Extensive Reading and Science Vocabulary Learning in L2: Comparing Reading-Only and Reading-While-Listening
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Extensive Reading
1.2. Reading Only (RO) versus Reading-While-Listening (RWL)
1.3. Research Gaps and Research Questions
- To what extent can primary school students learn science vocabulary through an ER program including graded readers of scientific content?
- Are there differences between RO and RWL?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. The ER Program
2.3. Reading Procedure
2.4. Vocabulary Tests
2.5. Data Collection Procedure
2.6. Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Vocabulary Learning in Term 1
3.2. Vocabulary Learning in Term 2
4. Discussion
4.1. Vocabulary Learning in Term 1
4.2. Vocabulary Learning in Term 2
4.3. Limitations and Future Research
5. Conclusions and Pedagogical Implications
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
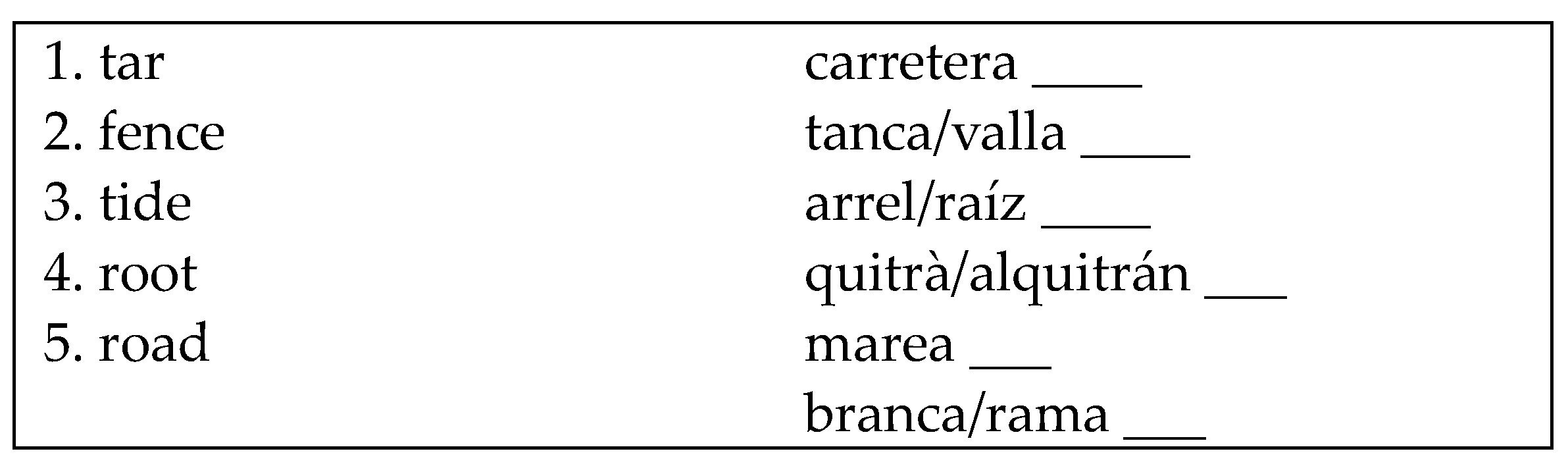
Appendix A
| Test 1 | Test 2 | ||||||||
| Words | Freq. Band | Freq. Readers | Freq. Glossary | Freq. Courseb. | Words | Freq. Band | Freq. Readers | Freq. Glossary | Freq. Courseb. |
| bark | 2 | 4 | 2 | 0 | arrow | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| bat | 2 | 14 | 0 | 1 | lane | 2 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| beetle | 6 | 27 | 0 | 1 | cattle | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| blood | 1 | 8 | 0 | 0 | stream | 2 | 6 | 1 | 0 |
| bone | 1 | 12 | 3 | 2 | glass | 1 | 32 | 2 | 0 |
| brain | 2 | 8 | 0 | 0 | goods | 3 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| bud | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | race | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| burrow | 6 | 4 | 1 | 0 | law | 1 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| claw | 5 | 3 | 1 | 2 | candle | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| crust | 4 | 15 | 1 | 5 | saddle | 5 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| eagle | 4 | 8 | 0 | 1 | tar | 7 | 10 | 1 | 0 |
| feather | 2 | 15 | 2 | 2 | fence | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| field | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | tide | 2 | 6 | 0 | 1 |
| flea | 7 | 12 | 0 | 0 | root | 2 | 10 | 0 | 1 |
| flock | 4 | 7 | 0 | 0 | road | 1 | 15 | 2 | 0 |
| flood | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | shelter | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| fox | 2 | 11 | 2 | 0 | shark | 5 | 58 | 0 | 2 |
| fur | 2 | 33 | 3 | 2 | squid | 8 | 10 | 0 | 1 |
| hill | 1 | 5 | 0 | 2 | heat | 1 | 10 | 0 | 6 |
| hole | 1 | 14 | 3 | 0 | cliff | 2 | 15 | 0 | 3 |
| kite | 6 | 14 | 0 | 0 | steam | 2 | 5 | 1 | 0 |
| land | 1 | 26 | 1 | 19 | nostril | 6 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| moth | 6 | 10 | 0 | 0 | gold | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| mud | 2 | 13 | 0 | 2 | reef | 5 | 17 | 1 | 0 |
| nest | 2 | 26 | 2 | 0 | layer | 3 | 14 | 0 | 14 |
| paw | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0 | hut | 4 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| poison | 2 | 9 | 2 | 0 | shield | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| pond | 4 | 4 | 0 | 1 | path | 2 | 13 | 0 | 0 |
| seal | 2 | 8 | 2 | 0 | army | 2 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| seed | 2 | 25 | 2 | 1 | earthquake | 5 | 12 | 1 | 4 |
| silk | 3 | 12 | 2 | 0 | shell | 2 | 7 | 1 | 4 |
| skin | 1 | 13 | 1 | 4 | eel | 8 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| sloth | 11 | 6 | 1 | 0 | pipe | 2 | 10 | 0 | 1 |
| slug | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | patern | 2 | 5 | 1 | 0 |
| snail | 6 | 11 | 0 | 1 | health | 1 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| soil | 2 | 15 | 3 | 2 | stall | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| stem | 3 | 12 | 0 | 1 | crop | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| swarm | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | fin | 6 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| tadpole | 10 | 10 | 2 | 0 | lake | 1 | 36 | 1 | 4 |
| tail | 1 | 12 | 2 | 10 | clay | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| tooth | 1 | 6 | 1 | 0 | wall | 1 | 14 | 0 | 2 |
| trunk | 2 | 7 | 1 | 5 | coal | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| tusk | 10 | 12 | 1 | 0 | concrete | 3 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| walrus | 12 | 2 | 1 | 0 | jellyfish | 9 | 0 | 1 | |
| wasp | 6 | 13 | 0 | 0 | twin | 2 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| wave | 1 | 7 | 0 | 3 | octopus | 9 | 6 | 0 | 1 |
| web | 4 | 10 | 1 | 0 | limestone | 19 | 0 | 0 | |
| wheel | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | cabbage | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| wing | 2 | 48 | 1 | 6 | danger | 1 | 12 | 3 | 0 |
| wolf | 2 | 6 | 1 | 0 | rope | 2 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| Mean | 3.66 | 11.3 | 0.9 | 1.46 | Mean | 3.12 | 9.08 | 0.36 | 0.98 |
| Median | 2 | 10 | 1 | 0 | Median | 2 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
References
- Nation, P. Is It Worth Teaching Vocabulary? TESOL J. 2021, 12, e564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nation, P. The Four Strands. Innov. Lang. Learn. Teach. 2007, 1, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nation, P.; Waring, R. Teaching Extensive Reading in Another Language; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi, T. A Meta-Analysis of Extensive Reading Research. TESOL Q. 2015, 49, 6–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, R.R.; Bamford, J. Top Ten Principles for Teaching Extensive Reading. Read. Foreign Lang. 2002, 14, 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, S.; Chang, A.C.-S. Second Language Vocabulary Learning through Extensive Reading with Audio support: How do frequency and distribution of occurrence affect learning? Lang. Teach. Res. 2015, 19, 667–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, S.; Chang, A.C.-S. How Does Mode of Input Affect the Incidental Learning of Collocations? Stud. Second Lang. Acquis. 2022, 44, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.; Waring, R.; Donkaewbua, S. Incidental Vocabulary Acquisition from Reading, Reading-While-Listening, and Listening to Stories. Read. Foreign Lang. 2008, 20, 136–163. [Google Scholar]
- Tuzcu, A. The Effects of Input Mode in Learning Declarative and Nondeclarative Knowledge of L2 Collocations. System 2023, 113, 103006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, R.; McLean, S. Exploration of the Core and Variable Dimensions of Extensive Reading Research and Pedagogy. Read. Foreign Lang. 2015, 27, 160–167. [Google Scholar]
- Beglar, D.; Hunt, A. Pleasure Reading and Reading Rate Gains. Read. Foreign Lang. 2014, 26, 29–48. [Google Scholar]
- Beglar, D.; Hunt, A.; Kite, Y. The Effect of Pleasure Reading on Japanese University EFL Learners’ Reading Rates. Lang. Learn. 2012, 62, 665–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.; Macalister, J. Online Extensive Reading in an EFL Context: Investigating Reading Fluency and Perceptions. Read. Foreign Lang. 2021, 33, 1–29. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10125/67391 (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- McLean, S.; Rouault, G. The Effectiveness and Efficiency of Extensive Reading at Developing Reading Rates. System 2017, 70, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, T. Extensive Reading: Speed and Comprehension. Read. Matrix 2001, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Krashen, S. Extensive Reading in English as Foreign Language by Adolescents and Young Adults: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Foreign Lang. Teach. 2007, 7, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Waring, R.; Takaki, M. At What Rate Do Learners Learn and Retain New Vocabulary from Reading a Graded Reader? Read. Foreign Lang. 2003, 15, 130–163. [Google Scholar]
- Pellicer-Sánchez, A.; Schmitt, N. Incidental Vocabulary Acquisition from an Authentic Novel: Do Things Fall Apart? Read. Foreign Lang. 2010, 22, 31–55. [Google Scholar]
- Pigada, M.; Schmitt, N. Vocabulary Acquisition from Extensive Reading: A Case Study. Read. Foreign Lang. 2006, 18, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, S.A.; Chang, A.C.-S. Vocabulary Learning through Assisted and Unassisted Repeated Reading. Can. Mod. Lang. Rev. 2012, 68, 267–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C. Integrating Extensive Reading in the Task-Based Curriculum. ELT J. 2005, 59, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutorwick, T.J.; Macalister, J.; Elgort, I. Two Approaches to Extensive Reading and Their Effects on L2 Vocabulary Development. Read. Foreign Lang. 2019, 31, 150–172. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, E.; Hulstijn, J.H.; Sercu, L.; Lutjeharms, M. Learning L2 German Vocabulary through Reading: The Effect of Three Enhancement Techniques Compared. Lang. Learn. 2009, 59, 113–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonbul, S.; Schmitt, N. Direct Teaching of Vocabulary after Reading: Is It Worth the Effort? ELT J. 2010, 64, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tragant, E.; Pellicer-Sánchez, A. Young EFL Learners’ Processing of Multimodal Input: Examining Learners’ Eye Movements. System 2019, 80, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicer, A.; Tragant, E.; Conklin, K.; Rodgers, M.; Serrano, R.; Llanes, À. Young Learners’ Processing of Multimodal Input and Its Impact on Reading Comprehension: An Eye-Tracking Study. Stud. Second Lang. Acquis. 2020, 42, 577–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, R.; Pellicer, A. Young L2 Learners’ Online Processing of Information in a Graded Reader during Reading-Only and Reading-While-Listening Conditions: A Study of Eye-Movements. Appl. Linguist. Rev. 2022, 13, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero Perez, M. Second or Foreign Language Learning through Watching Audio-Visual Input and the Role of On-Screen Text. Lang. Teach. 2022, 55, 163–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.V.; Peters, E. Incidental Learning of Collocations from Meaningful Input: A Longitudinal Study into Three Reading Modes and Factors that Affect Learning. Stud. Second Lang. Acquis. 2021, 43, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.N.Y.; Lu, C.; Webb, S. Incidental Learning of Collocations in an Academic Lecture through Different Input Modes. Lang. Learn. 2022, 72, 728–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conklin, K.; Alotaibi, S.; Pellicer-Sánchez, A.; Vilkaite-Lozdiene, L. What Eye-Tracking Tells Us about Reading-Only and Reading-While-Listening in a First and Second Language. Second Lang. Res. 2020, 36, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.N.Y.; Lu, C.; Webb, S. Open Access Academic Lectures as Sources of Incidental Vocabulary Learning: Examining the Role of Input Mode, Frequency, Type of Vocabulary, and Elaboration. Appl. Linguist. 2022, amac044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightbown, P.M. Can They Do It Themselves? A Comprehension-Based ESL Course for Young Children. In Comprehension-Based Second Language Teaching; Courchene, R., St John, J., Therrien, C., Glidden, J., Eds.; University of Ottawa Press: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1992; pp. 353–370. [Google Scholar]
- Tragant, E.; Muñoz, C.; Spada, N. Maximizing Young Learners’ Input: An Intervention Program. Can. Mod. Lang. Rev. 2016, 72, 234–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tragant, E.; Vallbona, A. Reading while Listening to Learn: Young EFL learners’ Perceptions. ELT J. 2018, 72, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tragant, E.; Llanes, À.; Pinyana, À. Linguistic and Non-Linguistic Outcomes of a Reading-while-listening Program for Young Learners of English. Read. Writ. 2019, 32, 819–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, T.; Lextutor. Vocabprofile [Computer Program]. Available online: https://www.lextutor.ca/vp/comp/ (accessed on 17 March 2023).
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 27.0; IBM Corp: Armonk, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Laufer, B. Vocabulary Acquisition in a Second Language: Do Learners Really Acquire Most Vocabulary by Reading? Some Empirical Evidence. Can. Mod. Lang. Rev. 2003, 59, 567–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group | Pre-Test/50 | Post-Test/50 | Delayed Post-Test/50 | Immediate Gains (%) | Long-Term Gains (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RO (n = 22) | 27.31 (10.5) | 37.09 (10.8) | 35.94 (10.3) | 46.7% (27.5) | 44.9 (24.7) |
| RWL (n = 47) | 28.97 (9.4) | 39.00 (9.9) | 38.04 (9.5) | 54.1% (27.0) | 50.4% (26.2) |
| Control (n = 25) | 28.96 (9.3) | 33.80 (9.7) | 32.80 (10.5) | 20.9% (36.0) | 12.6% (37.9) |
| Group | Pre-Test/50 | Post-Test/50 | Immediate Gains (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RO (n = 24) | 28.83 (9.6) | 30.50 (8.71) | 5.90% (26.77) |
| RWL (n = 47) | 28.59 (10.3) | 33.04 (9.6) | 17.92% (35.4) |
| Control (n = 25) | 27.76 (8.7) | 31.48 (11.2) | 14.84% (37.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serrano, R. Extensive Reading and Science Vocabulary Learning in L2: Comparing Reading-Only and Reading-While-Listening. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13050493
Serrano R. Extensive Reading and Science Vocabulary Learning in L2: Comparing Reading-Only and Reading-While-Listening. Education Sciences. 2023; 13(5):493. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13050493
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerrano, Raquel. 2023. "Extensive Reading and Science Vocabulary Learning in L2: Comparing Reading-Only and Reading-While-Listening" Education Sciences 13, no. 5: 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13050493
APA StyleSerrano, R. (2023). Extensive Reading and Science Vocabulary Learning in L2: Comparing Reading-Only and Reading-While-Listening. Education Sciences, 13(5), 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13050493





