An Exploratory Intervention Program on Chinese Culture among CFL Students at a Vietnamese University
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Context of the Study
3. Literature Review
3.1. Language and Culture
3.2. Cultural Teaching Approaches
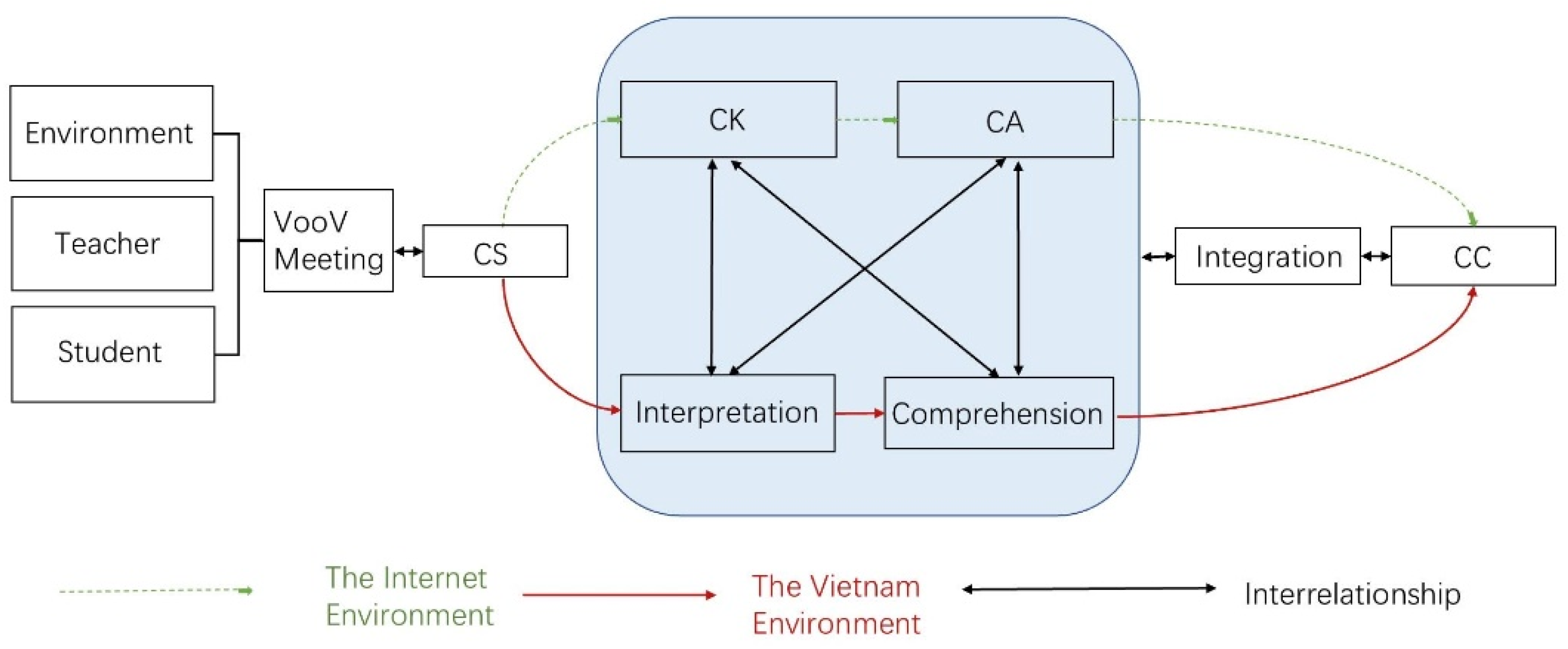
4. The Cultural Intervention Program
4.1. Program Description
4.2. Program Design and Teaching Process
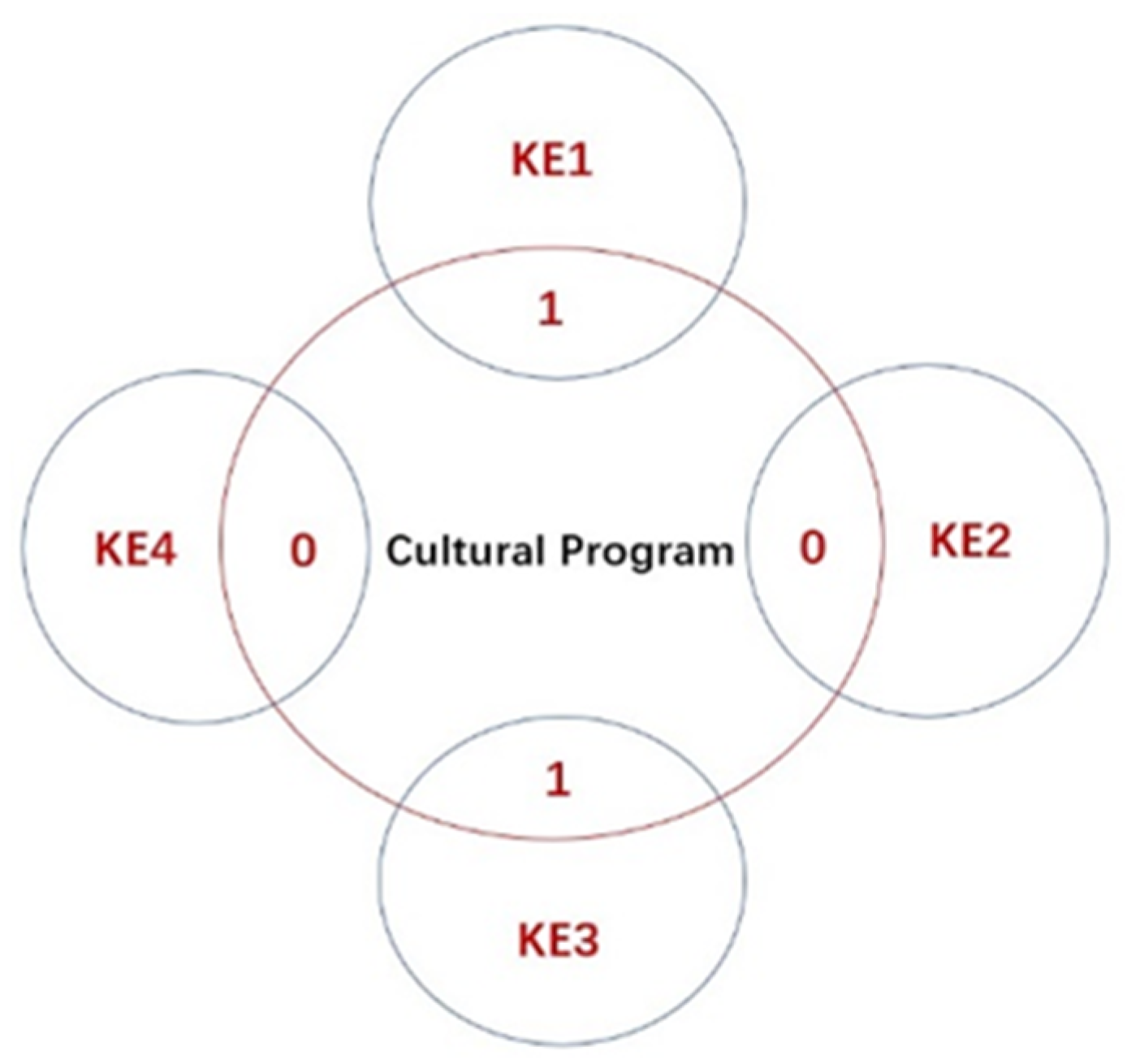
4.3. Program Contents
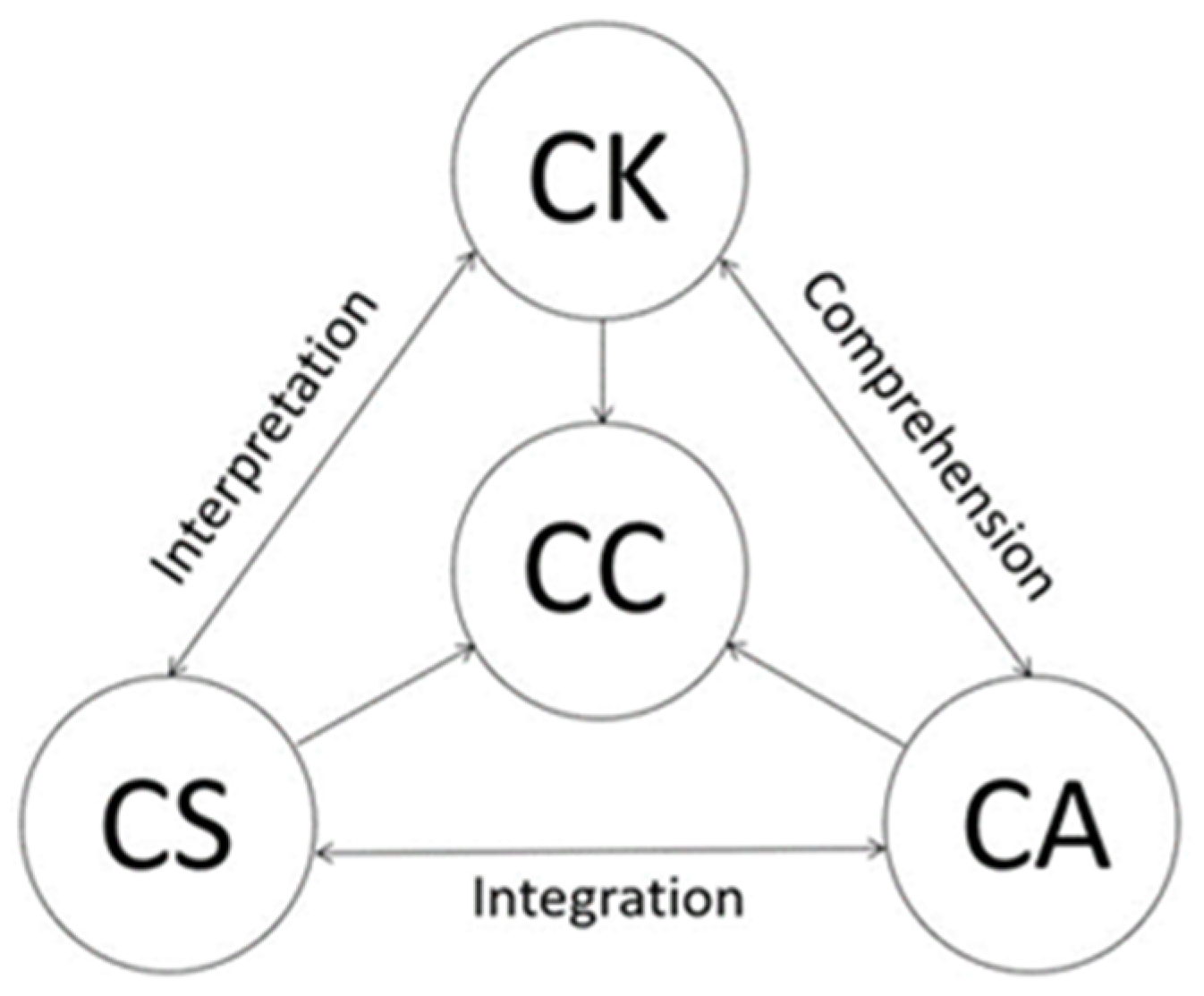
5. The Study
- What are students’ perceptions of cultural knowledge, cultural awareness, and cultural competence in relation to learning Chinese culture?
- What strategies do students employ to acquire cultural knowledge and develop cultural awareness and competence?
- What are the benefits and challenges of learning Chinese culture using technology from students’ perspectives?
- To what extent does this intensive cultural program enhance students’ Chinese language learning?
5.1. Research Instrument
5.2. Research Participants
5.3. Research Data Analysis
6. Results
6.1. Quantitative Data Result
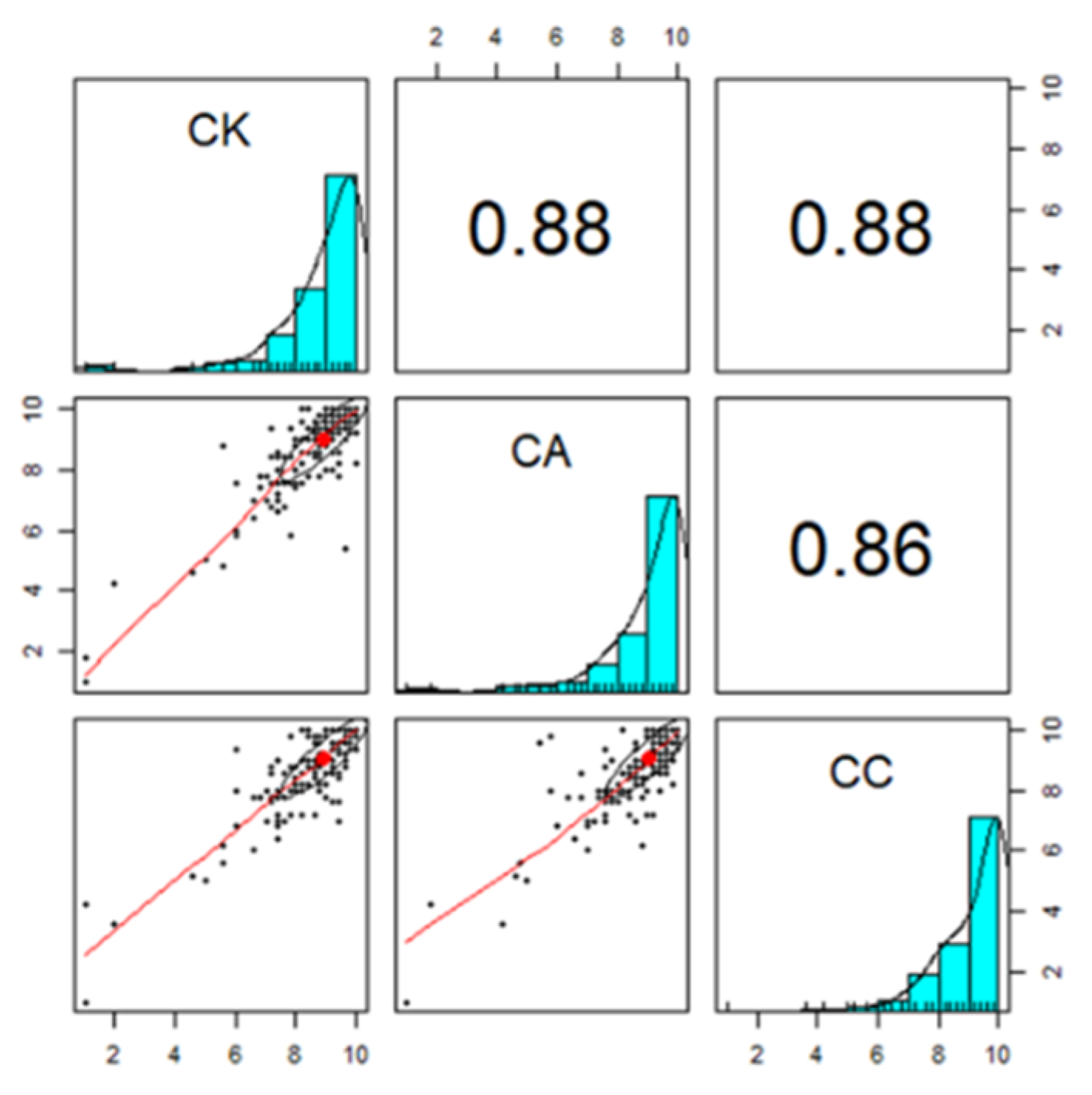
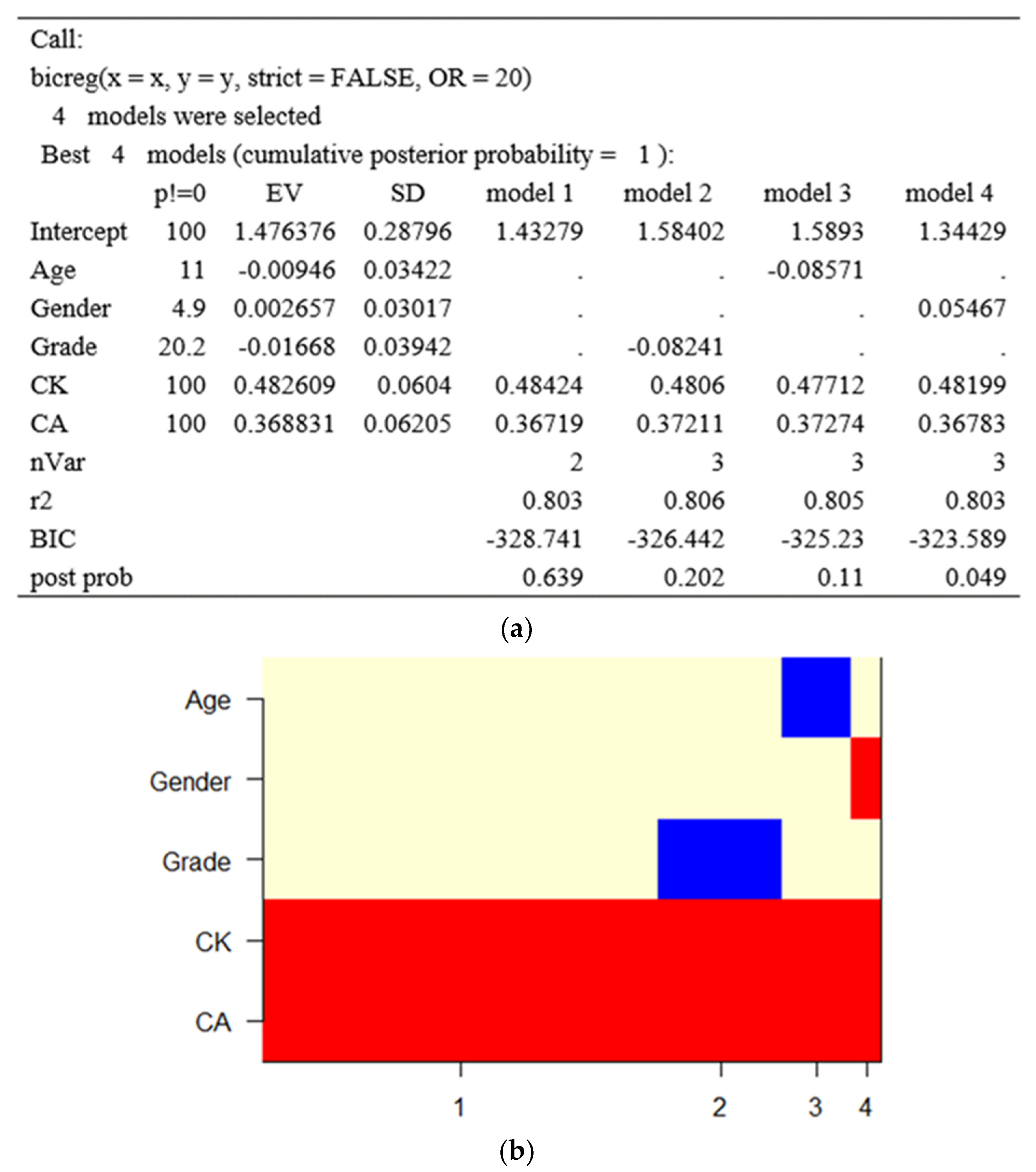
- Model 1: Participants’ predicted CC was equal to 1.43 + 0.48(CK) + 0.36(CA). R2 = 0.803, post prob = 0.639. When CK increased by 0.48 and CA increased by 0.36, then CC increased by 1. Both CK and CA were significant predictors of CC.
- Model 2: Participants’ predicted CC was equal to 1.58–0.08(grade) + 0.48(CK) + 0.37(CA). R2 = 0.806, post prob = 0.202. When grade increased by −0.08, CK increased by 0.48 and CA increased by 0.37, then CC increased by 1. Grade, CK and CA were significant predictors of CC.
- Model 3: Participants’ predicted CC was equal to 1.58–0.09(age) + 0.48(CK) + 0.37(CA). R2 = 0.805, post prob = 0.110. When age increased by −0.08, CK increased by 0.48 and CA increased by 0.37, then CC increased by 1. Age, CK and CA were significant predictors of CC.
- Model 4: Participants’ predicted CC was equal to = 1.58 + 0.05 (gender)+ 0.48(CK) + 0.37(CA). R2 = 0.803, post prob = 0.049. When male or female increased by −0.08, CK increased by 0.48 and CA increased by 0.37, then CC increased by 1. Gender (male or female), CK and CA were significant predictors of CC.
6.2. Qualitative Data Result
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nguyen, N.; Tran, L.T. Looking inward or outward? Vietnam higher education at the superhighway of globalization: Culture, values, and changes. J. Asian Public Policy 2018, 11, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Education and Training (MOET). Circular No. 23/2014/TT-BGDĐT: Regulations on High-Quality Programs in Universities; Ministry of Education and Training (MOET): Hanoi, Vietnam, 2014.
- Council of Europe. Common European Framework of Reference for Languages: Learning, Teaching, Assessment (CEFR). 2014. Available online: http://www.coe.int/t/dg4/linguistic/cadre1_en.asp (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Hoang, V.V. The roles and status of English in present-day Vietnam: A Socio-cultural analysis. VNU J. Foreign Stud. 2020, 36, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Vietnamese Government. Decision No. 1400/Qđ-Ttg Dated 30 September 2008 by the Prime Minister on the Approval of the Proposed Project Entitled: “Teaching and Learning of Foreign Languages in the National Educational System”; Vietnamese Government: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2008.
- Vietnamese Government. Decision No. 2080/Qđ-Ttg Dated 22 December 2017 by the Prime Minister on the Approval of Adjusting and Supplementing the Foreign Language Teaching and Learning Project in the National System for the 2017–2025 Period; Vietnamese Government: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2017.
- Selezneva, N.V. Learning Chinese in Vietnam: The Role of the Confucius Institute. Russ. J. Vietnam. Stud. 2021, 5, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VnExpress International. Available online: https://e.vnexpress.net/news/economy/chinese-speakers-in-demand-as-factories-expand-4459711.html (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Pae, H.K. Chinese, Japanese, and Korean Writing Systems: All East-Asian but Different Scripts. In Script Effects as the Hidden Drive of the Mind, Cognition, and Culture; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 71–105. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, M.; Chan, S.D. Effects of Word Semantic Transparency, Context Length, and L1 Background on CSL Learners’ Incidental Learning of Word Meanings in Passage-Level Reading. J. Psycholinguist. Res. 2022, 51, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Ha, P.; Ha, V.H.; Dat, B. Language policies in modern-day Vietnam: Changes, challenges, and complexities. In Language, Education and Nation-Building; Sercombe, P., Tupas, R., Eds.; Palgrave Studies in Minority Languages and Communities; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2014; pp. 232–244. [Google Scholar]
- Schumann, J.H. Social distance as a factor in second language acquisition. Lang. Learn. 1976, 26, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadiev, R.; Wang, X.; Wu, T.-T.; Huang, Y.-M. Review of Research on Technology-Supported Cross-Cultural Learning. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Liu, Z. An Exploration of Vietnamese Language and Culture; The Ethnic Publishing: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Everson, M.E.; Xiao, Y. Teaching Chinese as a Foreign Language: Theories and Applications; Cheng & Tsui: Boston, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Garrett-Rucks, P. A discussion-based online approach to fostering deep cultural inquiry in an introductory language course. Foreign Lang. Ann. 2013, 46, 191–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.T.K. Addressing culture in EFL classrooms: The challenge of shifting from a traditional to an intercultural stance. Electron. J. Foreign Lang. Teach. 2009, 6, 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Valdes, J.M. Culture in literature. In Culture Bound; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1986; pp. 137–147. [Google Scholar]
- Dellit, J. Getting Started with Intercultural Language Learning: A Resource for Schools. In Asian Languages Professional Learning Project; Asia Education Foundation: Melbourne, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, H. Issues and Options in Language Teaching; Allen, P., Harley, B., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Liddicoat, A.J.; Papademetre, L.; Scarino, A.; Kohler, M. Report on Intercultural Language Learning; Commonwealth of Australia: Canberra, Australia, 2003.
- Zhang, G.; Gong, Q. The retention of Year 11/12 Chinese in Australian schools: A relevance theory perspective. In Critical Perspectives on Language Education; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 119–140. [Google Scholar]
- Shadiev, R.; Yu, J. Review of research on computer-assisted language learning with a focus on intercultural education. Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. 2022, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, D.P.; Bown, J.; Baker, W.; Martinsen, R.A.; Gold, C.; Eggett, D. Language use in six study abroad programs: An exploratory analysis of possible predictors. Lang. Learn. 2014, 64, 36–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chastain, K. Developing Second-Language Skills: Theory and Practice, 3rd ed.; Harcourt College Publishers: San Diego, CA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Liddicoat, A.J.; Scarino, A. Intercultural Language Teaching and Learning; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Piątkowska, K. From cultural knowledge to intercultural communicative competence: Changing perspectives on the role of culture in foreign language teaching. Intercult. Educ. 2015, 26, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenner, A.B. Cultural awareness. Approaches to Materials Design in European Textbooks: Implementing Principles of Authenticity, Learner Autonomy, Cultural Awareness; Fenner, A.B., Newby, D., Eds.; European Centre for Modern Language: Graz, Austria, 2000; pp. 142–152.
- Peirce, C.S. Illustrations of the Logic of Science; Open Court: Chicago, IL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiou, M. Intercultural Competence in Foreign Language Teaching and Learning: Action Inquiry in a Cypriot Tertiary Institution. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Larzén, E. Pursuit of an Intercultural Dimension in EFL-Teaching: Exploring Cognitions among Finland-Swedish Comprehensive Schoolteachers; Åbo Akademi University Press: Pargas, Finland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.T.T. Integrating culture into language teaching and learning: Learner outcomes. Read. Matrix 2017, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar]
- Byram, M. Teaching and Assessing Intercultural Communicative Competence: Revisited; Multilingual Matters: Bristol, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Polanyi, M.; Knowledge, P. Towards a Post-Critical Philosophy; Harper Torchbooks: New York, NY, USA, 1958; pp. 266–267. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, E.T.; Hall, T. The Silent Language; Anchor Books: Prescott, AZ, USA, 1959; Volume 948. [Google Scholar]
- Bloom, B.S. Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, Handbook I: The Cognitive Domain; David McKay Co Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, J.C.; Richards, J.C.; Renandya, W.A. Methodology in Language Teaching: An Anthology of Current Practice; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Centre for Language Education and Cooperation. The Framework of Reference for Chinese Culture and Society in International Chinese Language Education; Sinolingua: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- White, L.A. The Symbol: The Origin and Basis of Human Behavior; Ardent Media: Geneva, WI, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka, I.; Takeuchi, H. The Knowledge-Creating Company: How Japanese Companies Create the Dynamics of Innovation; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, P.R.; Lu, Z. Teaching Culture: Perspectives in Practice; Heinle & Heinle Boston: Boston, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, R.B. Introduction to Research Methods, 4th ed.; Sage: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Denscombe, M. The Good Research Guide for Small Scale Social Research Projects, 2nd ed.; Open University Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Munro, B.H. Statistical Methods for Health Care Research, 5th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, V.; Braun, V.; Hayfield, N. Qualitative Psychology: A Practical Guide to Research Methods. In Thematic Analysis; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; p. 248. [Google Scholar]
- Boyatzis, R.E. Transforming Qualitative Information: Thematic Analysis and Code Development; Sage: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Tuckett, A.G. Applying thematic analysis theory to practice: A researcher’s experience. Contemp. Nurse 2005, 19, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, K.; Bazeley, P. Qualitative Data Analysis with Nvivo; Sage: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Saldaña, J. The Coding Manual for Qualitative Researchers; Sage: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pallant, J. SPSS Survival Manual: A Step by Step Guide to Data Analysis Using IBM SPSS; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, J.Z. Teaching and Learning Chinese as a Foreign Language: A Pedagogical Grammar; Hong Kong University Press: Hong Kong, China, 2006; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Cardon, P.W. Using Films to Learn About the Nature of Cross-Cultural Stereotypes in Intercultural Business Communication Courses. Bus. Commun. Q. 2010, 73, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angelova, M.; Zhao, Y. Using an online collaborative project between American and Chinese students to develop ESL teaching skills, cross-cultural awareness and language skills. Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. 2016, 29, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks-Lewis, K.A. Adult Learners’ Perceptions of the Significance of Culture in Foreign Language Teaching and Learning. J. Educ. Train. Stud. 2014, 2, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, M.-M.; Lai, C.-C. Linguistics across Cultures: The Impact of Culture on Second Language Learning. J. Foreign Lang. Instr. 2006, 1, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Stockwell, E. Teaching Culture in Foreign Language Classes. Foreign Lang. Educ. Res. 2018, 22, 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Q. Students’ Perceptions of Teacher Impact on Their Self-Directed Language Learning with Technology Beyond the Classroom: Cases of Hong Kong and US. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2017, 65, 1105–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, B.; Qi, X. A Review of Research on Technology-Assisted Teaching and Learning of Chinese as a Second or Foreign Language from 2008 to 2018. Front. Educ. China 2020, 15, 142–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemshadsara, Z.G. Developing cultural awareness in foreign language teaching. Engl. Lang. Teach. 2012, 5, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Luk, J. Teachers’ ambivalence in integrating culture with EFL teaching in Hong Kong. Lang. Cult. Curric. 2012, 25, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orton, J.; Scrimgeour, A. Teaching Chinese as a Second Language: The Way of the learner; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, L.; Harvey, S.; Grant, L. What Teachers Say About Addressing Culture in Their EFL Teaching Practices: The Vietnamese Context. Intercult. Educ. 2016, 27, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, C.T.; Viên, T. Integrating Cultures into Teaching EFL in Vietnam: Teachers’ Perceptions. LEARN J. 2018, 11, 103–115. [Google Scholar]
- Ghavamnia, M. Iranian EFL teachers’ beliefs and perspectives on incorporating culture in EFL classes. Intercult. Educ. 2020, 31, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Grist, M.; Grant, S. Into the Real World: Autonomous and Integrated Chinese Language Learning through a 3D Immersive Experience. In Contextual Language Learning: Real Language Learning on the Continuum from Virtuality to Reality; Lan, Y., Grant, S., Eds.; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 119–145. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | n | Percent | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (N = 209) | Female | 184 | 88.0 |
| Male | 25 | 12.0 | |
| Grade (N = 209) | 1st year | 77 | 36.8 |
| 2nd year | 59 | 28.2 | |
| 3rd year | 73 | 34.9 | |
| Age (N = 209) | 18–21 years | 198 | 94.7 |
| >21 years | 11 | 5.3 | |
| Culture Dimensions | Question | Mean/M | Std. Deviation/SD | Cronbach’s Alpha |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultural Knowledge (CK) (M = 8.93, SD = 1.63, N = 209) CK Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.929 | Q8 | 9.14 | 1.58 | 0.91 |
| Q9 | 8.89 | 1.58 | 0.91 | |
| Q10 | 8.89 | 1.71 | 0.92 | |
| Q11 | 8.88 | 1.61 | 0.91 | |
| Q12 | 8.83 | 1.66 | 0.92 | |
| Cultural Awareness (CA) (M = 9.04, SD = 1.58, N = 209) CA Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.932 | Q13 | 9.15 | 1.64 | 0.93 |
| Q14 | 9.15 | 1.44 | 0.91 | |
| Q15 | 9.09 | 1.57 | 0.90 | |
| Q16 | 8.85 | 1.71 | 0.92 | |
| Q17 | 8.97 | 1.53 | 0.91 | |
| Cultural Competence (CC) (M = 9.07, SD = 1.46, N = 209) CC Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.937 | Q18 | 8.80 | 1.78 | 0.95 |
| Q19 | 9.15 | 1.38 | 0.91 | |
| Q20 | 9.03 | 1.38 | 0.92 | |
| Q21 | 9.20 | 1.40 | 0.92 | |
| Q22 | 9.19 | 1.35 | 0.92 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Wei, P.-L.; Nguyen, V.T. An Exploratory Intervention Program on Chinese Culture among CFL Students at a Vietnamese University. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12120887
Wang Y, Wei P-L, Nguyen VT. An Exploratory Intervention Program on Chinese Culture among CFL Students at a Vietnamese University. Education Sciences. 2022; 12(12):887. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12120887
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yanjun, Pei-Ling Wei, and Van Thanh Nguyen. 2022. "An Exploratory Intervention Program on Chinese Culture among CFL Students at a Vietnamese University" Education Sciences 12, no. 12: 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12120887
APA StyleWang, Y., Wei, P.-L., & Nguyen, V. T. (2022). An Exploratory Intervention Program on Chinese Culture among CFL Students at a Vietnamese University. Education Sciences, 12(12), 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12120887





