Proteomic Investigations of Proteases Involved in Cotyledon Senescence: A Model to Explore the Genotypic Variability of Proteolysis Machinery Associated with Nitrogen Remobilization Efficiency during the Leaf Senescence of Oilseed Rape
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.1. Study of Cotyledon Senescence under High N or Low N Conditions
2.2.2. Effect of the Phytohormone Infiltrations on the Senescence of Cotyledons
2.3. Detection and Identification of Active Proteases
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
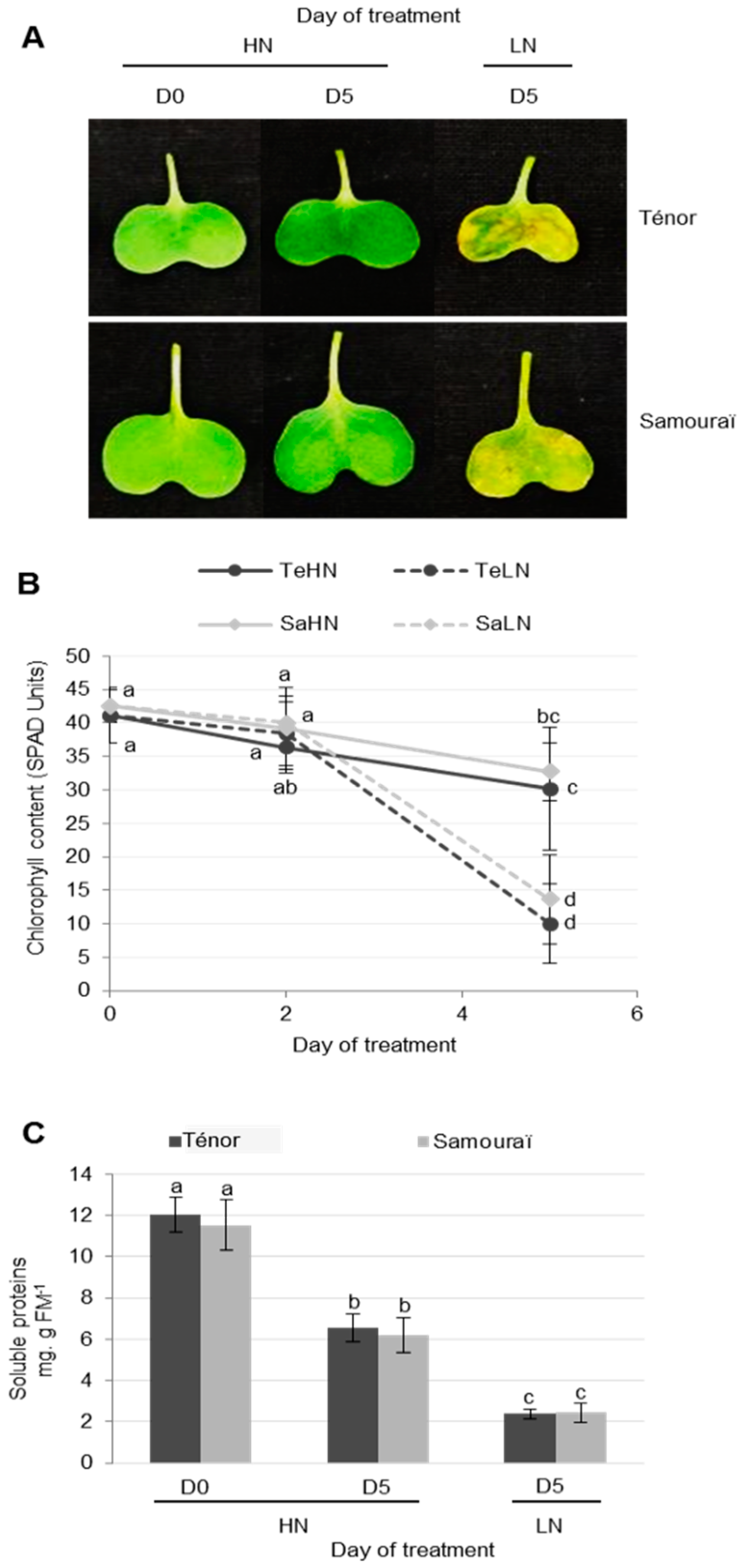
3.1. Characterization of Physiological and Proteolysis Events during Cotyledon Senescence in Two Genotypes of Oilseed Rape with Contrasted N Remobilization Efficiency
3.1.1. Physiological Modifications during Cotyledon Senescence
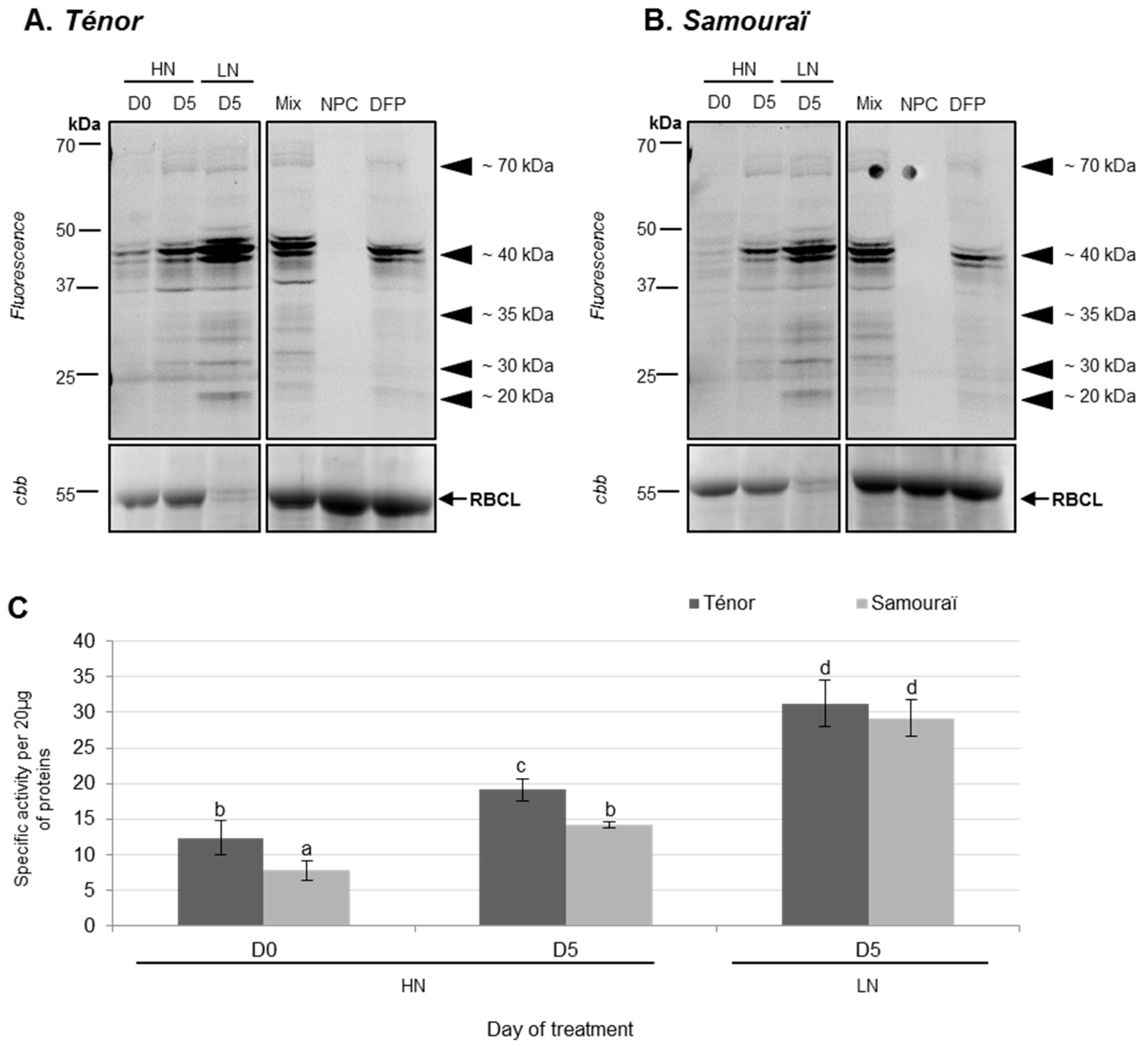
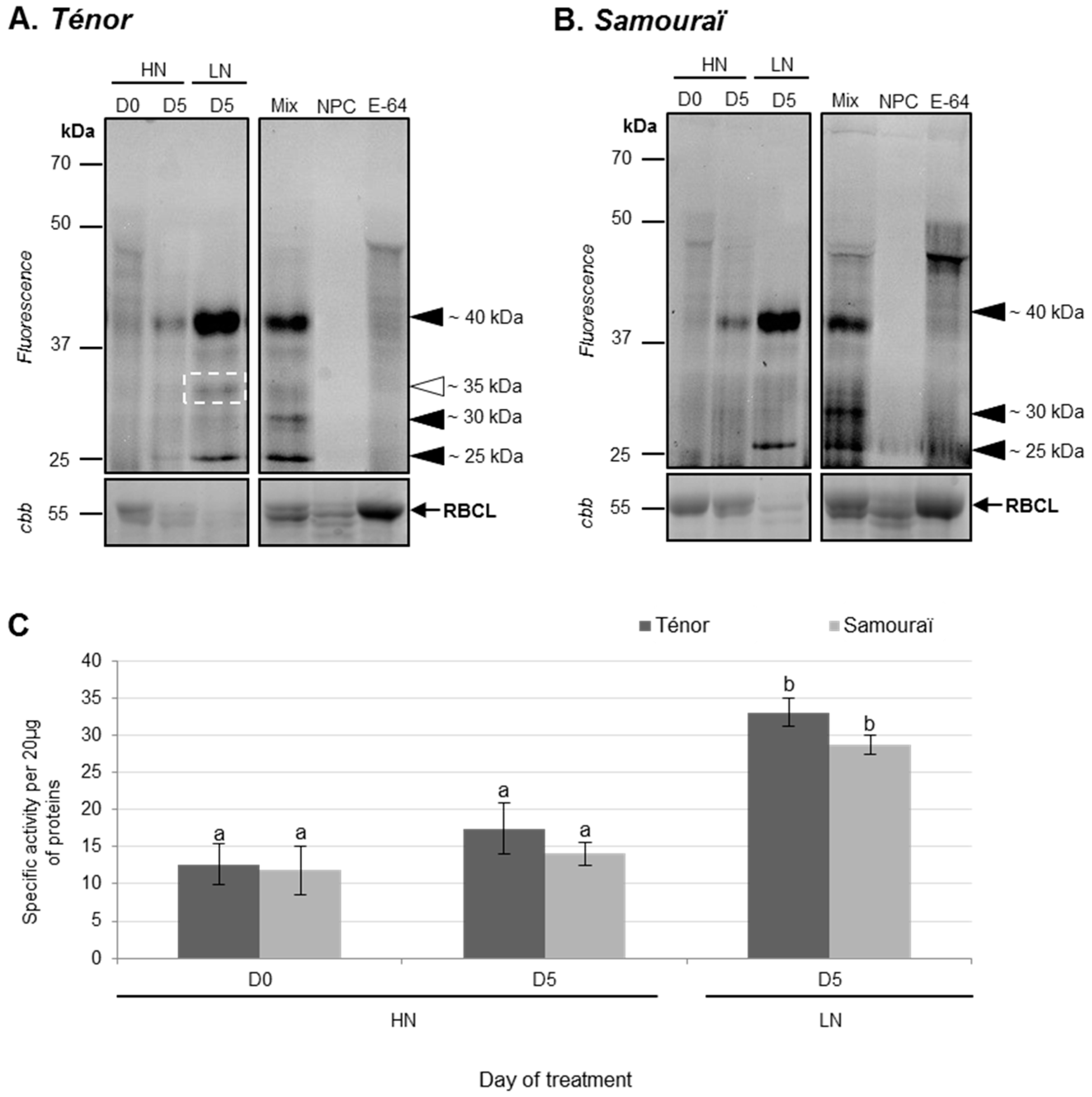
3.1.2. Modifications of Protease Activities during the Senescence of Cotyledons
3.2. Phytohormonal Regulation of Protease Activity during Senescence in Cotyledons
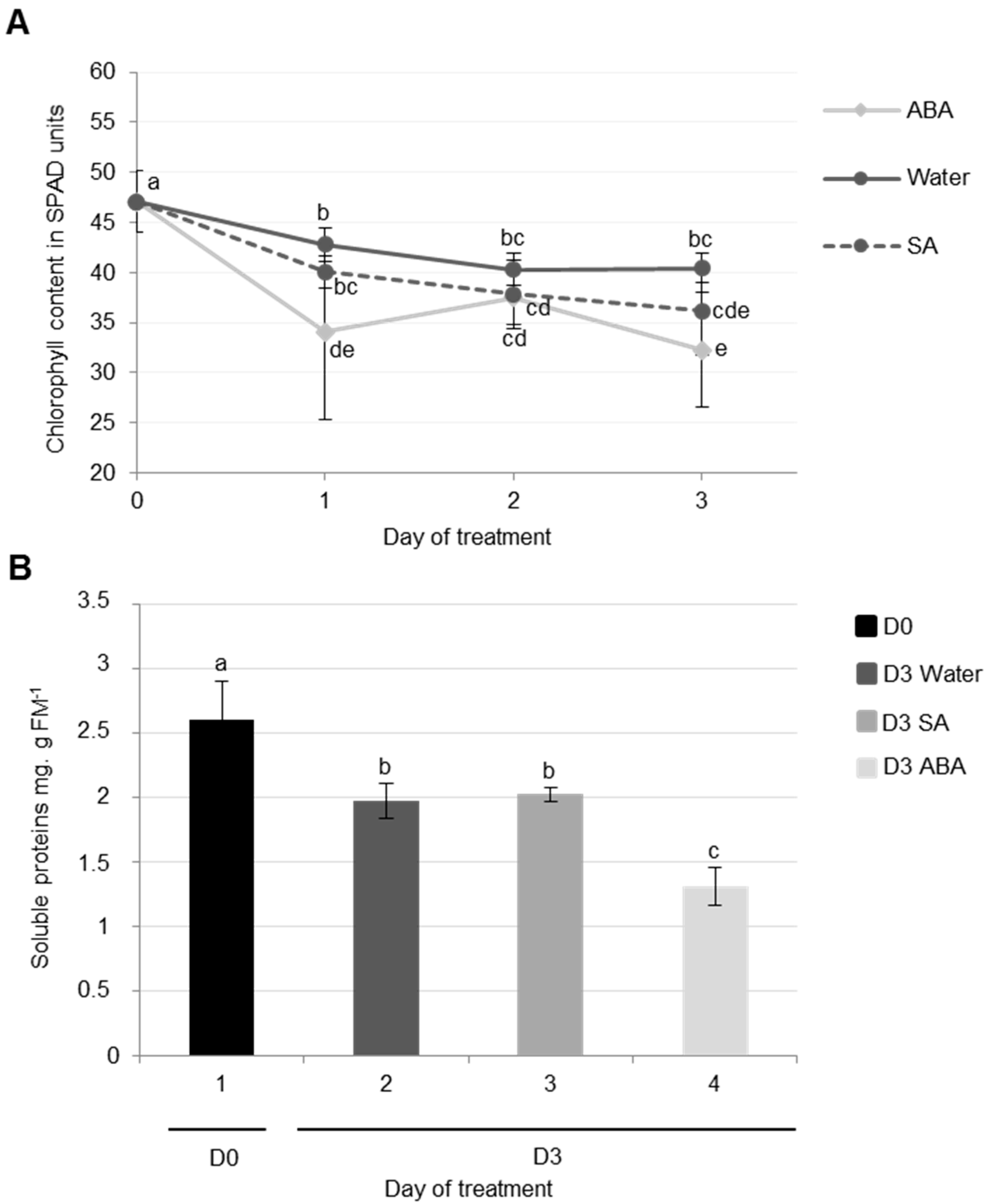
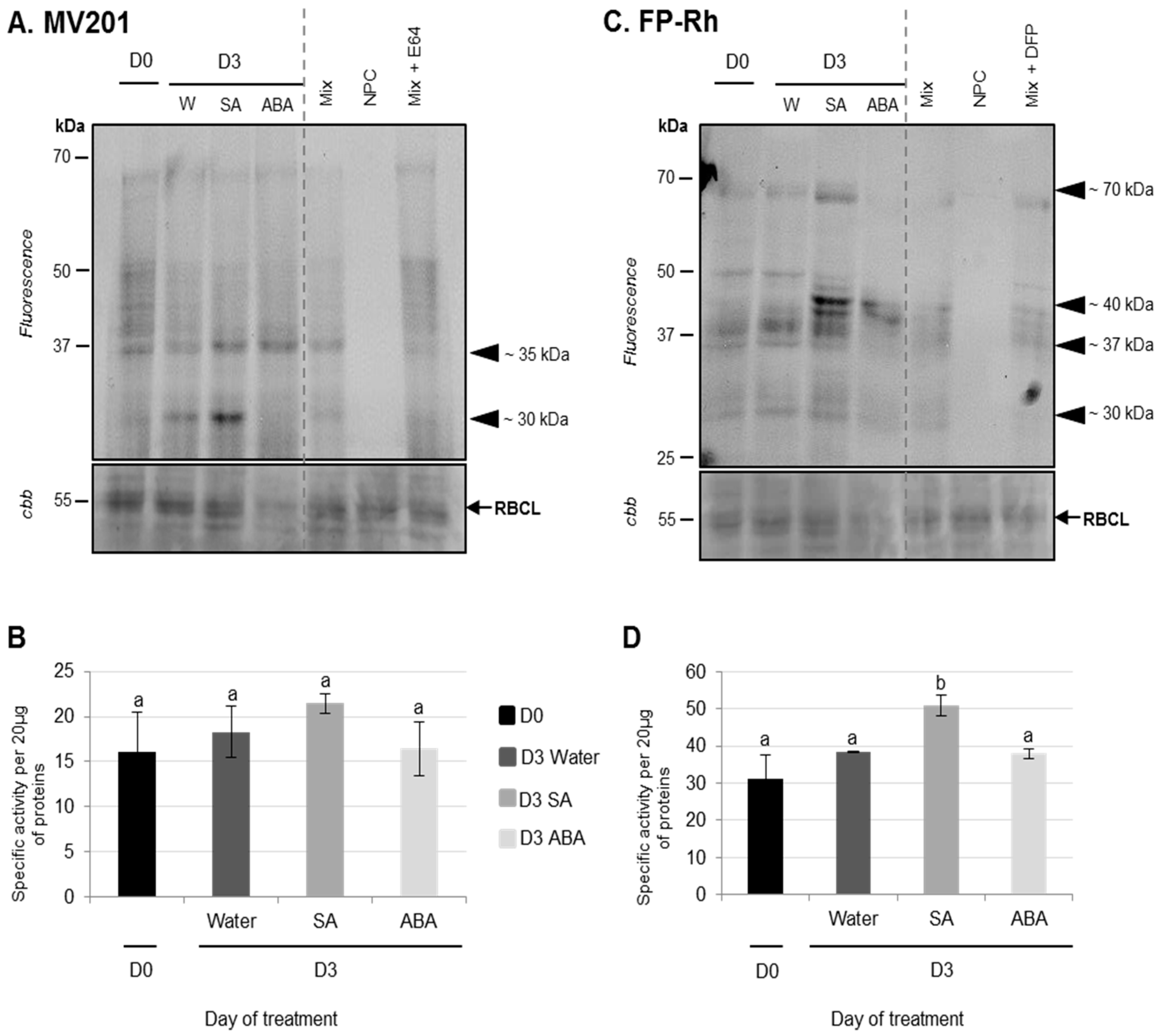
3.2.1. Physiological and Proteolysis Modifications during Cotyledon Senescence Associated with SA and ABA Infiltrations
Effects of ABA Infiltrations of Cotyledon Senescence
Effects of SA Infiltrations on Cotyledon Senescence in Ténor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AALP | aleurain-like protease |
| ABA | abscisic acid |
| CP | cysteine protease |
| HN | high nitrate |
| LN | low nitrate |
| PLCP | papain-like cysteine protease |
| RuBisCO | ribulose-1,5-biphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase |
| SA | salicylic acid |
| SH | serine hydrolase |
| SP | serine protease |
| VPE | vacuolar processing enzyme |
References
- Carré, P.; Pouzet, A. Rapeseed market, worldwide and in Europe. Oilseeds Fats Crop. Lipids 2014, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathke, G.W.; Christen, O.; Diepenbrock, W. Effects of nitrogen source and rate on productivity and quality of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) grown in different crop rotations. Field Crops Res. 2005, 94, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schjoerring, J.K.; Bock, J.G.H.; Gammelvind, L.; Jensen, C.R.; Mogensen, V.O. Nitrogen incorporation and remobilization in different shoot components of field-grown winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) as affected by rate of nitrogen application and irrigation. Plant Soil 1995, 177, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagoli, P.; Laîné, P.; Rossato, L.; Ourry, A. Dynamics of nitrogen uptake and mobilization in field-grown winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus) from stem extension to harvest II. An 15N-labelling-based simulation model of N partitioning between vegetative and reproductive tissues. Ann. Bot. 2005, 95, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malagoli, P.; Laîné, P.; Rossato, L.; Ourry, A. Dynamics of nitrogen uptake and mobilization in field-grown winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus) from stem extension to harvest: I. Global N flows between vegetative and reproductive tissues in relation to leaf fall and their residual N. Ann. Bot. 2005, 95, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gombert, J.; Etienne, P.; Ourry, A.; Le Dily, F. The expression patterns of SAG12/Cab genes reveal the spatial and temporal progression of leaf senescence in Brassica napus L. with sensitivity to the environment. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avice, J.C.; Etienne, P. Leaf senescence and nitrogen remobilization efficiency in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 3813–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girondé, A.; Poret, M.; Etienne, P.; Trouverie, J.; Bouchereau, A.; Le Cahérec, F.; Leport, L.; Orsel, M.; Niogret, M.F.; Deleu, C.; et al. A profiling approach of the natural variability of foliar N remobilization at the rosette stage gives clues to understand the limiting processes involved in the low N use efficiency of winter oilseed rape. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 2461–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girondé, A.; Poret, M.; Etienne, P.; Trouverie, J.; Bouchereau, A.; Le Cahérec, F.; Leport, L.; Niogret, M.F.; Avice, J.C. A comparative study of proteolytic mechanisms during leaf senescence of four genotypes of winter oilseed rape highlighted relevant physiological and molecular traits for NRE improvement. Plants 2016, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchet, A.S.; Laperche, A.; Bissuel-Belaygue, C.; Snowdon, R.; Nesi, N.; Stahl, A. Nitrogen use efficiency in rapeseed. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupinska, K.; Mulisch, M.; Hollmann, J.; Tokarz, K.; Zschiesche, W.; Kage, H.; Humbeck, K.; Bilger, W. An alternative strategy of dismantling of the chloroplasts during leaf senescence observed in a high-yield variety of barley. Physiol. Plant 2012, 144, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Woo, H.R.; Nam, H.G. Toward systems understanding of leaf senescence: An integrated multi-omics perspective on leaf senescence research. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Mendoza, M.; Velasco-Arroyo, B.; Santamaria, M.E.; González-Melendi, P.; Martinez, M.; Diaz, I. Plant senescence and proteolysis: Two processes with one destiny. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2016, 39, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, H.; Stoddart, J. Leaf senescence. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 1980, 31, 83–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.Y.; Kuai, B.K.; Jia, I.Z.; Jing, H.C. Regulation of leaf senescence and crop genetic improvement. J. Int. Plant Biol. 2012, 54, 936–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregersen, P.L.; Cutelic, A.; Boschian, L.; Krupinska, K. Plant senescence and crop productivity. Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 82, 603–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Gan, S.S. Leaf senescence: Signals, execution, and regulation. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2005, 71, 83–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kusaba, M.; Tanaka, A.; Tanaka, R. Stay-green plants: What do they tell us about the molecular mechanism of leaf senescence? Photosynth. Res. 2013, 117, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, P.O.; Kim, H.J.; Nam, H.G. Leaf senescence. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2007, 58, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jibran, R.; Hunter, D.A.; Dijkwel, P.P. Hormonal regulation of leaf senescence through integration of developmental and stress signals. Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 82, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarwat, M.; Naqvi, A.R.; Ahmad, P.; Ashraf, M.; Akram, N.A. Phytohormones and microRNAs as sensors and regulators of leaf senescence: Assigning macro roles to small molecules. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1153–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, C. Signal transduction in leaf senescence. Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 82, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Rozhon, W.; Poppenberger, B. The role of hormones in the aging of plants—A mini-review. Gerontology 2014, 60, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Gan, S.S. Translational researches on leaf senescence for enhancing plant productivity and quality. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 3901–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller-Roeber, B.; Balazadeh, S. Auxin and its role in plant senescence. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2014, 33, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, S.; Burch, D.; Badenhorst, P.; Palanisamy, R.; Mason, J.; Spangenberg, G. Regulated expression of a cytokinin biosynthesis gene IPT delays leaf senescence and improves yield under rainfed and irrigated conditions in canola (Brassica napus L.). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.F.; Zhao, D.G. Expression of IPT in Asakura-sanshoo (Zanthoxylum piperitum (L.) DC. f. inerme Makino) alters tree architecture, delays leaf senescence, and changes leaf essential oil composition. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2016, 34, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desclos-Théveniau, M.; Coquet, L.; Jouenne, T.; Etienne, P. Proteomic analysis of residual proteins in blades and petioles of fallen leaves of Brassica napus. Plant Biol. 2014, 17, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poret, M.; Chandrasekar, B.; van der Hoorn, R.A.L.; Avice, J.C. Characterization of senescence-associated protease activities involved in the efficient protein remobilization during leaf senescence of winter oilseed rape. Plant Sci. 2016, 246, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, I.N.; Caputo, C.; Criado, M.V.; Funk, C. Senescence-associated proteases in plants. Physiol. Plant. 2012, 145, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalerao, R.; Keskitalo, J.; Erlandsson, R.; Björkbacka, H.; Birve, S.J.; Karlsson, J.; Gardeström, P.; Gustafsson, P.; Lundeberg, J.; Jansson, S. Gene expression in autumn leaves. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, I.; Martinez, M. Plant C1A cysteine peptidases in germination and senescence. In Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes; Rawlings, N.D., Salvesen, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1853–1858. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Mendoza, M.; Velasco-Arroyo, B.; Gonzalez-Melendi, P.; Martinez, M.; Diaz, I. C1A cysteine protease-cystatin interactions in leaf senescence. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 3825–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidric, M.; Kos, J.; Sabotic, J. Protease and their endogenous inhibitors in the plant response to abiotic stress. Bot. Serbica 2014, 38, 139–158. [Google Scholar]
- Poret, M. Caractérisation de la Machinerie Protéolytique Associée à une Remobilisation Efficiente de L’azote Pendant la Sénescence Dans le but D’optimiser L’efficience D’usage de L’azote Chez le Colza (Brassica napus L.). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Caen Normandie, Caen, France, December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Patricelli, M.P.; Giang, D.K.; Stamp, L.M.; Burbaum, J.J. Direct visualization of serine hydrolase activities in complex proteomes using fluorescent active site-directed probes. Proteomics 2001, 1, 1067–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richau, K.H.; Kaschani, F.; Verdoes, M.; Pansuriya, T.C.; Niessen, S.; Stüber, K.; Colby, T.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Bogyo, M.; van der Hoorn, R.A.L. Subclassification and biochemical analysis of plant papain-like cysteine proteases displays subfamily-specific characteristics. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 1583–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, B.; Colby, T.; Emran Khan Emon, A.; Jiang, J.; Hong, T.N.; Villamor, J.G.; Harzen, A.; Overkleeft, H.S.; van der Hoorn, R.A.L. Broad-range glycosidase activity profiling. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 2787–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, H.; Beier, H.; Gross, H.J. Improved silver staining of plant proteins, RNA and DNA in polyacrylamide gel. Electrophoresis 1987, 8, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Mahoney, S.R.; Penterman, J.N.; Peirson, D.; Dumbroff, E.B. Ultrastructural and biochemical changes in chloroplasts during Brassica napus senescence. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2001, 39, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desclos, M.; Etienne, P.; Coquet, L.; Jouenne, T.; Bonnefoy, J.; Segura, R.; Reze, S.; Ourry, A.; Avice, J.C. A combined 15N tracing/proteomics study in Brassica napus reveals the chronology of proteomics events associated with N remobilisation during leaf senescence induced by nitrate limitation or starvation. Proteomics 2009, 9, 3580–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.J. Study of cotyledon senescence in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) based on expressed sequence tags and gene expression. J. Plant Biol. 2004, 47, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, D. Hormonal regulation of the expression of cysteine proteinase genes in germinated cotyledons of common bean seeds. Plant Biotechnol. 2007, 24, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.V.; Hudson, K.A. Developmental profiling of gene expression in soybean trifoliate leaves and cotyledons. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, T.; Yamada, K.; Hiraiwa, N.; Kondo, M.; Nishimura, M.; Hara-Nishimura, I. Vacuolar processing enzyme is up-regulated in the lytic vacuoles of vegetative tissues during senescence and under various stressed conditions. Plant J. 1999, 19, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Yu, S.; Xie, Q.; Han, X.; Fan, S. Identification of genes associated with cotyledon senescence in upland cotton. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.Q.; Kojima, T.; Shiraiwa, M.; Takahara, H. Cloning of two cysteine proteinase genes, CysP1 and CysP2, from soybean cotyledons by cDNA representational difference analysis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1627, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangerth, K.F. Basipetal auxin versus acropetal cytokinin transport, and their interaction with NO3 fertilisation in cotyledon senescence and sink: Source relationships in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Plant Biol. 2015, 17, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, L.M.; Gan, S.; Quirino, B.; Amasino, R.M. A comparison of the expression patterns of several senescence-associated genes in response to stress and hormone treatment. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 37, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Osaki, M.; Takebe, M.; Shinano, T.; Wasaki, J. Endogenous hormones and expression of senescence-related genes in different senescent types of maize. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breeze, E.; Harrison, E.; McHattie, S.; Hughes, L.; Hickman, R.; Hill, C.; Kiddle, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Penfold, C.A.; Jenkins, D.; et al. High-resolution temporal profiling of transcripts during Arabidopsis leaf senescence reveals a distinct chronology of processes and regulation. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 873–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.C.; Hong, S.W.; Whang, S.S.; Lim, P.O.; Nam, H.G.; Koo, J.C. Age-dependent action of an ABA-inducible receptor kinase, RPK1, as a positive regulator of senescence in Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Gan, S.S. An abscisic acid-AtNAP transcription factor-SAG113 protein phosphatase 2C regulatory chain for controlling dehydration in senescing Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamburenko, M.V.; Zubo, Y.O.; Vanková, R.; Kusnetsov, V.V.; Kulaeva, O.N.; Börner, T. Abscisic acid represses the transcription of chloroplast genes. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 4491–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukayama, H.; Abe, R.; Uchida, N. SDS-dependent proteases induced by ABA and its relation to Rubisco and Rubisco activase contents in rice leaves. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan-Wollaston, V.; Page, T.; Harrison, E.; Breeze, E.; Lim, P.O.; Nam, H.G.; Lin, J.F.; Wu, S.H.; Swidzinski, J.; Ishizaki, K.; et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals significant differences in gene expression and signalling pathways between developmental and dark/starvation-induced senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2005, 42, 567–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Graaff, E.; Schwacke, R.; Schneider, A.; Desimone, M.; Flugge, U.I.; Kunze, R. Transcription analysis of Arabidopsis membrane transporters and hormone pathways during developmental and induced leaf senescence. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 776–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, K.; Mackerness, S.A.H.; Page, T.; John, C.F.; Murphy, A.M.; Carr, J.P.; Buchanan-Wollaston, V. Salicylic acid has a role in regulating gene expression during leaf senescence. Plant J. 2000, 23, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doares, S.H.; Narvaez-Vasquez, J.; Conconi, A.; Ryan, C.A. Salicylic acid inhibits synthesis of proteinase inhibitors in tomato leaves induced by systemin and jasmonic acid. Plant Physiol. 1995, 108, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzman, R.A.; Brady, J.A.; Finlayson, S.A.; Buchanan, C.D.; Summer, E.J.; Sun, F.; Klein, P.E.; Klein, R.R.; Pratt, L.H.; Cordonnier-Pratt, M.M.; et al. Transcriptional profiling of sorghum induced by methyl jasmonate, salicylic acid, and aminocyclopropane carboxylic acid reveals cooperative regulation and novel gene response. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 352–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girondé, A.; Etienne, P.; Trouverie, J.; Bouchereau, A.; Le Caherec, F.; Leport, L.; Orsel, M.; Niogret, M.F.; Nesi, N.; Carole, D.; et al. The contrasting N management of two oilseed rape genotypes reveals the mechanisms of proteolysis associated with leaf N remobilization and the respective contributions of leaves and stems to N storage and remobilization during seed filling. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
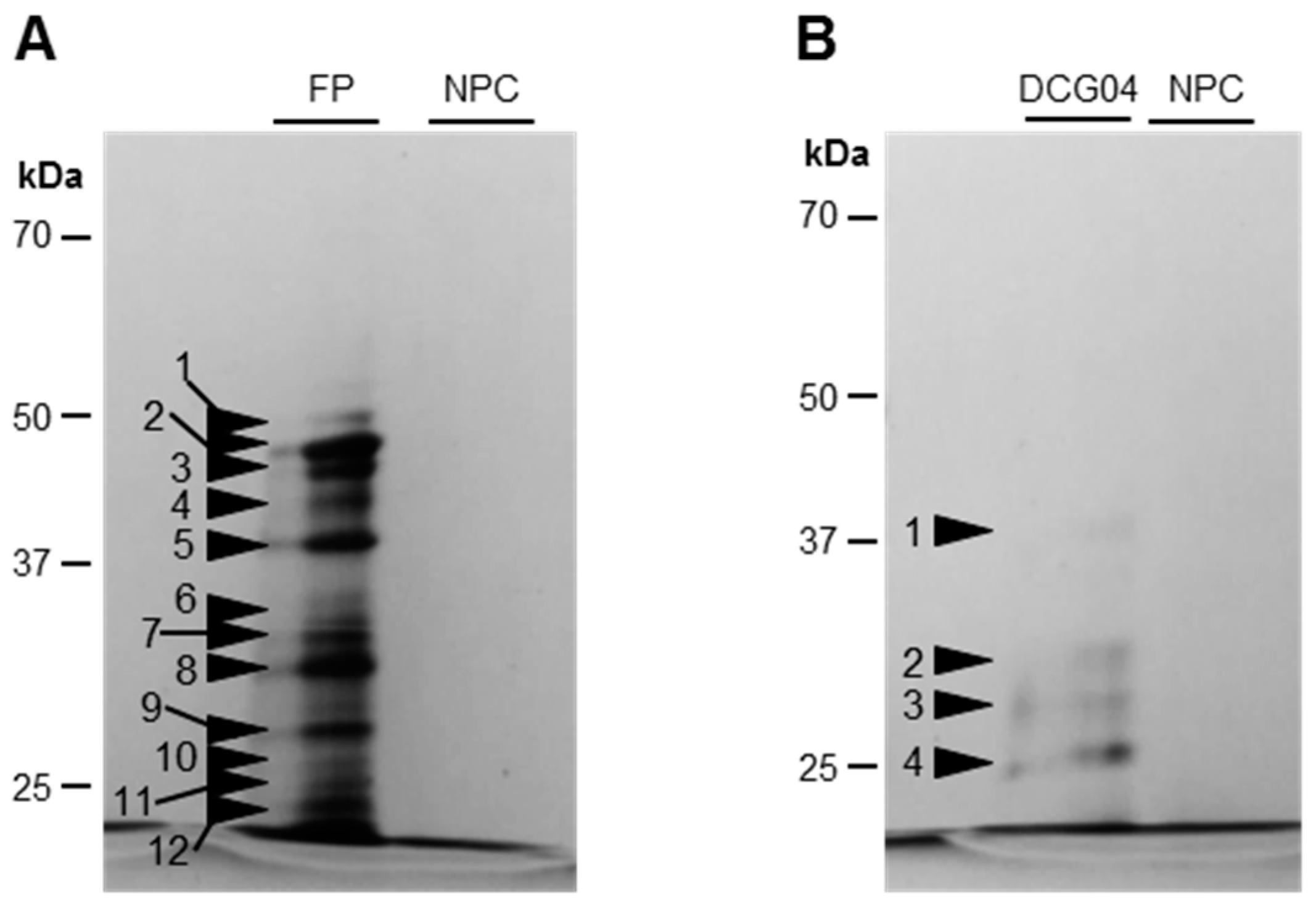
| Protein Accession No. [Brassica Napus]/Uniprot or NCBI Accession No. | Classification |
|---|---|
| Cysteine Proteases | |
| BnaA08g04080D [Brassica napus]/A0A078FVG4 | RD21-like |
| BnaA10g05390D [Brassica napus]/A0A078EXH0 | RD21-like |
| PREDICTED: cysteine proteinase RD21a [Brassica napus]/XP_013718810 | RD21-like |
| BnaA06g36920D [Brassica napus]/A0A078G7A3 | RD21-like |
| senescence-specific cysteine protease [Brassica napus]/AAD53011 | SAG12-like |
| Serine Proteases | |
| PREDICTED: serine carboxypeptidase-like 49 [Brassica napus]/XP_013676539 | S10 |
| BnaA06g18620D [Brassica napus]/A0A078EDE5 | S10 |
| BnaA01g06330D [Brassica napus]/A0A078GRW5 | S10 |
| BnaA10g23100D [Brassica napus]/A0A078BZ09 | S10 |
| PREDICTED: serine carboxypeptidase-like 35 [Brassica napus]/XP_013701943 | S10 |
| BnaCnng56420D [Brassica napus]/A0A078JMY7 | S10 |
| PREDICTED: serine carboxypeptidase-like 29 [Brassica napus]/XP_013750696 | S10 |
| BnaA04g07190D [Brassica napus]/A0A078HQ25 | S10 |
| PREDICTED: serine carboxypeptidase-like 29 [Brassica napus]/XP_013730766 | S10 |
| BnaA08g12880D [Brassica napus]/A0A078GF58 | S10 |
| BnaA04g16130D [Brassica napus]/A0A078GVN3 | S10 |
| PREDICTED: serine carboxypeptidase-like 20 [Brassica napus]/XP_013696030 | S10 |
| PREDICTED: subtilisin-like protease SBT1.7 [Brassica napus]/XP_013654072 | Subtilisin S8 |
| PREDICTED: protease Do-like 1, chloroplastic [Brassica napus]/XP_013644609 | Deg protease |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poret, M.; Chandrasekar, B.; Van der Hoorn, R.A.L.; Coquet, L.; Jouenne, T.; Avice, J.-C. Proteomic Investigations of Proteases Involved in Cotyledon Senescence: A Model to Explore the Genotypic Variability of Proteolysis Machinery Associated with Nitrogen Remobilization Efficiency during the Leaf Senescence of Oilseed Rape. Proteomes 2017, 5, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes5040029
Poret M, Chandrasekar B, Van der Hoorn RAL, Coquet L, Jouenne T, Avice J-C. Proteomic Investigations of Proteases Involved in Cotyledon Senescence: A Model to Explore the Genotypic Variability of Proteolysis Machinery Associated with Nitrogen Remobilization Efficiency during the Leaf Senescence of Oilseed Rape. Proteomes. 2017; 5(4):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes5040029
Chicago/Turabian StylePoret, Marine, Balakumaran Chandrasekar, Renier A. L. Van der Hoorn, Laurent Coquet, Thierry Jouenne, and Jean-Christophe Avice. 2017. "Proteomic Investigations of Proteases Involved in Cotyledon Senescence: A Model to Explore the Genotypic Variability of Proteolysis Machinery Associated with Nitrogen Remobilization Efficiency during the Leaf Senescence of Oilseed Rape" Proteomes 5, no. 4: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes5040029
APA StylePoret, M., Chandrasekar, B., Van der Hoorn, R. A. L., Coquet, L., Jouenne, T., & Avice, J.-C. (2017). Proteomic Investigations of Proteases Involved in Cotyledon Senescence: A Model to Explore the Genotypic Variability of Proteolysis Machinery Associated with Nitrogen Remobilization Efficiency during the Leaf Senescence of Oilseed Rape. Proteomes, 5(4), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes5040029






