Abstract
Ongoing technology progress sustains innovative teaching approaches. Mobile devices, augmented reality (AR), and games are a few of the new resources that teachers have at their disposal to promote student learning. However, their effective integration into practices requires training, so there is a need to analyze the impact of training initiatives on teacher professional development. A case study is being conducted on the development process of mobile AR games for Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) learning by 14 Portuguese in-service teachers in a 50 h workshop. This contribution refers to the analysis of this training’s impact on teacher professional development through a questionnaire filled in at the beginning and end of the workshop. This study registered a higher impact on teachers’ understanding of AR educative use, the less-known approach, compared to mobile and game-based learning. Moreover, teachers became more experienced with these approaches as learners, and reported having explored them with their students during the workshop period. Teacher ability to identify benefits and barriers in these approaches increased with the workshop, particularly the learning that could be promoted with mobile AR games. The presented set of barriers to implementation is relevant to future teacher professional-development initiatives.
1. Introduction
Mobile technologies’ versatility and relatively low cost may be two factors concurring to their pervasiveness in modern industrialized societies. Hence, the availability of a resource that allows performing a variety of tasks, namely some related to information seeking and treatment, makes their integration in teaching and learning practices a logical step to take, having given rise to the term “mobile learning”.
Mobile learning can be defined in different ways. Perspectives may fall into one of the following categories: (1) technocentric, referring to learning processes that occur through the use of handheld technologies, such as mobile phones; (2) mobility of the technology, highlighting the portability allowed by the small size of the supporting technologies; (3) relationship to e-learning, with mobile learning being considered an extension of e-learning; (4) augmenting formal education, as a way of extending face-to-face education; (5) learner-centered, referring to learning when the learner is not at a fixed location, thus focusing on the learner’s mobility [1,2,3]. Despite the perspective adopted, the use of mobile devices for educational purposes has been a growing field of research with a history of positive empirical results [4], and their use in game-based learning approaches has also been documented as effective [5].
Game-based learning usually refers to the use of gameplay with the purpose of promoting determined learning objectives [6]. With the motivation factor being one of the most cited arguments in the literature [7,8,9,10], other positive results include student satisfaction with the learning experience [11], increased student achievement across all schooling levels [12]; and facilitation of students’ 21st-century skill development [13]. To achieve these positive results, some caution is required, namely incorporating learning theories into the game design [13], taking into account learners’ personal factors, such as learning achievement or learning styles [14], and challenging players in a way that matches students’ abilities [15]. Additionally, the competition created by games may increase students’ engagement in challenging learning situations and improve their overall sense of enjoyment. When game-winning conditions require working with other players, collaborative dynamics can also be promoted [16].
Despite being considered effective learning tools [8], in real formal education scenarios, accepting digital games in the classroom is one of the initial barriers to overcome, which may be related to factors such as the availability (and reliability) of the supporting technology, prerequisite knowledge required of the teacher, and even financial and licensing issues [17]. For example, a study conducted by Russo, Bragg, and Russo [18] highlighted that although Australian mathematic primary teachers mentioned frequently using games in their practices, digital games were virtually not among their favorite types of games, which may be interpreted as a reluctancy to incorporate digital technologies to support game-based learning.
Future developments in mobile and game-based learning involve evaluating and analyzing game usage data, providing powerful tools on how to create better learning experiences, and developing game-based learning, supported by significant data about users’ perception and their performance while playing [19].
These educational approaches, when combined with emerging augmented reality (AR) technologies, can enhance learning experiences, as they can enrich and contextualize learning information offered to learners [20]. AR supported by mobile games can move learning to outdoor settings, fostering authentic learning, and also personal and collaborative learning with a lifelong learning perspective [21]. Other authors [7,22] stress the unique affordances of AR, as an “immersive” interface that enables participants to interact with digital information embedded within the physical environment, supporting situated learning. Outdoor collaborative learning activities using AR become an approach scarcely found in the educational context, although with high potential in education [7,22]. Moreover, the incorporation of AR into educational practices for effective learning, instead of for merely beautiful scenography, requires teacher training in teaching methodologies with AR technologies [23], as teachers are often reluctant to use or integrate them into their science curriculum [24,25].
There is a scarcity of educational resources, such as educational mobile games, that integrate curriculum contents. Considering this scarcity, the EduPARK project: http://edupark.web.ua.pt/?lang=en (accessed on 3 August 2021) developed and evaluated an app [26] that can be used autonomously, and at any time, using the ”game” mode or the ”explore freely” mode. It promotes authentic learning so that visitors can enjoy a healthy walk while learning. The game includes several learning guides for different target groups: teachers and students from basic to higher education, and also for park visitors and the public, from a lifelong learning perspective. The tourist guide is also offered in English. The guides integrate multidisciplinary issues under the Portuguese National Education Curriculum and propose interdisciplinary questions articulated to educational challenges along the park using the logic of a treasure hunt. The game enables visitors to explore and access information about the plant species living in the city park, historical references, different multimedia contents, and a park map, allowing interaction. The goal is to accumulate points by answering the questions correctly, visualizing AR marker contents that help to answer questions, and finding virtual caches/treasures (3D images) [27].
The literature has noted that teachers’ adoption of mobile technologies may be influenced by factors such as their digital literacy, ICT anxiety, teaching self-efficacy, and perceived ease of use and usefulness [28]. Moreover, teachers need to develop the ability to implement technology in their practices [28]. Hence, the EduPARK project has organized several short-term workshops for teachers so they can feel confident in using them in their practices, widening the use of mobile and game-based learning. However, the need to involve teachers in the creation of games and of educational resources to integrate into games encouraged the authors of this paper to propose, as trainers, a long-term accredited course with impact on teachers’ career progression. The course was directed at Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) teachers, and allowed them time to explore and experiment with tools for game-based learning, prompting teachers to develop learning content, as advised by De Freitas [29]. Hence, teachers were not only users, but also creators of educational games integrating AR contents.
The scarcity of teacher training on mobile game-based learning with AR makes it relevant to analyze their potential for teachers’ practice changes, starting with the perceptions of the involved stakeholders [30]. In this paper, the authors take one step forward by analyzing not just teachers’ perceptions, but also the impact of this workshop on the teacher trainees’ professional development with respect to the main concepts/teaching approaches it addresses: mobile learning, AR use in education, and game-based-learning. This research comprises training opportunities that revolve around mobile game-based learning with AR, which are innovative, and therefore it is important to analyze their potential in teachers’ practice changes.
The next sections briefly present and discuss the adopted materials and methods, and the results concerning the impact of this workshop on the teacher trainees’ professional development around the three main concepts of this study: (i) mobile learning, (ii) AR use in education, and (iii) game-based-learning. Finally, the Conclusions section summarizes the main findings, some limitations, and lines of future work.
2. Materials and Methods
This research was conducted under a case study [31]. Case studies are acknowledged in the literature as effective methodologies to investigate and understand complex issues in real-world settings that do not aim to extrapolate probabilities through statistical generalization [31,32]. This research approach is adequate when researchers’ want to understand a real-world case and assume that such an understanding is likely to involve important contextual conditions’ [31].
The case in this study was the development process of educational resources by 14 in-service teachers during a 50 h workshop (25 h face-to-face and 25 h autonomous work) developed in the Center Region of Portugal between October 2020 and January 2021. The workshop aimed to promote the collaborative development of open digital educational resources that foster STEM learning based on a game approach and supported by mobile devices.
The research question that guided the work reported in this contribution was: What is the impact of this workshop on the teacher trainees’ professional development with respect to: (i) mobile learning, (ii) AR use in education, and (iii) game-based-learning, in what concerns: (a) basic knowledge, (b) teacher experience as a learner, (c) reported use in teaching practice, and (d) opinions about benefits and barriers?
To answer the research question, an adaptative online questionnaire was applied at the beginning of the workshop and right after its end, so the results could be compared to analyze the workshop’s impact on the teacher trainees’ professional development.
The initial questionnaire comprised a sum of closed- and open-ended questions and was organized into four sections:
- Motivations and expectations, with a multiple-choice question on motivations to attend the workshop and an open-ended question on expectations;
- Conditions for the use of digital technologies in the teachers’ educational context, with a few closed-ended questions on the types of digital technologies (e.g., desktop computers, smartphones, internet connection) available for their practice, for students’ learning and school policy on mobile devices use, and also an optional open-ended question for additional comments on this topic;
- Workshop teaching approaches: (i) mobile learning, (ii) AR use in education, and (iii) game-based-learning; all these topics included a mixture of open- and closed-ended questions for data collection on teacher-trainees’ basic knowledge, previous experience and frequency of use, perceptions about benefits and barriers, and additional comments on the topic;
- Demographic data, such as gender, academic qualifications, years of teaching experience, subjects, schoolyears that they were teaching, and average number of students in their classes;
The final questionnaire was quite similar to the initial one, but without the demographic data section, as the population was already characterized. Hence, it comprised three sections:
- Workshop assessment, with a set of multiple-choice questions on aspects such as the methodology, level of difficulty of the proposed activities, and reported readiness to explore the teaching approaches, as well as a few optional open-ended questions to deepen teachers’ perspectives;
- Differences in the conditions for the use of digital technologies in the teachers’ educational context, with a multiple-choice question, as well as an optional open-ended question for additional comments;
- Workshop teaching approaches, similar to the initial questionnaire.
For questionnaire content validity, both versions were analyzed by two educational researchers with different experiences. One was a teacher who was undertaking her doctoral studies. The other was an experienced researcher and methodology professor at a public university, with a Ph.D. and postdoctoral training. After introducing changes suggested by the educational researchers, they considered the questionnaire clear, understandable, and suitable for the target population.
In the present study, only data regarding the research question was analyzed (Appendix A presents Section 3 questions of the initial—Table A1—and final questionnaires—Table A2). The analysis included descriptive statistics for answers to closed-ended questions and content analysis for answers to open-ended questions. When relevant, initial and final responses were compared.
For the content analysis related to teachers’ basic knowledge on the considered topics, each answer was classified as correct, partially correct, or incorrect, in accordance with the researchers’ own perspectives on the topics. These were in line with the workshop activities, as the researchers were also the teacher trainers.
For the content analysis of the benefits and barriers associated with each teaching approach, the analysis categories developed in the previous study [30] were revised. For example, two categories (“It is easy or quick to find information” and “Supports higher interaction”) were included in a broader category (”Supports better learning”). Moreover, in each teacher answer, the number of different types of benefits or barriers was identified.
Study Participants
The study participants were characterized according to their: (i) Demographic data; (ii) Motivations and expectations concerning the workshop; and (iii) Conditions for technology use in schools. These data are available in the previous study of Marques and Pombo [30]. To comply with the General Data Protection Regulations, the questionnaire included a closed-ended question respecting for informed consent to participate in this study. Out of 16 teachers attending the workshop, 14 agreed and signed the informed consent, so the following data are related only to those 14 teachers.
Concerning demographic data, in terms of gender, 12 were females and 2 were males. Ten teachers had a high degree, mandatory by Portuguese law, one had a post-graduation course, and three had a master’s degree. All teachers were experienced: (i) two had 11 to 20 years of experience; (ii) eight had between 21 and 30 years, and (iii) four had more than 31 years of experience.
Three teachers lectured Mathematics in the 3rd cycle of basic education (CBE, corresponding to school years 7 to 9) or in secondary teaching (ST, years 10 to 12), six teachers lectured Physics and Chemistry in the 3rd CBE or SE, one teacher lectured Nature Sciences in the 3rd CBE, and six teachers lectured Mathematics or Nature Sciences in the 2nd CBE (years 5 and 6). Their classes varied from 16 to 20 students (4 teachers), 21 to 25 students (4), and 26 to 30 students (4).
With respect to motivations, in the closed-ended question regarding reasons for attending the workshop, the participant teachers selected: “Updating or acquiring knowledge” and ”Possibility to have access to new resources” with 12 mentions each; and “Combination of the workshop topics”, “Possibility of changing teaching practice” and “Professional valorization” with 10 mentions each. Concerning their expectations regarding the workshop, teachers mentioned they expected to learn more about the workshop approaches (9 mentions) to improve their teacher practice (7 mentions) and, consequently, to have an impact on students’ motivation to learn (6), achievement (3), and behavior (1). Three teachers also mentioned they were curious about the workshop topics.
Concerning conditions for technology use, results indicated that participating teachers and their students had conditions from the technological point of view, although students had lower access to technology than teachers. All teachers reported to have data shown in the classroom, and seven had an interactive board. Students’ access to these resources was lower—only two and five, respectively.
All teachers mentioned having computer access for their teaching practices, either desktop, portable, or tablet, and the same applied to the students of 12 of the 14 respondents. One teacher, who in a previous question reported tablet and laptop access only for teachers, highlighted in the open-ended question that it is unreliable technology: “The school has some laptops and some tablets, not always in the best conditions and some rooms have a desktop computer. All classrooms have a projector, but teachers need to use their own laptops.” (Q5).
Twelve teachers reported having either a feature phone (2) or a smartphone (10), and one stated having both. Schools provided students’ access to mobile phones in only five cases in this cohort. In addition, 12 teachers mentioned having an email account, whereas nine respondents revealed their students had access to email accounts.
Although the results revealed that teachers and students mostly had access to technology to use in the school, 11 classified the technology as reasonable, one as bad and another as good. It is worth noting that one teacher mentioned their school did not provide students access to any type of the considered technology, providing only internet access.
All respondents reported internet access for themselves and their students, although only classifying it as reasonable (13), and feeling some constraints in its use, such as slowness and insecurity, among others. Only one teacher classified their school internet connection as good.
As to the school policy on mobile devices use in classrooms, seven teachers mentioned it was allowed, five said it was forbidden, and two acknowledged not knowing. One step further, six respondents mentioned that the school provided guidance to students on the proper use of mobile devices, five reported this did not happen in their school, and three did not know.
No relevant technology-conditions changes were reported by the teachers at the end of the workshop.
3. Results and Discussion
This section presents and discusses the results obtained through the initial and final questionnaires, with the aim of analyzing the impact of the workshop on the teacher trainees’ professional development. Therefore, it is organized according to the dimensions of the research question—basic knowledge, teacher experience as a learner, reported use in teaching practice, and opinions about benefits and barriers—for all the training topics (mobile learning, AR use in education, and game-based learning).
3.1. Basic Knowledge
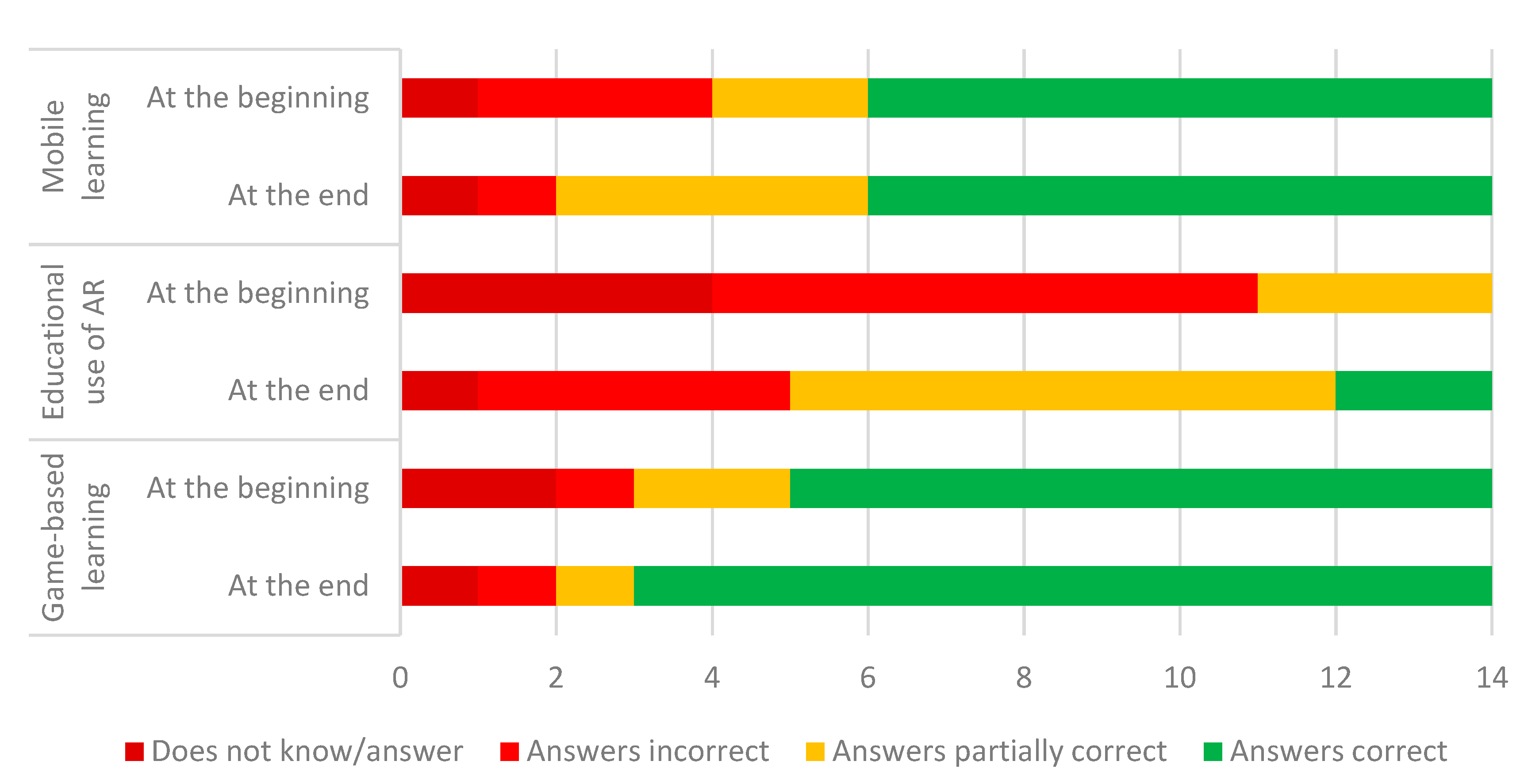
Figure 1 presents the overall results regarding teachers’ answers to the prompt to explain the concepts of mobile learning, educational use of AR, and game-based learning. Detailed analysis is presented, with the support of tables dedicated to each key concept.
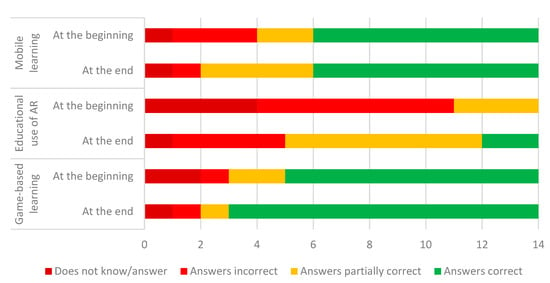
Figure 1.
Frequency of teachers’ types of answers to the questions on basic knowledge about mobile learning, educational use of AR, and game-based learning.
Table 1 presents the types of answers given by teachers, their frequency, and examples of citations that illustrate each type of answer given by teachers when asked about the meaning of mobile learning, at the beginning and end of the workshop. It reveals that the number of incorrect answers decreased (from 3 to 1), the number of partially correct answers increased (from 2 to 4), and the correct answers remained the same (8); hence, small positive differences between the initial and the final phases of the workshop were registered.

Table 1.
Comparison of teachers’ answers on their understanding of the mobile-learning concept, at the beginning and end of the workshop.
It is noteworthy to highlight that, even at the end of the workshop, all answers considered correct were simple and technocentric definitions of mobile learning, not considering, e.g., the mobility of learner [1,2,3], despite these issues being discussed in face-to-face sessions.
At the end of the workshop, when questioned about examples of mobile learning projects or initiatives, 10 teachers mentioned at least one educational mobile app example, which was an increase compared to the eight teachers in the first questionnaire [30]. Most teachers (8) mentioned the EduPARK app, which was used during the training. The Khan Academy was mentioned twice, the same as at the beginning of the workshop, although this platform is not necessarily used in mobile contexts.
The results presented above indicate a small impact of the workshop on teachers’ ability to explain the concept of mobile learning. The strategies explored in the workshop included discussion in face-to-face sessions, analyzing texts about mobile learning to produce a reflexive text, and using mobile devices to learn in a training context. However, their impact on teachers’ learning fell behind what was initially expected. Moreover, practical tasks, such as naming examples of mobile learning, seemed to be easier for teachers when compared to theoretical tasks, such as defining the concept. This was reinforced by a teacher’s answer to the questionnaire prompt “Indicate at least one [workshop] activity that was too difficult and explain why”: “The initial reflection was too theoretical. In my opinion, teachers mainly need to have a practical component in training. I think that searching a certain topic adds little to the improvement of teaching practice” (Q6). This teacher revealed that they did not value the literature search’s potential contribution to teaching practice.
Table 2 reveals the types of answers given by teachers when asked about the meaning of educative use of AR, at the beginning and end of the workshop. It is possible to identify a decrease in the number of teachers acknowledging not knowing or not answering, from 4 to 1, and of teachers answering incorrectly, from 7 to 4. The same table also shows an increase in the number of teachers answering partially correct (usually only defining AR, and not mentioning its potential for education), from 3 to 7, and in the correct answers, from 0 to 2. These results revealed the trainees’ difficulty in explaining the educative use of AR, although progress was made by teachers concerning this topic.

Table 2.
Comparison of teachers’ answers on their understanding of the use of AR for educational purposes, at the beginning and end of the workshop.
Again, at the end of the training, when questioned about examples of AR use in education, 9 teachers presented at least one educational AR example; all mentioned the one explored in the workshop. Compared with the results from the beginning of the workshop, only 2 teachers mentioned adequate examples, and 12 did not present any example at all [30]—there was an evident impact at this level. From these results, it is reasonable to claim that the workshop had an impact on teachers’ knowledge of educative use of AR, particularly in what concerns the ability to provide concrete examples.
Finally, Table 3 presents the types of answers given by teachers when asked about their understanding of game-based learning, at the beginning and end of the workshop. The table reveals small differences between the initial and the final phases of the workshop, regarding ”Did not know/answer”, from 2 to 1, and ”Answered correct, but in a simple way”, from 9 to 11.

Table 3.
Comparison of teachers’ answers on their understanding of game-based learning, at the beginning and end of the workshop.
At the end of the training, when questioned about examples of game-based learning, 12 teachers presented at least one illustrative example, and 7 mentioned the one explored in the workshop. At the beginning of the workshop, only 5 teachers were able to present valid examples of game-based learning [30], so the cohort of teachers revealed progress at this level.
In summary, the presented results indicated that the workshop had a higher impact on the topic about which teachers knew less: the educative use of augmented reality. A smaller impact was registered concerning mobile learning and game-based learning. The impact was more evident, in all topics, when teachers were asked to mention examples.
3.2. Teacher Experience as A Learner
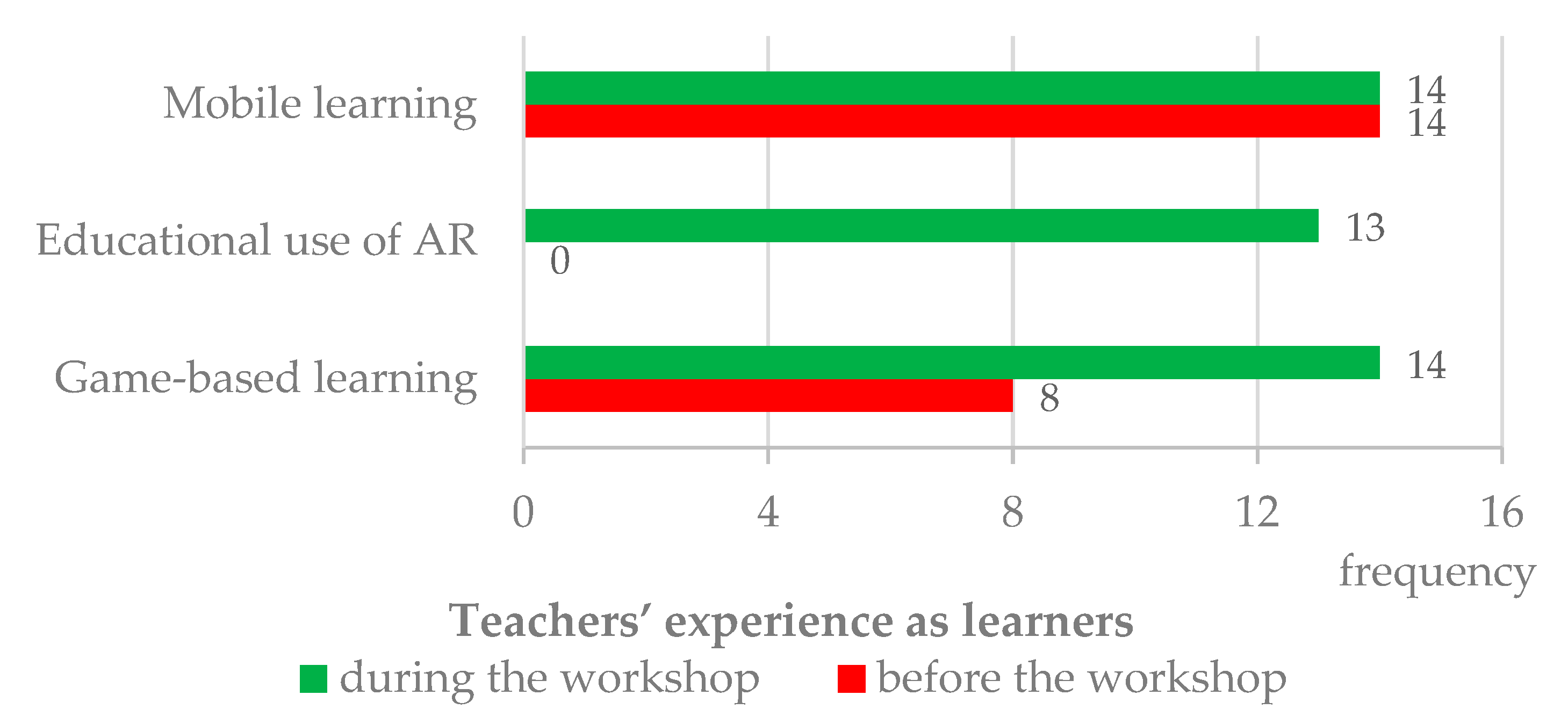
Figure 2 summarizes teachers’ experience, as learners, with mobile learning, AR educational use, and game-based learning. At the beginning of the workshop, teachers reported the following previous experience: (a) All (14) had experienced mobile learning, even though only 6 presented valid examples; (b) none had learned with AR; and (c) 8 had experienced game-based learning [30].
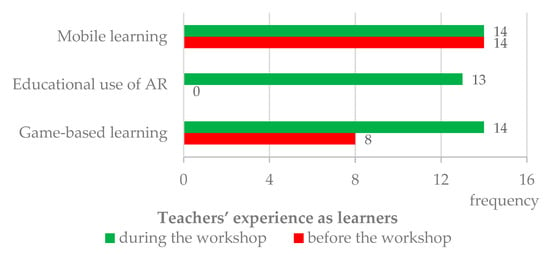
Figure 2.
Comparison of teachers’ experience as learners with mobile devices, AR, and game(s), before and during the workshop.
When asked if they had used mobile devices, AR, and/or games to learn during the workshop, 13 teachers mentioned they experienced the three approaches; 1 teacher reported having used only mobile devices and games to learn, but not AR. When comparing these results with teachers’ previous experience, it is possible to claim that all became more experienced with these approaches, particularly concerning AR. For 13 respondents, the workshop allowed them to experience this technology to learn for the first time. Only 1 teacher mentioned not using AR to learn during the workshop. This result may be interpreted in two different ways. Either this individual did not use AR technology, despite being given the opportunity to do so, or this teacher used it, but considered that this experience did not provide learning. As the questionnaires were anonymous, it was not possible to explore further this issue.
3.3. Reported Use in Teaching Practice
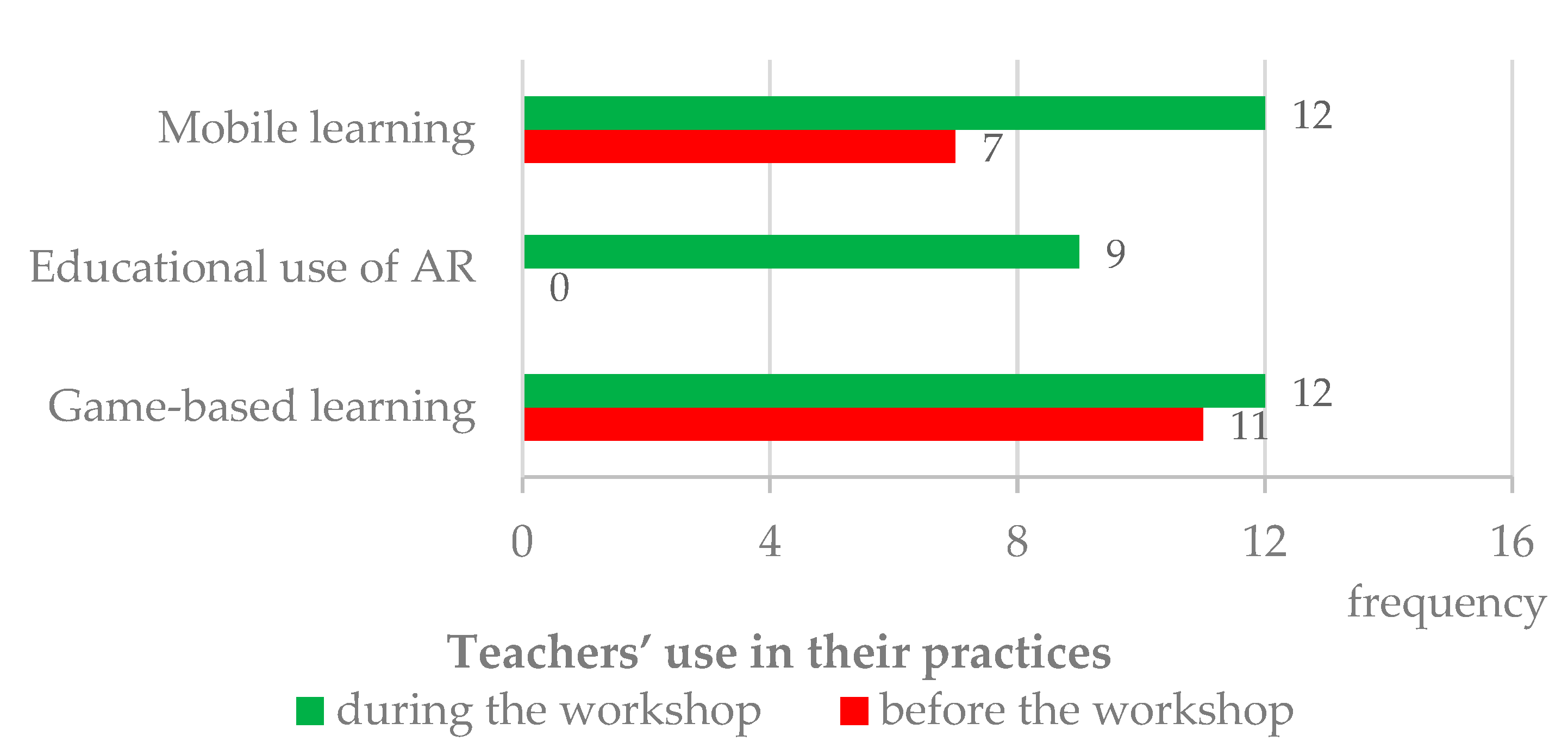
Figure 3 summarizes teachers’ exploration of the workshop approaches in their practices. At the beginning of the workshop, 11 teachers reported previous experience in exploring mobile devices with their students to promote learning, although only 6 presented valid examples in response to the following question. These results seem to indicate that teachers are beginning to integrate mobile learning in their practices [30], as advocated by several Horizon Reports [33,34,35]. The fact that teachers began to promote mobile learning was in line with a previous study [24] and with the Portuguese State of Education Report [36].

Figure 3.
Comparison of teachers’ use of mobile devices, AR, and game(s) in their practices, before and during the workshop.
Teachers who reported never having used mobile devices in their teaching practices before the workshop mentioned they could change that due to two main factors: (a) using mobile devices may increase students’ motivation to learn; and (b) mobile devices’ availability to most students [30].
No teacher had previous experience in using AR to promote their students’ learning [30]. The Horizon initiative [37] has placed AR technology in the time-to-adopt group for K-12 educational contexts, highlighting its potential to provide powerful, contextual, and in situ visual and interactive learning experiences. However, our empirical results indicated that about 8 years later, teachers are still not exploring this technology with high educational value. Factors that could change this situation, according to teachers, are: (a) teacher knowledge on how to use AR to promote learning, developed in professional development initiatives; (b) knowing that the use of AR technology may increase students’ motivation to learn; (c) AR may facilitate teaching and learning processes; and (d) teacher willingness to change practice [30].
Seven teachers reported previous experience in promoting game-based learning [30]. From these, 6 presented valid examples, usually mentioning a quiz format. The game approach is one with high expression in international reports. In the Horizon series, it is presented as an effective and versatile approach with gains in student engagement, creativity, and authentic learning [38,39]. However, this seems to still be an approach with limited expression in teacher practices. This result contrasts with Russo, Bragg, and Russo’s study [18], in which the majority of teachers mentioned using educational games at least once a week, revealing this approach can be popular among Australian practitioners.
According to this study’s teacher cohort, factors that could promote higher exploration of games in formal education are: (a) using games, which may increase students’ motivation to learn; (b) teacher knowledge of games that can be explored to promote learning; and (c) access to resources, either the games or their supporting technologies [30].
Regarding the use of mobile devices, AR, and games in teaching practices, during about three months, which corresponded to the workshop period, 12 teachers mentioned they promoted mobile and/or game-based learning, and 9 teachers mentioned using AR. As to the reasons for not exploring these approaches, teachers mentioned: (a) lack of opportunities or time (“It was not timely” (Q4)); (b) lack of resources (“Did not have conditions in the classroom” (Q16)); (c) lack of teacher readiness (“Because I still don’t feel comfortable using it” (Q9)); (d) lack of students’ skills (“Because students don’t know how to use it for this purpose” (Q16)); and (e) COVID-related barriers (“Considering the pandemic context that we live in” (Q15)).
Moreover, teachers had the opportunity to present additional (optional) comments on the workshop topics, and their answers revealed teachers generally sustained positive perceptions, as revealed by the following citations: ”It [mobile leaning] is an asset for the knowledge acquisition in a more fun and motivating way” (Q2); “AR is a tool that should be explored in lessons’ (Q5); and ‘It [the game] is an excellent tool for motivation” (Q1). On the other hand, some teachers seemed to envision difficulties: “I would like to be able to use them [mobile devices] in the classroom” (Q16); and “It [AR] is still not very disseminated in the teaching community” (Q14).
Facing these results, it is reasonable to consider that the workshop had an impact on teachers’ practices, according to their self-reports. However, it is worthwhile to note that even after long-term training, a small group of teachers (2 to 5, varying with the considered approach) remained reluctant to try out the approaches for which they were training. These reluctancy and lack of readiness to explore mobile, AR, and game-based learning were not evident during the face-to-face training sessions, so it seems reasonable to assume that teachers tended to contribute less to the large-group discussion when they did not agree or did not feel comfortable with the approaches under analysis. In the future, teacher trainers must take this result into account in order to have a deeper impact on the practices of teachers who are reluctant regarding the exploration of mobile learning, AR, and game-based learning.
3.4. Opinions about Benefits and Barriers
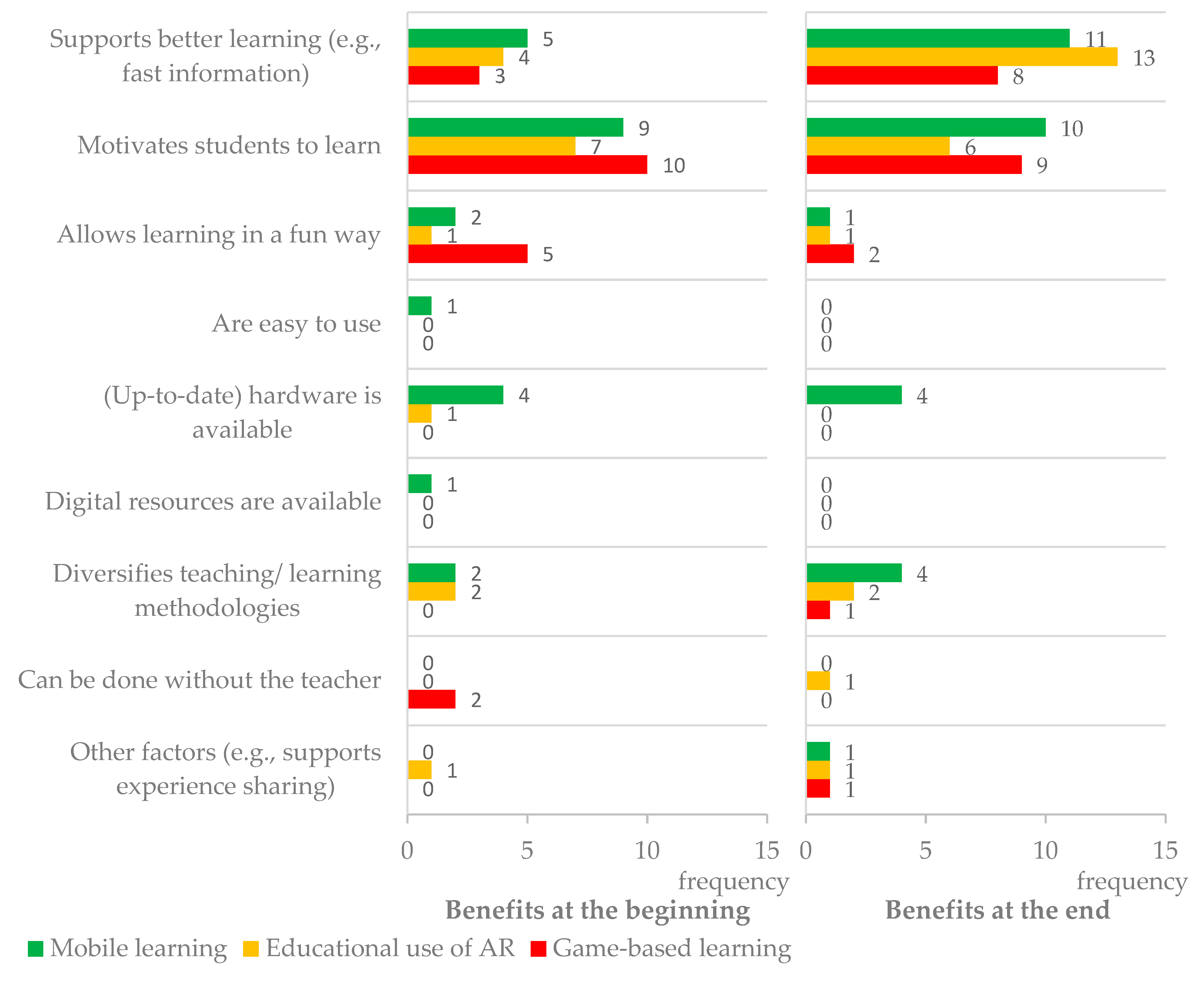
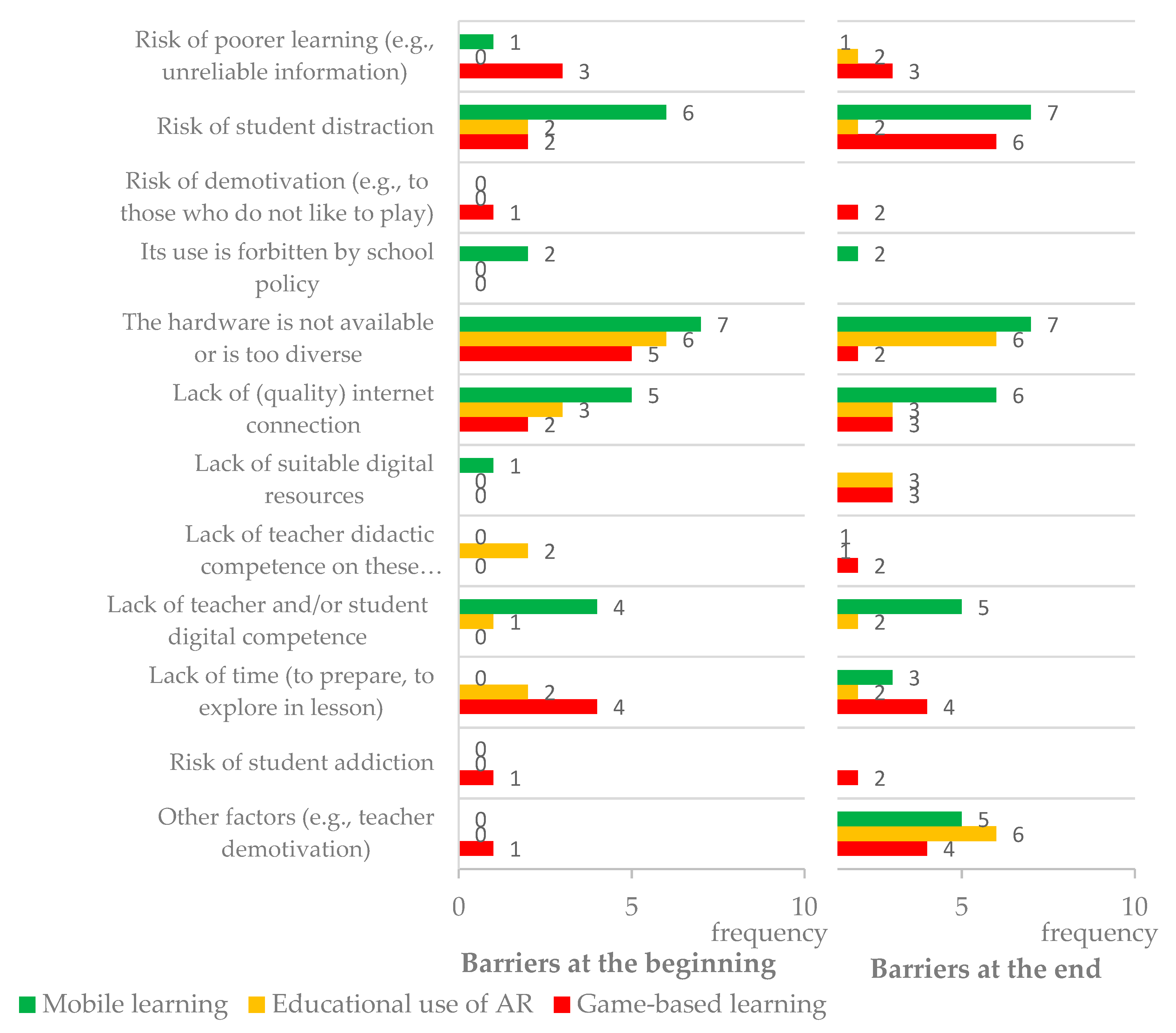
Figure 4 and Figure 5 and Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6 summarize teachers’ answers to the open-ended question “What potential/advantages do you identify in using [mobile devices/AR/game(s)] to promote learning?”.
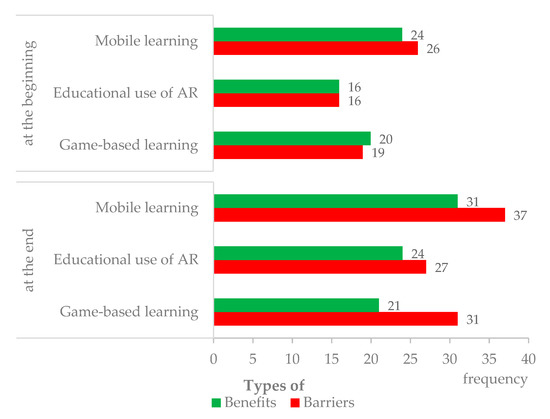
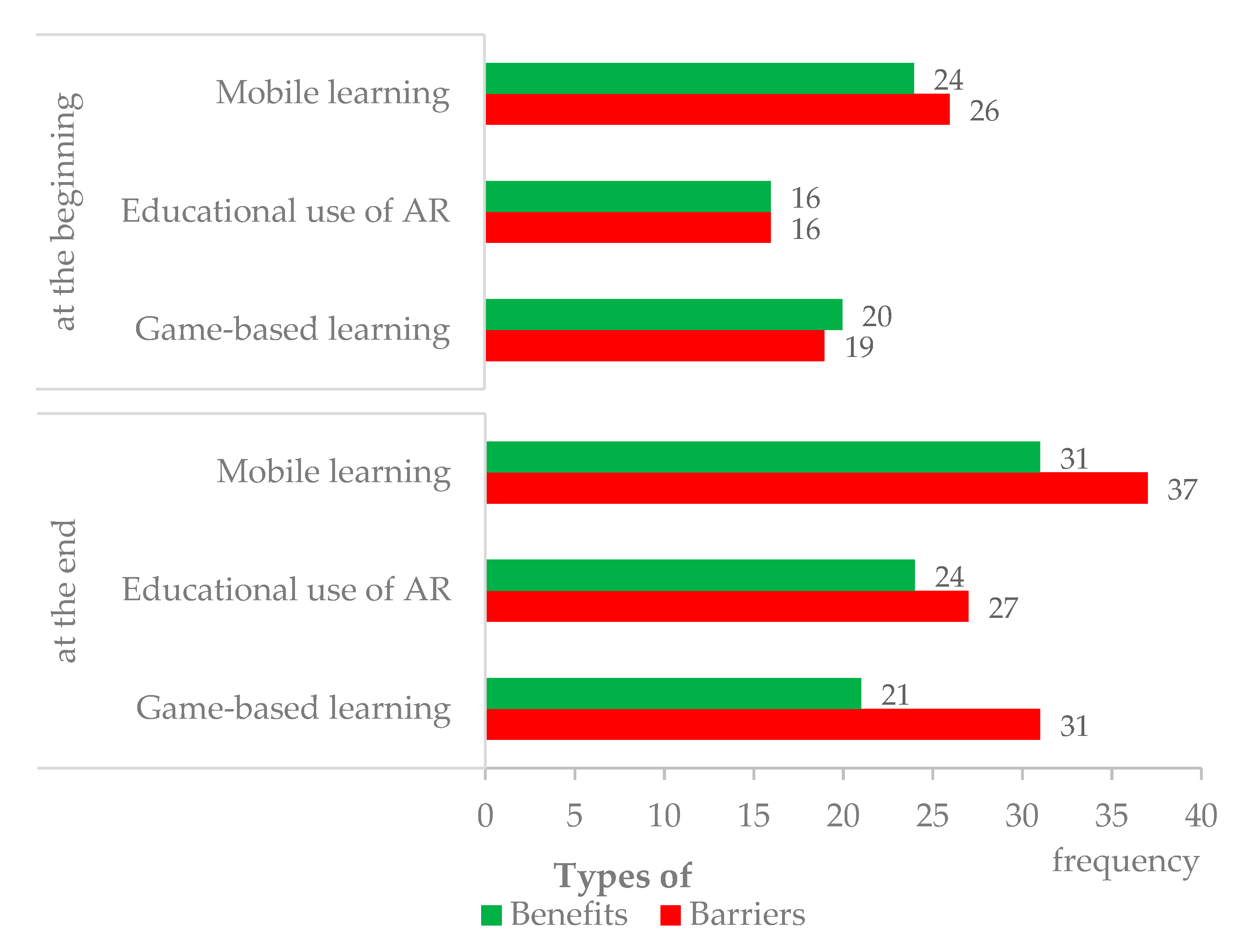
Figure 4.
Comparison of the frequency of types of benefits and barriers, identified by teachers, on mobile learning, educative use of AR, and game-based learning, at the beginning and end of the workshop.
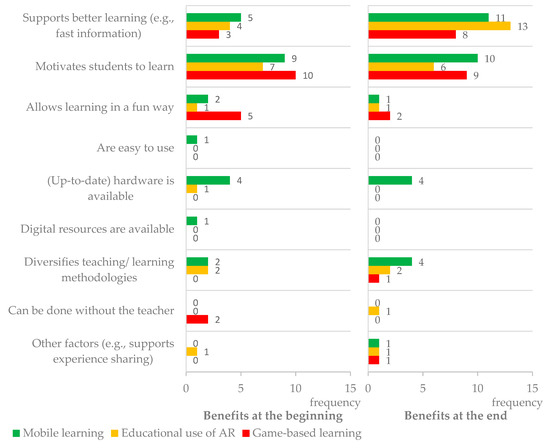
Figure 5.
Comparison of the frequency of each type of benefit identified by teachers on mobile learning, educative use of AR, and game-based learning, at the beginning and end of the workshop.

Table 4.
Numbers of types of benefits and barriers on the educative use of mobile devices, AR, and game(s), according to teachers at the beginning and end of the workshop.

Table 5.
Benefits of exploration of mobile devices, AR, and game(s) in teaching practices, according to teachers at the beginning and end of the workshop.

Table 6.
Barriers to exploration of mobile devices, AR, and game(s) in teaching practices, according to teachers at the beginning and end of the workshop.
Figure 4 reveals that teachers were able to mention more types of benefits and barriers at the end of the workshop, when comparing to the beginning. For example, teachers identified 24 types of benefits of mobile learning at the beginning, and 31 benefits at the end. Similarly, teachers identified 26 types of barriers for mobile learning at the beginning and 37 barriers at the end. Thus, the workshop seems to have had an impact on teachers’ ability to acknowledge both benefits and barriers to the educative use of mobile devices, AR, and games.
Taking into account that the more benefits teachers identified, the more positive their perspectives could be considered, and that the more barriers teachers identified, the more negative their perspectives could be considered, Figure 4 seems to indicate that the workshop had a more intense impact regarding the barriers, which may indicate a moderate negative view. This was a surprising result after training on these educational approaches, but it is possible to hypothesize that knowing the approaches better made teachers more conscious of potential barriers to their implementation.
Presenting results in more detail, Table 4 shows that at the beginning of the workshop, teachers pointed toward 0 to 3 different types of benefits and barriers for each workshop approach. They reported a total of 60 benefits (24 for mobile learning, 16 for AR, and 20 for games) and 61 barriers (26, 16, and 19, respectively), which seemed to reveal teachers’ initial neutral perspective on the educative use of mobile devices, AR, and games [30].
After the workshop, teachers pointed toward 0 to 4 types of benefits and 7 types of barriers for each workshop approach. They identified a total of 76 (31 for mobile learning, 24 for AR, and 21 for games) types of benefits and 95 (37, 27, and 31 respectively) types of barriers.
It is notable how, at both data collection moments, teachers seemed to associate the benefits and the barriers of mobile learning with the ones of AR, and also with those of game-based learning. For example, even at the end of the workshop, teachers mentioned similar benefits to all the approaches, as illustrated by the following citations from Q7: “[Mobile devices] promote engagement and motivation in students.”; ”[AR] fosters motivation, commitment, and enthusiasm for learning.”; and ”Extrinsic motivation is enhanced by the strategies of the game.” This result may be related to the fact that all the approaches were focused on the same training course and exemplified with the same educational resource, a mobile app that supports both gaming and AR. However, even in the initial questionnaire, teachers associated these three approaches in similar ways. This was illustrated by the benefits of mobile learning, AR, and game-based learning reported in Q4: “Learning in a playful way” (the same sentence included in all the answers). Therefore, it seems that the association between the approaches occurred before the training.
Figure 5 summarizes the frequency for each type of benefit teachers mentioned in their answers at the beginning and at the e2nd of the workshop. For the two most frequent benefits, “Supports better learning” and “Motivates students to learn”, there was an increase of frequency after the workshop.
In a more detailed analysis, Table 5 shows that initially, the most pointed types of benefits were: (a) ”Motivates students to learn” (total of 26 teacher mentions); (b) “Supports better learning” (total of 12); and (c) “Allows learning in a funny way” (total of 8), with this last one having more expression regarding the game-based learning approach. At the end of the workshop, motivation (total of 25 mentions) was surpassed by better learning (total of 32), these being the most relevant benefits for the majority of teachers. These results were in line with a previous study [10], related to a short-term teacher training on the same topics, but focused on mobile learning, where student motivation, ease in finding information (which in this study was included in the better learning category), and technology availability stood out. The results indicated that teacher training supported more teachers in identifying learning promoted by these approaches, although with less intensity for games (an increase from 3 to 8 mentions in the present study) and higher intensity for AR (an increase from 4 to 13 mentions). Therefore, the workshop seems to have had a greater impact on teachers’ ability to acknowledge how a technology, unknown to most of the cohort before the training (the AR), can support learning. Moreover, teachers’ answers were longer and more elaborated at the end of the workshop, which may be interpreted as an impact of the workshop on teachers’ understanding of the learning that can be potentiated by the approaches. This is illustrated by the following citations: “[AR] improves knowledge” (Q9 at the beginning); and “[AR] shows in three dimensions (3D) some topics covered in the classroom, so that the student can better understand the «reality». Greater interactivity” (Q9 at the end of the workshop).
Fun learning is a theme that was present in all workshop topics; however, teachers’ focus on this feature decreased (from a total of 8 to a total of 4 mentions). This result seems to point out that training in these approaches contributes to the transformation of teachers’ perceptions of mobile devices, AR, and games being used just for fun to perceptions that these approaches can effectively support deeper learning. The articulation of these elements may sustain mentality changes regarding learning, which is a claim that has been made previously [10].
Other types of benefits pointed out by teachers included aspects related to the availability of technological hardware (usually, associated with mobile devices) and software, its ease of use, and the fact that by using these approaches, teachers and students diversify teaching and learning experiences, particularly in formal education contexts. Some benefits frequently selected by teachers in the previous study [10] were not mentioned by this study’s cohort, specifically ”The information is up-to-date”, ”Does not waste paper”, or ”Facilitates teachers work, namely in assessment”.
Figure 6 summarizes the frequency of each type of barrier teachers mentioned in their answers at the beginning and end of the workshop. Overall, most barriers registered higher frequencies at the end of the workshop.
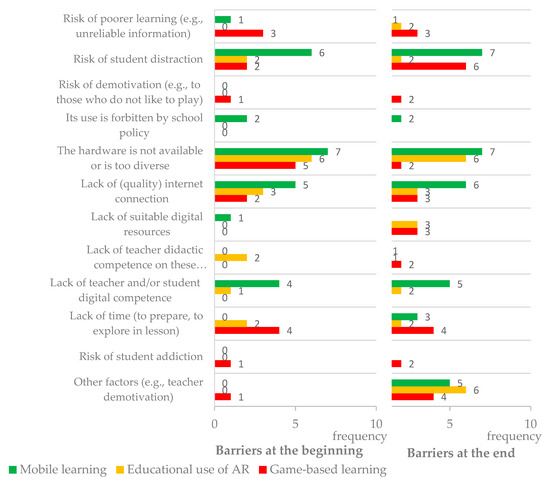
Figure 6.
Comparison of the frequency of each type of barrier, identified by teachers on mobile learning, educative use of AR, and game-based learning, at the beginning and end of the workshop.
In a more detailed analysis, Table 6 shows that the most frequent types of barriers were: (a) “The hardware is not available or is too diverse” (from 18 teacher mentions to 15); (b) “Lack of (quality) internet connection” (from 10 mentions to 12); and (c) ”Risk of student distraction” (from 10 mentions to 15). All these barriers were found in a previous study [10], although with a much smaller expression: (a) 1 teacher (in a total of 26) mentioned the lack of access to mobile devices for some students; (b) 5 teachers selected the need for an internet connection or its lack of quality; and (c) 9 teachers selected student access to distractions. In fact, in the previous study, the most expressed barriers were the risk of developing mobile-device dependence, increased battery consumption, and school prohibition of mobile device use in classes. All these barriers emerged in the present study as well, but with different intensities. Nevertheless, these issues need to be considered by teachers and teacher trainers in order to effectively promote mobile learning, AR, and game-based approaches in teacher practices.
Other types of barriers pointed out by teachers at both data-collection moments included aspects related to lack of time (from 6 to 9 mentions), lack of teacher or student digital competence (from 5 to 7), risk of poorer learning (from 4 to 6), and lack of suitable digital resources (from 1 to 6). None of these barriers were identified in the previous study [10]. However, other themes in common with the previous study, which emerged with small expression in this study, were: (a) School prohibition of use in classes (only for mobile devices); (b) Lack of teacher didactic competence in these approaches; and (c) Risk of student addiction (only for mobile devices in the first study and only for games in the present study). So, once again the same barrier themes were identified in both studies, although with different intensities.
Finally, it is noteworthy to highlight that teachers pointed out some barriers that were not exclusive to these approaches. For example, regarding lack of time, a teacher mentioned at the end of the workshop: “The time spent on classroom with gaming activities may lead to not being able to teach all the [curricular] content” (Q4). The same may be said regarding most teaching approaches that teachers do not know yet, which require a higher investment in terms of planning and implementation during lessons.
4. Conclusions
This work addresses the need to analyze the impact of continuous teacher training initiatives concerning new technology supporting teaching approaches on professional development. It WAS conducted under a case study [31] on the development process of mobile AR games for STEM learning by 14 in-service teachers during a 50 h workshop in Portugal. Hence, the present paper presented the analysis of the impact of this workshop on teacher trainees’ professional development through a questionnaire filled in at the beginning and end of the workshop.
Regarding teachers’ understanding of mobile learning, AR, and game-based learning, this study registered a higher impact on AR educative use, which was the less-known approach for teachers, compared to mobile and game-based learning. Teachers revealed difficulties in explaining concepts’ definitions even at the end of the workshop; however, they demonstrated increased understanding and increased ability to provide concrete examples of each teaching approach.
In what concerns teachers’ experience in educational contexts, teachers became more experienced with mobile learning, AR, and game-based learning as learners themselves, and reported having explored them with their students during the three-month workshop period. Hence, this study’s results support the claim that the analyzed workshop promoted teacher practice changes, although only through self-reports. Future investigations may include teacher practice observations to ascertain the accuracy of teachers’ claims.
Finally, teachers’ ability to identify benefits and barriers through the workshop teaching approaches increased with the training, although with more intensity with respect to barriers. Nevertheless, the most mentioned benefits pointed out by teachers were related to the improved student learning and motivation that may be promoted by mobile AR games. On the other hand, among the barriers to the implementation of these approaches in teaching practices that stood out was the unavailability of proper hardware to support them, or even the hardware diversity that emerges from the bring-your-own-device option, the risk of student distraction, and lack of a quality internet connection. These barriers gain higher relevance if the 2019 State of Education Report [36] is considered, as it mentions the wear and tear of the Portuguese schools’ computer park, and the internet connection fragility in the majority of schools. Therefore, the presented set of barriers to implementation is relevant both for in-service teachers and for teacher trainees preparing future professional development initiatives.
With only 14 participant teachers, this study did not aim to provide results generalizable to the entire Portuguese teacher population. However, this teacher cohort very closely reflected the Portuguese teacher profile [23,24] in terms of gender and experience. Hence, this study could be a good indicator of the teacher population status on these matters.
In sum, this study presented empirical evidence that long-term teacher training concerning the educative exploration of new technologies, which includes the creation of educational resources, may contribute to the transformation of teachers’ perceptions. These seemed to evolve from a perspective that mobile devices, AR, and game-based approaches are considered just for the fun they provide, to perceptions that these approaches can effectively support deeper learning, and hence changing mentalities on how people can learn [40]. Consequently, a recommendation to educational researchers and teacher trainers emerged: to build upon these workshop methodologies in order to have an impact on teacher professional development in what concerns the integration of innovative teaching technologies in their practice.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.M. and L.P.; data curation and formal analysis, M.M.M.; investigation, M.M.M. and L.P.; methodology, M.M.M. and L.P.; project administration, M.M.M. and L.P.; writing—original draft, M.M.M. and L.P.; writing—review and editing, M.M.M. and L.P. Both authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work of the first author was funded by national funds (OE), through the University of Aveiro, in the scope of the framework contract foreseen in the numbers 4, 5, and 6 of Article 23 of the Decree-Law 57/29 August 2016, changed by Law 57/19 July 2017.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, due to being a study involving a small number of healthy adults, participating under informed consent, and with no sensitive data collection.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy issues.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the participating teachers for accepting taking part of this study. The authors also thank the reviewers for their insightful comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Questions of the Section 3 of the Initial Questionnaire.
Table A1.
Questions of the Section 3 of the Initial Questionnaire.
| Question ID | Type | Questions in English (in Portuguese in the Original Questionnaire) |
|---|---|---|
| G4Q01 | open-ended | Explain, in your own words or citing authors in the literature, what you mean by mobile learning. |
| G4Q02 | open-ended | If you know of any educational initiatives or projects involving mobile devices, briefly describe an example. |
| G4Q03 | closed-ended, one | Have you ever used mobile devices to learn? Yes No I don’t know/I don’t remember |
| G4Q04 | open-ended | Briefly describe an experience where you have used a mobile device to learn. |
| G4Q05 | closed-ended, one option selection | How often do you use mobile devices to promote learning? Never used Sometimes Periodically (e.g., twice a month per class) Very often (for example, almost every day) |
| G4Q06 | open-ended | What could motivate you to use mobile devices to promote learning? |
| G4Q07 | open-ended | Briefly describe an experience where you have used mobile devices to promote learning. |
| G4Q08 | open-ended | What potential/advantages do you identify in the use of mobile devices to promote learning? (Please clearly present at least three strengths/advantages that may affect the teaching class) |
| G4Q09 | open-ended | What barriers/constraints do you recognize in using mobile devices to promote learning? (Please clearly state at least three barriers/constraints that can affect teachers) |
| G4Q10 | open-ended | Do you have any comments regarding mobile learning? |
| G5Q01 | open-ended | Explain, in your own words or citing authors in the literature, what you mean by educational use of augmented reality. |
| G5Q02 | open-ended | If you know any educational initiatives or projects that involve augmented reality, briefly describe an example. |
| G5Q03 | closed-ended, one option selection | Have you ever had any experience in augmented reality (regardless of context)? Yes No I don’t know/I don’t remember |
| G5Q04 | open-ended | Briefly describe an experience in which you have used augmented reality (regardless of context). |
| G5Q05 | closed-ended, one option selection | Have you ever used augmented reality to learn? Yes No I don’t know/I don’t remember |
| G5Q06 | open-ended | Briefly describe an experience in which you have used augmented reality to learn. |
| G5Q07 | closed-ended, one option selection | How often do you use augmented reality to promote learning? Never used Sometimes Periodically (e.g., twice a month per class) Very often (for example, almost every day) |
| G5Q08 | open-ended | What could motivate you to use augmented reality to promote learning? |
| G5Q09 | open-ended | Briefly describe an experience in which you have used augmented reality to promote learning. |
| G5Q10 | open-ended | What potential/advantages do you identify in using augmented reality to promote learning? (Please clearly present at least three strengths/advantages that may affect teachers.) |
| G5Q11 | open-ended | What barriers/constraints do you recognize in the use of augmented reality to promote learning? (Please clearly state at least three barriers/constraints that can affect teachers.) |
| G5Q12 | open-ended | Do you have any comments regarding the educational use of augmented reality? |
| G6Q01 | open-ended | Explain, in your own words or citing authors in the literature, what you mean by game-based learning. |
| G6Q02 | open-ended | If you know any educational initiatives or projects that involve the use of game(s), briefly describe an example. |
| G6Q03 | closed-ended, one option selection | Have you ever used game(s) to learn? Yes No I don’t know/I don’t remember |
| G6Q04 | open-ended | Briefly describe an experience in which you have used game(s) to learn. |
| G6Q05 | closed-ended, one option selection | How often do you use game(s) to promote learning? Never used Sometimes Periodically (e.g., twice a month per class) Very often (for example, almost every day) |
| G6Q06 | open-ended | What could motivate you to use game(s) to promote learning? |
| G6Q07 | open-ended | Briefly describe an experience where you have used game(s) to promote learning. |
| G6Q08 | open-ended | What potential/advantages do you identify in using game(s) to promote learning? (Please clearly present at least three strengths/advantages that may affect teachers.) |
| G6Q09 | open-ended | What barriers/constraints do you recognize in using game(s) to promote learning? (Please clearly state at least three barriers/constraints that can affect teachers.) |
| G6Q10 | open-ended | Do you have any comments regarding game-based learning? |

Table A2.
Questions of the Section 3 of the Final Questionnaire.
Table A2.
Questions of the Section 3 of the Final Questionnaire.
| Question ID | Type | Questions—in English (in Portuguese in the Original Questionnaire) |
|---|---|---|
| G4Q01 | open-ended | Explain, in your own words or citing authors in the literature, what you mean by mobile learning. |
| G4Q02 | open-ended | If you know of any educational initiatives or projects involving mobile devices, briefly describe an example. |
| G4Q03 | closed-ended, one option selection | In this Training Workshop did you use mobile devices to learn? Yes No |
| G4Q04 | closed-ended, one option selection | During the period in which this Training Workshop took place, did you use mobile devices to promote learning? Yes No |
| G4Q05 | open-ended | Why did you decide not to use mobile devices to promote learning during the period in which this Training Workshop took place? |
| G4Q06 | open-ended | What potential/advantages do you identify in the use of mobile devices to promote learning? (Please clearly present at least three strengths/advantages that may affect teachers) |
| G4Q07 | open-ended | What barriers/constraints do you recognize in using mobile devices to promote learning? (Please clearly state at least three barriers/constraints that can affect teachers) |
| G4Q08 | open-ended | Do you have any comments regarding mobile learning? |
| G5Q01 | open-ended | Explain, in your own words or citing authors in the literature, what you mean by educational use of augmented reality. |
| G5Q02 | open-ended | If you know any educational initiatives or projects that involve augmented reality, briefly describe an example. |
| G5Q03 | closed-ended, one option selection | In this Training Workshop did you use augmented reality to learn? Yes No |
| G5Q04 | closed-ended, one option selection | During the period in which this Training Workshop took place, did you use augmented reality to promote learning? Yes No |
| G5Q05 | open-ended | Why did you decide not to use augmented reality to promote learning during the period in which this Training Workshop took place? |
| G5Q06 | open-ended | What potential/advantages do you identify in using augmented reality to promote learning? (Please clearly present at least three strengths/advantages that may affect teachers) |
| G5Q07 | open-ended | What barriers/constraints do you recognize in the use of augmented reality to promote learning? (Please clearly present at least three barriers/constraints that may affect teachers) |
| G5Q08 | open-ended | Do you have any comments regarding the educational use of augmented reality? |
| G6Q01 | open-ended | Explain, in your own words or citing authors in the literature, what you mean by game-based learning. |
| G6Q02 | open-ended | If you know any educational initiatives or projects that involve the use of game(s), briefly describe an example. |
| G6Q03 | closed-ended, one option selection | In this Training Workshop did you use game(s) to learn? Please select only one of the following options: Yes No |
| G6Q04 | closed-ended, one option selection | During the period in which this Training Workshop took place, did you use game(s) to promote learning? Please select only one of the following options: Yes No |
| G6Q05 | open-ended | Why did you decide not to use game(s) to promote learning during the period this Training Workshop took place? |
| G6Q06 | open-ended | What potential/advantages do you identify in using game(s) to promote learning? (Please clearly present at least three strengths/advantages that may affect teachers) |
| G6Q07 | open-ended | What barriers/constraints do you recognize in using game(s) to promote learning? (Please clearly state at least three barriers/constraints that can affect teachers) |
| G6Q08 | open-ended | Do you have any comments regarding game-based learning? |
References
- Winters, N. What is mobile learning? In Big Issues in Mobile Learning: Report of a Workshop by the Kaleidoscope Network of Excellence Mobile Learning Initiative; Sharples, M., Ed.; University of Nottingham: Nottingham, UK, 2006; pp. 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Farley, H.; Murphy, A.; Rees, S. Revisiting the Definition of Mobile Learning. In Proceedings of the ASCILITE—Australian Society for Computers in Learning in Tertiary Education Annual Conference, Sydney, Australia, 1–4 December 2013; pp. 283–287. Available online: https://www.learntechlib.org/p/171139/ (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Traxler, J. Learning in a Mobile Age. Int. J. Mob. Blended Learn. 2009, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zydney, J.M.; Warner, Z. Mobile apps for science learning: Review of research. Comput. Educ. 2016, 94, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-L.; Chang, D.-F.; Wu, B. Mobile Game-Based Learning with a Mobile App: Motivational Effects and Learning Performance. J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform. 2017, 21, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plass, J.L.; Homer, B.D.; Kinzer, C.K. Foundations of Game-Based Learning. Educ. Psychol. 2015, 50, 258–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, T. Mobile Educational Augmented Reality Games: A Systematic Literature Review and Two Case Studies. Computers 2018, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Freitas, S. Are Games Effective Learning Tools? A Review of Educational Games. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2018, 21, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, S.; Fletcher, J.D.; Wind, A.P. Game-Based Learning. In Handbook of Research on Educational Communications and Technology; Spector, J., Merrill, M., Elen, J., Bishop, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 485–503. ISBN1 978-1-4614-3184-8. ISBN2 978-1-4614-3185-5. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, M.M.; Pombo, L. Game-Based Mobile Learning with Augmented Reality: Are Teachers Ready to Adopt It? In Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 158, ISBN 9789811396519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Li, L.; Sun, Y. A systematic review of mobile game-based learning in STEM education. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2020, 68, 1791–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakoç, B.; Eryılmaz, K.; Özpolat, E.T.; Yıldırım, İ. The Effect of Game-Based Learning on Student Achievement: A Meta-Analysis Study. Technol. Knowl. Learn. 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Clark, K.R. Game-based Learning and 21st century skills: A review of recent research. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 63, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-Y.; Hwang, G.-J. Trends in Digital Game-Based Learning in the Mobile Era: A Systematic Review of Journal Publications from 2007 to 2016; Int. J. Mob. Learn. Organ. 2019, 13, 68–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Jabbar, A.I.; Felicia, P. Gameplay Engagement and Learning in Game-Based Learning: A Systematic Review. Rev. Educ. Res. 2015, 85, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.-J.; Wu, P.-H.; Chen, C.-C.; Tu, N.-T. Effects of an augmented reality-based educational game on students’ learning achievements and attitudes in real-world observations. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2016, 24, 1895–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivec, P. Game-Based Learning or Game-Based Teaching? (Report No. 1509); British Educational Communications and Technology Agency (BECTA). 2009. Available online: http://www.becta.org.ukhttp//www.becta.org.uk (accessed on 12 May 2021).
- Russo, J.A.; Bragg, L.; Russo, T. How Primary Teachers Use Games to Support Their Teaching of Mathematics. Int. Electron. J. Elem. Educ. 2021, 13, 407–419. [Google Scholar]
- Groff, J.; Clarke-Midura, J.; Owen, V.E.; Rosenheck, L.; Beall, M. Better Learning in Games: A Balanced Design Lens for a New Generation of Learning Games; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; Available online: http://education.mit.edu/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/BalancedDesignGuide2015.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2021).
- Markouzis, D.; Fessakis, G. Rapid Prototyping of Interactive Storytelling and Mobile Augmented Reality Applications for Learning and Entertainment—The case of “k-Knights”. Int. J. Eng. Pedagog. 2016, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, M. A Study of Adults’ Perception and Needs for Smart Learning. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 191, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akçayır, M.; Akçayır, G. Advantages and challenges associated with augmented reality for education: A systematic review of the literature. Educ. Res. Rev. 2017, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabero, J.; Barroso, J. The educational possibilities of Augmented Reality. New Approaches Educ. Res. 2016, 5, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pombo, L.; Marques, M.M.; Carlos, V. Mobile augmented reality game-based learning: Teacher training using the EduPARK app. Da Investig. às Práticas. 2019, 9, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertmer, P.A.; Ottenbreit-Leftwich, A.T. Teacher technology change: How knowledge, confidence, beliefs, and culture intersect. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 2010, 42, 255–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pombo, L.; Marques, M.M.; Afonso, L.; Dias, P.; Madeira, J. Evaluation of a mobile augmented reality game application as an outdoor learning tool. Int. J. Mob. Blended Learn. 2019, 11, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pombo, L. Learning with an app? It’s a walk in the park. Prim. Sci. 2018, 12–15. Available online: https://www.learntechlib.org/p/190712/ (accessed on 18 May 2021).
- Jeffrey, K.; Kinshuk, L. Factors Impacting Teachers’ Adoption of Mobile Learning. Available online: http://www.jite.org/documents/Vol13/JITEv13ResearchP141-162MacCallum0455.pdf (accessed on 17 April 2021).
- De Freitas, S. Learning in Immersive Worlds A Review of Game-Based Learning Prepared for the JISC e-Learning Programme. Available online: http://www.jisc.ac.uk/media/documents/programmes/elearninginnovation/gamingreport_v3.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Marques, M.M.; Pombo, L. Teachers’ experiences and perceptions regarding mobile augmented reality games: A case study of a teacher training. In Proceedings of the INTED2021 Conference; Chova, L.G., Martínez, A.L., Torres, I.C., Eds.; IATED: Online, 2021; pp. 8938–8947. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, R.K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods, 6th ed.; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, H.; Birks, M.; Franklin, R.; Mills, J. Case study research: Foundations and methodological orientations. Forum Qual. Sozialforsch. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horizon Project Advisory Board. Horizon Report 2007 Edition (NMC and Educause); The New Media Consortium: Stanford, CA, USA, 2007; ISBN 0976508745. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, L.; Adams, S.; Estrada, V.; Freeman, A. NMC Horizon Report: 2015 K-12 Edition; The New Media Consortium: Austin, TX, USA, 2015; ISBN 9780991482856. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, L.; Smith, R.; Levine, A.; Haywood, K. 2010 Horizon Report: K-12 Edition; The New Media Consortium: Austin, TX, USA, 2010; ISBN 9780982533444. [Google Scholar]
- Conselho Nacional de Educação. Estado da Educação 2019; Conselho Nacional de Educação: Lisboa, Portugal, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, L.; Adams, S.; Cummins, M. NMC Horizon Report: 2012 K-12 Edition; The New Media Consortium: Austin, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, L.; Adams, S.; Haywood, K. NMC Horizon Report: 2011 K-12 Edition; The New Media Consortium: Austin, TX, USA, 2011; ISBN 9780982829097. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, L.; Becker, S.A.; Estrada, V.; Freeman, A. NMC Horizon Report: 2014 K-12 Edition; The New Media Consortium: Austin, TX, USA, 2014; ISBN 9780991482856. [Google Scholar]
- Pombo, L.; Marques, M.M. An App that Changes Mentalities about Mobile Learning—The EduPARK Augmented Reality Activity. Computers 2019, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).