Exploring the Type and Quality of Peer Feedback in a Graduate-Level Blended Course
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Peer Feedback
1.2. Higher Education Students Engaged in Peer Feedback
1.3. The Function, Levels, and Quality of Feedback
- What is the function, level, and quality of peer feedback used by graduate students during online learning tasks taking place in a blended course?
2. Methodology
2.1. Participants
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
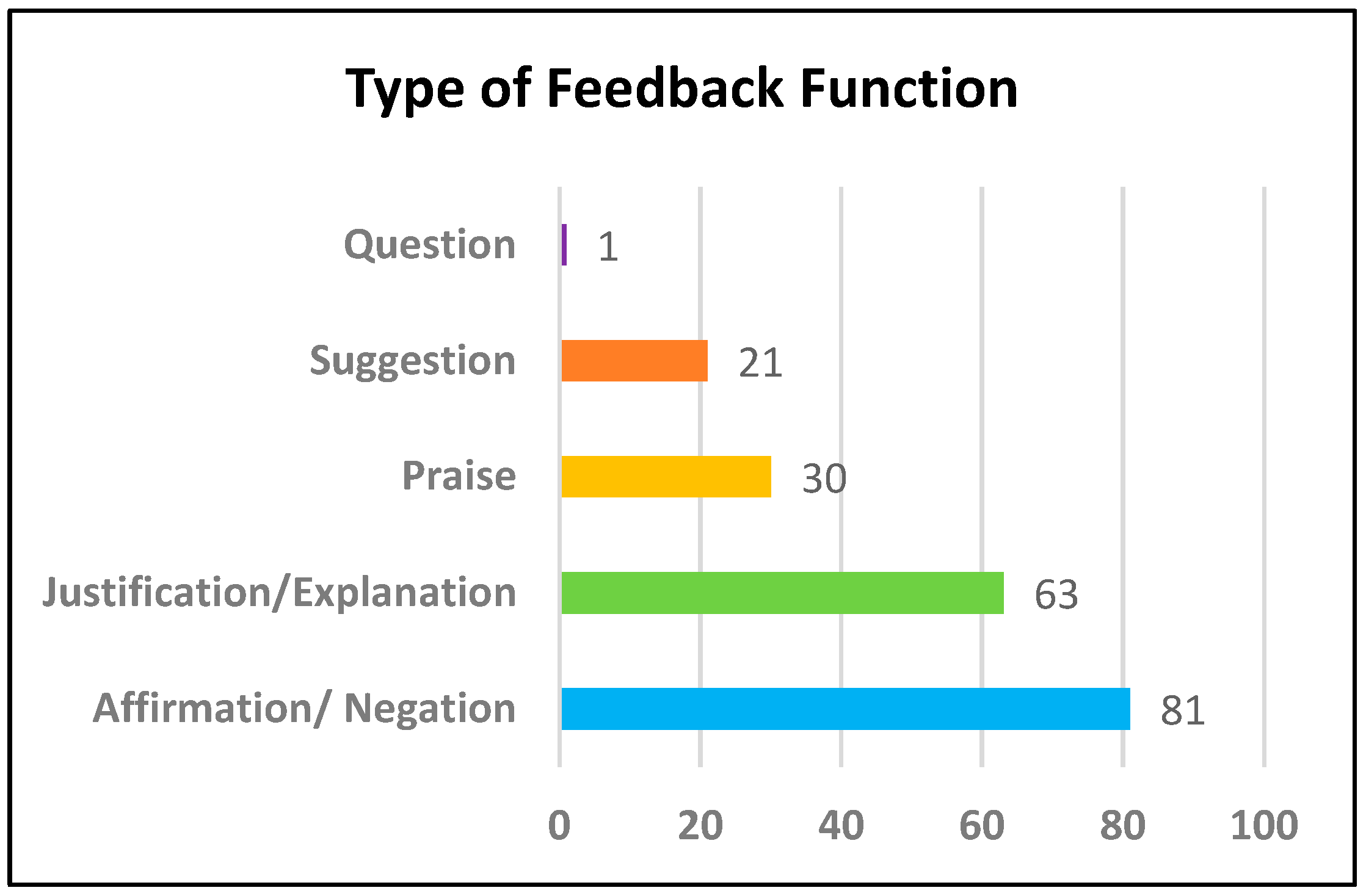
3.1. Type of Feedback Function
- -
- Good example [Praise]: Procedural understanding is when students carry on steps and algorithms and here they follow steps to add numbers using the number line, so they rarely make deep connections during instruction [Justification/Explanation]. (Learning Activity 1).
- -
- I agree with you it is routine [Affirmation] because it is one step equation. Also, students must know the concept of solving one step equation [Justification/Explanation]. (Learning Activity 2).
- -
- A good example for grade 3 students, and the rubric is clear [Praise]. (Learning Activity 2).
- -
- This question is not appropriate for grade 3. [Negation]. (Learning Activity 3).
- -
- The suggesting (22%) and questioning (1%) types of communication occurred the least, compared to the other three categories. There was only one piece of feedback that included a question:
- -
- Yes, it is clear and understandable [Affirmation]. Can you put the units in the multiple choices? [Question] (Learning Activity 3).
- -
- Perfect example related to conceptual and procedural [Praise]. Even better: Explain the reason why its procedural [Suggestion]. (Learning Activity 1).
- -
- …it is a conceptual question [Affirmation] because students can use more than one concept to create this answer. it is a good question! [Praise] provide the rubric for the question please! [Suggestion]. (Learning Activity 2).
- -
- For the question to be more clear change it to the following “Fatima wants to select an excellent location to sell tickets for a graduation ceremony.” [Suggestion]. (Learning Activity 3).
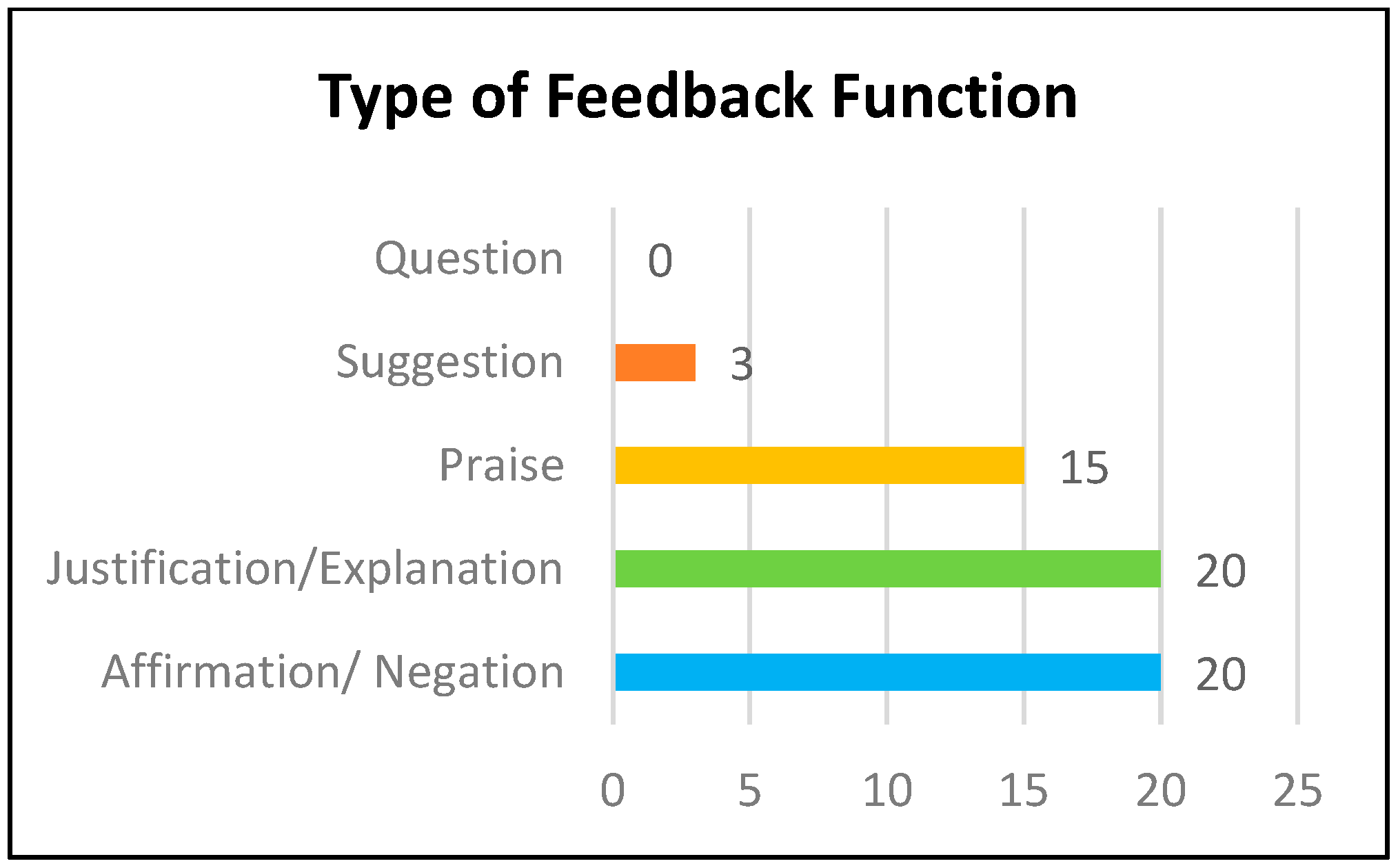
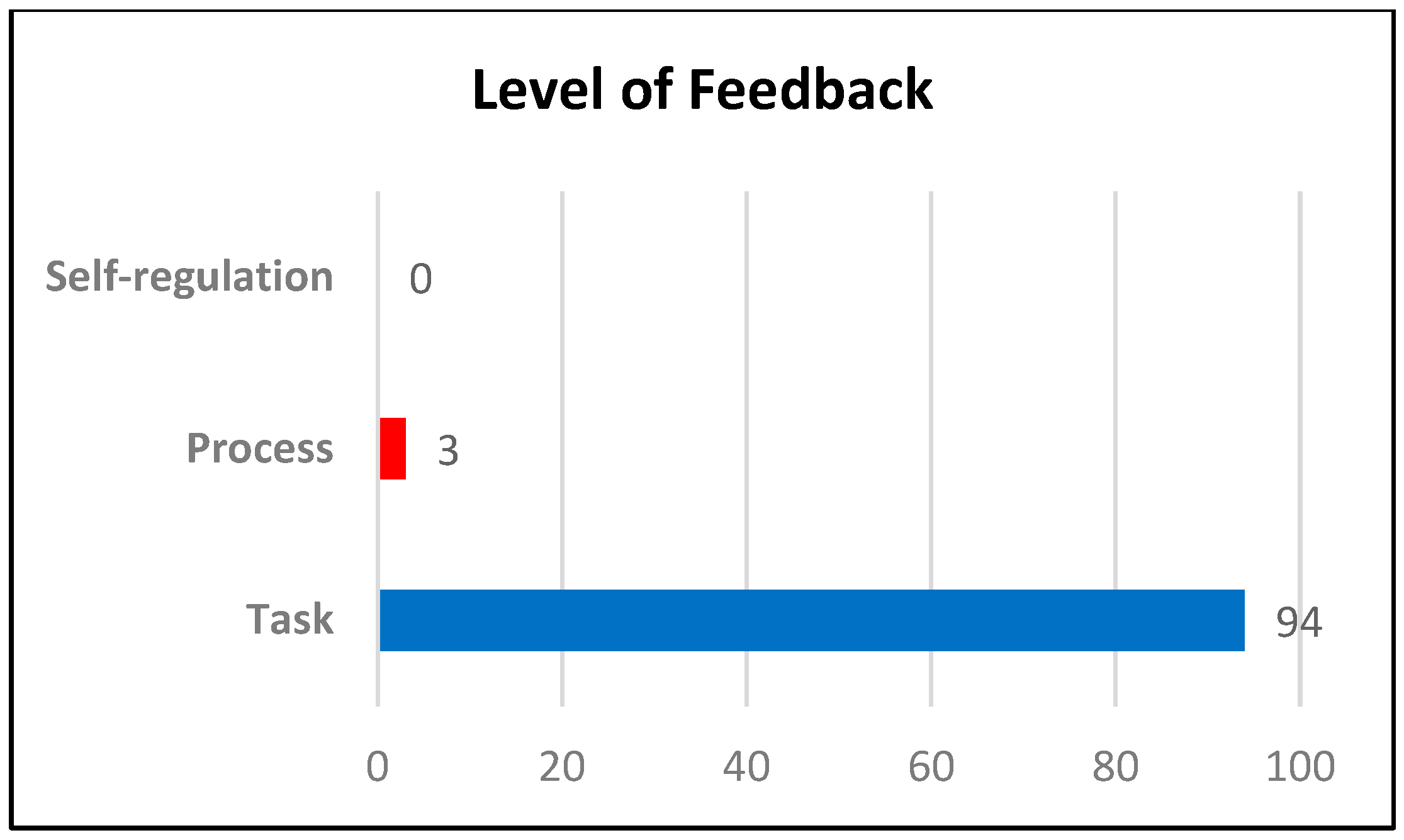
3.2. Level of Feedback
- -
- I agree with you because the example for conceptual involves understanding the relationship between the graph and the radius and procedural question includes operation and action sequence for solving problems. (Learning Activity 1).
- -
- Modify the wording of question 3 by clarifying the phrase ‘cubes of numbers of each cube consisting of 6 numbers’ so it does not cause confusion to the student. (Learning Activity 3).
- -
- Good question. But the rubric is a self-assessment type, I think it is better to change it to three levels of understanding. (Learning Activity 2).
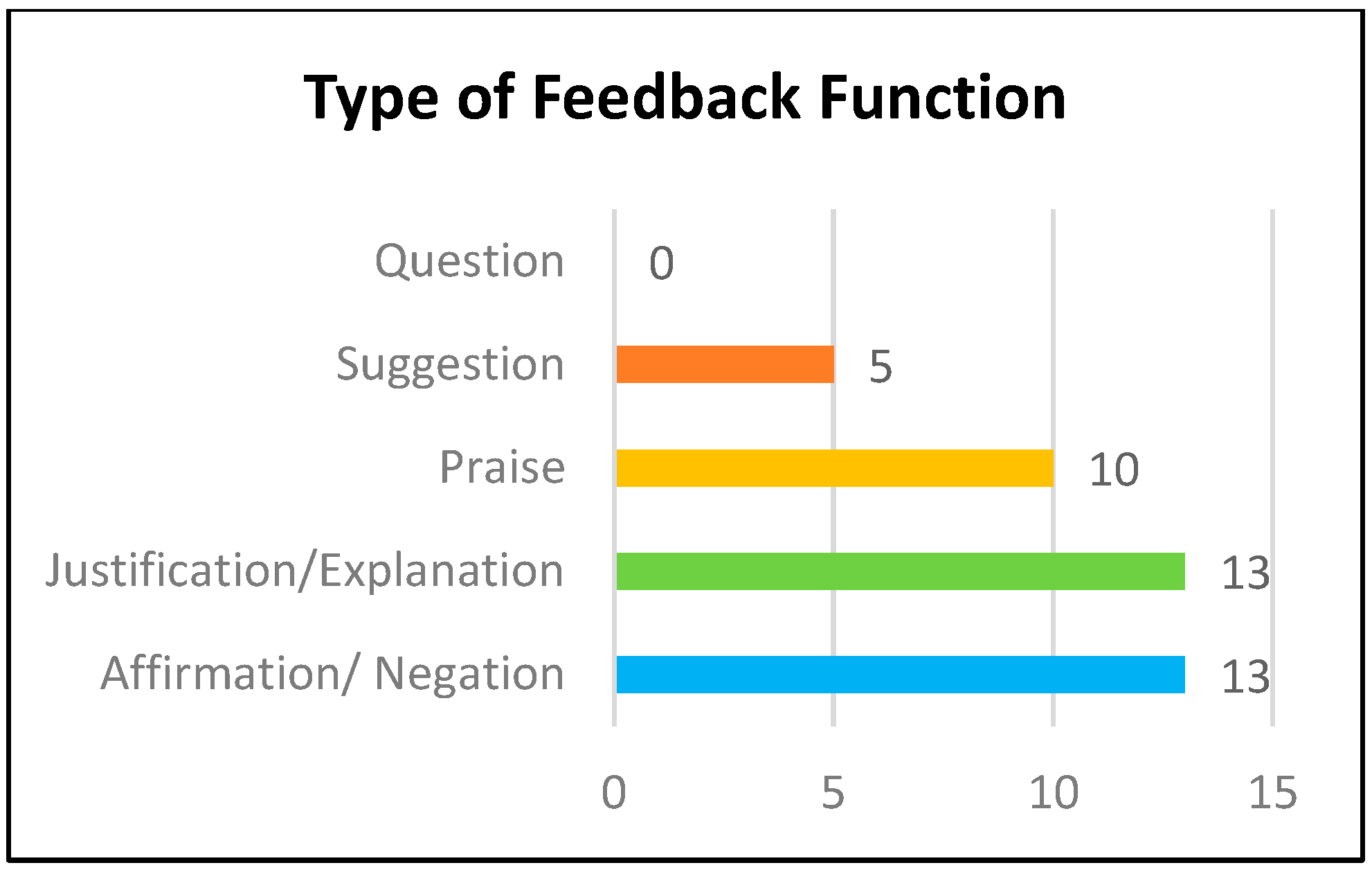
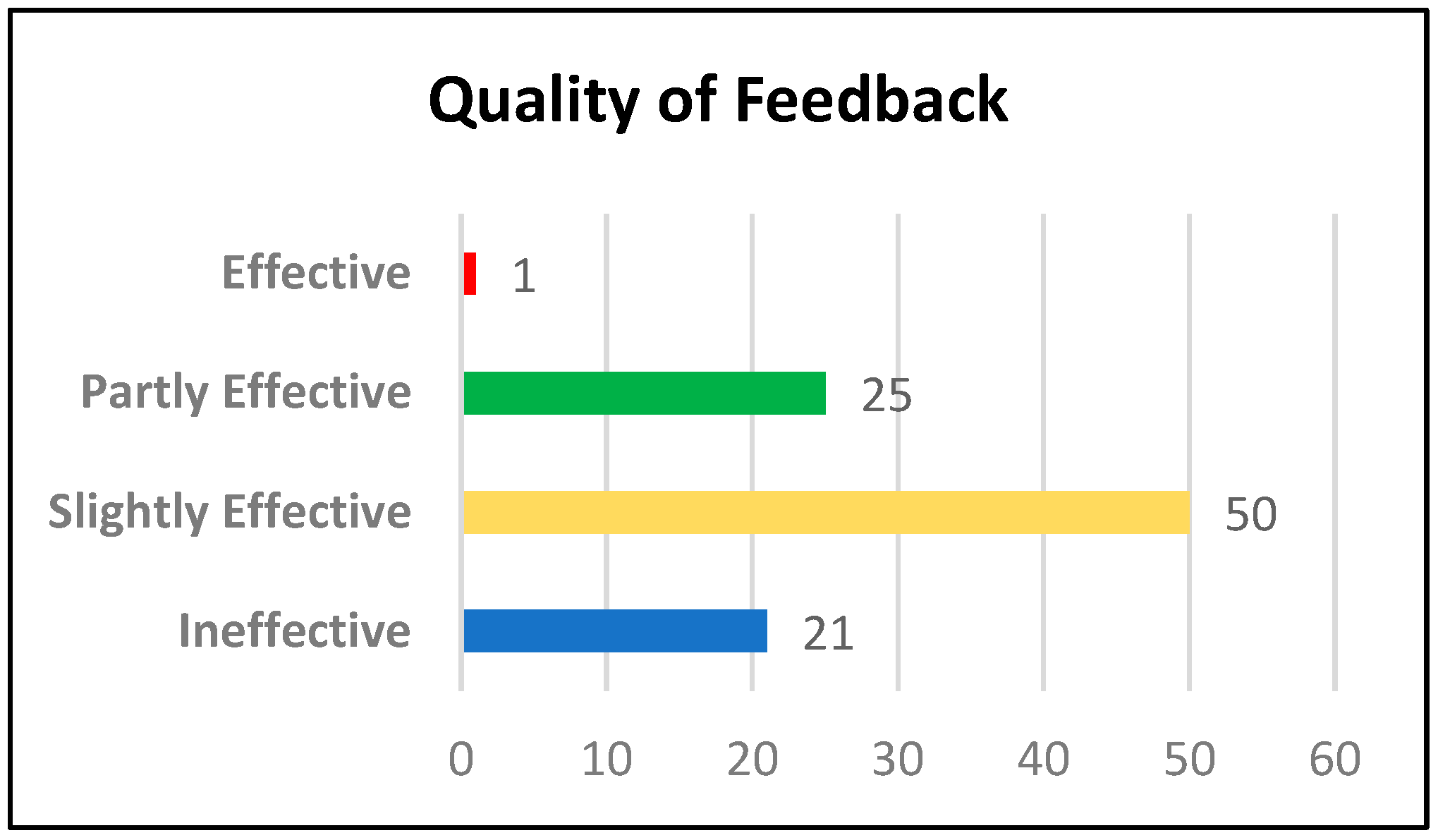
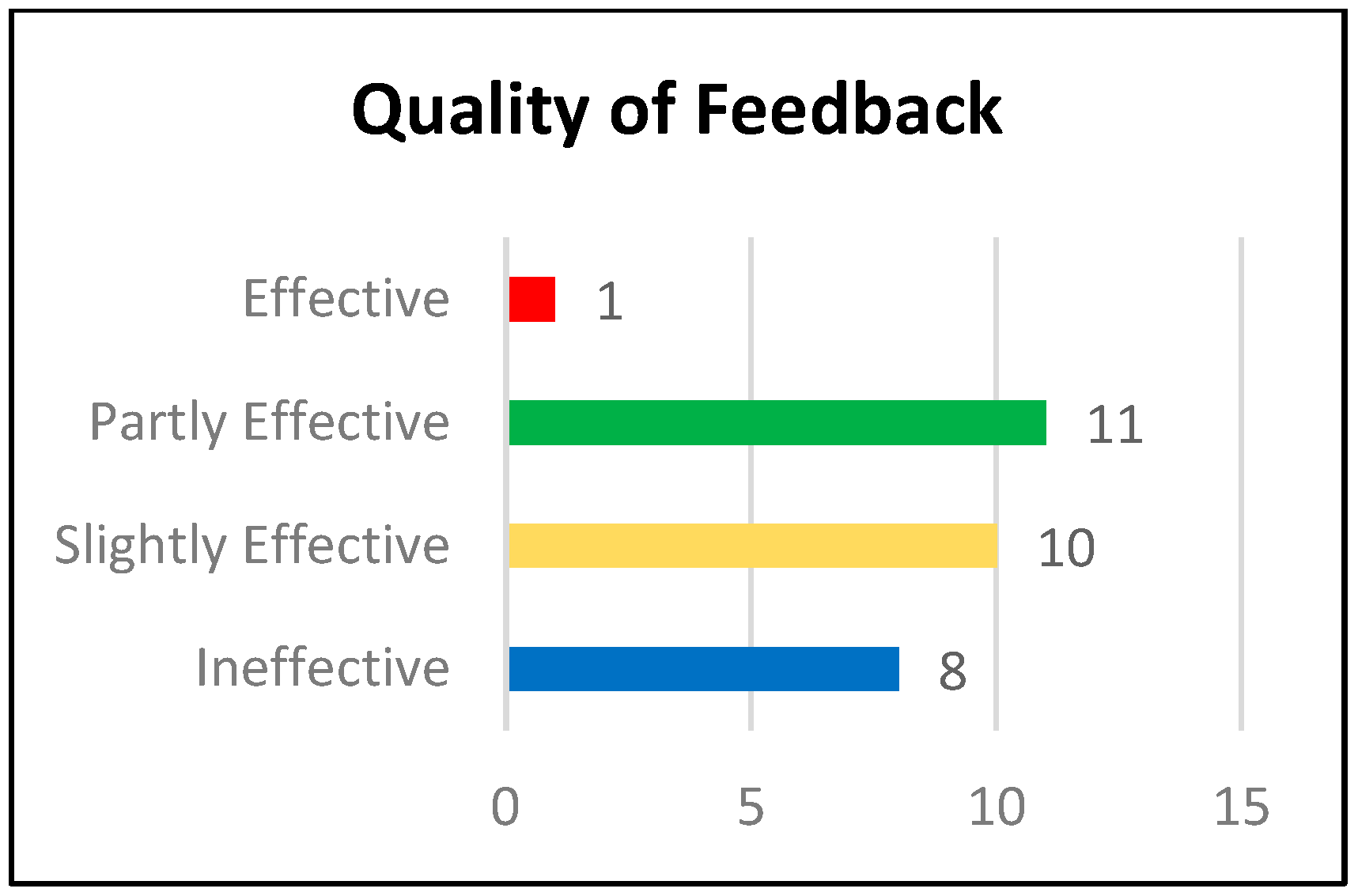
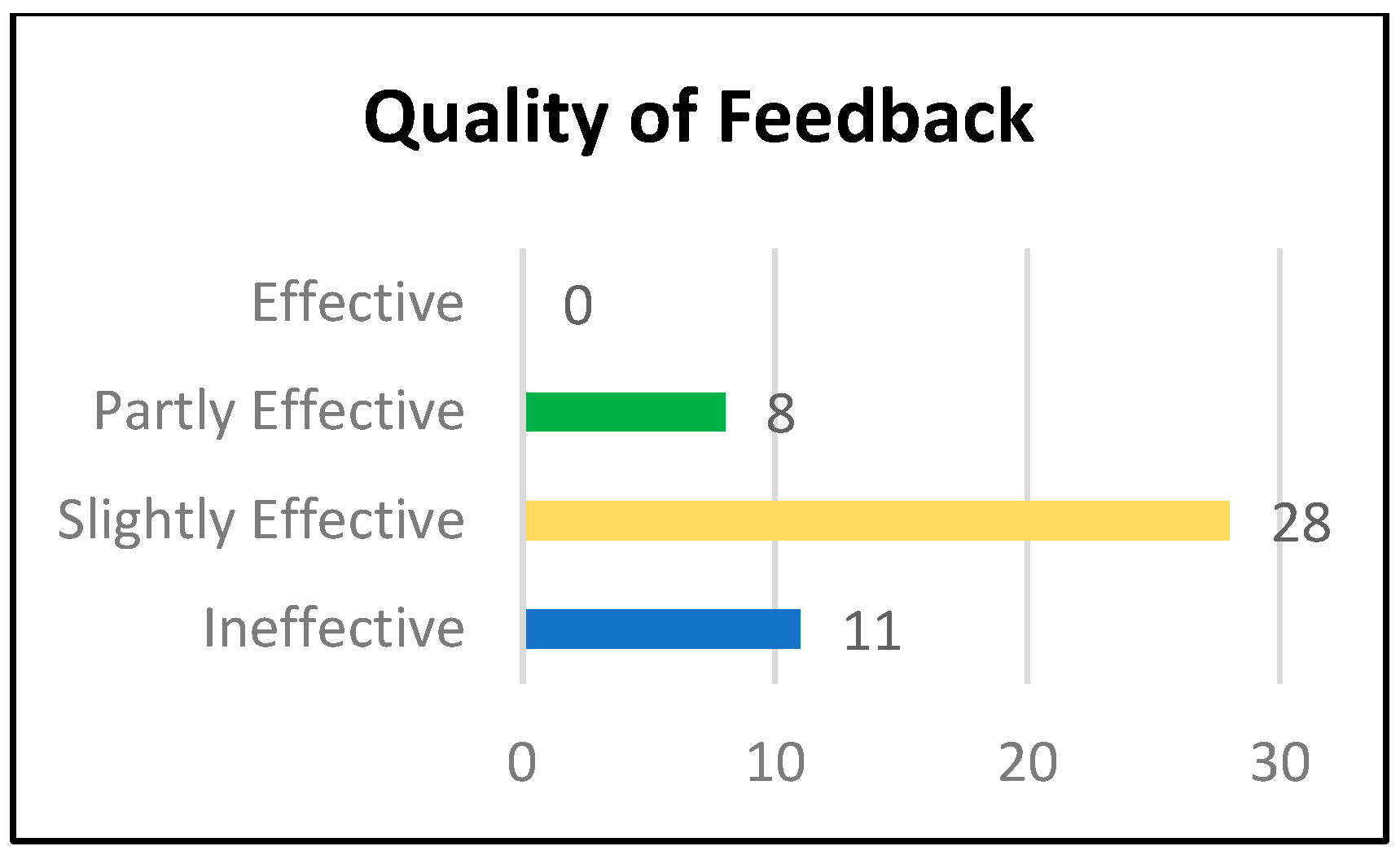
3.3. Quality of Feedback
- -
- Good example: Procedural understanding is when students carry on steps and algorithms and here they follow steps to count units and add numbers to find perimeter and multiply them to find area, so they rarely make deep connections during instruction.
- -
- I think both examples assess Procedural understanding, you could find a non-routine problem to assess conceptual understanding. [Effective] (Learning Activity 1).
- -
- I agree with you that it is routine because the student used to solve this type of question during the lesson but I think it is procedural because you need to follow a procedure to find the perimeter. [Partly Effective] (Learning Activity 2).
- -
- Very clear examples and reasons. [Ineffective] (Learning Activity 1).
- -
- I agree with you, to specify the student who is required to understand the four concepts. [Ineffective] (Learning Activity 2).
- -
- The question is clear and understandable for the student. [Ineffective] (Learning Activity 3).
- -
- A good question that reflects the student’s understanding of the concepts of division, multiplication, and the connection between them. [Slightly Effective] (Learning Activity 3).
- -
- Yes, the students would be able to understand. The pictures help students understand and solve the problem. [Slightly Effective] (Learning Activity 3)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ertmer, P.A.; Richardson, J.C.; Belland, B.; Camin, D.; Connolly, P.; Coulthard, G.; Lei, K.; Mong, C. Using Peer Feedback to Enhance the Quality of Student Online Postings: An Exploratory Study. J. Comput. Commun. 2007, 12, 412–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilporn, G.; Lakhal, S.; Bélisle, M. An examination of teachers’ strategies to foster student engagement in blended learning in higher education. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2021, 18, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, I.; Espasa, A.; Guasch, T. The value of feedback in improving collaborative writing assignments in an online learning environment. Stud. High. Educ. 2012, 37, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espasa, A.; Meneses, J. Analysing feedback processes in an online teaching and learning environment: An exploratory study. High. Educ. 2009, 59, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgermeister, A.; Glogger-Frey, I.; Saalbach, H. Supporting Peer Feedback on Learning Strategies: Effects on Self-Efficacy and Feedback Quality. Psychol. Learn. Teach. 2021, 20, 383–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delante, N.L. Perceived impact of online written feedback on students’ writing and learning: A reflection. Reflective Pract. 2017, 18, 772–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattie, J.; Timperley, H. The Power of Feedback. Rev. Educ. Res. 2007, 77, 81–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, B.; Saab, N.; Broek, P.V.D.; Van Driel, J. The impact of formative peer feedback on higher education students’ academic writing: A Meta-Analysis. Assess. Evaluation High. Educ. 2019, 44, 863–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, D.J.; Macfarlane-Dick, D. Formative assessment and self-regulated learning: A model and seven principles of good feedback practice. Stud. High. Educ. 2006, 31, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsmeier, B.A.; Peiffer, H.; Flaig, M.; Schneider, M. Peer Feedback Improves Students’ Academic Self-Concept in Higher Education. Res. High. Educ. 2020, 61, 706–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Popta, E.; Kral, M.; Camp, G.; Martens, R.L.; Simons, P.R.-J. Exploring the value of peer feedback in online learning for the provider. Educ. Res. Rev. 2017, 20, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, P.; Harrison, C.; Lee, C.; Marshal, B.; Wiliam, D. Assessment for Learning: Putting It into Practice; Open University Press: Maidenhead, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Black, P.; Wiliam, D. Assessment and classroom learning. Assess. Educ. Princ. Policy Pract. 1998, 5, 7–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattie, J.; Clarke, S. Visible Learning: Feedback; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kingston, N.; Nash, B. Formative Assessment: A Meta-Analysis and a Call for Research. Educ. Meas. Issues Pract. 2011, 30, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.T.L.; Peterson, E.R.; Yao, E.S. Student conceptions of feedback: Impact on self-regulation, self-efficacy, and academic achievement. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 2016, 86, 606–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojeij, Z.; Baroudi, S. Student perceptions on peer feedback training using a blended method: A UAE case. Issues Educ. Res. 2018, 28, 655–678. [Google Scholar]
- Huisman, B.; Saab, N.; Van Driel, J.; Broek, P.V.D. Peer feedback on academic writing: Undergraduate students’ peer feedback role, peer feedback perceptions and essay performance. Assess. Evaluation High. Educ. 2017, 43, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, Y.-H.; Hsu, Y.-C. Peer feedback to facilitate project-based learning in an online environment. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 2013, 14, 258–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.Z.F.; Lee, C.Y. Using peer feedback to improve learning via online peer assessment. Turk. Online J. Educ. Technol. 2013, 12, 187–199. [Google Scholar]
- Sharp, L.A.; Rodriguez, R.C. Technology-based peer review learning activities among graduate students: An ex-amination of two tools. J. Educ. Online 2020, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.-F. Transforming and constructing academic knowledge through online peer feedback in summary writing. Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. 2015, 29, 683–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hew, K.F. Student perceptions of peer versus instructor facilitation of asynchronous online discussions: Further findings from three cases. Instr. Sci. 2014, 43, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggins, G. Seven Keys to Effective Feedback. Educ. Leadersh. 2012, 70, 10–16. Available online: https://www.ascd.org/publications/educational-leadership/sept12/vol70/num01/Seven-Keys-to-Effective-Feedback.aspx (accessed on 30 April 2022).
- Silvervarg, A.; Wolf, R.; Blair, K.P.; Haake, M.; Gulz, A. How teachable agents influence students’ responses to critical constructive feedback. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 2020, 53, 67–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchikov, N. Learning Together: Peer Tutoring in Higher Education; Routledge Falmer: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.-F.; Carless, D.R. Peer feedback: The learning element of peer assessment. Teach. High. Educ. 2006, 11, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pellisa, T.; Rotger, N.; Rodríguez-Gallego, F. Collaborative writing at work: Peer feedback in a blended learning environment. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2020, 26, 1293–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazier, R.A. Building Rapport to Improve Retention and Success in Online Classes. J. Political Sci. Educ. 2016, 12, 437–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.; Rossen, S. Teaching Online: A Practical Guide; Houghton-Mifflin: Boston, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Black, A. The Use of Asynchronous Discussion: Creating a Text of Talk. Contemp. Issues Technol. Teach. Educ. 2005, 5. Available online: http://www.citejournal.org/vol5/iss1/languagearts/article1.cfm (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Azaza, M. The Effect of Peer Editing on Improving the Writing Mechanics of Arab Learners. In Achieving Excellence through Life Skills Education; Davidson, P., Al-Hamly, M., Coombe, C., Troudi, S., Gunn, C., Eds.; TESOL Arabia Publications: Dubai, United Arab Emirate, 2013; pp. 299–312. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ghazali, F. Peer feedback for peer learning and sharing. Learn. Teach. High. Educ. Gulf Perspect. 2015, 12, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shine, E.A. Written Feedback in a Freshman Writing Course in the UAE: Instructors’ and Students’ Perspectives on Giving, Getting and Using Feedback. Ph.D. Thesis, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, I.V.D.; Admiraal, W.; Pilot, A. Designing student peer assessment in higher education: Analysis of written and oral peer feedback. Teach. High. Educ. 2006, 11, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ion, G.; Barrera-Corominas, A.; Tomàs-Folch, M. Written peer-feedback to enhance students’ current and future learning. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2016, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.L.; Erbilgin, E. Examining the supervision of mathematics student teachers through analysis of conference communications. Educ. Stud. Math. 2009, 72, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Law, N. Online peer assessment: Effects of cognitive and affective feedback. Instr. Sci. 2011, 40, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattie, J. Visible Learning for Teachers: Maximizing Impact on Learning; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- State Government of Victoria. 2022. Feedback and Reporting. Available online: https://www.education.vic.gov.au/school/teachers/teachingresources/practice/Pages/insight-feedback.aspx#link84 (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Swedberg, R. Exploratory research. In The Production of Knowledge: Enhancing Progress in Social Science; Elman, C., Gerring, J., Mahoney, J., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020; pp. 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldaña, J. The Coding Manual for Qualitative Researchers; SAGE: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Petronzi, R.; Petronzi, D. The Online and Campus (OaC) model as a sustainable blended approach to teaching and learning in higher education: A response to COVID-19. J. Pedagog. Res. 2020, 4, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewski, B.; Zierer, K.; Hattie, J. The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback re-search. Front. Psychol. 2020, 10, 3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spall, S. Peer Debriefing in Qualitative Research: Emerging Operational Models. Qual. Inq. 1998, 4, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarrell, H.; Verbeem, J. Motivating revision of drafts through formative feedback. ELT J. 2007, 61, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, J. Communication for Business and the Professions: Strategies and Skills; Pearson: New South Wales, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Boom, G.v.D.; Paas, F.; van Merriënboer, J.J.; van Gog, T. Reflection prompts and tutor feedback in a web-based learning environment: Effects on students’ self-regulated learning competence. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2004, 20, 551–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Toit, E. Constructive feedback as a learning tool to enhance students’ self-regulation and performance in higher education. Perspect. Educ. 2012, 30, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, D.; Mills, A. The impact of second language proficiency in dyadic peer feedback. Lang. Teach. Res. 2014, 20, 498–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmation/Negation | Feedback shares aspects that the feedback provider agrees or disagrees with the student on in a direct or indirect way. | I agree that the question is procedural. (Direct affirmation) |
| Justification/Explanation | Feedback includes explaining their own perspectives and arguments drawing from related literature and/or personal experiences. | … because usually, students are more familiar with questions that require formulas and steps rather than questions that ask them to explain a statement. |
| Praise | Feedback provides a positive assessment of aspects of the student’s work using favorable comments. | Great questions for grade 5. |
| Suggestion | Feedback gives advice on how to improve the student’s work. | Maybe provide extra paper so students can cut and paste to compare between triangles. |
| Question | Feedback includes asking questions to request further clarification, or explanation or to promote reflection. | Can you put the units in the multiple choices? |
| Level | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Task | Feedback focuses on the quality of how the task was performed. It may include information on the correctness of the assignment, links between concepts, and the acquisition of more knowledge. | A good question that reflects the student’s understanding of the concepts of division, multiplication, and the connection between them. |
| Process | Feedback is about the processes used to complete the task. It may involve a reassessment of the used approaches, offering ways to detect errors, and using different strategies and processes. | I think both examples assess procedural understanding, you could find a non-routine problem to assess conceptual understanding. |
| Self-regulation | Feedback aims at increasing the student’s autonomy in their learning. It may contain comments about self-assessment, reflection, and self-management. | [The current data did not include any feedback that fell into the self-regulation category.] |
| Quality | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Ineffective | Feedback focuses on the student rather than on the task or processes used. Feedback does not provide information about how to improve learning. Feedback includes general comments (praise or criticism) without details. | I agree with you for both questions and reasons. |
| Slightly Effective | Feedback includes information about the task performance or processes used but includes limited details that make it difficult for the student to utilize the feedback to improve their learning. | I agree with you that they can compare and that leads them to do critical thinking. |
| Partly Effective | Feedback involves information about the task performance or processes used. There are justifications, suggestions, or questions that can be used to improve learning; however, these ideas do not promote the use of different processes or self-regulation. | Good example. I agree with you it is routine because it is one step equation. Also, students must know the concept of solving one step equation. But, better if you replace (if not explain her mistake and correct it) by (explain your answer) because your question gave the students the idea that the answer is not correct. |
| Effective | Feedback addresses task goals and the quality of the student’s performance with detailed comments. There are justifications, suggestions, or questions that would lead to enhanced learning, the use of different processes, or self-regulation. | Good example: Procedural understanding is when students carry on steps and algorithms and here they follow steps to count units and add numbers to find perimeter and multiply them to find area, so they rarely make deep connections during instruction. I think both examples assess procedural understanding, you could find a non-routine problem to assess conceptual understanding. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Erbilgin, E.; Robinson, J.M.; Jarrah, A.M.; Johnson, J.D.; Gningue, S.M. Exploring the Type and Quality of Peer Feedback in a Graduate-Level Blended Course. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13060548
Erbilgin E, Robinson JM, Jarrah AM, Johnson JD, Gningue SM. Exploring the Type and Quality of Peer Feedback in a Graduate-Level Blended Course. Education Sciences. 2023; 13(6):548. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13060548
Chicago/Turabian StyleErbilgin, Evrim, Jennifer M. Robinson, Adeeb M. Jarrah, Jason D. Johnson, and Serigne M. Gningue. 2023. "Exploring the Type and Quality of Peer Feedback in a Graduate-Level Blended Course" Education Sciences 13, no. 6: 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13060548
APA StyleErbilgin, E., Robinson, J. M., Jarrah, A. M., Johnson, J. D., & Gningue, S. M. (2023). Exploring the Type and Quality of Peer Feedback in a Graduate-Level Blended Course. Education Sciences, 13(6), 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13060548








