Abstract
The separation of ampholytic components according to isoelectric point has played an important role in isolating, reducing complexity and improving peptide and protein detection. This brief review outlines the basics of isoelectric focusing, including a summary of the historical achievements and considerations in experimental design. Derivative methodologies of isoelectric focusing are also discussed including common detection methods used. Applications in a variety of fields using isoelectric point based separations are provided as well as an outlook on the field for future studies.
1. Introduction
The separation of biomolecules, particularly proteins, in the presence of an electric field (e.g., electrophoresis) has given rise to an array of methodologies to reduce the complexity of samples to probe the physiochemical properties of such biomolecules. Proteins and peptides represent possibly the most highly studied class of molecules that are interrogated by electrophoretic methods. These methods include: agarose and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2DE), capillary electrophoresis, isotachophoresis and others.
One such electrophoretic technique is isoelectric focusing (IEF) which provides separation of ampholytic components, molecules that act as weak acids and bases, according to their isoelectric points. In IEF, ampholytes travel according to their charge under the influence of an electric field, in the presence of a pH gradient, until the net charge of the molecule is zero (e.g., isoelectric point, pI). When considering peptides and proteins, the separation is deemed according to the composition of amino acids and exposed charged residues, which behave as weak acids and bases (Figure 1). The migration of the ampholytic species will follow basic principles of electrophoresis; however, the mobility will change in the presence of the pH gradient by slowing down migration at values close to the pI value. Even the simplest ampholytes (e.g., amino acids) can create a pH gradient and act as an isoelectric buffer.
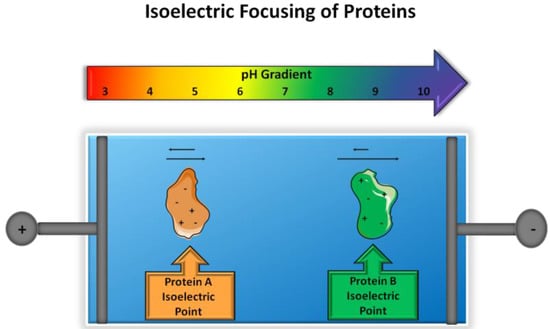
Figure 1.
Principle of isoelectric focusing. Two proteins with varying isoelectric points will migrate in the presence of a pH gradient and electric field until the net charge of a protein is zero, in which migration will cease.
The history of IEF begins with early work carried out by A.J.P. Martin [1] who made several contributions in the field of electrophoresis. Martin also contributed significantly to the field of chromatography and was awarded a Novel Prize for his efforts. The work of P.G. Righetti has been paramount in the ability to separate biomolecules electrophoretically, particularly according to isoelectric point. To fully understand these contributions, one must review the details of the experiment, particularly establishing the pH gradient. Furthermore, classical work regarding ampholytes was carried out by Svensson in the early 1960s [2,3,4].
Carrier ampholytes are the most commonly used chemical components used to generate pH gradients. The chemistry of carrier ampholytes was originally generated via pentaethylenehexamine and addition of acrylic acid. A second generation approach in carrier ampholyte synthesis was performed by Vesterberg [5], in which a heterogeneous mixture of amines was reacted with acrylic acid and a complex product resulted in the generation of thousands of molecules with varying pI values, yet very small changes in pI values across a pH range. Therefore, an ideal carrier ampholyte mixture is generated—a large number of components with close pI values resulting in a linear pH gradient. With regard to gels, carrier ampholytes can also be embedded into acrylamide gels and separation carried out in slab/flatbed format. Details regarding the specifics of carrier ampholyte synthesis and history have been previously reviewed [6,7].
A major achievement, which was an extension of the synthesis of carrier ampholytes, was the generation of immobilized pH gradients in 1982 [8]. Bjellqvist et al. utilized acrylamide as a backbone incorporating amino and carboxyl groups via radical mediated reactions allowing for branching and crosslinking with carrier ampholytes of different pKa values. The resulting product is a pH gradient that is immobile in an electric field and acts as a buffer. The values of pH range from 1 to 13 and can be synthesized in linear and nonlinear forms. The length of the IEF setup that is used plays a role in the desired resolution needed. This major advancement opened doors for various applications of isoelectric focusing for the separation of biological molecules, especially peptides and proteins. The resolving power of IEF (ΔpI) is determined by a series of factors in the experiment including the diffusion coefficient, conductivity and the electric current density. Properties of the gradient include the slope and the charge curve near the focusing point. These properties and relationships have been reviewed in detail [6,9].
IEF can be performed in a variety of formats, including preparative, analytical and microscale. On the larger end, IEF has proven to be beneficial as a preparative method due to its ability to separate large amounts of samples providing high resolution with large recovery yields. Notably, this separation method is advantageous in its ability to concentrate large quantities of samples while simultaneously removing common interfering agents or unwanted analytes. Additionally, IEF can be carried out in capillaries, microfluidic channels and multi-compartment electrolyzers (MCE) as described below. In general, IEF is an extremely powerful technique that, when used in any format, allows for the fractionation of samples resulting in reduced sample complexity and more in-depth analysis.
2. 2DE and IPG Strips
Building upon synthetic methods for carrier ampholytes, it was realized that coupling protein and peptide separation according to pI with other electrophoretic methods would be powerful. O’Farrell described in 1975 the combination of tubular IEF with sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis separation in which radiolabeling was used for detection [10]. Additional related methods were also reported [11,12]. The report of immobilizing the pH gradient in 1982 [8] would provide further robustness of the method and provide a means for orthogonal and high resolution separation of proteins prior to downstream detection or characterization methods. Bjellqvist and colleagues report the linking of Immobilines™ to an acrylamide matrix to carry out IEF prior to a second dimension of separation [13,14]. Although this method proved to be beneficial in regards to it resolving power, the fragile tube gels lacked reproducible pH gradients. Perhaps one of the most significant advancements was the use of immobilized pH gradients (IPG) on plastic strips first introduced by Gorg and colleagues [15,16]. These strips are highly advantageous as pointed out by Westermeier, in that, after gel formation, all polymerization catalysts and unreacted compounds are washed away, providing the low electrical conductivity needed for IEF [17]. Furthermore, the more recent development of narrower gradient strips offers comparable resolution to longer strips of the same gradient. The use of immobilized pH gradients in strip format is now the standard procedure for carrying out 2DE [18,19]. Applications of 2DE span a broad range of disciplines and have been used for exploring the bacterial proteome [20], mapping protein phosphorylation sites [21,22] and expanding from two-dimensions. A report of a third dimension of electrophoresis has been used to eliminate co-migration challenges [23].
2.1. Capillary IEF (cIEF)
The development of carrier ampholytes provided the ability to perform solution-based IEF in a number of formats, with capillary separation being widely accepted. Building on the advantages of capillary electrophoresis, cIEF provides another dimension of separation in a small-volume format [24]. In cIEF, the gradient is generated across the capillary with the use of carrier ampholytes where the anode is immersed in an acidic solution and the cathode in a basic solution. Capillaries are coated at times; however, not all perform this step prior to electrophoretic migration. cIEF offers short separation times, high resolution separation and high peak capacity for small sample volumes. Separation of peptides by cIEF can be coupled with additional separation platforms or mass spectrometry [25]. Challenges arise after the separation, with regard to detection, as discussed later [26]. A series of secondary experimental procedures have been performed following cIEF. These include monolithic immobilized pH gradient columns in which carrier ampholytes are bound to the monolith within the column [27]. cIEF performed as a first dimension has been coupled with capillary electrophoresis experiments in which carrier ampholytes are removed and subsequently coupled with additional chromatographic methodologies [28].
2.2. Large-Format Devices
The use of carrier ampholytes to perform IEF separations has been carried out using several other types of devices beyond gel and capillary formats. The IsoPrime (Hoefer, GE, Little Chalfont, UK) was developed by Righetti and coworkers [29,30] to provide large-scale separations according to pI. The Rotofor [31] (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) contains cylindrical focusing chambers with divisions into 20 compartments. Large amounts of proteins can be loaded (e.g., 1 mg) and the separation volume is upward of 55 mL. A smaller scale version of the Rotofor termed the “mini” is also available commercially. The mini Rotofor contains 18 mL of separation volume as compared to the larger device. It is important to note that, while the technique is not carrier ampholyte nor electrophoretic-based, chromatofocusing is another analytical method in which proteins or other ampholytes can be separated according to isoelectric point [32,33]. Typically, chromatofocusing utilizes ion exchange resins and changes in buffer pH to separate species according to their isoelectric point.
2.3. Small Scale Multi-Compartment Electrolyzers (MCE)
A number of small-scale IEF devices have been developed. The Zoom IEF device described by Speicher et al. [34,35] is a small scale MCE with acrylamide buffering membranes that can be used to perform solution-based IEF. Notably, Zoom IEF can also be classified as an IET device (described below) as it uses membranes with defined pH values and the addition of carrier ampholytes is optional. The Zoom IEF provided an appropriate means to fractionate ampholytes prior to downstream analysis. However, given that the device was made from plastic and had a fixed number of wells, the anode to cathode distance and maximal power load were drawbacks. Separations typically took hours albeit quicker than IPG methods. Other in-house developed devices have been described including a modification for two-dimensional separation [36], and Tran et al. reported a microscale, eight chamber device that was used for solution IEF separations on the time scale of one hour [37,38].
The OFFGEL Fractionator (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) is a hybrid-type MCE that also incorporates an IPG strip [39,40]. Fractionation is obtained via a two-phase system: the upper liquid phase is divided into wells with a lower phase consisting of an IPG gel strip and can be used to separate peptides or proteins. Ampholytes diffuse into the gel where the separation takes place on the strip. Then, fractions in solution are collected following the IEF process. Advantages of this technique include recovery of sample in the liquid phase, high resolution separation and little interference [41]. Those using this device have noted the long separation time needed, high amount of protein needed due to sample loss when fractionating proteins, poor resolution under non-denaturing conditions, and cathodic drift observed for proteins with alkaline pI values [41]. The majority of reports have utilized the OFFGEL device for peptide-based fractionation where it has been used for fractionation followed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) analysis [42].
The smallest scale IEF separations are performed in microfluidic devices. Microfluidic devices provide advantages over more common analytical platforms owing to the small sample volumes and multiplexing capabilities [43,44]. Both carrier ampholyte and natural pH-gradient generation have been reported [45,46]. Coupling microfluidic separations, however, can prove challenging unless these methodologies are included in the microfluidic device. The small sample volumes can also result in difficulties in detection depending on the instrumentation being used. Righetti et al. proposed that the future for microchip electrophoresis lies within liquid polymer “sieving” capabilities [47]. Taken together, microfluidic IEF has been carried out for proteins [48,49] and peptides [50].
2.4. Isoelectric Trapping—IEF without Carrier Ampholytes
Unlike the generation of a continuous pH gradient as obtained commonly with the use of carrier ampholytes, separation according to pI without carrier ampholytes can be performed using buffering membranes only, termed isoelectric trapping (IET). In IET experiments, a series of buffering membranes are used to generate a step-wise pH gradient. The buffering membranes have been generated using an acrylamide backbone and co-polymerizing with carrier ampholytes (e.g., Immobilines). Acrylamide buffering members are extremely useful for such experiments and are used in small scale devices described above. However, it should be noted that acrylamide stability can be problematic at the extremes of pH (acidic and basic) and result in hydrolysis. As an alternative, poly(vinyl alcohol)-based (PVA) membranes were developed. PVA membranes are hydrolytically stable and have been used in a variety of IET experiments. The PVA membranes have tunable pH values based upon general acid-base chemistry. Other buffering membrane chemistries have been reported including agarose and poly(acryloylaminoethoxyethanol) [51].
In IET, ampholytic components migrate according to their in-solution charge, which is in accordance with the amino acid sequence. Upon migration through the membranes into a well in which the pI falls between the pH values of the two adjacent buffering membranes, the ampholyte will then continuously migrate between the two buffers exchanging charge. Therefore, it is trapped (Figure 2). Given that the ampholyte is continuously charged, this reduces problems of solubility that are often observed when proteins are separated according to their pI where solubility remains low. To further address this, work has been done using pH-biasers added to the multi-compartment electrolyzer (MCE) to maintain pH and charge. Isoelectric buffers included have pI values that fall between the pH values of the two adjacent membranes. Common isoelectric buffers used in IET are single amino acids as well as synthetic buffers [52,53]. IET can be carried out in any MCE that contains buffering membranes. Lim et al. developed a small scale device termed “Membrane-Separated Wells for Isoelectric Focusing and Trapping” (MSWIFT) [54]. The MSWIFT device has a customizable number of wells that can be used for separation. Features of the MSWIFT include excellent heat dissipation, thereby having a high potential drop across the device and rapid separation. Various reports have highlighted the advantages of the MSWIFT device including desalting procedures, separation of small and large ampholytic components [54], bottom-up proteomic studies [55,56], and unique applications for purification [57]. Other IET devices have been constructed including the ConFrac [58,59] and TRECS [60,61] systems. It should be noted that any MCE that utilizes buffering membranes can be operated in IET mode.
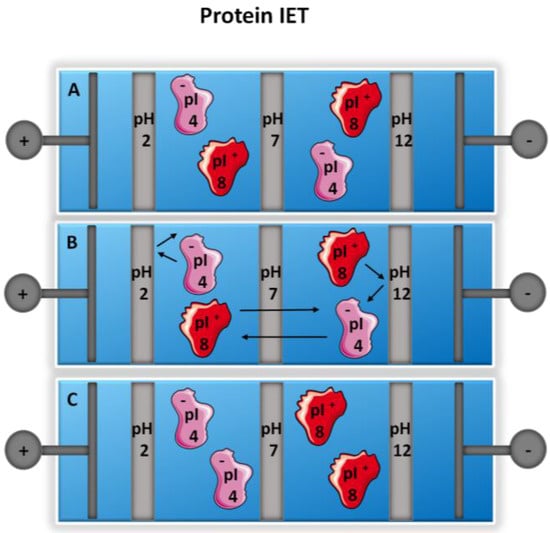
Figure 2.
Isoelectric trapping (IET) of proteins. (A) Two proteins with differing isoelectric points are introduced into multi-compartment electrolyzer (MCE) assembled with pH buffering membranes; (B) the proteins migrate under the application of a potential and when the proteins reach a well in which two buffering membranes bracket the isoelectric point, the proteins are then trapped; and (C) migration continues between the two membranes, with continuous protonation and deprotonation of the protein. Adapted from references [54,55].
3. Detection of Peptides and Proteins
Following the separation of ampholytic components, one must consider how the resulting separation will be analyzed. This detection preference will also depend on the type of information that is needed as well as the format of separation. In gel-based separations such as IEF or 2DE, typically imaging is performed following the separation to visualize bands. From the image, one can then deduce and approximate the pI value and molecular weight of a band of interest. With regard to protein identification, the band is typically excised and mass spectrometry detection is performed. Capillary-based separations also suffer from challenges in detection, including consideration that ampholytes can be focused past the detector point. Pressure can be used post separation to mobilize the analytes across a detector. This can be ultraviolet (UV) detection where carrier ampholytes do not interfere or fluorescence detection can be used if fluorophores are present [62]. Detection can be obtained either at a single point or as full column imaging [63]. To address an issue of post-detector focusing, a blocker can be integrated into the capillary preventing the migration past the detector position. Salt can be used to mobilize focused ampholytes. Electrochemical detection has also been used [64]. Finally, in the majority of large-scale proteome studies currently being carried out, the mass spectrometer is used as the final detector. Therefore, consideration of compatibility must be included.
4. Applications of Isoelectric Focusing and Related Methodologies
4.1. Protein Identification and Post-Translational Modifications
Protein identification from complex samples (e.g., cell and tissue lysates, plasma etc.) has been enabled by IEF. Given the orthogonal separations, in any format that IEF is used, it is possible to highly resolve complex samples allowing for deeper analysis of the proteome. Specifically, the power of 2DE can be realized when proteoforms are present, indicating modifications of the protein that can change the pI or molecular weight, information easily obtained with 2DE. There are reports of many examples demonstrating the power of 2DE in protein identification, characterization and determination of post-translational modifications, as recently reviewed [19]. Additional methodologies that incorporate IEF include separation of proteolytic digests using IPG strips [65]. The use of narrow-range IPG-IEF strips has been combined with nanoLC-MS in order to characterize the change in peptide pI and retention time due to various post-translational modifications [66]. Additionally, the use of high-resolution isoelectric focusing (HiRIEF) has recently been used for proteogenomic analysis, allowing for deeper proteome coverage and the discovery of new protein-coding loci [67]. Other applications include: analysis of sequential phosphorylation by protein kinases using fluorescent peptide substrates and microfluidic isoelectric focusing [68], monitoring protein folding dynamics [69] as well as two-dimensional approaches including the use of cIEF [70,71,72,73].
4.2. Separations for Mass Spectrometry Analysis
Perhaps the greatest power of 2DE and related IEF techniques is the complementarity with mass spectrometry. When used together, this approach is able to reduce proteome complexity with enough resolution that single proteoforms can be analyzed with far more depth compared to a standard shotgun approach. Figure 3 depicts several possible experimental IEF methodologies coupled with mass spectrometry. While the image obtained from the gel-based experiment provides information about the protein composition, complete determination of the protein in the absence of a standard is challenging. It is now common practice to perform 2DE in order to separate proteins and visualize spots while also obtaining quantitative information, followed by excision of the spot and downstream mass spectrometry analysis. Mass spectrometry plays a crucial role in analyte identification and characterization, particularly for peptide and protein analysis with the advancement in soft ionization techniques (e.g., matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) and electrospray ionization (ESI)).
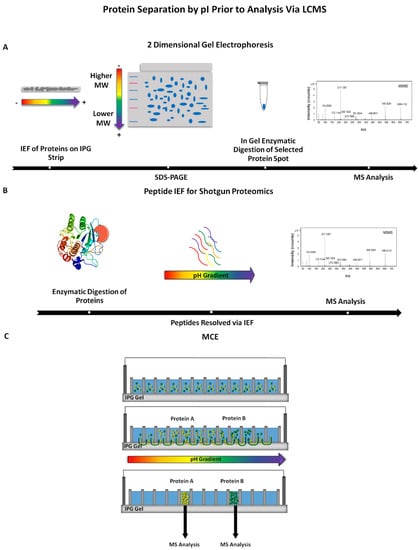
Figure 3.
Examples of isoelectric focusing (IEF) methods incorporated prior to mass spectrometry (MS) detection. (A) Proteins are resolved by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2DE) and visualized with a stain. Spots are excised, subjected to proteolytic digestion and the resulting solution is analyzed via mass spectrometry; (B) Intact proteins, simple or complex mixtures, are proteolytically cleaved followed by the resulting peptides being fractionated according to pI. Separated peptides are then detected by mass spectrometry; (C) Separation of peptides or proteins in an MCE (i.e., OFFGEL) followed by analysis via mass spectrometry [39,40].
Although there have been significant advances in regards to proteomic analysis via mass spectrometry, undersampling of the proteome and consequently the inability to obtain deep proteome coverage remains a problem when analyzing complex samples. For this reason, the use of multidimensional separation methods including IEF have been employed in order to reduce sample complexity prior to analysis. With the development of multidimensional protein identification technology (MudPIT, also termed shotgun), in which two-dimensional chromatography was carried out, extensive proteome coverage was obtained [74]. Following this development, a variety of alternative approaches were reported, many including the use of pI-based separations to fractionate prior to mass spectrometry analysis [75]. There are numerous reports in the literature that compare different separation methods that encompass IEF prior to tandem mass spectrometry. One of the most common orthogonal approaches used to resolve highly complex proteomes is the use of IEF-IPG and reverse phase liquid chromatography [76]. Another study showed that a three-dimensional IEF based approach provided superior resolution compared to previously reported 2D-gel electrophoresis results for the discovery of biomarkers when exploring the microbial metaproteomes in plants [77]. Interestingly, the use of high-pH reverse phase fractionation prior to mass spectrometry analysis has shown to result in a more uniform distribution of unique peptides across all fractions collected compared to off-gel IEF [78]. It is important to note, however, that interfering agents, found in common isobaric labeling kits (e.g., iTRAQ, Sciex, Framingham, MA, USA and TMT, TheroFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) cannot be removed via this method. Lengqvist and colleagues demonstrated that not only is IPG-IEF compatible with labeling techniques such as iTRAQ, but this separation method is also able to provide additional experimental data such as peptide pI in addition to high resolution fractionation [79]. Many of the above-mentioned techniques have been used in this approach for high resolution fractionation, protein identification and quantification by mass spectrometry.
4.3. Novel Approaches
There are many other novel approaches found in the literature that incorporate the use of IEF. For example, a unique methodology that incorporates IPG strips and MALDI mass spectrometry is the generation of a “virtual” 2D gel proteome. This is obtained by separation of proteins via isoelectric focusing in strip format followed by imaging mass spectrometry by MALDI [69]. Other electrophoretic methods including CE have been coupled to mass spectrometry [70,71] for a variety of proteomic applications including biomarker discovery in clinical specimens [72]. Complementary approaches have been described particularly in the development of new devices for electrophoretic separations. Herzog et al. described the generation of an on-chip reactor to fluorescently label proteins prior to separation according to charge [80]. In an effort to perform isoelectric point based fractionation without carrier ampholytes or isoelectric buffers, Chen and colleagues described a capillary method in which sample pH and the pH of the anolyte and catholyte solutions are tailored to perform fractionation steps according to charge and, therefore, pI [81]. The generation of dynamic pH profiles in an ampholyte-free separation has also been reported [82]. Related, tunable IEF has been reported by use of moving reaction boundary theory coupled with sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and resulted in an increase in protein spots and resolution [83]. Additionally, the use of microfluidic devices such as cIEF combined with online trypsin digestion, followed by analysis via nano reverse-phase LC-MS analysis [84], has proven to be advantageous in that few samples are needed, and it allows for the high-throughput analysis of low abundance proteins while reducing direct sample handling.
5. Conclusions
Taken together, there are several steps to consider when using IEF for separating peptides or proteins. A general schematic of this workflow is provided in Figure 4 in which inherent properties are also included for the separation modality and detection modes. Once the sample has been identified, one must consider the necessary preparation steps prior to the electrophoretic separation. This may include buffer conditions that are suitable for electrophoresis, potential chemical interferents and whether the goal is to separate the peptide or protein component. Next, the separation technique should be determined. The selection of the separation technique will depend on a variety of factors including sample quantity, resolution desired and time needed to perform the separation. Furthermore, consideration of a second dimension of separation must be included. Finally, the detection of the analytes must be incorporated. If peptides or proteins are being detected, UV/Vis spectroscopy can be used, in which native absorbance relies on the peptide backbone and aromatic amino acids. Alternatively, more sensitive techniques such as fluorescence require the presence of a fluorophore that can be introduced in the sample preparation stage. If peptide or protein identification is needed, then coupling downstream with mass spectrometry would be the method of choice. The flexibility of the experimental design and compatibility with several analytical techniques makes isoelectric focusing an ideal method to include in biomolecule separation and characterization.
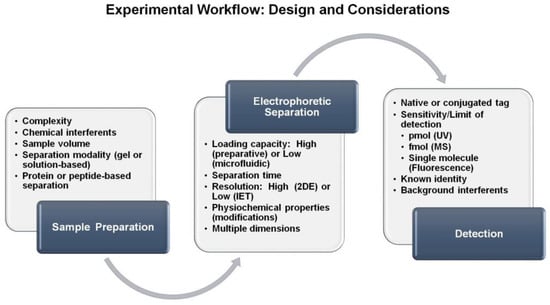
Figure 4.
Experimental workflow summarizing important factors that should be considered when selecting an electrophoretic separation method for the analysis of protein and peptide samples.
The development of isoelectric focusing to separate ampholytes according to isoelectric point has made significant impacts in the fields of separation science, mass spectrometry and proteomics. Regardless of format used, the benefits of this separation have been invaluable for peptide and protein studies. Given the advancements in the field of proteomics particularly incorporating mass spectrometry detection, the need for advanced separations will continue. The complexity of starting materials continues to be a problem in the analysis of peptides and proteins, and the interest in low abundance proteins and protein modifications are of great importance. Generation of a variety of devices to perform these electrophoretic separations is also expected to continue. While complexity is great, sample resources can also be limited. Therefore, small scale devices and microfluidics are likely to make significant contributions. In the past 40 plus years, impressive and significant achievements have been seen in electrophoresis and separation science. We will likely see continued growth in development in the future.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Department of Chemistry, College of Liberal Arts and Sciences, University of Illinois at Chicago.
Author Contributions
M.R.P. and S.M.C. conceived and drafted the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| 2DE | Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis |
| cIEF | Capillary isoelectric focusing |
| ESI | Electrospray ionization |
| HiRIEF | High-resolution isoelectric focusing |
| IEF | Isoelectric focusing |
| IET | Isoelectric trapping |
| IPG | Immobilized pH gradients Immobilized pH gradients |
| MALDI | Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization |
| MCE | Multi-compartment electrolyzers |
| MSWIFT | Membrane-separated wells for isoelectric focusing and trapping |
| pI | Isoelectric point |
| PVA | Poly(vinyl alcohol) |
References
- Consden, R.; Gordon, A.H.; Martin, A.J. Ionophoresis in Silica Jelly; a method for the separation of amino-acids and peptides. Biochem. J. 1946, 40, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, H. Isoelectric fractionation, analysis, and characterization of ampholytes in natural pH gradients. I. The differential equation of solute concnetrations at a steady state and its solution for simple cases. Acta Chem. Scand. 1961, 15, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, H. Isoelectric fractionation, analysis, and characterization of ampholytes in natural pH gradients. II. Buffering capacity and conductance of isoionic ampholytes. Acta Chem. Scand. 1962, 16, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, H. Isoelectric fractionation, analysis and characterization of ampholytes in natural pH gradient III. Description of apparatus for electrolysis in columns stabilized by denisty gradient and direct gradients and direct determination of isoelectric point. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1962, (Suppl. 1), 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesterberg, O. Synthesis and isoelectric fractionation of carrier ampholytes. Acta Chem. Scand. 1969, 23, 2653–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righetti, P.G.; Simo, C.; Sebastiano, R.; Citterio, A. Carrier ampholytes for IEF, on their fortieth anniversary (1967–2007), brought to trial in court: The verdict. Electrophoresis 2007, 28, 3799–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righetti, P.G.; Candiano, G. Recent advances in electrophoretic techniques for the characterization of protein biomolecules: A poker of aces. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 8727–8737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjellqvist, B.; Ek, K.; Righetti, P.G.; Gianazza, E.; Gorg, A.; Westermeier, R.; Postel, W. Isoelectric focusing in immobilized pH gradients: Principle, methodology and some applications. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 1982, 6, 317–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanov, A. Ief-based multidimensional applications in proteomics: Toward higher resolution. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 3281–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Farrell, P.H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1975, 250, 4007–4021. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Farrell, P.H.; O’Farrell, P.Z. Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic fractionation. Methods Cell Biol. 1977, 16, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Farrell, P.Z.; Goodman, H.M.; O’Farrell, P.H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell 1977, 12, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ek, K.; Bjellqvist, B.; Righetti, P.G. Preparative isoelectric focusing in immobilized pH gradients. I. General principles and methodology. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 1983, 8, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanov, A.V.; Righetti, P.G. pH changes in immobiline gels due to low-molecular mass ion adsorption and conditions for salt front formation during electrophoretic desorption. Electrophoresis 1997, 18, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorg, A.; Postel, W.; Westermeier, R. Ultrathin-layer isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gels on cellophane. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 89, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorg, A.; Postel, W.; Westermeier, R.; Gianazza, E.; Righetti, P.G. Gel gradient electrophoresis, isoelectric focusing and two-dimensional techniques in horizontal, ultrathin polyacrylamide layers. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 1980, 3, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermeier, R. Method 10—Ief in Immobilized pH Gradients, 4th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- Westermeier, R. 2D gel-based proteomics: There’s life in the old dog yet. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 122, 236–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westermeier, R. Looking at proteins from two dimensions: A review on five decades of 2D electrophoresis. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 120, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curreem, S.O.; Watt, R.M.; Lau, S.K.; Woo, P.C. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis in bacterial proteomics. Protein Cell 2012, 3, 346–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, K.; Albrecht, S.; Schaller, A. Targeted analysis of protein phosphorylation by 2D electrophoresis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1306, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maccarrone, G.; Filiou, M.D. Protein profiling and phosphoprotein analysis by isoelectric focusing. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1295, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mauro, S.; Colignon, B.; Dieu, M.; Delaive, E.; Raes, M. Three-dimensional electrophoresis for quantitative profiling of complex proteomes. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1295, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Jong, C.A.; Risley, J.; Lee, A.K.; Zhao, S.S.; Chen, D.D. Separation of recombinant therapeutic proteins using capillary gel electrophoresis and capillary isoelectric focusing. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1466, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mokaddem, M.; d’Orlye, F.; Varenne, A. Online capillary isoelectric focusing-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (CIEF-ESI MS) in glycerol-water media for the separation and characterization of hydrophilic and hydrophobic proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1466, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.Y.; Speicher, D.W. Complex proteome prefractionation using microscale solution isoelectrofocusing. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2005, 2, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Ma, J.; Zhu, G.; Shan, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Integration of capillary isoelectric focusing with monolithic immobilized pH gradient, immobilized trypsin microreactor and capillary zone electrophoresis for on-line protein analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 3194–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasicka, V. Recent developments in CE and CEC of peptides (2009–2011). Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 48–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righetti, P.G.; Wenisch, E.; Faupel, M. Preparative protein-purification in a multi-compartment electrolyzer with immobiline membranes. J. Chromatogr. 1989, 475, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righetti, P.G.; Wenisch, E.; Jungbauer, A.; Katinger, H.; Faupel, M. Preparative purification of human monoclonal-antibody isoforms in a multicompartment electrolyzer with immobiline membranes. J. Chromatogr. 1990, 500, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egen, N.B.; Thromann, W.; Twitty, G.E.; Bier, M. A new preparative isoelectric focusing apparatus. In Electrophoresis; Hirai, H., Ed.; de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1984; pp. 547–549. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.; Li, X.; Bieberich, C.J.; Frey, D.D. Reducing sample complexity in proteomics by chromatofocusing with simple buffer mixtures. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 424, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sluyterman, L.A.A.; Elgersma, O. Chromatofocusing: Isoelectric focusing on ion-exchange columns. J. Chromatogr. 1978, 150, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Speicher, D.W. A method for global analysis of complex proteomes using sample prefractionation by solution isoelectrofocusing prior to two-dimensional electrophoresis. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 284, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, X.; Speicher, D.W. Comprehensive analysis of complex proteomes using microscale solution isoelectrofocusing prior to narrow pH range two-dimensional electrophoresis. Proteomics 2002, 2, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Fu, Z.; Gutierrez, P.; Fenselau, C. Solution isoelectric focusing for peptide analysis: Comparative investigation of an insoluble nuclear protein fraction. J. Proteome Res. 2005, 4, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, J.C.; Doucette, A.A. Rapid and effective focusing in a carrier ampholyte solution isoelectric focusing system: A proteome prefractionation tool. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, J.C.; Wall, M.J.; Doucette, A.A. Evaluation of a solution isoelectric focusing protocol as an alternative to ion exchange chromatography for charge-based proteome prefractionation. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2009, 877, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros, A.; Faupel, M.; Mees, H.; Oostrum, J.; Ferrigno, R.; Reymond, F.; Michel, P.; Rossier, J.S.; Girault, H.H. Protein purification by off-gel electrophoresis. Proteomics 2002, 2, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, P.E.; Reymond, F.; Arnaud, I.L.; Josserand, J.; Girault, H.H.; Rossier, J.S. Protein fractionation in a multicompartment device using off-gel (TM) isoelectric focusing. Electrophoresis 2003, 24, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreda-Pineiro, A.; Garcia-Otero, N.; Bermejo-Barrera, P. A review on preparative and semi-preparative offgel electrophoresis for multidimensional protein/peptide assessment. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 836, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magdeldin, S.; Elguoshy, A.; Yoshida, Y.; Hirao, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Takimoto, H.; Fujinaka, H.; Kinoshita, N.; et al. Complementary protein and peptide offgel fractionation for high-throughput proteomic analysis. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 8481–8488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasicka, V. Recent developments in capillary and microchip electroseparations of peptides (2013-middle 2015). Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 162–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepanova, S.; Kasicka, V. Analysis of proteins and peptides by electromigration methods in microchips. J. Sep. Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branan, N. Microfluidic IEF without carrier molecules. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macounova, K.; Cabrera, C.R.; Holl, M.R.; Yager, P. Generation of natural pH gradients in microfluidic channels for use in isoelectric focusing. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 3745–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righetti, P.G.; Sebastiano, R.; Citterio, A. Capillary electrophoresis and isoelectric focusing in peptide and protein analysis. Proteomics 2013, 13, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yang, S.; Lee, C.S.; DeVoe, D.L. Polyacrylamide gel plugs enabling 2-D microfluidic protein separations via isoelectric focusing and multiplexed sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 2241–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlckova, M.; Kalman, F.; Schwarz, M.A. Pharmaceutical applications of isoelectric focusing on microchip with imaged UV detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1181, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkonen, S.; Jacksen, J.; Roeraade, J.; Thormann, W.; Emmer, A. Microfluidic isoelectric focusing of amyloid beta peptides followed by micropillar-matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 10044–10051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiari, M.; Micheletti, C.; Nesi, M.; Fazio, M.; Righetti, P.G. Towards new formulations for polyacrylamide matrices—N-acryloylaminoethoxyethanol, a novel monomer combining high hydrophilicity with extreme hydrolytic stability. Electrophoresis 1994, 15, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalwani, S.; Vigh, G. A family of high-buffering capacity diamino sulfate isoelectric buffers for ph-biased isoelectric trapping separations. Electrophoresis 2005, 26, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalwani, S.; Tutu, E.; Vigh, G. Synthesis and characterization of quaternary ammonium dicarboxylic acid isoelectric buffers and their use in pH-biased isoelectric trapping separations. Electrophoresis 2005, 26, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, P.; North, R.; Vigh, G. Rapid isoelectric trapping in a micropreparative-scale multicompartment electrolyzer. Electrophoresis 2007, 28, 1851–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cologna, S.M.; Russell, W.K.; Lim, P.J.; Vigh, G.; Russell, D.H. Combining isoelectric point-based fractionation, liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry to improve peptide detection and protein identification. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 21, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cologna, S.M.; Williams, B.J.; Russell, W.K.; Pai, P.J.; Vigh, G.; Russell, D.H. Studies of histidine as a suitable isoelectric buffer for tryptic digestion and isoelectric trapping fractionation followed by capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry for proteomic analysis. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8108–8114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pai, P.J.; Cologna, S.M.; Russell, W.K.; Vigh, G.; Russell, D.H. Efficient electrophoretic method to remove neutral additives from protein solutions followed by mass spectrometry analysis. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 2814–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, P.J.; Vigh, G. Concentration and fractionation by isoelectric trapping in a micropreparative-scale multicompartmental electrolyzer having orthogonal pH gradients. Part 1. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lim, P.J.; Vigh, G. Concentration and fractionation by isoelectric trapping in a micropreparative-scale multicompartmental electrolyzer having orthogonal pH gradients. Part 2. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 1654–1658. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- North, R.Y.; Vigh, G. Preparative-scale isoelectric trapping by recursive electrophoresis in a compartmentalized system having orthogonal primary and secondary pH gradients. Part 1—Construction and standard operation. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 2797–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- North, R.Y.; Vigh, G. Preparative-scale isoelectric trapping by recursive electrophoresis in a compartmentalized system having orthogonal primary and secondary pH gradients. Part 2—Operation in cascade mode. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 2805–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Campana, A.M.; Taverna, M.; Fabre, H. LIF detection of peptides and proteins in CE. Electrophoresis 2007, 28, 208–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Tragas, C.; Wu, J.; Mao, Q.; Pawliszyn, J. Recent developments in capillary isoelectric focusing with whole-column imaging detection. Electrophoresis 1998, 19, 2290–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gencoglu, A.; Minerick, A.R. Electrochemical detection techniques in micro- and nanofluidic devices. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2014, 17, 781–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkelman, T.; Bandhakavi, S.; Paulus, A. In-gel peptide ief sample preparation for LC/MS analysis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1295, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lengqvist, J.; Eriksson, H.; Gry, M.; Uhlen, K.; Bjorklund, C.; Bjellqvist, B.; Jakobsson, P.J.; Lehtio, J. Observed peptide pI and retention time shifts as a result of post-translational modifications in multidimensional separations using narrow-range IPG-IEF. Amino Acids 2011, 40, 697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branca, R.M.; Orre, L.M.; Johansson, H.J.; Granholm, V.; Huss, M.; Perez-Bercoff, A.; Forshed, J.; Kall, L.; Lehtio, J. Hirief LC-MS enables deep proteome coverage and unbiased proteogenomics. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Choi, N.; Lim, B.; Kim, T.W.; Song, S.; Kim, Y.P. Sequential phosphorylation analysis using dye-tethered peptides and microfluidic isoelectric focusing electrophoresis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 73, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, P.K.; Harrata, A.K.; Lee, C.S. Monitoring protein refolding induced by disulfide formation using capillary isoelectric focusing electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 2044–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tragas, C.; Pawliszyn, J. On-line coupling of high performance gel filtration chromatography with imaged capillary isoelectric focusing using a membrane interface. Electrophoresis 2000, 21, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Z.; Lee, C.S.; Shen, Y.F.; Smith, R.D.; Baehrecke, E.H. Integration of capillary isoelectric focusing with capillary reversed-phase liquid chromatography for two-dimensional proteomics separation. Electrophoresis 2002, 23, 3143–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, L.Y.; Liu, H.C.; Zhang, W.B.; Zhang, Y.K. Two-dimensional capillary electrophoresis involving capillary isoelectric focusing and capillary zone electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1018, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickerson, J.A.; Ramsay, L.M.; Dada, O.O.; Cermak, N.; Dovichi, N.J. Two-dimensional capillary electrophoresis: Capillary isoelectric focusing and capillary zone electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 2650–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washburn, M.P.; Wolters, D.; Yates, J.R., 3rd. Large-scale analysis of the yeast proteome by multidimensional protein identification technology. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millioni, R.; Franchin, C.; Tessari, P.; Polati, R.; Cecconi, D.; Arrigoni, G. Pros and cons of peptide isolectric focusing in shotgun proteomics. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1293, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiser, L.; Vaezzadeh, A.R.; Deshusses, J.M.; Hochstrasser, D.F. Shotgun proteomics: A qualitative approach applying isoelectric focusing on immobilized pH gradient and LC-MS/MS. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 681, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kohrs, F.; Heyer, R.; Magnussen, A.; Benndorf, D.; Muth, T.; Behne, A.; Rapp, E.; Kausmann, R.; Heiermann, M.; Klocke, M.; et al. Sample prefractionation with liquid isoelectric focusing enables in depth microbial metaproteome analysis of mesophilic and thermophilic biogas plants. Anaerobe 2014, 29, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, D.R.; Hu, X.; McCorrister, S.J.; Westmacott, G.R.; Plummer, F.A.; Ball, T.B.; Carpenter, M.S. High pH reversed-phase chromatography as a superior fractionation scheme compared to off-gel isoelectric focusing for complex proteome analysis. Proteomics 2013, 13, 2956–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lengqvist, J.; Uhlen, K.; Lehtio, J. Itraq compatibility of peptide immobilized pH gradient isoelectric focusing. Proteomics 2007, 7, 1746–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, C.; Poehler, E.; Peretzki, A.J.; Borisov, S.M.; Aigner, D.; Mayr, T.; Nagl, S. Continuous on-chip fluorescence labelling, free-flow isoelectric focusing and marker-free isoelectric point determination of proteins and peptides. Lab. Chip 2016, 16, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, H.; Lu, J.J.; Liu, S. Simple means for fractionating protein based on isoelectric point without ampholyte. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 9293–9299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brod, E.; Ben-Yosef, V.S.; Bandhakavi, S.; Sivan, U. Charge-based separation of proteins and peptides by electrically induced dynamic pH profiles. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1431, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.G.; Shang, Z.; Yan, J.; Li, S.; Li, G.Q.; Liu, R.Z.; Qing, Y.; Fan, L.Y.; Xiao, H.; Cao, C.X. A tunable isoelectric focusing via moving reaction boundary for two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and proteomics. Talanta 2015, 137, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Ma, J.; Wu, S.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Integrated platform of capillary isoelectric focusing, trypsin immobilized enzyme microreactor and nanoreversed-phase liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry for online protein profiling. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 2848–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).