Multiplex Targeted Proteomic Analysis of Cytokine Ratios for ICU Mortality in Severe COVID-19
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
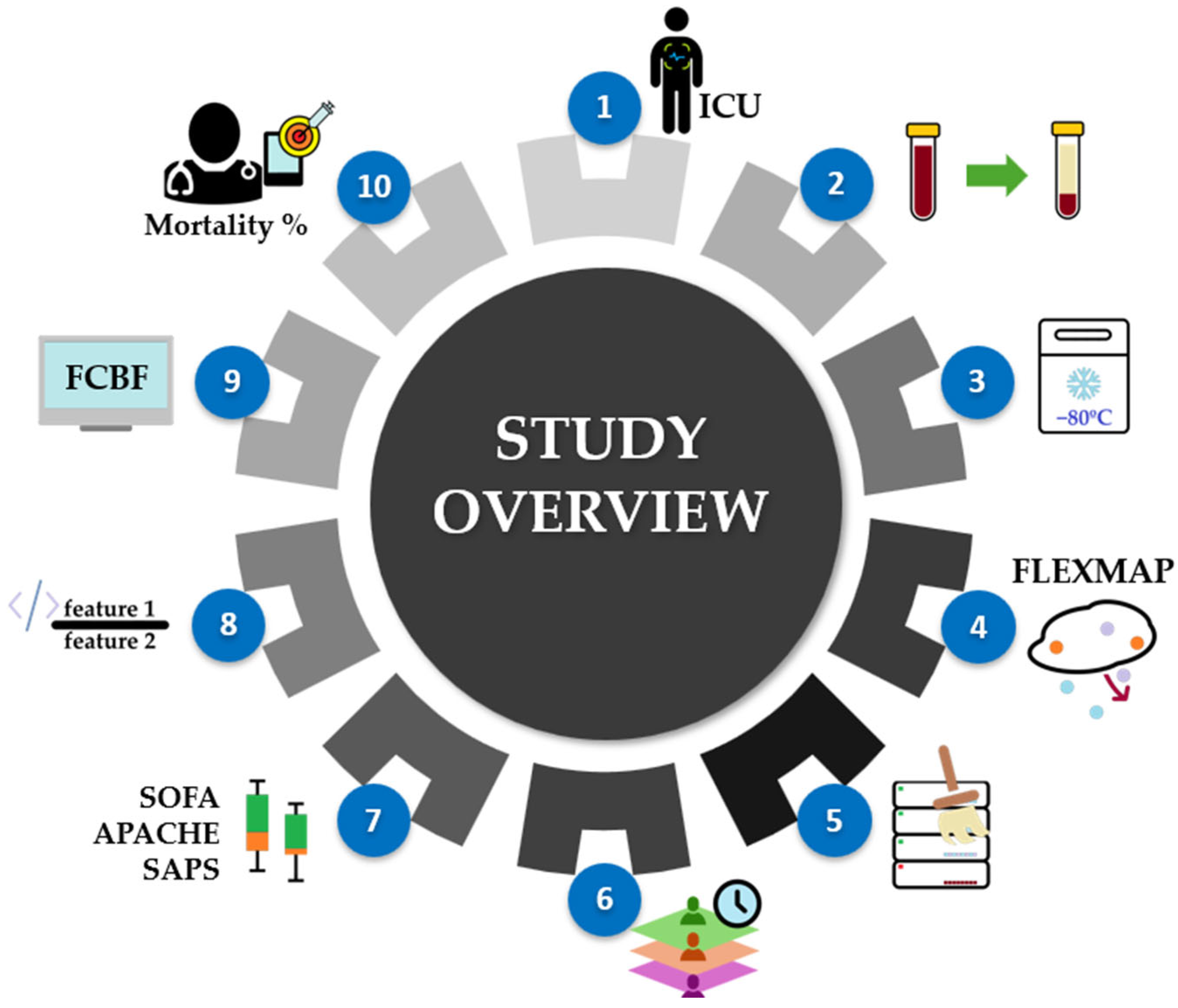
2.1. Workflow Overview
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Collection of Biological Samples
2.4. Proteomic Cytokine Profile by Multiplex Immunoassay
2.5. Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Study Population Characteristics
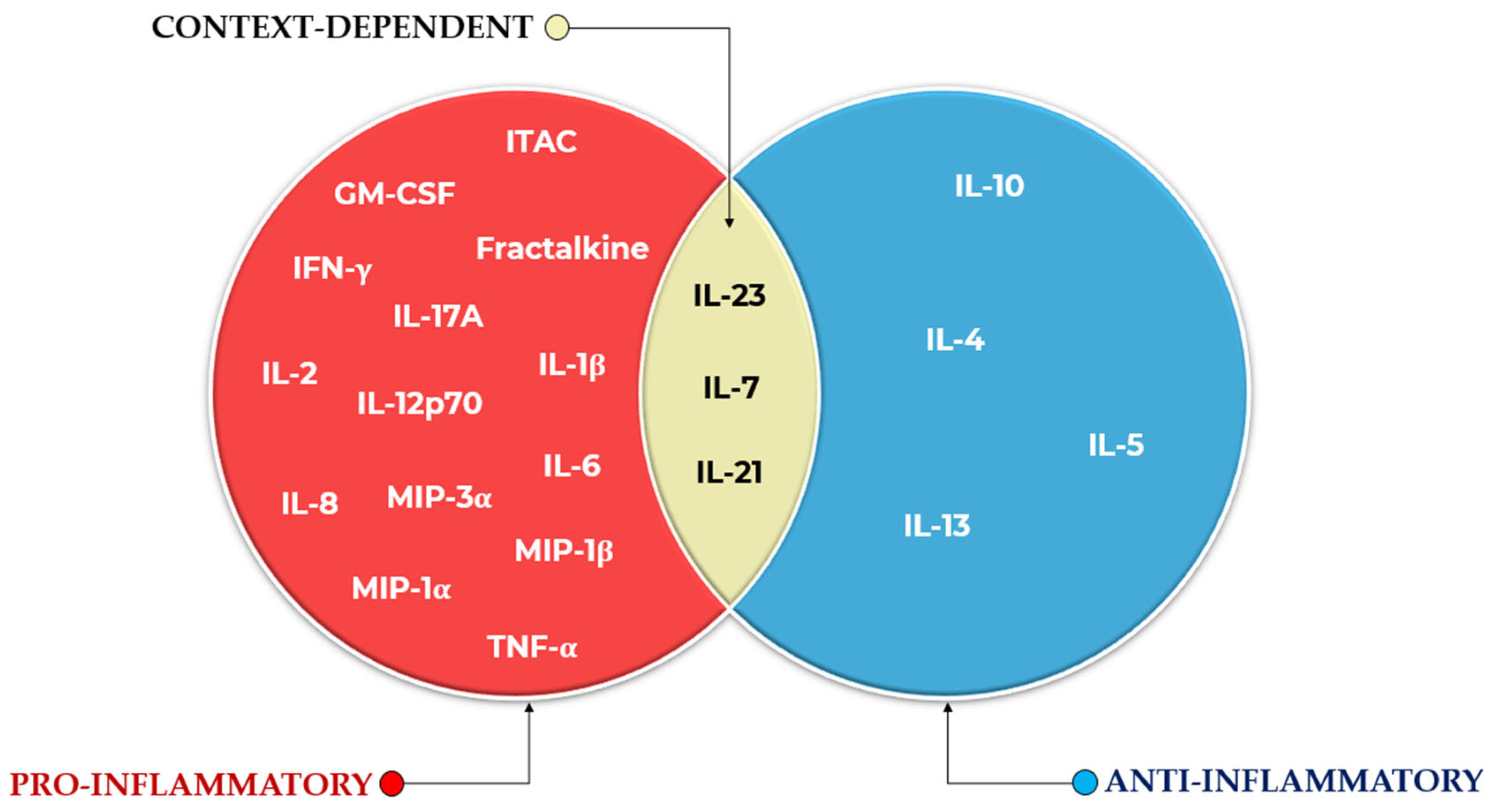
3.2. Commonly Reported Cytokines and Ratios
Convergence with and Divergence from the Literature
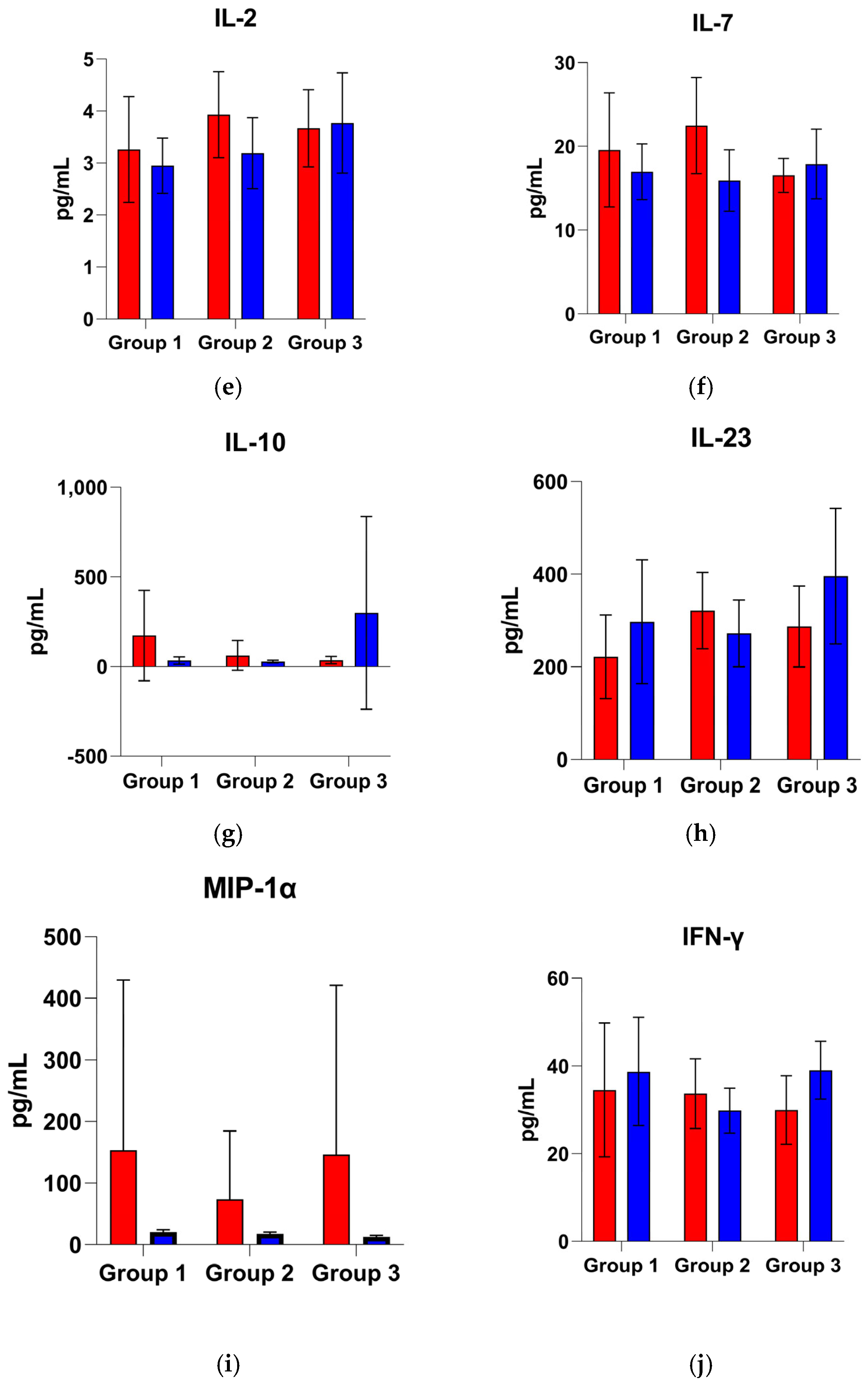
3.3. Univariate Cytokine Analysis
3.3.1. Group 1: Early Outcome (≤48 h)
3.3.2. Group 2: Intermediate Outcome (>48 h to ≤7 Days)
3.3.3. Group 3: Late Outcome (>7 Days to ≤14 Days)
3.4. Multivariate Cytokine Analysis
3.4.1. Individual Cytokine Analysis
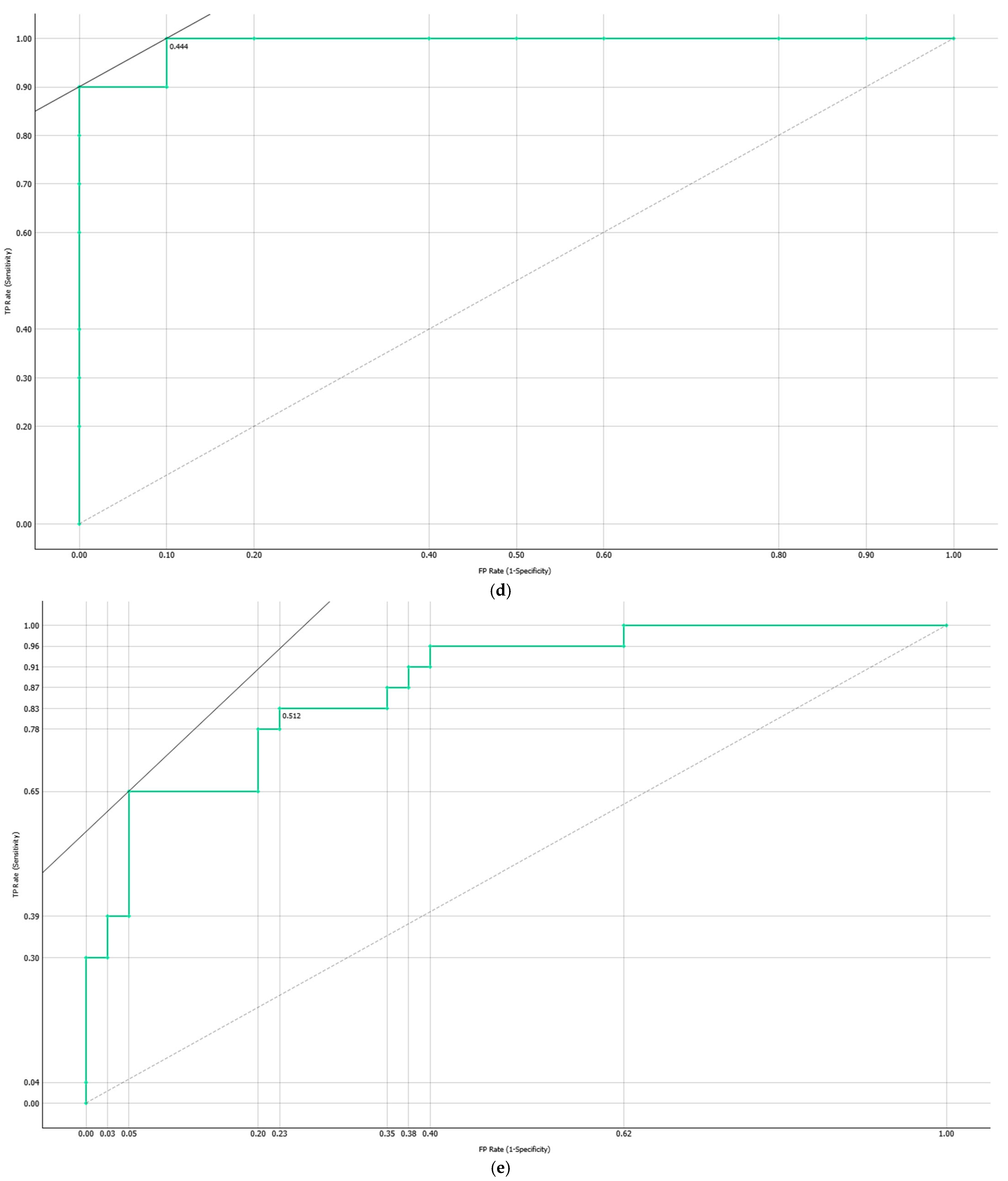
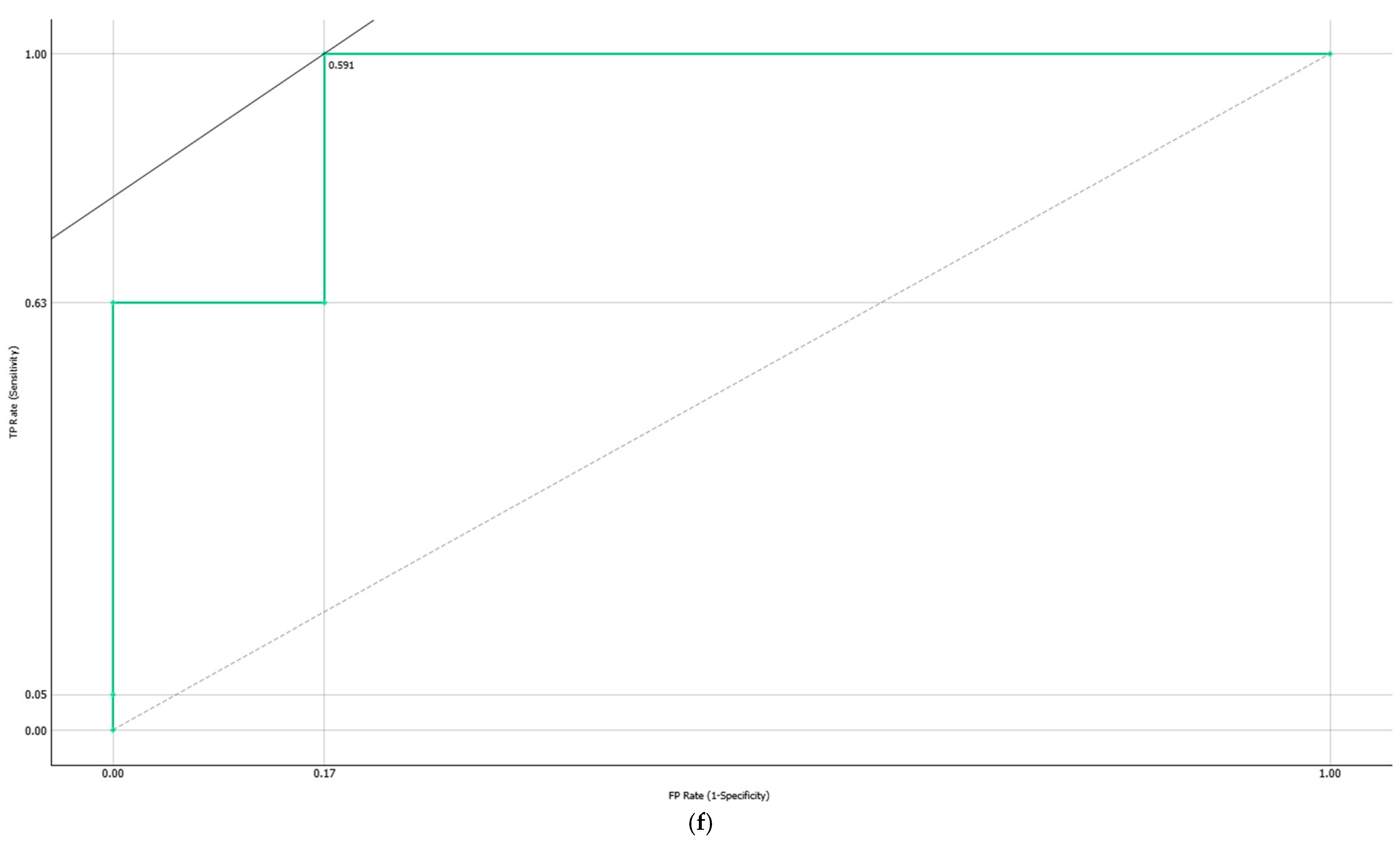
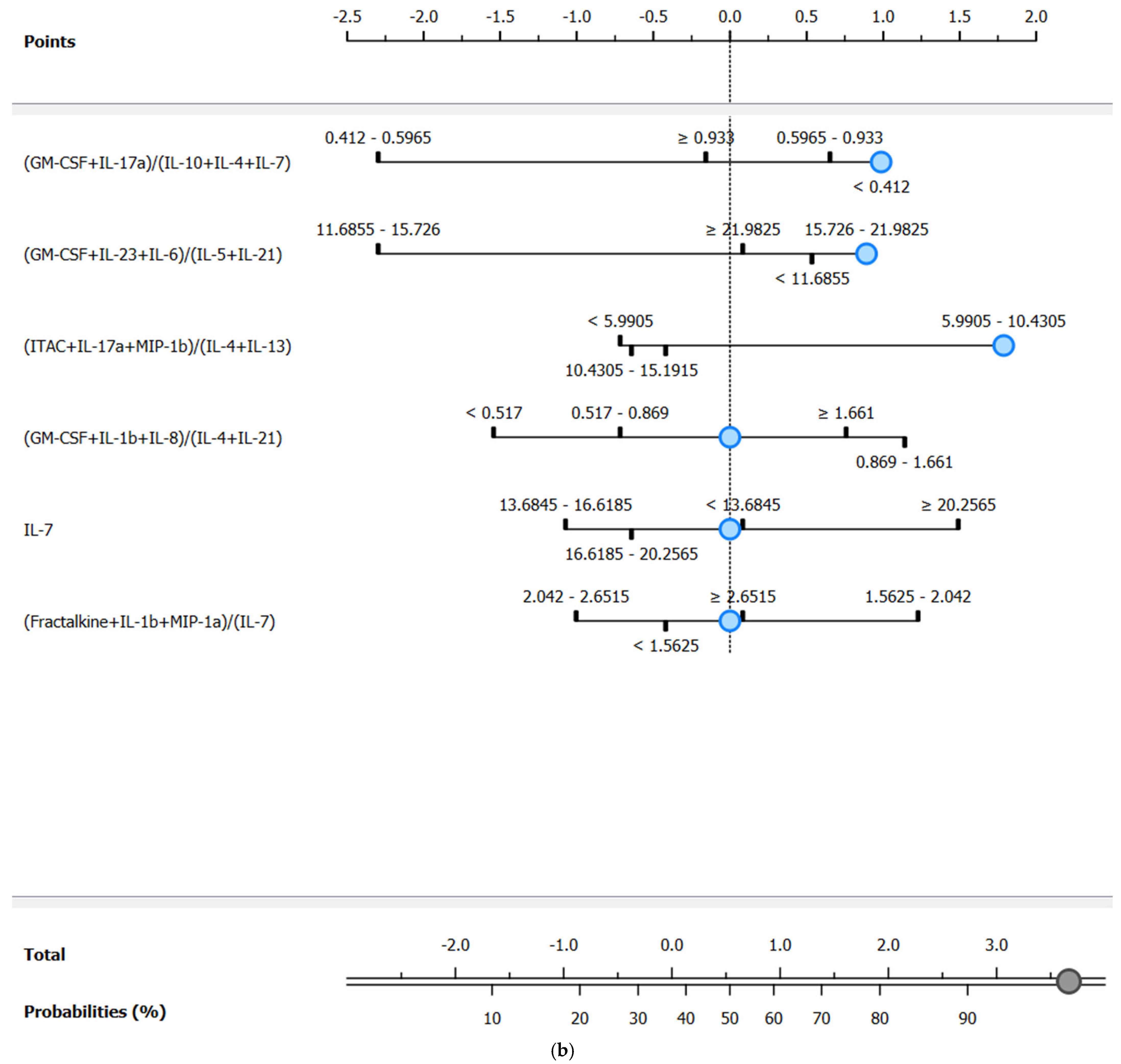
3.4.2. Computationally Generated Cytokine Ratios
3.5. Methodological Considerations and Graphical Summary of Key Findings
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APACHE II | Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II |
| ARDS | Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| c-SAPS3 | customized Simplified Acute Physiology Score 3 |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| ECMO | Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation |
| FC | Fold change |
| FCBF | Fast Correlation-Based Filter |
| GCS | Glasgow Coma Scale |
| G-CSF | Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-gamma |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| IL-2 | Interleukin-2 |
| IL-4 | Interleukin-4 |
| IL-5 | Interleukin-5 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-7 | Interleukin-7 |
| IL-8 | Interleukin-8 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| IL-12p70 | Interleukin-12p70 |
| IL-13 | Interleukin-13 |
| IL-17A | Interleukin-17A |
| IL-21 | Interleukin-21 |
| IL-23 | Interleukin-23 |
| IMV | Invasive Mechanical Ventilation |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| ITAC | Interferon-inducible T cell Alpha Chemoattractant |
| KNN | k-Nearest Neighbors |
| MIP-1α | Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-1 alpha |
| MIP-1β | Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-1 beta |
| MIP-3α | Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-3 alpha |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio |
| OASIS | Oxford Acute Severity of Illness Score |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PREMO | Predictive Models of COVID-19 Outcomes for Higher-risk Patients Towards a Precision Medicine |
| RT-PCR | Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction tests |
| SAPS | Simplified Acute Physiology Score |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| SICULA | Super ICU Learner Algorithm |
| SIRS | Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome |
| SOFA | Sequential Organ Failure Assessment |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| t-SNE | t-distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
References
- Veldhoen, R.A.; Howes, D.; Maslove, D.M. Is Mortality a Useful Primary End Point for Critical Care Trials? Chest 2020, 158, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, R.A.; Kane, A.D.; Kursumovic, E.; Oglesby, F.C.; Cook, T.M. Mortality in Patients Admitted to Intensive Care with COVID-19: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Observational Studies. Anaesthesia 2021, 76, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrentieva, A.; Kaimakamis, E.; Voutsas, V.; Bitzani, M. An Observational Study on Factors Associated with ICU Mortality in COVID-19 Patients and Critical Review of the Literature. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M.; Bangash, H.I.; Habiba, M.; Lei, Y.; Xie, T.; Sun, J.; Wei, Z.; Hong, Z.; Shao, L.; Zhang, Q. Immune Dysregulation and System Pathology in COVID-19. Virulence 2021, 12, 918–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Huang, J.; Yu, J.; Li, B.; Wei, S.; Cen, W.; Xuan, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, Y.; Mo, J.; et al. Immune Dysregulation in COVID-19 Induced ARDS in Kidney Transplant Recipients Revealed by Single-Cell RNA Sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez Hernández, R.; Ramasco Rueda, F. Biomarkers as Prognostic Predictors and Therapeutic Guide in Critically Ill Patients: Clinical Evidence. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fika, S.; Nanas, S.; Baltopoulos, G.; Myrianthefs, P. Prognostic Scoring Systems and Outcome Markers in ICU Patients. Arch. Hell. Med. 2014, 31, 541. [Google Scholar]
- Villar, J.; González-Martin, J.M.; Añón, J.M.; Ferrando, C.; Soler, J.A.; Mosteiro, F.; Mora-Ordoñez, J.M.; Ambrós, A.; Fernández, L.; Montiel, R.; et al. Clinical Relevance of Timing of Assessment of ICU Mortality in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumtaz, H.; Ejaz, M.K.; Tayyab, M.; Vohra, L.I.; Sapkota, S.; Hasan, M.; Saqib, M. APACHE Scoring as an Indicator of Mortality Rate in ICU Patients: A Cohort Study. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 85, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misset, B. Scoring Systems for Comparison of Disease Severity in Intensive Care Unit Patients. In Critical Care Secrets, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 567–571. ISBN 978-1-4160-3206-9. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, H.P.; Schuster, F.P.; Ritschel, P.; Wilts, S.; Bodmann, K.F. The Ability of the Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS II) to Predict Outcome in Coronary Care Patients. Intensive Care Med. 1997, 23, 1056–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Diao, X.; Chen, H.; Cai, K.; Ma, X.; Wang, S. Dynamic APACHE II Score to Predict the Outcome of Intensive Care Unit Patients. Front. Med. 2022, 8, 744907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, C.; Pompei, M.; Burmistrov, D.; Pompei, F. Mortality Rates among Adult Critical Care Patients with Unusual or Extreme Values of Vital Signs and Other Physiological Parameters: A Retrospective Study. Acute Crit. Care 2024, 39, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, R.P.; Metnitz, P.G.H.; Almeida, E.; Jordan, B.; Bauer, P.; Campos, R.A.; Iapichino, G.; Edbrooke, D.; Capuzzo, M.; Le Gall, J.-R.; et al. SAPS 3—From Evaluation of the Patient to Evaluation of the Intensive Care Unit. Part 2: Development of a Prognostic Model for Hospital Mortality at ICU Admission. Intensive Care Med. 2005, 31, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poncet, A.; Perneger, T.V.; Merlani, P.; Capuzzo, M.; Combescure, C. Determinants of the Calibration of SAPS II and SAPS 3 Mortality Scores in Intensive Care: A European Multicenter Study. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Ye, X.; Liu, H.; Wei, J. SAPS III is Superior to SOFA for Predicting 28-Day Mortality in Sepsis Patients Based on Sepsis 3.0 Criteria. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 114, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, Y.; Krauss, C.; Amaral, A.C.K.B.; Réa-Neto, A.; Specht, M.; Reinhart, K.; Marx, G. Comparison of the Performance of SAPS II, SAPS 3, APACHE II, and Their Customized Prognostic Models in a Surgical Intensive Care Unit. Br. J. Anaesth. 2008, 101, 798–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, R.; Singer, M.; Rhodes, A. Why the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score Needs Updating? Crit. Care Sci. 2024, 36, e20240296en. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, A.; Tyagi, S.; Agrawal, A.; Mohan, A.; Garg, D.; Salhotra, R.; Saxena, A.K.; Goel, A. Early Warning Scores at Time of ICU Admission to Predict Mortality in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. Disaster Med. Public Health Prep. 2022, 16, 2371–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monk, M.; Torres, J.; Vickery, K.; Jayaraman, G.; Sarva, S.T.; Kesavan, R. A Comparison of ICU Mortality Scoring Systems Applied to COVID-19. Cureus 2023, 15, e35423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirracchio, R.; Petersen, M.L.; Carone, M.; Rigon, M.R.; Chevret, S.; Van Der Laan, M.J. Mortality Prediction in Intensive Care Units with the Super ICU Learner Algorithm (SICULA): A Population-Based Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, P.; Ferrer, M.; Martí, V.; Reyes, S.; Martínez, R.; Menéndez, R.; Ewig, S.; Torres, A. Inflammatory Biomarkers and Prediction for Intensive Care Unit Admission in Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, E.J. Understanding Cytokines Part I: Physiology and Mechanism of Action. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2000, 2, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, I.B. Cytokines. In Oxford Textbook of Medicine; Firth, J., Conlon, C., Cox, T., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 236–245. ISBN 978-0-19-874669-0. [Google Scholar]
- HamzicMehmedbasic, A. Inflammatory Cytokines as Risk Factors for Mortality After Acute Cardiac Events. Med. Arh. 2016, 70, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, E.M.; Himmelfarb, J.; Sezer, M.T.; Chertow, G.M.; Mehta, R.L.; Paganini, E.P.; Soroko, S.; Freedman, S.; Becker, K.; Spratt, D.; et al. Plasma Cytokine Levels Predict Mortality in Patients with Acute Renal Failure. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, W.; Bernhagen, J.; Bucala, R. Cytokines in Sepsis: Potent Immunoregulators and Potential Therapeutic Targets—An Updated View. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 165974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Lu, J. Progress in Cytokine Research for ARDS: A Comprehensive Review. Open Med. 2024, 19, 20241076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meduri, G.U.; Headley, S.; Kohler, G.; Stentz, F.; Tolley, E.; Umberger, R.; Leeper, K. Persistent Elevation of Inflammatory Cytokines Predicts a Poor Outcome in ARDS. Chest 1995, 107, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, H.O.; Braim, S.A.; Rasool, M.A.; Abdalla, D.M.; Hamad, D.Q.; Ahmad, D.K.; Mustafa, A.M.; Abdullah, F.; Mahmood, Y.M.; Hiwa, D.S.; et al. Role of Inflammatory Markers in Severity, ICU Admission, and Mortality in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 79,934 Patients. Barw Med. J. 2024, 2, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, D.M.; Kim-Schulze, S.; Huang, H.-H.; Beckmann, N.D.; Nirenberg, S.; Wang, B.; Lavin, Y.; Swartz, T.H.; Madduri, D.; Stock, A.; et al. An Inflammatory Cytokine Signature Predicts COVID-19 Severity and Survival. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidan, A.A.; Gad, A.Y.S.; Zakaria, N.H.; El-Hariri, H.M.; Elsharnouby, N.M.; Helmy, M.W.; El-Setouhy, M. The Use of Interleukin-10 (IL-10) and Phosphorus Levels as Predictors of the Time to Improvement in COVID-19 Patients: A Prospective Study. Egypt J. Bronchol. 2024, 18, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuk, S.; Sipahioğlu, H.; Karahan, S.; Yeşiltepe, A.; Kuzugüden, S.; Karabulut, A.; Beştepe Dursun, Z.; Akın, A. Cytokine Levels and Severity of Illness Scoring Systems to Predict Mortality in COVID-19 Infection. Healthcare 2023, 11, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notz, Q.; Schmalzing, M.; Wedekink, F.; Schlesinger, T.; Gernert, M.; Herrmann, J.; Sorger, L.; Weismann, D.; Schmid, B.; Sitter, M.; et al. Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Responses in Severe COVID-19-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome—An Observational Pilot Study. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 581338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turtle, L.; Thorpe, M.; Drake, T.M.; Swets, M.; Palmieri, C.; Russell, C.D.; Ho, A.; Aston, S.; Wootton, D.G.; Richter, A.; et al. Outcome of COVID-19 in Hospitalised Immunocompromised Patients: An Analysis of the WHO ISARIC CCP-UK Prospective Cohort Study. PLoS Med. 2023, 20, e1004086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalicińska, E.; Szymczak, D.; Zińczuk, A.; Adamik, B.; Smiechowicz, J.; Skalec, T.; Nowicka-Suszko, D.; Biernat, M.; Bogucka-Fedorczuk, A.; Rybka, J.; et al. Immunosuppression as a Hallmark of Critical COVID-19: Prospective Study. Cells 2021, 10, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bost, P.; De Sanctis, F.; Canè, S.; Ugel, S.; Donadello, K.; Castellucci, M.; Eyal, D.; Fiore, A.; Anselmi, C.; Barouni, R.M.; et al. Deciphering the State of Immune Silence in Fatal COVID-19 Patients. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngs, J.; Provine, N.M.; Lim, N.; Sharpe, H.R.; Amini, A.; Chen, Y.-L.; Luo, J.; Edmans, M.D.; Zacharopoulou, P.; Chen, W.; et al. Identification of Immune Correlates of Fatal Outcomes in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rad, F.; Dabbagh, A.; Dorgalaleh, A.; Biswas, A. The Relationship between Inflammatory Cytokines and Coagulopathy in Patients with COVID-19. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeachy, M.J.; Cua, D.J.; Gaffen, S.L. The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Health and Disease. Immunity 2019, 50, 892–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Zou, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Zheng, D.; Zhou, G. Association between Inflammatory Biomarkers and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome or Acute Lung Injury Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2022, 134, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qahtani, A.A.; Alhamlan, F.S.; Al-Qahtani, A.A. Pro-Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Interleukins in Infectious Diseases: A Comprehensive Review. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.E.; Skon-Hegg, C.; Badovinac, V.P.; Griffith, T.S. The Calm after the Storm: Implications of Sepsis Immunoparalysis on Host Immunity. J. Immunol. 2023, 211, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicchese, J.M.; Evans, S.; Hult, C.; Joslyn, L.R.; Wessler, T.; Millar, J.A.; Marino, S.; Cilfone, N.A.; Mattila, J.T.; Linderman, J.J.; et al. Dynamic Balance of Pro- and Anti-inflammatory Signals Controls Disease and Limits Pathology. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 285, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltendorf, S.; Vogel, K.; Thurm, C.; Prätsch, F.; Reinhold, A.; Färber, J.; Heuft, H.; Kaasch, A.J.; Hachenberg, T.; Weinzierl, S.; et al. IL-13 Determines Specific IgE Responses and SARS-CoV-2 Immunity after Mild COVID-19 and Novel mRNA Vaccination. Eur. J. Immunol. 2022, 52, 1972–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.; Jeon, I.; Kim, B.-S.; Park, M.; Bae, E.-A.; Song, B.; Koh, C.-H.; Shin, K.-S.; Kim, I.-K.; Choi, K.; et al. IL-21-Mediated Reversal of NK Cell Exhaustion Facilitates Anti-Tumour Immunity in MHC Class I-Deficient Tumours. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, Y.; Hu, C.; Wan, K.; Hu, P.; Wang, R.; Luo, J.; Li, T.; Ping, R.; Hu, Q.; Sun, Y.; et al. Cytokine Release Syndrome in COVID-19: A Major Mechanism of Morbidity and Mortality. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 41, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xie, X.; Tu, Z.; Fu, J.; Xu, D.; Zhou, Y. The Signal Pathways and Treatment of Cytokine Storm in COVID-19. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, R.; Ramalhete, L.; Von Rekowski, C.P.; Fonseca, T.A.H.; Bento, L.; R. C. Calado, C. Early Mortality Prediction in Intensive Care Unit Patients Based on Serum Metabolomic Fingerprint. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, R.; Ramalhete, L.; Von Rekowski, C.P.; Fonseca, T.A.H.; Calado, C.R.C.; Bento, L. Cytokine-Based Insights into Bloodstream Infections and Bacterial Gram Typing in ICU COVID-19 Patients. Metabolites 2025, 15, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidet, B.; Jung, C.; Flaatten, H.; Fjølner, J.; Artigas, A.; Pinto, B.B.; Schefold, J.C.; Beil, M.; Sigal, S.; Van Heerden, P.V.; et al. Increased 30-Day Mortality in Very Old ICU Patients with COVID-19 Compared to Patients with Respiratory Failure without COVID-19. Intensive Care Med. 2022, 48, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Pan, H.; Li, R.; He, K.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L. Increased Circulating Cytokines Have a Role in COVID-19 Severity and Death With a More Pronounced Effect in Males: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 802228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Rathore, S.S.; Khan, H.; Karale, S.; Chawla, Y.; Iqbal, K.; Bhurwal, A.; Tekin, A.; Jain, N.; Mehra, I.; et al. Association of Obesity With COVID-19 Severity and Mortality: An Updated Systemic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 780872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez, W.; Abdelshakor, M.; Kishk, S.; Gebril, A.; Gador, M.; Osman, S.; Abuelsaoud, H.M.; Abdelrahman, A. Body Mass Index and Clinical Outcomes in Adult COVID-19 Patients of Diverse Ethnicities. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khedr, A.; Al Hennawi, H.; Rauf, I.; Khan, M.K.; Mushtaq, H.A.; Lodhi, H.S.; Garces, J.P.D.; Jain, N.K.; Koritala, T.; Khan, S.A. Differential Mortality with COVID-19 and Invasive Mechanical Ventilation between High-Income and Low-and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression. Le Infez. Med. 2022, 30, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, L.; Araya, K.; Becerra, M.; Pérez, C.; Valenzuela, J.; Lera, L.; Lizana, P.A.; del Sol, M.; Muñoz-Cofré, R. Predictive Value of Invasive Mechanical Ventilation Parameters for Mortality in COVID-19 Related ARDS: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertini, P.; Guarracino, F.; Falcone, M.; Nardelli, P.; Landoni, G.; Nocci, M.; Paternoster, G. ECMO in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2022, 36, 2700–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supady, A.; Combes, A.; Barbaro, R.P.; Camporota, L.; Diaz, R.; Fan, E.; Giani, M.; Hodgson, C.; Hough, C.L.; Karagiannidis, C.; et al. Respiratory Indications for ECMO: Focus on COVID-19. Intensive Care Med. 2022, 48, 1326–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liu, H. Feature Selection for High-Dimensional Data: A Fast Correlation-Based Filter Solution. In Proceedings of the 20th international conference on machine learning (ICML-03), Washington, DC, USA, 21–24 August 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Guyon, I.; Elisseeff, A. An Introduction to Variable and Feature Selection. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 1157–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Lustgarten, J.L.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Visweswaran, S. Measuring Stability of Feature Selection in Biomedical Datasets. AMIA Annu. Symp. Proc. 2009, 2009, 406–410. [Google Scholar]
- Maaten, L.V.D. Geoffrey Hinton Visualizing Data Using T-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Demšar, J.; Curk, T.; Erjavec, A.; Gorup, Č.; Hočevar, T.; Milutinovič, M.; Možina, M.; Polajnar, M.; Toplak, M.; Starič, A.; et al. Orange: Data Mining Toolbox in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2013, 14, 2349–2353. [Google Scholar]
- Lyle, P. The Construction of Nomograms for Use in Statistics: Part I. True and Empirical Nomograms. Appl. Stat. 1954, 3, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, R.; Ramalhete, L.; Viegas, A.; Von Rekowski, C.P.; Fonseca, T.A.H.; Calado, C.R.C.; Bento, L. Simplifying Data Analysis in Biomedical Research: An Automated, User-Friendly Tool. Methods Protoc. 2024, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Paoletti, G.; Puggioni, F.; Racca, F.; Pelaia, G.; Canonica, G.W.; Heffler, E. Interleukin-5 in the Pathophysiology of Severe Asthma. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikker, A.; Erik Hack, C.; Lafeber, F.P.J.G.; Van Roon, J.A.G. Interleukin-7: A Key Mediator in T Cell-Driven Autoimmunity, Inflammation, and Tissue Destruction. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 2347–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zeng, J.; Hao, W.; Sun, R.; Tuo, Y.; Tan, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, R.; Bai, H. IL-21/IL-21R Promotes the Pro-Inflammatory Effects of Macrophages during C. Muridarum Respiratory Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Wang, Z.; Ye, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Chen, J.; Wan, J. Interleukin-5 Levels Are Decreased in the Plasma of Coronary Artery Disease Patients and Inhibit Th1 and Th17 Differentiation in Vitro. Rev. Española De Cardiol. (Engl. Ed. ) 2020, 73, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Waickman, A.T.; Castro, E.; Flomerfelt, F.A.; Hawk, N.V.; Kapoor, V.; Telford, W.G.; Gress, R.E. Distinct IL-7 Signaling in Recent Thymic Emigrants versus Mature Naïve T Cells Controls T-cell Homeostasis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 1669–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, L.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, J. IL-21 Impairs pro-Inflammatory Activity of M1-like Macrophages Exerting Anti-Inflammatory Effects on Rheumatoid Arthritis. Autoimmunity 2022, 55, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, A.N.A.; Tauber, P.A.; Stieger, R.B.; Kratzer, B.; Pickl, W.F. The T-Cell Growth Factor Interleukin-2, Which Is Occasionally Targeted by Autoantibodies, Qualifies as Drug for the Treatment of Allergy, Autoimmunity, and Cancer: Collegium Internationale Allergologicum (CIA) Update 2024. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2024, 185, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatzmann, D.; Abbas, A.K. The Promise of Low-Dose Interleukin-2 Therapy for Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, S.N.; Dao, C.X.; Nguyen, T.A.; Nguyen, M.H.; Pham, D.T.; Nguyen, N.T.; Huynh, D.Q.; Hoang, Q.T.A.; Bui, C.V.; Vu, T.D.; et al. Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) Score for Predicting Mortality in Patients with Sepsis in Vietnamese Intensive Care Units: A Multicentre, Cross-Sectional Study. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e064870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruserud, Ø.; Haaland, Ø.A.; Kvåle, R.; Buanes, E.A. A First-Level Customization Study of SAPS II with Norwegian Intensive Care and Pandemic Registry (NIPaR) Data. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2023, 67, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allyn, J.; Ferdynus, C.; Bohrer, M.; Dalban, C.; Valance, D.; Allou, N. Simplified Acute Physiology Score II as Predictor of Mortality in Intensive Care Units: A Decision Curve Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minne, L.; Abu-Hanna, A.; De Jonge, E. Evaluation of SOFA-Based Models for Predicting Mortality in the ICU: A Systematic Review. Crit. Care 2008, 12, R161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilfong, E.M.; Lovly, C.M.; Gillaspie, E.A.; Huang, L.-C.; Shyr, Y.; Casey, J.D.; Rini, B.I.; Semler, M.W. Severity of Illness Scores at Presentation Predict ICU Admission and Mortality in COVID-19. J. Emerg. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehryar, H.R.; Yarahmadi, P.; Anzali, B.C. Mortality Predictive Value of APACHE II Scores in COVID-19 Patients in the Intensive Care Unit: A Cross-Sectional Study. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 85, 2464–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demichev, V.; Tober-Lau, P.; Nazarenko, T.; Lemke, O.; Kaur Aulakh, S.; Whitwell, H.J.; Röhl, A.; Freiwald, A.; Mittermaier, M.; Szyrwiel, L.; et al. A Proteomic Survival Predictor for COVID-19 Patients in Intensive Care. PLoS Digit. Health 2022, 1, e0000007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili Tarki, F.; Afaghi, S.; Rahimi, F.S.; Kiani, A.; Varahram, M.; Abedini, A. Serial SOFA-score Trends in ICU-admitted COVID-19 Patients as Predictor of 28-day Mortality: A Prospective Cohort Study. Health Sci. Rep. 2023, 6, e1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, J.M.; Krijthe, J.H.; Endeman, H.; Tintu, A.N.; De Rijke, Y.B.; Gommers, D.A.M.P.J.; Cremer, O.L.; Bosman, R.J.; Rigter, S.; Wils, E.-J.; et al. Dynamic Prediction of Mortality in COVID-19 Patients in the Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Multi-Center Cohort Study. Intell. Based Med. 2022, 6, 100071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigmohammadi, M.T.; Amoozadeh, L.; Rezaei Motlagh, F.; Rahimi, M.; Maghsoudloo, M.; Jafarnejad, B.; Eslami, B.; Salehi, M.R.; Zendehdel, K. Mortality Predictive Value of APACHE II and SOFA Scores in COVID-19 Patients in the Intensive Care Unit. Can. Respir. J. 2022, 2022, 5129314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprockel, J.J.; Murcia, A.L.; Díaz, M.C.; Rios, L.F.; Quirós, O.I.; Parra, J.E. Performance of APACHE II, SOFA, and CURB-65 for Death Prognosis in COVID-19 Critical Patients: A Prospective Cohort Study. Acta Colomb. De Cuid. Intensivo 2024, 24, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrijevic, I.; Matijasevic, J.; Andrijevic, L.; Kovacevic, T.; Zaric, B. Interleukin-6 and Procalcitonin as Biomarkers in Mortality Prediction of Hospitalized Patients with Community Acquired Pneumonia. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2014, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Shi, S.; Xiao, J. Association between IL-6 and Severe Disease and Mortality in COVID-19 Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Postgrad. Med. J. 2022, 98, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderkamp, S.G.; Niazy, M.; Stegelmeier, A.A.; Stinson, K.J.; Ricker, N.; Bridle, B.W. Cytokine, Chemokine, and Acute-Phase Protein Profiles in Plasma as Correlative Biomarkers of Clinical Outcomes for Patients with COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 15397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Lai, T.; Peng, H.; Gui, L.; He, W. Interleukin-6 Is Better than C-Reactive Protein for the Prediction of Infected Pancreatic Necrosis and Mortality in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 933221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos Medeiros, S.M.D.F.R.; Sousa Lino, B.M.N.; Perez, V.P.; Sousa, E.S.S.; Campana, E.H.; Miyajima, F.; Carvalho-Silva, W.H.V.; Dejani, N.N.; De Sousa Fernandes, M.S.; Yagin, F.H.; et al. Predictive Biomarkers of Mortality in Patients with Severe COVID-19 Hospitalized in Intensive Care Unit. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1416715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, F.J.; Botero, L.E.; Isaza, J.P.; Cano, L.E.; López, L.; Hoyos, L.M.; Correa, E.; Torres, A. Cytokine Levels as Predictors of Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia: Case-Control Study Nested within a Cohort in Colombia. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1005636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Hu, X.; Wang, D.; Gong, R.; Wang, Q.; Ren, F.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Xiong, X.; Li, H.; et al. Multi-Cohort Study on Cytokine and Chemokine Profiles in the Progression of COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Liu, M.; Fu, Y.-J.; Jiang, Y.-J.; Zhang, Z.-N. Alterations in Levels of Cytokine Following Treatment to Predict Outcome of Sepsis: A Meta-Analysis. Cytokine 2023, 161, 156056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimazui, T.; Oami, T.; Shimada, T.; Tomita, K.; Nakada, T. Age-Dependent Differences in the Association between Blood Interleukin-6 Levels and Mortality in Patients with Sepsis: A Retrospective Observational Study. J. Intensive Care 2025, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurumi, A.; Que, Y.-A.; Ryan, C.M.; Tompkins, R.G.; Rahme, L.G. TNF-α/IL-10 Ratio Correlates with Burn Severity and May Serve as a Risk Predictor of Increased Susceptibility to Infections. Front. Public Health 2016, 4, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, R.; Kumar, S.; Ahmad, M.K.; Singh, R.; Pradhan, A.; Chandra, S.; Kumar, S. TNF-α/IL-10 Ratio: An Independent Predictor for Coronary Artery Disease in North Indian Population. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2018, 12, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaiz, M.B.; Jemaa, A.B.; Sellami, W.; Romdhani, C.; Ouslati, R.; Gharsallah, H.; Ghazouani, E.; Ferjani, M. Deciphering the Balance of IL-6/IL-10 Cytokines in Severe to Critical COVID-19 Patients. Immunobiology 2022, 227, 152236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luporini, R.L.; Rodolpho, J.M.D.A.; Kubota, L.T.; Martin, A.C.B.M.; Cominetti, M.R.; Anibal, F.D.F.; Pott-Junior, H. IL-6 and IL-10 Are Associated with Disease Severity and Higher Comorbidity in Adults with COVID-19. Cytokine 2021, 143, 155507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Cao, L.; Wu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Han, M.; Liu, H.; Huang, S.; Bai, Z.; Wu, S. The Evaluation of Cytokines in Predicting the Organ Injury of Critically Pediatric Patients: A Retrospective Study. Transl. Pediatr. 2024, 13, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leija-Martínez, J.J.; Huang, F.; Del-Río-Navarro, B.E.; Sanchéz-Muñoz, F.; Muñoz-Hernández, O.; Giacoman-Martínez, A.; Hall-Mondragon, M.S.; Espinosa-Velazquez, D. IL-17A and TNF-α as Potential Biomarkers for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Mortality in Patients with Obesity and COVID-19. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 144, 109935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.-H.; Tian, G.-X.; Wang, Y.-D.; Liu, T.-Y.; Shi, P.; Ying, J.-Y.; Chen, W.-M.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Lu, G.-P.; Zhang, C.-Y. The Effect of GM-CSF and Predictors of Treatment Outcome in Pediatric Septic Shock Patients. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2025, 51, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvain, J.; Kerneis, M.; Zeitouni, M.; Lattuca, B.; Galier, S.; Brugier, D.; Mertens, E.; Procopi, N.; Suc, G.; Salloum, T.; et al. Interleukin-1β and Risk of Premature Death in Patients With Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1763–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wei, Q.; Hu, Y.; Wang, C. Role of Fractalkine in Promoting Inflammation in Sepsis-Induced Multiple Organ Dysfunction. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 85, 104569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, G.; Tan, J.; Cao, Y.; Long, X.; Luo, H.; Tang, Q.; Jiang, T.; Wang, W.; Zhou, J. Scoring Cytokine Storm by the Levels of MCP-3 and IL-8 Accurately Distinguished COVID-19 Patients with High Mortality. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binneboessel, S.; Bruno, R.R.; Wernly, B.; Masyuk, M.; Flaatten, H.; Fjølner, J.; Wolff, G.; Kelm, M.; Beil, M.; Sviri, S.; et al. Cytokine Absorption in Critically Ill Old COVID-19 Patients with Renal Failure: A Retrospective Analysis of 503 Intensive Care Unit Patients. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2023, 85, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, M.; Jiang, J.; Yin, H.; Dauphars, D.J.; Li, S.-Y.; Li, Y.; He, Y.-W. Preventing Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: Which Cytokine to Target in a Raging Storm? Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvera, O.I.A.; Silva, J.A.V.; López, G.L.A.; Gomez, G.A.A.; Velázquez, G.L.; Chaves, J.C.M. Prognostic Value of IL-6/Lymphocyte Ratio to Predict Mortality in Severe Pneumonia in an Intensive Care Unit of a Northeast Hospital in Mexico. J. Crit. Care 2024, 81, 154729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Pang, X.; Huang, Y.; Yang, B.; Yang, Y.; Chen, K.; Liu, X.; Mao, P.; Li, Y. Interleukin-10/Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Mortality in Severe Septic Patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Făgărășan, I.; Rusu, A.; Comșa, H.; Simu, T.-D.; Vulturar, D.-M.; Todea, D.-A. IL-6 and Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio as Markers of ICU Admittance in SARS-CoV-2 Patients with Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bülow Anderberg, S.; Luther, T.; Berglund, M.; Larsson, R.; Rubertsson, S.; Lipcsey, M.; Larsson, A.; Frithiof, R.; Hultström, M. Increased Levels of Plasma Cytokines and Correlations to Organ Failure and 30-Day Mortality in Critically Ill Covid-19 Patients. Cytokine 2021, 138, 155389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Jeon, K.; Park, M.-J.; Song, W.; Jeong, S. Predicting Survival in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Based on Cytokines and Soluble Immune Checkpoint Regulators. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1397297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattanaik, S.S.; Das, B.K.; Tripathy, R.; Prusty, B.K.; Parida, M.K.; Tripathy, S.R.; Panda, A.K.; Ravindran, B.; Mukherjee, R. Machine Learning Identifies Cytokine Signatures of Disease Severity and Autoantibody Profiles in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus—A Pilot Study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignoli, A.; Tenori, L.; Morsiani, C.; Turano, P.; Capri, M.; Luchinat, C. Serum or Plasma (and Which Plasma), That Is the Question. J. Proteome Res. 2022, 21, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirumalai, R.S.; Chan, K.C.; Prieto, D.A.; Issaq, H.J.; Conrads, T.P.; Veenstra, T.D. Characterization of the Low Molecular Weight Human Serum Proteome. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2003, 2, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.M.; Martins, T.B.; Peterson, L.K.; Hill, H.R. Clinical Significance of Measuring Serum Cytokine Levels as Inflammatory Biomarkers in Adult and Pediatric COVID-19 Cases: A Review. Cytokine 2021, 142, 155478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhong, Y.; Ali, M.M.; McGuire, F.; Nagarkatti, P.S.; Nagarkatti, M. Role of Cytokines as a Double-Edged Sword in Sepsis. Vivo 2013, 27, 669–684. [Google Scholar]
- Maaß, H.; Ynga-Durand, M.; Milošević, M.; Krstanović, F.; Matešić, M.P.; Žuža, I.; Jonjić, S.; Brizić, I.; Šustić, A.; Bloos, F.; et al. Serum Cytokine Dysregulation Signatures Associated with COVID-19 Outcomes in High Mortality Intensive Care Unit Cohorts across Pandemic Waves and Variants. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, B.R.; Campany, M.; Sayles, H.; Roul, P.; Yang, Y.; Ganti, A.K.; Sokolove, J.; Robinson, W.H.; Reimold, A.M.; Kerr, G.S.; et al. Associations of Serum Cytokines and Chemokines with the Risk of Incident Cancer in a Prospective Rheumatoid Arthritis Cohort. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 97, 107719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, E.; Youn, S.; Kwon, K.T.; Kim, S.C.; Jo, H.-Y.; Jung, I. Disease Progression Associated Cytokines in COVID-19 Patients with Deteriorating and Recovering Health Conditions. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajgenbaum, D.C.; June, C.H. Cytokine Storm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2255–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruth, J.H.; Shahrara, S.; Park, C.C.; Morel, J.C.M.; Kumar, P.; Qin, S.; Koch, A.E. Role of Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-3α and Its Ligand CCR6 in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Lab. Investig. 2003, 83, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieu-Nosjean, M.-C.; Massacrier, C.; Homey, B.; Vanbervliet, B.; Pin, J.-J.; Vicari, A.; Lebecque, S.; Dezutter-Dambuyant, C.; Schmitt, D.; Zlotnik, A.; et al. Macrophage Inflammatory Protein 3α Is Expressed at Inflamed Epithelial Surfaces and Is the Most Potent Chemokine Known in Attracting Langerhans Cell Precursors. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.A.; Beamer, M.; Ahmed, S. Fractalkine/CX3CL1: A Potential New Target for Inflammatory Diseases. Mol. Interv. 2010, 10, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umehara, H.; Bloom, E.T.; Okazaki, T.; Nagano, Y.; Yoshie, O.; Imai, T. Fractalkine in Vascular Biology: From Basic Research to Clinical Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshkian, F.; Shahriarirad, R.; Mahram, H. An Overview of the Role of Chemokine CX3CL1 (Fractalkine) and CX3C Chemokine Receptor 1 in Systemic Sclerosis. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2024, 12, e70034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alex, P.; Szodoray, P.; Knowlton, N.; Dozmorov, I.M.; Turner, M.; Frank, M.B.; Arthur, R.E.; Willis, L.; Flinn, D.; Hynd, R.F.; et al. Multiplex Serum Cytokine Monitoring as a Prognostic Tool in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2007, 25, 584–592. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Chu, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; George, J.; Young, H.A.; Liu, G. Cytokines: From Clinical Significance to Quantification. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, B.; Sturm, R.; Henrich, D.; Lupu, L.; Rottluff, K.; Marzi, I.; Leppik, L. Diagnostic and Prognostic Potential of Exosomal Cytokines IL-6 and IL-10 in Polytrauma Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewarpai, T.; Ekchariyawat, P.; Phunpang, R.; Wright, S.W.; Dulsuk, A.; Moonmueangsan, B.; Morakot, C.; Thiansukhon, E.; Day, N.P.J.; Lertmemongkolchai, G.; et al. Longitudinal Profiling of Plasma Cytokines in Melioidosis and Their Association with Mortality: A Prospective Cohort Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 783.e1–783.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unsinger, J.; McGlynn, M.; Kasten, K.R.; Hoekzema, A.S.; Watanabe, E.; Muenzer, J.T.; McDonough, J.S.; Tschoep, J.; Ferguson, T.A.; McDunn, J.E.; et al. IL-7 Promotes T Cell Viability, Trafficking, and Functionality and Improves Survival in Sepsis. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3768–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifi, S.Q.; O’Riordan, M.A.; Levine, A.D. Interleukin-10 Controls the Onset of Irreversible Septic Shock. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 4441–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döcke, W.-D.; Randow, F.; Syrbe, U.; Krausch, D.; Asadullah, K.; Reinke, P.; Volk, H.-D.; Kox, W. Monocyte Deactivation in Septic Patients: Restoration by IFN-γ Treatment. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujishima, S.; Sasaki, J.; Shinozawa, Y.; Takuma, K.; Kimura, H.; Suzuki, M.; Hori, S.; Aikawa, N.; Kanazawa, M. Serum MIP-1α and IL-8 in Septic Patients. Intensive Care Med. 1996, 22, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongzhi, X. COVID-19-Associated Cytokine Storm Syndrome and Diagnostic Principles: An Old and New Issue. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monastero, R.N.; Pentyala, S. Cytokines as Biomarkers and Their Respective Clinical Cutoff Levels. Int. J. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 4309485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kany, S.; Vollrath, J.T.; Relja, B. Cytokines in Inflammatory Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, J.M.; Jiménez-Valverde, A.; Real, R. AUC: A Misleading Measure of the Performance of Predictive Distribution Models. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2008, 17, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.S.; Bosch, N.; Hutt, S.; Zambrano, A.F.; Bowers, A.J. On Fixing the Right Problems in Predictive Analytics: AUC Is Not the Problem. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffarpour, S.; Ghazanfari, T.; Ardestani, S.K.; Naghizadeh, M.M.; Vaez Mahdavi, M.R.; Salehi, M.; Majd, A.M.M.; Rashidi, A.; Chenary, M.R.; Mostafazadeh, A.; et al. Cytokine Profiles Dynamics in COVID-19 Patients: A Longitudinal Analysis of Disease Severity and Outcomes. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 14209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smail, S.W.; Babaei, E.; Amin, K.; Abdulahad, W.H. Serum IL-23, IL-10, and TNF-α Predict in-Hospital Mortality in COVID-19 Patients. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1145840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozger, H.S.; Karakus, R.; Kuscu, E.N.; Bagriacik, U.E.; Oruklu, N.; Yaman, M.; Turkoglu, M.; Erbas, G.; Atak, A.Y.; Senol, E. Serial Measurement of Cytokines Strongly Predict COVID-19 Outcome. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, J.; Gao, M.; Fan, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, J.; Kim, J.; Aliyari, R.; et al. Interleukin-8 as a Biomarker for Disease Prognosis of Coronavirus Disease-2019 Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 602395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Fang, C.; Zhao, X.; Qian, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, J.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Q.; et al. The Prognostic Value of IL-8 for the Death of Severe or Critical Patients with COVID-19. Medicine 2021, 100, e23656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozza, F.A.; Salluh, J.I.; Japiassu, A.M.; Soares, M.; Assis, E.F.; Gomes, R.N.; Bozza, M.T.; Castro-Faria-Neto, H.C.; Bozza, P.T. Cytokine Profiles as Markers of Disease Severity in Sepsis: A Multiplex Analysis. Crit. Care 2007, 11, R49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravetti, C.G.; Moura, A.D.; Vieira, É.L.; Pedroso, Ê.R.P.; Teixeira, A.L. sTREM-1 Predicts Intensive Care Unit and 28-Day Mortality in Cancer Patients with Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock. J. Crit. Care 2015, 30, 440.e7–440.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElvaney, O.J.; Hobbs, B.D.; Qiao, D.; McElvaney, O.F.; Moll, M.; McEvoy, N.L.; Clarke, J.; O’Connor, E.; Walsh, S.; Cho, M.H.; et al. A Linear Prognostic Score Based on the Ratio of Interleukin-6 to Interleukin-10 Predicts Outcomes in COVID-19. EBioMedicine 2020, 61, 103026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, R.; Sasaki, J.; Shibusawa, T.; Nakada, T.; Mayumi, T.; Takasu, O.; Matsuda, K.; Shimazui, T.; Otsubo, H.; Teshima, Y.; et al. Accuracy for Mortality Prediction With Additive Biomarkers Including Interleukin-6 in Critically Ill Patients: A Multicenter Prospective Observational Study. Crit. Care Explor. 2021, 3, e0387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellum, J.A. Understanding the Inflammatory Cytokine Response in Pneumonia and Sepsis: Results of the Genetic and Inflammatory Markers of Sepsis (GenIMS) Study. Arch Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jogan, M.; Kurada, S.; Vasisht, S.; Singh, V.; Hashimoto, D.A. Quality over Quantity? The Role of Data Quality and Uncertainty for AI in Surgery. Glob. Surg. Educ. J. Assoc. Surg. Educ. 2024, 3, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, L.; Nabian, M.; Brochini, L.; Amelung, P.J. Machine Learning for Benchmarking Critical Care Outcomes. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2023, 29, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Shao, F.; Yuan, W.; Wu, J.; Qi, X.; Gao, J.; Shao, R.; Tang, Z.; Wang, T. Predicting Sepsis In-Hospital Mortality with Machine Learning: A Multi-Center Study Using Clinical and Inflammatory Biomarkers. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, S.A.; Strümke, I.; Thambawita, V.; Hammou, M.; Riegler, M.A.; Halvorsen, P.; Parasa, S. On Evaluation Metrics for Medical Applications of Artificial Intelligence. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bröcker, J. Reliability, Sufficiency, and the Decomposition of Proper Scores. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. A J. Atmos. Sci. Appl. Meteorol. Phys. Oceanogr. 2009, 135, 1512–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assel, M.; Sjoberg, D.D.; Vickers, A.J. The Brier Score Does Not Evaluate the Clinical Utility of Diagnostic Tests or Prediction Models. Diagn. Progn. Res. 2017, 1, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockenschaub, P.; Akay, E.M.; Carlisle, B.G.; Hilbert, A.; Wendland, J.; Meyer-Eschenbach, F.; Näher, A.-F.; Frey, D.; Madai, V.I. External Validation of AI-Based Scoring Systems in the ICU: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2025, 25, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockenschaub, P.; Hilbert, A.; Kossen, T.; Elbers, P.; Von Dincklage, F.; Madai, V.I.; Frey, D. The Impact of Multi-Institution Datasets on the Generalizability of Machine Learning Prediction Models in the ICU. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 52, 1710–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bludau, I.; Frank, M.; Dörig, C.; Cai, Y.; Heusel, M.; Rosenberger, G.; Picotti, P.; Collins, B.C.; Röst, H.; Aebersold, R. Systematic Detection of Functional Proteoform Groups from Bottom-up Proteomic Datasets. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Po, A.; Eyers, C.E. Top-Down Proteomics and the Challenges of True Proteoform Characterization. J. Proteome Res. 2023, 22, 3663–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu-Caraus, O.; Aicher, A.; Kernbach, J.M.; Regli, L.; Serra, C.; Staartjes, V.E. A Critical Moment in Machine Learning in Medicine: On Reproducible and Interpretable Learning. Acta Neurochir. 2024, 166, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Soltan, A.A.S.; Clifton, D.A. Machine Learning Generalizability across Healthcare Settings: Insights from Multi-Site COVID-19 Screening. NPJ Digit. Med. 2022, 5, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Deceased (n = 10) | Discharged (n = 10) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 68 (12) | 51 (8) | 0.000 (***) ^ | |
| Gender, n (%) | Female | 4 (0.40) | 0 (0.00) | 0.087 + |
| Male | 6 (0.60) | 10 (1.00) | ||
| ECMO, n (%) | No | 9 (0.90) | 9 (0.90) | 1.000 + |
| Yes | 1 (0.10) | 1 (0.10) | ||
| IMV, n (%) | No | 1 (0.10) | 7 (0.70) | 0.020 + |
| Yes | 9 (0.90) | 3 (0.30) | ||
| BMI, median (IQR) | 29 (8) | 28 (2) | 0.710 # | |
| Deceased (n = 23) | Discharged (n = 40) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 67 (8) | 52 (14) | 0.000 (***) ^ | |
| Gender, n (%) | Female | 5 (0.22) | 11 (0.28) | 0.837 * |
| Male | 18 (0.78) | 29 (0.72) | ||
| ECMO, n (%) | No | 23 (1.00) | 35 (0.88) | 0.149 + |
| Yes | 0 (0.00) | 5 (0.12) | ||
| IMV, n (%) | No | 5 (0.22) | 23 (0.57) | 0.013 + |
| Yes | 18 (0.78) | 17 (0.42) | ||
| BMI, median (IQR) | 26 (8) | 29 (8) | 0.922 # | |
| Deceased (n = 19) | Discharged (n = 23) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 61 (8) | 56 (10) | 0.038 # | |
| Gender, n (%) | Female | 4 (0.21) | 10 (0.43) | 0.191 + |
| Male | 15 (0.79) | 13 (0.57) | ||
| ECMO, n (%) | No | 14 (0.74) | 23 (1.00) | 0.014 + |
| Yes | 5 (0.26) | 0 (0.00) | ||
| IMV, n (%) | No | 0 (0.00) | 4 (0.17) | 0.114 + |
| Yes | 19 (1.00) | 19 (0.83) | ||
| BMI, median (IQR) | 26 (6) | 28 (7) | 0.527 # | |
| Group | Feature | ICU Mortality: Deceased vs. Discharged | |
|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value 1 | Elevated In | ||
| Group 1 3 | Traditional Severity Markers 2 | ||
| APACHE II | 0.277 | Discharged | |
| SAPS II | 0.125 | Discharged | |
| SOFA | 1.000 | Discharged | |
| Cytokines | |||
| Fractalkine | 0.094 | Deceased | |
| GM-CSF | 0.629 | Discharged | |
| IFN-γ | 0.571 | Deceased | |
| IL-1β | 0.780 | Deceased | |
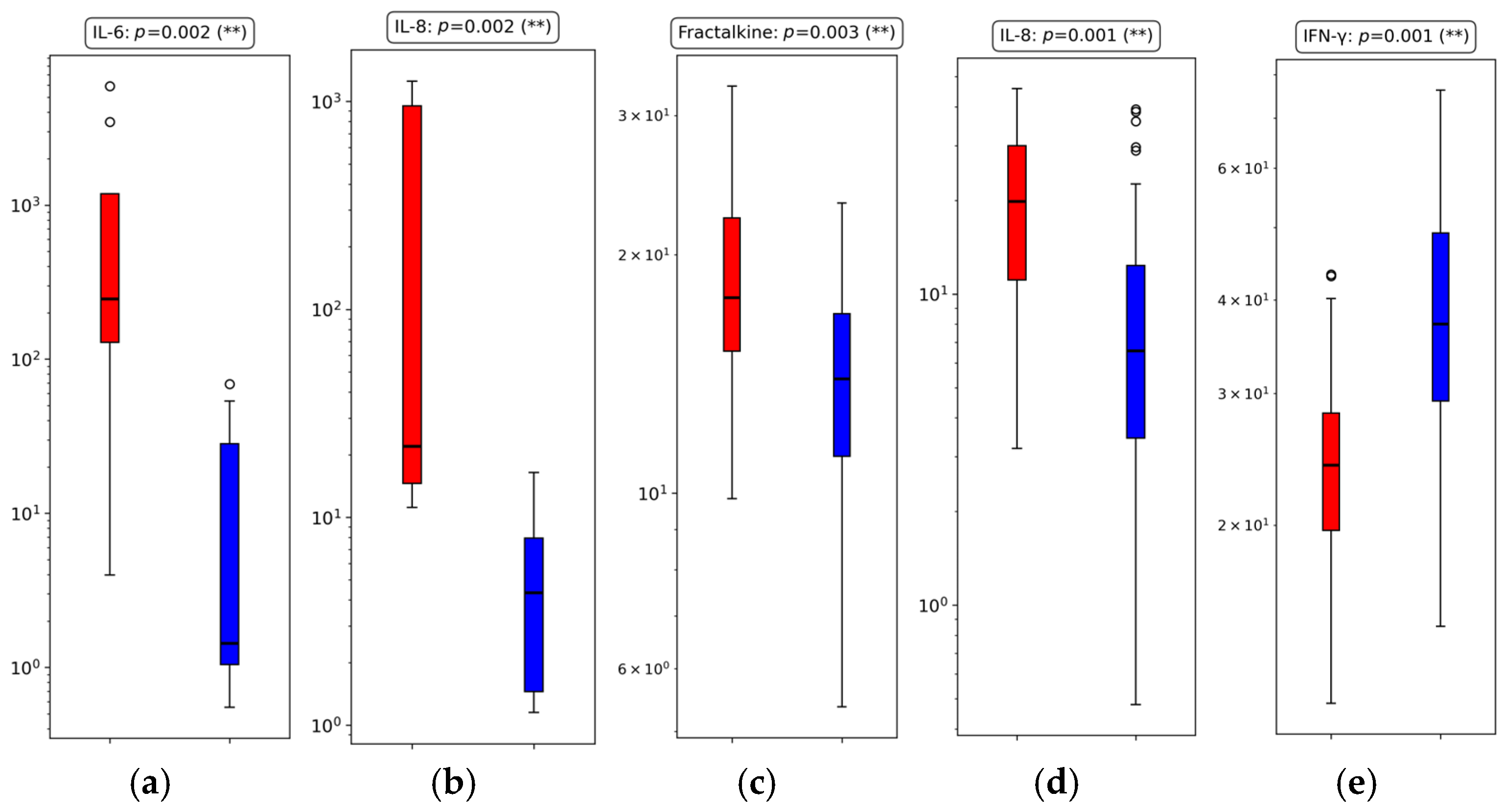
| IL-6 | 0.002 (**) | Deceased | |
| IL-8 | 0.002 (**) | Deceased | |
| IL-10 | 0.173 | Deceased | |
| IL-17A | 0.116 | Deceased | |
| TNF-α | 0.066 | Deceased | |
| Simple Ratios 6 | |||
| IL-1β/IL-10 | 0.043 (*) | Discharged | |
| IL-6/IL-10 | 0.002 (**) | Deceased | |
| IL-6/Lymphocytes | 0.010 (*) | Deceased | |
| IL-10/Lymphocytes | 0.040 (*) | Deceased | |
| Neutrophil/Lymphocytes | 0.015 (*) | Deceased | |
| TNF-α/IL-10 | 0.048 (*) | Discharged | |
| Group 2 4 | Traditional Severity Markers | ||
| APACHE II | 0.825 | None 7 | |
| SAPS II | 0.438 | Deceased | |
| SOFA | 0.316 | Deceased | |
| Cytokines | |||
| Fractalkine | 0.003 (**) | Deceased | |
| GM-CSF | 0.131 | Deceased | |
| IFN-γ | 0.320 | Deceased | |
| IL-1β | 0.060 | Deceased | |
| IL-6 | 0.079 | Deceased | |
| IL-8 | 0.001 (**) | Deceased | |
| IL-10 | 0.015 (*) | Deceased | |
| IL-17A | 0.176 | Deceased | |
| TNF-α | 0.102 | Deceased | |
| Simple Ratios 6 | |||
| IL-1β/IL-10 | 0.097 | Discharged | |
| IL-6/IL-10 | 0.479 | Discharged | |
| IL-6/Lymphocytes | 0.001 (**) | Deceased | |
| IL-10/Lymphocytes | 0.000 (***) | Deceased | |
| Neutrophil/Lymphocytes | 0.009 (**) | Deceased | |
| TNF-α/IL-10 | 0.018 (*) | Discharged | |
| Group 3 5 | Traditional Severity Markers | ||
| APACHE II | 0.699 | Deceased | |
| SAPS II | 0.861 | Deceased | |
| SOFA | 0.755 | None 7 | |
| Cytokines | |||
| Fractalkine | 0.458 | Deceased | |
| GM-CSF | 0.899 | Deceased | |
| IFN-γ | 0.001 (**) | Discharged | |
| IL-1β | 0.639 | Discharged | |
| IL-6 | 0.186 | Deceased | |
| IL-8 | 0.070 | Deceased | |
| IL-10 | 0.479 | Discharged | |
| IL-17A | 0.536 | Discharged | |
| TNF-α | 0.369 | Discharged | |
| Simple Ratios 6 | |||
| IL-1β/IL-10 | 0.719 | None 8 | |
| IL-6/IL-10 | 0.029 (*) | Deceased | |
| IL-6/Lymphocytes | 0.313 | Deceased | |
| IL-10/Lymphocytes | 0.911 | Deceased | |
| Neutrophil/Lymphocytes | 0.617 | Discharged | |
| TNF-α/IL-10 | 0.255 | Deceased | |
| Cytokine | Group 1 p-Value | Group 2 p-Value | Group 3 p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fractalkine | 0.094 | 0.003 (**) | 0.458 |
| GM-CSF | 0.629 | 0.131 | 0.899 |
| IFN-γ | 0.571 | 0.320 | 0.001 (**) |
| IL-1β | 0.780 | 0.060 | 0.639 |
| IL-2 | 0.349 | 0.022 (*) | 0.935 |
| IL-4 | 0.951 | 0.497 | 0.242 |
| IL-5 | 0.515 | 0.071 | 0.403 |
| IL-6 | 0.002 (**) | 0.079 | 0.186 |
| IL-7 | 0.744 | 0.033 (*) | 0.102 |
| IL-8 | 0.002 (**) | 0.001 (**) | 0.070 |
| IL-10 | 0.173 | 0.015 (*) | 0.479 |
| IL-12p70 | 0.221 | 0.298 | 0.784 |
| IL-13 | 0.992 | 0.582 | 0.438 |
| IL-17A | 0.116 | 0.176 | 0.536 |
| IL-21 | 0.850 | 0.201 | 0.235 |
| IL-23 | 0.822 | 0.020 (*) | 0.382 |
| ITAC | 0.231 | 0.407 | 0.915 |
| MIP-1α | 0.166 | 0.034 (*) | 0.159 |
| MIP-1β | 0.178 | 0.560 | 0.337 |
| MIP-3α | 0.048 (*) | 0.186 | 0.543 |
| TNF-α | 0.066 | 0.102 | 0.369 |
| Group | Cytokine | Deceased Median (IQR) | Discharged Median (IQR) | Abs. Diff. | % Diff. | Fold Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
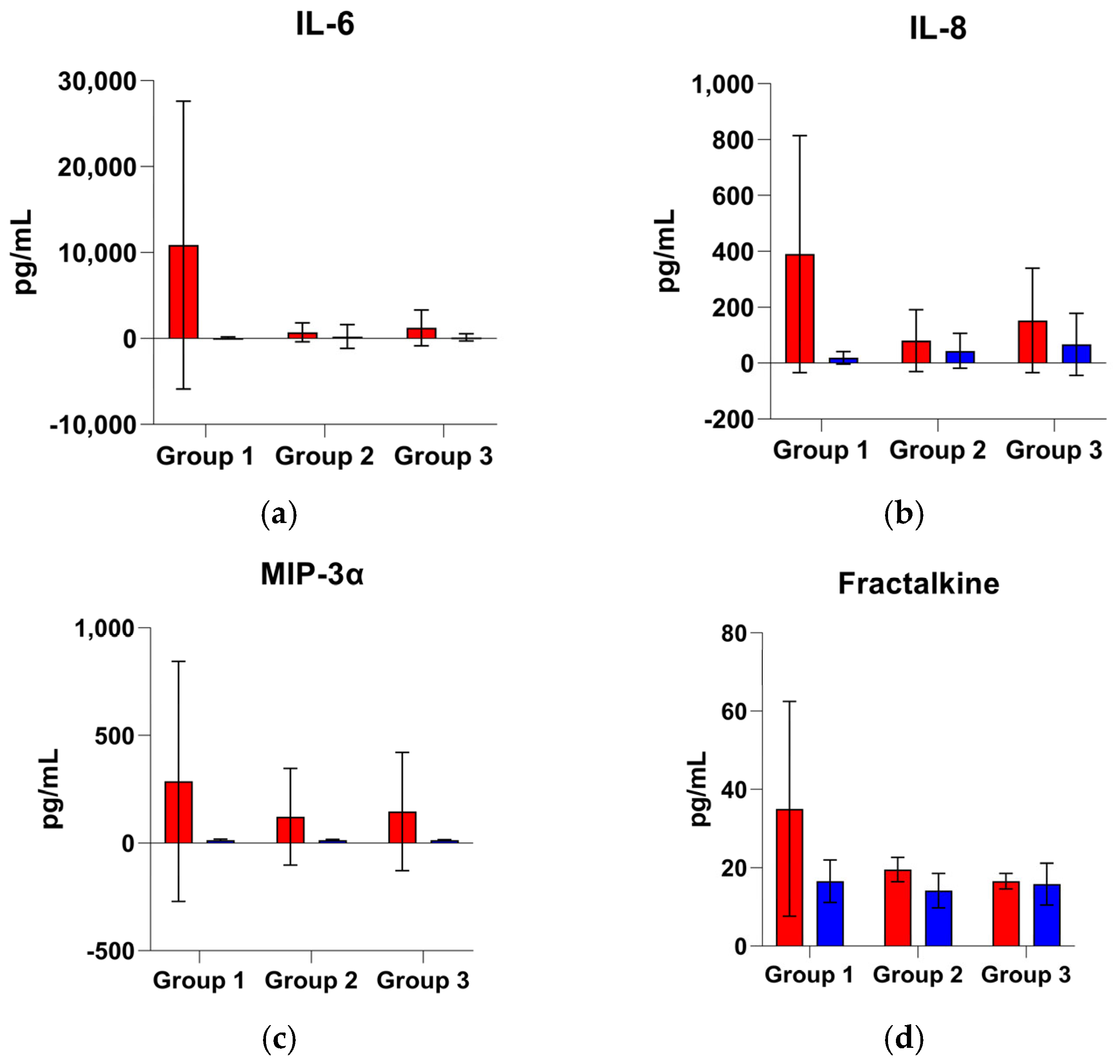
| Group 1 | Fractalkine | 21.95 (13.53) | 15.32 (7.75) | 6.63 | 30.22 | 1.43 |
| GM-CSF | 7.74 (4.87) | 8.16 (2.61) | 0.42 | −5.42 | 0.95 | |
| IFN-γ | 32.54 (12.42) | 30.56 (13.99) | 1.98 | 6.07 | 1.06 | |
| IL-1β | 1.25 (0.89) | 1.16 (0.35) | 0.09 | 7.50 | 1.08 | |
| IL-2 | 3.17 (1.39) | 2.97 (0.59) | 0.20 | 6.44 | 1.07 | |
| IL-4 | 14.32 (9.22) | 12.17 (4.65) | 2.15 | 15.02 | 1.18 | |
| IL-5 | 6.77 (3.94) | 4.52 (5.21) | 2.24 | 33.13 | 1.50 | |
| IL-6 | 355.71 (5119.42) | 1.45 (46.12) | 354.26 | 99.59 | 244.56 | |
| IL-7 | 17.02 (10.28) | 17.64 (2.70) | 0.62 | −3.64 | 0.96 | |
| IL-8 | 21.94 (937.13) | 6.43 (12.38) | 15.50 | 70.67 | 3.41 | |
| IL-10 | 41.77 (121.49) | 21.54 (37.08) | 20.23 | 48.43 | 1.94 | |
| IL-12p70 | 4.93 (3.39) | 5.29 (1.77) | 0.36 | −7.32 | 0.93 | |
| IL-13 | 2.86 (2.40) | 2.59 (1.54) | 0.27 | 9.43 | 1.10 | |
| IL-17A | 31.82 (27.09) | 24.78 (6.93) | 7.04 | 22.11 | 1.28 | |
| IL-21 | 12.23 (6.79) | 11.53 (2.48) | 0.70 | 5.71 | 1.06 | |
| IL-23 | 214.19 (164.28) | 235.19 (26.45) | 21.00 | −9.81 | 0.91 | |
| ITAC | 81.96 (77.07) | 59.06 (65.15) | 22.90 | 27.94 | 1.39 | |
| MIP-1α | 27.47 (36.49) | 20.91 (6.81) | 6.56 | 23.87 | 1.31 | |
| MIP-1β | 22.15 (32.38) | 18.57 (14.90) | 3.59 | 16.19 | 1.19 | |
| MIP-3α | 15.39 (50.11) | 12.10 (4.67) | 3.29 | 21.39 | 1.27 | |
| TNF-α | 13.59 (18.18) | 7.78 (6.52) | 5.81 | 42.76 | 1.75 | |
| Group 2 | Fractalkine | 17.68 (7.33) | 13.94 (5.72) | 3.75 | 21.19 | 1.27 |
| GM-CSF | 7.32 (7.62) | 7.31 (4.37) | 0.02 | 0.25 | 1.00 | |
| IFN-γ | 28.98 (17.36) | 24.80 (18.39) | 4.18 | 14.42 | 1.17 | |
| IL-1β | 1.27 (0.73) | 0.99 (0.63) | 0.28 | 21.88 | 1.28 | |
| IL-2 | 3.37 (2.95) | 2.82 (2.04) | 0.55 | 16.36 | 1.20 | |
| IL-4 | 13.14 (12.62) | 10.09 (10.85) | 3.05 | 23.22 | 1.30 | |
| IL-5 | 7.45 (8.33) | 4.81 (3.85) | 2.64 | 35.46 | 1.55 | |
| IL-6 | 14.24 (45.25) | 2.66 (11.10) | 11.59 | 81.36 | 5.36 | |
| IL-7 | 20.43 (8.53) | 15.55 (4.98) | 4.87 | 23.86 | 1.31 | |
| IL-8 | 23.92 (24.91) | 7.14 (15.79) | 16.77 | 70.13 | 3.35 | |
| IL-10 | 35.02 (43.04) | 23.10 (16.95) | 11.91 | 34.02 | 1.52 | |
| IL-12p70 | 6.01 (3.43) | 4.35 (3.21) | 1.66 | 27.64 | 1.38 | |
| IL-13 | 3.12 (3.10) | 2.87 (2.29) | 0.25 | 7.88 | 1.09 | |
| IL-17A | 32.24 (34.43) | 25.38 (17.40) | 6.86 | 21.28 | 1.27 | |
| IL-21 | 12.61 (6.87) | 10.96 (6.77) | 1.65 | 13.10 | 1.15 | |
| IL-23 | 291.97 (227.01) | 207.29 (128.71) | 84.68 | 29.00 | 1.41 | |
| ITAC | 82.06 (94.83) | 79.91 (76.65) | 2.15 | 2.62 | 1.03 | |
| MIP-1α | 19.11 (8.15) | 15.19 (11.52) | 3.91 | 20.48 | 1.26 | |
| MIP-1β | 15.93 (19.02) | 14.11 (20.22) | 1.82 | 11.43 | 1.13 | |
| MIP-3α | 12.34 (6.93) | 8.98 (7.88) | 3.37 | 27.27 | 1.37 | |
| TNF-α | 10.01 (6.31) | 9.30 (5.53) | 0.71 | 7.07 | 1.08 | |
| Group 3 | Fractalkine | 15.53 (3.90) | 14.07 (5.60) | 1.46 | 9.40 | 1.10 |
| GM-CSF | 7.47 (4.41) | 7.10 (4.67) | 0.38 | 5.03 | 1.05 | |
| IFN-γ | 24.48 (17.43) | 37.15 (19.86) | 12.66 | −51.72 | 0.66 | |
| IL-1β | 1.06 (0.56) | 1.19 (0.68) | 0.13 | −11.75 | 0.89 | |
| IL-2 | 3.05 (1.72) | 3.51 (2.42) | 0.47 | −15.34 | 0.87 | |
| IL-4 | 12.65 (8.21) | 11.21 (8.13) | 1.44 | 11.37 | 1.13 | |
| IL-5 | 6.12 (4.35) | 6.20 (5.68) | 0.08 | −1.24 | 0.99 | |
| IL-6 | 33.92 (153.62) | 6.80 (65.22) | 27.13 | 79.97 | 4.99 | |
| IL-7 | 14.89 (4.71) | 17.71 (3.66) | 2.82 | −18.93 | 0.84 | |
| IL-8 | 18.92 (34.97) | 11.24 (13.62) | 7.68 | 40.62 | 1.68 | |
| IL-10 | 28.52 (18.41) | 30.74 (16.10) | 2.21 | −7.76 | 0.93 | |
| IL-12p70 | 3.76 (4.56) | 4.78 (2.84) | 1.02 | −26.98 | 0.79 | |
| IL-13 | 2.45 (1.17) | 2.65 (2.28) | 0.19 | −7.82 | 0.93 | |
| IL-17A | 26.85 (23.26) | 29.58 (19.98) | 2.73 | −10.18 | 0.91 | |
| IL-21 | 9.78 (5.38) | 12.15 (7.70) | 2.37 | −24.18 | 0.81 | |
| IL-23 | 215.79 (123.55) | 237.36 (365.18) | 21.57 | −10.00 | 0.91 | |
| ITAC | 71.73 (123.92) | 92.99 (72.44) | 21.26 | −29.65 | 0.77 | |
| MIP-1α | 24.93 (21.65) | 19.84 (12.86) | 5.09 | 20.43 | 1.26 | |
| MIP-1β | 15.87 (13.48) | 11.07 (17.52) | 4.80 | 30.27 | 1.43 | |
| MIP-3α | 12.15 (10.85) | 11.26 (8.15) | 0.89 | 7.29 | 1.08 | |
| TNF-α | 8.44 (6.35) | 9.06 (6.51) | 0.62 | −7.31 | 0.93 |
| Target Group * | Model | AUC | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | kNN | 0.800 | 0.500 | 0.800 |
| Naïve Bayes | 0.650 | 0.500 | 0.700 | |
| Random Forest | 0.725 | 0.500 | 0.600 | |
| SVM | 0.500 | 0.600 | 0.700 | |
| Decision Tree | 0.525 | 0.500 | 0.600 | |
| Group 1 Ranked: FCBF (3 features) | kNN | 0.850 | 0.600 | 0.900 |
| Naïve Bayes | 0.775 | 0.500 | 0.600 | |
| Random Forest | 0.675 | 0.500 | 0.600 | |
| SVM | 0.850 | 0.300 | 0.400 | |
| Decision Tree | 0.575 | 0.700 | 0.600 | |
| Group 2 | kNN | 0.573 | 0.217 | 0.800 |
| Naïve Bayes | 0.689 | 0.522 | 0.625 | |
| Random Forest | 0.716 | 0.348 | 0.850 | |
| SVM | 0.693 | 0.435 | 0.875 | |
| Decision Tree | 0.574 | 0.435 | 0.700 | |
| Group 2 Ranked: FCBF (2 features) | kNN | 0.704 | 0.348 | 0.825 |
| Naïve Bayes | 0.781 | 0.435 | 0.850 | |
| Random Forest | 0.646 | 0.391 | 0.800 | |
| SVM | 0.751 | 0.217 | 0.925 | |
| Decision Tree | 0.613 | 0.522 | 0.775 | |
| Group 3 | kNN | 0.493 | 0.474 | 0.522 |
| Naïve Bayes | 0.244 | 0.316 | 0.217 | |
| Random Forest | 0.505 | 0.263 | 0.696 | |
| SVM | 0.367 | 0.158 | 0.565 | |
| Decision Tree | 0.371 | 0.474 | 0.435 | |
| Group 3 Ranked: FCBF (1 feature) | kNN | 0.542 | 0.526 | 0.696 |
| Naïve Bayes | 0.647 | 0.474 | 0.696 | |
| Random Forest | 0.450 | 0.421 | 0.609 | |
| SVM | 0.441 | 0.000 | 0.957 | |
| Decision Tree | 0.521 | 0.684 | 0.348 |
| Target Group * | Model | AUC | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | kNN | 0.850 | 0.600 | 0.900 |
| Naïve Bayes | n.a. 1 | 0.700 | 0.800 | |
| Random Forest | 0.800 | 0.500 | 0.800 | |
| SVM | 0.425 | 0.600 | 0.500 | |
| Decision Tree | 0.625 | 0.900 | 0.400 | |
| Group 1 Ranked: FCBF (8 features) | kNN | 0.900 | 0.700 | 1.000 |
| Naïve Bayes | 1.000 | 0.900 | 0.900 | |
| Random Forest | 0.900 | 0.900 | 0.900 | |
| SVM | 0.450 | 0.700 | 0.800 | |
| Decision Tree | 0.800 | 0.800 | 0.500 | |
| Group 2 | kNN | 0.637 | 0.304 | 0.875 |
| Naïve Bayes | n.a. 1 | 0.652 | 0.500 | |
| Random Forest | 0.622 | 0.435 | 0.675 | |
| SVM | 0.420 | 0.043 | 0.950 | |
| Decision Tree | 0.619 | 0.435 | 0.750 | |
| Group 2 Ranked: FCBF (6 features) | kNN | 0.722 | 0.261 | 0.925 |
| Naïve Bayes | 0.918 | 0.826 | 0.775 | |
| Random Forest | 0.774 | 0.522 | 0.800 | |
| SVM | 0.750 | 0.261 | 0.925 | |
| Decision Tree | 0.666 | 0.652 | 0.700 | |
| Group 3 | kNN | 0.472 | 0.579 | 0.435 |
| Naïve Bayes | n.a. 1 | 0.526 | 0.522 | |
| Random Forest | 0.570 | 0.316 | 0.609 | |
| SVM | 0.537 | 0.000 | 0.957 | |
| Decision Tree | 0.533 | 0.526 | 0.565 | |
| Group 3 Ranked: FCBF (7 features) | kNN | 0.593 | 0.421 | 0.696 |
| Naïve Bayes | 0.930 | 1.000 | 0.826 | |
| Random Forest | 0.891 | 0.632 | 0.870 | |
| SVM | 0.384 | 0.053 | 0.826 | |
| Decision Tree | 0.662 | 0.632 | 0.696 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Araújo, R.; Von Rekowski, C.P.; Fonseca, T.A.H.; Calado, C.R.C.; Ramalhete, L.; Bento, L. Multiplex Targeted Proteomic Analysis of Cytokine Ratios for ICU Mortality in Severe COVID-19. Proteomes 2025, 13, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes13030035
Araújo R, Von Rekowski CP, Fonseca TAH, Calado CRC, Ramalhete L, Bento L. Multiplex Targeted Proteomic Analysis of Cytokine Ratios for ICU Mortality in Severe COVID-19. Proteomes. 2025; 13(3):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes13030035
Chicago/Turabian StyleAraújo, Rúben, Cristiana P. Von Rekowski, Tiago A. H. Fonseca, Cecília R. C. Calado, Luís Ramalhete, and Luís Bento. 2025. "Multiplex Targeted Proteomic Analysis of Cytokine Ratios for ICU Mortality in Severe COVID-19" Proteomes 13, no. 3: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes13030035
APA StyleAraújo, R., Von Rekowski, C. P., Fonseca, T. A. H., Calado, C. R. C., Ramalhete, L., & Bento, L. (2025). Multiplex Targeted Proteomic Analysis of Cytokine Ratios for ICU Mortality in Severe COVID-19. Proteomes, 13(3), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes13030035







