Abstract
Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD) exhibit high comorbidity and variability in terms of dominant comorbid factors across the lifespan. Given the high comorbidity between these disorders, the transdiagnostic factors that may underlie them and could be used to develop effective treatments are of great importance. The focus of this research was on the role of impulsivity as a transdiagnostic factor in the development of ADHD and ODD symptoms in primary and secondary school students. Data were collected from 1161 primary (5th to 8th grade) and secondary (1st to 4th grade) school students (624 females and 537 males). Two models were tested, one for primary and one for secondary school students. Both models propose a significant relationship between ADHD symptoms and ODD, with an emphasis on the relationship between impulsivity and angry/irritable mood. The model for secondary school students does not fit the data, while the model for primary school students fits the data but emphasises attention as the most important factor. These results can be explained by the context of developmental changes and the school environment, both of which influence the stability and intensity of ADHD symptoms.
1. Introduction
Comorbidity of childhood disorders is one of the most important constructs in the phenomenology of disorders in developmental psychopathology, and its occurrence is the rule rather than the exception [1]. Cicchetti [2] points out that understanding child psychopathology requires a multilevel approach that incorporates the developmental perspective when trying to understand adaptive and maladaptive strategies that occur at different stages of development. This approach involves defining different types of comorbidity, such as homotypic (occurring between disorders within the same diagnostic group), heterotypic (occurring between disorders in different diagnostic groups), simultaneous (occurring at the same age) and successive (occurring at different developmental periods) [3]. Externalised disorders (Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder—ADHD, Oppositional Defiant Disorder—ODD, Conduct Disorder—CD, etc.) and the behaviours describing them belong to a group of highly comorbid behaviours that interact with each other in different ways [4]. Therefore, a successive sequence of disorders belonging to the same diagnostic group, such as ADHD, ODD and CD [5,6] and the overlap of their symptoms can be defined as homotypic successive comorbidity. When antisocial personality (Fischer et al., 1993a, according to [5]), and substance abuse [7] are added to this developmental trajectory, heterotypic successive comorbidity emerges. Furthermore, comorbidity of disorders is often present simultaneously in early childhood, as a clearer separation of the different disorders only occurs at a later age. Steinhoff et al. [8], for example, point out that the clinical picture of ADHD becomes clearer at school age, which is confirmed by the authors Nigg and Barkley [5]. According to these authors, ADHD in early childhood is defined and described by two dimensions (hyperactivity/impulsivity and attention), whereas in adulthood, hyperactivity and impulsivity are separated into two dimensions. In preschool and school age, externalised behaviours are most commonly used to describe ADHD, ODD and later CD [9]. These behaviours may develop in the preschool years when children have difficulty establishing appropriate social relationships. Social relationships at this age include sharing attention and play materials with others, suppressing aggressive behaviours and destructive impulses, delaying immediate gratification, and listening to and responding appropriately to instructions [10]. Problems in these aspects of social behaviour can be reduced to three basic types of externalised problems [11]: Aggressiveness, Delinquency and Hyperactivity. Aggressiveness can be defined as innate behaviour, as learned and motivational behaviour (frustration-aggression theory), as behaviour related to cognitive development and socio-cognitive processes, or as behaviour caused by a number of different factors [12]. Aggressiveness peaks at preschool age. If the child does not build appropriate social relationships, acquire self-regulatory skills, develop a theory of mind and have good relationships with parents, aggressive behaviour will not decrease [2,10,13]. Difficulties in developing these skills can lead to the onset of externalised problems and the development of externalised disorders in preschool (ADHD, ODD and later CD). Given the significant role of comorbidity and the often vague clinical picture of preschool disorders, there is a growing need to find specific factors underlying a wider range of disorders in order to plan interventions appropriately. Recently, a transdiagnostic approach to the aetiology of disorders has been used to identify these factors. The transdiagnostic approach is defined by a search for the specific factors underlying a range of disorders. It focuses on the relative contribution of different factors to the development of particular disorders and the use of these factors in describing the underlying symptoms in broader categories of disorders [14]. Before describing the transdiagnostic approach to interpreting externalised disorders, we need to point out that ADHD and ODD disorders are most common in preschool and school-age children and that, as mentioned earlier, comorbidity between these two disorders is high.
Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Oppositional Defiant Disorder: Comorbidity and the Transdiagnostic Approach
There are different ways to interpret ADHD and ODD comorbidity. ADHD occurring in early childhood may be a risk factor for the development of ODD and, subsequently, CD and possibly antisocial personality disorder. This form of association of ADHD with ODD, CD and antisocial personality disorder makes it one of the most reliable predictors of these disorders (Fischer et al., 1993a; according to [5]). According to the DSM 5 [9] (p. 65), ODD “occurs in about half of children with the combined type of ADHD and in about a quarter of children with predominant inattention.” The comorbidity of ADHD with ODD represents the highest comorbidity of ADHD with any other disorder [15], with a percentage of 45–84% of children diagnosed with ADHD and ODD, with or without CD (Wilens et al. according to [16]). The prevalence of ADHD in children is between 5 and 7%, and of ODD, 3.3% [17,18]. One study found that 40% of children diagnosed with ADHD met the criteria for ODD, and 14.3% met the criteria for CD, while another reported 62% of preschool children and 59% of school children with comorbid ADHD and ODD [19]. One of the most important transdiagnostic factors in interpreting the comorbidity of these disorders is impulsivity [4] or, more specifically, emotional impulsivity [16]. Nigg and Barkley [5] also emphasise the role of hyperactivity/impulsivity in the association between ADHD and ODD. Barkley [20] proposed a model that explains the comorbidity of ADHD and ODD with emotional dysregulation and with emotional impulsivity (emotional impulsivity-deficient emotional self-regulation; EI-DESR). According to this model, emotionally impulsive individuals are more prone to react in different situations with the first emotion they feel, and this reaction is faster compared to individuals of the same age who are not emotionally impulsive. The construct of emotional dysregulation is defined as the inability to inhibit an inappropriate response related to strong negative or positive emotions, the inability to calm oneself when faced with a strong emotional response, the inability to divert attention, and the inability to organise coordinated actions to achieve a specific goal [21,22]. The first step in emotional dysregulation (inability to inhibit an inappropriate response) is emotional impulsivity. This construct is one of the basic risk factors and also an integral part of the clinical picture of ADHD [22] and is associated with the behavioural symptoms of this disorder. According to this model, an individual not only has the capacity to choose and construct alternative behavioural responses to a particular situation but also has the capacity to choose and construct alternative emotional responses to the same situation. People with ADHD will be as careless in behavioural actions as they are in emotional actions because these two components are interconnected, i.e., inseparable in response [20]. Therefore, if a person shows difficulties related to behavioural impulsivity, they will also show difficulties related to emotional impulsivity. In addition, the symptoms describing emotional impulsivity have been used to form a new, separate disorder in the DSM-III—oppositional defiant disorder, which was previously described as part of ADHD. ODD is now defined as a disorder that encompasses two dimensions: emotional and behavioural (social) conflict. The behavioural-social component of this disorder may be associated with parenting difficulties and stressors that occur in the family (Burke et al., 2008; according to [20]), while the emotional component may be associated with a deficit in emotional impulsivity and, accordingly, difficulties with self-regulation, as is the case with ADHD in this model. Finally, the symptoms of emotional impulsivity (emotional irritability, low frustration tolerance and frequent anger) [20] are similar to the symptoms describing the angry/irritable mood dimension in ODD (rapid arousal, frequent sensitivity or distress, frequent anger or offending) [9]. According to this model, it is emotional impulsivity that links ADHD and ODD, as they share common diagnostic criteria. Indeed, if ADHD includes emotional impulsivity as a diagnostic criterion and emotional impulsivity is present in ODD, a person with an ADHD diagnosis and marked emotional impulsivity meets almost all diagnostic criteria for ODD. Furthermore, Pliszka [16] rules out the possibility that this association is a by-product of a third disorder. Emotional dysregulation is also connected to disruptive mood dysregulation disorder, a disorder characterised by irritability, anger and temper outbursts, which may connect this disorder with ADHD and ODD through the same mechanisms. Nevertheless, this disorder is a newly defined disorder which cannot be diagnosed with ODD and is still not included in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD—11) due to the lack of empirical evidence [23,24]. Finally, whether or not the child is eventually diagnosed with ADHD or ODD, the symptoms that describe these disorders are most apparent in the school environment. The aim of this research was, therefore, to examine the relationship between the symptoms describing ADHD and ODD, focusing on the relationship between impulsivity and angry/irritable behaviour and the role of impulsivity as a transdiagnostic factor in the development of symptoms of ADHD and ODD in primary and secondary school students.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
Data were collected from a sample of 1161 students (624 girls and 537 boys) in grades 5–8 of primary school and grades 1–4 of secondary school (Table 1). In the Republic of Croatia, where the research was conducted, primary school lasts eight years (children aged 7–14), and secondary school lasts four years (children aged 14–18). The grade was chosen as a category variable representing the age and the developmental and educational level of children and adolescents. Although this is not the most accurate indicator of the chronological age of the groups, it is the most common way of grouping participants in similar research where participants are primary and secondary school students.

Table 1.
The age structure of the participants (N = 1161).
2.2. Measures
The Aggressiveness Scale for Children and Adolescents (SNOP; [25]) is designed to assess three basic models of behaviours: (1) negativistic, hostile and defiant behaviour, (2) aggressive and non-aggressive behaviour that threatens the basic rights of others or violates important social norms, and (3) bullying, in which a child is mistreated or bullied by another child or group of children. This measure consists of forty items divided into four scales: Opposition and Defiance (ODD, nine items), Conduct (O, fifteen items), Sacrifice (Ž, nine items) and Bullying (N, seven items). These four scales may be used independently of one another, and for the purposes of this research, the results of the Opposition and Defiance scale (ODD) were used. This scale is constructed the same way as most scales for ODD are, by including and adapting items from DSM-IV-TR [26] and V [9] to describe this disorder. The psychometric properties of the ODD scale and its subscales are shown in Table 2. The Angry/Irritable Mood (AIM), Argumentative/Defiant Behaviour (ADB) and Vindictiveness (V) subscales are based on the symptom categories used to describe this disorder in the DSM-IV-TR [26]. All items are listed in Appendix A. The response options are described on a five-point Likert scale, and the participants are asked to decide how often the described behaviour was present in the last six months, with one meaning never and five meaning almost always. The scoring includes calculating the results for each subscale by adding the circled numbers next to the corresponding items for each subscale. Additionally, there is the option of calculating the overall score by adding the scores for each subscale. Higher scores indicate more severe symptoms.

Table 2.
Descriptive parameters for HIP and ODD scales and their subscales.
The Hyperactivity-Impulsivity-Attention Scale (HIP; [27]) is used to assess hyperactive (H) and impulsive behaviour (I) as well as problems in directing attention (P). It consists of nineteen items and is based on the symptom categories used to describe this disorder in the DSM-IV-TR [26], items from psychodiagnostic instruments used to measure ADHD symptoms, and theoretical interpretations of this symptomatology. The items of this scale are grouped into three subscales: Hyperactivity (H, six items), Impulsivity (I, four items) and Attention (P, nine items). The response options are described on a five-point Likert scale, and the participants are asked to decide how often the described behaviour was present in the last six months, with one meaning never and five meaning almost always. The scoring includes calculating the results for each subscale by adding the circled numbers next to the corresponding items for each subscale. Additionally, there is the option of calculating the overall score by adding the scores for each subscale. Higher scores indicate more severe symptoms. The psychometric indicators are listed in Table 2. All items are listed in Appendix A.
2.3. Procedure
All questionnaires were completed in class during regular school hours. A psychologist and a psychology student applied all the questionnaires. Before the beginning, the psychologist explained the aim of the research to all participants, and they were then instructed on how to complete the questionnaire. All of the relevant approvals were collected before the beginning of the research. The research was approved by the Ethical Committee of the University of Zadar and was carried out according to the ethical principles of the Croatian Psychological Society. Since this research included participants from primary and secondary schools, approval was obtained from the relevant ministry, principals of the schools, parents of the participants and the participants themselves. All participants were informed that anonymity is assured. All the schools that were included in this research were contacted via e-mail, and the research was explained to the principals. The schools from this research were from the greater Zadar city area. After the approval was obtained from the ministry and the principals agreed to participate in the research, students were given an informed consent form which their parents had to sign. The final part of this procedure included the participant's consent. All measures used in this research were created for primary and secondary school participants, keeping in mind the level of their reading skills, and were originally developed in the student's primary language. In this research, there was no cut-off point for ADHD or ODD, but the symptoms of these disorders were treated as dimensions. In order to analyse the data, jamovi Computer Software (version 2.2.5) was used.
3. Results
In order to meet the aim of this research, two models that describe the influence of ADHD dimensions (hyperactivity, impulsivity and attention) on the dimensions of ODD (angry/irritable mood, argumentative/defiant behaviour and vindictiveness) were tested, one for primary and one for secondary school students. Impulsivity was assumed to be the most significant predictor of angry/irritable mood. Because data were missing from several participants for each variable, the number of results analysed varied from variable to variable. For the SEM analysis, a robust maximum likelihood estimator was used to correct for the non-normality of the data and the bias (robust parameter estimation method). This approach is recommended by Satorra and Bentler [28] and Curran, West & Finch [29]. In addition, due to the overcorrection of this method, some recommend samples with more than 250 participants [30]. In our research, the sample size is always at least twice as large. Table 2 shows the descriptive parameters for each subscale of the scales HIP and ODD. In addition, the internal reliability of each subscale was tested using the McDonald’s Omega (ω). All coefficients of internal reliability are satisfactory (Table 2).
Before testing the fit of the model, the normality of the distribution for the results on all subscales of HIP and ODD was examined in relation to gender and the level of education. The results (Table 3) show that all distributions deviate from the normal distribution, and all further analyses are non-parametric.

Table 3.
Normality testing and descriptive parameters for HIP and ODD subscales in relation to gender and the level of education.
In addition, the difference in hyperactivity, impulsivity and attention, angry/irritable mood, argumentative/defiant behaviour and vindictiveness was examined in relation to gender and educational level using the Mann-Whitney test. Gender differences were not significant, except for angry/irritable mood, where female students scored higher (Table 4, medianF = 8, medianM = 7) and vindictiveness, where male students scored higher (Table 4, medianF = 1, medianM = 2). The differences in hyperactivity, impulsivity and attention, angry/irritable mood, argumentative/defiant behaviour and vindictiveness in relation to educational level, i.e., between primary and secondary students, were all statistically significant, and the scores in all subscales are higher for secondary students (Table 5).

Table 4.
Testing the difference between male and female students in Hyperactivity, Impulsivity, Attention, Angry/irritable mood, Argumentative/defiant behaviour and Vindictiveness with the Mann-Whitney test.

Table 5.
Testing the difference in Hyperactivity, Impulsivity, Attention, Angry/Irritable mood, Argumentative/Defiant behaviour, and Vindictiveness with regard to the level of education using the Mann-Whitney test.
Table 6 and Table 7 show correlations for each subscale of the HIP scale and correlations for each subscale of the ODD scale separately for primary and secondary school students. The correlations between hyperactivity, impulsivity and attention are statistically significant and moderate for both primary and secondary students. The correlations between angry/Irritable mood, argumentative/defiant behaviour and vindictiveness are also statistically significant and low to moderate for both primary and secondary students. The correlations of the total HIP scale with each subscale and the ODD scale with each subscale are statistically significant and moderate to strong for both primary and secondary school students. Such results are to be expected as the subscales are low to moderately correlated with each other, while their correlation with the total score on the overall scale is moderate to strong. This indicates the existence of separate but correlated constructs. The correlations between the HIP and ODD subscales were low to low moderate for both primary and secondary school students, justifying the use of structural modelling to define the relationship between these constructs. The significance but weak strength of this correlation is crucial for further statistical analyses, as it indicates the existence of separate constructs that nevertheless show significant conformity in changes.

Table 6.
Kendall Tau correlation coefficients between HIP and ODD subscales in primary school students.

Table 7.
Kendall Tau correlation coefficients between HIP and ODD subscales in secondary school students.
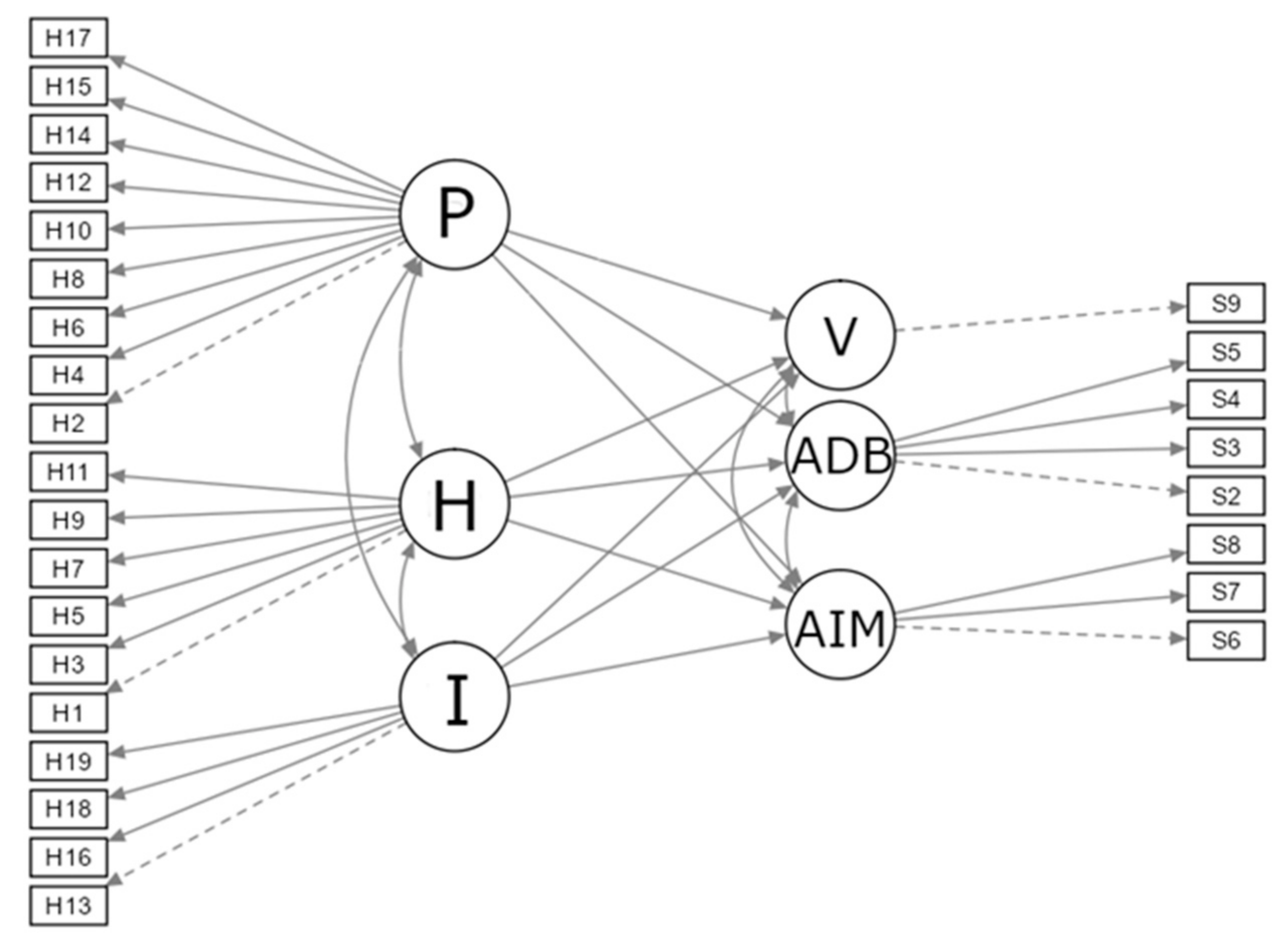
Finally, to meet the aim of this research, a model was tested describing the influence of ADHD dimensions (hyperactivity, impulsivity and attention) on the dimensions of ODD (angry/irritable mood, argumentative/defiant behaviour and vindictiveness), assuming that the most significant predictor of angry/irritable mood was impulsivity (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
Proposed model of the relationship between ADHD and ODD components. Angry/Irritable Mood (AIM), Argumentative/Defiant Behaviour (ADB) and Vindictiveness (V), Hyperactivity (H), Impulsivity (I), and Inattention (P).
3.1. SEM Analyses
Since the significance of the ADHD factors changes with age, it was decided to test the fit of the model for the two groups independently. Two SEM analyses were conducted, one for primary school students and one for secondary school students. First, the chi-square values are significant, which usually indicates the inadequacy of the model. However, the chi-square test depends on the number of participants (the sample size). Since this research was conducted on a large sample, it is not recommended to use this indicator [31]. In addition, to compensate for the non-normality of the distribution and to correct for standard error bias, a robust method of parameter estimation (Robust Maximum Likelihood) was used. Finally, in addition to ML SEM with a robust method of parameter estimation, PLS-SEM was also performed. The results obtained using PLS-SEM for both samples show the same results in terms of predictor significance. Due to the simplicity of ML SEM, it was decided to present only the results obtained with this method in this paper. Furthermore, the PLS-SEM methodology does not allow the association of predictors and their covariance in the model, which is one of the most important criteria of the ADHD and ODD dimensions. The parameters of the model for primary school students (Model 1) are presented first, followed by the parameters for secondary school students (Model 2).
3.1.1. Model 1
The fit indices for the model are presented in Table 8 and show that the model fits the data (estimation method= robust ML). Besides the chi-square test, the other three fit indices indicate a satisfactory fit of the model (SRMR = 0.047, CFI = 0.906, RMSEA = 0.049). The parameter estimates are significant for impulsivity, which predicts argumentative/Defiant behaviour, and attention, which predicts all three dimensions of ODD (Table 9). The residual covariances do not indicate a significant correlation between the item residuals.

Table 8.
Fit indices for Model 1.

Table 9.
Parameters for the structural model for Model 1.
For the measurement model, the standardised regression weights of all items forming a particular factor are acceptable and significant (β of 0.50–0.77).
The percentage of variance explained for angry/irritable mood with attention is 40.2% (R2 = 0.402). It can be seen from Table 9 that attention is the only significant predictor of angry/irritable mood. The percentage of explained variance of argumentative/defiant behaviour with impulsivity and attention is 57.2% (R2 = 0.572), with impulsivity being the most significant predictor in this case (Table 9). Finally, the percentage of explained variance of Vindictiveness with Attention is 23.5% (R2 = 0.235).
3.1.2. Model 2
The fit indices for the model are presented in Table 10 and show that the model does not fit the data (estimation method = robust ML; SRMR = 0.062, CFI = 0.847, RMSEA = 0.074). Parameter estimates are significant for hyperactivity for predicting angry/irritable mood and argumentative/defiant behaviour, impulsivity for predicting argumentative/defiant behaviour and vindictiveness, and attention for predicting angry/irritable mood (Table 11). Residual covariances do not indicate a significant correlation between the item residuals.

Table 10.
Fit indices for Model 2.

Table 11.
Parameters for the structural model for Model 2.
For the measurement model, the standardised regression weights of all items forming a particular factor are acceptable and significant (β of 0.50–0.81).
4. Discussion
This research examined the fit of models implying a significant influence of the dimensions describing hyperactivity, impulsivity, and attention on the ODD dimensions, focusing on the influence of impulsivity on angry/irritable mood.
These relationships were observed with respect to the educational level, and the obtained indices (Table 8, Table 9, Table 10 and Table 11) show that the model for primary school students (Model 1) fits the data well. However, in this model, attention is the most significant predictor, while impulsivity is not a significant predictor for the dimensions of ODD, with the exception of argumentative/defiant behaviour. The model for secondary school students (Model 2) does not fit the data well.
It is important to point out that the items used to measure the dimensions of hyperactivity and impulsivity (Appendix A) correspond to the description of emotional impulsivity proposed by Barkley and Fischer [32]. They define emotional impulsivity as impatience, low tolerance to frustration, quickness to anger, irritability, and easy emotional excitability. Defined in this way, emotional impulsivity can lead to internalised and externalised behaviour problems. However, in our research, hyperactivity and impulsivity were not measured exclusively as emotional components but as behavioural also, and it is possible that the questionnaire examining the former component exclusively would be associated differently with angry/irritable mood. Although a questionnaire focused exclusively on emotional impulsivity would be a better option, it is difficult to separate these two components since they are both included in a response in regard to a particular situation (they are unique in their response) [25,33]. In other words: If an individual exhibits difficulties related to behavioural impulsivity, they will also exhibit difficulties related to emotional impulsivity to the same degree, i.e., they are unique in their responses [20]. This explanation, along with the items used in our research, which coincide with the description of emotional impulsivity, provides a basis for testing the fit of this model in relation to the influence of hyperactivity and impulsivity on angry/irritable mood.
Hyperactivity and impulsivity are two important dimensions of ADHD but are often described as one dimension in research. This grouping is most pronounced in childhood, whereas they begin to separate in adulthood, and impulsivity becomes more important [17,33,34]. The importance of dimensions of ADHD also changes with age. At preschool age, more emphasis is placed on hyperactivity and impulsivity, while maintaining and focusing attention to solve certain educational materials is not as important. This is somewhat to be expected, as preschool-age children often spend more time engaging their peers and less time maintaining attention to solve educational tasks. Attention becomes more important when children need to solve educational materials the preparation for school. Moreover, the expression of ADHD symptoms normatively decreases with age, as confirmed by objective measures of attention and impulsivity, i.e., it is not based solely on parent/caregiver assessments [35]. Interestingly, hyperactivity/impulsivity symptoms, in particular, are less stable and tend to decline more with age than attention symptoms [36]. In primary school, attention symptoms are most prominent and most responsible for learning difficulties. This trend continues in secondary school, where they become even more significant [37,38]. These findings may also explain the results of the present study. From Table 6 and Table 7, it can be seen that attention has one of the highest correlations with ODD. In addition, when the two models examined in this study are compared (Table 8, Table 9, Table 10 and Table 11), it is clear that the model for the sample of secondary students does not fit the data, while the model for elementary students does fit the data. These results may indicate the developmental progression of ADHD and changes in the importance of different groups of dimensions. In the model for elementary school students, it is also clear that attention is the only predictor that is significant for all dimensions of ODD and the most significant predictor for angry/irritable mood, whereas impulsivity is a significant predictor (borderline significant) only for argumentative/defiant behaviour. The theory of the importance of impulsivity as a transdiagnostic factor underlying the dimensions of ADHD and ODD relates mainly to preschool children, and the results obtained in this research raise the question of the extent to which it is also applicable to a later stage of education and older age. The diagnosis of ADHD at preschool age can lead to the occurrence of ODD in school age and later life, but only if the impulsivity-hyperactivity dimension is the dominant dimension in preschool age, which is confirmed by quite a few research. For example, Harty et al. [39] point out that the children diagnosed with ADHD with comorbid ODD showed more aggressive behaviours associated with increased emotionality expressed through anger. This description of symptoms is similar to that of Emotional Dysregulation—Impulsivity, with an emphasis on an angry/irritable mood. According to Roberts, Milich and Barkley [17], Emotional Dysregulation—Impulsivity is associated with the emotional component of ODD, with emotional inhibition having an important impact on the development of ODD. Barkley [20] highlights angry/irritable mood in explaining the link between ADHD and ODD. The symptoms describing emotional impulsivity have been used to form ODD in the DSM-III, which until then had been described along with ADHD. Therefore, considerable similarities with emotional impulsivity can be found in the description of ODD. For example, both authors emphasise the association of emotional impulsivity with angry/irritable mood. It is interesting to note that Karalunas et al. [40] highlight three specific types of ADHD: mild, characterised by normative emotion regulation; developing, characterised by extreme levels of positive motivation; and irritable, characterised by extreme levels of negative emotionality, anger and poor emotion regulation skills. In later research, Karalunas et al. [41] defined a group of children with ADHD and irritability, characterised by a category defined as a combination of ADHD and ODD symptoms, describing irritability as a specific aspect of ADHD. In addition, emotional dysregulation, which involves sudden changes in emotions, is associated with irritable and aggressive behaviour and is often in comorbidity with ODD [42]. Beauchaine et al. [7] found that impulsivity, in combination with emotional dysregulation, may be a precursor to the development of comorbidity between ADHD and ODD. Their research assumes an inherited risk for the development of impulsivity, which in combination with a non-supportive high-risk environment, leads to reduced development of emotion regulation skills, which in turn promotes the onset of ADHD and comorbid ODD and, in later life, CD and antisocial personality disorder. On the other hand, pronounced symptoms of inattention in preschool age may later cause the development of sluggish cognitive tempo, which includes the following symptoms: daydreaming, difficulty maintaining alertness/caution, mental fog/light confusion, absence, lethargy, decreased activity, slowness in movement, emotional distancing, loss of thought, slowness in performing tasks and low level of initiative [20]. It is clear that the relationship between ADHD and ODD is not a simple one and cannot be described with just the developmental and school factors. Harvey et al. [43] state that the comorbidity between ADHD and AIM may be explained with the correlated risk factors model, and the comorbidity between ADHD and ADB may be better explained with the developmental precursor model. The correlated risk factor model suggests that the comorbidity occurs due to shared genetic or environmental factors [44]. The developmental precursor model assumes that ADHD in children causes stress and negatively influences family functioning, as well as peer relationships, leading to an increased risk of ODD, specifically the development of ADB. Additionally, these two models have a significant interaction, which contributes to the complexity of the comorbidity between these two disorders. Executive functions (EF) might play a significant role in the comorbidity of ADHD and ODD as well. Although some research underlines [5,20,45] the connection between “hot” EF and emotional dysregulation, others [46] did not find a correlation between "hot" EF, ADHD and ODD but between "cold" EF and ADHD.The relationship between ADHD and ODD is complex, but there is a need for clarification since these two disorders are highly comorbid. The results of this research might offer additional evidence that this relationship changes with age but does not offer insight as to the causes of this change. Finally, the models tested in this research were based on a theory that is significant for understanding this form of comorbidity in preschool age. Since the data in this research were collected at a single point of measurement, no conclusions can be drawn about the causal relationship between the predictors and the criteria. This is important when explaining the significance of the model for primary school children, i.e., the significance of attention as a predictor of all ODD symptoms. In this case, it is possible to write and interpret only the relationship since the research does not offer the developmental course that would connect these symptoms.
5. Conclusions
In this research, two models that imply a significant influence of hyperactivity, impulsivity and attention on ODD symptoms were tested, with an emphasis on the influence of Impulsivity on angry/irritable mood. The relationship between these variables was based on the theory that confirms this relationship in the sample of preschool children. In this research, this theory was tested on the samples of primary and secondary school students, and it was shown how the fit of the model changes depending on the level of education of students. The assumed model for elementary school students is still acceptable in explaining the data, while for secondary school students, it no longer is. In the first model, attention was singled out as the most significant predictor, while impulsivity was significant only for argumentative/defiant behaviour. These results are not surprising, especially when taking into account the normative reduction of ADHD symptoms and the greater decline and lower stability of symptoms of hyperactivity and impulsivity when compared to attention [35,36]. In primary school, attention symptoms begin to take on a more dominant role, and this continues through secondary school [37,38] and may also be associated with slow cognitive tempo [12]. Although the results in this research were obtained on a large sample of primary and secondary school students, a longitudinal design that begins at preschool age and includes monitoring potential changes in the dimensions of ADHD and ODD could yield more reliable results about the transdiagnostic role of emotional dysregulation and impulsivity in the potential development of these disorders.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.B. and A.V.-P.; methodology, B.B.; validation, A.V.-P.; formal analysis, B.B.; investigation, B.B. and A.V.-P.; resources, A.V.-P.; data curation, A.V.-P.; writing—original draft preparation, B.B.; writing—review and editing, A.V.-P.; visualization, B.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethical Committee of the University of Zadar (protocol code 0070012, 21.02.2006) for studies involving humans.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. ADHD and ODD Items (in Croatian and Translated into English)
| Hyperactivity (6) | |
| H1 | Teško mi je mirno sjediti na jednom mjestu. It is hard for me to sit still in one place. |
| H3 | Ne mogu biti miran i sjediti na jednom mjestu, već moram ustajati, mahati nogama i vrpoljiti se. I can’t be still and sit in one place, I have to stand up and fidget. |
| H5 | Za mene se može reći da sam nemirna i pretjerano aktivna osoba. I am a restless and overly active person. |
| H7 | Nemam strpljenja za aktivnosti i obaveze koje se moraju obavljati polako i tiho. I have no patience for activities and obligations that must be done slowly and quietly. |
| H9 | Nikad nemam mira. I am never at peace. |
| H11 | Brbljav sam i previše pričam. I’m chatty and I talk too much. |
| Impulsivity (4) | |
| H13 | Dajem odgovore i prije nego što čujem pitanje do kraja. I answer before I hear the end of the question. |
| H16 | Nemam strpljenja čekati u redu. I have no patience to wait in line. |
| H18 | Upadam drugima u razgovor. I interrupt other people’s conversations. |
| H19 | Prekidam ili ometam druge u onome što rade ili govore. I interrupt or disrupt others in what they are doing or saying. |
| Attention (9) | |
| H2 | Griješim u pisanju školske zadaće jer se ne mogu koncentrirati na ono što radim. I make mistakes in my homework because I can’t concentrate on what I’m doing. |
| H4 | Teško mi je održati pažnju tijekom pisanja zadaće ili neke igre. It’s hard for me to pay attention while doing homework or playing a game. |
| H6 | Ne slušam druge čak i kad mi se izravno obraćaju. I don’t listen to others even when they speak directly to me. |
| H8 | Događa mi se da ne završim školsku zadaću ili učenje do kraja jer više nemam strpljenja. I do not finish my homework because I lose focus and patience. |
| H10 | Teško mi je organizirati moje obveze, aktivnosti, učenje i dr. It is difficult for me to organize my obligations, activities, learning, etc. |
| H12 | Izbjegavam zadatke i obveze koji zahtijevaju dužu koncentraciju i veće mentalne napore. I avoid tasks and obligations that require longer concentration and greater mental effort. |
| H14 | Spadam u one učenike koji često gube stvari, na primjer školski pribor, knjige i sl. I often lose school things like supplies, books, etc. |
| H15 | Čini mi se da me sve oko mene može vrlo lako omesti. It seems to me that everything around me can easily distract me. |
| H17 | Zaboravljam i svakodnevne obveze. I forget my day-to-day obligations. |
| Angry/Irritable Mood (3) | |
| S6 | Lako sam se uzrujao. I often lose temper. |
| S7 | Bio sam osjetljiv na postupke drugih. I am often touchy or easily annoyed. |
| S8 | Bio sam ljutit i srdit. I am often angry and resentful. |
| Argumentative/Defiant Behaviour (4) | |
| S2 | Svađao sam se s odraslima. I often argue with authority figures or adults. |
| S3 | Aktivno sam se suprotstavljao ili odbijao pokoriti zahtjevima i pravilima odraslih. I often actively defy or refuse to comply with requests from authority figures or with rules. |
| S4 | Namjerno sam ometao druge ljude. I often deliberately annoy others. |
| S5 | Okrivio sam druge za vlastite pogreške ili loše ponašanje. I often blame others for my mistakes or misbehavior. |
| Vindictiveness (1) | |
| S9 | Bio sam zloban i osvetoljubiv. I have been spiteful or vindictive. |
References
- Moreno-De-Luca, A.; Myers, S.M.; Challman, T.D.; Moreno-De-Luca, D.; Evans, D.W.; Ledbetter, D.H. Developmental brain dysfunction: Revival and expansion of old concepts based on new genetic evidence. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicchetti, D. Developmental psychopathology. In Developmental Psychopathology: Volume 1. Theory and Method, 2nd ed.; Cicchetti, D., Cohen, D.J., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Angold, A.; Costello, E.J.; Erkanli, A. Comorbidity. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 1999, 40, 57–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauchaine, T.P.; McNulty, T. Comorbidities and continuities as ontogenic processes: Toward a developmental spectrum model of externalizing psychopathology. Dev. Psychopathol. 2013, 25, 1505–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigg, J.T.; Barkley, R.A. Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. In Child Psychopathology: Third Edition; Mash, E.J., Barkley, R.A., Eds.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 75–145. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, R.; Costello, J.; Angold, A.; Copeland, W.E.; Maughan, B. Developmental pathways in oppositional defiant disorder and conduct disorder. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2010, 119, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauchaine, T.P.; Hinshaw, S.P.; Pang, K.L. Comorbidity of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and early onset conduct disorder: Biological, environmental, and developmental mechanisms. Clin. Psychol. Sci. Pract. 2010, 17, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhoff, K.W.; Lerner, M.; Kapilinsky, A.; Kotkin, R.; Wigal, S.; Steinberg-Epstein, R.; Wigal, T.; Swanson, J.M. Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. In Handbook of Preschool Mental Health: Development, Disorders, and Treatment; Luby, J.L., Ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 63–80. [Google Scholar]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, S.L.; Choe, D.E.; Sameroff, A.J. Trajectories of child externalizing problems between ages 3 and 10 years: Contributions of children’s early effortful control, theory of mind, and parenting experiences. Dev. Psychopathol. 2017, 29, 1333–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Childhood externalizing behavior: Theory and implications. J. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Nurs. 2004, 17, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersan, C.; Tok, Ş. The study of the aggression levels of preschool children in terms of emotion expression and emotion regulation. Educ. Sci. 2020, 45, 359–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, D.F.; Payne, A.; Chadwick, A. Peer relations in childhood. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2004, 45, 84–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenreich-May, J.; Chu, B.C. Overview of transdiagnostic mechanisms and treatments for youth psychopathology. In Transdiagnostic Treatments for Children and Adolescents: Principles and Practice; Ehrenreich-May, J., Chu, B.C., Eds.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Newcorn, J.H.; Halperin, J.M.; Miller, C.J. ADHD with oppositionality and aggression. In ADHD Comorbidities: Handbook for ADHD Complications in Children and Adults; Brown, T.E., Ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; pp. 157–176. [Google Scholar]
- Pliszka, S. Comorbid Psychiatric Disorders in Children with ADHD. In Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Handbook for Diagnosis & Treatment; Barkley, R.A., Ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 81–116. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, W.; Milich, R.; Barkley, R.A. Primary symptoms, diagnostic criteria, subtyping, and prevalence of ADHD. In Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Handbook for Diagnosis & Treatment; Barkley, R.A., Ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 51–81. [Google Scholar]
- Canino, G.; Polanczyk, G.; Bauermeister, J.J.; Rohde, L.A.; Frick, P.J. Doest the prevalence of CD and ODD vary across cultures? Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2010, 45, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, J.; Arnold, E.; Kraemer, H.; Hechtman, L.; Molina, B.; Hinshaw, S.; Vitiello, B.; Jensen, P.; Steinhoff, K.; Lerner, M.; et al. Evidence, interpretation, and qualification from the multiple reports of long-term outcomes in the Multimodal Treatment study of Children With ADHD (MTA): Part I: Executive summary. J. Atten. Disord. 2008, 12, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkley, R.A. Emotional dysregulation is a core component of ADHD. In Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Handbook for Diagnosis & Treatment; Barkley, R.A., Ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 81–116. [Google Scholar]
- Gottman, J.M.; Katz, L.F. Effects of marital discord on young children’s peer interaction and health. Dev. Psychol. 1989, 25, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Stralen, J. Emotional dysregulation in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. ADHD Atten. Deficit Hyperact. Disord. 2016, 8, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, M.; Quinn, M.; Duncan, D.; Graham, T.; Balbuena, L. Oppositional defiant disorder I better conceptualized as a disorder of emotional regulation. J. Atten. Disord. 2016, 21, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, J.D.; Romano-Verthelyi, A.M. Oppositional defiant disorder. In Developmental Pathways to Disruptive, Impulse-Control and Conduct Disorders; Martel, M.M., Ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 21–52. [Google Scholar]
- Vulić-Prtorić, A. Skala agresivnosti za djecu i adolescente. In Zbirka psihologijskih skala i upitnika 4; Penezić, Z., Ćubela Adorić, V., Proroković, A., Tucak Junaković, I., Eds.; Sveučilište u Zadru: Zadar, Croatia, 2018; pp. 83–99. [Google Scholar]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th revised ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Vulić-Prtorić, A. Skala hiperaktivnosti–impulzivnosti–pažnje–HIP. In Zbirka psihologijskih skala i upitnika 3; Ćubela Adorić, V., Proroković, A., Penezić, Z., Tucak, I., Eds.; Sveučilište u Zadru: Zadar, Croatia, 2006; pp. 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Satorra, A.; Bentler, P.M. Corrections to test statistics and standard errors in covariance structure analysis. In Latent Variables Analysis: Applications for Developmental Research; von Eye, A., Clogg, C.C., Eds.; Sage Publications, Inc.: London, UK, 1994; pp. 399–419. [Google Scholar]
- Curran, P.J.; West, S.G.; Finch, J.F. The robustness of test statistics to nonnormality and specification error in confirmatory factor analysis. Psychol. Methods 1996, 1, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.Y.; Muthén, B. Evaluation of Model Fit Indices for Latent Variable Models with Categorical and Continuous Outcomes; Technical Report; Graduate School of Education & Information Studies, University of California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, K.-H. Fit indices versus test statistics. Multivar. Behav. Res. 2005, 40, 115–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkley, R.A.; Fischer, M. The unique contribution of emoional impulsiveness to impairment in major life activities in hyperactive children as adults. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2010, 49, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkley, R.A. Barkley Adult ADHD Rating Scale—IV (BAARS-IV); The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Willcutt, E.G.; Nigg, J.T.; Pennington, B.F.; Solanto, M.V.; Rohde, L.A.; Tannock, R.; Loo, S.K.; Carlson, C.L.; McBurnett, K.; Lahey, B.B. Validity of DSM-IV attention deficit/Hyperactivity disorder symptom dimensions and subtypes. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2012, 121, 991–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, E.B.; Cardoos, S.L.; Hinshaw, S.P. Developmental progression and gender differences among individuals with ADHD. In Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Handbook for Diagnosis & Treatment; Barkley, R.A., Ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 223–256. [Google Scholar]
- Biderman, J.; Petty, C.R.; Evans, M.; Small, J.; Faraone, S.V. How persistent is ADHD? A controlled 10-year follow-up study of boys with ADHD. Psychiatry Res. 2010, 177, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuPaul, G.J.; Langberg, J. Educational impairments in children with ADHD. In Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Handbook for Diagnosis & Treatment; Barkley, R.A., Ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 169–191. [Google Scholar]
- Langberg, J.M.; Brooke, S.G.; Molina, L.; Eugene, A.; Epstein, J.N.; Altaye, M.; Hinshaw, S.P.; Swanson, J.M.; Wigal, T.; Hechtman, L. Patterns and predictors of adolescent academic achievement and performance in a sample of children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 2011, 40, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harty, S.C.; Miller, C.J.; Newcorn, J.H.; Halperin, J.M. Adolescents with childhood ADHD and comorbid disruptive behavior disorders: Aggression, anger and hostility. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2009, 40, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karalunas, S.L.; Fair, D.; Musser, E.D.; Aykes, K.; Iyer, S.P.; Nigg, J.T. Subtyping Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder using temperament dimensions. JAMA Psychiatry 2014, 71, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karalunas, S.L.; Gustafsson, H.C.; Fair, D.; Musser, E.D.; Nigg, J.T. Do we need an irritable subtype of ADHD? Replication and extension of a promising temperament profile approach to ADHD subtyping. Psychol. Assess. 2019, 1, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringaris, A. Irritability in children and adolescents: A challenge for DSM-5. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2011, 20, 21–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, E.A.; Breaux, R.P.; Lugo-Candelas, C.I. Early development of comorbidity between symptoms of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and oppositional defiant disorder (ODD). J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2016, 125, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, S.A.; Krueger, R.F.; McGue, M.; Iacono, W.G. Sources of covariation among attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, oppositional defiant disorder, and conduct disorder: The importance of shared environment. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2001, 110, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonini, T.N.; Becker, S.P.; Tamm, L.; Epstein, J.N. Hot and cool executive functions in children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and comorbid oppositional defiant disorder. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2015, 21, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luman, M.; Sergeant, J.A.; Knol, D.L.; Oosterlaan, J. Impaired decision making in oppositional defiant disorder related to altered psychophysiological responses to reinforcement. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 68, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).