Conflicting Demands of Chemistry and Inclusive Teaching—A Video-Based Case Study
Abstract
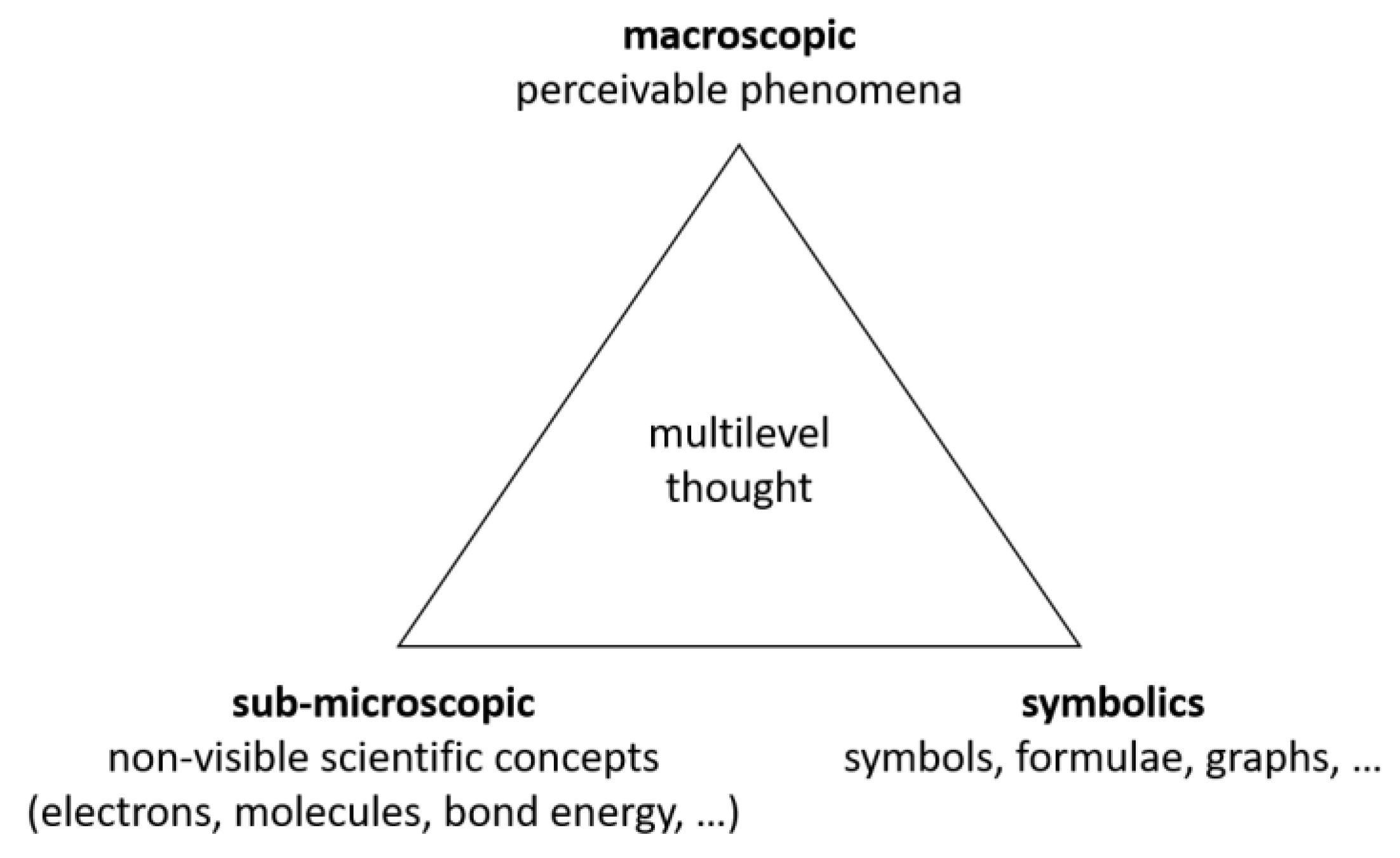
:1. Introduction
“Inclusive pedagogy focuses on extending what is ordinarily available as part of the routine of classroom life as a way of responding to differences between learners rather than specifically individualizing for some. It represents a shift in thinking about teaching and learning from that which works for most learners along with something ‘different’ or additional’ for those who experience difficulties, to an approach to teaching and learning that involves the creation of a rich learning environment characterized by lessons and learning opportunities that are sufficiently made available to everyone so that all are able to participate in classroom life”.[8] (p. 370)
“science education fosters inclusion by facilitating participation in science specific learning processes for all learners. By appreciating the diversity and individual prerequisites, science education involves individual and joint teaching and learning processes to promote scientific literacy”.[17] (p. 270)
“Implications for practice include the need for general education preservice and in-service professional development on differentiation for students with LD (learning disabilities) in science inclusion classrooms, especially when utilizing an inquiry-based curriculum.”[27] (p. 140)
2. Data Source and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Method
- A formative interpretation
- A reflective interpretation
- Reconstructing orientational frameworks
3. Results
3.1. Formative Interpretation
3.2. Reflecive Interpretation
3.2.1. Reflective Interpretation—Lesson Phase 2 on Atomic Structure
| 18 T: | […] and how is the core [of an atom] charged? (I) |
| 19 Sf7: | Positive. (R) |
| 20 T: | It is positive, ok. (E) So I have a positive charged core in the middle and then |
| 21 | I have around the... (I) |
| 22 Sm3: | Negative (R) |
| 23 T: | The... (E) |
| 24 Sf7: | Electrons. (R) |
| 25 T: | Electrons and where can they be found (I) … where do we imagine this… |
| 26 Sf9: | In shells. (R) |
| 27 T: | In shells, exactly. (E) […] |
| 28 T: | […] in the core there are protons and neutrons. What can you identify within |
| 29 | the word neutron? |
| 30 Sm2: | neu |
| 31 Sm3: | tron |
| 32 T: | neutr - al |
| 33 Sm3: | neutral. |
| 34 T: | What is the meaning of that word? |
| 35 Sm3: | It is neither positive, nor negative. |
| 36 Sm2: | It is not charged. Neutral—it is in the middle. |
| 37 Sf9: | It is something like a filling. |
| 38 T: | Exactly. It is something like a filling, so that it becomes heavier. And how is |
| 39 | the core charged then? |
| 40 T: | Look at Neon. |
| […] | |
| 43 Sm2: | Where is Neon? |
| 44 T: | Neon? |
| 45 Sm2: | Ah// here ten |
| 46 T: | //a noble gas |
| 47 Sm2: | ten |
| 48 Sm3: | ten |
| 49 Sm3: | Neon is a gas? |
| 50 Sm2: | It has eh // |
| 51 Sm3: | // It is a color also? |
| 52 Sm2: | //It has two rings. |
| 53 T: | Yes, it has two shells |
3.2.2. Reflective Interpretation—Lesson Phase 3
| 54 Sm4: | (Raised his hand and points to the chemistry book in his hand) But you cannot |
| 55 | freeze hydrogen so long till it happens, till it becomes helium.// Or is that |
| 56 | possible? |
| 57 T: | Aha. No, we won´t. Pay attention! We will not convert two elements, we will |
| 58 | ditch together two (She shows that with her hands). |
| 59 Sm4: | Ah, we only want that it is again… |
| 60 Sm2: | Making one positive and one negative. |
| 61 T: | Yes |
| 62 Sm5: | We want. |
| 63 Sm2: | Maybe in the heat //SM3: Yes heat .// the negative goes away and in the cold |
| 64 | the negative stays or the other way round? |
| 65 Sm3: | And then it mixes in some way. |
| 66 T: | Okay, let’s look at it. |
| 67 Sm2: | The one heating up, the other cooling down and then. |
| 68 Sm5: | Or we heat up water, and then evaporate it. |
| 69 T: | And the electrons evaporate suddenly? |
| 70 (Sm2 laughs) | |
| 71 Sm4: | Forget it. |
| 72 Sm5: | Don´t know, it is flying away? |
| 73 Sm2: | (laughs) No it goes. |
| 74 Sm3: | Why not? |
| 75 Sm2: | It breaks up. |
| 76 Sm5: | It is in a cloud. |
| 77 T: | And then? |
| 78 Sm3: | It rains. |
| 79 (Everyone laughs) | |
| 80 Sm2: | It rains electrons (laughs) |
- The communication remains indefinite and implicit. No participant in the conversation asks for clarification or explication of terms.
- The teacher does not act as an instructor.
- The conversation continues to be characterized by a high tolerance towards the students’ statements. It seems there are no false answers for the teacher.
- The conversation is still highly interactive. Almost all participants in the discussion remain constantly in conversation.
3.3. Orientational Framework
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnstone, A.H. Teaching of chemistry—Logical or psychological? Chem. Educ. Res. Pract. Eur. 2000, 1, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kultusministerium, N. Kerncurriculum für die Oberschule Schuljahrgänge 5–10 Naturwissenschaften; Unidruck: Hannover, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sjøberg, S.; Schreiner, C. How do learners in different cultures relate to science and technology? Asia-Pac. Forum Sci. Learn. Teach. 2005, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Anderson, C. Recontextualization of Science from Lab to School: Implications for Science Literacy. Sci. Educ. 2009, 18, 1253–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höft, L.; Bernholt, S.; Blankenburg, J.S.; Winberg, M. Knowing more about things you care less about: Cross-sectional analysis of the opposing trend and interplay between conceptual understanding and interest in secondary school chemistry. J. Res. Sci. Teach. 2019, 56, 184–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräber, W. German High School Students’ Interest in Chemistry—A Comparison between 1990 and 2008. Educ. Quim. 2011, 22, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Guidelines for Inclusion: Ensuring Access to Education for All. Available online: http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0014/001402/140224e.pdf (accessed on 11 January 2012).
- Florian, L.; Linklater, H. Preparing teachers for inclusive education: using inclusive pedagogy to enhance teaching and learning for all. Cambridge J. Educ. 2010, 40, 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florian, L.; Black-Hawkins, K. Exploring Inclusive Pedagogy. Br. Educ. Res. J. 2011, 37, 813–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, S.; Sharma, U.; Hoffmann, L. How inclusive are the teaching practices of my German, Maths and English Teachers? —Psychometric Properties of a Newly Developed Scale to Assess Personalisation and Differentiation in Teaching Practices. Int. J. Incl. Educ. 2019, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Heidinger, C.; Abels, S.; Plotz, T.; Koliander, B. Inclusion and Chemistry teaching—Deliberating Conflicting Demands. In Electronic Proceedings of the ESERA 2017 Conference. Research, Practice and Collaboration in Science Education; Finlayson, O.E., McLoughlin, E., Erduran, S., Childs, P., Eds.; Dublin City University: Dublin, Ireland, 2018; pp. 1611–1619. [Google Scholar]
- Abels, S. Scaffolding Inquiry-Based Science and Chemistry Education in Inclusive Classrooms. In New Developments in Science Education Research; Yates, N.L., Ed.; Nova: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 77–96. [Google Scholar]
- Mumba, F.; Banda, A.; Chabalengula, V.M. Chemistry Teachers’ Perceived Benefits and Challenges of Inquiry-based Instruction in Inclusive Chemistry Classrooms. Sci. Educ. Int. 2015, 26, 180–194. [Google Scholar]
- Tolsdorf, Y.; Kousa, P.; Markic, S.; Aksela, M. Learning to Teach at Heterogeneous and Diverse Chemistry Classes—Methods for University Chemistry Teacher Training Courses. EURASIA J. Math. Sci Tech. Educ. 2018, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Abels, S. Science Teacher Professional Development for Inclusive Practice. Int. J. Phys. Chem. Educ. 2019, 11, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Markic, S.; Abels, S. Heterogeneity and Diversity—A Growing Challenge or Enrichment for Science Education in German Schools? EURASIA J. Math. Sci Tech. Educ. 2014, 10, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkowiak, M.; Rott, L.; Abels, S.; Nehring, A. Network and Work for Inclusive Science Education. In Building Bridges across Disciplines; Eilks, I., Markic, S., Ralle, B., Eds.; Shaker: Aachen, Germany, 2018; pp. 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Abels, S.; Minnerop-Haeler, L. Lernwerkstatt: An Inclusive Approach in Science Education. In Science Education towards Inclusion; Markic, S., Abels, S., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 137–156. [Google Scholar]
- Klika, D.; Abels, S. Scaffolding guided inquiry-based chemistry education at an inclusive school. In Electronic Proceedings of the ESERA 2015 Conference; Lavonen, J., Juuti, K., Lampiselkä, J., Uitto, A., Hahl, K., Eds.; University of Helsinki: Helsinki, Finland, 2016; pp. 1030–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Abels, S.; Puddu, S. Inquiry-based Learning Environments to Welcome the Diversity of a Chemistry Class. In E-Book Proceedings of the ESERA 2013 Conference: Science Education Research For Evidence-based Teaching and Coherence in Learning; Constantinou, C.P., Papadouris, N., Hadjigeorgiou, A., Eds.; European Science Education Research Association: Nicosia, Cyprus, 2014; pp. 122–130. [Google Scholar]
- Therrien, W.J.; Taylor, J.C.; Hosp, J.L.; Kaldenberg, E.R.; Gorsh, J. Science Instruction for Students with Learning Disabilities: A Meta-Analysis. Learn. Disabil. Res. Pract. 2011, 26, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, M.G.; Taylor, J.A.; Therrien, W.J.; Hand, B. Science education for students with special needs. Stud. Sci. Educ. 2012, 48, 187–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scruggs, T.E.; Mastropieri, M.A.; Okolo, C.M. Science and social studies for students with disabilities. Focus Except. Child. 2008, 41, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Brigham, F.; Scruggs, T.E.; Mastropieri, M.A. Science Education and Students with Learning Disabilities. Learn. Disabil. Res. Pract. 2011, 26, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, O.; Deaktor, R.; Hart, J.; Cuevas, P.; Enders, C. An Instructional Intervention’s Impact on the Science and Literacy Achievement of Culturally and Linguistically Diverse Elementary Students. J. Res. Sci. Teach. 2005, 42, 857–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.R.; Wang, Y.C.; Tai, H.J.; Chen, W.J. Investigating the Effectiveness of Inquiry-Based Instruction on Students with Different Prior Knowledge And Reading Abilities. Int. J. Sci. Math. Educ. 2010, 8, 801–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, A.L.; Hughes, M.T. Students with Learning Disabilities in Inquiry-Based Science Classrooms: A Cross-Case Analysis. Learn. Disabil. Q. 2018, 41, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ødegaard, M.; Klette, K. Teaching Activities and Language Use in Science Classrooms. In Science Education Research and Practice in Europe; Jorde, D., Dillon, J., Eds.; Sense Publishers: Rotterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA; Taipei, Taiwan, 2012; pp. 181–202. [Google Scholar]
- Abels, S. Inklusiver naturwissenschaftlicher Unterricht in der Lernwerkstatt Donaustadt. In Grundlagen Inklusiver Bildung. Teil 1. Inklusive Unterrichtspraxis Und-Entwicklung; Siedenbiedel, C., Theurer, C., Eds.; Prolog: Immenhausen bei Kassel, Germany, 2015; pp. 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Bohnsack, R.; Pfaff, N.; Weller, W. (Eds.) Qualitative Analysis and Documentary Method in International Educational Research; Barbara Budrich Publisher: Opladen, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kuckartz, U.; Dresing, T.; Rädiker, S.; Stefer, C. Qualitative Evaluation. DerEinstieg in die Praxis; VS Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet, A. Die Dokumentarische Methode in der Unterrichtsforschung: ein integratives Forschungsinstrument für Strukturrekonstruktion und Kompetenzanalyse. Z. Qual. Forsch. 2009, 10, 219–240. [Google Scholar]
- Ruhrig, J.; Höttecke, D. Components of Science Teachers’ Professional Competence and Their Orientational Frameworks When Dealing with Uncertain Evidence in Science Teaching. Int. J. Sci. Math. Educ. 2015, 13, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, N.; Bohnsack, R.; Weller, W. Brazilian and German educational science: an introduction. In Qualitative Analysis and Documentary Method in International Educational Research; Bohnsack, R., Pfaff, N., Weller, W., Eds.; Barbara Budrich Publisher: Opladen, Germany, 2010; pp. 7–38. [Google Scholar]
- Bohnsack, R. Documentary Method and group discussions. In Qualitative Analysis and Documentary Method in International Educational Research; Bohnsack, R., Pfaff, N., Weller, W., Eds.; Barbara Budrich Publisher: Opladen, Germany, 2010; pp. 99–124. [Google Scholar]
- Bohnsack, R. Dokumentarische Methode und die Logik der Praxis. In Pierre Bourdieus Konzeption Des Habitus. Grundlagen, Zugänge, Forschungsperspektiven; Lenger, A., Schneickert, C., Schumacher, F., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 175–200. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, F. Classroom Discourse as Improvisation: Relationships between Academic Task Structure and Social Participation Structure in Lessons. In Communicating in the classroom; Wilkinson, L.C., Ed.; Language, Thought, and Culture; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 153–181. [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone, A.H. Why is Science Difficult to Learn? Things are Seldom What They Seem. J. Comput. Assist. Lear. 1991, 7, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer, E.F.; Scott, P. Meaning Making in Secondary Science Classrooms; Open University Press: Maidenhead, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Taber, K.S. Revisiting the Chemistry Triplet: Drawing Upon the Nature of Chemical Knowledge and the Psychology Of Learning To Inform Chemistry Education. Chem. Educ. Res. Pract. 2013, 14, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Phase | Time [min] | Social Form | Subject Matter |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | Individual work | Atomic structure |
| 2 | 50 | Teacher-led classroom discourse | Atomic structure |
| 3 | 15 | Teacher-led classroom discourse | Atomic bonding |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abels, S.; Koliander, B.; Plotz, T. Conflicting Demands of Chemistry and Inclusive Teaching—A Video-Based Case Study. Educ. Sci. 2020, 10, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci10030050
Abels S, Koliander B, Plotz T. Conflicting Demands of Chemistry and Inclusive Teaching—A Video-Based Case Study. Education Sciences. 2020; 10(3):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci10030050
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbels, Simone, Brigitte Koliander, and Thomas Plotz. 2020. "Conflicting Demands of Chemistry and Inclusive Teaching—A Video-Based Case Study" Education Sciences 10, no. 3: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci10030050
APA StyleAbels, S., Koliander, B., & Plotz, T. (2020). Conflicting Demands of Chemistry and Inclusive Teaching—A Video-Based Case Study. Education Sciences, 10(3), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci10030050





