The Dynamic Impacts of Monetary Policy Uncertainty Shocks
Abstract
1. Introduction
Uncertainty in the Literature
2. Empirical Framework
- Draw (multivariate normal);
- Draw ) (inverse Wishart);
- Draw ) (independent inverse gammas);
- Draw (multivariate normal).
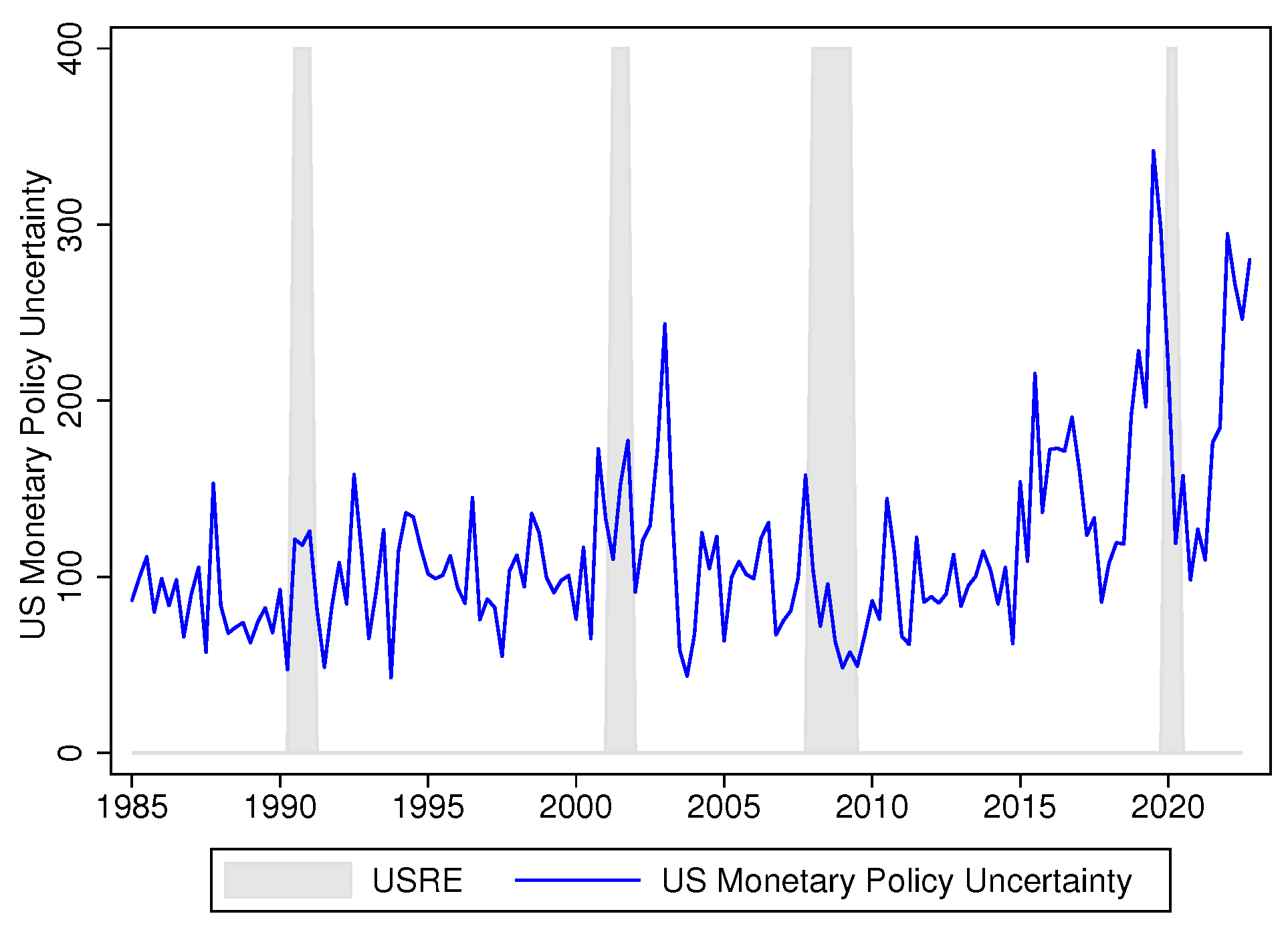
2.1. Variables in the System and Identification Strategy
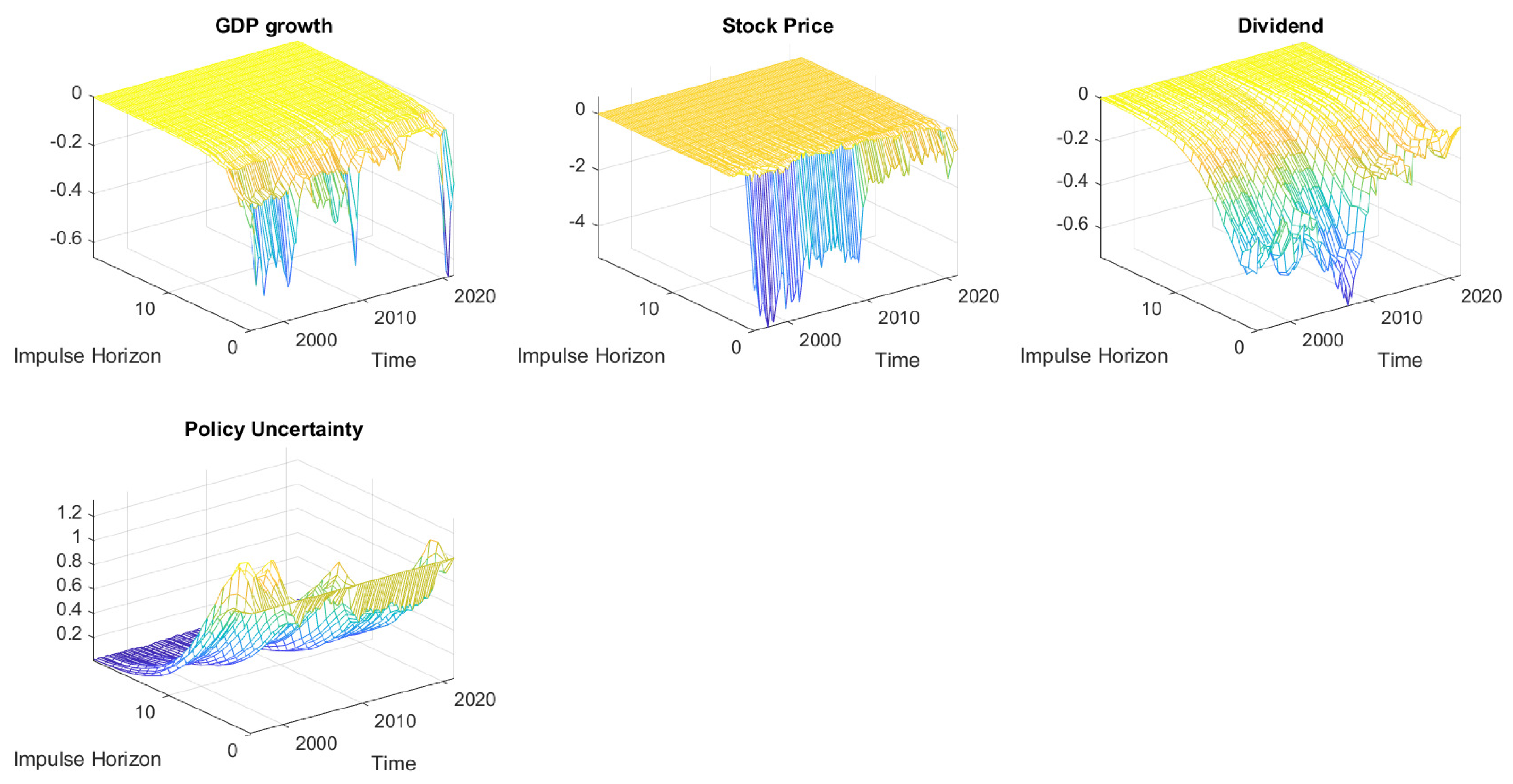
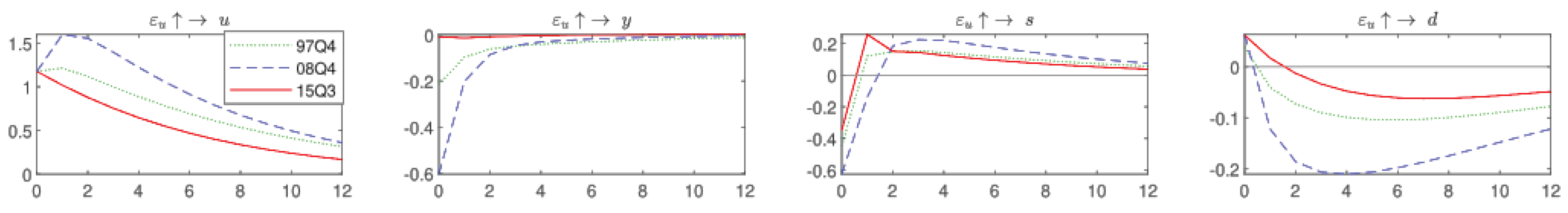
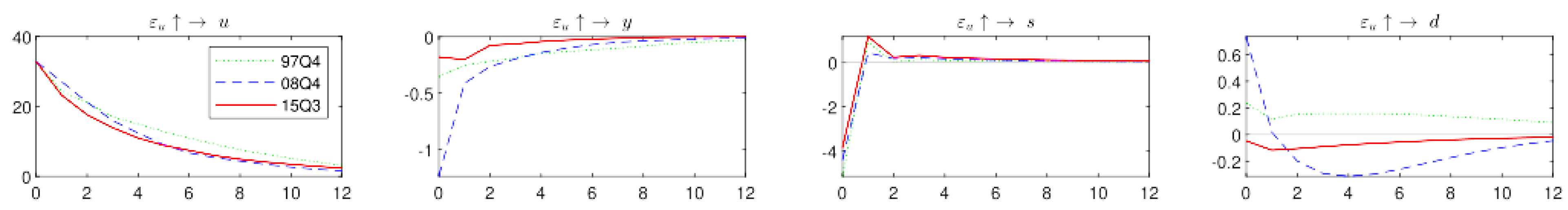
2.2. Impulse Response to Uncertainty Shocks
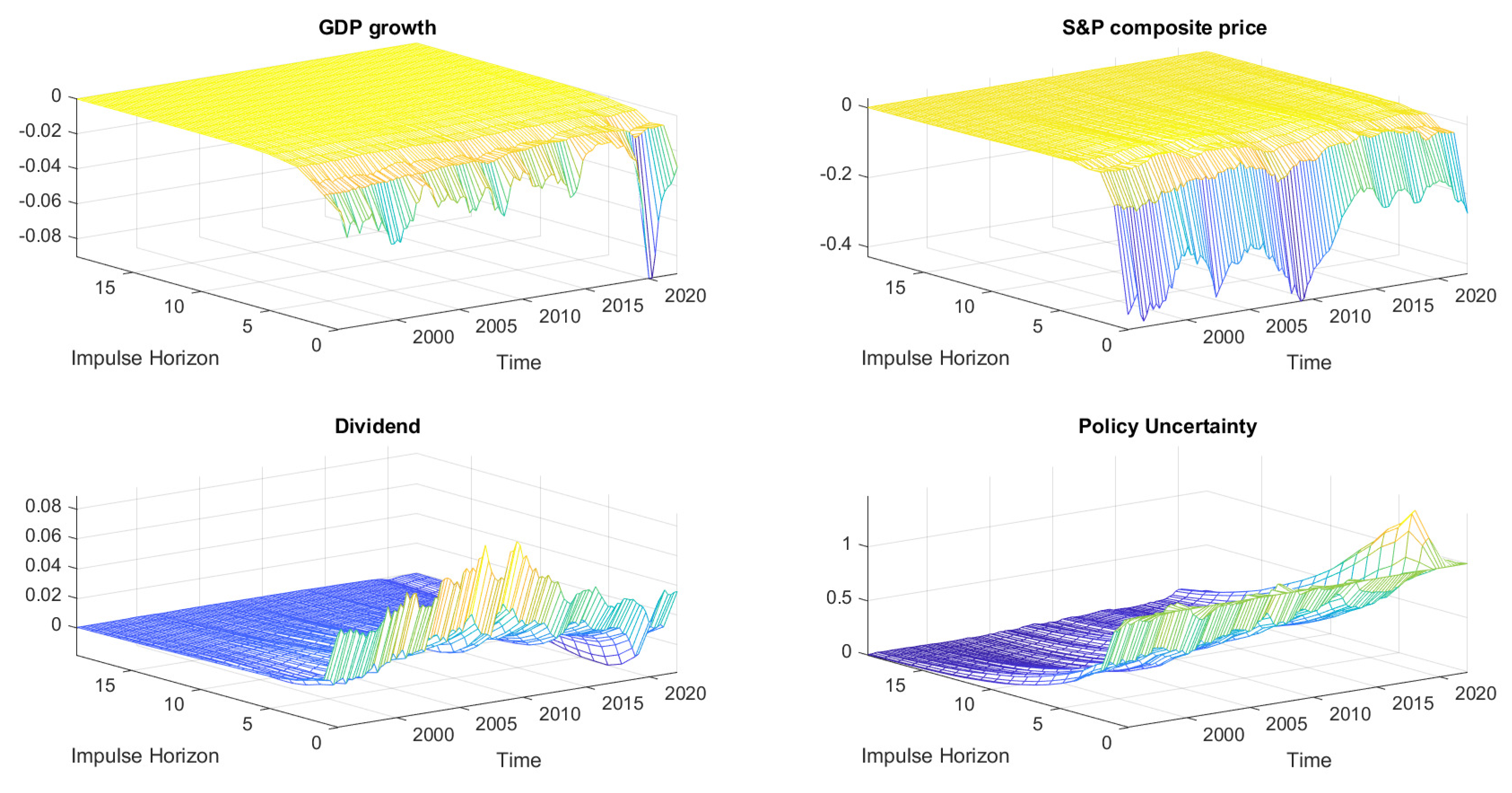
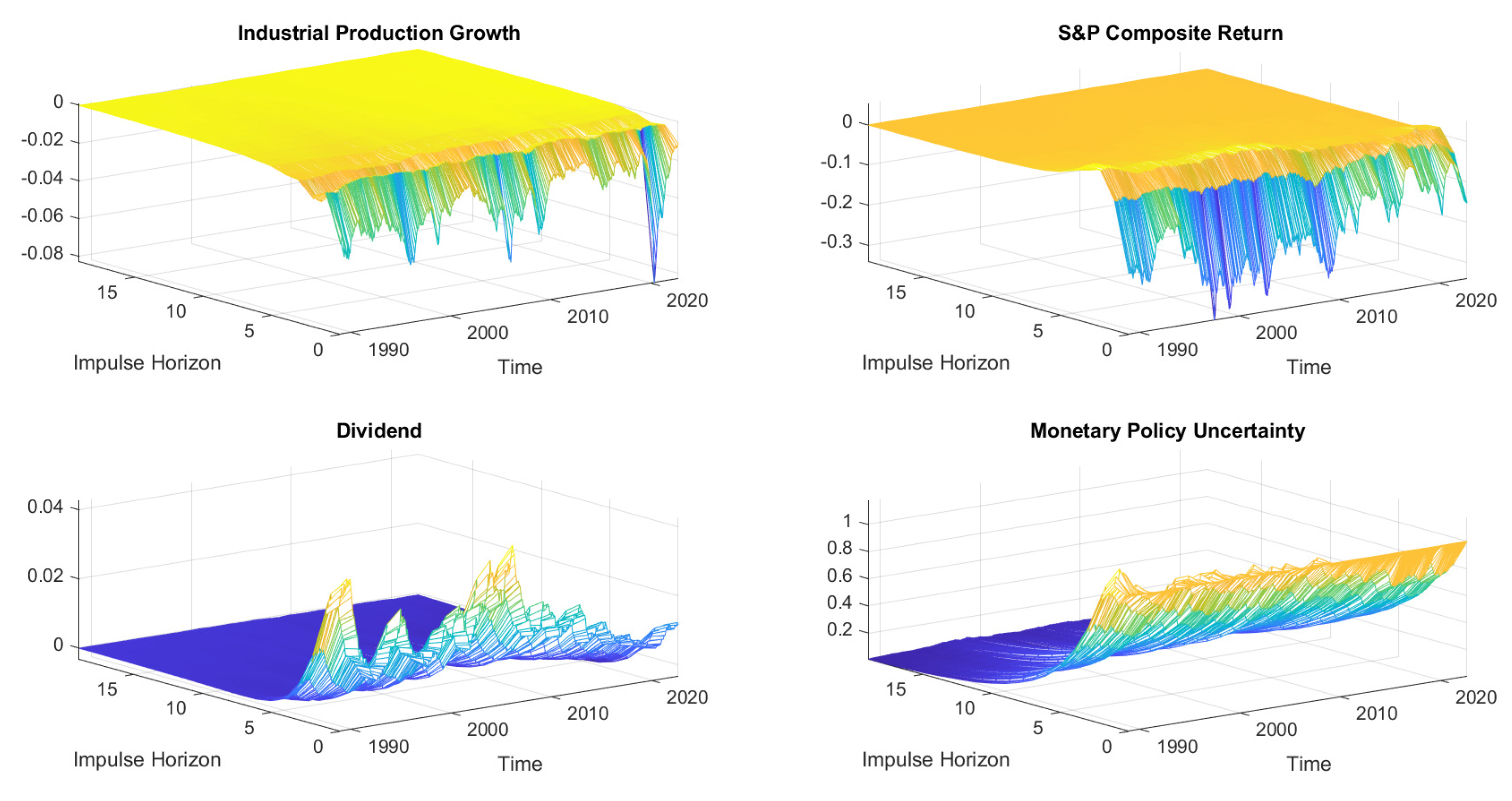
2.3. Robustness Checks
Dynamic Impacts of Uncertainty Shocks Using Monthly Data
3. A Monte Carlo Experiment: A DSGE Analysis
3.1. Household Sector
Wage Setting
3.2. Firms
3.2.1. Final Good Producers
3.2.2. Intermediate Goods Producers
3.3. Monetary Policy
3.4. Market Clearing Conditions
- Goods markets:
- Asset Markets:
- Stock Markets:
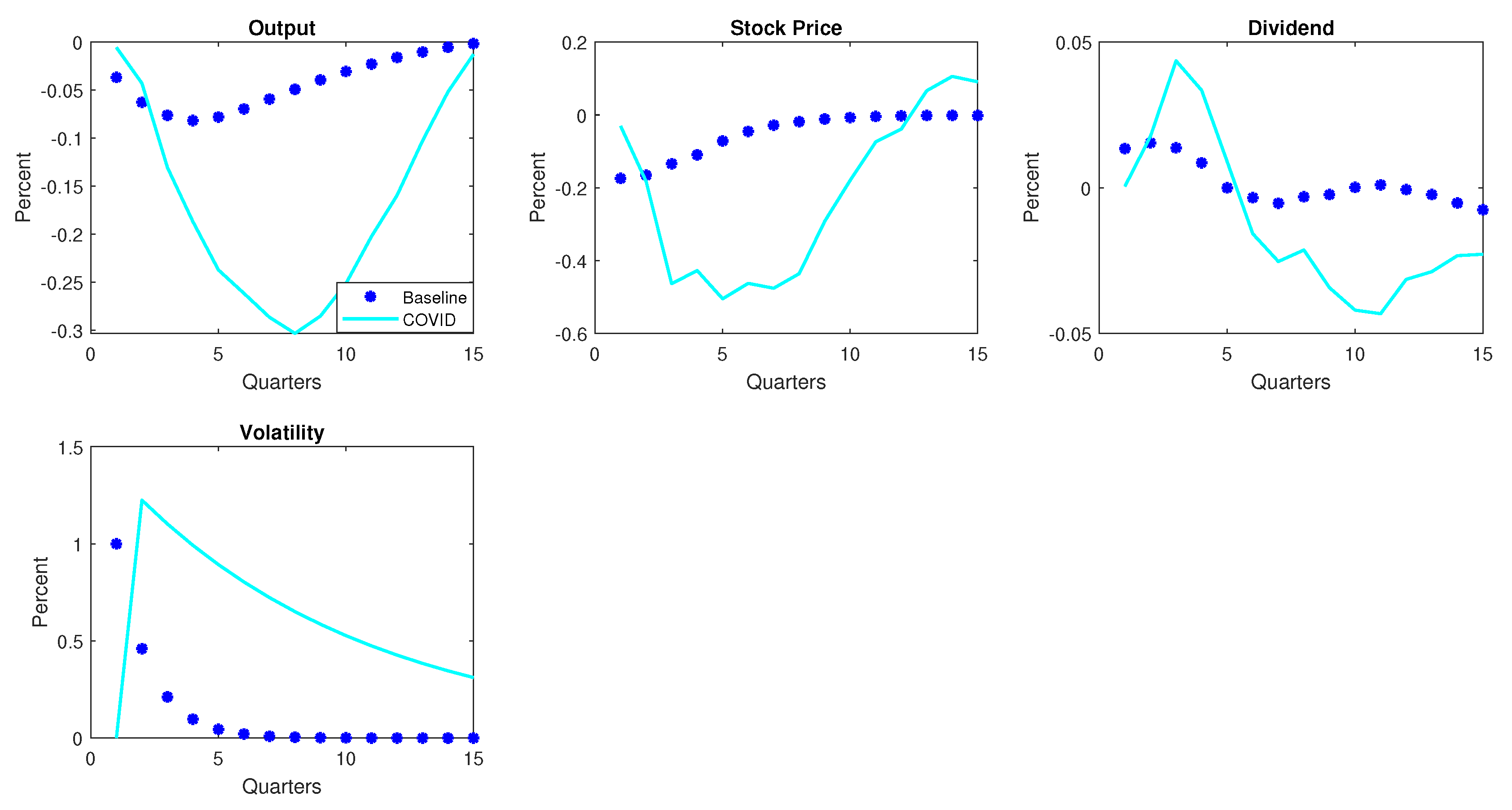
3.5. COVID-19 and Uncertainty Shocks
3.6. Parameterization of the Model
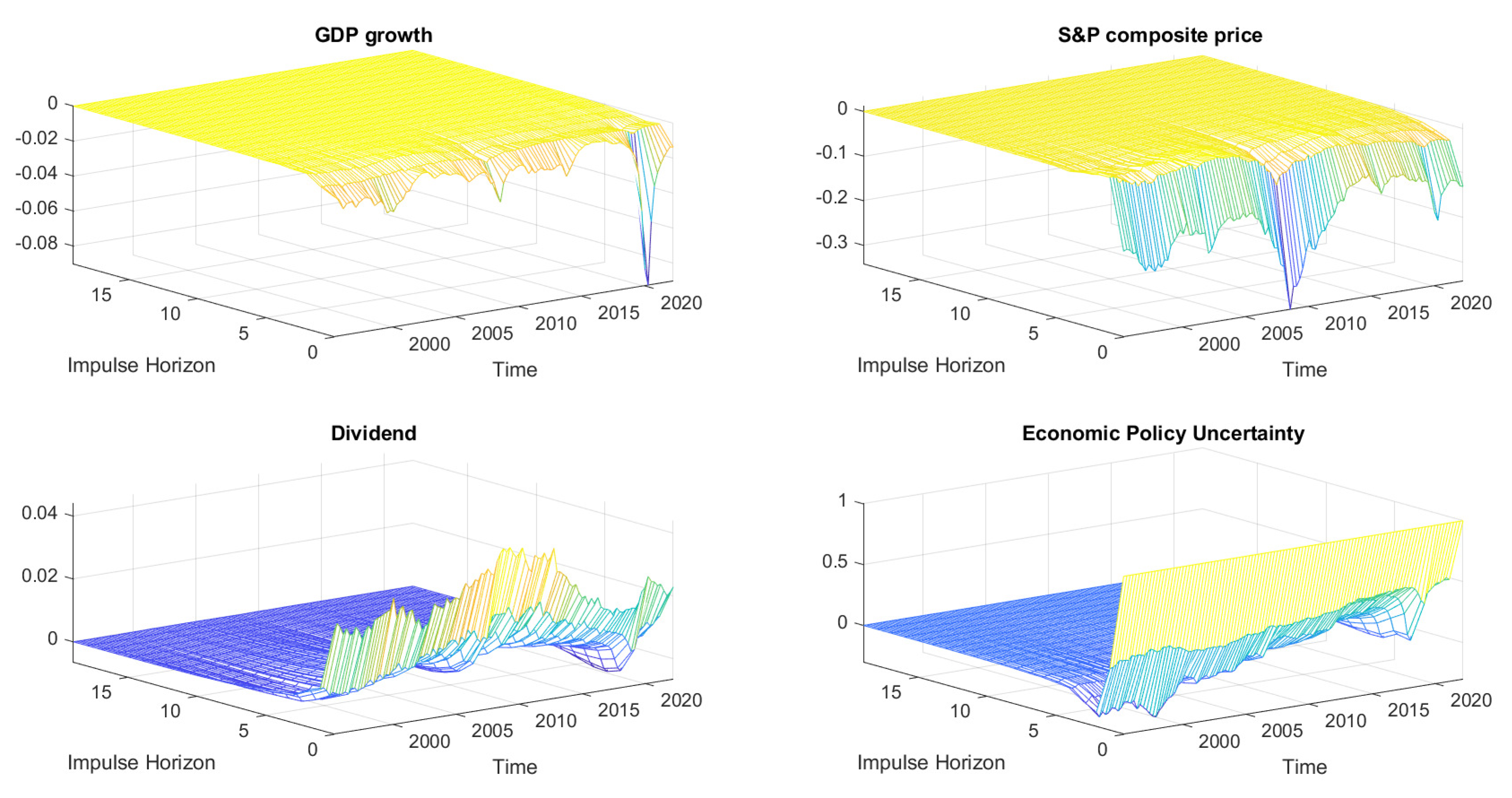
3.6.1. DSGE Interpretation of Empirical Results
3.6.2. COVID-19 and Uncertainty Shocks
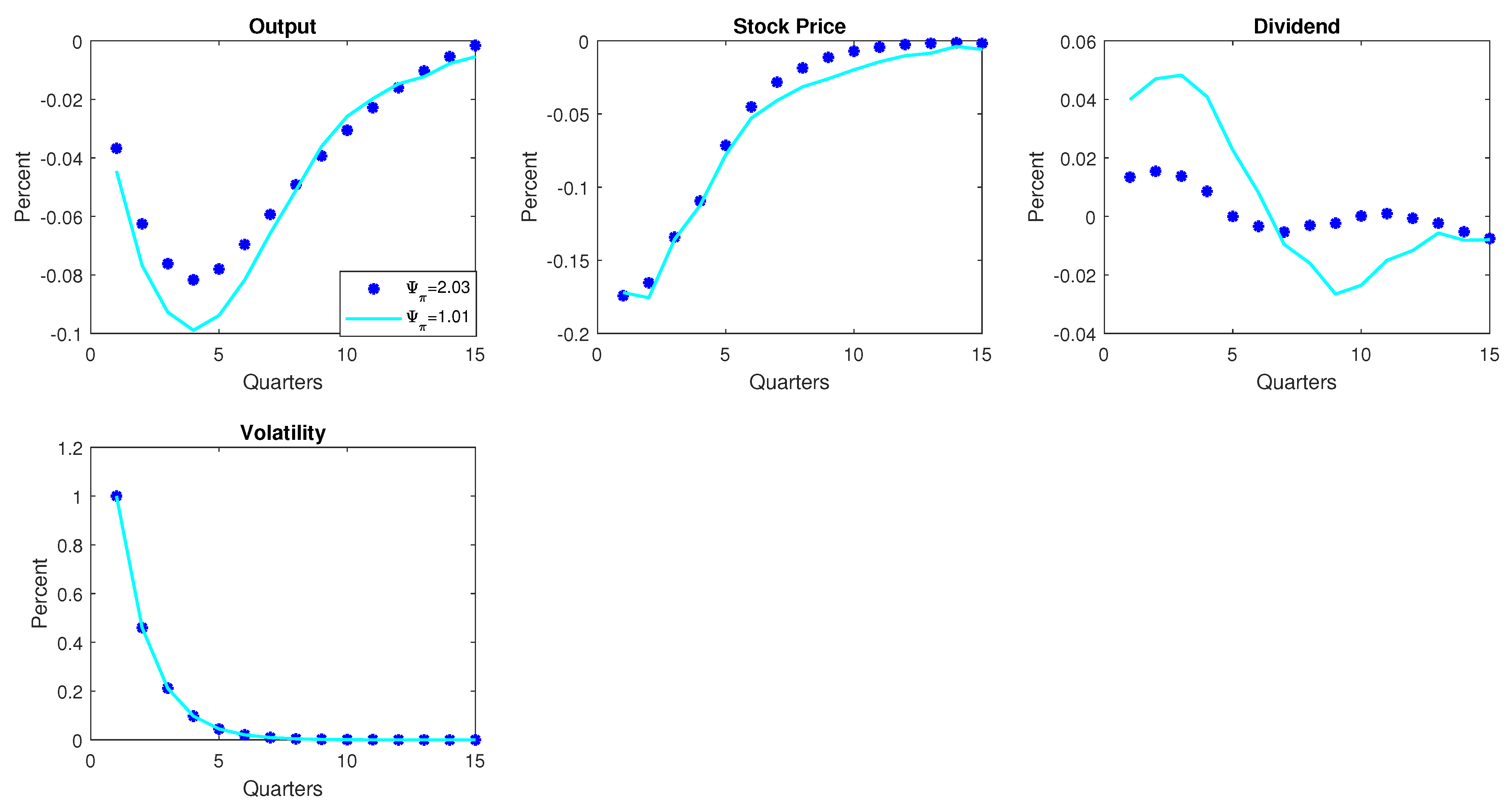
3.6.3. Hawkish/Dovish Monetary Policy
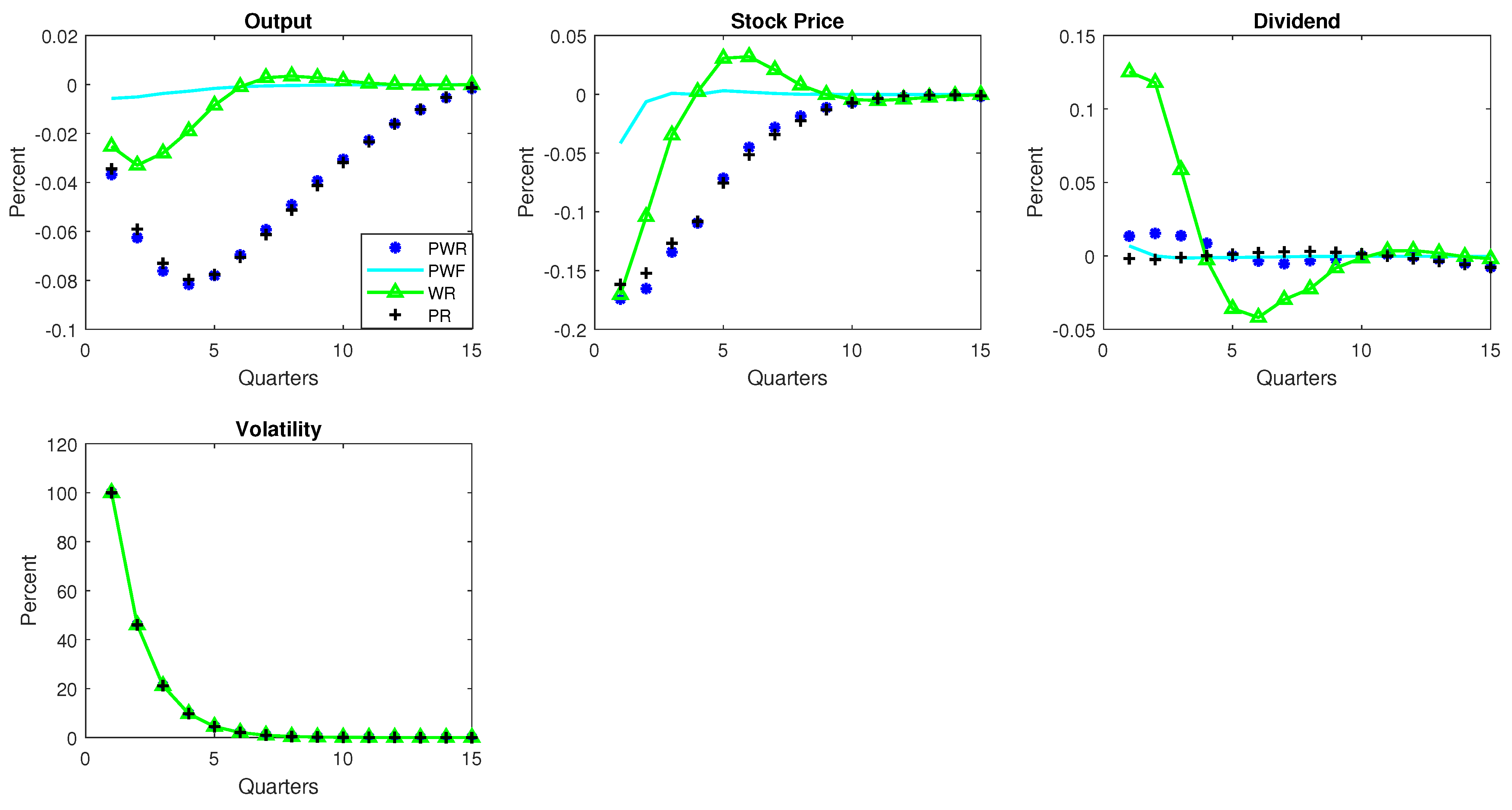
3.6.4. Price and Wage Rigidity
4. Conclusions and Discussions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Uncertainty Impacts Using the Michigan Uncertainty Proxy
References
- Abel, Andrew B. 1983. Optimal Investment under Uncertainty. American Economic Review 73: 228–33. [Google Scholar]
- Aghion, Philippe, Abhijit Banerjee, and Thomas Piketty. 1999. Dualism and Macroeconomic Activity. Quarterly Journal of Economics 114: 1359–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, Scott R., Nicholas Bloom, and Steven J. Davis. 2015. Measuring Economic Policy Uncertainty. The Quarterly Journal of Economics 131: 1593–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, Ravi, and Amir Yaron. 2004. Risks for the Long Run: A Potential Resolution of Asset Pricing Puzzles. The Journal of Finance 59: 1481–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, Susanto, and Brent Bundick. 2017. Uncertainty Shocks in a Model of Effective Demand. Econometrica 85: 937–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beetsma, Roel, and Massimo Giuliodori. 2012. The Changing Macroeconomic Response to Stock Market Volatility Shocks. Journal of Macroeconomics 34: 281–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernanke, Ben S. 1983. Irreversibility, uncertainty, and cyclical investment. Quarterly Journal of Economics 98: 85–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, Ambrogio, and Emilio Fernandez Corugedo. 2018. Uncertainty, Financial Frictions, and Nominal Rigidities: A QUantitative Investigation. Journal of Money, Credit, and Banking 50: 603–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, Nicholas. 2009. The Impact of Uncertainty Shocks. Econometrica 77: 623–85. [Google Scholar]
- Bordo, Michael D., John V. Duca, and Christoffer Koch. 2016. Economic policy uncertainty and the credit channel:Aggregate and bank level U.S. evidence over several decades. Journal of Financial Stability 26: 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, Benjamin, and Johannes Pfeifer. 2014. Policy risk and the business cycle. Journal of Monetary Economics 68: 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, Thomas, Marlène Isoré, and Fabien Tripier. 2019. Uncertainty shocks and firm creation: Search and monitoring in the credit market. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Contorl 99: 19–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canova, Fabio, and Luca Sala. 2009. Back to Square one: Identification issues in DSGE models. Journal of Monetary Economics 56: 431–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriero, Andrea, Haroon Mumtaz, Konstantinos Theodoridis, and Angeliki Theophilopoulou. 2015. The Impact of Uncertainty Shocks under Measurement Error: A Proxy SVAR Approach. Journal of Money, Credit, and Banking 47: 1221–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Joshua, Gary Koop, Dale J. Poirier, and Justin L. Tobias. 2020. Bayesian Econometric Methods, 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Sangyup, Davide Furceri, Yi Huang, and Prakash Loungani. 2018. Aggregate uncertainty and sectoral productivity growth: The role of credit constraints. Journal of International Money and Finance 88: 314–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiano, Lawrence J., Roberto Motto, and Massimo Rostagno. 2014. Risk Shocks. American Economic Review 104: 27–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challe, Edouard, and Chryssi Giannitsarou. 2014. Stock Prices and Monetary Policy Shocks: A General Equilibrium Approach. Journal of Economic Control and Dynamics 40: 46–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davig, Troy, and Eric M. Leeper. 2007. Generalizing the Taylor Principle. American Economic Review 97: 607–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Villaverde, Jesus, Pablo Guerron-Quintana, Juan F. Rubio-Ramirez, and Martin Uribe. 2011. Risk Matters: The Real Effects of Volatility Shocks. The American Economic Review 101: 2530–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, Simon, Jae W. Sim, and Egon Zakrajsek. 2017. Uncertainty, Financial Frictions, and Investment Dynamics. NBER Working Paper 20038. Cambridge: National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc. [Google Scholar]
- Hartman, Richard. 1972. The effects of price and cost uncertainty on investment. The Journal of Economic Theort 5: 258–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, Boris, Gert Peersman, and Roland Straub. 2012. Time variation in U.S. wage dynamics. Journal of Monetary Economics 59: 769–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husted, Lucas, John Rogers, and Bo Sun. 2017. Monetary Policy Uncertainty. Journal of Monetary Economics 115: 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leduc, Sylvain, and Zheng Liu. 2016. Uncertainty Shocks are Aggregate Demand Shocks. Journal of Monetary Economics 82: 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, Haroon, and Konstantinos Theodoridoris. 2018. The Changing Transmission of Uncertainty Shocks in the US. Journal of Business and Economic Statistics 36: 239–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, Haroon, and Paolo Surico. 2018. Policy uncertainty and aggregate fluctuations. Journal of Applied Econometrics 33: 319–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oi, Walter Y. 1961. The desirability of price instability under perfect competition. Econometrica 29: 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smets, Frank, and Rafael Wouters. 2007. Shocks and Frictions in U.S. Business Cycles: A Bayesian DSGE Approach. American Economics Review 97: 586–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, Fabian. 2017. Aggregate Uncertainty and the Supply of Credit. Journal of Banking and Finance 81: 150–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kamara, A.; Koirala, N.P. The Dynamic Impacts of Monetary Policy Uncertainty Shocks. Economies 2023, 11, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies11010017
Kamara A, Koirala NP. The Dynamic Impacts of Monetary Policy Uncertainty Shocks. Economies. 2023; 11(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies11010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleKamara, Ahmed, and Niraj P. Koirala. 2023. "The Dynamic Impacts of Monetary Policy Uncertainty Shocks" Economies 11, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies11010017
APA StyleKamara, A., & Koirala, N. P. (2023). The Dynamic Impacts of Monetary Policy Uncertainty Shocks. Economies, 11(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/economies11010017




