Learning and Well-Being in Educational Practices with Children and Adolescents Undergoing Cancer Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
3. Materials and Methods
- (a)
- “Learning” aspect: the practices should work on logical reasoning and linguistic development, through activities that develop critical thinking, problem solving, writing and reading texts, use of educational digital games, discussion of various subjects, among others;
- (b)
- “Well-being/Quality of life” aspect: the practices should promote the patients’ well-being through activities and games that were also playful, fun, challenging, and interactive. In addition, patients could also choose games during the learning process.
4. Results
4.1. Conducting the Workshops
4.2. Analysis of the Results
- Do you think that the workshops are helping you to better understand the contents worked on at school?
- What did you most enjoy learning and doing in the workshops?
- Do you feel that the workshops help you at school? Why?
- For you, is learning using games interesting? Why or why not?
- How do you feel about accessing game networks to learn new subjects or remember content you have already seen in school? Why or why not?
4.2.1. Patient 1 (Case A)
4.2.2. Patient 2 (Case B)
4.2.3. Patient 5 (Case C)
4.2.4. Patient 8 (Case D)
4.2.5. Patient 9 (Case E)
5. Discussion
6. Final Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMO | The Support Association in Oncopediatrics |
| ICT | Information Communication Technologies |
| INCA | National Cancer Institute |
| RPG | Role-Playing Game |
References
- Bassani, P.B.S.; Barbosa, D.N.F. Experiences with web 2.0 in school settings: A framework to foster educational practices based on a personal learning environment perspective. Educ. Rev. 2018, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barbosa, D.N.F.; Barbosa, J.L.V. Learning with Mobility and Ubiquitous Learning. In Informática na Educação: Técnicas e Tecnologias Computacionais; Pimentel, M., Sampaio, F.F., Santos, E.O., Eds.; Brazilian Computer Society: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2019; Available online: https://ieducacao.ceie-br.org/aprendizagemmobilidadeubiqua (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Prensky, M. Learning Based on Digital Games; Editora Senac: São Paulo, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, A.; Barbosa, J.; Barbosa, D. A model for profile management applied to ubiquitous learning environments. Exp. Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 2023–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.L.V.; Kich, M.R.; Barbosa, D.N.F.; Klein, A.Z.; Rigo, S.J. DeCom: A model for context-aware competence management. Comput. Ind. 2015, 72, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deegan, R.; Rothwell, P.A. Classification of M-Learning Applications from a Usability Perspective. J. Res. Cent. Educ. Technol. 2010, 6, 6–27. Available online: https://sacj.cs.uct.ac.za/index.php/sacj/article/download/240/153 (accessed on 29 June 2021).
- García, M.I.; Tadeu, P.J.A.; Ubago, J.J.L.; Brigas, C. Pedagogical Coordination in Secondary Schools from a Distributed Perspective. Adaptation of the Distributed Leadership Inventory (DLI) in the Spanish Context. Educ. Sci. 2020, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianna, H.D.; Barbosa, J.L.V. A model for ubiquitous care of noncommunicable diseases. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2013, 18, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vianna, H.D.; Barbosa, J.L.V. Pompilos, a Model for Augmenting Health Assistant Applications with Social Media Content. J. Univers. Comput. Sci. 2020, 26, 4–32. Available online: http://www.jucs.org/jucs_26_1/pompilos_a_model_for/jucs_26_01_0004_0032_vianna.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Dias, L.P.S.; Barbosa, J.L.V.; Vianna, H.D. Gamification and serious games in depression care: A systematic mapping study. Telemat. Inform. 2018, 35, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, F.; Crovari, P.; Masciadri, A.; Bianchi, S.; Pasquarelli, M.G.G.; Toldo, M.; Comai, S.; Imtiaz, A.; Yuyar, E. Clone: A promising system for the remote monitoring of Alzheimer’s patients an experimentation with a wearable device in a village for Alzheimer’s care. In ACM International Conference Proceeding Series; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Lai Kwan, C.; Mahdid, Y.; Motta Ochoa, R.; Lee, K.; Park, M.; Blain-Moraes, S. Wearable technology for detecting significant moments in individuals with dementia. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 6515813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, L.P.S.; Barbosa, J.L.V.; Feijo, L.P.; Viana, H.D. Development and testing of iAware model for ubiquitous care of patients with symptoms of stress, anxiety and depression. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2020, 187, 105113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavaresco, R.; Barbosa, J.L.V.; Vianna, H.D.; Buttenbender, P.C.; Dias, L.P.S. Design and evaluation of a context-aware model based on psychophysiology. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2020, 189, 105–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, N.; Sayyed, A.; Dal Sasso, G.T.M.; Khanum, S.; De Souza, M.D.L. SavingLife: An Educational Technology for Basic and Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support. Educ. Sci. 2018, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larentis, A.V.; Barbosa, D.N.F.; da Silva, C.R.; Barbosa, J.L.V. Applied computing to education on noncommunicable chronic diseases: A systematic mapping study. Telemed. e-Health 2020, 26, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, C.E.; Fernandes, R.; Santos, C.X.; Boccaletti, K.W.; Pellizzon, A.C.A.; Barbosa, J.H.O. Feasibility of mobile applications for remote support of radiation therapy patients. J. Braz. Med. Assoc. 2019, 65, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, G.T.; Barbosa, D.N.F.; dos Santos, P.R.; Barbosa, J.L.V. Evaluation of Usability and Gameplay of Games on Mobile Platforms for Young People on Oncological Treatment. RENOTE-New Technol. Educ. J. 2019, 17, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermo, V.C.; Lourencatto, G.N.; Medeiros, T.D.S.; Anders, J.C.; Souza, A.A.I.J. Early diagnosis of childhood cancer: The journey made by families. Anna Nery Sch. J. Nurs. 2014, 18, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Leandro, T.A.; Silva, V.M.; Lopes, M.V.O.; Guedes, N.G.; Nunes, M.M.; Sousa, T.M. Poor comfort in children and adolescents with cancer. Braz. J. Nurs. 2018, 71, 934–941. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, D.N.F.; Bassani, P.B.S.; Mossmann, J.B.; Schneider, G.T.; Reategui, E.; Branco, M.A.A.; Meyrer, L.S.; Nunes, M. Mobile Learning and Games: Experiences with mobile games development for children and teenagers undergoing oncological treatment. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2014, 8495, 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Masini, A.; Gori, D.; Marini, S.; Lanari, M.; Scrimaglia, S.; Esposito, F.; Campa, F.; Grigoletto, A.; Ceciliani, A.; Toselli, S.; et al. The Determinants of Health-Related Quality of Life in a Sample of Primary School Children: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2021, 18, 3251. [Google Scholar]
- Helseth, S.; Haraldstad, K. Child Well-Being. In Encyclopedia of Quality of Life and Well-Being Research; Michalos, A.C., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vianna, H.D.; Barbosa, J.L.V.; Pittoli, F. In the Pursuit of Hygge Software. IEEE Softw. 2017, 34, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianna, H.D.; Barbosa, J.L.V.; Gluz, J.C.; Santos, R. Design of an ontology for detecting the social influence on non-communicable diseases risk factors. Int. J. Metada Semat. Ontol. 2018, 13, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.Z.; Freitas, J.C.S.; Baldasso, L.; Barbosa, J.L.V.; Mattiello, J. The Educational Affordances of Mobile Instant Messaging (MIM): Results of Whatsapp Used in Higher Education. Int. J. Distance Educ. Technol. 2018, 16, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.L.V.; Hahn, R.; Barbosa, D.N.F.; Segatto, W. Intensive Use of Mobile Technologies in a Computer Engineering Course. Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ. 2014, 22, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccol, A.Z.; Barbosa, J.L.V.; Schlemmer, E.; Reinhard, N. Mobile learning in organizations: Lessons learned from two case studies. Int. J. Inf. Commun. Technol. Educ. 2011, 7, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severin, E.; Capota, C.C. One-to-one computing: New perspectives. Iberoam. J. Educ. 2011, 56, 31–48. Available online: http://sgpwe.izt.uam.mx/files/users/uami/ana/SeverinYCapotaProgsDotComputAmLat.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2021).
- Moreira, M.A. Los efectos del modelo 1: 1 in educational change in schools. Evidence and challenges for Ibero-American policies. Iberoam. J. Educ. 2011, 56, 49–74. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, J.L.V.; Barbosa, D.N.F.; Oliveira, J.M.; Rabello, S.A. A Decentralized Infrastructure for Ubiquitous Learning Environments. J. Univers. Comput. Sci. 2014, 20, 1649–1669. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, J.L.V.; Hahn, R.; Barbosa, D.N.F.; Saccol, A.I.C.Z. A Ubiquitous Learning Model Focused on Learner Integration. Int. J. Learn. Technol. 2011, 6, 62–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leithardt, V.R.Q. Percontrol: A pervasive system for educational environments. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC), Maui, HI, USA, 30 January–2 February 2012; pp. 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, L.G.A.; Matter, V.K.; Barbosa, D.N.F.; Gluz, J.C.; Barbosa, J.L.V. Using Learners Group Profile for Content Recommendation in Ubiquitous Environments. Int. J. Inf. Commun. Technol. Educ. 2020, 16, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, R.L.A.; Peña, A.A. Ubiquitous learning: A systematic review. Telemat. Inform. 2018, 35, 1097–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.G.; Neto, E.G.D.A.; Francisco, R.; Barbosa, J.L.V.; Silva, L.A.; Leithardt, V.R.Q. ULearnEnglish: An Open Ubiquitous System for Assisting in Learning English Vocabulary. Electronics 2021, 10, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, R.; Marques Vieira, R.; Pedro, L. Mobile App for Science Education: Designing the Learning Approach. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, H.; Encinas, F.G.; Leithardt, V.R.Q.; González, G.V. Physical Movement Helps Learning: Teaching Using Tracking Objects with Depth Camera. In Trends and Applications in Information Systems and Technologies; Rocha, Á., Adeli, H., Dzemyda, G., Moreira, F., Ramalho Correia, A.M., Eds.; WorldCIST; Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 1368. [Google Scholar]
- Lähteenmäki, P.M.; Huostila, J.; Hinkka, S.; Salmi, T.T. Childhood cancer patients at school. Eur. J. Cancer 2002, 38, 1227–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, G.; Kelly, P.; Chesters, H.; Franklin, J.; Griffiths, H.; Langton, L.; Langton, L.; Wakefield, C.E.; Gibson, F. Access to and experience of education for children and adolescents with cancer: A scoping review protocol. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.J.; Temple, J.A.; Ou, S.R.; Robertson, D.L.; Mersky, J.P.; Topitzes, J.W.; Niles, M.D. Effects of a school-based, early childhood intervention on adult health and well-being: A 19-year follow-up of low-income families. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2007, 161, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.H. The Design of Applying Gamification in an Immersive Virtual Reality Virtual Laboratory for Powder-Bed Binder Jetting 3DP Training. Educ. Sci. 2020, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, J.D.V.; Silva, J.R.C.; Ribeiro, A.F.S.; Gomes, R.M.M.; Ferreira, J.C.; Matos, F.B. Aprendizagem Significativa por meio do Uso de TICs: Survey of Teaching Area Productions from 2016 to 2018. Renote J. 2019, 17, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Brandão, I.D.A.; Whitaker, M.C.O.; Oliveira, M.M.C.; Lessa, A.B.S.L.; Lopes, T.F.S.; Camargo, C.L.D.; Silva, J.C.D.; Moraes, J.A.S.D. Electronic games in health care of children and adolescents: Integrative review. Acta Paul. Nurs. 2019, 32, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhof, S.L.; Vinkers, C.H.; van Geelen, S.M.; Duijff, S.N.; Achterberg, E.M.; Van Der Net, J.; Lesscher, H.M. Healthy play, better coping: The importance of play for the development of children in health and disease. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 9, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitosa, J.C.; Braga, J.R.F. Kimo: A Serious Game for Children and Adolescents With Cancer. In Proceedings of the XVII SBGames, Foz do Iguaçu, Brazil, 29 October–1 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, J.; Teles, A.; Teixeira, S. An Augmented Reality-Based Mobile Application Facilitates the Learning about the Spinal Cord. Educ. Sci. 2020, 10, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, B.B.; Barbosa, D.N.F.; Mossmann, J.B.; Cardoso, C.O.; Barbosa, J.L.V. Inhibitory control stimulation in elementary school children through digital games: A systematic mapping study. Appl. Neuropsychol. Child 2020, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassani, P.B.; Barbosa, D.N.F. Designing for Authorship: Students as Content Creators Using Mobile Devices in Educational Settings. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning and Collaboration Technologies, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 15–20 July 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Cerqueira, B.B.; Barbosa, D.N.F.; Mossmann, J.B.; Barbosa, J.L.V. Adaptation of an educational Exergame to mobile platforms: A development process. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2018, 1, 287–298. [Google Scholar]
- Park, R.; Burgess, E. Introduction to the Science of Sociology; Originally Published 1921; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, D.N.F.; Bassani, P.B.S.; Martins, R.L.; Mossmann, J.B.; Barbosa, J.L.V. Using Mobile Learning in Formal and Non-formal Educational Settings. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2016, 9743, 269–280. [Google Scholar]
- Kersh, D.F.; Coscarelli, C.V.; Cani, J.B. Multiliteracies and Multimodality: Pedagogical Actions Applied to Language. Campinas: Editora Pontes. 2016. Available online: https://educationendowmentfoundation.org.uk/tools/guidance-reports/improving-literacy-in-secondary-schools/ (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Guardians of the Waters: Feevale. Available online: http://games.feevale.br/loa/guardioesdasaguas (accessed on 27 June 2021).
- Machado, S.D.; Tavares, J.E.R.; Martins, M.G.; Barbosa, J.L.V.; Gonzalez, G.V.; Leithardt, V.R.Q. Ambient Intelligence Based on IoT for Assisting People with Alzheimer?s Disease Through Context Histories. Electronics 2021, 10, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.; Tavares, J.; Cardoso, I.; Alves, B.; Martini, B. TrailCare: An indoor and outdoor Context-aware system to assist wheelchair users. Int. J.-Of Hum. Comput. Stud. 2018, 116, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.K.; Abowd, G.D.; Salber, D. A conceptual framework and a toolkit for supporting the rapid prototyping of context-aware applications. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2001, 16, 97–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, J.E.R.; Barbosa, J.L.V. Ubiquitous healthcare on smart environments: A systematic mapping study. J. Ambient. Intell. Smart Environ. 2020, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Aranda, J.A.S.; Bavaresco, R.S.; Carvalho, J.V.D.; Yamin, A.C.; Tavares, M.C.; Barbosa, J.L.V. A computational model for adaptive recording of vital signs through context histories. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, J.H.; Barbosa, J.L.V.; Kich, M.; Brito, L. A Multi-Temporal Context-aware System for Competences Management. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2015, 25, 455–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, B.G.; Helfer, G.A.; Barbosa, J.L.V.; Modolo, R.C.E.; Silva, M.R.; Figueiredo, R.M.; Mendes, A.S.; Silva, L.A.; Leithardt, V.R.Q. IndoorPlant: A Model for Intelligent Services in Indoor Agriculture Based on Context Histories. Sensors 2021, 21, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, D.; Barbosa, J.L.V.; Alves, B.M. CHSPAM: A multi-domain model for sequential pattern discovery and monitoring in contexts histories. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2020, 23, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, J.H.; Barbosa, J.L.; Ribeiro, G.D. ORACON: An adaptive model for context prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 45, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.M.; Dias, L.P.S.; Rigo, S.J.; Anjos, J.C.S.; Geyer, C.F.R.; Leithardt, V.R.Q.; Barbosa, J.L.V. Learning analytics and collaborative groups of learners in distance education: A systematic mapping study. Inform. Educ. 2021, 1, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, T.L.; Rigo, S.J.; Barbosa, J.L.V. Active Methodology, Educational Data Mining and Learning Analytics: A Systematic Mapping Study. Inform. Educ. 2021, 1, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Filippetto, A.S.; Lima, R.; Barbosa, J.L.V. A risk prediction model for software project management based on similarity analysis of context histories. Inf. And Softw. Technol. 2021, 131, 106497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedemann, T.; Barbosa, J.L.V.; Matter, V.K.; Gonçales, L.J.; Nesi, L.C.; Rigo, S.J.; Oliveira, K.S.F. SIMCOP: A framework for similarity analysis of context histories. Int. J. Bus. Inf. Syst. 2021, 1, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
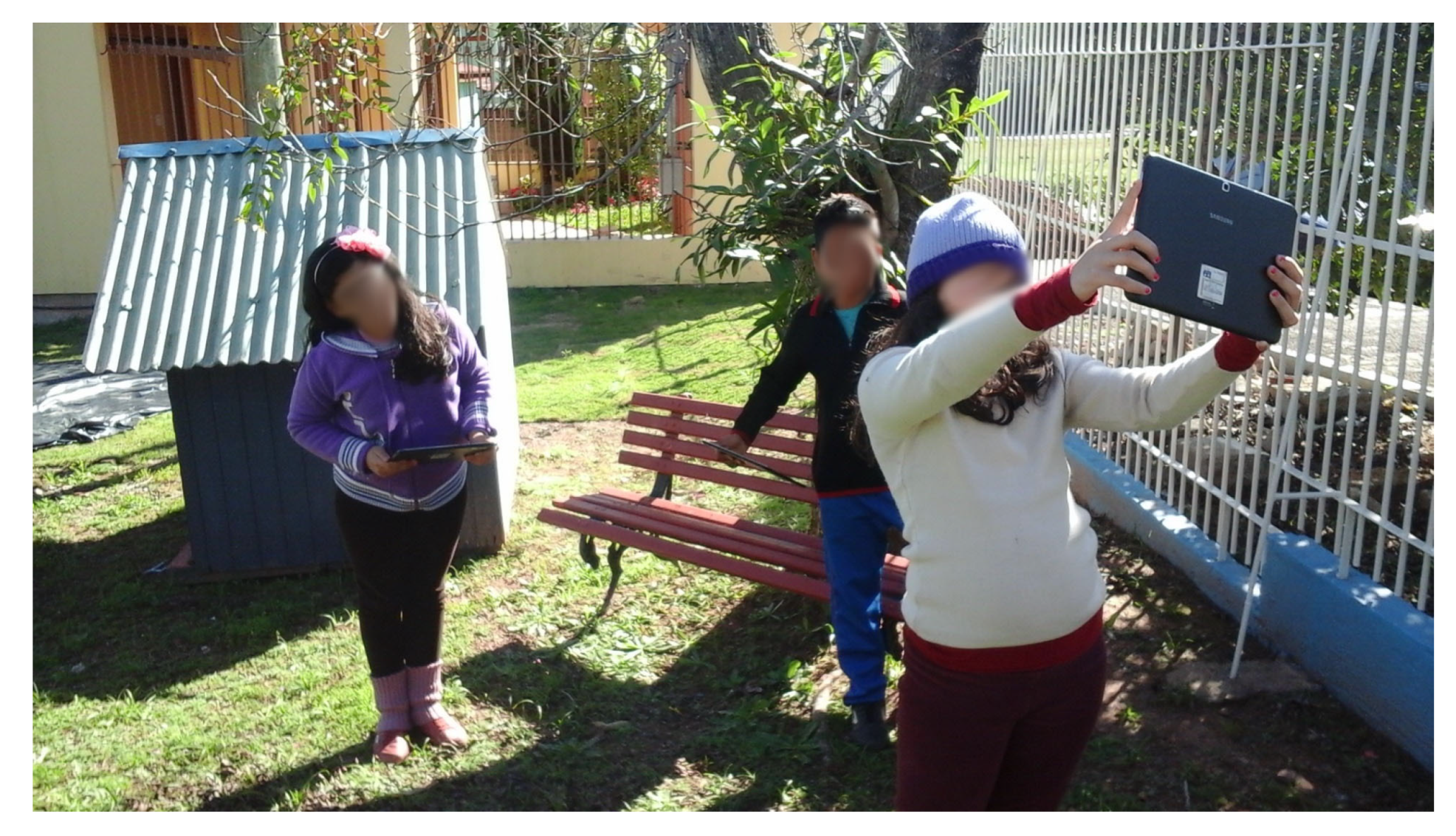
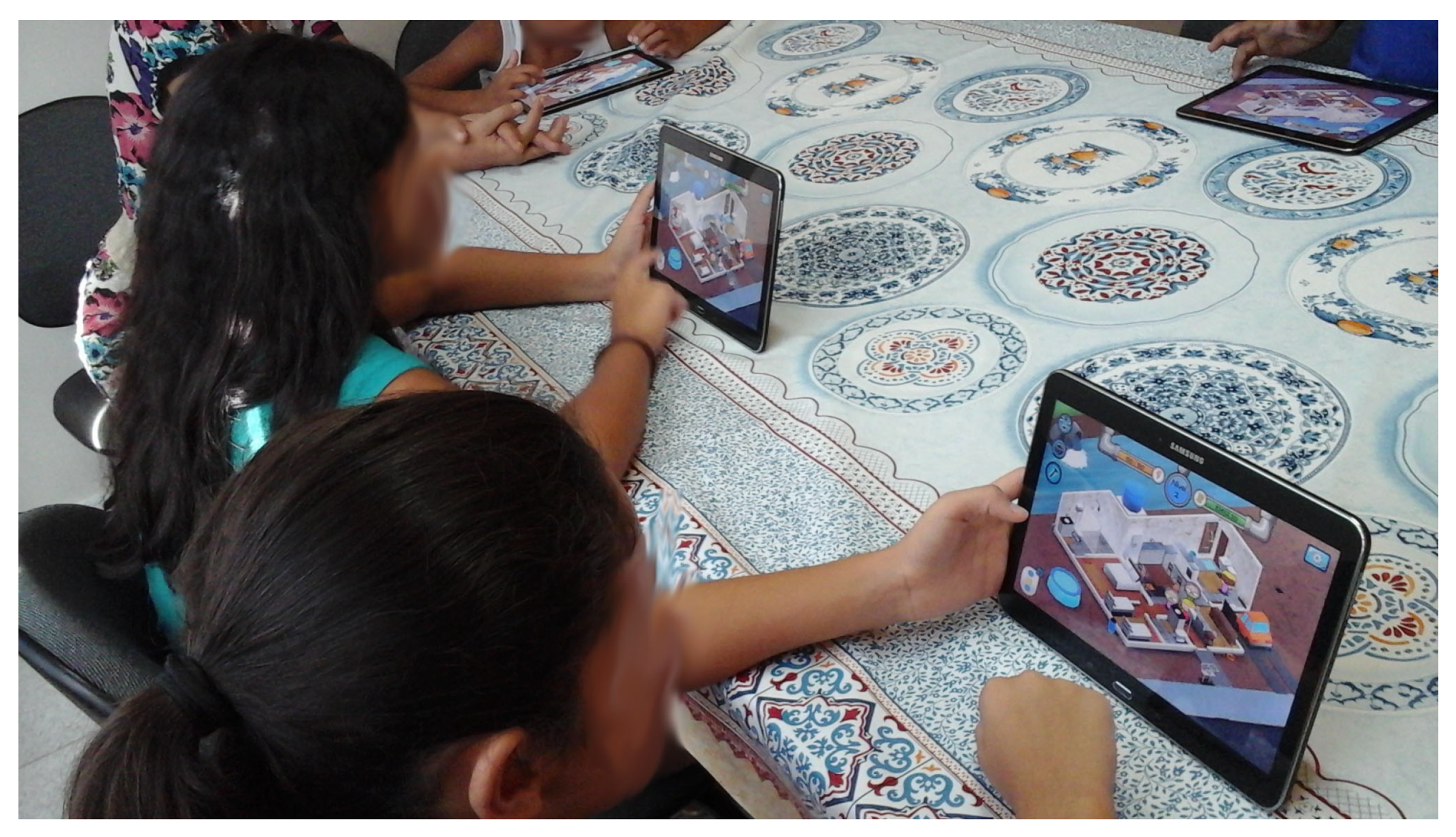





| Year | Main Learning Activities | Learn Goals | Main Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | Searching about identity and history. | To think and to learn more about their own identity using technology. Linguistic development through the creation of comics and short stories. To develop logical reasoning. | Comic Strip IT. Supernote. Evernote. |
| 2016 | Developing logical programming using code.org. Producing stories about digital games and RPGs. Playing RPGs with mobile devices. | To develop logical reasoning and computational thinking. Linguistic development through the creation of short stories. | Code.org. Google Docs. Evernote. Qr.Code Reader. |
| 2017 | Developing debates, readings, texts, and use of games related to the sustainable use of water. | To develop the theme “sustainability of water resources”. | Water Generation game. Google Docs. Google Chrome. |
| 2018 | Writing micro-stories with the theme “identity and personal history”, discussing about personal tastes, routine, dreams, interests, among others. | To develop logical reasoning. Linguistic development through the creation of micro-stories. | Google Docs. Autodesk Sketchbook. Google Classroom. |
| 2019 | Free activities involving reading and writing with tablets. Playing the project “Guardians of the Waters An RPG Adventure” with mobile devices | To think about environmental sanitation and water preservation. To develop logical reasoning and decision making. Linguistic development through role-playing activities | Guardians of the Waters game. Free app to write text. |
| Question | Response |
|---|---|
| 1 | Yes, because they worked on about commas and writing, helping me in the school. |
| 2 | Code.org, I enjoyed learning the right and left turn phases and the writing parts as it helped me to write faster. |
| 3 | Yes, because in the workshops I learn not to confuse letters like “C” and “S” and so I do better in school. |
| 4 | Yes, because we can play and learn at the same time. |
| 5 | Cool, because we can review content that we didn’t see right at school. |
| Question | Patient Response |
|---|---|
| 1 | Yes, because the Code.org game helps to learn some things like left and right. |
| 2 | Play Code.org |
| 3 | Yes, I started to pay more attention in class, because in games we have to pay attention to do it right. |
| 4 | Yes, we learn while being distracted by the game. |
| 5 | It is very cool, because I like to compare the results and be the best. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
dos Santos, P.R.; Barbosa, D.N.F.; Neto, E.G.A.; Barbosa, J.L.V.; Correia, S.D.; Leithardt, V.R.Q. Learning and Well-Being in Educational Practices with Children and Adolescents Undergoing Cancer Treatment. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11080442
dos Santos PR, Barbosa DNF, Neto EGA, Barbosa JLV, Correia SD, Leithardt VRQ. Learning and Well-Being in Educational Practices with Children and Adolescents Undergoing Cancer Treatment. Education Sciences. 2021; 11(8):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11080442
Chicago/Turabian Styledos Santos, Paulo Ricardo, Débora N. F. Barbosa, Eduardo G. Azevedo Neto, Jorge L. V. Barbosa, Sérgio D. Correia, and Valderi R. Q. Leithardt. 2021. "Learning and Well-Being in Educational Practices with Children and Adolescents Undergoing Cancer Treatment" Education Sciences 11, no. 8: 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11080442
APA Styledos Santos, P. R., Barbosa, D. N. F., Neto, E. G. A., Barbosa, J. L. V., Correia, S. D., & Leithardt, V. R. Q. (2021). Learning and Well-Being in Educational Practices with Children and Adolescents Undergoing Cancer Treatment. Education Sciences, 11(8), 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11080442










