Abstract
In recent years, many research studies have focused on personalized e-learning. One of the most crucial parts of any learning environment is having a learning style that focuses on individual learning. In this paper, we propose an approach to personalizing learning resources based on students’ learning styles in a virtual learning environment to enhance their academic performance. Students’ interactions with the learning management system are utilized to analyze learners’ behaviors. The Felder–Silverman Learning Style Model (FSLSM) is used to map students’ interactions with online learning resources to learning style (LS) features. The learning style and demographic features are then utilized for training machine learning models to predict students’ academic performance in each quarter of courses. The most accurate prediction model for each quarter is then used to find learning style features that maximize students’ pass rates. We statistically prove that students whose actual learning style features were close enough to the ones calculated by the approach achieved better grades. To improve students’ academic performance each quarter, we suggest two strategies based on the learning style features calculated by the process.
1. Introduction
Through online platforms, virtual learning has emerged as a potential educational method in recent years. Computer technology and Internet availability play a significant role in this. The recent COVID-19 pandemic has also highlighted the necessity and significance of virtual education.
One of the most crucial parts of any learning environment is having a learning style that focuses on individual learning. A student’s learning style can be defined as a way to improve concentration while learning using their behavior, such as reading, seeing, observing, and imitating [1]. A student’s learning style profile indicates possible strengths as well as potential habits or tendencies that could cause academic difficulty. In the education environment, most studies find that learning style impacts students’ learning attitude, satisfaction level, and academic achievement. It can have a significant impact on learning attitudes. On the contrary, the effectiveness of learning is reduced when students’ learning styles are mismatched [2]. Previous researchers have argued for considering learning styles in developing e-learning systems in order to maintain students’ interest, so they can learn more effectively [3]. In the e-learning system, it is crucial to analyze students’ behaviors to find appropriate learning styles. During the learning process, students’ interactions with online learning platforms are captured in large amounts of data. The learners’ behaviors during the learning period can be analyzed using the collected data [4].
In this paper, we propose a new framework to detect students’ learning styles based on their behaviors in an online learning environment to improve their academic performance. Specifically, we aim to answer two main research questions: (1) How can students’ learning styles be detected in online learning environments? (2) In Virtual Learning Environments, how can students’ learning styles be utilized to enhance their pass rate? The Open University Learning Analytics Dataset (OULAD) was utilized to test the proposed approach. The Felder–Silverman Learning Style Model (FSLSM) was used to map students’ interactions with online learning resources to learning style (LS) features. The learning style and demographic features were then utilized for training machine learning models to predict students’ academic performance in each quarter of courses. The most accurate prediction model for each quarter was then used to find learning style features that maximize students’ pass rates. We statistically prove that students whose actual learning style features were close enough to the ones calculated by the approach achieved better grades. To improve students’ academic performance each quarter, we suggest two strategies based on the learning style features calculated by the process.
The online learning process involves teaching remote audiences using an innovative approach via the Internet [5]. In e-learning, information technology is considered a bridge of interaction between teachers, students, and the learning content [6]. Although the Internet can be used as a means of communication to connect teachers, students, and learning content, an online information system is required to manage the progress of students who have been monitored by teachers, including learning management systems (LMS), course management systems (CMS), massive open online courses (MOOCs), virtual learning environments (VLEs), and intelligent tutoring systems (ITS) [7].
An individual’s learning style describes how they process information and approach learning tasks [8]. Several studies have been conducted on learning styles. In one comprehensive study, 71 different learning style models were identified [1]. This context makes it difficult to select an appropriate model. The Felder–Silverman Learning Style Model (FSLSM) categorizes learners as visual or verbal, active or reflective, sensitive or intuitive, and sequential or global; the Myers–Briggs Type Indicator classifies the cognitive functions of learners into the categories of extraversion or introversion, sensing or intuition, thinking or feeling, and judging or perceiving [9]; the Honey and Mumford model groups learners into four learning styles named activist, reflector, theorist, and pragmatist [10]; the Kolb learning model classifies learners into the categories of concrete experience or abstract conceptualization and active experimentation or reflective observation [11]; the VARK learning style categorizes the learning styles of learners as visual, aural, read/write, and kinesthetic [12]. Online learning has the advantage of taking individual characteristics into account. In education, personalized learning refers to a model that considers the differences between students. By taking into account students’ interests and abilities, personalized learning supports students’ ability to master the material [13].
In the current literature, two main techniques have been utilized to detect learning styles: (1) collaborative techniques which are based on a questionnaire and (2) automatic approaches in which learners’ learning styles can be detected based on their behaviors and actions during a learning session automatically [14]. In collaborative techniques, learners’ learning styles are determined based on a questionnaire designed by different learning style models such as Honey and Mumford, Kolb, Vak, and FSLSM. Then machine learning, data mining, and rule-based methods are employed to detect the learning styles [15,16,17]. Recently, most researchers have opted for an automatic approach. By capturing real data about learners’ behaviors, several approaches have been employed in automatic techniques to detect learning styles [18,19,20].
Some research studies employ machine learning techniques to analyze student behavior and predict students at risk of failing [21,22,23]. Machine learning techniques such as support vector machines (SVM), naïve Bayes (NB), logistic regression, random forest (RF), and XGBoost (XGB) are utilized by Holsta et al. to identify at-risk students within a specified deadline. Based on updated data about the entities, predictions are calculated at different time instants [24]. Another set of studies in the literature uses a sequential approach to convert the duration of the course into a weekly basis and assesses student performance based on their interactions with the learning environment. For instance, Marbouti and Diefes-Dux employed machine learning algorithms to predict at-risk-of-failure students in their first engineering year’s 2nd, 4th, and 9th weeks [25]. Adnan et al. divided the course into 20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, and 100% of its length and proposed a predictive model to facilitate instructors’ timely interventions. They used machine learning and deep learning algorithms to identify at-risk students early in the course. The experimental results revealed that the predictive model trained by RF gave the most accurate results [26].
Alhakbani and Alnassar systematically reviewed the benchmark studies performed using OULAD as one of the most comprehensive datasets in the learning analytics domain for evaluating students’ performance in a VLE [27]. Based on their review paper, a wide range of learning-based algorithms have been reported in the literature to address the problem, including GMM, k-NN, LR, SVM, NB, RF, XGBoost, LR, ANN, LSTM, DRF, GBM, GLM, RTV-SVM, RNN-GRU, IOHMM, DT, PNN, LDA, BLR, RLR, ANOVA, RFECV, MLP, SC-GAN, ID3, and CART. In addition, the OULAD dataset was reported to detect at-risk students, detect early dropouts, and predict performance on final exams.
2. Materials and Methods
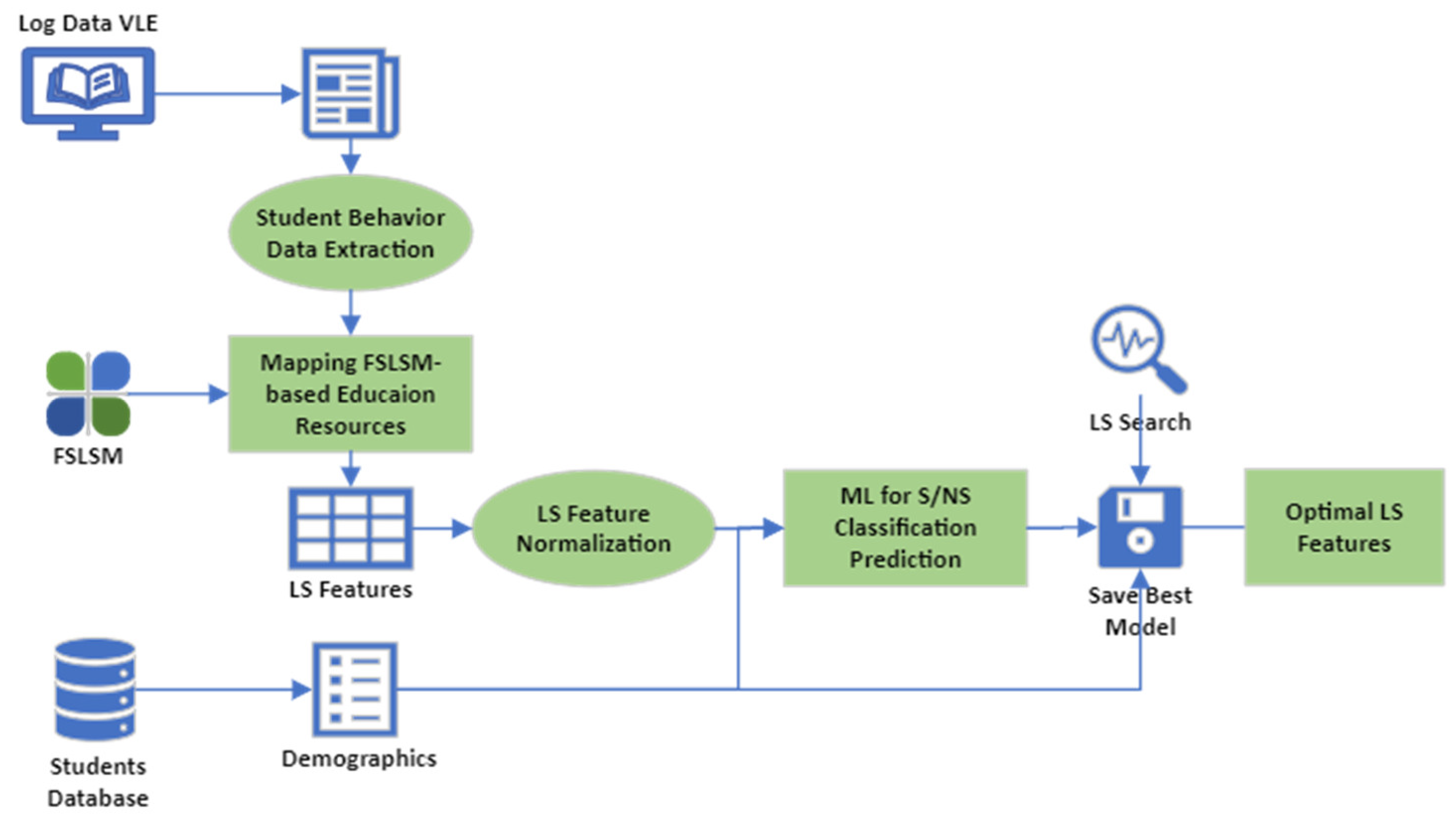
Figure 1 describes a general description of the LSOpt (Learning Style Optimization) system:
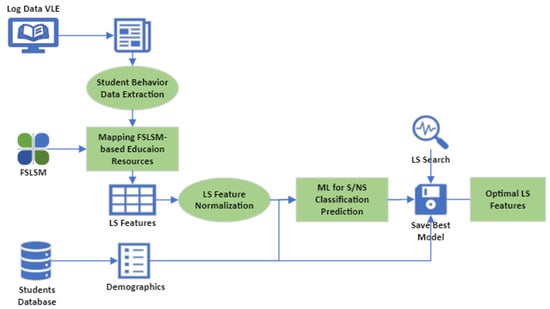
Figure 1.
LSOpt System Design.
Figure 1 shows the system design for LSOpt. Students’ behaviors are captured using their activity logs in the VLE. Using FSLSM, we label education resources and assign each VLE activity type to FSLSM-based classes. Each LS feature is the sum of the students’ visits to each VLE activity type (learning objective) set to that feature. The normalized LS features and the students’ demographics are considered the input variables to train machine learning models to predict the probability of satisfactory grades that students achieved. Therefore, the output is the students’ pass rate. The best model with the highest AUC and accuracy will be saved. Then, we do a grid search to find the LS features that maximize the probability of satisfactory grades. The process detects students’ learning styles based on their behavior and interactions with the VLE to enhance their academic performance. The system consists of two main steps and the input and output variables are different in each step, which will be described in detail in Section 2.2.
2.1. Dataset
This research is based on the publicly available dataset called Open University Learning Analytics Dataset (OULAD), provided by the Open University (OU), U.K. [28]. Data were collected from courses presented at the OU from 2013 to 2014. Courses are called modules at the OU and can be offered multiple times during the year. The dataset contains seven selected courses (22 module presentations) with 32,593 registered students. Typically, presentations take nine months to complete. The VLE system makes module resources available a few weeks before the start of the presentation. Several months before the module’s start date, students can sign up for it. They can do this until two weeks after the official start date of the module. Several assessments are included in each module. The dataset is available as a set of separate CSV files (comma-separated values), and each file contains one ‘database’ table. Generally, this dataset has three types of data: demographics, performance, and learning behavior. In preprocessing steps, first, we removed students who withdrew from the module presentations. Our goal was the early prediction of at-risk students based on their learning behavior. We divided the length of the courses into four different quarters in which there was at least one assessment in each quarter of each course. Each course group was divided into quarters to contain 25 percent of the course length. After that, we removed the students that received zero in their assessment scores in all quarters of the course. The details of the 22 module presentations after preprocessing are described in Table 1.

Table 1.
Module presentation details after preprocessing.
In each quarter of the course, we mapped students’ learning behaviors (interactions with VLE) to learning style features based on FSLSM. OULAD offers various learning resources for learners to learn and communicate, such as video, wiki, discussion forums, assessments, etc. There are 20 different activity types in the “vle” table that capture all learners’ interactions (click streams) with the VLE during the length of the course. The FSLSM is used to map the learners’ behaviors. This is carried out using the literature to determine which category of learning style a student belongs to, based on the student’s behavioral characteristics, as shown in Table 2 [29,30].

Table 2.
Mapping activity types to learning style features based on FSLSM.
Table 3 represents all categories of features, including demographic characteristics, learning style features, and assessment grades.

Table 3.
Features categories in each quarter.
2.2. Methodology
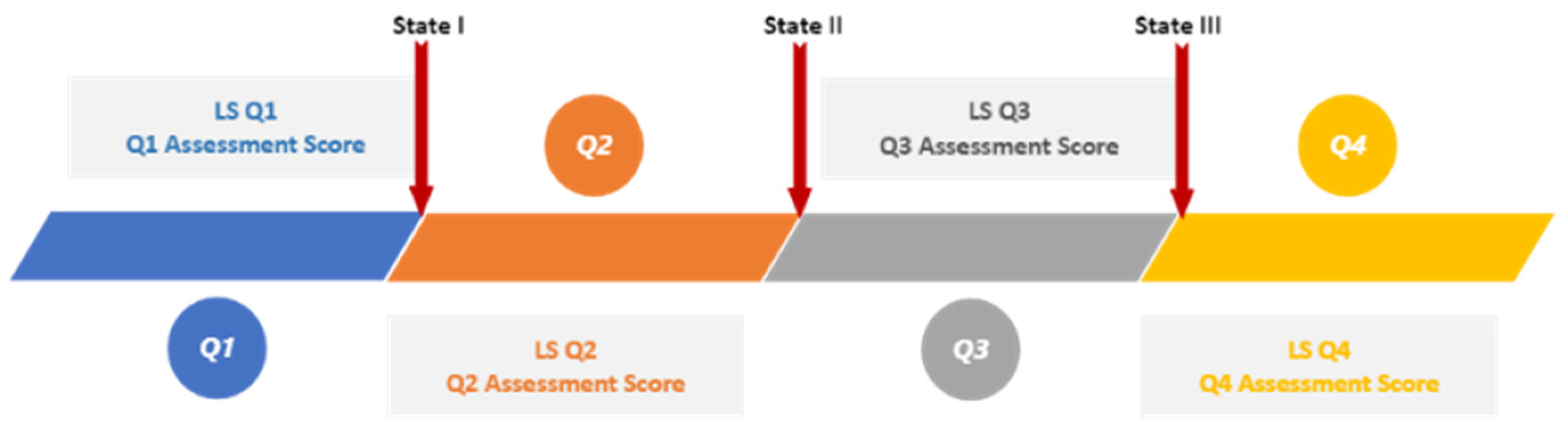
We aimed to find the learning style features that maximize the probability of satisfactory grades in each quarter. We also wanted to see how students’ learning behaviors change over time as they approach the end of a course. Figure 2 shows features including LS features and assessment grades in each quarter.
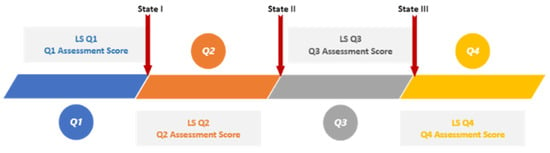
Figure 2.
Module presentation quarters and features.
As Figure 2 illustrates, we considered three states to find the LS features that maximize the probability of satisfactory grades. The process is quite similar in all states, but the input features and target variables differ based on the quarter. In the following sections, we explain the process in each state.
- (1)
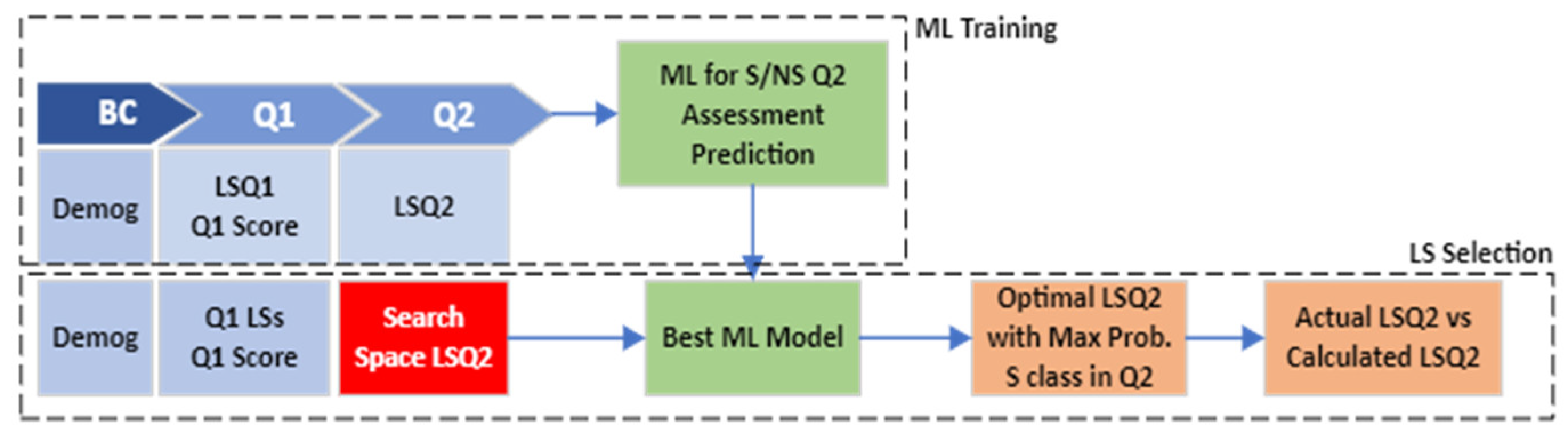
- State I—Beginning of Q2: Find LSs in Q2 that maximize the probability of satisfactory grades in Q2. Figure 3 explains the approach used in State I. It consists of two main processes including ML Training and LS Selection.
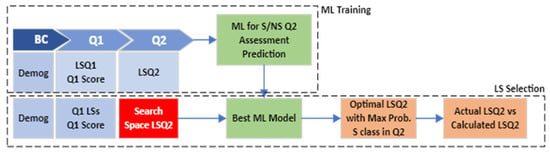 Figure 3. State I modeling process.
Figure 3. State I modeling process.
In ML Training, we aim to consider a binary classification problem in which the classes are satisfactory or not satisfactory (S/NS) assessment grades that students achieved in Q2. We assumed the assessment grades less than 70 as NS; otherwise, S. The input variables include demographic characteristics, LS features in Q1, assessment grades in Q1, and LS features in Q2. We divided the data into 70% and 30% as training and test sets and applied 10-fold cross-validation and feature normalization to improve the performance of the model. After training different machine learning models, we chose the best model based on the AUC score, evaluated it on the test set, and saved the best model.
LS Selection is the process of selecting the learning style features in Q2 to maximize the probability of satisfactory assessment grades in Q2. Demographics, LSs in Q1, and Q1 assessment scores are input variables to the prediction model. However, instead of LSs in Q2, we conducted a grid search on LS space to find the LS values in Q2 that maximize the probability of satisfactory grades in Q2. We considered the LSs as decision variables and defined some criteria to calculate them. The criteria for the grid search are: (1) each LS feature should be between zero and one; (2) the summation of the LS values should be equal to one. In each iteration, we generated a different set of values for LSs, then combined them with the demographic features, LSs in Q1, and Q1 assessment grade and give them with the saved best model as inputs. The outputs are the probability of the S or NS classes. Our goal here was to maximize the probability of satisfactory results for each student. Therefore, for each student, we drew the LS search space and selected the ones that maximize the probability of the S class.
We defined a threshold for comparing the actual LS features and calculated ones in Q2. If the difference between the actual and calculated LS features was less than the thresholds, we classified those instances in the “Supported” category; otherwise, they were classified in the “Not Supported” category. Finally, the assessment grades in Q2 were statistically compared between the Supported and Not Supported categories.
- (2)
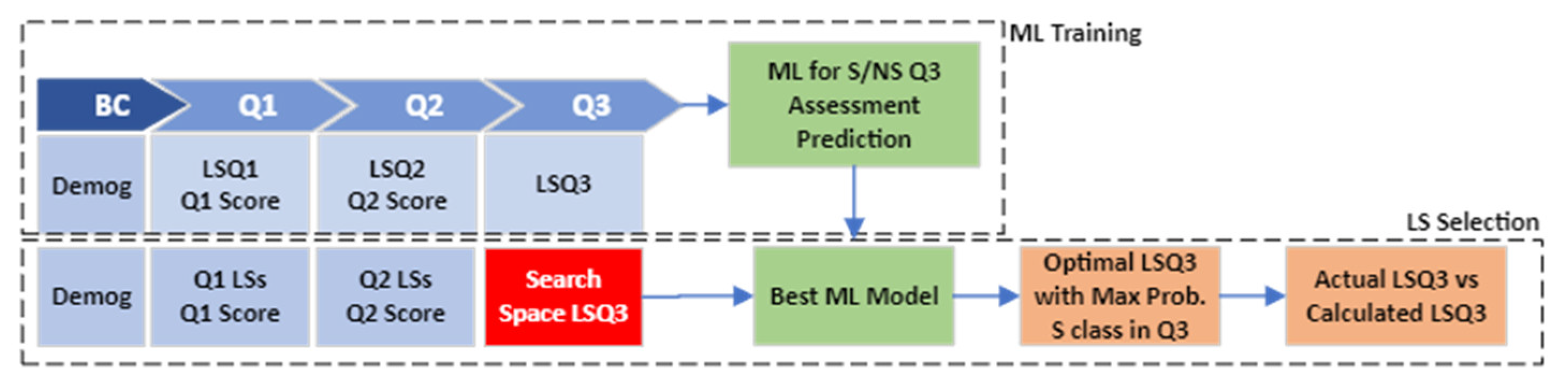
- State II—Beginning of Q3: Find LSs in Q3 to maximize the probability of satisfactory grades in Q3. The modeling process in state II is shown in Figure 4. It also consists of the same steps in state I including ML Training and LS Selection.
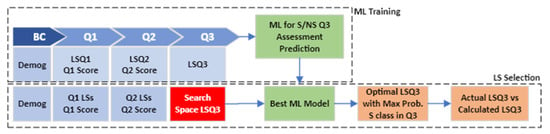 Figure 4. State II modeling process.
Figure 4. State II modeling process.
Here, in the ML Training section, the input variables are demographics, LSs in Q1, assessment grades in Q1, LSs in Q2, assessment grades in Q2, and LSs in Q3, which are used to train machine learning models to predict the S/NS classes in Q3. Moreover, in the LS Selection process, the grid search is conducted on the LS space to find the values that maximize the probability of satisfactory grades in Q3. Then, the actual LSs in Q3 are compared with the calculated ones based on a defined threshold. Finally, the Q3 assessment grades are statistically compared between the Supported and Not Supported categories.
- (3)
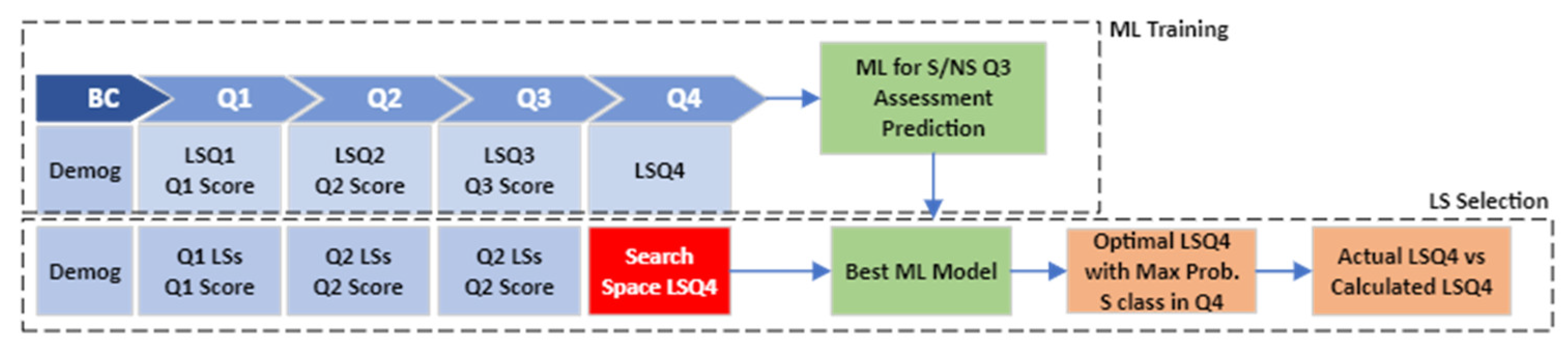
- State III—Beginning of Q4: Find LSs in Q4 to maximize the probability of satisfactory grades in Q4. Figure 5 depicts the modeling process in state III, which includes ML Training and LS Selection steps.
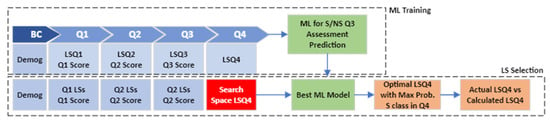 Figure 5. State III modeling process.
Figure 5. State III modeling process.
In the ML Training section of this state, we utilized demographic features, students’ interactions (LS features) in all quarters, and assessment grades in three previous quarters to train machine learning models for predicting the S/NS classes in Q4. In addition, the grid search in the LS Selection process is conducted to discover the LS values in Q4 that maximize the probability of satisfactory grades in Q4. The comparisons are then made based on the defined threshold between actual and calculated LSs in Q4. Lastly, statistical tests are utilized to compare the Q4 assessment grades between the Supported and Not Supported categories.
3. Results
This section represents the results of machine learning models of the ML Training process in all states. As mentioned in the previous section, 70% of the data are used for the training set, and 30% are considered the test set. A 10-fold cross-validation was also used to avoid overfitting. Table 4 summarizes the accuracy, AUC, recall, precision, and F1 score of different machine learning algorithms on the training set in state I (beginning of Q2). All experiments were performed using Python version 3.9.0.

Table 4.
Results of machine learning models—State I.
Table 4 represents that the gradient boosting classifier (GBC) outperforms other algorithms in terms of AUC. The evaluation results using the test set are also shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Evaluation results of the best model using the test set—State I.
Table 6 represents the prediction results of different machine learning algorithms on the training set in state II (beginning of Q3). Regarding AUC, the gradient boosting classifier performs better than the other machine learning models.

Table 6.
Results of machine learning models—State II.
Table 7 also summarizes the accuracy, AUC, recall, precision, and F1 score of the best model (gradient boosting classifier) on the test set.

Table 7.
Evaluation results of the best model using the test set—State II.
The accuracy, AUC, recall, precision, and F1 scores of different machine learning algorithms on the training set in state III (beginning of Q4) are presented in Table 8.

Table 8.
Results of machine learning models—State III.
The results show that the light gradient boosting machine (LGBM) outperforms other algorithms in terms of AUC. The evaluation results using the test set are also presented in Table 9.

Table 9.
Evaluation results of the best model using the test set—State III.
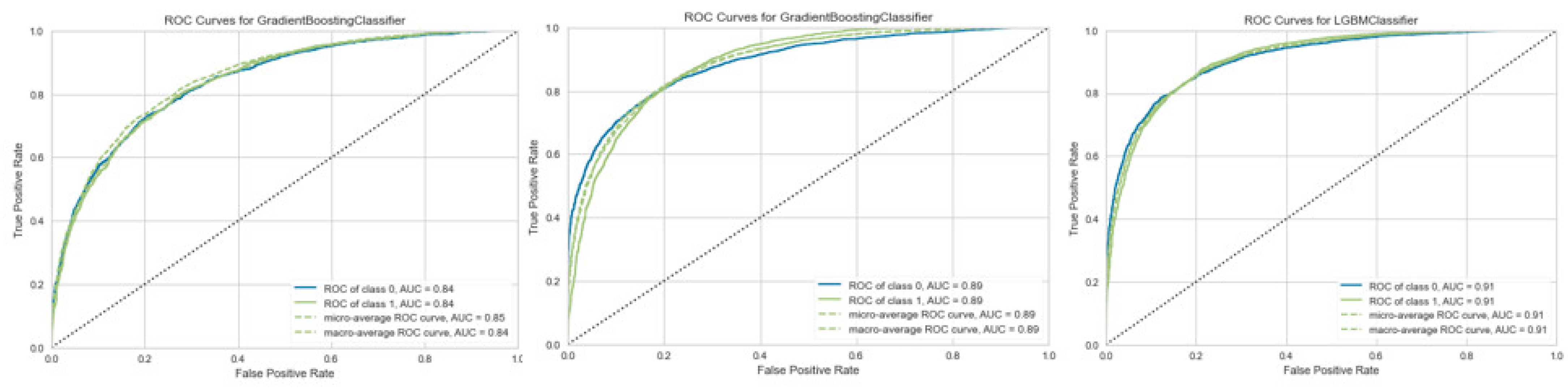
Figure 6 represents ROC curves for the best models in each state. A receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve is a graphical plot used to present a binary classifier’s diagnostic ability. The ROC curve illustrates the trade-off between sensitivity and specificity. The performance of classifiers is better when their curves are closer to the top-left corner. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) is a common approach to comparing different classifiers.
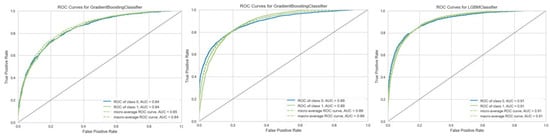
Figure 6.
ROC curves for the best models: the left graph shows the ROC for the GB Classifier in state I, the middle graph represents the ROC curve for the GB Classifier in state II, and the right graph shows the ROC curve for the LGBM in state III.
Figure 6 specifies that the AUC measure of the best models (in the test sets) is 0.84, 0.89, and 0.91 in states I, II, and III, respectively. These models were saved to be used in the LS Selection process in Q2, Q3, and Q4.
4. Discussion
This section discusses the comparison results of actual and calculated learning style features in Q2, Q3, and Q4. We also suggest two strategies for utilizing learners’ learning styles in order to enhance their academic performance.
We calculated the difference (absolute value) between the actual LSs for each student and the calculated ones using the proposed approach in Q2, Q3, and Q4. We specified a threshold, compared the difference with the threshold, and classified students. If the difference between the actual LS and the calculated one was less than the threshold, we classified the student into the “Supported” category; otherwise, “Not Supported.” The assessment grades students achieved in Q2, Q3, and Q4 were then statistically compared between the Supported and Not Supported categories. Table 10 summarizes the results of the statistical comparisons.

Table 10.
Statistical comparisons of assessment grades between Supported and Not Supported categories.
In Table 10, “VV_Diff”, “AR_Diff”, and “SI_Diff” mean the difference between actual and calculated visual/verbal, active/reflective, and sensitive/intuitive learning style features, respectively. In addition, each quarter initially has four learning style features. However, we made comparisons only for visual/verbal, active/reflective, and sensitive/intuitive since the last one (sequential/global) depends on the other three learning style features.
We aimed to understand if there is a significant difference in students’ assessment grades between the Supported and Not Supported groups. In other words, we wanted to understand if the students in the Supported category achieved better grades than those in the Not Supported category. Welch’s t-test was employed to compare the average grades since the distribution of the students’ grades follows the normal distribution. The statistical comparisons were conducted using the threshold value of 0.08.
Table 10 illustrates that all p-values are significant at the level of one percent. Moreover, the one-tailed tests were conducted to understand which category performed better in the assessments. The results confirm that students in the Supported category outperformed those in the Not Supported one. In other words, students whose actual learning styles are close enough to those calculated using the proposed approach achieved better grades compared with the other category.
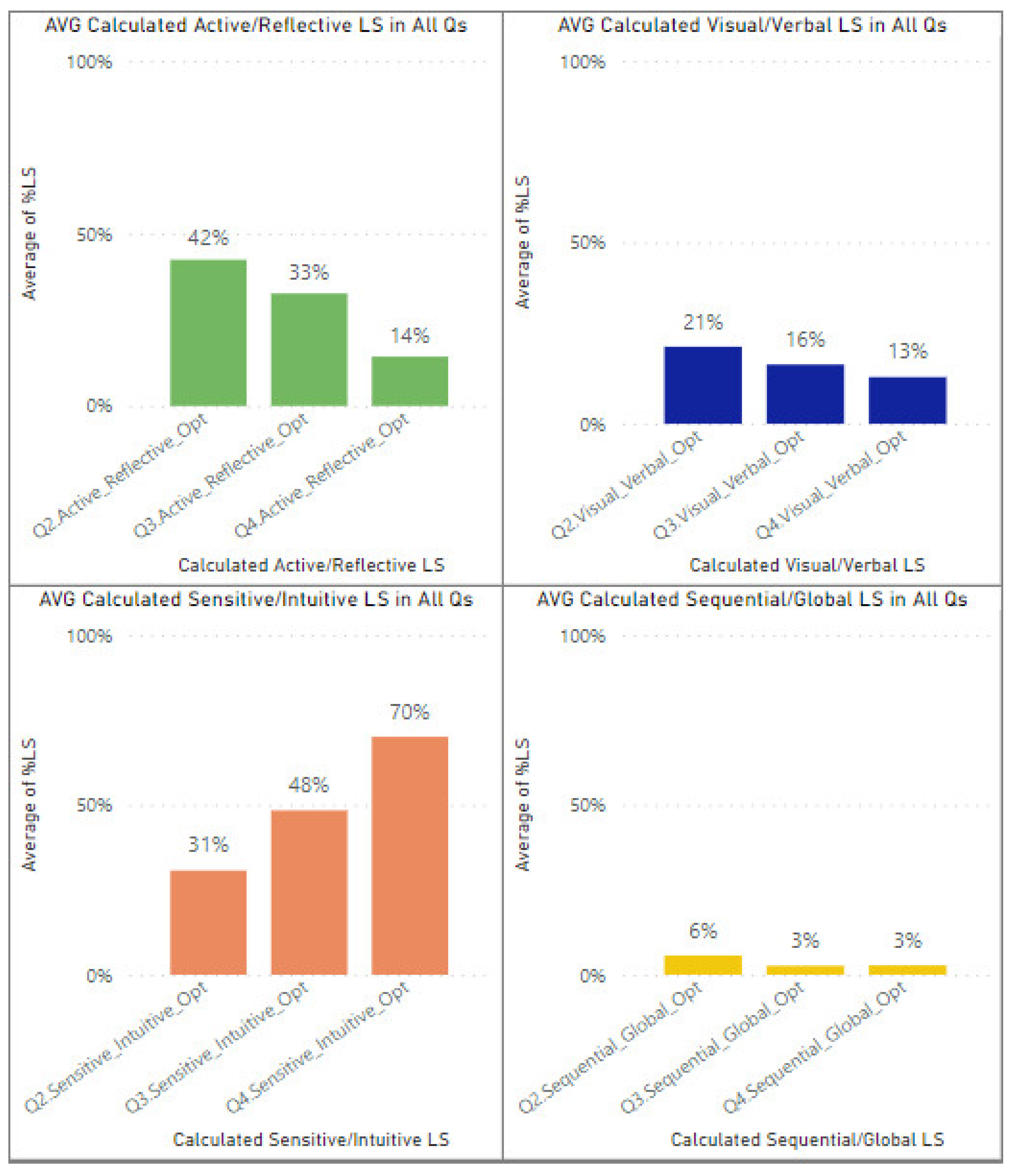
Figure 7 depicts the average of all calculated learning style features, including visual/verbal, active/reflective, sensitive/intuitive, and sequential/global, using the proposed modeling approach in Q2, Q3, and Q4. The bar charts represent that in Q2, the processing (active/reflective) learning style feature has the highest average percentage compared with other LSs (42%); however, in Q3 and Q4, the perception (sensitive/intuitive) learning style feature has the most significant values in terms of average percentage (48% and 70%). Moreover, from Q2 to Q4, the average percentage of visual/verbal, active/reflective, and sequential/global learning style features decreased. At the same time, it increased in terms of sensitive/intuitive learning style features.
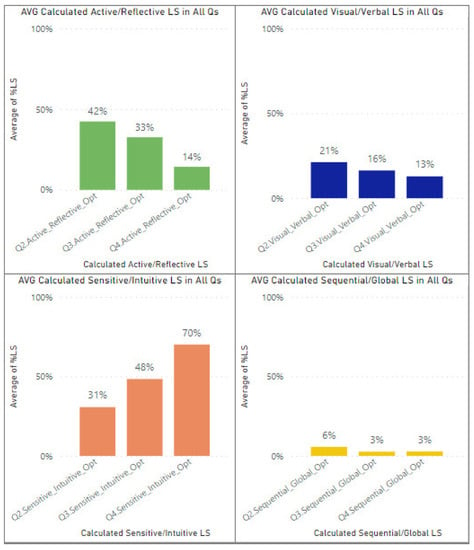
Figure 7.
Average of calculated learning style features in Q2, Q3, and Q4.
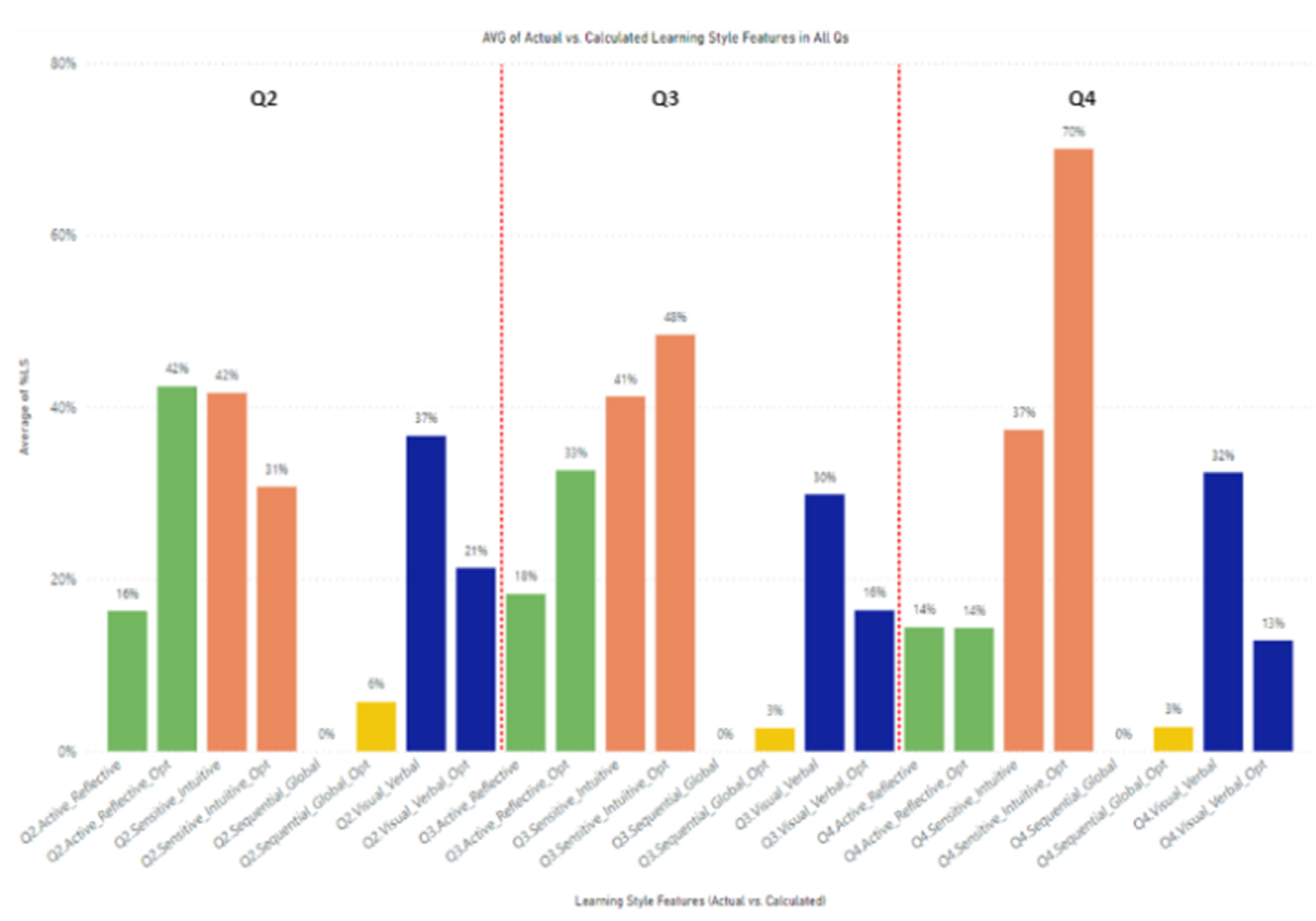
Figure 8 compares the average percentage of actual and calculated learning style features using the proposed approach in Q2, Q3, and Q4. On average, the calculated visual/verbal learning style feature has always been less than the actual one. On the other hand, the calculated active/reflective leaning style feature is greater than or equal to the actual one in all three mentioned quarters. Moreover, the students did not interact with sequential/global learning resources in all quarters.
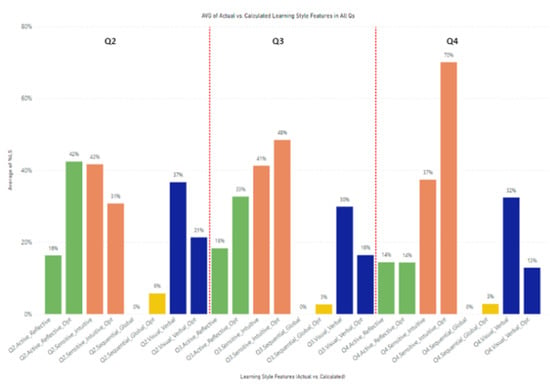
Figure 8.
Comparing actual and calculated learning style features in Q2, Q3, and Q4.
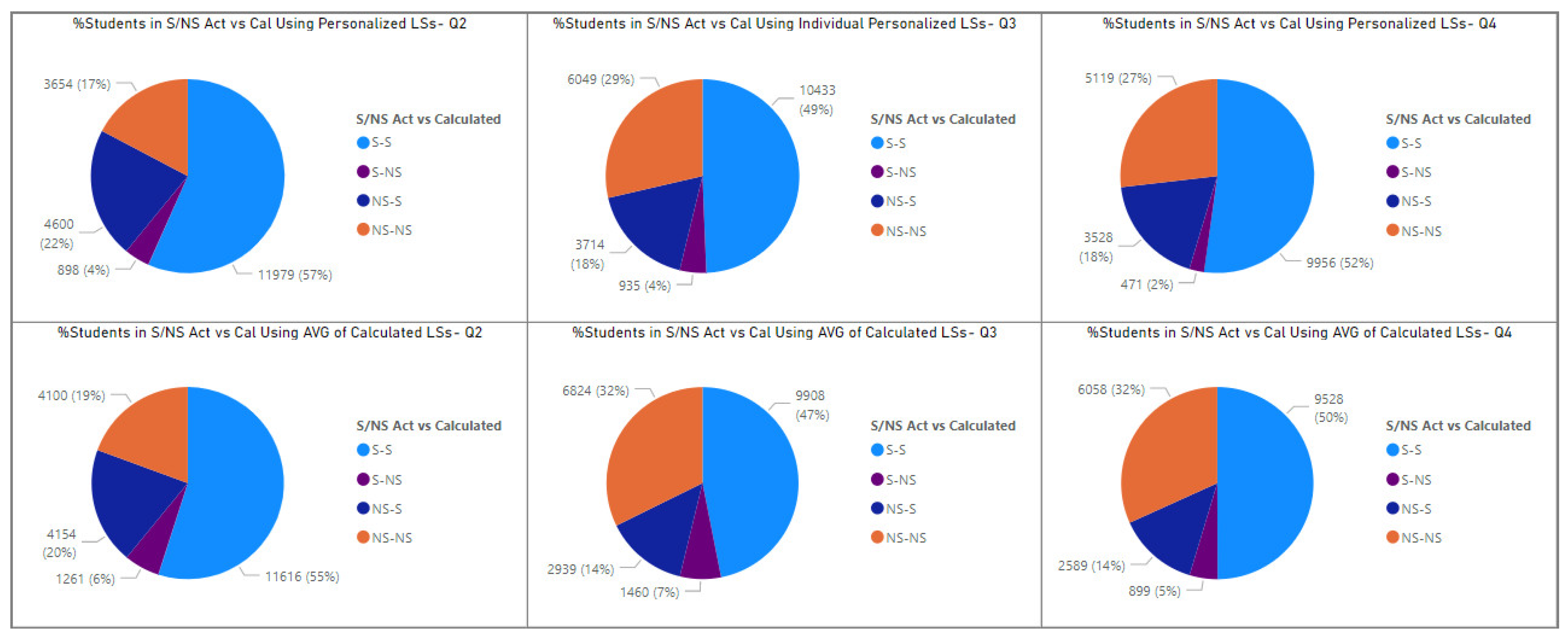
Figure 9 compares assessment grade classes (satisfactory/not satisfactory) using actual learning styles versus calculated ones.
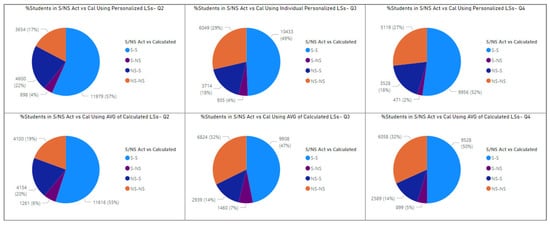
Figure 9.
Comparing the percentage of S/NS transitions using personalized and the average of calculated LSs in Q2, Q3, and Q4. * In Q4, module presentation E is excluded.
In Figure 9, NS-S indicates that the student received a “Not Satisfactory” grade in the assessment using the actual learning style features but would receive a “Satisfactory” grade if the calculated learning style features were used. Moreover, S-NS implies that if the calculated learning style features were used, the student would receive a “Not Satisfactory” grade rather than a “Satisfactory” grade in the assessment. Furthermore, S-S and NS-NS indicate that the student’s assessment grade class would not change.
Figure 9 proposes two strategies using calculated learning style features to improve students’ academic performance each quarter. The pie charts in the first row represent how assessment grade classes (S/NS) change when the personalized calculated learning style features are employed, i.e., when the learning resources are personalized based on each learner’s learning styles. According to the top left graph, 22% of students’ grades in Q2 would change from NS to S if the calculated personalized learning style features were utilized. In Q3 and Q4, this percentage decreases to 18%. On the other hand, the percentage of changes from S to NS is only 4% in Q2 and Q3 and decreases to 2% in Q4.
However, personalizing learning resources based on each student’s learning style is quite expensive in most classes. Furthermore, we propose a strategy based on the average of the calculated learning style features. In other words, in each quarter, instead of each student’s calculated LS features, we propose giving their average in that quarter to the saved ML model and predicting the probability of S/NS classes. For instance, in Q2, the average of active/reflective, visual/verbal, sensitive/intuitive, and sequential/global learning style features are 42%, 21%, 31%, and 6%, respectively. Therefore, for all students in Q2, we consider these values as LSs in Q2 and give them along with demographic and LS features in Q1 to the saved model and predict the probability of S/NS classes in the Q2 assessment grade. In Figure 9, the graphs in the second row represent the results of this strategy. The bottom left graph indicates that using the average LS policy, 20% of students’ grades in Q2 would change from NS to S. In Q3 and Q4, this percentage decreases to 14%. The percentage of changes from S to NS is 6% in Q2, and 7% and 5% in Q3 and Q4, respectively.
5. Conclusions
Students’ performance can be significantly improved by adopting an appropriate educational intervention based on their learning styles. In this research study, we propose a framework to detect students’ learning styles based on their behaviors in a virtual learning environment to improve their academic performance. We utilized the Felder–Silverman Learning Style Model, one of the most effective models in online learning in the literature, to map learning resources to learning style features. We defined three states based on course length and employed two main processes, ML Training and LS Selection, to find the individual learning style features that maximize learners’ academic performance in each state. We utilized the Open University Learning Analytics Dataset to test the proposed approach.
Future research can be conducted to enhance machine learning algorithms and utilize deep learning models. Moreover, further development can be carried out on the search algorithm to find optimal learning style features.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.N. and H.D.; methodology, R.N. and H.D.; validation, R.N. and H.D.; formal analysis, R.N. and H.D.; data curation, R.N. and H.D.; writing—original draft preparation, R.N.; writing—review and editing, R.N. and H.D.; visualization, R.N.; supervision, H.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
This research was conducted based on a publicly available dataset, OULAD, https://analyse.kmi.open.ac.uk/open_dataset.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Felder, R.M.; Silverman, L.K. Learning and Teaching Styles in Engineering Education. Eng. Educ. 1988, 78, 674–681. [Google Scholar]
- Graf, S.; Liu, T.-C. Kinshuk Analysis of learners’ navigational behaviour and their learning styles in an online course: Analysis of navigational behaviour. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2010, 26, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Tasir, Z.; Kasim, J.; Sahat, H. Automatic Detection of Learning Styles in Learning Management Systems by Using Literature-based Method. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 103, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, S.-F.; Tsao, Y.-W.; Yu, L.-C.; Chan, C.-L.; Lai, K.R. Who will pass? Analyzing learner behaviors in MOOCs. Res. Pract. Technol. Enhanc. Learn. 2016, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.H. Web-Based Instruction; Educational Technology: NJ, USA, 1997; ISBN 0-87778-296-2. [Google Scholar]
- Pardamean, B.; Suparyanto, T.; Cenggoro, T.W.; Sudigyo, D.; Anugrahana, A. AI-Based Learning Style Prediction in Online Learning for Primary Education. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 35725–35735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, H.; Hassan, S.-U.; Aljohani, N.R.; Hardman, J.; Alelyani, S.; Nawaz, R. Predicting academic performance of students from VLE big data using deep learning models. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2020, 104, 106189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felder, R.M. Matters of Style. ASEE Prism 1996, 6, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, I.B.; Myers, P.B. Gifts Differing: Understanding Personality Type; Davis-Black: Mountain View, CA, USA, 1995; ISBN 978-0-89106-074-1. [Google Scholar]
- Honey, P.; Mumford, A. Learning Styles Questionnaire; Organization Design and Development: Maidenhead, UK, 1989; Incorporated. [Google Scholar]
- Kolb, D.A. The Kolb Learning Style Inventory; Hay Resources Direct: Boston, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, N.D. Facts, Fallacies and Myths: VARK and Learning Preferences. Retrieved from vark-learn.com/Introduction-to-Vark/the-Vark-Modalities. 2012. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjtoIaEw8v-AhVbAYgKHSf-AxYQFnoECA0QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fvark-learn.com%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2014%2F08%2FSome-Facts-About-VARK.pdf&usg=AOvVaw0exKq7uf-fZ6G0bkrMQH5g (accessed on 24 March 2023).
- Basham, J.D.; Hall, T.E.; Carter, R.A., Jr.; Stahl, W.M. An operationalized understanding of personalized learning. J. Spec. Educ. Technol. 2016, 31, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Muhammad, B.; Qi, C.; Wu, Z.; Kabir Ahmad, H. GRL-LS: A learning style detection in online education using graph representation learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 201, 117138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziedzic, M.; de Oliveira, F.B.; Janissek, P.R.; Dziedzic, R.M. Comparing learning styles questionnaires. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE), Oklahoma City, OK, USA, 23–26 October 2013; pp. 973–978. [Google Scholar]
- Oranuch, P.; Monchai, T. Using Decision Tree C4. 5 Algorithm to Predict VARK Learning Styles. Int. J. Comput. Internet Manag. 2016, 24, 58–63. Available online: http://cmruir.cmru.ac.th/handle/123456789/428 (accessed on 24 March 2023).
- Hasibuan, M.S.; Nugroho, L.E.; Santosa, P.I. Model Detecting Learning Styles with Artificial Neural Network. J. Technol. Sci. Educ. 2019, 9, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.A.; Akbar, A.; Altaf, M.; Tanoli, S.A.K.; Ahmad, A. Automatic Student Modelling for Detection of Learning Styles and Affective States in Web Based Learning Management Systems. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 128242–128262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzi, I.; Jeghal, A.; Radouane, A.; Yahyaouy, A.; Tairi, H. A robust classification to predict learning styles in adaptive E-learning systems. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2020, 25, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, F.; Wahid, A. Learning style detection in E-learning systems using machine learning techniques. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 174, 114774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.B.; Fonseca, B.; Santana, M.A.; de Araújo, F.F.; Rego, J. Evaluating the effectiveness of educational data mining techniques for early prediction of students’ academic failure in introductory programming courses. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 73, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.-U.; Waheed, H.; Aljohani, N.R.; Ali, M.; Ventura, S.; Herrera, F. Virtual learning environment to predict withdrawal by leveraging deep learning. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2019, 34, 1935–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasif, M.; Waheed, H.; Aljohani, N.R.; Hassan, S.-U. Understanding student learning behavior and predicting their performance. In Cognitive Computing in Technology-Enhanced Learning; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hlosta, M.; Zdrahal, Z.; Zendulka, J. Are we meeting a deadline? classification goal achievement in time in the presence of imbalanced data. Knowl. Based Syst. 2018, 160, 278–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbouti, F.; Diefes-Dux, H.A.; Strobel, J. Building course-specific regression-based models to identify at-risk students. In Proceedings of the 2015 ASEE Annual Conference & Exposition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–17 June 2015; pp. 26.304.1–26.304.11. [Google Scholar]
- Adnan, M.; Habib, A.; Ashraf, J.; Mussadiq, S.; Raza, A.A.; Abid, M.; Bashir, M.; Khan, S.U. Predicting at-risk students at different percentages of course length for early intervention using machine learning models. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 7519–7539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhakbani, H.A.; Alnassar, F.M. Open Learning Analytics: A Systematic Review of Benchmark Studies Using Open University Learning Analytics Dataset (OULAD). In Proceedings of the 2022 7th International Conference on Machine Learning Technologies (ICMLT), Rome, Italy, 11–13 March 2022; pp. 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzilek, J.; Hlosta, M.; Zdrahal, Z. Open university learning analytics dataset. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, P.; Amandi, A.; Schiaffino, S.; Campo, M. Evaluating Bayesian networks’ precision for detecting students’ learning styles. Comput. Educ. 2007, 49, 794–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, S.; Kinshuk; Liu, T.-C. Supporting teachers in identifying students’ learning styles in learning management systems: An automatic student modelling approach. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2009, 12, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).