Like Factor in Stress Tolerance and Adherence of Lactobacillus Acidophilus NCFM. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5005–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, M.; Gobbetti, M. Environmental Stress Responses in Lactobacillus: A Review. Proteomics 2004, 4, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.; Maguire, P.B.; Bennett, M.; Fitzgerald, D.J.; Edwards, R.J.; Thiede, B.; Treumann, A.; Collins, J.K.; O’Sullivan, G.C.; Shanahan, F.; et al. Correlation of Probiotic Lactobacillus Salivarius Growth Phase with Its Cell Wall-Associated Proteome. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 252, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.P.A.; Renes, J.; Bouwman, F.G.; Zoetendal, E.G.; Mariman, E.; de Vos, W.M.; Vaughan, E.E. Proteomic Analysis of Log to Stationary Growth Phase Lactobacillus Plantarum Cells and a 2-DE Database. Proteomics 2006, 6, 6485–6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullen, M.J.; Sanozky-Dawes, R.B.; Crowell, D.C.; Klaenhammer, T.R. Use of the DNA Sequence of Variable Regions of the 16S RRNA Gene for Rapid and Accurate Identification of Bacteria in the Lactobacillus Acidophilus Complex. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 89, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, R.A.; Mazzeo, M.F. Molecular Mechanisms of Probiotic Action: A Proteomic Perspective. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, C.H.; Wallis, R.; Allcock, N.; Barnes, K.B.; Richards, M.I.; Auty, J.M.; Galyov, E.E.; Harding, S.V.; Mukamolova, G.V. The Lytic Transglycosylase, LtgG, Controls Cell Morphology and Virulence in Burkholderia Pseudomallei. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, G.; Zhai, Z.; Zhou, P.; Hao, Y. Global Transcriptomic Analysis and Function Identification of Malolactic Enzyme Pathway of Lactobacillus Paracasei L9 in Response to Bile Stress. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Wang, C. Proteomic Analysis Reveals the Temperature-Dependent Presence of Extracytoplasmic Peptidases in the Biofilm Exoproteome of Listeria Monocytogenes EGD-e. J. Microbiol. 2020, 58, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Lian, S.; Guo, W.; Yang, H.; Kong, F.; Zhen, L.; Guo, L.; et al. Progress in the Biological Function of Alpha-Enolase. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 2, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kainulainen, V.; Korhonen, T.K. Dancing to Another Tune-Adhesive Moonlighting Proteins in Bacteria. Biology 2014, 3, 178–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
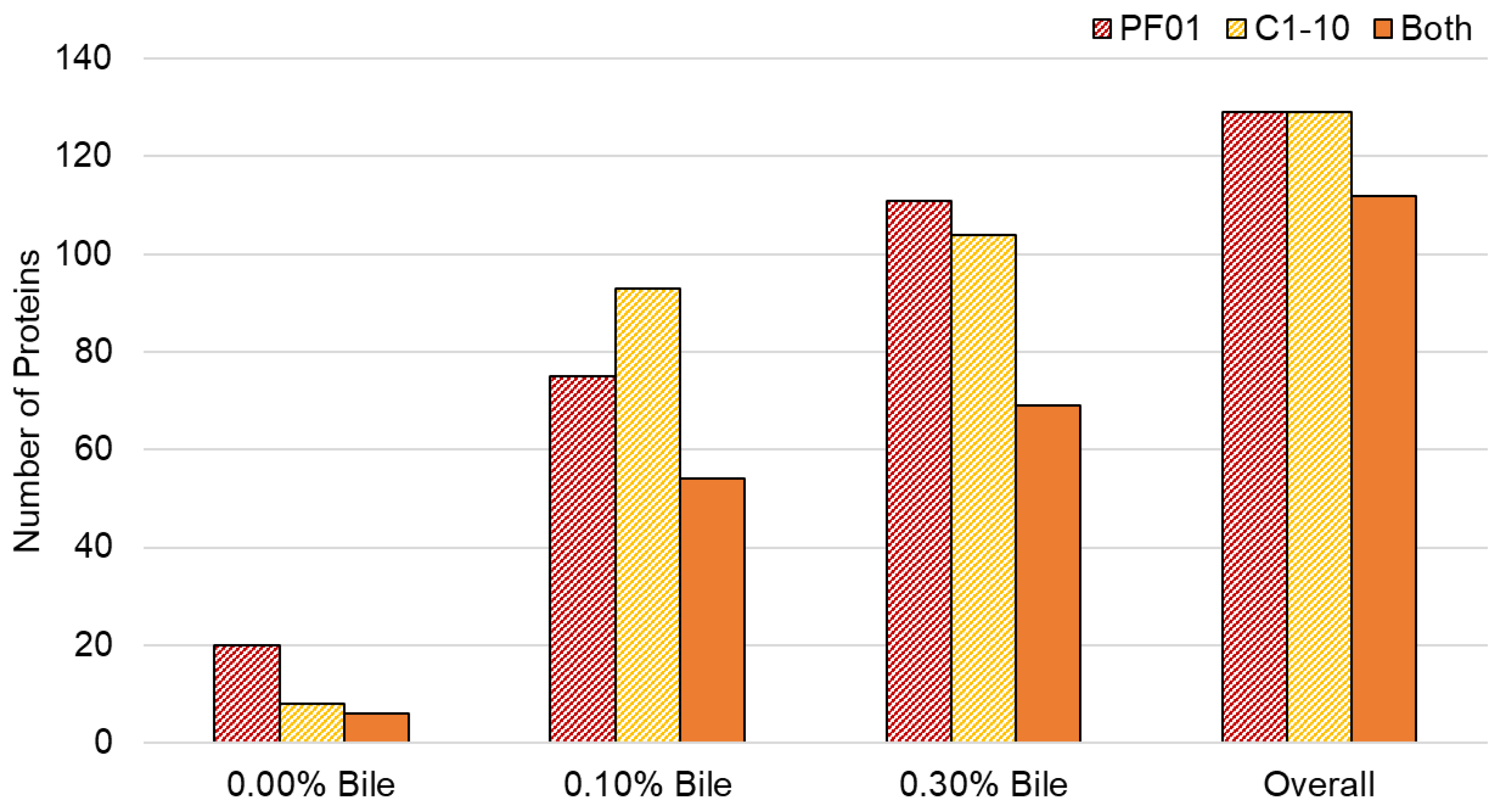


| Classification | Lactobacillus johnsonii | |
|---|---|---|
| PF01 | C1-10 | |
| Cellular Destination | ||
| Cytoplasmic | 116 | 123 |
| Membrane | 8 | 4 |
| Cell Wall | 2 | 2 |
| Extracellular | 3 | 0 |
| Subcellular Localization | ||
| Intracellular | 116 | 123 |
| N-terminally anchored | 4 | 4 |
| Lipid-anchored | 0 | 0 |
| LPXTG Cell-wall anchored | 2 | 2 |
| Multi-transmembrane | 4 | 0 |
| Secretory | 3 | 0 |
| Localization Class | ||
| Cytoplasm | 114 | 117 |
| Inner membrane | 3 | 0 |
| Periplasm | 1 | 1 |
| Secreted | 11 | 11 |
| Effect of Bile on Expression (Treatment) | Locus Tag (PF01 Genome) | Protein Name | COG Gene | Detected in Other Bacteria during Bile Stress | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upregulation (0.00%, 0.10%, and 0.30% bile) | PF01_08830 | enolase | Eno | Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG; Bifidobacterium longum, Enterococcus faecalis V583, Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens M1 | [8,15,21,22] |
| PF01_13820 | phosphoglycerate kinase | Pgk | L. rhamnosus GG, B. longum BBMN68, B. longum NCIMB 8809 | [15,23,24] | |
| PF01_07580 | pyridoxamine 5′-phosphate oxidase | COG3576 | |||
| Induction and upregulation (0.10% and 0.30% bile) | PF01_04460 | 50S ribosomal protein L7/L12 | RplL | ||
| PF01_12550 | 5′-methylthioadenosine/S-adenosylhomocysteine nucleosidase | Pfs | |||
| PF01_13430 | acetate kinase | ackA | B. longum BBMN68; B. longum NCIMB 8809 | [23,24] | |
| PF01_08750 | adenine phosphoribosyltransferase | Apt | |||
| PF01_18670 | aluminum resistance protein | COG4100 | |||
| PF01_04210 | aminopeptidase C | PepC | Bifidobacterium breve UCC2003 | [25] | |
| PF01_07460 | aminopeptidase N | PepN | |||
| PF01_01440 | D-alanine–D-alanine ligase | DdlA | |||
| PF01_00770 | D-lactate dehydrogenase | LdhA | L. kefiranofaciens M1 | [22] | |
| PF01_02700 | DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit delta | RpoE | |||
| PF01_03440 | elongation factor P | FusA | Campylobacter jejunii; B. longum NCIMB 8809 | [24,26] | |
| PF01_08410 | elongation factor Ts | Tsf | B. longum BBMN68, L. kefiranofaciens M1 | [22,23] | |
| PF01_13800 | enolase | Eno | L. rhamnosus GG; B. longum, E. faecalis V583, L. kefiranofaciens M1 | [8,15,21,22] | |
| PF01_05530 | fructose-bisphosphate aldolase | Fba | |||
| PF01_13280 | glucose-6-phosphate isomerase | Pgi | |||
| PF01_04250 | glutamyl-tRNA synthase | GlnS | |||
| PF01_13830 | glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | GapA | B. longum BBMN68, B. longum NCIMB 8809 | [23,24,27] | |
| PF01_15290 | hypothetical protein PF01_15290/C1-10_153 | COG3679 | |||
| PF01_03250 | L-lactate dehydrogenase | Mdh | L. rhamnosus GG, L. kefiranofaciens M1 | [15,22] | |
| PF01_07330 | methionine aminopeptidase | Map | B. longum NCIMB 8809 | [24] | |
| PF01_04920 | molecular chaperone GroEL | GroL | L. rhamnosus GG, Bacillus cereus ATCC 14570; B. longum, Lactobacillus casei Zhang, L. kefiranofaciens M1, Listeria monocytogenes | [8,15,22,28,29,30] | |
| PF01_16360 | N-acetylglucosamine kinase | COG2971 | |||
| PF01_17540 | NADPH-dependent FMN reductase | COG0431 | |||
| PF01_01610 | nucleoside deoxyribosyltransferase | COG3613 | |||
| PF01_05020 | oligoribonuclease | COG0618 | B. longum BBMN68 | [23] | |
| PF01_16660 | oxidoreductase | COG2461 | |||
| PF01_01930 | peptidase M13 | PepO | |||
| PF01_14360 | phosphocarrier protein HPr | FruB | L. rhamnosus GG, E. faecalis V583 | [15,21] | |
| PF01_17320 | phosphofructokinase | FruK | L. casei Zhang, L. monocytogenes | [29,30] | |
| PF01_06630 | phosphoketolase | COG3957 | |||
| PF01_13700 | phosphotransacetylase | Pta | |||
| PF01_08430 | ribosome recycling factor | Frr | B. longum NCIMB 8809 | [24] | |
| PF01_15140 | thioredoxin | TrxA | B. cereus ATCC 14570, E. faecalis V583 | [21,28] | |
| PF01_14000 | thioredoxin reductase | TrxB | B. cereus ATCC 14570 | [28] | |
| PF01_14910 | threonyl-tRNA synthase | ThrS | |||
| PF01_14660 | transcription elongation factor GreA | GreA | B. longum BBMN68 | [23] | |
| PF01_11380 | transcriptional regulator | HimA | L. rhamnosus GG; E. faecalis V583; B. breve UCC2003 | [15,21,25] | |
| PF01_13810 | triosephosphate isomerase | TpiA | L. kefiranofaciens M1 | [22] | |
| PF01_16120 | UDP-glucose 4-epimerase | GalE | B. longum NCIMB 8809 | [24] | |
| Stop expression (0.00% only) | PF01_02040 | N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase, family 4 | FlgJ | L. monocytogenes | [30] |
| PF01_15900 | surface protein, aggregation promoting factor | Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM | [31] |
| Locus Tag | Lactobacillus johnsonii | COG Gene | Secretion Pathway | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PF01 | C1-10 | |||
| PF01_15900 | surface protein, aggregation promoting factor | Sec-(SPI), Possibly Tat | ||
| PF01_02040 | N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase, family 4 | FlgJ | Sec-(SPI), Possibly Tat | |
| PF01_02390 | cellobiose-specific PTS sugar transporter | CelA | Sec-(SPI) | |
| PF01_04660 | hypothetical protein PF01_04660 | Smc | Sec-(SPI) | |
| PF01_11380 | transcriptional regulator | HimA | Possibly Tat/Sec-(SPI) | |
| PF01_02050 | lysozyme | Acm | Sec-(SPI) | |
| PF01_17030 | hydrolase | Spr | Sec-(SPI) | |
| PF01_03320 | cell division protein FtsH | FtsH | Sec-(SPI) | |
| PF01_08990 | asparaginase | AnsB | Sec-(SPI) | |
| PF01_14190 | cell division protein FtsK | FtsK | Sec-(SPI) | |
| PF01_07170 | lytic transglycosylase | LtgG | Sec-(SPI) | |
| PF01_00790 | glutamate:gamma-aminobutyrate antiporter | PotE | Sec-(SPI) | |
| PF01_13400 | levansucrase | SacC | Possibly Tat/Sec-(SPI) | |
| PF01_11710 | hypothetical protein C1-10_104 | Possibly Tat/Sec-(SPI) | ||
| PF01_01320 | hypothetical protein C1-10_30 | COG4086 | Sec-(SPI) | |
| PF01_08830 | enolase | Eno | Possibly Tat/No Pathway | |
| PF01_13800 | enolase | Eno | Possibly Tat/No Pathway | |
| PF01_07580 | pyridoxamine 5′-phosphate oxidase | COG3576 | Possibly Tat/No Pathway | |
| PF01_13820 | phosphoglycerate kinase | Pgk | Possibly Tat/No Pathway | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bagon, B.B.; Valeriano, V.D.V.; Oh, J.K.; Pajarillo, E.A.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Kang, D.-K. Exoproteome Perspective on the Bile Stress Response of Lactobacillus johnsonii. Proteomes 2021, 9, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes9010010
Bagon BB, Valeriano VDV, Oh JK, Pajarillo EAB, Lee JY, Kang D-K. Exoproteome Perspective on the Bile Stress Response of Lactobacillus johnsonii. Proteomes. 2021; 9(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes9010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleBagon, Bernadette B., Valerie Diane V. Valeriano, Ju Kyoung Oh, Edward Alain B. Pajarillo, Ji Yoon Lee, and Dae-Kyung Kang. 2021. "Exoproteome Perspective on the Bile Stress Response of Lactobacillus johnsonii" Proteomes 9, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes9010010
APA StyleBagon, B. B., Valeriano, V. D. V., Oh, J. K., Pajarillo, E. A. B., Lee, J. Y., & Kang, D.-K. (2021). Exoproteome Perspective on the Bile Stress Response of Lactobacillus johnsonii. Proteomes, 9(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes9010010