Abstract
Research has shown that natural disasters can be prevented or mitigated effectively through education which provides knowledge and skills for the young generation to protect themselves and act to protect the community. The current study investigated the level of natural-disaster-prevention literacy and analyzed its predictors among high school students in Vietnam. This study adopted a cross-sectional school-based design, using an online survey. There were 807 students from seven public schools participating in this study. The results show that the natural-disaster-prevention knowledge, perception, skills, and overall literacy are above average, with knowledge having the highest score. Significant differences exist in natural-disaster-prevention literacy and its components by gender, grade, location, and residence. Age, location, residence, knowledge, and perception can predict participants’ skills of natural-disaster prevention. This study highlights the necessity of teaching natural-disaster prevention in schools, across grades, and focusing on providing the students with the knowledge and perception needed to improve their natural-disaster-prevention skills. This will contribute to helping the country meet the goal of education for sustainable development.
1. Introduction
Natural disasters are uncontrollable and can cause massive financial, social, economic, and environmental losses, such as deaths, severe injuries, food shortages, communicable diseases, and psychological impairment [1]. They occur due to the action of natural forces, including climate and geology. People consider natural disasters unfortunate but inevitable [1]. Some common sudden-onset disasters worldwide include earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, cyclones or typhoons, tornados, fires, tsunamis or storm surges, avalanches, volcanic eruptions, extreme cold or blizzards, and heat waves. In contrast, slow-onset ones include drought, famine, desertification, deforestation, and pest infestation [1]. According to the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) 2021 report “WMO Atlas of Mortality and Economic Losses from Weather, Climate and Water Extremes (1970–2019)”, the world has witnessed more than 11,000 natural disasters from 1970 to 2019, causing more than 2 million human deaths and USD 3640 billion in damage. Over the past 50 years, there has been an average of one natural disaster related to weather, climate, flood, and drought each day, resulting in 115 deaths and USD 202 million in damage per day. More than 91% of deaths occur in developing countries. According to the report, natural disasters have increased fivefold during the above period, primarily due to the Earth’s warming. The report also emphasized the weather phenomena, extreme climate, and drought are becoming more frequent and severe in many parts of the world [2].
Vietnam is a Southeast Asian country along the Pacific Coast, with three sides bordering the sea. The territory has a narrow S shape. Hills and mountains occupy a quarter of the land area. Vietnam is located in the storm center of the South China Sea. In 2017, Vietnam ranked sixth globally on the list of countries most affected by natural disasters due to climate change [3]. According to the statistics of the Vietnam Central Steering Committee for Natural Disaster Prevention and Control, in the past 20 years alone in Vietnam, natural disasters such as storms, floods, and landslides have killed more than 13,000 people, with nearly 400 deaths or missing people each year, and destroyed over USD 6.4 billion of property, about 60% of the land area (Figure 1). Each year, the GDP is reduced by about 1–1.5% due to natural disasters, and this reduction has been increasing in recent years. More than 70% of the population was at risk of being affected by natural disasters [4]. Within the country, the Central and Central Highland regions, including 19 provinces and cities, are complex topographical areas. The Central Vietnam areas cover over 1900 km of coastline, while the Central Highlands include dense, short, and steep system of rivers and streams with over 740 rivers. This area suffers from the most types of natural disasters in Vietnam, with higher frequency and severity than other regions [5].
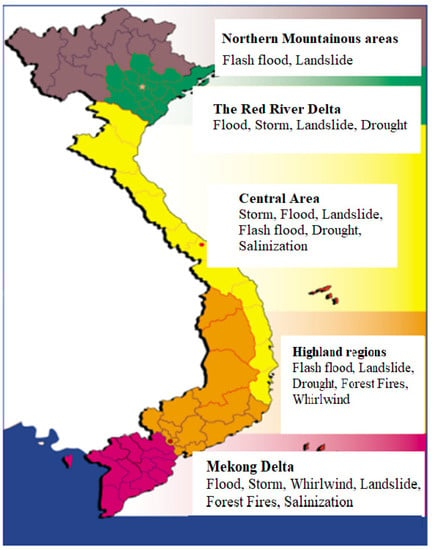
Figure 1.
Map of major natural disasters in regions of Vietnam (Ministry of Education and Training, 2012).
Previous evidence has shown that injury and damage caused by natural disasters can be prevented or mitigated by various solutions, including education [6,7,8]. The role of education is highlighted as an essential strategy to achieve the four priorities outlined in the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015–2030 [9]. Disaster education’s function, operational aspect, and cost-effective nature make it a valuable risk management tool [10]. The education of disaster-related information aims to improve disaster literacy. It is an individual’s ability to read, use, and understand disaster information in disaster mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery [11]. Without knowledge of natural disasters, students are vulnerable to unverified information circulating in cyberspace, creating feelings of fear and intimidation [12]. The existence of disaster literacy can reduce or even eliminate the loss and injury caused by natural disasters. Disaster literacy can encourage students’ efforts to understand what they have to do with disasters, forming students’ responsibility and practice independence in the event of a disaster [11].
Besides having the knowledge of disaster (disaster literacy), it is also important to also have natural-disaster-prevention (NDP) literacy, which is defined as a person’s personal knowledge, attitudes, and skills toward preventing disaster caused by the nature. It consists of three main components: disaster-prevention knowledge, disaster-prevention attitude, and disaster-prevention skills [13]. The NDP literacy is also understood as the development of proactive attitudes to apply disaster-prevention knowledge to respond to natural disasters and resilience and improve life after disasters [14]. NDP literacy is also defined as the sum total of abilities and skills, including perceptions, skills, and emotions, that enable an individual to respond, analyze, and reflect in the face of disaster for the sake of their lives. In general, NDP literacy involves having a correct understanding of life-threatening disasters, proactive attitude toward disaster information and disaster prevention, and adequate capabilities and skills for disaster prevention [14]. NDP literacy includes three indicators: disaster awareness, prevention knowledge, and response knowledge [15]. Attitudes toward NDP are assessed by indicators of sensitivity of disaster prevention, values related to NDP and responsibility for NDP, sensitivity of NDP, disaster-prevention-related value, and responsibility toward disaster prevention. NDP skills are a combination of preparedness and response activities [15]. Currently, different terms are used to refer to disaster education, such as “disaster education”, “disaster-risk education”, “disaster-reduction education”, and “disaster-prevention education”. Shaw et al. argue that all of the above terms are just different expressions of the same problem, and the basic meaning is natural-disaster-risk-reduction education [16]. As a country with many natural disasters, Vietnam quite commonly uses the above terms. In this study, we use the term “natural-disaster-prevention education” as a solution to provide knowledge and information about natural disasters for students and improve students’ awareness and attitudes about natural disasters and response to natural disasters at the same time. This could help give students the skills to protect themselves, reduce damage, and overcome the consequences caused by natural disasters.
Some researchers confirmed that low perception and lack of understanding of risk negatively impact people’s reactions to hazard warnings, personal protection measures, and recovery [17,18]. NDP literacy education aims to provide knowledge and skills for individuals and groups to take action to reduce their vulnerability before and during the disaster [19]. Children, in general, and school students are among the most vulnerable people in natural disasters. However, they can participate in disaster-response activities at home, at school, and in their community to manage the challenging situations they might counter before, during, and after natural disasters [20]. Disaster-prevention-literacy education in schools will be an excellent approach for children to equip them with knowledge and skills to protect themselves and help others. In addition, children can be a bridge to disseminate disaster-risk-reduction knowledge within their families and communities [20].
Nonetheless, education in natural-disaster-prevention (NDP) literacy in Vietnam has not shown the necessary effectiveness that requires scientists and educators to find out the reasons and the difficulties in this practice [21]. In recent years, the Vietnamese Government as well as the Ministry of Education and Training (MOET) of Vietnam have begun to focus on education on NDP and climate change in schools through circulars, decrees, policies, action plans, educational programs and projects, and projects in association with domestic and foreign organizations. Since the early 2010s, many educational projects have focused on climate-change response and risk reduction. Natural disasters have occurred in many provinces throughout Vietnam. Most of these projects promote two main initiatives: making schools safer and integrating climate-change and disaster-risk reduction into school curricula. Most notably, 14 major programs and projects are implemented by the MOET of Vietnam and other organizations, piloted in some schools, and implemented in a number of at-risk areas on natural disasters in order to develop educational manuals on disaster prevention for some localities in Vietnam. More than 50% of these programs and projects are implemented by International Non-Governmental Organizations (INGOs) and NGOs in Vietnam.
Disaster-prevention education in Vietnamese schools is mainly carried out through extracurricular lessons, experiences, organized drills, injury-prevention practice, swimming lessons, and events; a natural-disaster-prevention exam; integration into the curriculum of subjects with relevant knowledge in high schools; and the development manuals for students, teaching materials for teachers, and training for teachers and students. With the positive results, many schools and high school students in the country have had positive changes in their awareness, knowledge, and skills of disaster prevention. However, due to limitations in funding, time, location, materials, and difficulties in integrating them into the curricula in high schools, the effect has not been widespread. The locality has not yet had access to disaster-prevention education. Natural disasters continue to happen and are becoming more and more anomalous and unpredictable, causing considerable consequences for the country and the people of Vietnam. Therefore, disaster-prevention education needs to be carried out regularly and continuously in many respects [22,23]. This study investigated the level of NDP literacy and analyzed the predictors of NDP literacy and its components among high school students in Vietnam.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
This study used a cross-sectional design to collect data from students at high schools in Vietnam’s Central and Central Highland areas. The study employed a purposive sampling method. The two selected study settings suffer from the most frequent and severe natural disasters each year in this country, in the form of storms, floods, landslides, flash floods, droughts, salinization, forest fires, and tornados [24]. There were 807 completed questionnaires (response rate 93.3%), of which 62.7% were completed by female students. The mean age was 17.06 (SD = 0.82). A brief summary of the participants’ demographic information is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Demographic information regarding participants.
2.2. Procedure
The data collection was conducted from September 2021 to December 2021. Due to the complicated situation of COVID-19, the survey was conducted online via Google Forms. The public schools that are in the area with a high risk of natural disasters were introduced by the Provincial Department of Education and Training. Principals of potential randomly selected schools were contacted with a clear explanation of aims, processes, and participants’ tasks. Schools that agreed to participate would be contacted for the next step. Three high schools in Thua Thien Hue Province (Cao Thang, Nguyen Truong To, and Tam Giang) and four in Ayun pa, Gia Lai Province (Phan Chu Trinh, Nguyen Tat Thanh, Le Thanh Tong, and Ly Thuong Kiet) agreed to participate the study. Classes within these schools were randomly selected. The principals then informed classroom teachers. The research team then contacted them and scheduled times to visit the online class to work with potential participants. All information related to the study, including participants’ tasks, benefits, and risks, as well as the voluntary nature of the participation and withdrawal, was clearly explained to students. Participants understood that they needed to get permission from parents before completing the questionnaire. A study information sheet and consent form were delivered via email to each student to bring home and seek permission from parents by having them sign the consent form. All students in selected classes were invited to participate in the study. The research team joined the online class one week later to collect the consent forms and start the data collection. The online Google Form questionnaire (in Vietnamese language) was delivered to students by classroom teachers during one online class. Students completed the online questionnaire on their own time. If the students completed and submitted the questionnaire, this meant that they and their parent(s) agreed to participate in the study. The email address and contact number of the researcher team was available in the online form for students and parents to contact for further information. The questionnaire took the students around 20 min to complete.
2.3. Materials
This study investigated the status of NDP capacity among high school students, including knowledge, perception, skills, and access level. A self-reported questionnaire was developed specifically for this study based on numerous reliable references (Table 2). The questionnaire includes 44 items in a five-option Likert scale design (see Appendix A). The knowledge component, which is the fact or condition of knowing something with a considerable degree of familiarity through experience, association, or contact, consists of nine items. The perception component, which is the awareness of the importance and necessity for preparing for natural disasters, includes eighteen items. Skill, which refers to the ability to act for natural disaster prevention, contains ten items, and access level to NDP education consists of seven items. The score for each subscale was calculated by determining the average of all relevant items.

Table 2.
Questionnaire’s components and reference sources.
Two experts in education and geography evaluated the questionnaire. The questionnaire’s first version was pilot tested on 27 high school students in Hue City. Students in the pilot study were excluded from the main survey. Comments from students were collected. The experts re-evaluated the questionnaire to finalize the last version used for the main analysis. This study used internal reliability with Cronbach’s Alpha index. According to Lance and his colleagues, a Cronbach’s Alpha above 0.70 is acceptable [31]. The Cronbach’s Alpha for NDP knowledge, perception, and skills and overall NDP in this study were 0.94, 0.98, 0.96, and 0.98, respectively.
2.4. Data Analysis
In order to test the construct validity of the questionnaire, we submitted the data to a confirmation factor analysis (CFA), using Amos version 20.0 software, to evaluate the model’s fit. We used the maximum likelihood and covariance matrices. According to Hu and Bentler [32] and Kline [33], the index for a fit model includes Normed (/df) ≤ 5; CFI > 0.90; RMSEA ≤ 0.08; SRMR ≤ 0.08. We conducted the three-factor model (knowledge, perception, and skill) based on the NDP framework, conceptualizing NDP as an umbrella term for a variety of interdependent and integrated factors. The indexes for the three-factor model are Normed χ2 (χ2/df) = 3.448; CFI = 0.957; RMSEA = 0.055; SRMR = 0.0233 (Figure 1). The model fits these data (Figure 2).
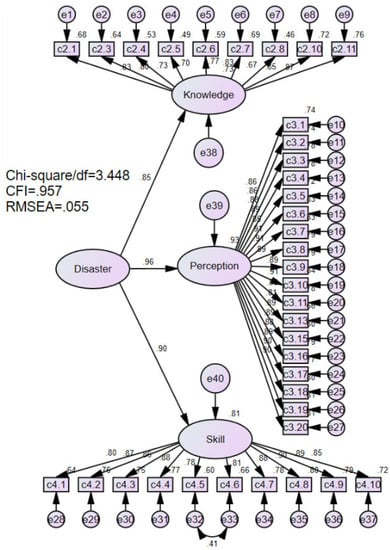
Figure 2.
Three-factor model of the NDP questionnaire.
Descriptive statistics were run to identify the mean and standard deviation of natural disaster knowledge, perception, and skills. Demographic variables (sex, grade, urban/rural, and residence location) were collected. An independent t-test was used to examine the differences between groups in natural-disaster knowledge, perception, and skills. The correlation between knowledge, perception, and skills related to natural disasters among students was identified by Pearson value r, in which the correlation was counted with a significant p-value under 0.05 [34]. Several stepwise linear regressions were conducted to investigate the predictive roles of different factors in natural-disaster-prevention literacy. The first stepwise linear regression included knowledge of natural-disaster prevention as an outcome variable, and demographic information and level of access to NDP education as independent variables. Perception about NDP was an outcome variable in the second linear regression, with the independent variables being demographic characteristics, level of access to NDP, and NDP knowledge. Potential predictive factors of NDP skills were examined in the third stepwise linear regression, in which demographic characteristics, level of access to NDP, NDP knowledge, and perception were independent variables.
3. Results
3.1. Preliminary Analyses of Natural-Disaster-Prevention Literacy among Vietnamese Students
The data in Table 3 show that students’ knowledge, perception, and skills are above average (mean ranges from 3.22 to 3.73). The total NDP score is 10.75, which is above average. There are significant positive correlations between knowledge, perception, and skills of NDP (p < 0.05). All of the three components are well correlated with the total score of NDP (p < 0.01). Moreover, positive correlations are found significantly among knowledge, perception, skills (p < 0.05), NDP literacy (p < 0.01), and the level of access to NDP education.

Table 3.
Preliminary analyses of NDP literacy among Vietnamese students.
3.2. Sex as an Independent Level
The results from the t-test analysis show that female students are significantly higher than male students in all components of natural disaster literacy, including knowledge, perception, and skills (p < 0.05). Overall, females show significantly higher scores in NDP literacy than their male counterparts (p < 0.01). They also show a higher level of access to natural-disaster-prevention education (p < 0.05) (Table 4).

Table 4.
Differences in natural-disaster-prevention literacy by sex among Vietnamese students.
3.3. Grade as Independent Level
Regarding the total NDP score, three grade groups of 10, 11, and 12 were considered. Overall, there are significant differences across groups in NDP knowledge, perception, skills, and overall literacy. Specifically, students in grade 10 have higher scores in knowledge (p < 0.001), perception (p < 0.001), skills (p < 0.01) and overall literacy (p < 0.001) than those in grade 11. Grade 10 students are higher than their grade 12 schoolmates in the score of knowledge (p < 0.05), perception (p < 0.05), and overall literacy (p < 0.05). When comparing between grades 11 and 12, grade-12 students seem to have higher scores in skills and overall NDP score. There are no differences in knowledge and skills between grades 11 and 12. Moreover, all three grades show no disparities in accessing NDP education (p > 0.05) (Table 5).

Table 5.
Differences in natural-disaster-prevention literacy by grade among Vietnamese students.
3.4. Location as Independent Level
Observing the result from the t-test analysis, we see that students in Thua Thien Hue are significantly higher than students in Gia Lai in NDP literacy and all its components, including knowledge, perception, and skills (p < 0.001). However, there is no difference in the level of access to natural-disaster-prevention education (p > 0.05) (Table 6).

Table 6.
Differences in natural-disaster-prevention literacy by location among Vietnamese students.
3.5. Residence as Independent Level
An independent samples t-test was used to examine whether there is any difference in NDP overall score among students living in rural and urban areas. There are statistically significant differences in students’ NDP overall score in urban and rural areas of Vietnam. The analysis revealed that urban students are better in regard to knowledge, perception, skills, and overall score in NDP (p < 0.001) (Table 7). They are also the group with higher access to NDP education than those growing up in rural areas.

Table 7.
Differences in NDP literacy by residence among Vietnamese students.
3.6. The Potential Predictive Factors of Natural-Disaster-Prevention Literacy among Vietnamese Students
Three stepwise linear regressions were conducted with the outcome variables NDP knowledge, perception, and skills, respectively. The final stepwise results are illustrated in Table 8.

Table 8.
Predictive factors to natural-disaster-prevention literacy among Vietnamese students.
Our study shows that demographic information, including age, location, and residence, can predict and explain 3.9% variance of the students’ knowledge of NDP (p < 0.05). It can explain 4.7% variance of the NDP perception (p < 0.05), but it is unable to predict NDP skills (p > 0.05). The education-access level significantly predicts NDP knowledge, perception, and skills (p < 0.001), and it contributes to 23.7%, 31.5%, and 35.4% the variance of the NDP knowledge, perception, and skills, respectively.
Among various components of NDP literacy, knowledge plays a role in predicting perception and contributing to 31.5% variance of this variable. Both knowledge and perception positively predict skills with the contribution of 21.4% and 13.2% variance of the skill variable.
4. Discussion
This study is the first of its kind in Vietnam investigating the predictors of NDP. A rational statistical analysis was used to reach the study’s aims. Data from this study were obtained by school-based surveys in Central and Central Highland public schools of Vietnam with an acceptable sample size and high response rate.
To ensure objective research results, scales were built and evaluated for reliability and validity. The research results show that the scales have satisfactory reliability based on Cronbach’s Alpha values [31]. The structural brute force is in agreement with the data of this study [32,33]).
4.1. Overall Natural-Disaster Prevention
Overall, NDP knowledge, skills, and perception among high school students in this sample is relatively high. Recently, the Government and the Ministry of Education and Training of Vietnam have begun to focus on disaster-prevention and climate-change education in schools through circulars, decrees, policies, action plans, and educational programs and projects associated with domestic and foreign organizations. Since the early 2010s, many educational projects on climate-change response and risk reduction of natural disasters have been carried out in many provinces throughout Vietnam. The most significant are 14 major programs and projects implemented by the Ministry of Education and Training of Vietnam and other organizations. More than 50% of programs and projects are implemented by International Non-Governmental Organizations (INGOs) and NGOs in Vietnam. Disaster-prevention education in Vietnamese schools is carried out mainly through extracurricular lessons, integration into the curriculum of subjects with relevant knowledge in high schools, development of references for students, teaching materials for teachers, and training for teachers and students. Many schools and high school students across the country have benefited from these projects and positively changed NDP’s perception, knowledge, and skills. However, looking closer at this study’s result, we see that the level of NDP overall score is not as high as expected. This might be due to limitations regarding time and materials, difficulties in integrating them into the curricula in high schools, and the fact that the effect has not yet been scaled up properly. Natural disasters continue to happen and are becoming increasingly unconventional and unpredictable, causing significant consequences for the country and the people of Vietnam. Therefore, in many aspects, NDP overall score education must be carried out regularly and continuously [35].
It seems that knowledge is the component that the school and teachers need to focus on improving for students. Although perception is the strength of students, it appears to be lower than expected, as perception plays a crucial role in students’ decision to improve knowledge and skills. A study by Wei et al. [36] found that participants with lower knowledge of NDP are more likely to have lower coping skills and are more vulnerable to disasters. Previous studies shared similar findings among schoolteachers and administrators [14,37], in which participants’ knowledge and perception of disaster prevention were high.
Our findings confirmed a significant correlation between different components of the NDP overall score. In other words, NDP knowledge, perception, and skills are highly associated. The conclusion is supported by the model of disaster-prevention literacy recommended by Yeh [13].
4.2. Natural-Disaster Prevention by Demographic Information
It is found that female students have better performances of NDP in knowledge, perception, and skills. Similarly, Ku and Li [38] found that females had better average scores than males in terms of perception. This is also consistent with some previous studies that suggest that women’s awareness, knowledge, and attitudes toward natural disasters are higher than men’s because women are among the vulnerable groups when natural disasters occur, so they are more at risk than men [28,39,40]. Differences in knowledge and vulnerability make women more prone to anxiety and appreciate the importance of disaster preparedness than men [41]. Therefore, women will pay more attention to raising awareness, equipping them with knowledge and skills for disaster prevention to feel secure and ensure their own safety. Thus, in disaster-prevention education, gender should also be paid attention to in order to have appropriate educational activities. Female students should be more involved in education and disaster-prevention practices to improve their ability to cope with disasters and reduce stress and anxiety.
However, this finding is also different from results among schoolteachers and administrators in Taiwan [36] and Turkey [42], in which there was no disparity between males and females across three components of NDP. A study by [43] among teachers and students in Indonesia found that males had higher levels of disaster literacy than females. One possible explanation for this disparity is the difference in the samples’ age. The participants engaging in these studies included adults and elementary students. Furthermore, females are taught in school that they are at higher risk of being vulnerable to natural disasters than males due to their limited physical health because of biological differences and nutrition deficits, as well as the lack of survival skills such as swimming and tree climbing, which are traditionally taught to males [44]. Hence, females are more likely to pay more attention to improving their NDP literacy than their male counterparts.
Among grades 10, 11, and 12, it seems that grade 10 students were better than their elder peers. Specifically, grade 10 students had the highest knowledge, perception, and literacy scores. Grade 10 students also had a higher score in perception than grade 11 but not significantly higher than grade 12 students. Grade 12 students were better in skills than their grade 11 counterparts but still lower than those in grade 10. Grade 11 students seemed to have the lowest scores across components and overall score. It can be explained that NDP had been included in the national curriculum in Vietnam, especially in geography. The background knowledge of NDP had been included in grade 10’s curriculum, and the NDP skills had been included in grade 12’s curriculum, while grade 11′s curriculum included little NDP overall score. One suggestion might be that the NDP content should be carried out continuously across three grades in high schools to consolidate knowledge and serve as a background for the transition from knowledge and perceptions to skills. Thus, the ability to put it into practice when a natural disaster occurs can bring greater efficiency.
Our study reveals that the NDP overall score differs by province and residence. It is more likely that students in Thua Thien Hue province and urban areas had higher scores in all aspects of NDP than those from Gia Lai province and those living in rural areas. Gia Lai Province is a mountainous area with many minor ethnic communities. This area’s local economy and quality of life are low compared to other sites. The lack of materials and facilities is one of the most widespread problems in this area. Some students over 14 tend to be absent from school to take care of housework or farm work. Therefore, the capacity to approach NDP education and absorb knowledge is under-expected. On the other hand, Thua Thien Hue Province includes a big city with services as the main background of the local economy. Thua Thien Hue is considered the oldest educational and cultural center in Vietnam. Hence, the accessibility of students to education and NDP education is better. Our finding is in line with the study by [45], which concluded that students living in the city were more confident and had higher coping skills toward natural disasters.
Another noticeable finding in this study is that the level of access to NDP education remains similar across the high school students of different sex, grade, location, and residence. This may indicate that the access to NDP education of high school students is mainly through the national education program and projects, which is compulsory programs at schools in Vietnam; therefore, the level of access to NDP seems to be the same across groups.
4.3. Natural-Disaster Prevention and Predictive Factors
Educational access level seems essential in predicting high school students’ knowledge, perception, and skills. The opportunities for students to expose themselves to NDP education, such as workshops, short training courses, literacy competitions, and campaign involvements, can improve students’ perception, understanding, and skills in countering and coping with natural disasters. Besides the national curriculum, schools should provide students with more NDP-related activities.
There are some relationships between knowledge, perception, and skills. Knowledge can strongly predict perception. Knowledge and perception can strongly predict skills. The appropriate perception is the guideline leading to the appropriate actions. To be well aware of NDP, students first need to have a clear understanding of natural disasters and prevention measures. Therefore, it is necessary to teach students about this issue through different informative channels. However, the proper knowledge and perceptions themselves are not enough for high school students to have the ability to respond to natural disasters. It is necessary to train students to have related skills. Disaster-prevention skills are built on the knowledge base and practical activities and experiences to help students effectively perform an action when a disaster occurs. For example, swimming skills are helpful in floods, and first-aid skills and escape skills are needed in urgent cases, as well as protecting-the-house skills, preparing emergency bags and search and rescue, and propaganda skills.
4.4. Limitations and Direction for Future Research
There are several limitations that the readers should be aware of while interpreting this study’s findings. First, this is a cross-sectional study; hence, any found correlations and predictions are well applied to the point of conducting the study only. Future studies should employ a longitudinal design to enhance the reliability of the study. Second, the current study focuses only on some factors, such as age, location, and residence. The findings from current study call for further exploration into the impact of other factors on knowledge, awareness, and skills of disaster prevention of Vietnamese high school students, such as experience of natural disasters, home education, and parents’ education level, in future research. Third, the study focused on two regions in the Vietnam’s Central and Central Highland areas, including seven schools. This limitation may influence the generalizability of the findings. It puts forward the importance to replicate the study by expanding the research scale and research area in order to attract a large number of high school students from many provinces in Vietnam to participate. Fourth, the exclusion of out-of-school students is another limitation of this study. This suggests that the conclusion of this study should be interpreted with caution when applying in other populations.
5. Conclusions
This study investigated the NDP overall score and identified related factors among high school students in the Central Highland and Central areas of Vietnam. The study’s findings revealed that the NDP overall score among students was above average but under the expected level. There are many factors related to the NDP overall score, such as education-access level, age, location, and residence.
Considering the unexpected and increased frequency of natural disasters in Vietnam, especially in Central Highland and Central areas, the local government should develop a program of NDP throughout each high school grade, with numerous forms of teaching and learning activities. Extracurricular programs should include NDP content in their regular activities. Furthermore, improving skills should go together with enhancing the knowledge and perception of NDP. This will help the national education curriculum to meet the goal of education for sustainable development.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.D.V. and H.T.N.; methodology, H.-V.T.D. and Q.-A.N.N.; software, H.-V.T.D. and X.V.H.; validation, H.T.N. and H.-V.T.D.; formal analysis, H.-V.T.D. and Q.-A.N.N.; investigation, B.D.V. and H.T.N.; resources, H.T.N. and X.V.H.; data curation, H.-V.T.D. and H.T.N.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.-A.N.N.; writing—review and editing, X.V.H. and B.D.V.; visualization, Q.-A.N.N., H.-V.T.D., and H.T.N.; supervision, B.D.V.; project administration, H.T.N. and B.D.V.; funding acquisition, H.T.N. and B.D.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Ministry of Education and Training (Vietnam) under grant number B2021-HQG-02.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data of this research will be available by request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all participants and their parents for their cooperation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Questionnaire (English Version)

Table A1.
Below is a list of statements on Natural Disaster Prevention Literacy Education. Please indicate how strongly you agree or disagree with each statement.
Table A1.
Below is a list of statements on Natural Disaster Prevention Literacy Education. Please indicate how strongly you agree or disagree with each statement.
| No. | Statement | Level of Agreement | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Knowledge | Strongly Agree | Agree | Neutral | Disagree | Strongly Disagree |
| 1 | A natural disaster is an abnormal natural phenomenon that can cause damage to people, property, the environment, living conditions, and socioeconomic activities. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 2 | The increase in intensity, frequency, and anomalous degree of natural disasters in the current period is due to a combination of nature and human activities causing climate change. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 3 | Some natural disasters are predictable in terms of duration, intensity, and frequency. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 4 | Vietnam is one of the countries heavily affected by natural disasters and climate change. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 5 | Storms and floods are common natural disasters in many localities in Vietnam. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | Most natural disasters cause significant damage to people, properties, the environment, and socioeconomic activities. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 7 | The elderly and children are subject to high levels of vulnerability when natural disasters strike. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 8 | Natural disasters happen unexpectedly, but people can contribute to preventing and mitigating damage caused by natural disasters. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 9 | Disaster prevention is the responsibility of government agencies and individual, including students. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| II | Perception | Strongly Agree | Agree | Neutral | Disagree | Strongly Disagree |
| 1 | Skills of first aid, treating wounds, swimming, finding safe shelters, and keeping the water clean should be learned and practiced. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 2 | It is necessary to organize disaster-response drills for all social classes, including students. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 3 | It is necessary to be mentally active and ready to respond to natural disasters. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 4 | It is necessary to coordinate with family members to make a plan to respond to natural disasters. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 5 | It is necessary to tie up houses and have a plan to protect assets before a disaster strikes. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | When a natural disaster is about to strike, it is necessary to prepare food and essential items, clean water, and medical equipment which are enough to use for at least seven days. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 7 | It is necessary to keep up to date with disaster warnings through the media. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 8 | It is necessary to follow the disaster-response guidelines of the local government through the media. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 9 | It is necessary to keep important phone numbers and contacts in case of emergency. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 10 | It is necessary to learn the emergency evacuation routes that may need to be used in the event of a disaster. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 11 | It is necessary to stay in a house or a solid, safe area when a disaster strikes. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 12 | Electrical appliances need to be unplugged during a disaster. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 13 | It is necessary to keep up to date with the disaster situation through the media. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 14 | It is necessary to call emergency phone numbers immediately when in danger in a disaster. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 15 | It is necessary to evacuate with family to a safe place when feeling unsafe in the disaster. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 16 | In case of flooding, when moving, it is necessary to use life jackets or other floating objects. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 17 | Attention should be paid to the protection of the weak elderly, children, and people with disabilities in the event of natural disasters. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 18 | It is necessary to strictly follow the direction of the relevant authority or the local government where the disaster occurs. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| III | Skills | Strongly Agree | Agree | Neutral | Disagree | Strongly Disagree |
| 1 | I am aware of the natural disasters that may occur in the area where I live. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 2 | I can find and track disaster-related information. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 3 | I can coordinate and assign work with family members to respond to natural disasters. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 4 | I know what necessities and essentials need to be prepared before a disaster strikes. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 5 | I can give first aid to injuries caused by natural disasters. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | I know of places or channels of communication that can help my family and me when in danger of a natural disaster. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 7 | I am willing to join my family, school, and neighbors to participate in disaster-prevention activities such as pruning trees, bracing houses, protecting assets, and preparing emergency bags and necessities. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 8 | I am willing to join my family, school, and the residents in my neighborhood to participate in cleaning activities to overcome consequences after natural disasters. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 9 | I am willing to participate in voluntary activities to help the community to overcome the consequences of natural disasters. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 10 | I can disseminate knowledge, skills, and experience in disaster prevention to everyone. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |

Table A2.
Below are activities to help children learn disaster prevention skills. Could you please tell us the implementation level of these activities?
Table A2.
Below are activities to help children learn disaster prevention skills. Could you please tell us the implementation level of these activities?
| IV | Activities | Never | Rarely | Sometimes | Usually | Always |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | I receive disaster prevention education at school. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 2 | I receive disaster prevention education through related subjects. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 3 | I am educated about disaster prevention through propaganda and experiential activities organized by schools. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 4 | I receive disaster prevention education through books, documents, and information provided by teachers or schools. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 5 | I receive disaster prevention education through the Internet, TV, newspapers, radio, social networks. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | I am educated about disaster prevention through discussions with relatives and friends. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 7 | I am educated about disaster prevention through local propaganda activities. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
References
- Sena, L.; Michael, K.W. Disaster Prevention and Preparedness; Ethopia Public Health Training Initiative: Jimma, Ethopia, 2006; Volume 1, pp. 1–180. [Google Scholar]
- World Meteorological Organization. WMO Atlas of Mortality and Economic Losses from Weather, Climate and Water Extreme (1970–2019); World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein, D.; Künzel, V.; Schäfer, L. Global Climate Risk Index 2018: Who Suffers Most from Extreme Weather Events? Weather-related Loss Events in 2016 and 1997 to 2016. 2017. Available online: https://www.germanwatch.org/sites/default/files/publication/20432.pdf (accessed on 4 November 2022).
- Central Steering Committee for Natural Disaster Prevention and Control. Solutions for natural disaster prevention and control in the Central and Central Highlands regions. In Proceedings of the Conference on Solutions for Natural Disaster Prevention and Control in the Central and Central Highlands Regions, Hai Phong City, Vietnam, 4–5 August 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Japanese International Cooperation Association (JICA). Survey to Collect Data to Develop Disaster Risk Reduction Strategy in Vietnam. 2018. Available online: https://openjicareport.jica.go.jp/pdf/12323879.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Aldrich, N.; Benson, W.F. Disaster preparedness and the chronic disease needs of vulnerable older adults. In Preventing Chronic Disease: Public Health Research, Practice, and Policy; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2008; Volume 5, p. A27. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, K.A.; Adwards, M.T. Disaster risk reduction and vulnerable populations in Jamaica: Protecting children within the comprehensive disaster management framework. Child. Youth Environ. 2008, 28, 389–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuladhar, G.; Yatabe, R.; Dahal, R.K.; Bhandary, N.P. Assessment of disaster risk reduction knowledge of school-teachers in Nepal. Int. J. Health Syst. Disaster Manag. 2015, 3, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNFCCC. Adoption of the Paris Agreement. 2015. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/47778072/Science_and_Technology_in_Disaster_Risk_Reduction_in_Asia (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Kelman, I. Disaster Mitigation Is Cost-Effective. 2014. Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/16341/WDR14_bp_Disaster_Mitigation_is_Cost_Effective_Kelman.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Kesumaningtyas, M.A.; Hafida, S.H.N.; Musiyam, M. Analysis of disaster literacy on student behavioral responses in efforts to reduce earthquake disaster risk at SMA Negeri 1 Klaten. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 986, 12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.M.; Haun, J.N.; Peterson, L. A proposed disaster literacy model. Disaster Med. Public Health Prep. 2014, 8, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.C. Disaster Prevention Education Literacy Investigation for Grade 1–9 Students and Teachers; Technological Disaster Prevention Education and Cultivation Experiment Research and Development Programs; Report; Ministry of Education Advisory Office: Taipei, Taiwan, 2007. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.-C.; Yen, C.-J. Disaster Prevention Literacy among School Administrators and Teachers: A Study on the Plan for Disaster Prevention and Campus Network Deployment and Experiment in Taiwan. J. Life Sci. 2016, 10, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Lee, W.C. Damages to school infrastructure and development to disaster prevention education strategy after Typhoon Morakot in Taiwan. Disaster Prev. Manag. Int. J. 2012, 21, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, R.; Takeuchi, Y.; Gwee, Q.R.; Shiwaku, K. Disaster education: An introduction. In Disaster Education; Emerald Group Publishing Limited.: Bingley, UK, 2011; Volume 7, pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- UNICEF. Disaster Risk Reduction and Education. 2011. Available online: https://www.preventionweb.net/files/19890_drrandedbrochure1.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Wisner, B. A Review of the Role of Education and Knowledge in Disaster Risk Reduction. 2006. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/44836374_Let_our_children_teach_us_a_review_of_the_role_of_education_and_knowledge_in_disaster_risk_reduction#fullTextFileContent (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Rohrmann, B. Risk perception, risk attitude, risk communication, risk management: A conceptual appraisal. Presented at the 15th International Society of Emergency Management. 2008. Available online: https://tiems.info/dmdocuments/events/TIEMS_2008_Bernd_Rohrmann_Keynote.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Peek, R. Children and disasters: Understanding vulnerability, developing capacities, and promoting resilience—An introduction. Child. Youth Environ. 2008, 18, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEEDS Asia. Education handbook for disaster risk reduction for teachers. In Fostering Capacity for Disaster Risk Management Schools Based on Community in Central Vietnam; Asia, S., Ed.; SEED Asia: Danang, Vietnam, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, T.T.M.; Nguyen, D.T.H.; Hung, T.N.; Park, T.Y. The practice of education for disaster risk reduction in Vietnam: Lessons learned from a decade of implementation 2010–2020. In Interlocal Adaptations to Climate Change in East and Southeast Asia: Sharing Lessons of Agriculture, Disaster Risk Reduction, and Resource Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 101–112. Available online: https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/978-3-030-81207-2.pdf?pdf=button (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- Ueda, Y.; Shikada, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Shaw, R. Knowledge, education and training for risk reduction: Specific case of Myanmar, Vietnam, and Japan. In Civil Society Organization and Disaster Risk Reduction; Shaw, R., Izumi, T., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- JICA. National Report: Disaster Risk Evaluation and Developing Continuous Business Plan for ASEAN General Industry. 2015. Available online: https://openjicareport.jica.go.jp/pdf/12235677.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Marskole, P.; Mishra, A.; Kumar, P.; Gaur, P.; Aharwar, P.; Patidar, P.; Shejwar, P. A study to assess awareness of disaster management among school going children in Gwalior (MP). Int. J. Community Med. Public Health 2018, 5, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- General Department of Disaster Prevention. Manual of Disaster Prevention for Schools; Hanoi Agricultural Publisher: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dikmenli, Y.; Yakar, H.; Konca, A.S. Development of disaster awareness scale: A validity and reliability study. Rev. Int. Geogr. Educ. Online 2018, 8, 206–220. Available online: https://rigeo.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/Development-of-Disaster-Awareness-Scale_-A-Validity-and-Reliability-Study493842-591169.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2022).
- Mizrak, S.; Aslan, R. Disaster risk perception of university students. Risk Hazards Crisis Public Policy 2020, 11, 411–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinar, A. What is secondary school students’ awareness on disasters? A case study. In Rev. Int. Geogr. Educ. Online; 2017; 7, pp. 315–331. Available online: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1165608.pdf (accessed on 31 December 2022).
- Ozkazanc, S.; Yuksel, U.D. Evaluation of disaster awareness and sensitivity level of higher education students. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 197, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lance, C.E.; Butts, M.M.; Michels, M.C. The sources of four commonly reported cutoff criteria: What did they really say? Organ. Res. Methods 2006, 9, 202–220. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.T.; Bentler, P. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. Multidiscip. J. 1999, 6, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, P. An Easy Guide to Factor Analysis; Routledge: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, R.A. Statistical Methods for Research Workers; Hafner: New York, NY, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Torani, S.; Majd, P.M.; Maroufi, S.S.; Dowlati, M.; Sheikhi, R.A. The importance of education on disasters and emergencies. J. Educ. Health Promot. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Su, G.; Liu, F. Public response to earthquake disaster: A case study in Yushu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture. Nat. Hazards 2013, 69, 441–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wei, D.Y.; Zhu, X.L.; Yi, N. An investigation on disaster prevention literacy of secondary school teachers in China. J. Educ. Stud. 2012, 5, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Ku, W.H.; Li, M.K. A study on disaster prevention and mitigation literacy (DPML) of primary and secondary school teachers in Macao. Macau J. Nurs. 2017, 16, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourque, L.B.; Regan, R.; Kelley, M.M.; Wood, M.M.; Kano, M.; Mileti, D.S. An Examination of the Effect of Perceived Risk on Preparedness Behavior. Environ. Behav. 2013, 45, 615–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal, M.; Meyer, M.A. Women’s experiences across disasters: A study of two towns in Texas, United States. Disasters 2020, 44, 285–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhanizadeh, B.; Kermanshachi, S. Gender-based evaluation of physical, social, and economic challenges in natural disasters management. In Construction Research Congress 2020: Infrastructure Systems and Sustainability—Selected Papers from the Construction Research Congress; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2020; pp. 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genc, F.Z.; Yildiz, S.; Kaya, E.; Bilgili, N. Disaster literacy levels of individuals aged 18–60 years and factors affecting these levels: A web-based cross-sectional study. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 76, 102991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, R.; Yunus, M.; Maimun, M.; Fajfi, I. Environmental Education: A correlational study among environmental literacy, disaster knowledge, environmental sensitivity, and clean-living behaviour of post-tsunami disaster in Aceh communities, Indonesia, Polish. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 31, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annear, M.; Gwynn, J. A Practical Guide to Gender-Sensitive Approaches for Disaster Management; International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies: Geneva, Switzerland; Asia Pacific Zone Office: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2010; Available online: https://resourcecentre.savethechildren.net/pdf/6947.pdf/ (accessed on 13 January 2023).
- Zhu, T.T.; Zhang, Y.-J. An investigation of disaster education in elementary and secondary schools: Evidence from China. Nat. Hazards 2017, 89, 1009–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).