Abstract
The main aim of this study was to create a new test to assess the motor skills of children of preschool and early school age and to determine its reliability and validity. Thirty children (5–6 years old) were tested on two occasions 14 days apart. The testing procedures included measuring the participants’ performance on the Four Station Fundamental Motor Test (4-SFMT). The newly constructed 4-SFMT tested four fundamental skills/tasks: space covering (ROLL), overcoming resistance (PULL), object control (BALL), and overcoming obstacles (CLIMB). The performance was evaluated with a 22-point scale with different criteria for each skill, and the time taken to perform the test was measured. The concurrent validity was assessed by determining the correlation with a Test of Gross Motor Development (TGMD-2). The level of agreement across trials was statistically significant for all three raters, with two variables presenting excellent reliability (ICC > 0.9) and two variables having good reliability (ICC > 0.75 and <0.9). No significant differences were found between the test and retest scores, indicating the test’s high reliability. A factor analysis isolated only one motor factor (accounting for 43.99% of the variance with the eigenvalue of 1.768) from the four tasks. There was a large correlation (r = −0.576, p < 0.01) between the process- and product-oriented assessments of the 4-SFMT. Moreover, significant correlations were found between the 4-SFMT and TGMD-2 regarding the scores (r = 0.824, p < 0.001) and time taken to perform the tasks (r = −0.652, p < 0.001), which indicates the good concurrent validity of the newly constructed test. Small to moderate correlations between tasks (0.016 to 0.497) and no differences between boys and girls in the total score (p = 0.943) and time taken to complete the tasks (p = 0.49) were determined. The 4-SFMT appears to be a valid and reliable tool that can be used to evaluate motor skills performance in children between the ages of 5 and 6 and is reasonably simple to use.
1. Introduction
Human motor development is a process that includes progressions and regressions of motor competence throughout life [1]. The term “motor competence” (MC) is globally understood and refers to the level of proficiency with which children can execute fundamental motor skills [2]. Process-oriented MC assessments evaluate how a movement is performed, while product-oriented assessments evaluate the outcome of a movement. It is widely believed that motor development is the most important form of development throughout the lifespan, and that it takes place during the most sensitive phase between birth and six years of age. [3]. In that period, as many as three phases of motor development change (reflex phase, phase of elementary movements, and phase of basic motor patterns). It is believed that children can hardly reach their full motor potential if their motor development is not stimulated in this specified period [4]. This is extremely important knowledge because motor competence (MC) in children and adolescents is directly related to numerous health-related outcomes including physical activity [5], physical fitness [6], lower body mass index [7], cardiorespiratory fitness [8], well-being [9], and even cognitive health [10]. Although there is a relatively large number of tests that assess MC in children and adolescents, most of them were developed for clinical purposes and are used to identify children with motor impairments or medical deficits [11]. Moreover, the implementation of most tests takes a long time [12], and a good number of them require special equipment and props, which also reduces their practicality, i.e., applicability. On the other hand, it is known that testing children in early childhood is very demanding, and care should be taken to ensure that it does not take too long, that the environment is safe, and that, in general, the administration of the test is not a negative experience for these children [13].
The results of some studies are interesting as they show that in early childhood, there is a significantly different structure of motor dimensions when compared to the older population. Namely, at an early age, there is no clear differentiation between different motor abilities and motor skills, as is the case in adults [14,15]. It seems that in early childhood, only one motor factor dominates, which determines the motor competence of the child. In practice, this would mean that by determining only one motor segment of the child (regardless of whether motor performance or qualitative motor achievements were tested), the general state of the MC of that subject could be assessed. This assessment should be more accurate as the test becomes more complex. Therefore, is it justified to carry out long-term testing protocols with a whole series of subtests for the assessment of motor competence if it is possible to determine this with one simple and quick test? This is particularly relevant in situations where the testing time is limited, such as in preschool and school institutions during physical education lessons. The goal is not to determine motor impairment or medical deficits but simply to assess some of the fundamental motor skills as a part of the motor competence of preschool- or early school-age children, or for the possible identification sports talent [16]. However, caution is needed and further research on the young athletes’ population is still needed. Motor competence is often assessed within the general population to identify children who may benefit from additional training. Nevertheless, motor competence assessments for sports and talent identification are becoming increasingly prevalent [17].
For the purposes of this research, such a test was constructed. Its duration is relatively short and can be applied as a product- and process-oriented test or even both. Process-oriented MC assessments evaluate how a movement is performed, while product-oriented assessments evaluate the outcome of a movement. Additionally, the newly constructed test has a relatively high ecological validity because the tasks are carried out alternately in continuity [18] and it does not require expensive equipment. Therefore, the main goal of this research was to create a new test to assess the motor skills of children of preschool and early school age and to determine some of its psychometric properties. For the purposes of the psychometric properties assessment, the test–retest method was applied, and a comparison was made with the TGMD-2. Moreover, it was hypothesized that there would be sex differentiation and moderate correlations between the test items.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
The Four Station Fundamental Motor Test (4-SFMT) construction and evaluation process consisted of several phases: the development stage (identification of the 4-SFMT items/tasks); the reliability study stage (assessment of test consistency, where two aspects were addressed, i.e., test–retest reliability and inter-rater and intra-rater reliability); and the validation stage (comparison with the criterion test for concurrent validity assessment and correlation between tasks with sex differentiation for construct validity).
2.2. Participants
In order to establish the psychometric properties of the 4-SFMT, a convenience sample of 30 preschool children (12 girls and 18 boys) from 5 to 6 years old was recruited. There were no behavioral, executive function (e.g., attention deficit hyperactivity disorder), or musculoskeletal issues or learning impairments among the children who participated in this experiment. Before the children participated in this study, their parents and guardians received a letter with information about the study and signed the informed consent form. Parents were clearly informed that the child could withdraw from the experiment at any time without giving a reason.
2.3. 4-SFMT Development
The 4-SFMT was created by a group of four experts with extensive knowledge in motor skill development, early childhood physical education, measurement methodologies, and sports pedagogy. The panel group was requested to evaluate each skill for age appropriateness and feasibility. Additionally, experts were asked to give their opinions and suggestions about particular skills and the test. The 4-SFMT was designed to follow the curriculum for physical education, which defined minimal standards for preschools of the Republic of Croatia [19]. Children’s physical education classes were analyzed in order to evaluate the tasks and skills that kids typically use in these settings. Furthermore, test items (tasks) were categorized into the following groups according to their utility [20]: (1) space-covering skills (various types of rolling, looping, crawling, walking, and running that allow humans to cover distances on various types of surfaces and in various directions); (2) overcoming resistance skills (a variety of pushing, pulling, holding, and carrying techniques used to overcome the passive resistance of objects of different volumes and shapes); (3) object-control skills (simple and complex operations of managing objects that differ in quantity, shape, and volume in a specific time and place by using a variety of throwing and catching, targeting, and shooting skills); and (4) overcoming obstacles skills (different forms of crawling through a narrow space, climbing, landing, and jumping that assists us in overcoming various types of vertical, diagonal, and horizontal obstacles without the use of any technical or other types of devices).
After careful examination, the test was deemed to include only one task from all four groups of basic motor skills, which fulfilled the study’s main aim of constructing a simple and short test. Therefore, the expert panel proceeded to develop a framework for the 4-SFMT by selecting the four tasks that best represent a certain movement skills area:
- (1)
- Rolling on a mat in an upward arms position, which measures space-covering skills (ROLL). The task was performed on a soft mat with dimensions of 200 cm × 100 cm and a thickness of 5 cm. The child had to roll with their hands in an upward position from the beginning to the end of the mat.
- (2)
- Pulling one’s body on a bench, which measures overcoming resistance skills (PULL). The task was performed on a wooden bench with a 340 × 26 surface and a height of 36 cm. The child had to pull his body from the beginning of the bench to the end. Only cotton shirts were allowed to avoid unnecessary friction due to the nature of the material (e.g., plastic print).
- (3)
- Pushing a ball over a bench, which measures object-control skills (BALL). The task was performed on the same wooden bench that was used in the PULL task. The child had to take a 400 g plastic ball with a diameter of 20 cm (which is usually used in rhythmic gymnastics) and guide it on the surface of the bench from the beginning to the end. The task was performed with the child’s dominant hand, which was determined by having the kid do three unimanual tasks: drawing a line with a pencil, cutting paper with scissors, and inserting a peg in the instructor’s hand. The dominant hand is the hand used for most tasks [21].
- (4)
- Climbing on a wooden ramp, which measures overcoming obstacles skills (CLIMB). The task was performed on an 85 cm × 250 cm wooden ramp that was set on a Swedish ladder that was 110 cm tall. The ramp had twenty-nine 15 cm × 8 cm holes, which made climbing easier. The child had to climb the board and touch the mark set at 130 cm.
The final version of the test consisted of four tasks that the children were required to perform in one trial in a circular manner (Figure 1). Every task was photographed and shown to the children to ensure they understood the type of movement selected for the test. The exact order of execution was as follows: ROLL, PULL, BALL, and CLIMB. The tasks were arranged in this order to ensure the participating children’s safety and allow for several transitions between various skill sets. Additionally, it was observed that the children occasionally had difficulty transitioning easily from one skill to the next, so the less complex skills were administered first. Moreover, the CLIMB task was administered last to properly ensure a safe environment for the children. The performance assessment was conducted in two ways: quantitatively (by measuring time) and qualitatively (by scoring each task).
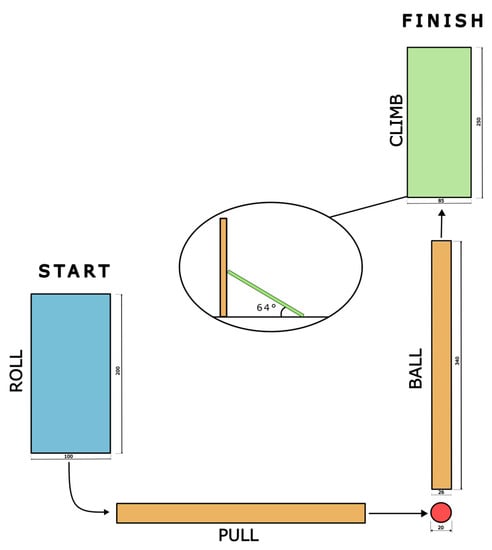
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the 4-SFMT. Dimensions are presented in centimeters.
2.4. Development of a 22-Point Skill Scale
To evaluate each task, a 22-point score assessment scale was developed. The scale consisted of different criterions for each task: three for the ROLL, BALL, and CLIMB, and two for the PULL. For each criterion, ratings of 0, 1, and 2 were assigned (a detailed description of each criterion is presented in Table 1). As a result, each participant had the chance to achieve a maximum of 22 points. The panel of three experts (research scientists with a Ph.D.) with a background in motor learning and skill development was recruited to establish the instrument’s face and content validity.

Table 1.
Description of a 22-point skill score.
2.5. Procedures
The experiment was conducted in a sports hall that resembled a typical preschool gymnasium during the day. Individual tests on the children were conducted by the principal researcher and an assistant (both kinesiology experts) trained in the testing procedures. First, the children performed the 4-SFMT. The children were given clear instructions on how to perform the test in the exact prescribed order, starting with ROLL and ending with CLIMB. Each item (station) was demonstrated and described to the children. Following the principal researcher’s example, the children completed two try-out trials, during which verbal assistance and feedback on how to properly execute the skills were given to the participants. This feedback enabled the children to perform the measurement trial independently. The principal researcher instructed the child to prepare and start the test by saying “Go!” while the assistant started measuring time with a stopwatch. The test was finished when the child performed the last task in the test. Each child performed the test only one time. After the 4-SFMT, the children were instructed to perform the Test of Gross Motor Development (TGMD-2) [22]. The test is divided into two subtests (the locomotor skills subtest and the object-control skills subtest) with six skills each. The locomotor subtest consists of the following six skills: run, gallop, hop, leap, jump, and slide. The object-control subtest consists of the following six skills: striking a stationary ball, stationary dribble, catching, kicking, overhand throw, and underhand roll. Depending on the test, each skill has a set of three to five criteria, and each one is scored with a 0 or 1. The child performs each skill twice; therefore, each skill’s maximum score ranges from 6 to 10. The test began when the principal researcher instructed the child to prepare and start the test at their free will.
2.6. Reliability Estimates
The reliability of a test can be described as the consistency of the test results, e.g., the extent to which that same test would produce the same results under the same conditions when repeated several times [23]. The consistency of the 4-SFMT was evaluated using test–retest and inter-rater/intra-rater reliability. Therefore, the children performed the 4-SFMT on two separate occasions with a time frame of two weeks between the test and retest. The amount of time between two test administrations can have an impact on the test–retest reliability. Carryover effects due to memory or practice are more likely if the length interval is very short, whereas a longer interval can increase the chances of changes in these parameters. Each performance was videotaped to assess the inter-rater and intra-rater reliability of a skill scale, and the participants were fully informed that they would be videotaped throughout the test. To improve the quality of the video assessment, two cameras were used to record the videos (GoPro Hero 7 Black; GoPro, San Mateo, CA, USA). After the video recordings were processed, three raters with extensive experience in physical education (all three were educated kinesiologists) conducted the performance evaluation. The recordings were given to the raters to evaluate (score) the performance using guidelines after they were briefed on the procedures and study aims. The following instructions were given to each rater: (a) strictly follow the assessment scoring scale; (b) when scoring is complete, do not rewind the clip; and (c) try to complete the evaluations at the same time of day [24]. The order of the videos was randomly chosen.
2.7. Validity
Newly constructed tests should be assessed for various types of validity when scores are used for their intended purpose. Two types of validity were tested for the 4-SFMT: concurrent and construct validity. Concurrent validity involves correlating a newly constructed instrument concurrently with some criterion (reference test). The TGMD-2 was the criterion used for comparison with the 4-SFMT. The TGDM-2 is widely considered to be a robust process-oriented tool and has been extensively used to assess the motor skill performance of children up to 10 years of age. Moreover, previous research has shown that this test is reliable and valid for this age group [25,26]. Construct validity refers to the degree to which a test measures the construct it was designed to measure, and several factors can be used to demonstrate this type of validity. For the purposes of this study, sex differentiation and the correlation between the four tasks was assessed. As this test consists of four tasks representing four groups of basic motor skills (dimensions) [20], each task should have a significant positive correlation with the overall test score and a moderate correlation with each other.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
All the data were analyzed with SPSS 28.0 statistical software (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA) and GraphPad Prism 9 (GraphPad Software, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) and are presented as the mean and standard deviation after the normality of the data was confirmed with a Shapiro–Wilk test. To evaluate the level of agreement across the trials to establish evidence of inter-rater and intra-rater objectivity and test–retest reliability, intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) with 95% confidence intervals (95%CI) were calculated from a two-way mixed-effects model for absolute agreement. The ICC is a value between 0 and 1, where values below 0.5 indicate poor reliability, values between 0.5 and 0.75 indicate moderate reliability, values between 0.75 and 0.9 indicate good reliability, and any value above 0.9 indicates excellent reliability [27]. A paired t-test was used to determine systematic bias/differences between two testing occasions (test/retest). Additionally, the standard error of measurement (SEm) and standard error of measurement expressed as a coefficient of variation (CV%) were calculated to determine within-individual variation, and a 95% confidence interval was also presented. Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity [28] and The Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin Measure (KMO) of Sampling Adequacy [29] was used to determine the suitability of the data for factor analysis, which was performed to find meaningful underlying dimensions. A value of 0.60 was the minimum standard to determine matrix factorability in the KMO. An exploratory factor analysis (EFA) was performed using principal component extraction and eigenvalues > 1. The scree test was used to decide how many factors to retain [30]. However, although considered the best and easy to administer, the scree test involves searches for sharp distinctions between the eigenvalues, and sometimes there may be more than one demarcation point. Moreover, the reliability of scree plot interpretations is found to be low [31]. Therefore, Parallel Analysis (PA) and Velicer’s Minimum Average Partial (MAP) test [32] were conducted as supplementary analyses. Both the PA and MAP were conducted using the O’Connor SPSS syntax [33]. As suggested by Comrey and Lee [34], the factor loadings were interpreted as excellent (>0.71), very good (>0.63 and <0.71), good (>0.55 and <0.63), fair (>0.45 and <0.55), and poor (>0.32 and <0.45). Values of 0.32 should be the minimum threshold used to identify significant factor loadings [35]. The Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient (r) associated with 95%CI and the coefficient of determination (R2) were calculated to examine the relationship between each item and the total score and performance time and to establish the relationship between the 4-SFMT and TGDM-2. The magnitude of the correlations was also determined using the modified scale by Hopkins [36]: 0.1, trivial; 0.1–0.3, small; 0.3–0.5, moderate; 0.5–0.7, large; 0.7–0.9, very large; 0.0.9, nearly perfect. An unpaired t-test was conducted to determine the differences in the 4-SFMT raw scores and the performance time between genders. All the effect sizes for the appropriate analyses were calculated using Cohen’s d [37], with values of <0.2, >0.2 and <0.6, >0.6 and <1.2, >1.2 and <2.0, and ≥2.0 considered as trivial, small, medium, large, and very large effects, respectively. The level of statistical significance for the analyses was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Inter-Rater and Intra-Rater Reliability
Intra- and inter-rater reliability values for the 4-SFMT score are presented in Table 2. Evidence for inter-rater objectivity was excellent (ICC > 0.9) for ROLL, PULL, and the overall score and was good (ICC > 0.75 and <0.9) for BALL and CLIMB. Evidence for intra-rater reliability for the skill score ranged from excellent for the overall score to moderate for BALL for all three raters.

Table 2.
Intra- and inter-rater reliability for 4-SFMT score.
3.2. Test–Retest Reliability
Table 3 shows the means and standard deviations of the test and retest scores, CV%, and the 95% confidence intervals for the ICCs and SEm. The ICCs between the test and retest scores ranged from 0.711 to 0.995. No significant differences were found between the test and retest scores, although small effects were detected for ROLL and CLIMB.

Table 3.
Means and standard deviations of test and retest scores and measures of reliability.
3.3. Determination of the Factorial Structure with EFA
The factorial structure of the 4-SFMT is presented in Table 4. The significant Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity (χ2 = 11.471, p = 0.075) and the KMO value of 0.61 indicates that the correlation matrix had significant correlations among some of its components and that the sample was adequate, respectively. By looking at the scree plot (not presented), one factor had an eigenvalue greater than one, accounting for 43.99% of the variance with the eigenvalue of 1.768. The PA revealed that the raw data eigenvalue from the actual data was greater than the eigenvalues of the 95th percentile of the random data distribution for one factor. Additionally, Velicer’s MAP test confirmed a one-factor solution. A chi-square goodness-of-fit test determined that the one-factor model fit the data well, χ2(2) = 0.18, p = 0.916. As shown in Table 4, ROLL and PULL had excellent loadings for Factor 1, while PULL and CLIMB had fair loadings.

Table 4.
Factor loadings from EFA.
3.4. Construct Validity
Table 5 shows the results of the correlation between the 4-SFMT total score and interitem correlation matrix. As expected, all the item correlations with the total score were positive and significant. The highest correlation with the total score was with BALL (R2 = 0.572, t = 6.122, very large). A significant negative correlation between the total score and performance time was observed (R2 = 0.332, t = −3.727, moderate). Correlations between scores on individual items were significant only between ROLL and BALL (R2 = 0.247, t = 3.03, small). Performance time significantly correlated with ROLL (R2 = 0.259, t = −3.127, small) and BALL (R2 = 0.218, t = −2.796, small).

Table 5.
Correlation analysis between 4-SFMT total test score and time and interitem correlation.
Differences between boys and girls regarding the 4-SFMT total score and performance time are presented in Table 6. There were no significant differences in both variables (total score (t = 0.072; d = 0.014: trivial) and performance time (t = 0.669; d = 0.14: trivial)).

Table 6.
Differences between boys and girls in 4-SFMT total score and performance time.
3.5. Concurrent Validity
Correlations between the 4-SFMT total score and performance time and the TGMD-2 score are presented in Figure 2 and Figure 3. Figure 2 shows significant positive correlations between the 4-SFMT total score and TGMD-2 score (r = 0.824, R2 = 0.679, t = 7.696 p < 0.001). The correlation between the 4-SFMT performance time and TGMD-2 score was significant and negative (r = −0.652, R2 = 0.425, t = −4.574, p < 0.001), as shown in Figure 3.
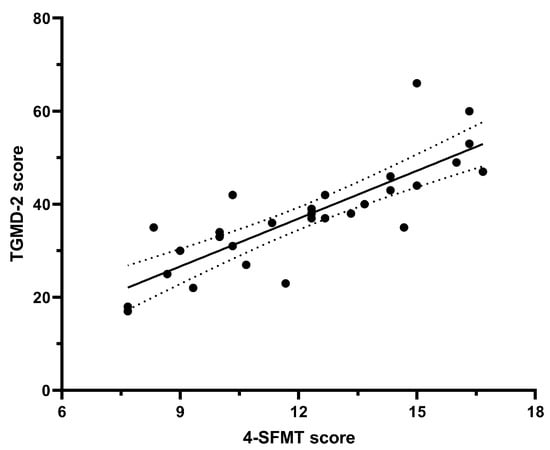
Figure 2.
Correlation between 4-SFMT total score and TGMD-2 score. The solid line represents the best fit, and the dotted lines represents the 95% confidence interval surrounding the line of best fit.
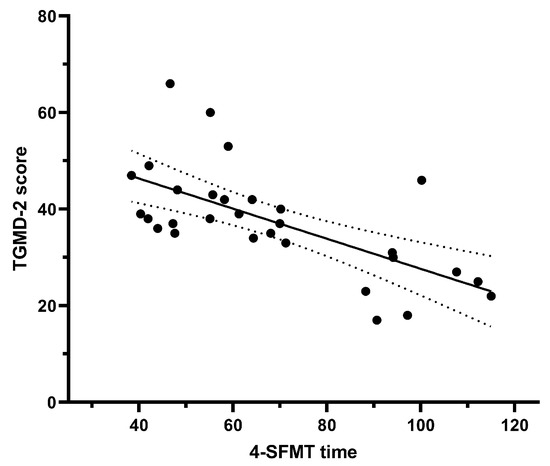
Figure 3.
Correlation between 4-SFMT performance time and TGMD-2 score. The solid line represents the best fit, and the dotted lines represents the 95% confidence interval surrounding the line of best fit.
4. Discussion
The main aim of this study was to create a new test to assess the motor skills of children of preschool and early school age and to determine its reliability and validity. The main findings were as follows: (a) all the ICC values that represent the level of agreement between the raters were statistically significant for all three raters, with two variables presenting excellent (ICC > 0.9) reliability and two variables having good reliability (ICC > 0.75 and <0.9); (b) no significant differences were found between the test and retest scores, although small effects were detected for two tasks, indicating the test’s high reliability; (c) through factor analysis, one motor factor F1 was isolated from the four tasks representing space covering, overcoming resistance, object control, and overcoming obstacles skills; (d) there was a moderate correlation between process- and product-oriented assessments of the 4-SFMT; (e) statistically significant correlations (from large to very large) were found between the process- and product-oriented assessments of the test 4-SFMT and test TGMD-2, which indicates the good concurrent validity of the newly constructed test; (f) there was no statistically significant difference in the quantitative and qualitative results of the newly constructed test between boys and girls.
The results confirmed that the criteria for evaluating certain motor skills with the 4-SFMT were well defined because all indicators of agreement between the experts had acceptable values (ICC from 0.778 to 0.953). These results are in line with other product-oriented assessment tests such as the Movement Assessment Battery for Children (MABC), Bruininks–Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency (BOT), and Körpercoordinationstest für Kinder (KTK), where values of inter-rater reliability were in the range from good (ICC > 0.75–0.9) to excellent (ICC > 0.9) in several studies [38,39,40]. Moreover, the excellent test–retest ICC values of 0.973 and 0.995 for score and time for the 4-SFMT are comparable with the Athletic Skills Track (AST; ICC = 0.891) [41] and Canadian Agility and Movement Skill Assessment (CAMSA; ICC = 0.91) [42]. Somewhat lower reliability values (test–retest scores) of the 4-SFMT could be observed only for one task, while the values of the remaining tasks as well as the overall process and product of the obtained results were excellent. The task with lower reliability values was the task used to assess object-control skills (BALL), whereby children had to roll a ball on a bench. This task was probably the most complex in terms of its structure and was less familiar to children than the other locomotor tasks in the test. It is known that object-control skills are acquired later and are generally more difficult than locomotor skills [1]. From the results of the intra-rater reliability (Table 2), it is also noticeable that all three experts showed the lowest values of agreement precisely in that task.
One of this study’s interesting findings is the factor analysis results. Namely, although the 4-SFMT included four items that assessed the slightly different skill domains of gross MC, the factor analysis isolated only one construct—the factor of general motor competence. Such results are in accordance with some previous findings [15,20] and confirm the hypothesis stated in the introduction regarding the absence of strict differentiation in MC in children of that age. However, further research on a larger sample of subjects and with a larger number of tests is necessary for such conclusions to receive relevant scientific confirmation. In other tests used to assess FMS, it was found that there was a different number of factors obtained through factor analysis. Regarding the MBAC test, there was a disagreement in the obtained structures, so different studies demonstrated a two-factor, three-factor, or even five-factor structure [43], for example. Furthermore, four factors were confirmed with the Polygon test [20]; however, due to a small number of studies on structural validity, these results should be taken with caution. In all variants of the TGDM test, a stable structure has been demonstrated where all studies confirmed a two-factor model (locomotion and object control) despite cultural differences [43]. Similar to the findings of the 4-SFMT, the KTK test also found to have a one-factor structure, with the factor being interpreted as the coordination of the body [44].
The correlation coefficients between the scores on individual items were relatively low and were significant only between ROLL and BALL (R2 = 0.247, t = 3.03). However, when determining the validity, it is recommended that the correlations between the tasks should not be too high because this would mean that they measure the same ability to the same degree and therefore are redundant [22]. On the other hand, there was a significant connection between performance time and total score, which points to the conclusion that the quality of the performance of given motor skills significantly affects the speed of performance of these skills. This is in line with previous empirical evidence that indicates a moderate to very large association between process- and product-oriented assessments [45,46]).
One of the goals of this research was to determine the concurrent validity of the newly constructed test. For this purpose, a Pearson’s correlation coefficient was calculated to determine the correlation between the performance time and total score of the 4-SFMT on the one hand and the results of the TGMD on the other (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Both correlations were significant, with a higher coefficient recorded in the total score compared to the performance time (r = 0.824 versus r = −0.652). Such a result was expected since the total score was obtained via a qualitative assessment of motor skills, which is very close to the method of evaluating the TGMD, which belongs to the category of criterion-referenced tests. Ultimately, no significant differences were found in the analyzed variables between boys and girls (total score (t = 0.072, p = 0.943); performance time (t = 0.669 p = 0.49)). This finding contradicts the hypothesis of sex differentiation in motor performance. However, there are numerous studies that have been conducted to determine the differences in MC between genders in preschool children, where a certain inconsistency has been observed in the results obtained [3]. Nevertheless, in most studies, boys performed better than girls in tasks assessing object-control skills, and girls performed better than boys in balancing and locomotor tasks. These differences in motor skills are attributed to environmental rather than biological factors [47].
This research also has certain limitations. For more relevant scientific conclusions, the sample of participants should be expanded in terms of number and age. Small samples can be a limitation in validity studies because they may not be representative of the larger population, which can lead to inaccurate or incomplete findings. Although concurrent validity was determined with large to very large correlations with the TGMD-2, the evidence for construct validity is weak. Therefore, future studies should include much larger samples with a wider age range as a variable to assess the construct validity. Additionally, it would be desirable for future research to include the body mass index (BMI) variable in children, which is directly related to performance in motor competence tests [48].
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the 4-SFMT is a new tool that can be used to assess the performance of motor skills of 5–6-year-old children. It is relatively easy to administer, whether as a process- or product-oriented test. It can be carried out quickly and it does not contain expensive props, which makes it ecologically valid. Overall, this study provides valuable insights into the assessment of motor skills in children and may have implications for future research in this area.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.P.L. and S.K.; methodology, S.K. and G.K.; validation, S.K. and G.K.; formal analysis, G.K.; investigation, P.P.L.; data curation, P.P.L.; writing—original draft preparation, P.P.L., S.K., A.D.G. and G.K.; writing—review and editing, P.P.L., S.K., A.D.G. and G.K.; supervision, S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All procedures were approved and in compliance with the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki’s ethical guidelines for scientific investigations involving human subjects and its subsequent amendments by the University of Split, Faculty of Kinesiology (number: 2181-205-02-01-21-013, date: 23 September 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Consent to participate in the study and to be videotaped was obtained from parents/guardians.
Data Availability Statement
Data can be provided upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the children and parents for their contributions to this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gallahue, D.L.; Ozmun, J.C.; Goodway, J. Understanding Motor Development: Infants, Children, Adolescents, Adults, 7th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Haywood, K.; Getchell, N. Life Span Motor Development, 7th ed.; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Iivonen, S.; Sääkslahti, A.K. Preschool Children’s Fundamental Motor Skills: A Review of Significant Determinants. Early Child Dev. Care 2014, 184, 1107–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, B.; Newman, P. Development Through Life: A Psychosocial Approach, 13th ed.; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Logan, S.W.; Webster, E.K.; Getchell, N.; Pfeiffer, K.A.; Robinson, L.E. Relationship Between Fundamental Motor Skill Competence and Physical Activity During Childhood and Adolescence: A Systematic Review. Kinesiol. Rev. 2015, 4, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utesch, T.; Bardid, F.; Büsch, D.; Strauss, B. The Relationship Between Motor Competence and Physical Fitness from Early Childhood to Early Adulthood: A Meta-Analysis. Sport. Med. 2019, 49, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Hondt, E.; Deforche, B.; Gentier, I.; de Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Vaeyens, R.; Philippaerts, R.; Lenoir, M. A Longitudinal Analysis of Gross Motor Coordination in Overweight and Obese Children versus Normal-Weight Peers. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okely, A.D.; Booth, M.L.; Patterson, J.W. Relationship of Cardiorespiratory Endurance to Fundamental Movement Skill Proficiency among Adolescents. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2001, 13, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, R.A.; Piek, J.P. Psychosocial Implications of Poor Motor Coordination in Children and Adolescents. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2001, 20, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haapala, E.A. Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Motor Skills in Relation to Cognition and Academic Performance in Children—A Review. J. Hum. Kinet. 2013, 36, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidén, A.; Lundqvist, C.; Nyberg, M. Development and Initial Validation of the NyTid Test: A Movement Assessment Tool for Compulsory School Pupils. Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2015, 19, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cools, W.; de Martelaer, K.; Samaey, C.; Andries, C. Movement Skill Assessment of Typically Developing Preschool Children: A Review of Seven Movement Skill Assessment Tools. J. Sport. Sci. Med. 2009, 8, 154. [Google Scholar]
- Cale, L.; Harris, J.; Chen, M.H. Monitoring Health, Activity and Fitness in Physical Education: Its Current and Future State of Health. Sport Educ. Soc. 2014, 19, 376–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, G.; Katić, R. Sex Differences in Anthropometric Characteristics, Motor and Cognitive Functioning in Preschool Children at the Time of School Enrolment. Coll. Antropol. 2009, 33, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Coppens, E.; Laureys, F.; Mostaert, M.; D’Hondt, E.; Deconinck, F.J.A.; Lenoir, M. Validation of a Motor Competence Assessment Tool for Children and Adolescents (KTK3+) With Normative Values for 6- to 19-Year-Olds. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien-Smith, J.; Tribolet, R.; Smith, M.R.; Bennett, K.J.M.; Fransen, J.; Pion, J.; Lenoir, M. The Use of the Körperkoordinationstest Für Kinder in the Talent Pathway in Youth Athletes: A Systematic Review. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2019, 22, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, A.R.; Bennett, K.J.M.; Beavan, A.; Pion, J.; Spiteri, T.; Fransen, J.; Lenoir, M. The Applicability of a Short Form of the Körperkoordinationstest Für Kinder for Measuring Motor Competence in Children Aged 6 to 11 Years. J. Mot. Learn. Dev. 2017, 5, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeboer, J.; Krijger-Hombergen, M.; Savelsbergh, G.; de Vries, S. Reliability and Concurrent Validity of a Motor Skill Competence Test among 4- to 12-Year Old Children. J. Sport. Sci. 2017, 36, 1607–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findak, V.; Delija, K. Physical Education in Preschool; Edip: Zagreb, Croatia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zuvela, F.; Bozanic, A.; Miletic, D. POLYGON—A New Fundamental Movement Skills Test for 8 Year Old Children: Construction and Validation. J. Sport. Sci. Med. 2011, 10, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Zysset, A.E.; Kakebeeke, T.H.; Messerli-Bürgy, N.; Meyer, A.H.; Stülb, K.; Leeger-Aschmann, C.S.; Schmutz, E.A.; Arhab, A.; Puder, J.J.; Kriemler, S.; et al. Stability and Prediction of Motor Performance and Cognitive Functioning in Preschoolers: A Latent Variable Approach. Infant Child Dev. 2020, 29, e2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, D.A. Test of Gross Motor Development; Pro-ed Publishers: Austin, TX, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Taherdoost, H. Validity and Reliability of the Research Instrument; How to Test the Validation of a Questionnaire/Survey in a Research. SSRN Electron. J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angioi, M.; Metsios, G.S.; Twitchett, E.; Koutedakis, Y.; Wyon, M. Association between Selected Physical Fitness Parameters and Esthetic Competence in Contemporary Dancers. J. Dance Med. Sci. 2009, 13, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Honrubia-Montesinos, C.; Gil-Madrona, P.; Losada-Puente, L. Motor Development among Spanish Preschool Children. Children 2021, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingberg, B.; Schranz, N.; Barnett, L.M.; Booth, V.; Ferrar, K. The Feasibility of Fundamental Movement Skill Assessments for Pre-School Aged Children. J. Sport. Sci. 2019, 37, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, M.S. A Note on the Multiplying Factors for Various Χ2 Approximations. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodological) 1954, 16, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, M.O. Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure for Identity Correlation Matrix. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1974, 52, 296–298. [Google Scholar]
- Cattell, R.B. The Scree Test For The Number Of Factors. Multivar. Behav. Res. 1966, 1, 245–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.R.; Crawford, A.; Lee, J.; Dennison, D. An Exploratory Analysis of Soft Skill Competencies Needed for the Hospitality Industry. J. Hum. Resour. Hosp. Tour. 2013, 12, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velicer, W.F.; Jackson, D.N. Component Analysis versus Common Factor Analysis: Some Issues in Selecting an Appropriate Procedure. Multivar. Behav. Res. 1990, 25, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, B.P. SPSS and SAS Programs for Determining the Number of Components Using Parallel Analysis and Velicer’s MAP Test. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 2000, 32, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comrey, A.L.; Lee, H.B. A First Course in Factor Analysis, 2nd ed.; Psychology Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781315827506. [Google Scholar]
- Tabachnick, B.G.; Fidell, L.S. Using Multivariate Statistics, 7th ed.; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, W.G. Measures of Reliability in Sports Medicine and Science. Sport. Med. 2000, 30, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 1992, 1, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits-Engelsman, B.C.; Fiers, M.J.; Henderson, S.E.; Henderson, L. Interrater Reliability of the Movement Assessment Battery for Children. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darsaklis, V.; Snider, L.M.; Majnemer, A.; Mazer, B. Assessments Used to Diagnose Developmental Coordination Disorder: Do Their Underlying Constructs Match the Diagnostic Criteria? Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2013, 33, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudd, J.; Butson, M.L.; Barnett, L.; Farrow, D.; Berry, J.; Borkoles, E.; Polman, R. A Holistic Measurement Model of Movement Competency in Children. J. Sport. Sci. 2016, 34, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeboer, J.; De Vries, S.; Krijger-Hombergen, M.; Wormhoudt, R.; Drent, A.; Krabben, K.; Savelsbergh, G. Validity of an Athletic Skills Track among 6- to 12-Year-Old Children. J. Sport. Sci. 2016, 34, 2095–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, N.; Morgan, P.J.; Salmon, J.; Logan, S.W.; Barnett, L.M. The Reliability and Validity of an Authentic Motor Skill Assessment Tool for Early Adolescent Girls in an Australian School Setting. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2017, 20, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, L.H.; Bingham, D.D.; Crossley, K.L.; Shahid, N.F.; Ellingham-Khan, M.; Otteslev, A.; Figueredo, N.S.; Mon-Williams, M.; Hill, L.J.B. The Validity and Reliability of Observational Assessment Tools Available to Measure Fundamental Movement Skills in School-Age Children: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, J.P.A.; Lopes, M.C.; Miranda-Júnior, M.V.; Valentini, N.C.; Lage, G.M.; Albuquerque, M.R. Körperkoordinationstest Für Kinder (KTK) for Brazilian Children and Adolescents: Factor Analysis, Invariance and Factor Score. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.; Vine, K.; Larkin, D. The Relationship of Process and Product Performance of the Two-Handed Sidearm Strike. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2007, 12, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, S.W.; Barnett, L.M.; Goodway, J.D.; Stodden, D.F. Comparison of Performance on Process- and Product-Oriented Assessments of Fundamental Motor Skills across Childhood. J. Sport. Sci. 2016, 35, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, T.L.; Sallis, J.F.; Broyles, S.L.; Zive, M.M.; Nader, P.R.; Berry, C.C.; Brennan, J.J. Childhood Movement Skills: Predictors of Physical Activity in Anglo American and Mexican American Adolescents? Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2013, 73, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandorpe, B.; Vandendriessche, J.; Lefevre, J.; Pion, J.; Vaeyens, R.; Matthys, S.; Philippaerts, R.; Lenoir, M. The KörperkoordinationsTest Für Kinder: Reference Values and Suitability for 6–12-Year-Old Children in Flanders. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2011, 21, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).