Developing a Novel Model for ICT Integration in South African Education: Insights from TIMSS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Importance of ICT Integration in the T&L of Mathematics
2.2. Technology Diffusion in South African Schools
2.3. Uses of ICT in South African Mathematics T&L
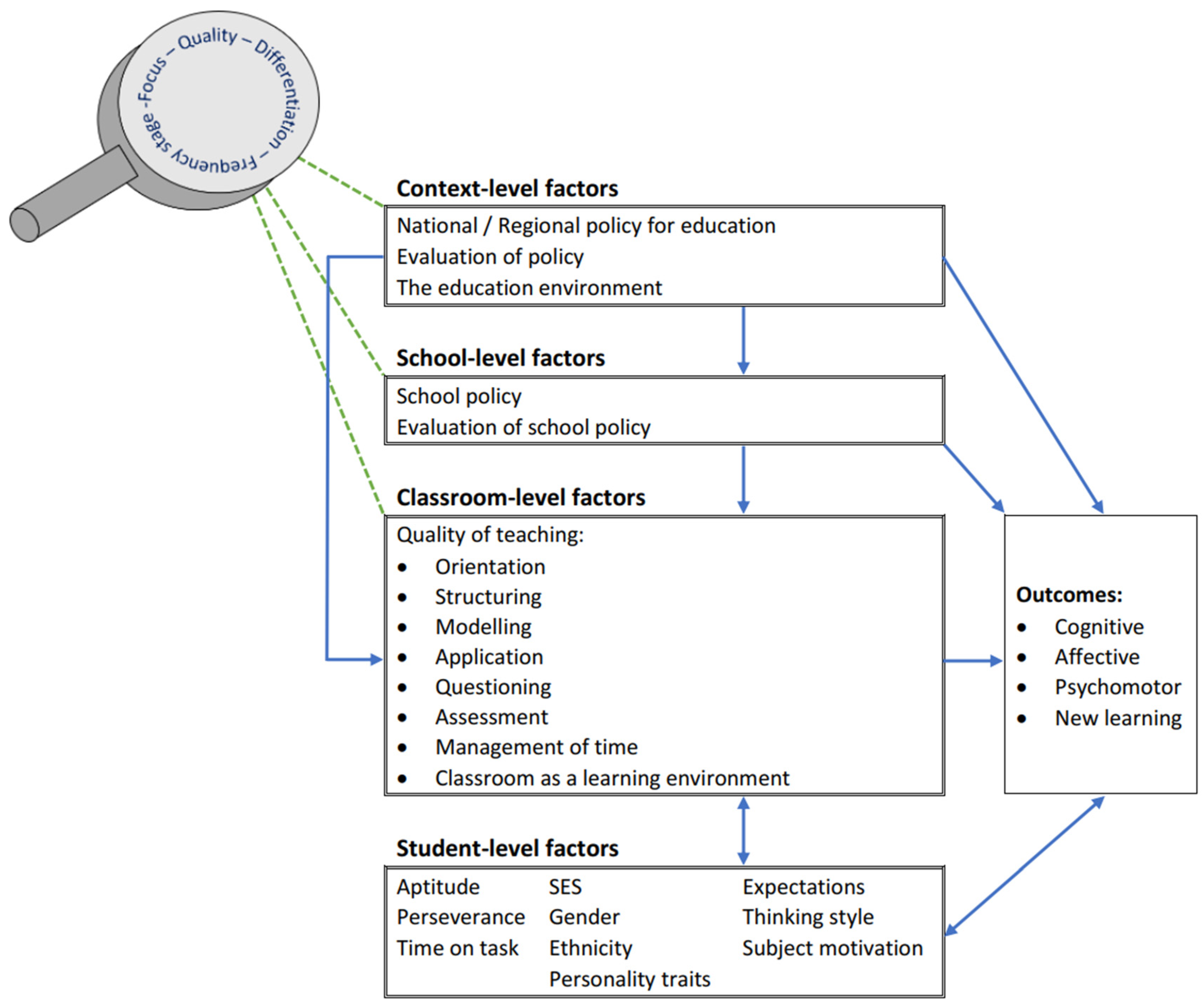
2.4. Conceptual Framework: Towards a Model for the Integration of ICT in School
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Approach and Design
3.2. Participants
3.3. Instruments and Quality Assurance
3.4. Data Analysis
4. Results
| TIMSS Question and Variable Name | Grade 5 | Grade 9 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TQ (Grade 5: Answered by 294 Mathematics Teachers; Grade 9: Answered by 543 Mathematics Teachers) | |||||||
| “If yes to having access to a computer or tablet in class, how often do you do activities on computers during mathematics lessons to support learning for”: | “Whole class” Grade 5: ATBM04CA Grade 9: BTBM17CA | “Never or almost never” (17.6%) “Once or twice a month” (34.1%) “Once or twice a week” (48.3%) “Every or almost every day” (0.0%) | ↘ ↗ ↘ ↗ | Never to 1–2 pm (51.7%) 1–2 pw to always (48.3%) | “Never or almost never” (48.4%) “Once or twice a month” (24.9%) “Once or twice a week” (18.4%) “Every or almost every day” (7.9%) | ↘ ↗ ↘ ↗ | Never to 1–2 pm (73.7%) 1–2 pw to always (26.3%) |
| “Low-performing students” Grade 5: ATBM04CB Grade 9: BTBM17CB | “Never or almost never” (29.8%) “Once or twice a month” (31.0%) “Once or twice a week” (36.3%) “Every or almost every day” (2.9%) | ↘ ↗ ↘ ↗ | Never to 1–2 pm (60.8%) 1–2 pw to always (39.2%) | “Never or almost never” (56.3%) “Once or twice a month” (23.8%) “Once or twice a week” (7.7%) “Every or almost every day” (12.2%) | ↘ ↗ ↘ ↗ | Never to 1–2 pm (80.1%) 1–2 pw to always (19.9%) | |
| “High-performing students” Grade 5: ATBM04CC Grade 9: BTBM17CC | “Never or almost never” (28.4%) “Once or twice a month (21.7%) “Once or twice a week” (44.6%) “Every or almost every day” (5.3%) | ↘ ↗ ↘ ↗ | Never to 1–2 pm (50.1%) 1–2 pw to always (49.9%) | “Never or almost never” (52.6%) “Once or twice a month” (25.0%) “Once or twice a week” (14.4%) “Every or almost every day” (8.1%) | ↘ ↗ ↘ ↗ | Never to 1–2 pm (77.5%) 1–2 pw to always (22.5%) | |
| “Students with special needs” Grade 5: ATBM04CD Grade 9: BTBM17CD | “Never or almost never” (38.2%) “Once or twice a month” (22.6%) “Once or twice a week” (31.0%) “Every or almost every day” (8.2%) | ↘ ↗ ↘ ↗ | Never to 1–2 pm (60.8%) 1–2 pw to always (39.2%) | “Never or almost never” (57.0%) “Once or twice a month” (20.9%) “Once or twice a week” (12.6%) “Every or almost every day” (9.5%) | ↘ ↗ ↘ ↗ | Never to 1–2 pm (77.9%) 1–2 pw to always (22.1%) | |
| TIMSS Question and Variable Name | Grade 5 | Grade 9 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ScQ (Grade 5: Answered by 297 Principals; Grade 9: Answered by 519 Principals) | |||||||
| “How many computers (including tablets and iPads) does your school have for use by Grade 5/9 students?” Grade 5: ACBG07 Grade 9: BCBG07 | Mean = 12.26 SD = 20.42 Median = 0.00 * Interquartile range = 20.00 | Mean = 21.79 SD = 42.45 Median = 0.00 ** Interquartile range = 30.00 | |||||
| “Does your school use an online learning management system to support learning (e.g., educator –student communication, management of grades, student access to course materials)?” Grade 5: ACBG09 Grade 9: BCBG09 | Yes (12.6%) No (87.4%) | Yes (25.5%) No (74.5%) | |||||
| “Does your school provide students with access to digital learning resources (e.g., books, videos)?” Grade 5: ACBG12 Grade 9: BCBG12 | Yes (39.9%) No (60.1%) | Yes (49.7%) No (50.3%) | |||||
| “How much is your school’s capacity to provide instruction affected by a shortage or inadequacy of”: | “Technologically competent staff” Grade 5: ACBG13AF Grade 9: BCBG13AF | “Not at all” (13.0%) “A little” (27.6%) “Some” (40.7%) “A lot” (18.7%) | ↘ ↗ ↘ ↗ | None to a little (40.6%) Some to a lot (59.4%) | “Not at all” (13.8%) “A little” (32.1%) “Some” (38.8%) “A lot” (15.2%) | ↘ ↗ ↘ ↗ | None to a little (46.0%) Some to a lot (54.0%) |
| “Audiovisual resources for delivery of instruction (e.g., interactive white boards, digital projectors)” Grade 5: ACBG13AG Grade 9: BCBG13AG | “Not at all” (29.7%) “A little” (20.5%) “Some” (16.3%) “A lot” (33.5%) | ↘ ↗ ↘ ↗ | None to a little (50.2%) Some to a lot (49.8%) | “Not at all” (20.8%) “A little” (27.4%) “Some” (29.7%) “A lot” (22.1%) | ↘ ↗ ↘ ↗ | None to a little (48.2%) Some to a lot (51.8%) | |
| “Computer technology for teaching and learning (e.g., computers or tablets for student use)” Grade 5: ACBG13AH Grade 9: BCBG13AH | “Not at all” (29.7%) “A little” (19.5%) “Some” (14.0%) “A lot” (36.8%) | ↘ ↗ ↘ ↗ | None to a little (49.2%) Some to a lot (50.8%) | “Not at all” (25.9%) “A little” (24.7%) “Some” (25.4%) “A lot” (24.0%) | ↘ ↗ ↘ ↗ | None to a little (50.6%) Some to a lot (49.4%) | |
| “Computer software/applications for mathematics instruction” Grade 5: ACBG13BB Grade 9: BCBG13BB | “Not at all” (29.0%) “A little” (24.1%) “Some” (18.8%) “A lot” (28.1%) | ↘ ↗ ↘ ↗ | None to a little (53.1%) Some to a lot (46.9%) | “Not at all” (25.2%) “A little” (25.5%) “Some” (29.0%) “A lot” (20.2%) | ↘ ↗ ↘ ↗ | None to a little (50.8%) Some to a lot (49.2%) | |
| TQ (Grade 5: answered by 294 mathematics teachers; Grade 9: answered by 543 mathematics teachers) | |||||||
| “Students in this class have computers (including tablets) available to use during their mathematics lessons,” Grade 5: ATBM04A Grade 9: BTBM17A | Yes (9.1%) No (90.9%) | Yes (12.3%) No (87.7%) | |||||
| “If yes to having access to a computer or tablet in class, what access do they have”: | “Each student has a computer” Grade 5: ATBM04BA Grade 9: BTBM17BA | Yes (4.5%) No (95.5%) | Yes (21.3%) No (78.7%) | ||||
| “The class has computers that students can share” Grade 5: ATBM04BB Grade 9: BTBM17BB | Yes (38.3%) No (61.7%) | Yes (12.4%) No (87.6%) | |||||
| “The school has computers that the class can use sometimes” Grade 5: ATBM04BC Grade 9: BTBM17BC | Yes (83.6%) No (16.4%) | Yes (53.7%) No (46.3%) | |||||
| “In the past two years, have you participated in professional development in integrating technology into mathematics instruction?” Grade 5: ATBM09AD Grade 9: BTBM22AD | Yes (44.8%) No (55.2%) | Yes (50.6%) No (49.4%) | |||||
| “Do you need future professional development in integrating technology into mathematics instruction?” Grade 5: ATBM09BD Grade 9: BTBM22BD | Yes (86.1%) No (13.9%) | Yes (85.0%) No (15.0%) | |||||
| StQ (Grade 5: answered by 22,903 students; Grade 9: answered by 20,829 students) | |||||||
| “Do you have any of these things at your home?” | “A computer or tablet” Grade 5: ASBG05A Grade 9: BSBG05A | Yes (56.9%) No (43.1%) | Yes (52.2%) No (47.8%) | ||||
| “Internet connection” Grade 5: ASBG05D Grade 9: BSBG05D | Yes (36.2%) No (63.8%) | Yes (43.0%) No (57.0%) | |||||
| “Your own cell phone” Grade 5: ASBG05E Grade 9: BSBG05E | Yes (67.8%) No (32.2%) | Yes (79.1%) No (20.9%) | |||||
| “Electricity” Grade 5: ASBG05G Grade 9: BSBG05G | Yes (83.5%) No (15.8%) | Yes (94.0%) No (6.0%) | |||||
5. Discussion
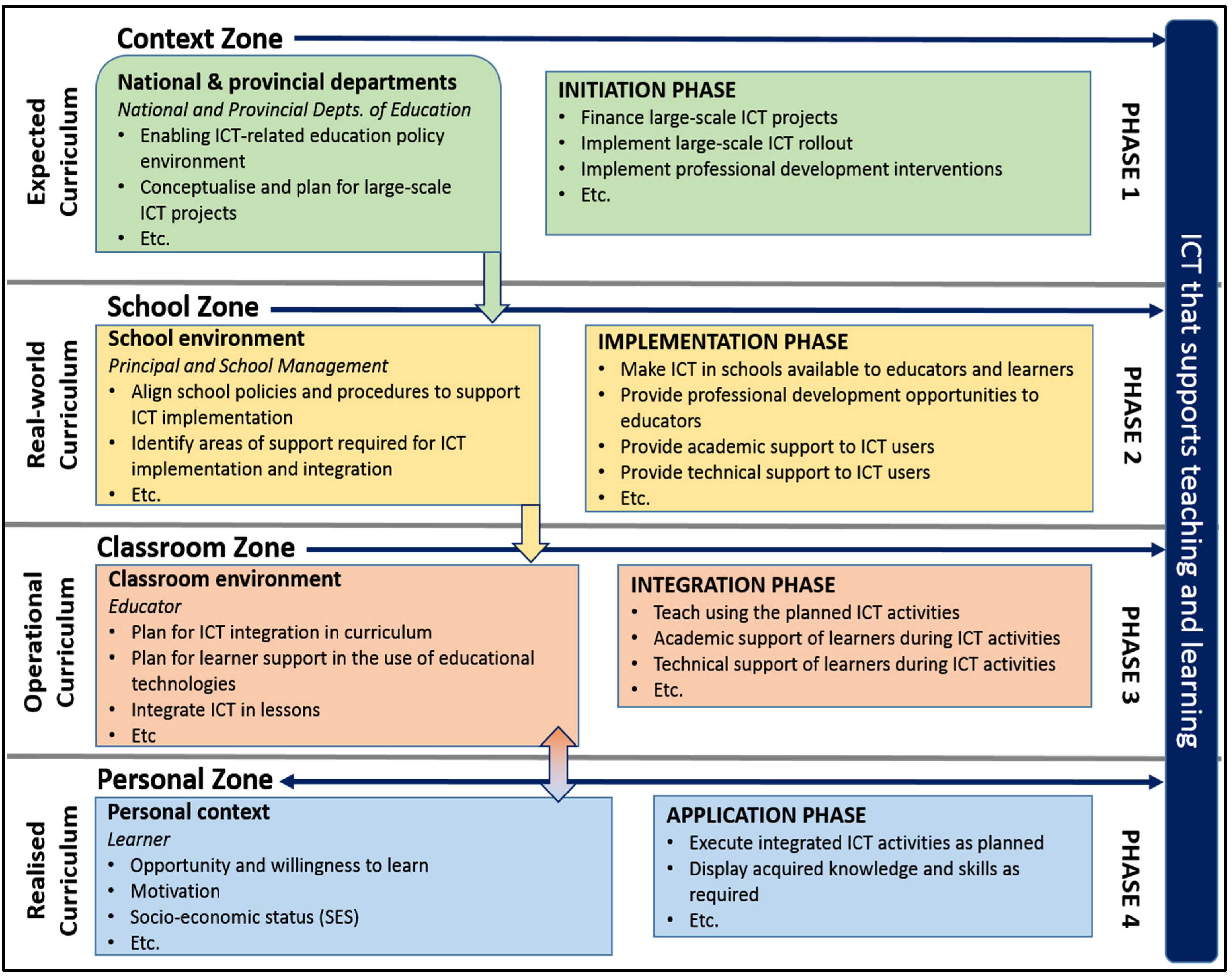
6. Improving the Integration of ICT in Schools to Show an Increased Educational Return on Investment
6.1. Reliability of the Four Zones Model
6.2. Validity of the Four Zones Model
7. Recommendations for Improved Implementation of ICT in Schools
7.1. The Context Zone (National and Provincial Departments of Education)
7.2. The School Zone (Principals and School Management)
7.3. The Classroom Zone (Educators)
7.4. The Personal Zone (Students)
8. Limitations
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reddy, V.; Zuze, T.L.; Visser, M.; Winnaar, L.; Juan, A.; Prinsloo, C.H.; Arends, F.; Rogers, S. Beyond Benchmarks: What Twenty Years of TIMSS Data Tell Us about South African Education; Human Sciences Research Council: Pretoria, South Africa, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, V.; Winnaar, L.; Juan, A.; Arends, F.; Harvey, J.; Hannan, S.; Namome, C.; Zulu, N. TIMSS 2019 Highlights of South African Grade 5 Results in Mathematics and Science; Department of Basic Education: Pretoria, South Africa, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, V.; Winnaar, L.; Juan, A.; Arends, F.; Harvey, J.; Hannan, S.; Namome, C.; Sekhejane, P.; Zulu, N. TIMSS 2019: Highlights of South African Grade 9 Results in Mathematics and Science; Department of Basic Education: Pretoria, South Africa, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dahshan, M.; Galanti, T. Teachers in the loop: Integrating computational thinking and mathematics to build early place value understanding. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, F.; Campitiello, L.; Todino, M.D.; Di Tore, P.A. Educational robots, emotion recognition and ASD: New horizon in special education. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. The Adequacy of Public Expenditure on Education and the Needs Post-COVID-19; World Bank Group: Bretton Woods, NH, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Rayan, B.; Watted, A. Enhancing education in elementary schools through gamified learning: Exploring the impact of Kahoot! on the learning process. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasdiana Wiyono, B.B.; Imron Al Rahma, L.; Arifah, N.; Azhari, R.; Elfira; Sibula, I.; Maharmawan, M.A. Elevating teachers’ professional digital competence: Synergies of principals’ instructional e-supervision, technology leadership and digital culture for educational excellence in digital-savvy era. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elecalde, R.G.; Garcia, J.C.; Martos AL, B.; Arnáez, B.S. Digital and social-civic skills in future primary education teachers: A study from the didactics of social sciences for the improvement of teacher training in competences. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrecht, J.; Borba, M.C. Recent developments in using digital technology in mathematics education. ZDM–Math. Educ. 2023, 56, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attard, C.; Holmes, K. Technology-Enabled Mathematics Education: Optimising Student Engagement; Routledge: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hansson, S.O. Technology and mathematics. Philos. Technol. 2020, 33, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- South African National Research Network. The South African NREN. SANReN. 2024. Available online: https://www.sanren.ac.za/south-african-nren/ (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Department of Communications. Broadcasting Digital Migration Policy for South Africa; Republic of South Africa: Pretoria, South Africa, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Infrastructure South Africa. SA Connect. Republic of South Africa. 2022. Available online: https://infrastructuresa.org/sip-projects/sa-connect-phase-2/ (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Barakabitze, A.A.; Lazaro, A.W.-A.; Ainea, N.; Mkwizu, M.H.; Maziku, H.; Matofali, A.X.; Iddi, A.; Sanga, C. Transforming African education systems in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) using ICTs: Challenges and opportunities. Educ. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 6946809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokotjo, L.; Mokhele, M.L. Challenges of integrating GeoGebra in the teaching of mathematics in South African high schools. Univers. J. Educ. Res. 2021, 9, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwapwele, S.D.; Marais, M.; Dlamini, S.; Van Biljon, J. Teachers’ ICT adoption in South African rural schools: A study of technology readiness and implications for the South Africa connect broadband policy. Afr. J. Inf. Commun. 2019, 24, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Mahwai, N.J.; Wotela, K. Integrating technology in teaching and learning: Have Seshego Circuit rural schools escaped the challenges? J. Public Adm. Dev. Altern. 2022, 7, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlamini, R. Factors constraining teacher integration of ICT in Gauteng schools. Indep. J. Teach. Learn. 2022, 17, 28–43. [Google Scholar]
- Ramafi, P. Investigating the barriers of ICT use in teaching and learning at public schools in South Africa. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Intelligent and Innovative Computing Applications, Balaclava, Mauritius, 8–9 December 2022; pp. 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.A.; Stols, G.; Kapp, R. Teacher practice and integration of ICT: Why are or aren’t South African teachers using ICTs in their classrooms. Int. J. Instr. 2020, 13, 749–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.A.; Stols, G.H.; Kapp, R. Integrating classroom technology: South African mathematics teachers. Comput. Sch. 2021, 38, 189–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, O.A.; Adu, E.O. The effectiveness of Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) in teaching and learning in high schools in Eastern Cape Province. S. Afr. J. Educ. 2018, 38, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisango, G.; Marongwe, N.; Mtsi, N.; Matyedi, T.E. Teachers’ perceptions of adopting information and communication technologies in teaching and learning at rural secondary schools in eastern cape. S. Africa. Afr. Educ. Rev. 2020, 17, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filita, N.; Jita, T. Teachers’ perspectives on the use of ICT in the teaching of a South African home language, Sesotho. J. Lang. Teach. 2021, 55, 219–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenda, R.; Dlamini, R. Examining factors that influence teachers to adopt information and communication technology in rural secondary schools: An empirical study. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 28, 815–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnisi, B.R.; Mtshali, T.I.; Moses, M. Moving beyond the challenges of learning through technologies: The current status of ICT integration in South African schools. J. Educ. e-Learn. Res. 2024, 11, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saal, P.E.; Van Ryneveld, L.; Graham, M.A. The relationship between using information and communication technology in education at the mathematics achievement of students. Int. J. Instr. 2019, 12, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saal, P.E.; Van Ryneveld, L.; Graham, M.A. Comparing the relationship between using educational technology in mathematics and student achievement in South Africa and Germany. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 2022, 54, 581–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Morris, M.G.; Davis, G.B.; Davis, F.D. User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saal, P.E.; Graham, M.A.; Van Ryneveld, L. Integrating educational technology in mathematics education in economically disadvantaged areas in South Africa. Comput. Sch. 2020, 37, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolobe, L.; Mihai, M. The integration of technology in supporting progressed learners in English First Additional Language comprehension. Perspect. Educ. 2021, 39, 303–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlo, L.; Waghid, Z. Exploring information and communication technology integration among teachers in township public primary schools. S. Afr. J. Educ. 2023, 43, 2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntsobi, M.; Nyamkure, B. Responsive ICT integration framework to enhance teaching and learning in Gauteng schools. In Proceedings of the 2024 8th World Conference on Qualitative Research, Azores (Portugal), Johannesburg (South Africa), and online, 23–25 January 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Creemers, B.P.; Kyriakides, L. School factors explaining achievement on cognitive and affective outcomes: Establishing a dynamic model of educational effectiveness. Scand. J. Educ. Res. 2010, 54, 263–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullis, I.V.S. Introduction. In TIMSS 2019 Assessment Frameworks; Mullis, I.V.S., Martin, M.O., Eds.; Boston College, TIMSS & PIRLS International Study Center: Chestnut Hill, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 3–10. Available online: https://timssandpirls.bc.edu/timss2019/frameworks/framework-chapters/context-questionnaire-framework/ (accessed on 27 April 2024).
- Antoniou, P.; Kyriakides, L.; Creemers, B.P.M. Investigating the effectiveness of a dynamic integrated approach to teacher professional development. CEPS J. Cent. Educ. Policy Stud. J. 2011, 1, 13–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creemers, B.P.; Kyriakides, L. The Dynamics of Educational Effectiveness: A Contribution to Policy, Practice, and Theory in Contemporary Schools; Routledge: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fishbein, B.; Foy, P.; Yin, L. TIMSS 2019 User Guide for the International Database, 2nd ed.; TIMSS & PIRLS International Study Center, Lynch School of Education, Boston College and International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement: Chestnut Hill, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.Z. Implementation of Grade 8 science curriculum 2012 in Bangladesh: Challenges and way forward. J. Educ. Res. 2019, 9, 93–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, M.; Mullis, I.V.S.; Martin, M.O.; Fishbein, B. TIMSS 2019 context questionnaire framework. In TIMSS 2019 Assessment Frameworks; Mullis, I.V.S., Martin, M.O., Eds.; Boston College, TIMSS & PIRLS International Study Center: Chestnut Hill, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 59–78. Available online: https://timssandpirls.bc.edu/timss2019/frameworks/framework-chapters/context-questionnaire-framework/ (accessed on 10 August 2020).
- Department of Basic Education. Curriculum Assessment Policy Statements (CAPS); Government Printers: Pretoria, South Africa, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.S.; Konge, L.; Artino, A.R., Jr. The positivism paradigm of research. Acad. Med. 2020, 95, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouton, J. How to Succeed in Your Master’s and Doctoral Studies: A South African Guide and Resource Book; Van Schaik: Pretoria, South Africa, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, Z. Cross-sectional studies: Strengths, weaknesses, and recommendations. Chest 2020, 158, S65–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C. The inconvenient truth about convenience and purposive samples. Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2021, 43, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRoche, S.; Joncas, M.; Foy, P. Sample design in TIMSS 2019. In Methods and Procedures: TIMSS 2019 Technical Report; Martin, M.O., von Davier, M., Mullis, I.V.S., Eds.; TIMSS & PIRLS International Study Center: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 51–83. [Google Scholar]
- Cotter, K.E.; Centurino, V.A.S.; Mullis, I.V.S. Developing the TIMSS 2019 mathematics and science achievement instruments. In Methods and Procedures: TIMSS 2019 Technical Report; Martin, M.O., von Davier, M., Mullis, I.V.S., Eds.; TIMSS & PIRLS International Study Center: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 6–41. [Google Scholar]
- Van Ginkel, J.R.; Linting, M.; Rippe, R.C.A.; Van der Voort, A. Rebutting existing misconceptions about multiple imputation as a method for handling missing data. J. Personal. Assess. 2020, 102, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study. Teacher Questionnaire: Grade 5. Boston College, TIMSS & PIRLS International Study Center. 2018. Available online: https://timssandpirls.bc.edu/timss2019/questionnaires/index.html (accessed on 10 August 2020).
- Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study. Teacher Questionnaire: Grade 9. Boston College, TIMSS & PIRLS International Study Center. 2018. Available online: https://timssandpirls.bc.edu/timss2019/questionnaires/index.html (accessed on 10 August 2020).
- Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study. School Questionnaire: Grade 5. Boston College, TIMSS & PIRLS International Study Center. 2018. Available online: https://timssandpirls.bc.edu/timss2019/questionnaires/index.html (accessed on 10 August 2020).
- Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study. School Questionnaire: Grade 9. Boston College, TIMSS & PIRLS International Study Center. 2018. Available online: https://timssandpirls.bc.edu/timss2019/questionnaires/index.html (accessed on 10 August 2020).
- Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study. Student Questionnaire: Grade 5. Boston College, TIMSS & PIRLS International Study Center. 2018. Available online: https://timssandpirls.bc.edu/timss2019/questionnaires/index.html (accessed on 10 August 2020).
- Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study. Student Questionnaire: Grade 9. Boston College, TIMSS & PIRLS International Study Center. 2018. Available online: https://timssandpirls.bc.edu/timss2019/questionnaires/index.html (accessed on 10 August 2020).
- Siew, P.H. Pedagogical change in mathematics learning: Harnessing the power of digital game-based learning. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2018, 21, 259–276. [Google Scholar]
- Janković, A.; Maričić, M.; Cvjetićanin, S. Comparing science success of primary school students in the gamified learning environment via Kahoot and Quizizz. J. Comput. Educ. 2024, 11, 471–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, N.S.; Okonkwo, C.W.; Anele, A. The impact of loadshedding on student academic performance: A data analytics approach. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference of Teaching, Assessment and Learning in the Digital Age, Cape Town, South Africa, 6–7 December 2023; pp. 329–341. [Google Scholar]

| TIMSS Context Questionnaire | Areas of Research |
|---|---|
| Mathematics curriculum questionnaire Country context | The mathematics curriculum as established by the Department of Education of the participating country. |
| ScQ School context | The educational environment in which both the student and instructor operate; this consists of elements like resource accessibility, the perception of safety on campus, and the support received from school administration. |
| TQ Educator and classroom context | The educator’s background and the impact they have on the efficacy of teaching and learning in the classroom are factors to consider. This encompasses the educator’s teaching methods, the practical implementation of acquired knowledge, and their educational credentials. |
| HQ Home context | Details concerning educational resources available at home, perspectives on the parents’ highest level of education and employment circumstances, evaluations of their child’s school, attendance record in preprimary education programmes, prioritisation of literacy and numeracy activities at home, and the parents’ literacy and numeracy proficiency at the start of the academic year are all pertinent information. |
| StQ Student context | Student-specific information, including student-related context such as the student’s home environment, academic motivation and application, and parental background and support availability, is encompassed within this category. |
| DMEE | TIMSS Curriculum Model | TIMSS Context Questionnaires and Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Context-level factors (country and region) | Intended curriculum | Mathematics curriculum—Mathematics Curriculum Questionnaire |
| School-level factors | Implemented curriculum | School context—ScQ |
| Classroom-level factors | Implemented curriculum | Classroom and educator context—TQ |
| Home-level factors | Implemented curriculum | Home context—HQ |
| Student-level factors | Attained curriculum | Student achievement in TIMSS –Mathematics assessment Student context and background—StQ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Graham, M.A.; Kruger, G.M.; van Ryneveld, L. Developing a Novel Model for ICT Integration in South African Education: Insights from TIMSS. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14080865
Graham MA, Kruger GM, van Ryneveld L. Developing a Novel Model for ICT Integration in South African Education: Insights from TIMSS. Education Sciences. 2024; 14(8):865. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14080865
Chicago/Turabian StyleGraham, Marien Alet, Guillaume Matthys Kruger, and Linda van Ryneveld. 2024. "Developing a Novel Model for ICT Integration in South African Education: Insights from TIMSS" Education Sciences 14, no. 8: 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14080865
APA StyleGraham, M. A., Kruger, G. M., & van Ryneveld, L. (2024). Developing a Novel Model for ICT Integration in South African Education: Insights from TIMSS. Education Sciences, 14(8), 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14080865










