Augmented Reality in Higher Education: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Literature from 2000 to 2023
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- What are the overall publication trends and characteristics of the distribution of AR applications across different disciplines in higher education?
- (2)
- What are the essential technical features and affordances of AR in higher education applications, and how are they evolving over time?
- (3)
- What instructional design approaches are used to facilitate teaching and learning in AR-supported higher education?
- (4)
- What are the common types of learning outcomes supported by AR in higher education, and how are they measured?
- (5)
- What is the overall effectiveness of the application of AR in higher education, and what are the moderating variables?
2. Method
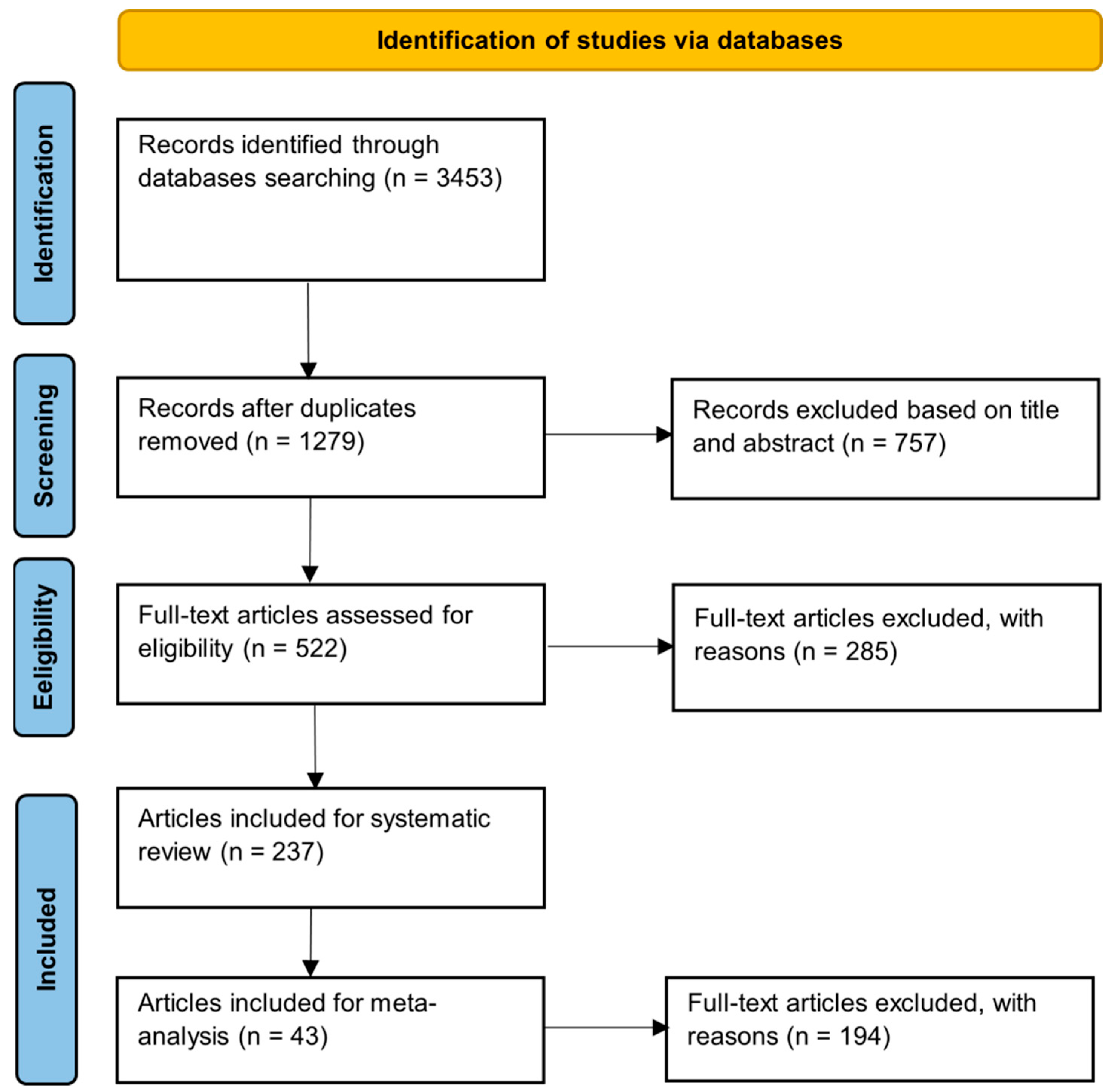
2.1. Identification
2.2. Manual Screening and Eligibility
2.3. Analytical Coding
2.4. Methods for Syntheses and Results Presentation
2.5. Methods for Meta-Analysis
2.6. Quality Appraisal
3. Systematic Review Results
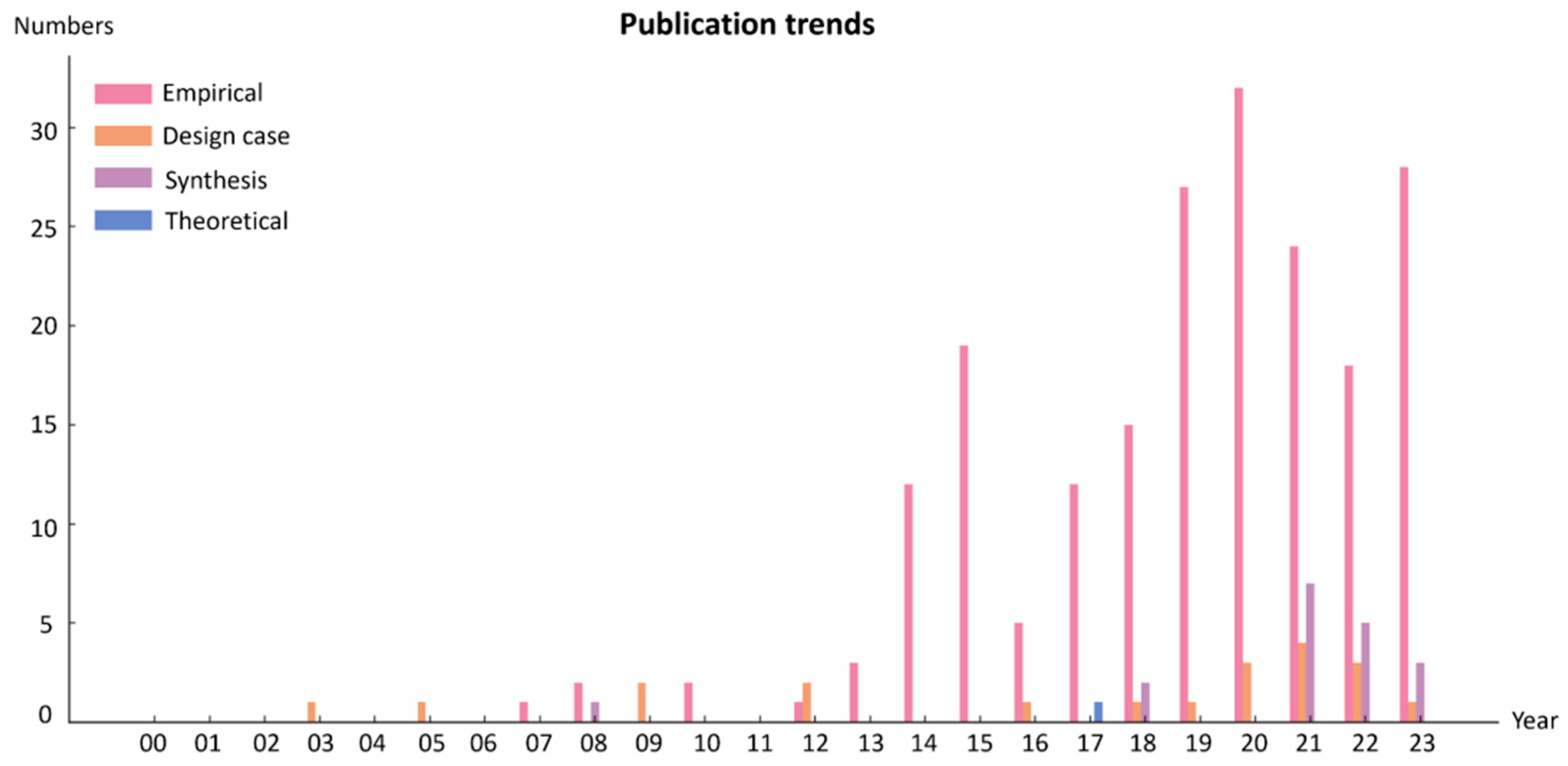
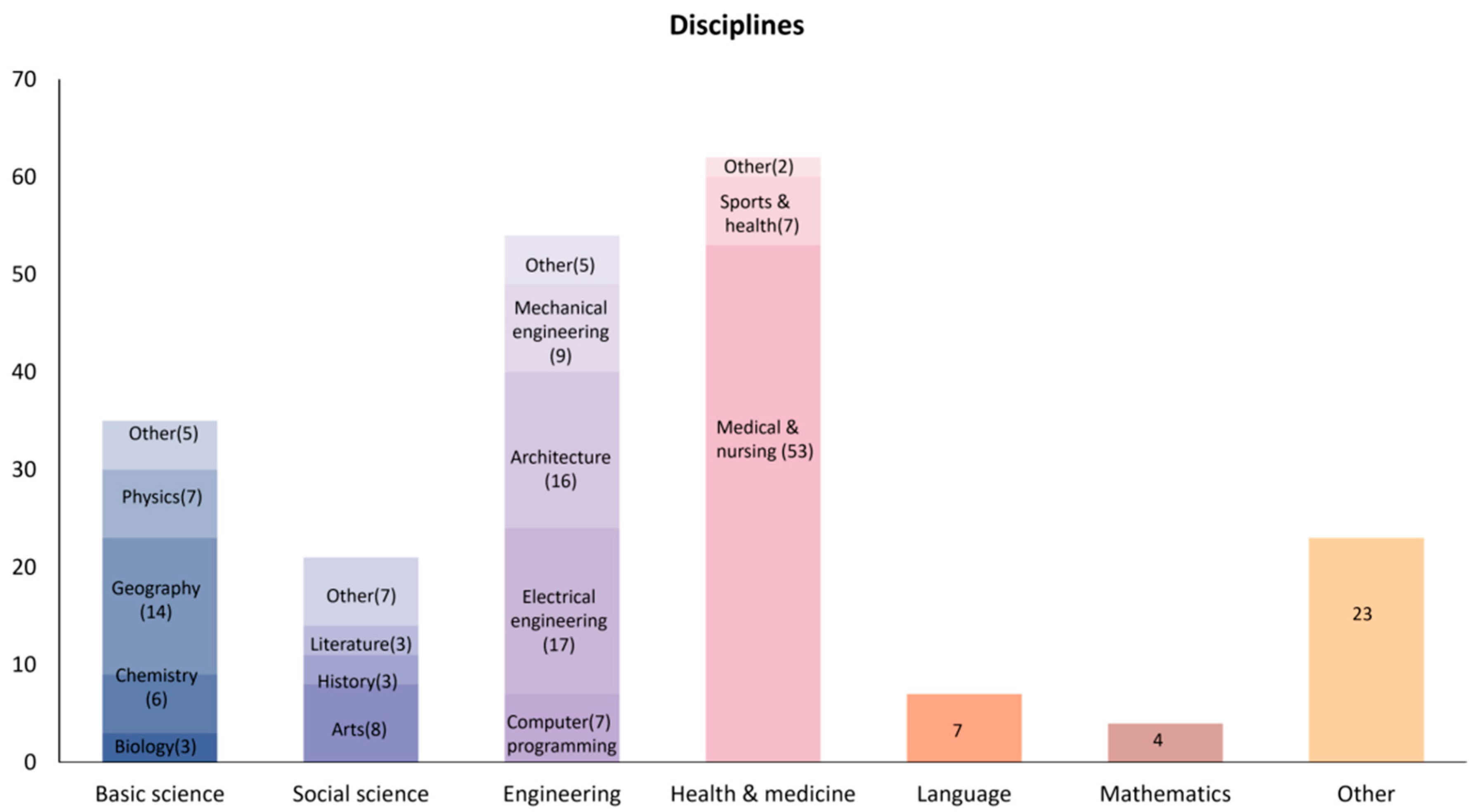
3.1. Publication Trends and Applied Disciplines
3.1.1. Publication Trends
3.1.2. Disciplines
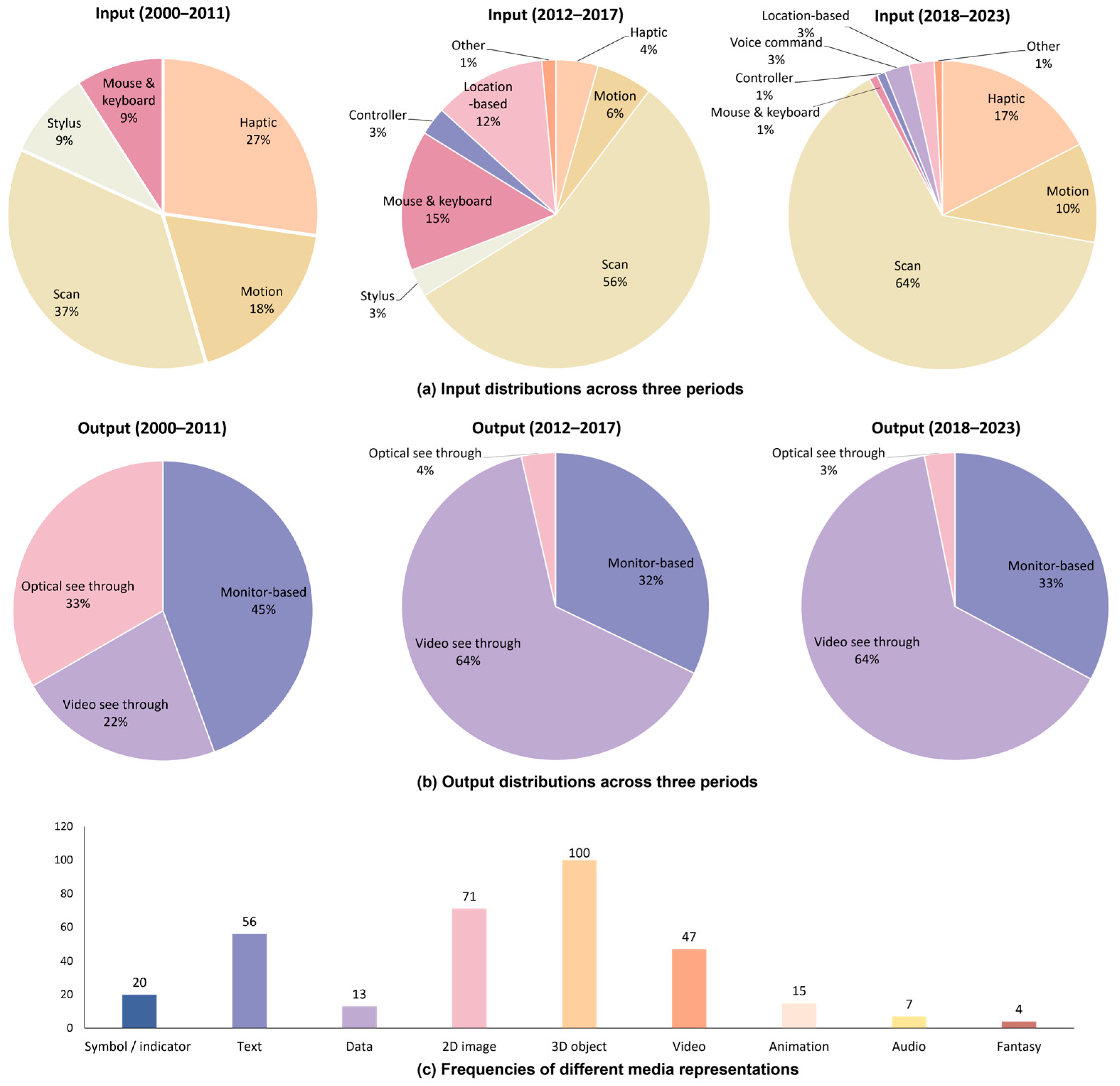
3.2. Technical Features and Affordance
3.2.1. Input
3.2.2. Output
3.2.3. Media Representation
3.3. Instructional Design
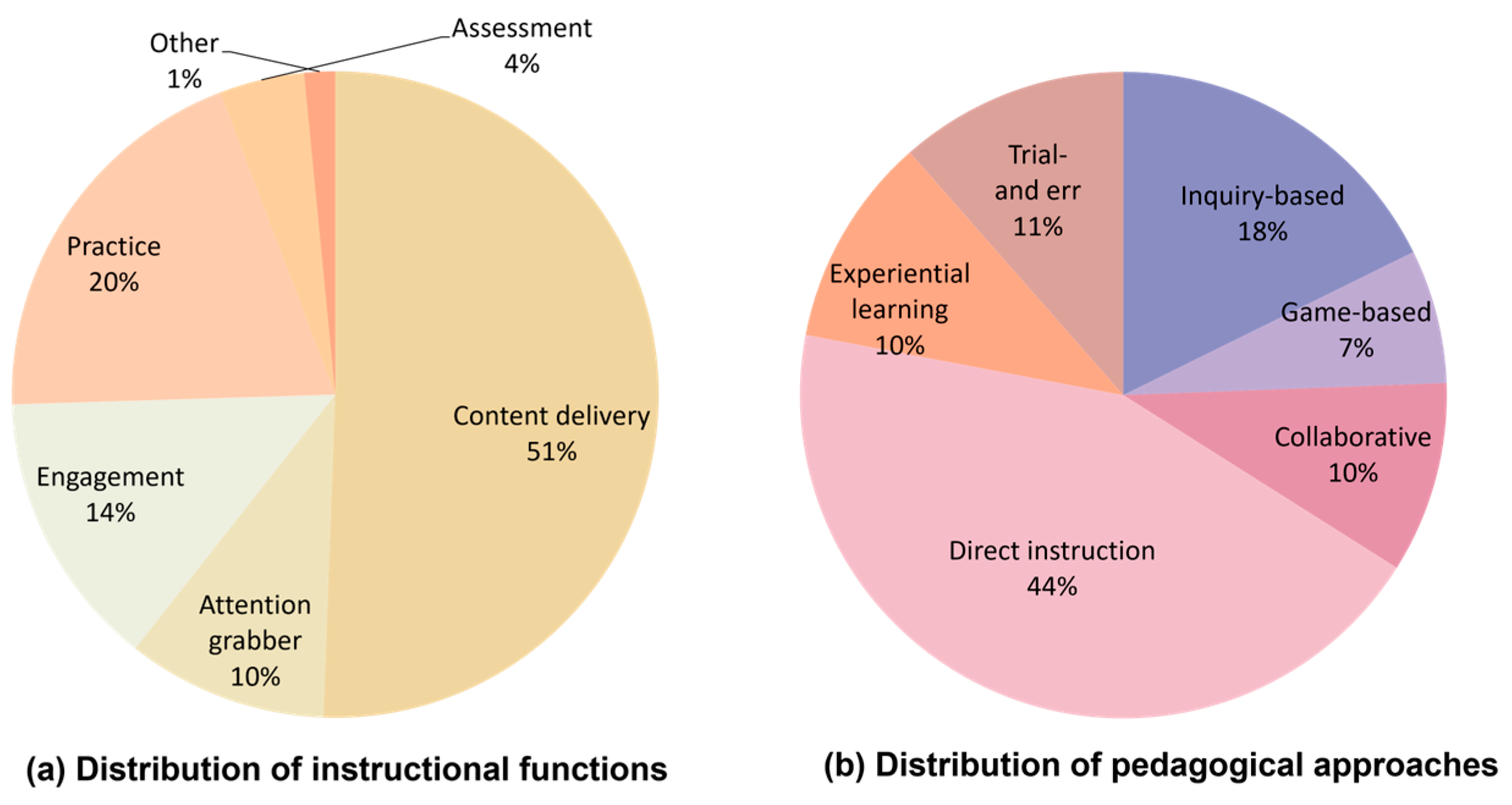
3.3.1. Instructional Functions
3.3.2. Pedagogy
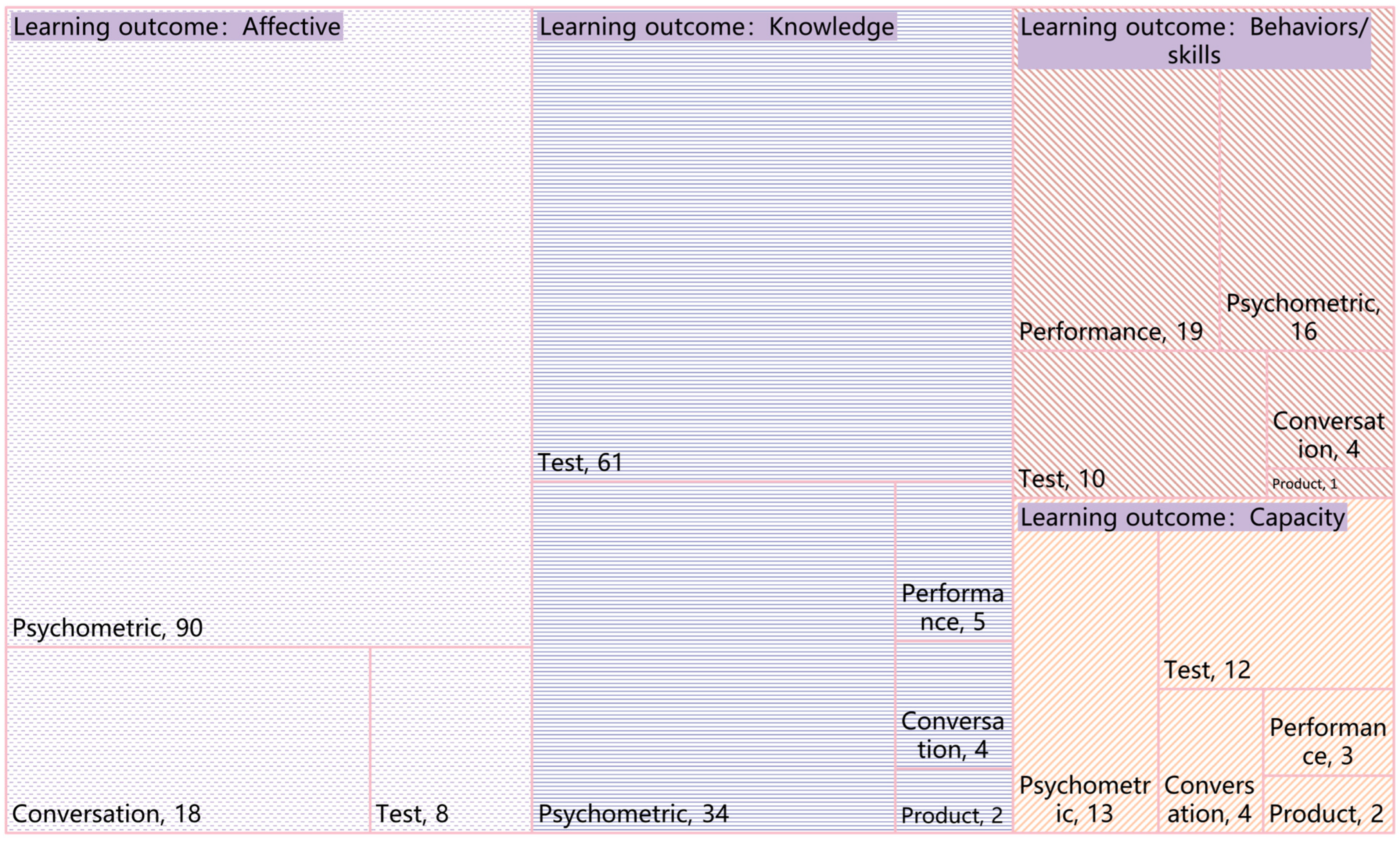
3.4. Learning Outcomes and Measurement Methods
4. Meta-Analysis Results
4.1. Publication Bias
4.2. Heterogeneity Test
4.3. Moderating Effect
4.4. Publication Bias and Sensitivity Analysis
5. Discussion
5.1. Discussion of the Systematic Review Results
5.2. Discussion of the Meta-Analysis Results
5.3. Implication
6. Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AR | Augmented reality |
| HMD | Head-mounted device |
| REM | random-effects model |
Appendix A
| Author and Year | Article Title | Hedges’s g | Standard Error | doi |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Martín-Gutiérrez & Luís Saorín1, 2010 | Design and validation of an augmented book for spatial abilities development in engineering students | 0.618 | 0.288 | 10.1016/j.cag.2009.11.003 |
| Martín-Gutiérrez & Luís Saorín2, 2010 | Design and validation of an augmented book for spatial abilities development in engineering students | 0.499 | 0.286 | 10.1016/j.cag.2009.11.003 |
| Kuo-En Chang, 2014 | Development and behavioral pattern analysis of a mobile guide system with augmented reality for painting appreciation instruction in an art museum | 0.721 | 0.22 | 10.1016/j.compedu.2013.09.022 |
| Mau-Tsuen Yang, 2014 | Computer-assisted culture learning in an online augmented reality environment based on free-hand gesture interaction | 0.525 | 0.301 | 10.1109/TLT.2014.2307297 |
| Albert Sánchez Riera, 2013 | Hand-held augmented reality: Usability and academic performance assessment in educational environments. Case study of an engineering degree course | 0.319 | 0.189 | NA |
| Mahmoudi, 2017 | AR-based value-added visualization of infographic for enhancing learning performance | 2.552 | 0.179 | 10.1002/cae.21853 |
| Turkan, 2017 | Mobile augmented reality for teaching structural analysis | 0.092 | 0.307 | 10.1016/j.aei.2017.09.005 |
| Christopoulos, A1, 2021 | The effects of augmented reality-supported instruction in tertiary-level medical education | 0.851 | 0.266 | 10.1111/bjet.13167 |
| Christopoulos, A2, 2021 | The effects of augmented reality-supported instruction in tertiary-level medical education | 1.009 | 0.157 | 10.1111/bjet.13167 |
| Chung & Awad, 2021 | Collaborative programming problem-solving in augmented reality: Multimodal analysis of effectiveness and group collaboration | −0.871 | 0.298 | 10.14742/ajet.7059 |
| Elfeky & AIM, 2021 | Developing skills of fashion design by augmented reality technology in higher education | 1.918 | 0.326 | 10.1080/10494820.2018.1558259 |
| Zhang & Robb, 2021 | Immersion Experiences in a Tablet-Based Markerless Augmented Reality Working Memory Game: Randomized Controlled Trial and User Experience Study | 0.282 | 0.256 | 10.2196/27036 |
| Zhao & Zhang1, 2022 | An Augmented Reality Based Mobile Photography Application to Improve Learning Gain, Decrease Cognitive Load, and Achieve Better Emotional State | 1.858 | 0.443 | 10.1080/10447318.2022.2041911 |
| Zhao & Zhang2, 2022 | An Augmented Reality Based Mobile Photography Application to Improve Learning Gain, Decrease Cognitive Load, and Achieve Better Emotional State | 1.23 | 0.402 | 10.1080/10447318.2022.2041911 |
| Zhao & Zhang3, 2022 | An Augmented Reality Based Mobile Photography Application to Improve Learning Gain, Decrease Cognitive Load, and Achieve Better Emotional State | 1.468 | 0.209 | 10.1080/10447318.2022.2041911 |
| Elford et al., 2022 | Fostering Motivation toward Chemistry through Augmented Reality Educational Escape Activities. A Self-Determination Theory Approach | 0.008 | 0.112 | 10.1021/acs.jchemed.2c00428 |
| Rodriguez-Abad&Rodriguez-Gonzalez, 2022 | Effectiveness of augmented reality in learning about leg ulcer care: A quasi-experimental study in nursing students | 0.363 | 0.172 | 10.1016/j.nedt.2022.105565 |
| Logishetty & Western, 2019 | Can an Augmented Reality Headset Improve Accuracy of Acetabular Cup Orientation in Simulated THA? A Randomized Trial | 1.656 | 0.461 | 10.1097/CORR.0000000000000542 |
| Singh & Mantri, 2019 | Evaluating the impact of the augmented reality learning environment on electronics laboratory skills of engineering students | 1.326 | 0.282 | 10.1002/cae.22156 |
| Yip & Wong, 2019 | Improving quality of teaching and learning in classes by using augmented reality video | 0.787 | 1.106 | 10.1016/j.compedu.2018.09.014 |
| Yu & Sun, 2019 | Effect of AR-based online wearable guides on university students’ situational interest and learning performance | 0.413 | 0.372 | 10.1007/s10209-017-0591-3 |
| AlNajdi & Alrashidi, 2020 | The effectiveness of using augmented reality (AR) on assembling and exploring educational mobile robot in pedagogical virtual machine (PVM) | 2.829 | 0.465 | 10.1080/10494820.2018.1552873 |
| Lee, I.-J., 2020 | Using augmented reality to train students to visualize three-dimensional drawings of mortise–tenon joints in furniture carpentry | 1.348 | 2.445 | 10.1080/10494820.2019.1572629 |
| Lee, J., 2020 | Problem-based gaming via an augmented reality mobile game and a printed game in foreign language education | 0.235 | 0.176 | 10.1007/s10639-020-10391-1 |
| Gonzalez & Lizana, 2020 | Augmented reality-based learning for the comprehension of cardiac physiology in undergraduate biomedical students | 5.954 | 0.464 | 10.1152/advan.00137.2019 |
| Bogomolova & van der Ham, 2020 | The Effect of Stereoscopic Augmented Reality Visualization on Learning Anatomy and the Modifying Effect of Visual-Spatial Abilities: A Double-Center Randomized Controlled Trial | 0.256 | 0.319 | 10.1002/ase.1941 |
| Conley & Atkinson1, 2020 | MantarayAR: Leveraging augmented reality to teach probability and sampling | 0.496 | 0.231 | 10.1016/j.compedu.2020.103895 |
| Conley & Atkinson2, 2020 | MantarayAR: Leveraging augmented reality to teach probability and sampling | 0.247 | 0.22 | 10.1016/j.compedu.2020.103895 |
| Conley & Atkinson3, 2020 | MantarayAR: Leveraging augmented reality to teach probability and sampling | 0.236 | 0.208 | 10.1016/j.compedu.2020.103895 |
| Conley & Atkinson4, 2020 | MantarayAR: Leveraging augmented reality to teach probability and sampling | 0.251 | 0.224 | 10.1016/j.compedu.2020.103895 |
| Mladenovic & Dakovic, 2020 | Effect of augmented reality simulation on administration of local anaesthesia in paediatric patients | 1.14 | 0.455 | 10.1111/eje.12529 |
| Lin&Liu, 2020 | The effects of an augmented-reality ubiquitous writing application: a comparative pilot project for enhancing EFL writing instruction | 0.536 | 0.341 | 10.1080/09588221.2020.1770291 |
| Mendez-Lopez & Juan, 2021 | Evaluation of an Augmented Reality Application for Learning Neuroanatomy in Psychology | 0.57 | 0.247 | 10.1002/ase.2089 |
| Noll1, 2017 | Mobile augmented reality as a feature for self-oriented, blended learning in medicine: Randomized controlled trial | 0.176 | 0.297 | 10.2196/mhealth.7943 |
| Noll2, 2017 | Mobile augmented reality as a feature for self-oriented, blended learning in medicine: Randomized controlled trial | 0.542 | 0.302 | 10.2196/mhealth.7943 |
| Bursztyn1, 2017 | Increasing undergraduate interest to learn geoscience with GPS-based augmented reality field trips on students’ own smartphones | 0.152 | 0.119 | 10.1130/GSATG304A.1 |
| Bursztyn2, 2017 | Increasing undergraduate interest to learn geoscience with GPS-based augmented reality field trips on students’ own smartphones | 0.442 | 0.168 | 10.1130/GSATG304A.1 |
| Bursztyn3, 2017 | Increasing undergraduate interest to learn geoscience with GPS-based augmented reality field trips on students’ own smartphones | 0.806 | 0.123 | 10.1130/GSATG304A.1 |
| Bursztyn (assessment), 2017 | Assessment of student learning using augmented reality Grand Canyon field trips for mobile smart devices | 0.117 | 0.171 | 10.1130/GES01404.1 |
| Carbonell, 2017 | Landscape interpretation with augmented reality and maps to improve spatial orientation skill | 0.987 | 0.19 | 10.1080/03098265.2016.1260530 |
| Akcayir, M. & Akcayir, G., 2016 | Augmented reality in science laboratories: The effects of augmented reality on university students’ laboratory skills and attitudes toward science laboratories | 0.557 | 0.232 | 10.1016/j.chb.2015.12.054 |
| Kücük, S & Kapakin, S, 2016 | Learning anatomy via mobile augmented reality: Effects on achievement and cognitive load | 0.666 | 0.243 | 10.1002/ase.1603 |
| Zhu & Feng1, 2018 | Increasing Enthusiasm and Enhancing Learning for Biochemistry-Laboratory Safety with an Augmented-Reality Program | 0.597 | 0.37 | 10.1021/acs.jchemed.8b00116 |
| Zhu & Feng2, 2018 | Increasing Enthusiasm and Enhancing Learning for Biochemistry-Laboratory Safety with an Augmented-Reality Program | 2.053 | 0.451 | 10.1021/acs.jchemed.8b00116 |
| Turan & Meral, 2016 | The impact of mobile augmented reality in geography education: achievements, cognitive loads and views of university students | 3.603 | 0.333 | 10.1080/03098265.2018.1455174 |
| Richardson & Sammons1, 2018 | Augmented affordances support learning: Comparing the instructional effects of the Augmented Reality Sandbox and conventional maps to teach topographic map skills | 0.069 | 0.29 | NA |
| Richardson & Sammons2, 2018 | Augmented affordances support learning: Comparing the instructional effects of the Augmented Reality Sandbox and conventional maps to teach topographic map skills | 1.217 | 0.316 | NA |
| Chang & Yu1, 2018 | Using augmented reality technologies to enhance students’ engagement and achievement in science laboratories | 0.388 | 0.093 | 10.4018/978-1-5225-8179-6.ch027 |
| Chang & Yu2, 2018 | Using augmented reality technologies to enhance students’ engagement and achievement in science laboratories | 0.568 | 0.21 | 10.4018/978-1-5225-8179-6.ch027 |
| Bacca & Baldiris, S, 2019 | Framework for designing motivational augmented reality applications in vocational education and training | 0.189 | 0.393 | 10.14742/ajet.4182 |
| Chin & Wang1, 2019 | Effects of an augmented reality-based mobile system on students’ learning achievements and motivation for a liberal arts course | 1.428 | 0.28 | 10.1080/10494820.2018.1504308 |
| Chin & Wang2, 2019 | Effects of an augmented reality-based mobile system on students’ learning achievements and motivation for a liberal arts course | 1.815 | 0.297 | 10.1080/10494820.2018.1504308 |
| Liu & Lu, 2019 | Comparison of AR and physical experiential learning environment in supporting product innovation | 0.071 | 0.38 | 10.1177/1847979019839578 |
| Mirmoghtadaie & Hosseinabadi1, 2023 | Is Using Blended Learning of Lab Skills by a Modest Augmented Reality-Based Educational Booklet Beneficial to Pharmacy Students? | −0.267 | 0.247 | 10.22062/sdme.2023.198379.1182 |
| Mirmoghtadaie & Hosseinabadi2, 2023 | Is Using Blended Learning of Lab Skills by a Modest Augmented Reality-Based Educational Booklet Beneficial to Pharmacy Students? | 7.675 | 0.717 | 10.22062/sdme.2023.198379.1182 |
| Martin & Castéra, 2023 | The use of augmented reality for inquiry-based activity about the phenomenon of seasons: effect on mental effort and learning outcomes | 0 | 0.34 | 10.3389/feduc.2023.1223656 |
| Mokmin & Hanjun1, 2023 | Impact of an AR-based learning approach on the learning achievement, motivation, and cognitive load of students on a design course | 1.324 | 0.292 | 10.1007/s40692-023-00270-2 |
| Mokmin & Hanjun2, 2023 | Impact of an AR-based learning approach on the learning achievement, motivation, and cognitive load of students on a design course | 0.692 | 0.272 | 10.1007/s40692-023-00270-2 |
| Felinska & Fuchs1, 2023 | Telestration with augmented reality improves surgical performance through gaze guidance | 0.959 | 0.583 | 10.1007/s00464-022-09859-7 |
| Felinska & Fuchs2, 2023 | Telestration with augmented reality improves surgical performance through gaze guidance | 0.273 | 0.311 | 10.1007/s00464-022-09859-7 |
References
- Akçayır, M., & Akçayır, G. (2017). Advantages and challenges associated with augmented reality for education: A systematic review of the literature. Educational Research Review, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçayır, M., Akçayır, G., Pektaş, H. M., & Ocak, M. A. (2016). Augmented reality in science laboratories: The effects of augmented reality on university students’ laboratory skills and attitudes toward science laboratories. Computers in Human Behavior, 57, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlNajdi, S. M., Alrashidi, M. Q., & Almohamadi, K. S. (2018). The effectiveness of using augmented reality (AR) on assembling and exploring educational mobile robot in pedagogical virtual machine (PVM). Interactive Learning Environments, 28, 964–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Marin, A., & Velazquez-Iturbide, J. A. (2021). Augmented reality and engineering education: A systematic review. IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies, 14, 817–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Marín, A., Velázquez-Iturbide, J. Á., & Castillo-Vergara, M. (2021). The acceptance of augmented reality in engineering education: The role of technology optimism and technology innovativeness. Interactive Learning Environments, 31, 3409–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacca, J., Baldiris, S., Fabregat, R., Graf, S., & Kinshuk. (2014). Augmented reality trends in education: A systematic review of research and applications. Educational Technology & Society, 17, 133–149. [Google Scholar]
- Buchner, J., & Kerres, M. (2023). Media comparison studies dominate comparative research on augmented reality in education. Computers & Education, 195, 104711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-E., Chang, C.-T., Hou, H.-T., Sung, Y.-T., Chao, H.-L., & Lee, C.-M. (2014). Development and behavioral pattern analysis of a mobile guide system with augmented reality for painting appreciation instruction in an art museum. Computers & Education, 71, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.-H., & Tsai, C.-C. (2013). Affordances of augmented reality in science learning: Suggestions for future research. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 22, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.-Y., Awad, N., & Hsiao, I. H. (2021). Collaborative programming problem-solving in augmented reality: Multimodal analysis of effectiveness and group collaboration. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 37, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfeky, A. I. M., & Elbyaly, M. Y. H. (2018). Developing skills of fashion design by augmented reality technology in higher education. Interactive Learning Environments, 29, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón, J., Kinshuk, Baldiris, S., Gutiérrez, J., & Pavón, J. (2020). How do pedagogical approaches affect the impact of augmented reality on education? A meta-analysis and research synthesis. Educational Research Review, 31, 100334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón, J., Pavón, J., & Baldiris, S. (2019). Systematic review and meta-analysis of augmented reality in educational settings. Virtual Reality, 23, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X., Chen, Y., Feng, Q., & Luo, H. (2022). Augmented reality in professional training: A review of the literature from 2001 to 2020. Applied Sciences, 12, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J. P. T. (2003). Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q. N., Gonzalez-Reyes, A., & Pluye, P. (2018). Improving the usefulness of a tool for appraising the quality of qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods studies, the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT). Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice, 24, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, M.-B., & Delgado-Kloos, C. (2018). Augmented reality for STEM learning: A systematic review. Computers & Education, 123, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalemkuş, J., & Kalemkuş, F. (2022). Effect of the use of augmented reality applications on academic achievement of student in science education: Meta analysis review. Interactive Learning Environments, 31, 6017–6034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, F., & Hsu, Y.-C. (2015). Mobile augmented-reality artifact creation as a component of mobile computer-supported collaborative learning. Internet and Higher Education, 26, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopfer, E., & Squire, K. (2008). Environmental detectives—the development of an augmented reality platform for environmental simulations. Educational Technology Research and Development, 56, 203–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J. (2020). Problem-based gaming via an augmented reality mobile game and a printed game in foreign language education. Education and Information Technologies, 27, 743–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logishetty, K., Western, L., Morgan, R., Iranpour, F., Cobb, J. P., & Auvinet, E. (2018). Can an augmented reality headset improve accuracy of acetabular cup orientation in simulated THA? A randomized trial. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 477, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, M. T., Mojtahedi, S., & Shams, S. (2017). AR-based value-added visualization of infographic for enhancing learning performance. Computer Applications in Engineering Education, 25, 1038–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrous, A., Elgreatly, A., Qian, F., & Schneider, G. B. (2021). A comparison of pre-clinical instructional technologies: Natural teeth, 3D models, 3D printing, and augmented reality. Journal of Dental Education, 85, 1795–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Gutiérrez, J., Luís Saorín, J., Contero, M., Alcañiz, M., Pérez-López, D. C., & Ortega, M. (2010). Design and validation of an augmented book for spatial abilities development in engineering students. Computers & Graphics, 34, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, C., Phelps, C., Redmond, P., & Stromberga, Z. (2020). HoloLens and mobile augmented reality in medical and health science education: A randomised controlled trial. British Journal of Educational Technology, 52, 680–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mystakidis, S., Christopoulos, A., & Pellas, N. (2021). A systematic mapping review of augmented reality applications to support STEM learning in higher education. Education and Information Technologies, 27, 1883–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H., & Hu, Y. (2019). Does augmented reality improve learning achievements? A meta-analysis based on 35 studies from 2010 to 2018. Open Education Research, 25, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes-Velasco, M., Velázquez-Iturbide, J. Á., & Gómez-Ríos, M. (2023). Augmented reality with algorithm animation and their effect on students’ emotions. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 82, 11819–11845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigott, T. D., & Polanin, J. R. (2020). Methodological guidance paper: High-quality meta-analysis in a systematic review. Review of Educational Research, 90, 24–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, I. (2014). Augmented reality in education: A meta-review and cross-media analysis. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing, 18, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2000). Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. American Psychologist, 55, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez Riera, A., Redondo, E., & Fonseca, D. (2015). Geo-located teaching using handheld augmented reality: Good practices to improve the motivation and qualifications of architecture students. Universal Access in the Information Society, 14, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazi, A., & Behzadan, A. H. (2015). Design and assessment of a mobile augmented reality-based information delivery tool for construction and civil engineering curriculum. Journal of Professional Issues in Engineering Education and Practice, 141, 04014012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sümer, M., & Vaněček, D. (2024). A systematic review of virtual and augmented realities in higher education: Trends and issues. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 62, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F., & Hannafin, M. J. (2005). Design-based research and technology-enhanced learning environments. Educational Technology Research and Development, 53, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J., Wolfer, V., Halbe, M., Maisano, F., Lohmeyer, Q., & Meboldt, M. (2021). Comparing the effectiveness of augmented reality-based and conventional instructions during single ECMO cannulation training. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 16, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C. H. S., Tsang, K. C. K., & Chiu, W.-K. (2021). Using augmented reality as a powerful and innovative technology to increase enthusiasm and enhance student learning in higher education chemistry courses. Journal of Chemical Education, 98, 3476–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-K., Lee, S. W.-Y., Chang, H.-Y., & Liang, J.-C. (2013). Current status, opportunities and challenges of augmented reality in education. Computers & Education, 62, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J., & Zhang, H. (2005). Testing intercoder reliability by multi-approaches in qualitative research. Journal of Psychological Science, 28, 1430–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, J., Wong, S.-H., Yick, K.-L., Chan, K., & Wong, K.-H. (2019). Improving quality of teaching and learning in classes by using augmented reality video. Computers & Education, 128, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Category | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Basic information | Title Authors Year | |
| Research type | Empirical/design case/theoretical/synthesis | |
| Empirical type | Experimental/quantitative/qualitative/mixed/survey/design-based research | |
| Disciplines | / | Basic science/social science/engineering/health & medicine/language/mathematics/other |
| Technology features | Input | Natural: voice command/motion/haptic/location-based Artificial: mouse & keyboard/scan/stylus/controller/other |
| Output | Monitor-based/video see-through/optical see-through | |
| Media representation | Symbol or indicator/text/data/2D image/3D object/animation/video/audio/fantasy | |
| Instructional design | Instructional function | Content delivery/attention grabber/engagement/practice/assessment/other |
| Pedagogy | Inquiry-based/game-based/collaborative/direct instruction/experiential learning/trial-and err | |
| Research results | Learning outcomes | Knowledge/affective/behavior or skills/capacity |
| Measurement format | Knowledge test/psychometric/conversation/performance/product/other | |
| Statistical results | Difference (T-test/analysis of variance/multi-variant analysis of variance/analysis of covariance/non-parametric) Association: structural equation modeling/regression/factor analysis |
| Moderator | K | g | 95% CI | QB | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discipline | 7.036 | 0.218 | |||
| Basic science | 21 | 0.740 b | [0.404–1.076] | ||
| Social science | 11 | 1.062 a | [0.588–1.536] | ||
| Engineering | 9 | 0.840 a | [0.298–1.381] | ||
| Health & medicine | 14 | 0.920 a | [0.493–1.348] | ||
| Language | 2 | 0.373 b | [−0.706–1.452] | ||
| Other | 3 | 2.081 a | [1.019–3.143] | ||
| Input | 2.071 | 0.150 | |||
| Natural | 25 | 0.713 b | [0.390–1.037] | ||
| Artificial | 35 | 1.024 a | [0.751–1.298] | ||
| Output | 0.373 | 0.830 | |||
| Monitor-based | 12 | 0.997 a | [0.515–1.480] | ||
| Video see through | 46 | 0.883 a | [0.640–1.127] | ||
| Optical see through | 2 | 0.637 b | [−0.520–1.793] | ||
| Pedagogy | 6.254 | 0.282 | |||
| Inquiry-based | 7 | 0.755 b | [0.061–1.449] | ||
| Game-based | 2 | 0.761 b | [−0.392–1.915] | ||
| Experiential learning | 11 | 0.693 b | [0.192–1.194] | ||
| Direct instruction | 26 | 1.213 a | [0.881–1.546] | ||
| Collaborative | 10 | 0.569 b | [0.052–1.085] | ||
| Trial-and err | 4 | 0.622 b | [−0.256–1.500] | ||
| Instructional function | 11.939 ** | 0.008 | |||
| Attention grabber | 5 | 0.265 c | [−0.426–0.956] | ||
| Content delivery | 31 | 1.224 a | [0.939–1.509] | ||
| Practice | 9 | 0.746 b | [0.166–1.327] | ||
| Engagement | 15 | 0.519 b | [0.118–0.920] | ||
| Learning outcomes | 11.069 * | 0.026 | |||
| Knowledge | 28 | 0.914 a | [0.062–1.225] | ||
| Behavior/skills | 8 | 1.846 a | [1.199–2.494] | ||
| Affective | 16 | 0.665 b | [0.248–1.803] | ||
| Capacity | 6 | 0.476 b | [−0.186–1.139] | ||
| Other | 2 | 0.731 b | [−0.468–1.930] | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Luo, H.; Chen, D.; Wang, P.; Yin, X.; Zhang, J. Augmented Reality in Higher Education: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Literature from 2000 to 2023. Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15060678
Li G, Luo H, Chen D, Wang P, Yin X, Zhang J. Augmented Reality in Higher Education: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Literature from 2000 to 2023. Education Sciences. 2025; 15(6):678. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15060678
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Gege, Heng Luo, Di Chen, Peiyu Wang, Xin Yin, and Jiakai Zhang. 2025. "Augmented Reality in Higher Education: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Literature from 2000 to 2023" Education Sciences 15, no. 6: 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15060678
APA StyleLi, G., Luo, H., Chen, D., Wang, P., Yin, X., & Zhang, J. (2025). Augmented Reality in Higher Education: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Literature from 2000 to 2023. Education Sciences, 15(6), 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15060678







