Abstract
A main goal of the university institution should be to reduce the desertion of its students, in fact, the dropout rate constitutes a basic indicator in the accreditation processes of university centers. Thus, evaluating the cognitive functions and learning skills of students with an increased risk of academic failure can be useful for the adoption of strategies for preventing and reducing school dropout. In this research, cognitive functions and learning skills in 284 university students were evaluated. Academic performance predictors were identified, and conglomerates analysis was carried out to establish groups according to those variables. The stability and validity of the conglomerates were tested with discriminant analyzes and comparison tests. The variables associated significantly to academic performance were: attention, intelligence, motivation, metacognition and affective components. The conglomerate analysis suggested a three-group solution: (1) students with cognitive skills of moderate to high, but deficient learning strategies; (2) students with cognitive and learning capabilities of moderate to high; (3) students with cognitive functions low and moderate learning capacity. Students from groups 1 and 3 showed worse academic performance; 83.3% of students at risk of desertion belonged to such groups. Two groups of students have been identified with the highest risk of academic failure: those with poor cognitive capacity and those with bad learning skills.
1. Introduction
It is a fact that investing in higher education and training brings benefits for both students and society [1]. Improving the formation of a society’s human capital is key to enhancing its economic development and overcoming inequalities between social classes [1,2].
Dropout in higher education not only has a considerable impact on a student’s self-esteem, well-being and employability, but also implies a high cost for institutions [3]. In fact, the dropout rate is an indicator of quality for university educational programs and may have an impact on their reputation, profit and funding [4]. In European countries, nearly 20% of students leave their studies before graduating [5,6].
Broadly speaking, university dropout can be due to involuntary reasons, such as failure to meet the academic standards and demands, or due to personal decisions, such as enrolment in a different university or educational program. The most critical time for dropout is the first four semesters of the degree [7]. Hicks and Heastie (2008) [8] highlighted that the first year of college is the most difficult period of adjustment students may face. Social challenges together with academic pressures are stressors for new students [9]. Higher education requires flexibility and the ability to adjust to a new learning environment that demands a more independent and autonomous approach to learning [10].
Literature about the causes and persistence of higher education dropout suggests individual, institutional and socioeconomical factors.
The most cited models by researchers in the field of education, to explain school dropout are based on Tinto’s Theory of Dropout [11,12]. The author, establishes the importance of the role played by the institutions in relation to the student’s decision to abandon his studies and considers that the risk of desertion of university students, can be explained with five factors (psychological, social, economic, economic, institutional and interactionist). He takes into account that the university student has personal attributes, family and social conditions, as well as previous experiences that are bidirectionally related to the commitments and initial goals that he establishes within the institution.
Students’ performance in secondary education has been reported as a predictor of university achievement [13,14,15,16,17]. Nevertheless, students with higher scores in secondary education are not always able to cope with academic demands and thus they do not always adjust to university so easily [18].
Currently, acceptance into university is determined by the qualifications obtained in both secondary education and entrance examinations, which reflect knowledge on different subjects. Although necessary, such selection criteria seem to be insufficient to ensure the completion of university. Academic achievement in secondary education is associated with students’ cognitive functions and personality traits that have not reached maturity yet [19,20]. Other factors that have effects on students’ performance are the knowledge and use of learning strategies [21]. Such strategies include “behavioural, cognitive, metacognitive, motivational, or affective processes or actions that facilitate understanding, learning, and meaningful encoding, as well as integration of new knowledge and skills into memory” [22]. High academic achieving university students show better use of learning strategies than students with lower academic performance [23,24,25]. In addition, complex interrelations between cognitive functions and some learning strategies have been suggested. In a similar sense, a positive association between the use of learning strategies and cognitive skills, such as scientific reasoning, has also been pointed out [26]. In addition, metacognitive competence was found to be positively correlated with exam anxiety [27]. Coping strategies are related to a more adaptive behavior and resilience [28]. In this same line of the importance of psychological factors, there are also the contribution of Roso-Bas, Pades and García-Buades (2016) [29] for whom students with high self-esteem is more resilient and, therefore, it is more likely to continue with their studies.
Given their effects on academic performance, it seems logical to think that low cognitive functions and poor use of metacognitive strategies might contribute to students’ failure and dropout. Therefore, the identification of student profiles according to cognitive variables and learning strategies would allow us to identify individuals at risk of academic failure, and thus develop more efficient preventive strategies. In this way, we might generate learning conditions that consider the specific needs of students with difficulties and ease their adaptation to university life.
The objectives of this work are: (a) to determine the existence of profiles of first-year university students based on their cognitive functions and learning strategies, and (b) to evaluate the relationship of such profiles with academic performance and risk of failure.
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
This study was carried out with first-year university students of degrees related to Health Sciences at the Catholic University of Murcia (UCAM). Convenience sampling was employed. Students with previous university studies or belonging to exchange programs were excluded. Participation in the research was absolutely voluntary. In order to guarantee freedom all potential participants were informed in detail of the project: of their goals, the information required, the expected results and the dissemination of the results. All participants were guaranteed anonymity. Under no circumstances would the identity of the participating subjects be known. The participants were assured the reception of the reports from the study. The Bioethics Committee of the Catholic University of Murcia approved of this study.
2.2. Instruments
2.2.1. D2 Test (Nicolás Seisdedos Cubero, Técnico del Departamento de I+D+i de TEA Ediciones, S.A.U.)
The D2 test is a cancellation test that measures facets of attention such as visual scanning speed, sustained attention and selective attention [30]. It consists of 14 rows, each one with 47 characters. Subjects have to identify and cross the characters consisting of “d” with two apostrophes a total of 299 elements ignoring the rest (359 irrelevant stimuli). The time limit is 20 s per row. The resulting scores are: TR (total number of answers attempted), TA (total number of correct answers), O (omissions or number of relevant elements tried but not crossed), C (commissions or number of irrelevant elements crossed), TOT (total effectiveness in the test: TR − (O + C), CON (concentration index or TA-C), TR + (line with the highest number of items attempted), TR − (line with the least number of items attempted) and VAR, variation index or difference between TR+ and TR−). For analyses TOT score was used.
2.2.2. Raven Progressive Matrices (Raven Matrices Progresivas. Copyright Edición Española © 1995, 1996 by TEA Ediciones, S.A. Madrid (España)I.S.B.N.: 84-7174-403-1Depósito Legal: M-535-1996)
It is a widely used instrument for measuring abstract reasoning. Its score is regarded as a non-verbal estimate of fluid intelligence. The general scale consisted of five sets (A to E) of 12 items each, becoming increasingly complex. The total score is the sum of the elements solved correctly (range: 0–60). In the present study, this test was collectively administered.
2.2.3. Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test (Rey A.Test de Copia de una Figura Compleja. Manuel. Adaptación española. Madrid: TEA Ediciones, 1997)
It is a well-known test for assessing visuospatial constructional ability and visual memory [31]. Commonly, the test is administered in three trials: copy, immediate memory and delayed memory (20–30 min after being shown). Two scores can be obtained in each trial: reproduction performance and organizational strategies [32]. The test was administered following the suggested procedure [33]. In the present study, reproduction performance in the delayed trial (30 min after copying the figure) was used as a predictor of academic performance.
2.2.4. Questionnaire to Assess the Learning Strategies of University Students (CEVEAPEU)
It is an instrument of 88 items related to the learning strategies followed by the students [34]. Each item is answered on a scale of 1–5 according to the degree of agreement with the statement it collects. The questionnaire is organized into two scales that include six subscales: motivational strategies (MOT), affective components (AFE), metacognitive strategies (MTC), strategies of context control, social interaction and resources management (ECC), strategies of searching and Information selection (EBI) and strategies of processing and information (EPI). The score of each subscale is the average of its item scores (it ranges from 1 to 5). The reliability and internal structure of the questionnaire has been proved [35].
2.2.5. Academic Performance
The percentage of credits earned and the weighted grade point average (GPA) were used as measures of academic performance. In addition, two groups of students were established according their percentage of earned credits. Students at risk of dropping out were those who earned less than 30% of credits.
2.2.6. Statistical Analysis
The selection of variables for cluster analysis was conducted based on their association with academic performance variables (Pearson’s correlations and χ2-square test). We did not include highly correlated variables into the analysis to prevent multicollinearity. Before undertaking the cluster analysis, the selected variables were standardized to control for unequal scaling of the data. Following the suggested by Hair et al. [36], the sample was split into two groups (n = 142). In the first group, a hierarchical cluster analysis following the Ward’s method was performed to find the appropriate number of clusters. The results of this analysis were confirmed in the second group using the k-mean methods. Finally, a k-means cluster analysis was carried out in the whole sample to determine the assignment of the individual cases into the clusters. Once group membership was determined, a discriminant function analysis was undertaken to confirm predicted membership. The generalizability of the clusters was assessed by comparing groups on demographics (sex and age) and type of career using ANOVA test and χ2-square statistic test. The analysis was conducted on the association between clusters and the variables related to academic performance and belonging to a risk group by using ANOVA test and χ2-scuare statistic.
3. Results
3.1. Classification Analyses
The sample consisted of 284 students, whose sociodemographic characteristics, scores in cognitive tests and in learning strategies instruments are shown in Table 1. The variables significantly correlated to academic performance measures were in TA, CON, RVN, MOT, AFE, MTC and ECC (Table 1). All but CON (also highly correlated with TA) were included in the cluster analysis. The first cluster analysis indicated the three clusters of students (highest average silhouette width). This result was confirmed with the k-means method. Figure 1 shows the standardized scores of the variables in each cluster. Three profiles of students are represented: those with high scores for care, intelligence, learning and metacognition strategies (Cluster 2), those who have high score in cognitive variables but low in learning and metacognition strategies (Cluster 1) and those characterized by low cognition and moderate puncture in learning and metacognition strategies.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics of cognitive and learning strategies variables and their correlations with academic outcome measures.
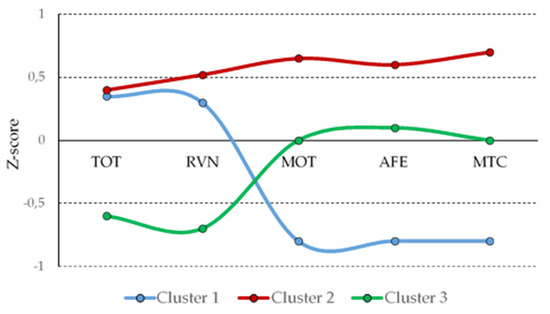
Figure 1.
Standardized scores of the variables in each cluster.
The results of discriminant analysis confirmed the relevance of all the variables in determining cluster membership. Two discriminant functions were obtained with eigenvalues of 1.93 and 0.86. The relative contribution of each variable to the discrimination between groups is displayed in Table 2. Accordingly, matrix structure coefficients indicated that MTC, MOT and AFE correlated with function 1 (0.65, 0.57 and 0.52, respectively) while TOT and RVN correlated with function 2 (r = 0.75 and 0.55, respectively). Figure 2 shows that function 1 discriminates mostly between clusters 2 and 3, whereas function 2 discriminates between clusters 1 and 2 and cluster 3.

Table 2.
Standardized coefficients for the variables for the discriminant functions.
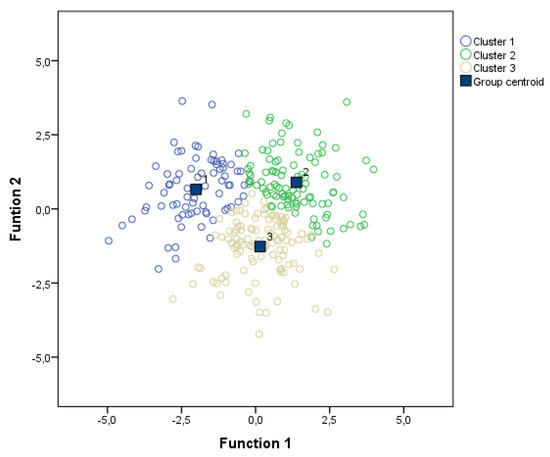
Figure 2.
Discriminant functions.
3.2. Interpretation of Clusters
Comparative analysis among clusters showed that RVN and learning strategies mean scores were higher in cluster 2 than in clusters 1 and 3 (Table 3). In addition, mean scores of both FCR-M and attentional measures were significantly higher in cluster 2 than in cluster 3. Finally, mean scores of cognitive measures were significantly higher in cluster 1 than in cluster 3 while learning strategies mean scores were significantly higher in cluster 3 than in cluster 1.

Table 3.
Differences in mean among clusters.
However, no significant differences were found among clusters in mean age (F (2, 281) =2.60, p = 0.08), by sex (χ2(2) = 3.47, p = 0.177) and type of career (χ2(8) = 15.57, p = 0.05).
Cluster 1 (n = 76) consisted of students with moderate to high attention and fluid intelligence scores but low scores in learning strategies. After the conversion of standard scores to percentile ranks, it was observed that 89.5% of these students’ MOT scores were below 50th centile. In 90.8% AFE scores were below 50th centile, and in 76.2% below 30th centile. In 94.7% MTC scores were below 50th centile and in 76.2% below 30th centile.
Cluster 2 (n = 99) consisted of students with moderate to high scores in attention, fluid intelligence and learning strategies. Actually, 52.1% of the students showed TOT scores above 70th centile. Concerning fluid intelligence, 58.8% of the students showed RVN scores higher 75th centile.
Cluster 3 (n = 109) included students with low scores in cognitive measures and moderate scores in learning strategies. More than a third of these students scored in TA and RVN more than 1 SD below the mean. Both TOT and CON scores were in 81.7 percent of the cases below 50th centile and in almost 51.7 percent of the cases were below 30th centile. Regarding fluid intelligence (RVN), 86.2 percent of these students were below the 50th centile.
3.3. Relation between Cluster and Academic Performance Measures
Planned comparisons among clusters showed that the percent of earned credits by cluster 2 (67.10 (SD = 25.22)) was significantly higher than those earned by cluster 1 (52.80 (SD = 27.32), and by cluster 3 (57.60 (SD = 27.70) with p < 0.05 for both contrasts. Additionally, the weighted grade point average was higher in cluster 2 (5.4 (SD = 1.30) than in cluster 1 (3.28 (SD = 1.68) and cluster 3 (3.79 (SD = 2.07) with p lower than 0.05 in both cases. The percentage of students who did not earn 30% of ECTS was higher in cluster 1 (25%) and in cluster 3 (23.8%) than in cluster 2 (9%), with p < 0.05 in both contrasts. Furthermore, 83.3% of students who did not earn one third of ECTS belonged to cluster 1 or 3. There was not a significant difference between cluster 1 and cluster 3 in the percent of earned ECTS (t(163) = −1.58, p = 0.115), the weighted GPA (t(183) = −1.15, p = 0.250) and the percentage of students who earned 30% of ECTS (χ2(1) = 0.24, p = 0.626).
4. Discussion and Conclusions
This study identified three distinct cognitive and learning profiles in first year university students.
The clusters were relatively balanced in size and stable across age, sex and type of career. One cluster (cluster 1; n = 76) was characterized by poor motivational, metacognitive and affective learning strategies but medium-high scores in attention and intelligence; another cluster (cluster 2; n = 79) was characterized by medium-high scores in both cognitive and learning strategies measures; the final cluster (cluster 3; n = 109) showed reduced performance in attention and intelligence but preservation of learning strategies.
Our findings indicate that in university students, differences in intelligence and attention may have an influence on academic performance. Students with lower intelligence and attention (cluster 3) earned early 50% of ECTS on average and have a low weighted grade point average. A quarter of these students were at risk of dropout (earned less than 30% of ECTS). These results agree with previous findings that deficits in sustaining attention in class were more common in students with poor self-regulation and learning difficulties [37]. Nevertheless, the low academic performance of students from cluster 3 might also be due to their lower intelligence as suggested in previous studies [38]. Intelligence is related to potential to learn and prior academic performance [39,40], which is a reward for engagement in learning processes [41]. Although intelligence is highly heritable, it has been shown to be malleable, especially in the youth [42]. In this sense, working memory training relates to a higher performance of top-down cognitive control mechanisms, such as selective attention and cognitive control, which positively correlated with fluid intelligence [43]. This type of training together is likely to improve the academic performance and retention of students with this profile.
On the other hand, our results confirm the importance of motivational, affective and metacognitive strategies on academic achievement suggested in the literature [23,24]. In fact, students from cluster 1, who have low scores in motivation, metacognitive and affective strategies, obtained a low weighted grade point average and just earned 50% of ECTS on average. In this regard, students with poor learning strategies are more likely to adopt a surface learning approach [44], which is related to worse academic achievement [45]. In our data, motivation, metacognition and emotional components are the learning strategies which best differentiate students on the basis of their academic performance. Actually, motivation, the force that encourages students to learn and face all challenges, is the main determinant of the learning approach [46]. Metacognitive strategies of learning included activities and processes which allowed students to be aware of their own thoughts and to monitor their learning progress [47]. Hence, the relevance of metacognitive strategies on learning processes seems to be greater than other learning strategies [48]. In spite of that, the implementation of learning strategies courses to improve metacognition in university students is still scarce [49]. Finally, affective strategies enabling emotional stability, and anxiety regulation may have large effects on academic performance and retention of students. Students with lower emotional intelligence are bound to show higher stress levels in the transition to university and might be more prone to dropout [26]. In addition, students who suffer higher anxiety before tests show a worse performance [50]. Thus, interventions to reduce anxiety before exams result in better academic performance in higher education students [51].
There is agreement, almost unanimous, that the problem of school desertion is multifactorial: psychological characteristics of students, family and social, organizational and institutional conditions. This research has focused on the analysis of individual, cognitive and metacognitive psychological characteristics. In each university center and in accordance with the identified profiles, programs should be developed to strengthen the skills and training resources of students.
Some of such strategies that could be implanted are the premature identification of student cognitive profile, the implementation of actions addressed to the development of cognitive skills (work memory training and cognitive control and courses of learning strategies to improve the metacognition of students. It would also be recommended monitoring with affective coping techniques that allow emotional stability and the regulation of anxiety.
The approach of this study is novel but there are some limitations. First, despite clusters being stable across age, sex and type of career, the non-random sampling used in this study may limit generalizability of their findings. Secondly, although the main predictors of academic performance have been considered, inter-cluster differences might be associated with other factors, such personality traits or socioeconomic status. Notwithstanding these limitations, this study suggests that distinct cognitive and learning strategies profiling has the potential to predict academic failure, and, therefore, individually tailored intervention strategies should be designed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.G.G. and J.C.G.G.; Methodology, M.G.G. and J.C.G.G. and A.P.P.d.l.C.; Software: M.G.G. and J.C.G.G.; Formal analysis, M.G.G. and J.C.G.G.; Investigation, M.G.G. and J.C.G.G.; Resources, M.G.G. and J.C.G.G. and Alfonso Palazón Perez de los Cobos; Data curation, M.G.G. and J.C.G.G.; Writing—original draft preparation: M.G.G. and J.C.G.G.; Writing—review and editing: M.G.G. and J.C.G.G.; Visualization: M.G.G. and J.C.G.G.; Supervision, M.G.G. and J.C.G.G.; Project administration, M.G.G. and J.C.G.G.; Funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Catholic University of Murcia (UCAM). Date of approval: 16 of November of 2019.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not Applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bowen, H.R. Investment in Learning. The Individual and Social Value of American Higher Education, 2nd ed.; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen, M.B. Recent research on the economics of attending college: Returns on investment and responsiveness in price. Res. High. Educ. 1998, 39, 471–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, L.A. Economic effects of student dropouts: A comparative study. J. Glob. Econ. 2015, 3, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce, M.; Crespo, B.; Míguez-Álvarez, C. Higher Education Drop-Out in Spain: Particular Case of Universities in Galicia. Int. Educ. Stud. 2015, 8, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, A.F.; Deil-Amen, R.; Prabju, R.; Lee, C.; Franklin, R.E. Feature articles: Theory, research, policy and practice: Increasing the College Preparedness of At-Risk Students. J. Lat. Educ. 2006, 5, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comisión Europea/EACEA/Eurydice, 2013. Cifras Clave del Profesorado y la Dirección de Centros Educativos en Europa; Edición 2013; Oficina de Publicaciones de la Unión Europea: Luxemburgo, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Castaño, E.; Gallón, S.; Gómez, K.; Vásquez, J. Deserción estudiantil universitaria: Una aplicación de modelos de duración. Lect. Econ. 2004, 60, 39–65. [Google Scholar]
- Hicks, T.; Heastie, S. High School to College Transition: A Profile of the Stressors, Physical and Psychological Health Issues That Affect the First-Year On-Campus College Student. J. Cult. Divers 2008, 15, 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, G.; Midford, R. Investigating first-year education students’ stress level. Aust. J. Teach. Educ. 2015, 40, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Frame, P.; Harwood, T.; Hoult, L.; Jenkins, M.; Lynch, K.; Volpe, G. Transitions into higher education: Processes, outcomes and collaborations. In Proceedings of the Association of Tertiary Learning Advisors Aotearoa, Supporting Learning in the 21st Century, Platform & workflow by OJS/PKP. Dunedin, New Zealand, 15–17 November; 2006; pp. 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Tinto, V. Dropout from higher education: A theoretical synthesis of recent research. Rev. Educ. Res. 1975, 45, 89–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinto, V. Leaving College: Rethinking the Causes and Cures of Student Attrition; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Bowles, A.; Fisher, R.; McPhail, R.; Rosenstreich, D.; Dobson, A. Staying the distance: Students’ perceptions of enablers of transitionto higher education. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2014, 33, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, K.; Schweitzer, R. Who Succeeds at University? Factors predicting academic performance in first year Australian university students. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2001, 20, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, M.; Bond, R.; Abraham, C. Psychological correlates of university students’ academic performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Bull. 2012, 138, 353–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, S.B.; Lauver, K.; Le, H.; David, D.; Langley, R. Do psychosocial and study skill factors predict college outcomes? A meta-analysis. Psychol. Bull. 2004, 130, 261–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shure, C.; Jansen, E.; Harskamp, E. Impact of degree program satisfaction on the persistence of college students. High. Educ. 2007, 54, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rooij, E.; Jansen, E.; Van de Grift, W. Correction to: First-year university students´s academic success: The importance of academic adjustment. Eur. J. Psychol. Educ. 2018, 33, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Vives, F.; Camps, E.; Dueñas, J.M. Predicting academic achievement in adolescents: The role of maturity, intelligence and personality. Psicothema 2020, 32, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigueros, R.; Aguilar-Parra, J.M.; Lopez-Liria, R.; Cangas, A.J.; González, J.J.; Álvarez, J.F. The role of perception of support in the classroom on the students’ motivation and emotions: The impact on metacognition strategies and academic performance in math and english classes. Front. Psychol. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, C.E.; Jung, J.; Acee, T.W. Learning strategies. In International Encyclopedia of Education; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, P.; Bernaras, E.; Elizalde, L.M.; Arrieta, M. Learning strategies and motivational patterns of students at the Campus of Gipuzkoa. J. Study Educ. Dev. 2009, 32, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargallo, B.; Almerich, G.; Garfella, P.; Fernández, A. Strategic learning in excellent and average university students. Bordon-Rev. Pedagog. 2011, 63, 43–64. Bordon-Rev. Pedagog. 2011, 63, 43–64. [Google Scholar]
- Yip, M.C.W. Differences between high and low academic achieving university students in learning and study strategies: A further investigation. Educ. Res. Eval. 2009, 15, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, M.C.W. Learning strategies and self-efficacy as predictors of academic performance: A preliminary study. Qual. High. Educ. 2012, 18, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizpurua, A.; Lizaso, I.; Iturbe, I. Learning strategies and reasoning skills of university students. Rev. Psicodidáctica 2018, 23, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İşgör, İ.Y. Metacognitive skills, academic success and exam anxiety as the predictors of psychological well-being. J. Educ. Train. Stud. 2016, 4, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Torres, M.C.; Artuch, R. Profiles of resilience and coping strategies at university: Contextual and demographic variables. Electron. J. Res. Educ. Psychol. 2014, 12, 621–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roso-Bas, F.; Pades, A.; García Buades, E. Emotional variables, dropout and academic perfomance in Spanish nursing students. Nurse Educ. Today 2016, 37, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brickenkamp, R. Test de atención d2. Ediciontes tea. Adaptación española: Nicolás Seisdedos Cubero. 4ª edición revisada. 2012. Available online: http://www.web.teaediciones.com/ejemplos/d2-extracto.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2021).
- Corwin, J.; Bylsma, F.W. Psychological examination of traumatic encephalopathy. Clin. Neuropsychol. 1993, 7, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, J. The Meyers Scoring System for the Rey Complex Figure and the Recognition Trial: Professional Manual; Psychological Assessment Resources: Odessa, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, M.-S.; Park, S.-Y.; Park, S.-R.; Seol, S.-H.; Kwon, J.S. Clinical and empirical applications of the Rey–Osterrieth complex figure test. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargallo, B.; Almerich, G.; Suárez-Rodríguez, J.M.; García-Félix, E. Estrategias de aprendizaje en estudiantes universitarios excelentes y medios. Suevolución a lo largo del primer año de carrera. Rev. Electron. Investig. Eval. Educ. 2012, 18, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargallo, B.; Suárez-Rodríguez, J.M.; Pérez-Pérez, C. El cuestionario CEVEAPEU. un instrumento para la evaluación de las estrategias de aprendizaje de los estudiantes universitarios. Rev. Electron. Investig. Eval. Educ. 2009, 15, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, F.; Hair, J.; Black, W.; Babin, B.; Anderson, R. Multivariate Data Analysis: A Global Perspective, 7th ed.; Pearson, Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F.-Y.F.; Wang, Y.K.; Klausner, M. Rethinking college students’ self-regulation and sustained attention: Does text messaging during class influence cognitive learning? Commun. Educ. 2012, 61, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miñano, P.; Gilar, R.; Castejón, J.L. A structural model of cognitive-motivational variables as explanatory factors of academic achievement in Spanish Language and Mathematics. Analesan Psicol. 2012, 28, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kuncel, N.R.; Kochevar, R.J.; Ones, D.S. A meta-analysis of letters of recommendation in college and graduate admissions: Reasons for hope. Int. J. Sel. Assess. 2004, 22, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, F.; Juntune, J.; Stough, L. Intelligence and Its relationship to achievement. İlköğretim Online 2015, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, H.W.; Martin, A.J. Academic self-concept and academic achievement: Relations and causal ordering. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 2011, 81, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plomin, R.; von Stumm, S. The new genetics of intelligence. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, A.R.A.; Getz, S.J.J. Cognitive Ability: Does Working Memory Training Enhance Intelligence? Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 362–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, F.; Berbén, A.B.G. University students’ achievement goals and approaches to learning in mathematics. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 2009, 79, 131–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosário, P.; Núñez, J.C.; Ferrando, P.J.; Paiva, M.O.; Lourenço, A.; Cerezo, R.; Valle, A. The relationship between approaches to teaching and approaches to studying: A two-level structural equation model for biology achievement in high school. Metacogn. Learn. 2013, 8, 47–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereles, A.; Núñez, J.C.; Rodríguez, C.; Fernández, E.; Rosário, P. Personal and instructional variables related to the learning process in postgraduate courses. Psicothema 2020, 32, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Malley, J.M.; Chamot, A.U.; Küpper, L. Listening comprehension strategies in second language acquisition. Appl. Linguist. 1989, 10, 418–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosnin, A.M. Self-regulated learning and academic achievement in Malaysian undergraduates. Int. Educ. J. 2007, 8, 221–228. [Google Scholar]
- Montero, C.R.; Sierra, B. Eficacia de un programa demejora de las estrategias de aprendizaje en la enseñanza superior. Psicothema 2017, 29, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanbeigi, A.; Askari, J.; Nakhjavani, M.; Shirkhoda, S.; Barzegar, K.; Mozayyan, M.R.; Fallahzadeh, H. The relationship between study skills and academic performance of university students. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2011, 30, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Gómez, J.I.; Balanza, S.; Leal-Llopis, J.; García-Méndez, J.A.; Oliva-Pérez, J.; Doménech-Tortosa, J.; Gómez-Gallego, M.; Simonelli-Muñoz, A.J.; Rivera-Caravaca, J.M. Effectiveness of music therapy and progressive muscle relaxation in reducing stress before exams and improving academic performance in Nursing students: A randomized trial. Nurse Educ. Today 2020, 84, 104217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).