A Study on the Effects of Digital Learning Sheet Design Strategy on the Learning Motivation and Learning Outcomes of Museum Exhibition Visitors
Abstract
:1. Foreword
- Explore how the exhibition objectives correspond and integrate with the educational objectives and educational contents in the exhibition planning framework.
- To understand how different digital learning sheet designs affect the learning motivation and learning outcomes of student visitors.
2. Literature Review
2.1. The Education of Museums
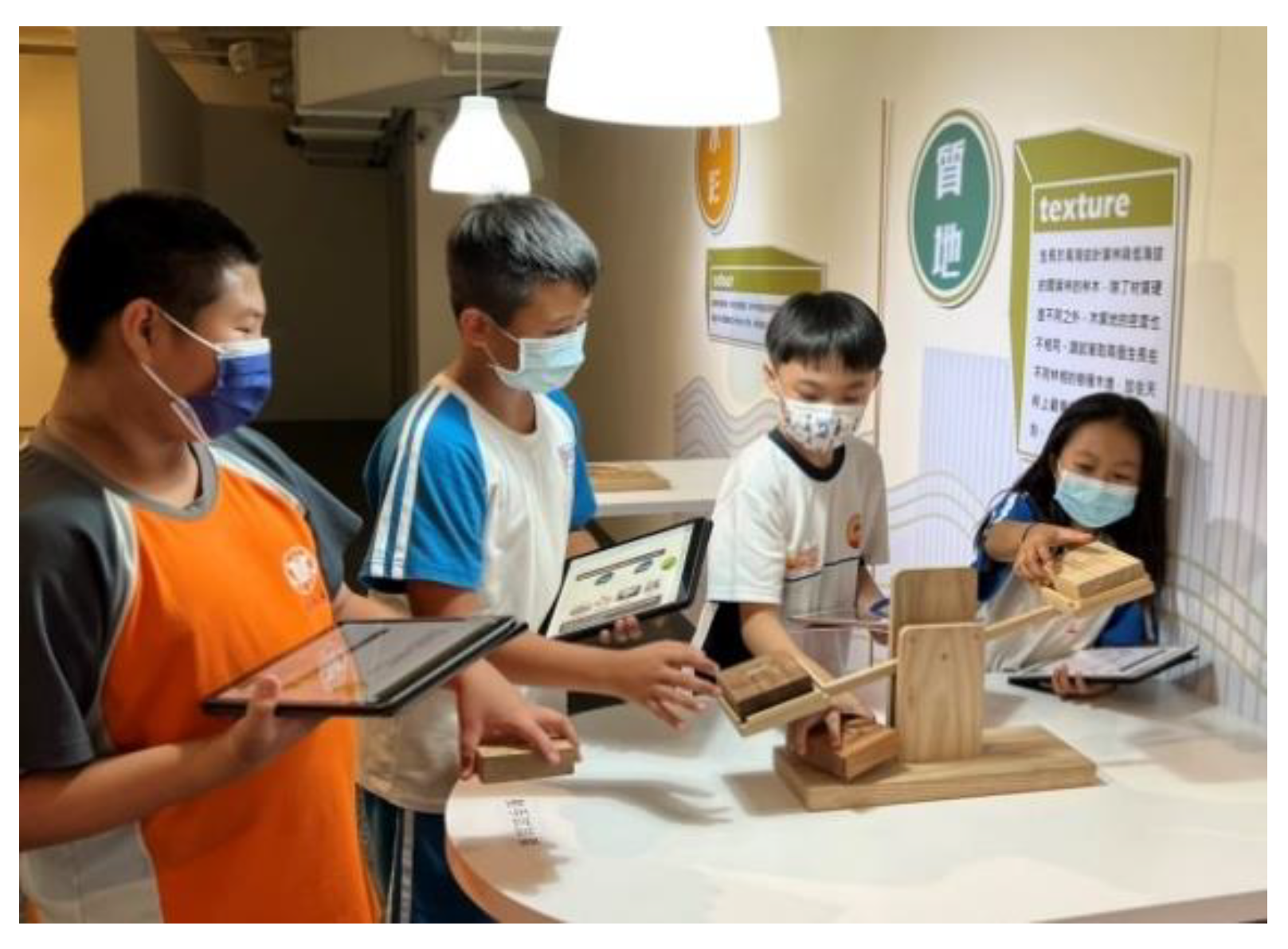
2.2. Educational Tools for Museums: Learning Sheets
2.3. Perspectives from Learning Theory
2.3.1. Constructivist Learning Theory
2.3.2. Perspectives from Educational Objectives
2.3.3. Learning Motivation and Outcomes
3. Study Methodology
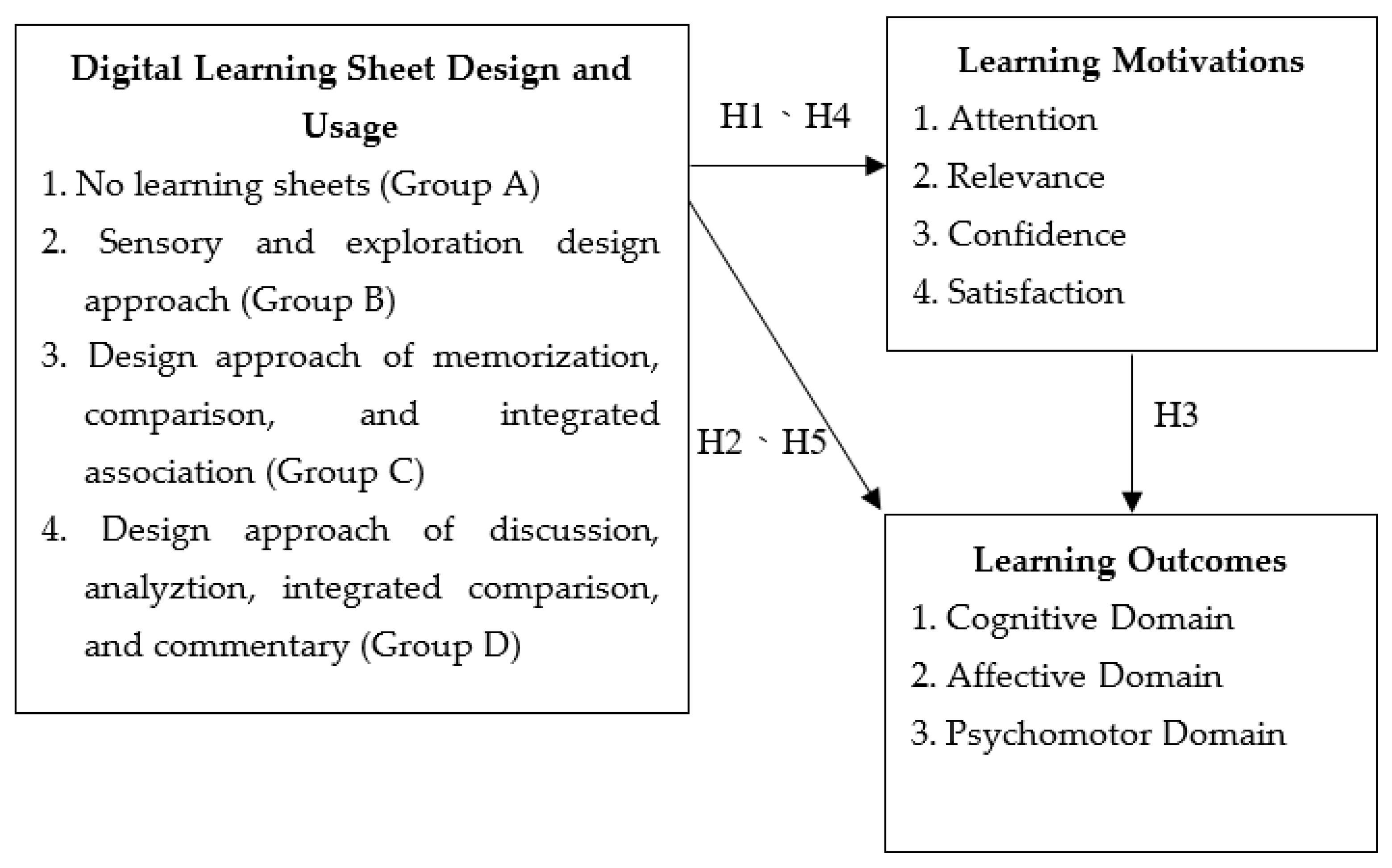
3.1. Framework and Hypotheses
3.2. Research Process
3.3. Research Tools and Analysis Strategies
3.3.1. Review of Learning Outcomes
3.3.2. Digital Learning Sheet Design
3.3.3. Reliability Analysis
4. Research Analysis
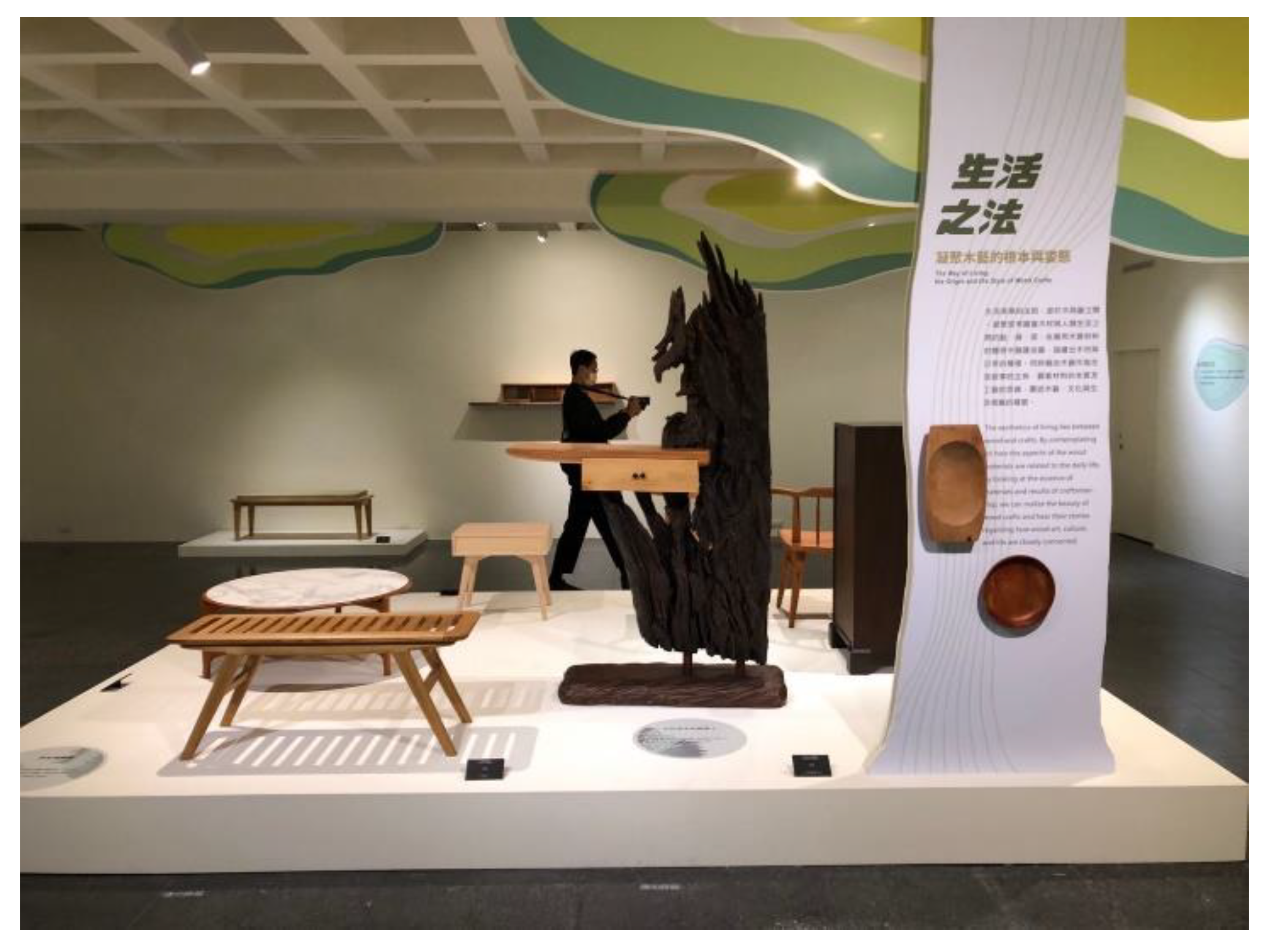
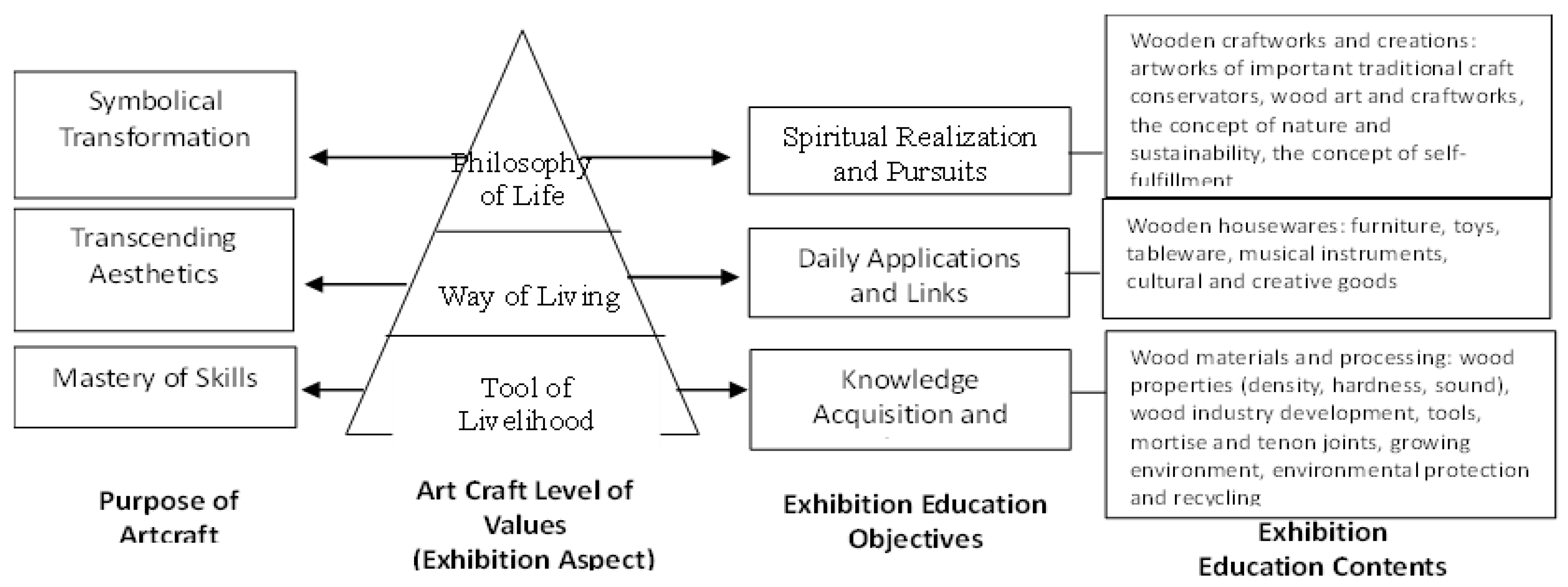
4.1. The First Stage of Study: The Interpretation of the Development of Taiwan Woodcraft Industry with the Concept of Survival, Living, and Philosophy of Life
4.2. The Second Stage of the Study: Verification of Research Hypotheses
4.2.1. Research Hypothesis 1: The “Learning Motivation” of the Group with Digital Learning Sheets Is Significantly Higher than That of the Group without Digital Learning Sheets
4.2.2. Research Hypothesis 2: The “Learning Outcomes” of the Groups with Digital Learning Sheet Are Significantly Higher than Those of the Groups without Digital Learning Sheet
4.2.3. Research Hypothesis 3: “Learning Motivation” Has a Significant and Positive Effect on “Learning Outcomes” with or without the Use of Digital Learning Sheets
4.2.4. Research Hypothesis 4: There Is a Significant Difference in the Effect of Different “Digital Learning Sheet Design Strategies” on “Learning Motivation”
4.2.5. Research Hypothesis 5: There Is a Significant Difference in the Impact of Different “Digital Learning Sheet Design Strategies” on “Learning Outcomes”
5. Conclusions and Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Pre-Test and Post-Test Questionnaires (The Implementation Is in the Chinese Version)
- Pre-test Questionnaires
- Post-test Questionnaire
Appendix B. Sensory and Exploration Design Approach Learning Sheet (B Group)



Appendix C. “Design Approach of Memorization, Comparison, and Integrated Association” (Group C)



Appendix D. “Design Approach of Discussion, Analyzation, Integrated Comparison, and Commentary” (Group D)



References
- Morgan, A.D. Learning communities, cities and regions for sustainable development and global citizenship. Local Environ. 2009, 14, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Institute for Lifelong Learning. Available online: https://uil.unesco.org/lifelong-learning/learning-cities/ (accessed on 30 July 2021).
- Hung, C.S.; Lee, Y.C. A Research on The Promotion Strategy of the Taichung Learning City Project as The Development Process of the Culture Identity of a City. In International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper-Greenhill, E.; Sandell, R.; Moussourl, T.; O’Rlain, H. Museums and Social Inclusion: The GLLAM Report; Research Centre for Museums and Galleries: Leicester, UK, 2000; pp. 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Altıntaş, B. Using museum education as a tolerance facilitator in multicultural societies: The case of Quincentennial (The 500. Years) Foundation Museum of Turkish Jews. IASSR Eur. J. Res. Educ. 2014, 2, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Hirzy, E.C. Excellence and Equity: Education and the Public Dimension of Museums; American Association of Museums: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, C.; Gandini, L.; Forman, G. Hundred Languages of Children: The Reggio Emilia Approach to Early Childhood Education, 2nd ed.; Ablex Publishing Corporation: Norwood, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bagnall, R. Alexandria: Library of dreams. Proc. Am. Philos. Soc. 2002, 146, 348–362. [Google Scholar]
- El-Abbadi, M. The Life and Fate of the Ancient Library of Alexandria; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1992; pp. 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- International Council of Museums. Available online: https://icom.museum/en/ (accessed on 18 September 2021).
- Talboys, G.K. Museum Educator’s Handbook, 3rd ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.; Wilkening, S. Museums and Society 2034: Trends and Potential Futures; American Association of Museums: Washington DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Henning, M. Museums, Media and Cultural Theory; Open University Press: Maidenhead, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Social Education Act (Taiwan). Available online: https://law.moj.gov.tw/LawClass/LawAll.aspx?pcode=H0080001/ (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Lifelong Learning Act (Taiwan). Available online: https://law.moj.gov.tw/LawClass/LawAll.aspx?pcode=H0080048/ (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- The Museum Act (Taiwan). Available online: https://law.moj.gov.tw/LawClass/LawAll.aspx?pcode=H0170101/ (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Hein, G.E. Learning in the Museum; Routledge: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Falk, J.H.; Dierking, L.D. The Museum Experience; Left Coast Press: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2011; pp. 83–114. [Google Scholar]
- Ansbacher, T. Making sense of experience: A model for meaning-making. Exhibitionist 2013, 32, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kolb, D. Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, T.; Bannon, L. Designing ubiquitous computing to enhance children’s learning in museums. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2006, 22, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, D.L. What Makes Learning Fun. Principles for the Design of Intrinsically Motivating Museum Exhibits; AltaMira: Lanham, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Berk, L.E.; Winsler, A. Scaffolding Children’s Learning: Vygotsky and Early Childhood Education; National Association for the Education of Young Children: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Grinder, A.L.; McCoy, E.S. The Good Guide: A Sourcebook for Interpreters, Docents and tour Guides; Ironwood: ArizonaAZ, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper-Greenhill, E. The Educational Role of the Museum. In Museum Education; Hooper-Greenhill, E., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 1994; pp. 229–257. [Google Scholar]
- White, R.; Gunstone, R. Probing Understanding; The Falmer Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Carey, S. Conceptual Change in Childhood; MIT Press: Massachusetts, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Lave, J.; Wenger, E. Situated Learning: Legitimate Peripheral Participation; Cambridge University Press: Massachusetts, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, H.; Johnson, P. Task knowledge structures: Psychological basis and integration into system design. Acta Psychol. 1991, 78, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasnitsky, A. Questioning Vygotsky’s Legacy: Scientific Psychology or Heroic Cult; Routledge: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zavershneva, E. The Cambridge Handbook of Cultural-Historical Psychology; Cambridge University Press: Massachusetts, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Piaget, J.; Inhelder, B. The Psychology of the Child; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Ormrod, J.E.; Jones, B. Essentials of Educational Psychology: Big Ideas to Guide Effective Teaching, 5th ed.; Pearson Education Inc.: Massachusetts, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh, Y. The Lost and Found Experience: Piaget Rediscovered. Constructivist 2005, 16, 1–11. Available online: http://www.odu.edu/educ/act/journal/vol16no1/hsueh.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2021).
- Harry, B. Piaget’s enduring contribution to developmental psychology. Dev. Psychol. 1992, 28, 191–204. [Google Scholar]
- Finder, M.; Gates, H.L. Educating America: How Ralph, W. Tyler Taught America to Teach; Praeger: Westport, CT, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bloom, B.S.; Engelhart, M.D.; Furst, E.J.; Hill, W.H.; Krathwohl, D.R. (Eds.) Taxonomy of Educational Objectives: Handbook I: Cognitive Domain; David Mckay: New York, NY, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, E. The Classification of Educational Objectives in the Psychomotor Domain: The Psychomotor Domain; Gryphon House: Washington, DC, USA, 1972; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, L.W.; Krathwohl, D.R.; Bloom, B.S. (Eds.) A Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching and Assessing: A Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives; Longman: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, H.D. Principles of Language Learning and Teaching; Longman: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hoper-Greenhill, E. Museums and Education: Purpose, Pedagogy, Performance; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, V.F.; Lin, S.W.; Chou, S.Y. The Museum Visitor Routing Problem. Appl. Math. Comput. 2010, 216, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, B. The Manual of Museum Learning; AltaMira Press: Lanham, MD, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, C. Museums and impact. Curator Mus. J. 2003, 46, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortham, S.C.; Barbour, A.; Desjean-Perrotta, B. Portifolio Assessment: A Handbook for Preschool and Elementary Educatiors; Association for Childhood Education International: Olney, MD, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Melograno, V.J. Portifolio Assessment: Documenting Authentic Student Learning. In Student Portfolios: A Collection of Articles; Noblitt, J., Ed.; IRI/Skylight Training and Publishing, Inc.: Palatine, IL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Small, R. Motivation in instructional design. Teach. Libr. 2000, 27, 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, J.M.; Koop, T. An Application of the ARCS Model of Motivational Design. In Instructional Theories in Action: Lessons Illustrating Selected Theories and Models; Reigeluth, C., Ed.; Lawerence Erlbaum: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, T.E.; Xu, L. Motivation student in credit-based information literacy courses: Theories and practice. Portal Libr. Acad. 2002, 2, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minchew, S.S. Teaching English with humor and fun. Am. Second. Educ. 2001, 30, 58–70. [Google Scholar]
- Dörnyei, Z. On the teachability of communication strategies. TESOL Q. 1995, 29, 55–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimche, L. Science centers: A potential for learning: Science centers are educational institutions designed around informal learning activities. Science 1978, 199, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semper, R.J. Science museums as environments for learning. Phys. Today 1990, 43, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Learning Motivation | Cronbach’s Alpha | |
|---|---|---|
| A | 0.857 | 0.916 |
| R | 0.805 | |
| C | 0.887 | |
| S | 0.840 | |
| Levene’s Equality of Variances Test | The t-Test for Equality of Means | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | Significance | t | df | Significance (Two-Tailed) | Average Difference | Standard Error | 95% Differences Confidence Interval | ||
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||||||||
| Using Equal Variances | 2.043 | 0.155 | −19.263 | 163 | 0.000 | −0.80290 | 0.04168 | −0.72060 | −0.88521 |
| Not using equal Variances | −19.186 | 153.010 | 0.000 | −0.80290 | 0.04185 | −0.72023 | −0.88558 | ||
| Levene’s Equality of Variances Test | The t-Test for Equality of Means | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | Significance | t | df | Significance (Two-Tailed) | Average Difference | Standard Error | 95% Differences Confidence Interval | ||
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||||||||
| Using Equal Variances | 2.428 | 0.210 | −13.219 | 163 | 0.000 | −0.89419 | 0.06765 | −1.02776 | −0.76062 |
| Not using equal Variances | −13.161 | 151.415 | 0.000 | −0.89419 | 0.06794 | −1.02843 | −0.75995 | ||
| Post Hoc Comparisons of the Attention Variance Analysis of Students in Groups B, C, and D | |||||||
| Group | N | Alpha = 0.05 Subset | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |||||
| B Group | 84 | 3.8214 | |||||
| C Group | 77 | 3.4221 | |||||
| D Group | 75 | 2.9933 | |||||
| Significance | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||||
| Post Hoc Comparisons of the Relevance Variance Analysis for Students in Groups B, C, and D | |||||||
| Group | N | alpha = 0.05 Subset | |||||
| 1 | 2 | ||||||
| B Group | 84 | 3.7589 | |||||
| C Group | 77 | 3.4643 | |||||
| D Group | 75 | 3.3533 | |||||
| Significance | 1.000 | 0.317 | |||||
| Post Hoc Comparisons of the Confidence Variance Analysis for Students in Groups B, C, and D | |||||||
| Group | N | alpha = 0.05 Subset | |||||
| 1 | 2 | ||||||
| B Group | 84 | 3.7946 | |||||
| C Group | 77 | 3.711 | 3.711 | ||||
| D Group | 75 | 3.5733 | |||||
| Significance | 1.000 | 0.534 | |||||
| Post Hoc Comparison of the Analysis of Satisfaction Variance among Students in Groups B, C, and D | |||||||
| Group | N | alpha = 0.05 Subset | |||||
| 1 | 2 | ||||||
| B Group | 84 | 3.872 | |||||
| C Group | 77 | 3.6461 | |||||
| D Group | 75 | 3.6233 | |||||
| Significance | 1.000 | 0.903 | |||||
| Post Hoc Comparison of Cognitive Variance Analysis of Students in Groups B, C, and D | |||
| Group | N | Alpha = 0.05 Subset | |
| 1 | 2 | ||
| B Group | 84 | 4.27 | |
| C Group | 75 | 4.12 | 4.12 |
| D Group | 77 | 3.86 | |
| Significance | 0.538 | 0.165 | |
| Post Hoc Comparisons of Psychomotor Variance Analysis for Students in Groups B, C, and D | |||
| Group | N | Alpha = 0.05 Subset | |
| 1 | 2 | ||
| B Group | 84 | 4.11 | |
| C Group | 75 | 3.57 | |
| D Group | 77 | 3.57 | |
| Significance | 1.000 | 1.000 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, T.-L.; Lee, Y.-C.; Hung, C.-S. A Study on the Effects of Digital Learning Sheet Design Strategy on the Learning Motivation and Learning Outcomes of Museum Exhibition Visitors. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12020135
Chen T-L, Lee Y-C, Hung C-S. A Study on the Effects of Digital Learning Sheet Design Strategy on the Learning Motivation and Learning Outcomes of Museum Exhibition Visitors. Education Sciences. 2022; 12(2):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12020135
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Tien-Li, Yun-Chi Lee, and Chi-Sen Hung. 2022. "A Study on the Effects of Digital Learning Sheet Design Strategy on the Learning Motivation and Learning Outcomes of Museum Exhibition Visitors" Education Sciences 12, no. 2: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12020135
APA StyleChen, T.-L., Lee, Y.-C., & Hung, C.-S. (2022). A Study on the Effects of Digital Learning Sheet Design Strategy on the Learning Motivation and Learning Outcomes of Museum Exhibition Visitors. Education Sciences, 12(2), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12020135








