A Reliability Generalization Meta-Analysis of “What Is Happening in This Class?” (WIHIC) Questionnaire
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Literature Search
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Approach to Analysis and Synthesis
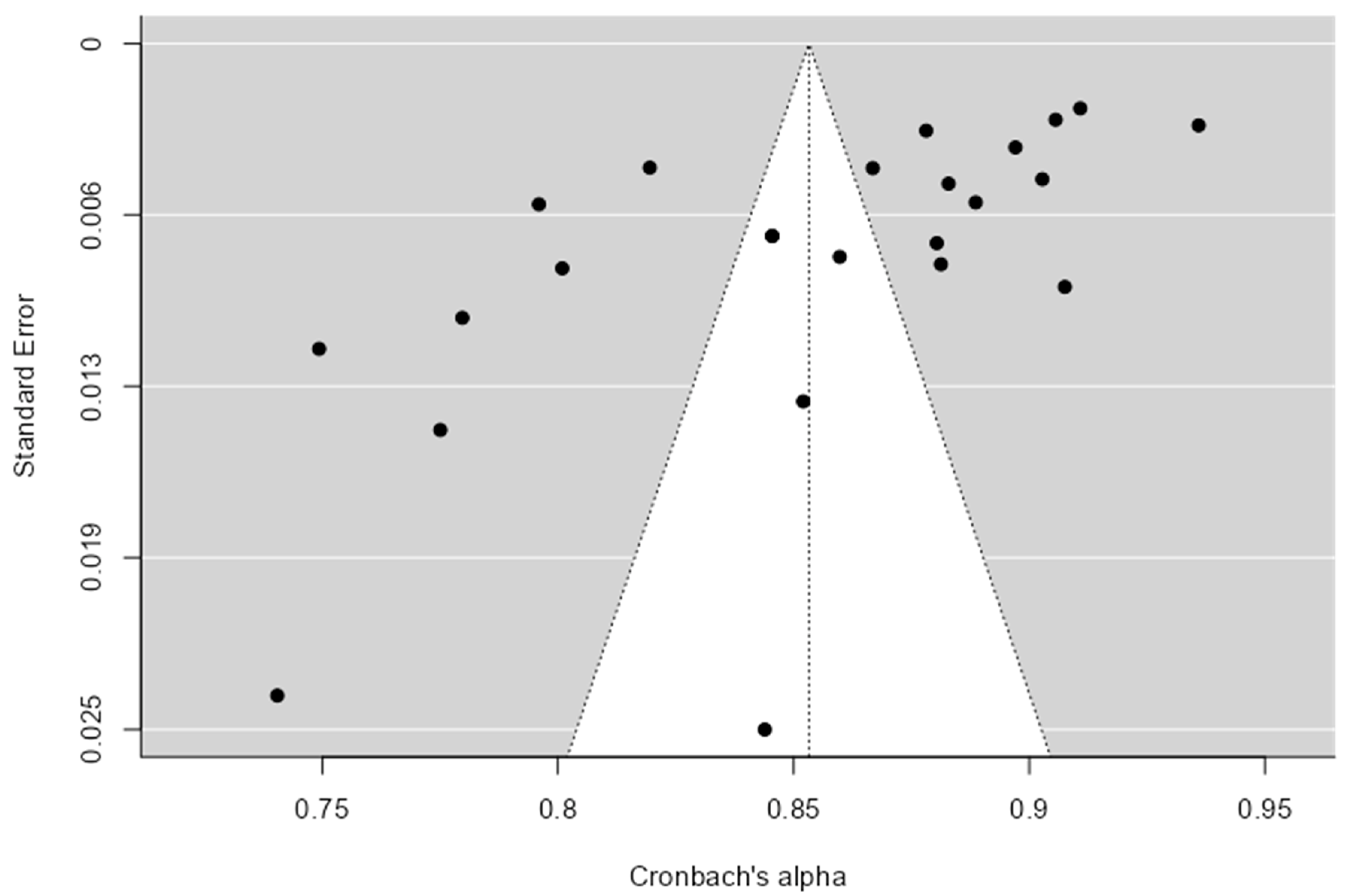
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Included Articles
| Authors | Country | Research Design | Methods | School Context | Translated/Original | Subscales |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adamski et al. [20] | USA | Quantitative | Survey | Mixed | Translated (Spanish) | 6 |
| Aldridge et al. [16] | Taiwan and Australia | Mixed-method | Survey, interviews, observations | Secondary | Translated (Chinese) | 7 |
| Allen and Fraser [25] | USA | Mixed-method | Survey, interviews, observations | Mixed | Original | 6 |
| den Brok et al. [26] | USA | Quantitative | Survey | Secondary | Original | 7 |
| den Brok et al. [22] | Turkey | Quantitative | Survey | Secondary | Translated (Turkish) | 7 |
| Charalampous and Kokkinos [27] | Africa | Mixed-method | Survey, interview | Primary | Original | 7 |
| Chionh and Fraser [28] | Asia | Quantitative | Survey | Secondary | Original | 7 |
| Dorman [29] | Australia | Quantitative | Survey | Secondary | Original | 7 |
| Dorman [30] | Australia | Quantitative | Survey | Secondary | Original | 7 |
| Helding and Fraser [31] | USA | Quantitative | Survey | Secondary | Original | 7 |
| Khalil and Aldridge [21] | Asia | Quantitative | Survey | Secondary | Translated (Arabic) | 5 |
| Kim et al. [23] | Asia | Quantitative | Survey | Secondary | Translated (Korean) | 7 |
| Koul and Fisher [32] | Asia | Quantitative | Survey | Secondary | Original | 7 |
| Lim and Fraser [33] | Asia | Quantitative | Survey | Secondary | Original | 6 |
| Liu et al. [18] | Asia | Mixed-method | Survey, interviews, observations | Secondary | Translated (Chinese) | 5 |
| Opolot-Okurut [34] | Africa | Quantitative | Survey | Secondary | Original | 5 |
| Rita and Mar-tin-Dunlop [35] | USA | Mixed-method | Survey, interview | Secondary | Original | 7 |
| Robinson and Fraser [19] | USA | Quantitative | Survey | Primary | Translated (Spanish) | 5 |
| Shadreck [36] | Africa | Quantitative | Survey | Secondary | Original | 7 |
| Stein and Klosterman [37] | USA | Quantitative | Survey | Secondary | Original | 6 |
| Taylor and Fraser [38] | USA | Quantitative | Survey | Secondary | Original | 7 |
| Wahyudi and Treagust [24] | Asia | Quantitative | Survey | Secondary | Translated (Indonesian) | 7 |
| Waldrip et al. [39] | Australia | Mixed-method | Survey, interview | Secondary | Original | 5 |
| Yang [17] | Asia | Quantitative | Survey | Secondary | Translated (Mandarin) | 7 |
3.2. Reliability and Heterogeneity
3.3. Analysis of Moderator Variables
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zandvliet, D.; Fraser, B. (Eds.) Thirty Years of Learning Environments: Looking Back and Looking Forward; Brill Sense: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Khine, M.S.; Fraser, B.J.; Afari, E. Structural relationships between learning environments and students’ non-cognitive outcomes: Secondary analysis of PISA data. Learn. Environ. Res. 2020, 23, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayubit, R.F.O. Why learning environment matters? An analysis on how the learning environment influences the academic motivation, learning strategies and engagement of college students. Learn. Environ. Res. 2022, 25, 581–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walberg, H.J.; Anderson, G.J. The Achievement-Creativity Dimension and Classroom Climate*. J. Creat. Behav. 1968, 2, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khine, M.S.; Fisher, D.L. Teacher-student interactions in science classrooms. J. Classr. Interact. 2003, 38, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, B.J.; Lee, S.S.U. Science laboratory classroom environments in Korean high schools. Learn. Environ. Res. 2009, 12, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, B.J.; Fisher, D.L.; McRobbie, C.J. Development, validation, and use of personal and class forms of a new classroom environment instrument. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New York, NY, USA, 8–12 April 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Khine, M.S.; Fraser, B.J.; Afari, E.; Oo, Z.; Kyaw, T.T. Students’ perceptions of the learning environment in tertiary science classrooms in Myanmar. Learn. Environ. Res. 2018, 21, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.S.; Sinclair, B.B.; Fraser, B.J.; Larson, T.R.; Harrell, P.E. Preservice teachers’ perceptions of learning environments before and after pandemic-related course disruption. Learn. Environ. Res. 2022, 25, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keramati, M.R.; Gillies, R.M. Perceptions of nursing students on the effect of cooperative learning on academic achievement and learning environment. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2022, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Wen, Q.; Lombaerts, K.; Jaime, I.; Cai, L. Assessing students’ perceptions about classroom learning environments: The New What Is Happening in this Class (NWIHIC) instrument. Learn. Environ. Res. 2022, 25, 601–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizimana, E.; Mutangana, D.; Mwesigye, A. Students’ perceptions of the classroom learning environment and engagement in cooperative mastery learning-based biology classroom instruction. Educ. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandisauskiene, A.; Buksnyte-Marmiene, L.; Cesnaviciene, J.; Daugirdiene, A.; Kemeryte-Ivanauskiene, E.; Nedzinskaite-Maciuniene, R. Sustainable school environment as a landscape for secondary school students’ engagement in learning. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacha-Haase, T. Reliability Generalization: Exploring variance in measurement error affecting score reliability across studies. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1998, 58, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 88, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldridge, J.M.; Fraser, B.J.; Huang, T.C.I. Investigating classroom environments in Taiwan and Australia with multiple research methods. J. Educ. Res. 1999, 93, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. Rural junior secondary school students’ perceptions of classroom learning environments and their attitude and achievement in mathematics in West China. Learn. Environ. Res. 2015, 18, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Zandvliet, D.B.; Hou, I.L. The learning environment associated with information technology education in Taiwan: Combining psychosocial and physical aspects. Learn. Environ. Res. 2012, 15, 379–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, E.; Fraser, B.J. Kindergarten students’ and parents’ perceptions of science classroom environments: Achievement and attitudes. Learn. Environ. Res. 2013, 16, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamski, A.; Fraser, B.J.; Peiro, M.M. Parental involvement in schooling, classroom environment and student outcomes. Learn. Environ. Res. 2013, 16, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, N.; Aldridge, J. Assessing students’ perceptions of their learning environment in science classes in the United Arab Emirates. Learn. Environ. Res. 2019, 22, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Brok, P.; Telli, S.; Cakiroglu, J.; Taconis, R.; Tekkaya, C. Learning environment profiles of Turkish secondary biology classrooms. Learn. Environ. Res. 2010, 13, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.B.; Fisher, D.L.; Fraser, B.J. Classroom environment and teacher interpersonal behaviour in secondary science classes in Korea. Eval. Res. Educ. 2000, 14, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyudi; Treagust, D.F. The status of science classroom learning environments in Indonesian lower secondary schools. Learn. Environ. Res. 2004, 7, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.; Fraser, B.J. Parent and student perceptions of classroom learning environment and its association with student outcomes. Learn. Environ. Res. 2007, 10, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Brok, P.; Fisher, D.; Rickards, T.; Bull, E. Californian science students’ perceptions of their classroom learning environments. Educ. Res. Eval. 2006, 12, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampous, K.; Kokkinos, C.M. The Greek elementary “What Is Happening in this Class?” (G-EWIHIC): A three-phase multi-sample mixed-methods study. Stud. Educ. Eval. 2017, 52, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chionh, Y.H.; Fraser, B.J. Classroom environment, achievement, attitudes and self-esteem in geography and mathematics in Singapore. Int. Res. Geogr. Environ. Educ. 2009, 18, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorman, J.P. Use of multitrait-multimethod modelling to validate actual and preferred forms of the What Is Happening in this Class? (WIHIC) questionnaire. Learn. Environ. Res. 2008, 11, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorman, J.P. Using student perceptions to compare actual and preferred classroom environment in Queensland schools. Educ. Stud. 2008, 34, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helding, K.A.; Fraser, B.J. Effectiveness of National Board Certified (NBC) teachers in terms of classroom environment, attitudes and achievement among secondary science students. Learn. Environ. Res. 2013, 16, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koul, R.B.; Fisher, D.L. Cultural background and students’ perceptions of science classroom learning environment and teacher interpersonal behaviour in Jammu, India. Learn. Environ. Res. 2005, 8, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.T.D.; Fraser, B.J. Learning environments research in English classrooms. Learn. Environ. Res. 2018, 21, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opolot-Okurut, C. Classroom learning environment and motivation towards mathematics among secondary school students in Uganda. Learn. Environ. Res. 2010, 13, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rita, R.D.; Martin-Dunlop, C.S. Perceptions of the learning environment and associations with cognitive achievement among gifted biology students. Learn. Environ. Res. 2011, 14, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadreck, M. Zimbabwean science students’ perceptions of their classroom learning environments and attitude towards science. Mediterr. J. Soc. Sci. 2012, 3, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, S.; Klosterman, P. Nature of learning environment in concurrent enrolment mathematics classrooms: A cluster analysis. Learn. Environ. Res. 2020, 23, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.A.; Fraser, B.J. Relationships between learning environment and mathematics anxiety. Learn. Environ. Res. 2013, 16, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldrip, B.G.; Fisher, D.L.; Dorman, J. Identifying exemplary science teachers through students’ perceptions of their learning environment. Learn. Environ. Res. 2009, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowder, J. How to Use the FISHER Function in Excel for Mac. Available online: https://turbofuture.com/computers/How-to-Use-the-FISHER-Function-in-Excel-For-Mac (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- George, D.; Mallery, P. Using SPSS for Windows Step by Step: A Simple Guide and Reference, 4th ed.; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]


| Scale | Description | Item |
|---|---|---|
| Student Cohesiveness | Extent to which students are friendly and supportive of each other. | I make friendships among students in this class. |
| Teacher Support | Extent to which the teacher helps, befriends, and is interested in students. | The teacher takes a personal interest in me. |
| Involvement | Extent to which students have attentive interest, participate in class, and are involved with other students in assessing the viability of new ideas. | I discuss ideas in class. |
| Investigation | Extent to which there is emphasis on the skills and of inquiry and their use in problem solving and investigation. | I carry out investigations to test my ideas. |
| Task Orientation | Extent to which it is important to complete planned activities and stay on the subject matter. | Getting a certain amount of work done is important to me. |
| Cooperation | Extent to which students cooperate with each other during activities. | I cooperate with other students when doing assignment work. |
| Equity | Extent to which the teacher treats students equally, including distributing praise, question distribution, and opportunities to be included in discussions. | The teacher gives as much attention to my questions as to other students’ questions. |
| Database | Syntax | Number of Articles |
|---|---|---|
| ProQuest | WIHIC AND “learning environment” | 133 |
| Scopus | TITLE-ABS-KEY (WIHIC) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (“learning environment”) | 68 |
| Web of Science | WIHIC (all fields) AND “Learning environment” (all fields) | 34 |
| Inclusion | Exclusion | |
|---|---|---|
| Population | School level | Not university or college level |
| Intervention | NA | NA |
| Comparison | NA | NA |
| Outcomes | Reported Cronbach’s alpha level: whether it is the overall alpha or alpha of the subscales for the WIHIC questionnaire | No Cronbach’s alpha value |
| Study Design | All empirical papers | Not review, discussion, or theoretical papers Non-English papers Not peer-review papers |
| Total Scale/Subscale | n | α | LL | UL | Q | I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Scale | 24 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.87 | 1481.074 * | 99.04% |
| Student Cohesiveness | 22 | 0.80 | 0.77 | 0.84 | 4705.848 * | 99.58% |
| Teacher Support | 23 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.90 | 1920.505 * | 99.32% |
| Involvement | 24 | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.87 | 1280.051 * | 99.1% |
| Investigation | 16 | 0.86 | 0.83 | 0.89 | 1914.472 * | 99.4% |
| Task Orientation | 22 | 0.82 | 0.79 | 0.86 | 4439.097 * | 99.55% |
| Cooperation | 22 | 0.86 | 0.84 | 0.89 | 5675.091 * | 99.51% |
| Equity | 22 | 0.88 | 0.86 | 0.91 | 2314.499 * | 99.47% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oo, C.Z.; Khine, M.S.; San, N.M.H. A Reliability Generalization Meta-Analysis of “What Is Happening in This Class?” (WIHIC) Questionnaire. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12120929
Oo CZ, Khine MS, San NMH. A Reliability Generalization Meta-Analysis of “What Is Happening in This Class?” (WIHIC) Questionnaire. Education Sciences. 2022; 12(12):929. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12120929
Chicago/Turabian StyleOo, Cherry Zin, Myint Swe Khine, and Nang Mo Hline San. 2022. "A Reliability Generalization Meta-Analysis of “What Is Happening in This Class?” (WIHIC) Questionnaire" Education Sciences 12, no. 12: 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12120929
APA StyleOo, C. Z., Khine, M. S., & San, N. M. H. (2022). A Reliability Generalization Meta-Analysis of “What Is Happening in This Class?” (WIHIC) Questionnaire. Education Sciences, 12(12), 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12120929








