The Effects of the Strategy and Goal on Business Performance as Mediated by Management Accounting Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Research Hypotheses
3. Methodology
3.1. Samples
3.2. Statistical Method
3.3. Scale Assessment Process
3.4. Variables Used in This Paper
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Characteristics of the Survey Respondents
4.2. Structural Equation Modeling Results
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
6. Research Limitations and Further Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | The costing system (CS) includes job process or job order techniques, cost behavior, activity-based costing, plant-wide overhead cost pr departmental overhead cost rate, standard costing, quality cost analysis, and the learning curve technique (seven variables). |
| 2 | Budgeting (B) includes budgeting for product cost controlling, budgeting for cash flow planning, activity-based budgeting, performing a financial statement, flexible budgeting, sensitivity analysis of cost, and zero-based budgeting (seven variables). |
| 3 | Performance evaluation (E) includes a balanced scorecard, financial measurements, non-financial measurements of customer satisfaction, non-financial measurements related to operation and innovation (e.g., patent certificates and awards), and non-financial measures related to employees (e.g., employee satisfaction, staff turnover, benchmarking, residual income, and economic value added) (eight variables). |
| 4 | Information for decision making (ID) includes break-even point analysis, stock control models, the evaluation of significant capital investment based on the discounted cash flow method, the evaluation of capital investment based on a payback period or the accounting rate of return, sensitivity analysis of the cost model, incremental analysis, profitability analysis, and customer profitability analysis (nine variables). |
References
- Abdel-Kader, Magdy G. 2011. Review of Management Accounting Research–2011. Macmillan: Palgrave. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Kader, Magdy G., and Robert G. Luther. 2008. The impact of firm characteristics on management accounting practices: A UK-based empirical analysis. British Accounting Review 40: 2–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahire, Sanjay L., Damodar Y. Golhar, and Matthew A. Waller. 1996. Development and validation of TQM implementation constructs. Decision Sciences 27: 23–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, Richard S., and Marilyn M. Helms. 2006. Linking strategic practices and organizational performance to Porter’s generic strategies. Business Process Management Journal 12: 433–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, Richard S., Marilyn M. Helms, Holly Jones, Margaret B. Takeda, and Charles S. White. 2007. Porter’s business strategies in Japan. Business Strategy Series 9: 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Omiri, Mohammed, and Colin Drury. 2007. A survey of factors influencing the choice of product costing systems in UK organizations. Management Accounting Research 18: 399–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banker, Rajiv D., Hsihui Chang, and Mina J. Pizzini. 2004. The balanced scorecard: Judgmental effects of performance measures linked to strategy. The Accounting Review 79: 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banker, Rajiv D., Seok-Young Lee, Gordon Potter, and Dhinu Srinivasan. 2000. An empirical investigation of an incentive plan that includes nonfinancial performance measures. The Accounting Review 75: 65–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, Phil B. 1993. Human Resource Management: Key Concepts and Skills’. London: Sage. [Google Scholar]
- Berraies, Sarra, and Manel Hamoud. 2018. Customer empowerment and firms’ performance: The mediating effects of innovation and customer satisfaction. International Journal of Bank Marketing 36: 336–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, Godfred O., Torsten B. Neilands, Edward A. Frongillo, Hugo R. Melgar-Quiñonez, and Sera L. Young. 2018. Best Practices for Developing and Validating Scales for Health. Social, and Behavioral Research: A Primer. Frontiers in Public Health 6: 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, Barbara M. 1998. Structural Equation Modeling with LISREL, PRELIS, & SIMPLIS: Basic Concepts, Applications, & Programming’. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. [Google Scholar]
- Chau, Patrick Y. K. 1997. Reexamining a Model for Evaluating Information Center Success Using a Structural Equation Modeling Approach. Journal of the Decision Sciences Institute 28: 309–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenhall, Robert H., and Kim Langfield-Smith. 1998a. Adoption and Benefits of Management Accounting Practices: An Australian Study. Management Accounting Research 9: 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenhall, Robert H., and Kim Langfield-Smith. 1998b. The relationship between strategic priorities, management techniques and management accounting: An empirical investigation using a systems approach. Accounting, Organizations and Society 23: 243–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenhall, Robert, and Frank Moers. 2007. The issue of endogeneity within theory-based, quantitative management accounting research. European Accounting Review 16: 173–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chepchirchir, Alice B., Francis Omillo, and Jennifer Munyua. 2018. Effect of Cost Leadership Strategy on Organizational Performance of Logistics Firms at Jomo Kenyatta International Airport, Kenya. European Journal of Management and Marketing Studies 3: 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, Chee W., Jean C. Cooper, and William S. Waller. 1988. Participative Budgeting: Effects of a Truth-Inducing Pay Scheme and Information Asymmetry on Slack and Performance. The Accounting Review 63: 111–22. [Google Scholar]
- Cronbach, Lee J., and Paul E. Meehl. 1955. Construct validity in psychological tests. Psychological Bulletin 52: 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delen, Dursun, Cemil Kuzey, and Ali Uyar. 2013. Measuring firm performance using financial ratios: A decision tree approach. Expert Systems with Applications 40: 3970–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Division of Statistics and Scientific Computation. 2012. The University of Texas at Austin. ‘Structural Equation Modeling Using AMOS an Introduction. Available online: https://stat.utexas.edu/images/SSC/Site/AMOS_Tutorial.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- Dotson, Jeffrey P., and Greg M. Allenby. 2010. Investigating the Strategic Influence of Customer and Employee Satisfaction on Firm Financial Performance. Marketing Science 29: 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, Peter J., and Randall S. Schuler. 1990. Human resource management. In Comparative Labor Law and Industrial Relations. Edited by R. Blanpain. Boston: Kluwer Law and Taxation Publishers. [Google Scholar]
- Drury, Colin, and Mike Tayles. 1994. Product costing in UK manufacturing organizations. European Accounting Review 3: 443–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, Colin, S. Braund, P. Osborne, and Mike Tayles. 1993. A Survey of Management Accounting Practices in UK Manufacturing Companies. London: Chartered Association of Certified Accountants. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, Marc J. 2002. Measuring the Payoffs of Corporate Actions: The Use of Financial and Non-Financial Indicators. Performance Measurement and Management Control 12: 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Yi, Jiquan Chen, Gabriela Shirkey, Ranjeet John, Susie R. Wu, Hogeun Park, and Changliang Shao. 2016. Applications of structural equation modeling (SEM) in ecological studies: An updated review. Ecological Processes 5: 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Firth, Michael. 1996. The diffusion of managerial accounting procedures in the People’s Republic of China and the influence of foreign partnered joint ventures. Accounting, Organizations and Society 21: 629–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullerton, Rosemary R., and Cheryl S. McWatters. 2002. The role of performance measures and incentive systems in relation to the degree of JIT implementation. Accounting, Organizations and Society 27: 711–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullerton, Rosemary R., and Cheryl S. McWatters. 2004. An empirical examination of cost accounting practices used in advanced manufacturing environments. Advances in Management Accounting 12: 85–113. [Google Scholar]
- Garver, Michael S., and John T. Mentzer. 1999. Logistics Research Methods: Employing Structural Equation Modeling to Test for Construct Validity. Journal of Business Logistics 20: 33–57. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, Lawrence A., and Danny Miller. 1976. A Contingency Framework for the Design of Accounting Information Systems. Accounting, Organizations and Society 1: 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, Robert T., and White. D. Phillip. 1976. Methodological Considerations in Cross-National Consumer Research. Journal of International Business Studies 7: 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldma, Toomas, and Kertu Lääts. 2002. Contingencies influencing the management accounting practices of Estonian manufacturing companies. Management Accounting Research 13: 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlavacka, Svatopluk, Ljuba Bacharova, Viera Rusnakova, and Robert Wagner. 2001. Performance implications of Porter’s generic strategies in Slovak hospitals. Journal of Management in Medicine 15: 44–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, Charles W., and Dan E. Schendel. 1978. Strategy Formulation: Analytical Concepts. St. Paul: West Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Hopper, Trevor, Tsutomu Koga, and Jitsuo Goto. 1999. Cost accounting in small and medium sized Japanese companies: An exploratory study. Accounting and Business Research 30: 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Li-tze, and Peter M. Bentler. 1999. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling 6: 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Tung-Chun. 2001. The effects of linkage between business and human resource management strategies. Personnel Review 30: 132–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunjra, Ahmed Imran, Farida Faisal, and Faiza Gulshion. 2017. The Impact of Cost Leadership Strategy and Financial Management Control Systems on Organizational Performance in Pakistan’s Services Sector. Lahore Journal of Business 6: 1–19. Available online: http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=bsu&AN=132768389&site=eds-live (accessed on 20 March 2020). [CrossRef]
- Hyvönen, Johanna. 2007. Strategy, performance measurement techniques and information technology of the firm and their links to organizational performance. Management Accounting Research 18: 343–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ittner, Christopher D., and David F. Larcker. 1998. Innovations in performance measurement: Trends and research implications. Journal of Management Accounting Research 10: 205–38. [Google Scholar]
- Ittner, Christopher D., and David F. Larcker. 2002. Empirical managerial accounting research: Are we just describing management consulting practice? European Accounting Review 11: 787–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jogaratnam, Giri, and Eliza Tse Ching-Yick. 2006. Entrepreneurial orientation and the structuring of organizations: Performance evidence from the Asian hotel industry. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management 18: 454–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joop, Hox, and Timo Bechger. 1999. An Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling. Family Science Review 11: 354–373. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, Robert S., and David P. Norton. 1996. The Balanced Scorecard: Translating Strategy into Action. Boston: Harvard Business School Press. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, Kamalesh, Ram Subramanian, and Charles Yauger. 1997. Pure Versus Hybrid: Performance Implications of Porter’s Generic Strategies. Health Care Management Review 22: 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, Bruce T., Dan Marlin, and James J. Hoffman. 1993. Porter’s generic strategies, discontinuous environments, and performance: A longitudinal study of changing strategies in the hospital industry. Health Services Research 28: 623–40. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Feng-Hui, Tzai-Zang Lee, and Wann-Yih Wu. 2010. The relationship between human resource management practices, business strategy and firm performance: Evidence from steel industry in Taiwan. International Journal of Human Resource Management 21: 1351–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, Jonathan, and Tony Siesfield. 1998. Measures that matter: Wall Street considers nonfinancial performance measures more than you think. Strategy & Leadership 26: 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lukason, Oliver, Erkki K. Laitinen, and Arto Suvas. 2019. Growth patterns of small manufacturing firms before failure: Interconnections with financial ratios and nonfinancial variables. International Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management 6: 59–66. Available online: http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=edselc&AN=edselc.2-52.0-84937694615&site=eds-live (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Melián-González, Santiago, Jacques Bulchand-Gidumal, and Beatriz González López-Valcárcel. 2015. New evidence of the relationship between employee satisfaction and firm economic performance. Personnel Review 44: 906–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, Raymond E., and Charles C. Snow. 1978. Organizational Strategy, Structure, and Process. New York: McGraw-Hill. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, Raymond E., and Charles C. Snow. 1984. Fit, failure and the hall of fame. California Management Review 26: 10–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, Danny. 1988. Relating Porter’s Business Strategies to Environment and Structure: Analysis and Performance Implications. The Academy of Management Journal 31: 280–308. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/256549 (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Murray, Alan I. 1988. A contingency view of Porter’s “Generic Strategies. Academy of Management Review 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musi, Yusef W., E. Mukulu, and Margaret Oloko. 2018. Influence of Strategic Planning to Firm Performance in Agricultural Research Based Institutions of Kenya. Journal of Management and Sustainability 8: 83. Available online: http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=edshol&AN=edshol.hein.journals.jms8.41&site=eds-live (accessed on 15 January 2020). [CrossRef]
- Nathan, Berg. 2005. Non-response bias. In Encyclopedia of Social Measure. Edited by K. Kempf-Leonard. London: Academic Press, vol. 2, pp. 865–73. [Google Scholar]
- Nurazi, Ridwan, and Berto Usman. 2015. Public Attention and Financial Information as Determinants of Firms Performance in the Telecommunication Sector. Journal Keuangan Dan Perbankan 19: 235–51. Available online: http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=edsdoj&AN=edsdoj.3a1f395d524847349a6ffedc8cda985c&site=eds-live (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- O’Connor, Neale Gilbert, Chee W. Chow, and Anne Wu. 2004. The adoption of “Western” management accounting/controls in China’s state-owned enterprises during economic transition. Accounting, Organizations and Society 29: 349–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odongo, Nickson Herbert, Daoping Wang, Shaldon Suntu Leparan, and Obadia Bishoge Kyetuza. 2019. Dimensions of organisational performance: A review. International Journal Manufacturing Technology and Management 33: 114–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olwande, Pauline. 2012. The Application of Porter’s Generic Business Strategies and Performance of Pharmaceutical Wholesalers in Kenya. Master’s thesis, Master of Business Administration, School of Business, University of Nairobi, Nairobi, Kenya. [Google Scholar]
- Phadoongsitthi, Monvika. 2003. The Role of Management Accounting in Emerging Economies: An Empirical Study of Thailand’. Ph.D. thesis, University of Maryland, College Park, MD, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Phadoongsitthi, Monvika. 2005. Management Accounting Practices, Concepts, and Cultures. Journal of Accounting Profession 1: 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ping, Robert, Jr. 2004. On assuring valid measures for theoretical models using survey data. Journal of Business Research 57: 125–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, Michael E. 1985. Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance. New York: Free Press. [Google Scholar]
- Premkumar, G., and Katikireddy Ramamurthy. 1995. The Role of Inter-organizational and Organizational Factors on the Decision Mode for the Adoption of Inter-organizational Systems. Decision Sciences 26: 303–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulaj, Enida, Vasilika Kume, and Amali Cipi. 2015. The impact of generic competitive strategies on organizational performance: The evidence from Albanian context. European Scientific Journal 11: 273–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ringov, Dimo, and Maurizio Zollo. 2007. The impact of national culture on corporate social performance. Corporate Governance 7: 476–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidat, Zaid, Mauricio Silva, and Claire Seaman. 2019. The relationship between corporate governance and financial performance: Evidence from Jordanian family and nonfamily firms. Journal of Family Business Management 9: 54–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scapens, Robert W., and Mostafa Jazayeri. 2003. ERP Systems and Management Accounting Change: Opportunities or Impacts? A Research Note. European Accounting Review 12: 201–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarbrough, Paul, Alfred J. Nanni, and Michiharu Sakurai. 1991. Japanese management accounting practices and the effects of assembly and process automation. Management Accounting Research 2: 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, Randall S., and Susan E. Jackson. 1987. Linking Competitive Strategies with Human Resource Management Practices. The Academy of Management Executive (1987–1989) 1: 207–19. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/4164753 (accessed on 15 September 2020). [CrossRef]
- Silveira, Alexandre Di Miceli. 2019. The Employee Is Always Right: Employee Satisfaction and Corporate Performance in Brazil. Revista de Administração Contemporânea 23: 739–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, Daniel H., and Miguel I. Gómez. 2014. Customer satisfaction, competition, and firm performance: An empirical investigation. Managerial and Decision Economics 35: 371–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škrinjar, Rok, Vesna Bosilj-Vukšić, and Mojca Indihar-Štemberger. 2008. The impact of business process orientation on financial and non-financial performance. Business Process Management Journal 14: 738–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista Research Department. 2020. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Contribution in Thailand in 2020, by Sector. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1023315/thailand-gdp-value-contribution-by-sector (accessed on 15 September 2021).
- Sulaiman, Suzana, Aliza Ramli, and Falconer Mitchell. 2008. What Factors Drive Change in Management Accounting in Malaysian Organisations? Malaysian Accounting Review 7: 61–76. [Google Scholar]
- Tavitiyaman, Pimtong, Hailin Qu, and Hanqin Zhang Qiu. 2011. The impact of industry force factors on resource competitive strategies and hotel performance. International Journal of Hospitality Management 30: 648–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toepoel, Vera, and Matthias Schonlau. 2017. Dealing with nonresponse: Strategies to increase participation and methods for postsurvey adjustments. Mathematical Population Studies 24: 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Towler, Annette, Daniel V. Lezotte, and Michael J. Burke. 2011. The service climate-firm performance chain: The role of customer retention. Human Resource Management 50: 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, Ann L. 2000. Hospital financial ratio classification patterns revisited: Upon considering nonfinancial information. Journal of Accounting and Public Policy 19: 73–95. Available online: http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=edsbl&AN=RN077117398&site=eds-live (accessed on 20 August 2020). [CrossRef]
- Wegmann, Grégory, and Evelyne Poincelot. 2012. Non-Financial Indicators and Strategic Management Accounting in Best Practices in Management Accounting. Macmillan: Palgrave. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Yinghong Susan, Saeed Samiee, and Ruby P. Lee. 2014. The influence of organic organizational cultures, market responsiveness, and product strategy on firm performance in an emerging market. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 42: 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, Rebecca, and Paul A. Gore. 2006. SEM 101: A brief guide to structural equation modeling. The Counseling Psychologist 34: 719–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Junjie, Agyenim Boateng, and Colin Drury. 2007. An analysis of the adoption, perceived benefits, and expected future emphasis of western management accounting practices in Chinese SOEs and JVs. The International Journal of Accounting 42: 171–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xydias-Lobo, Maria, David Forsaith, and Carol Tilt. 2004. The future of management accounting: A South Australian perspective. Journal of Management Accounting Research 2: 55–70. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa, Takeo, John Innes, and Falconer Mitchell. 1994. Applying functional cost analysis in a manufacturing environment. International Journal of Production Economics 36: 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
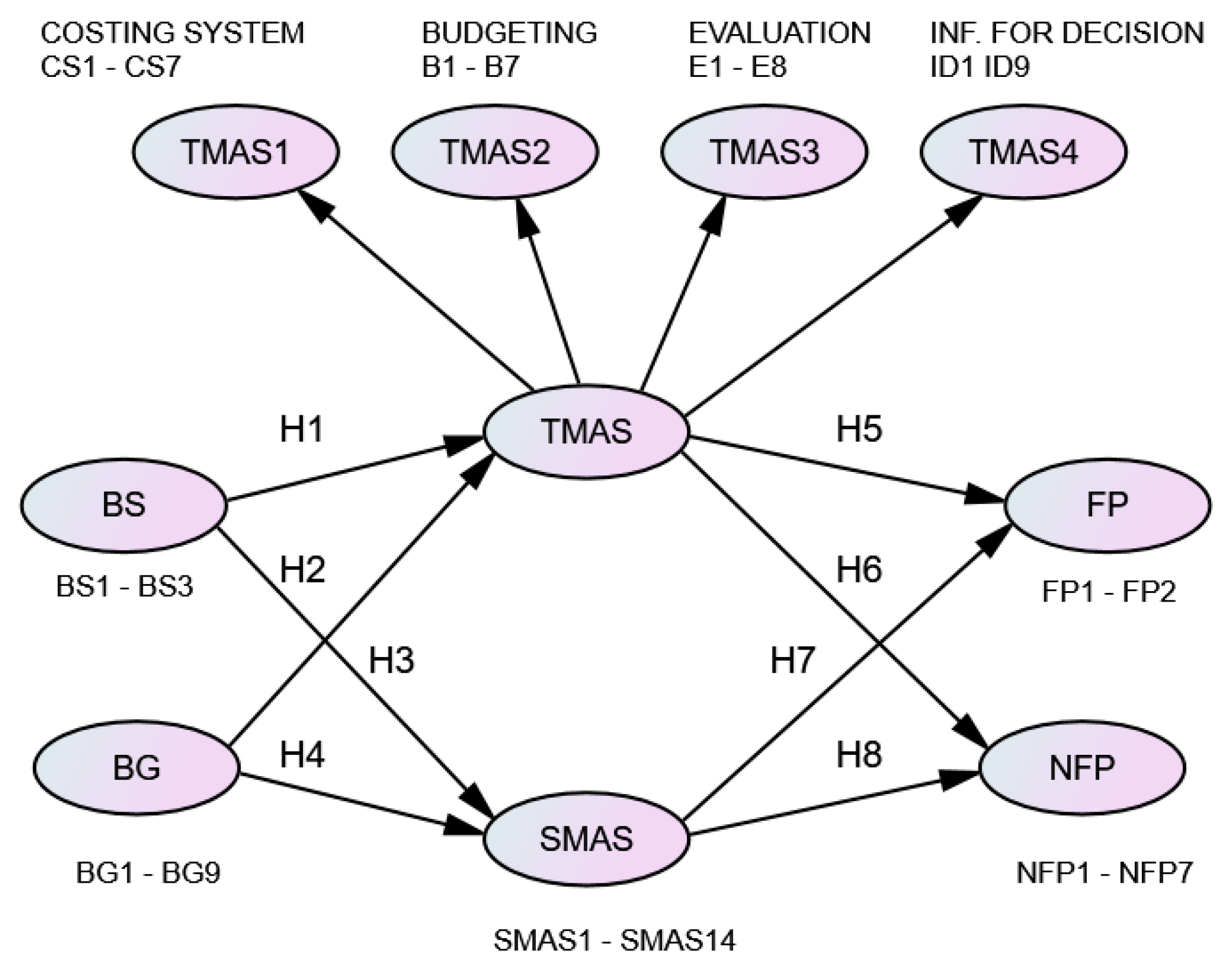
| Independent Variables | Mediated Variables | Dependent Variables | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Independent Variables | Mediated Variables | Dependent Variables | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BS: Business Strategy | TMAS: Traditional Management Accounting System | FP: Financial Performance | ||||||||||
| TMAS1 | TMAS2 | TMAS3 | TMAS4 | |||||||||
| Mean 3.05; SD. 0.94 | Mean 3.23; SD. 0.90 | Mean 3.22; SD. 0.95 | Mean 3.42; SD. 1.05 | |||||||||
| Number of Samples | Mean | Ratio (SD.) | ||||||||||
| BS1 | n = 132 (64.39%) | CS1 | 3.29 | B1 | 4.25 | E1 | 2.82 | ID1 | 3.64 | FP1 | 0.05 (0.10) | |
| BS2 | n = 76 (37.07%) | CS2 | 3.60 | B2 | 4.17 | E2 | 3.92 | ID2 | 3.01 | FP2 | 0.13 (0.55) | |
| BS3 | n = 97 (47.32%) | CS3 | 2.73 | B3 | 2.80 | E3 | 3.38 | ID3 | 3.55 | |||
| CS4 | 3.33 | B4 | 3.73 | E4 | 3.43 | ID4 | 3.78 | |||||
| CS5 | 3.47 | B5 | 2.81 | E5 | 3.07 | ID5 | 2.83 | |||||
| CS6 | 2.79 | B6 | 2.68 | E6 | 3.21 | ID6 | 3.11 | |||||
| CS7 | 2.17 | B7 | 2.18 | E7 | 3.13 | ID7 | 4.14 | |||||
| E8 | 2.77 | ID8 | 3.71 | |||||||||
| ID9 | 3.02 | |||||||||||
| BG: Business Goal | SMAS: Strategic Management Accounting System (Mean 3.07; SD. 1.38) | NFP: Non-Financial Performance | ||||||||||
| Mean | Mean | Mean | % (SD.) | |||||||||
| BG1 | 4.48 (0.66) | SMAS1 | 2.48 | SMAS8 | 3.27 | NFP1 | 86.06% (14.28) | |||||
| BG2 | 4.10 (0.91) | SMAS2 | 2.49 | SMAS9 | 2.71 | NFP2 | 83.13% (15.94) | |||||
| BG3 | 4.03 (0.77) | SMAS3 | 3.05 | SMAS10 | 3.43 | NFP3 | 82.75% (63.04) | |||||
| BG4 | 3.99 (0.84) | SMAS4 | 3.03 | SMAS11 | 3.26 | NFP4 | 78.55% (13.13) | |||||
| BG5 | 3.97 (0.90) | SMAS5 | 3.16 | SMAS12 | 3.51 | NFP5 | 77.99% (12.22) | |||||
| BG6 | 3.85 (0.86) | SMAS6 | 2.79 | SMAS13 | 3.64 | NFP6 | 77.91% (12.88) | |||||
| BG7 | 3.78 (0.95) | SMAS7 | 2.58 | SMAS14 | 3.58 | NFP7 | 72.29% (15.84) | |||||
| BG8 | 3.64 (0.88) | |||||||||||
| BG9 | 3.61 (0.85) | |||||||||||
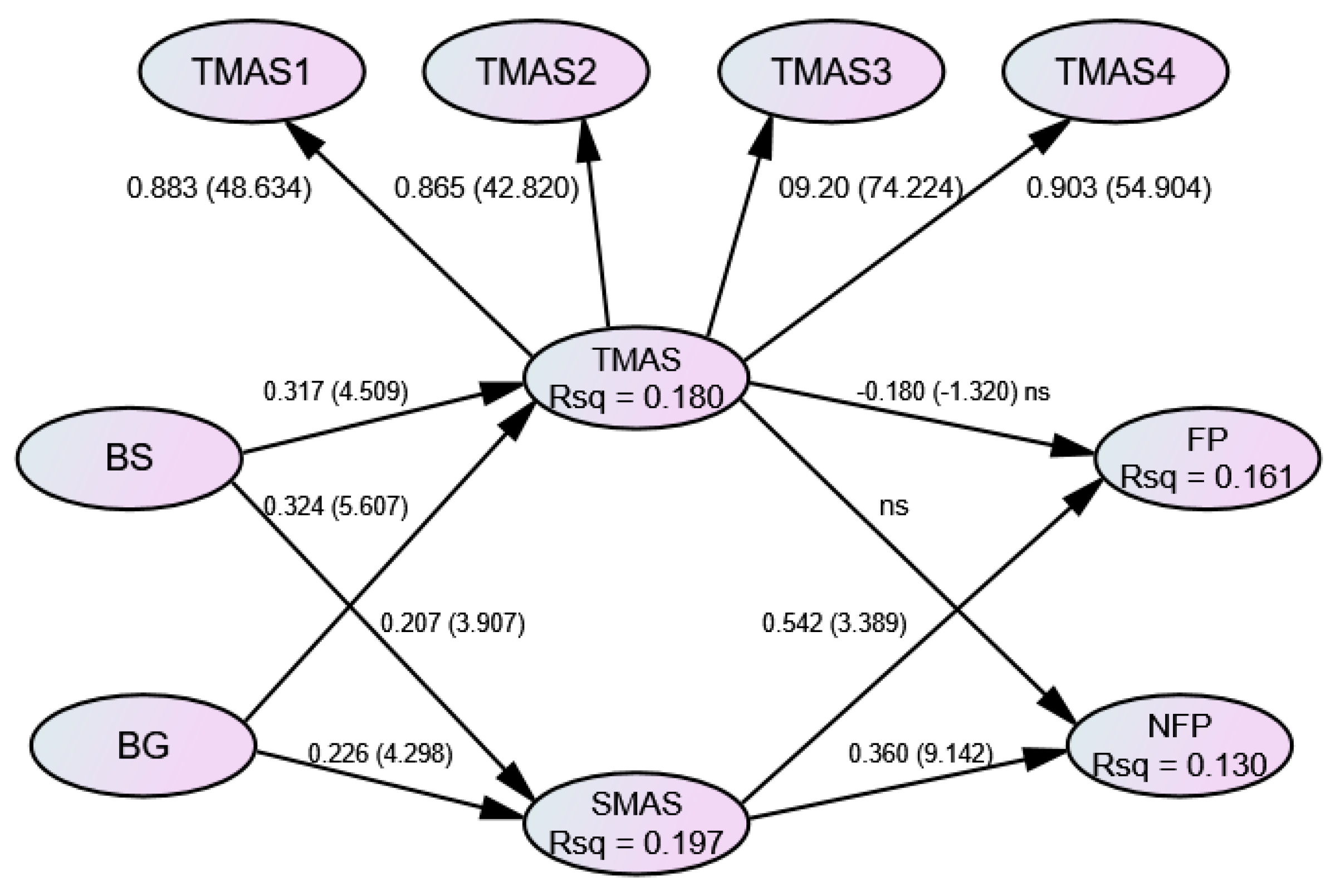
| Exogenous Variable | R-Square | Effect | Regression Coefficients of Independent Studies | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BS | BG | TMAS | SMAS | |||
| FP | 0.161 | Direct | 0.000 | 0.000 | −0.180 ns | 0.542 ** |
| Indirect | 0.119 | 0.085 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| Total | 0.119 | 0.085 | −0.180 | 0.542 | ||
| NFP | 0.130 | Direct | 0.000 | 0.000 | N/A | 0.360 ** |
| Indirect | 0.117 | 0.081 | N/A | 0.000 | ||
| Total | 0.117 | 0.081 | N/A | 0.360 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Visedsun, N.; Terdpaopong, K. The Effects of the Strategy and Goal on Business Performance as Mediated by Management Accounting Systems. Economies 2021, 9, 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies9040149
Visedsun N, Terdpaopong K. The Effects of the Strategy and Goal on Business Performance as Mediated by Management Accounting Systems. Economies. 2021; 9(4):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies9040149
Chicago/Turabian StyleVisedsun, Nimnual, and Kanitsorn Terdpaopong. 2021. "The Effects of the Strategy and Goal on Business Performance as Mediated by Management Accounting Systems" Economies 9, no. 4: 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies9040149
APA StyleVisedsun, N., & Terdpaopong, K. (2021). The Effects of the Strategy and Goal on Business Performance as Mediated by Management Accounting Systems. Economies, 9(4), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies9040149





