A Fused Variable by Night Light Images and MODIS Products for Improving Urban Built-Up Area Extraction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
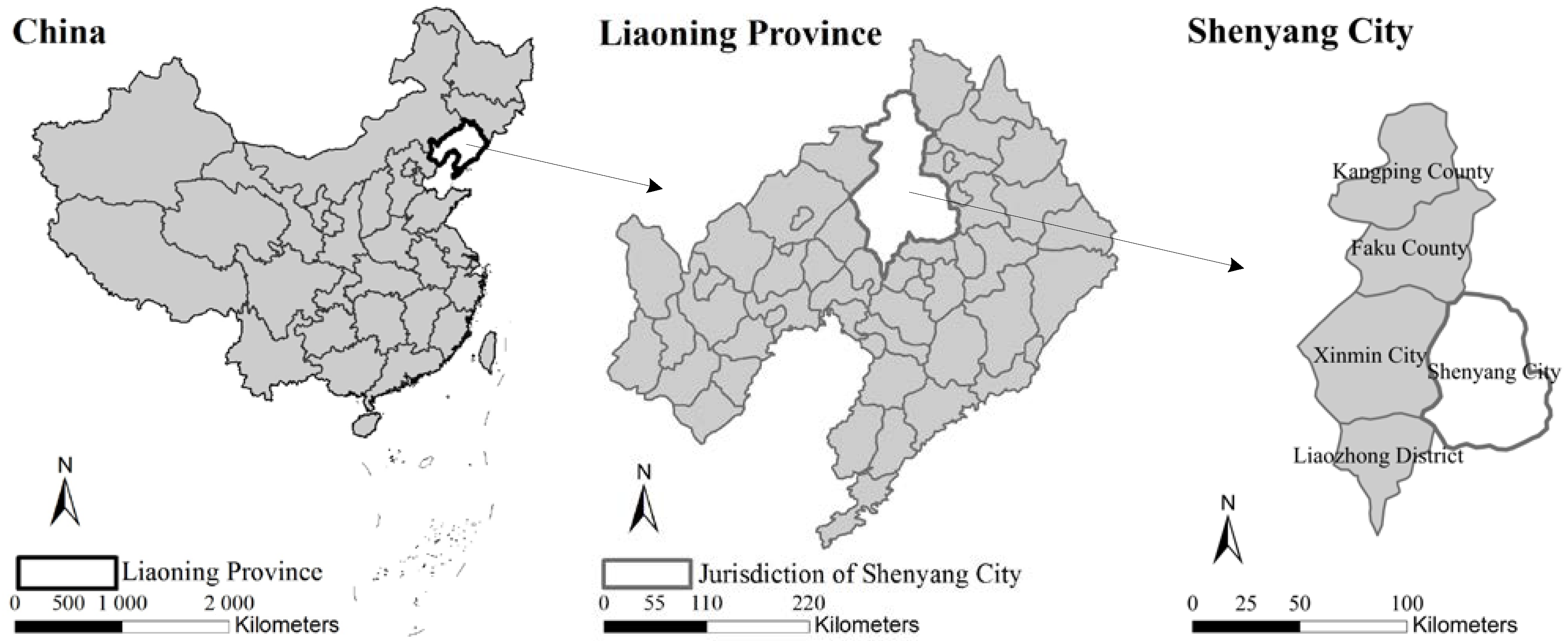
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
Extraction Areas
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Preprocessing
3.2. Normalized Urban Built-Up Area Index (NUBAI) Considering Surface Temperature and Vegetation Index
3.3. Threshold Determination by Reference Data from Landsat Images
3.4. Accuracy Assessment of Area Sizes and Spatial Locations
4. Results
4.1. Fusion Results of Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data
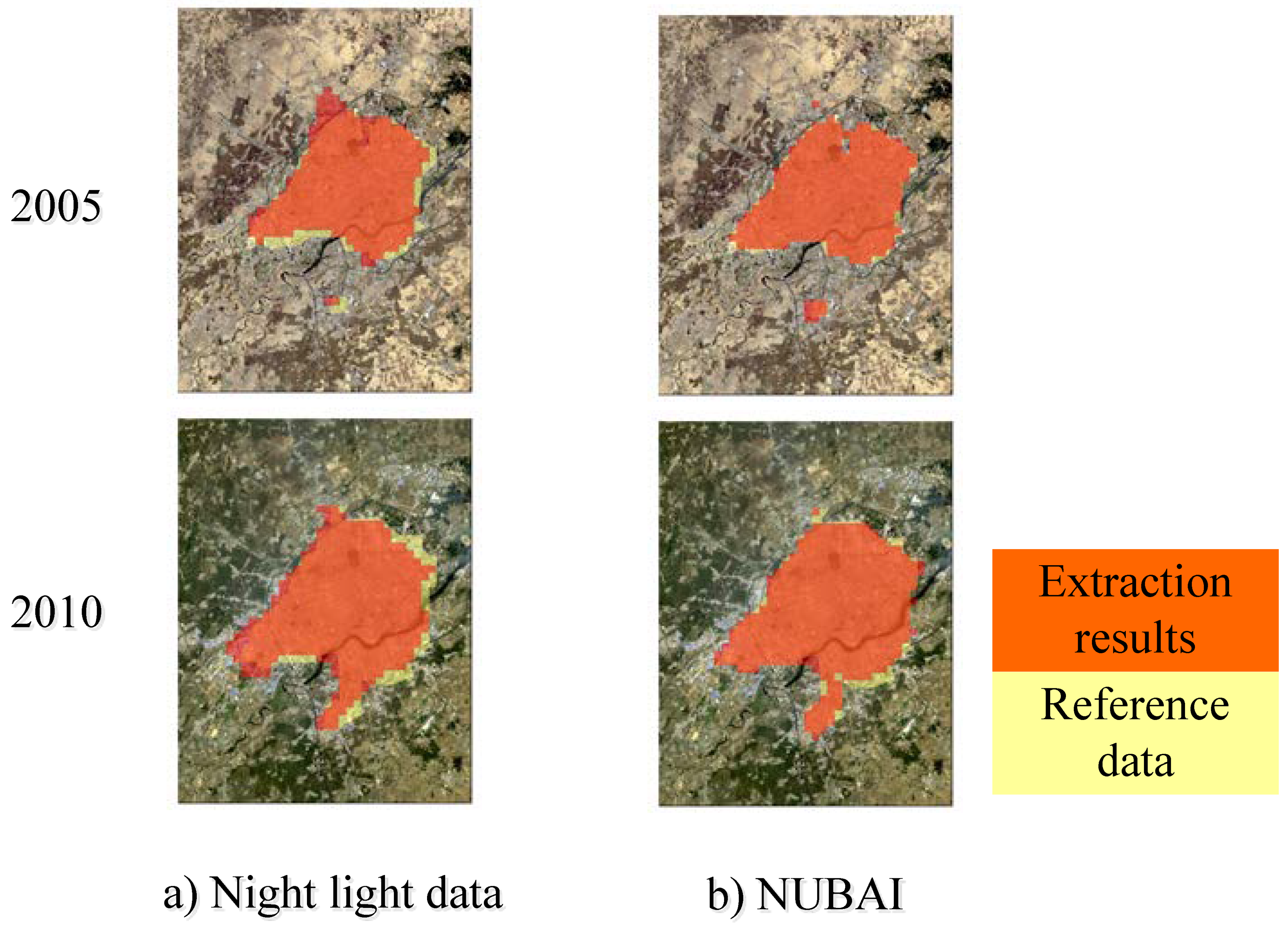
4.2. Extraction Results of Built-up Areas
4.2.1. Extraction Areas
4.2.2. Accuracy Analysis
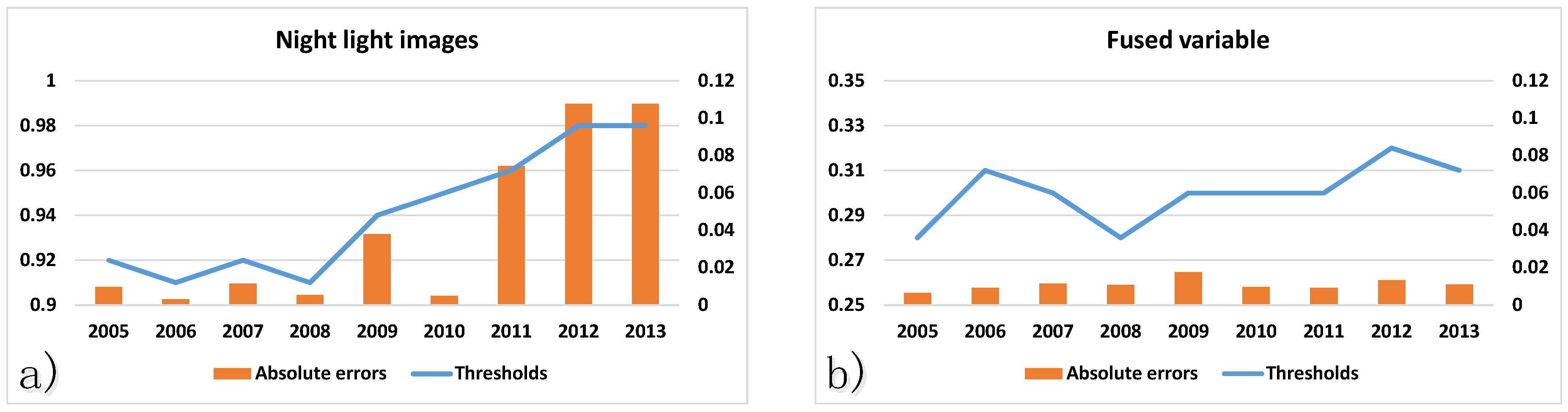
4.3. Optimal Thresholds for Different Periods
5. Discussions
5.1. Major Findings from the Experiments
5.2. Limitations of This Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, C.; Hu, L.; Cook, I.G. China’s urbanization in 1949–2015: Processes and driving forces. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Fang, S.; Gong, Y.; Tao, P.; Yang, G.; Gong, W. Understanding the Correlation between Landscape Pattern and Vertical Urban Volume by Time-Series Remote Sensing Data: A Case Study of Melbourne. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Ning, X.; Li, L. Gauging the impacts of urbanization on CO2 emissions from the construction industry: Evidence from China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsa-Barreiro, J.; Li, Y.; Morales, A.; Pentland, A.S. Globalization and the shifting centers of gravity of world’s human dynamics: Implications for sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Huang, C.; Yu, B.; Yin, B.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J. Evaluation of NPP-VIIRS night-time light composite data for extracting built-up urban areas. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Fan, P.; Chen, J. Urban Built-up Areas in Transitional Economies of Southeast Asia: Spatial Extent and Dynamics. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G. Urban Area Extraction by Regional and Line Segment Feature Fusion and Urban Morphology Analysis. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, H.; Song, W.; Yu, B.; Xiu, C. Normalization of time series DMSP-OLS nighttime light images for urban growth analysis with Pseudo Invariant Features. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 128, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Pei, T.; Haynie, S.; Fan, J. Quantitative estimation of urbanization dynamics using time series of DMSP/OLS nighttime light data: A comparative case study from China’s cities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Qi, K.; Guan, Q.; Wu, C.; Yu, J.; Qing, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wu, H.; Li, X. A Scientometric Visualization Analysis for Night-Time Light Remote Sensing Research from 1991 to 2016. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Xu, H.; Wu, C. Intercalibration between DMSP/OLS and VIIRS night-time light images to evaluate city light dynamics of Syria’s major human settlement during Syrian Civil War. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5934–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y. Extracting the dynamics of urban expansion in China using DMSP-OLS nighttime light data from 1992 to 2008. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 106, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; He, S.; Peng, J.; Li, W.; Zhong, X. Intercalibration of DMSP-OLS night-time light data by the invariant region method. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 7356–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milesi, C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Nemani, R.R.; Running, S.W. Assessing the impact of urban land development on net primary productivity in the southeastern United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, P. Modeling population density with night-time satellite imagery and GIS. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 1997, 21, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, P.; Roberts, D.; Elvidge, C.; Baugh, K. Census from Heaven: An estimate of the global human population using night-time satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 3061–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, M.L.; Lawrence, W.T.; Stutzer, D.C.; Elvidge, C.D. A technique for using composite DMSP/OLS ‘‘city lights’’ satellite data to map urban area. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, M.; Yeh, E.T.; Gong, P.; Elvidge, C.; Baugh, K. Validation of urban boundaries derived from global night-time satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Shi, P.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhuo, L.; Toshiaki, I. Restoring urbanization process in China in the 1990s by using non-radiance calibrated DMSP/OLS nighttime light imagery and statistical data. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 1614–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, J.; Imura, H.; Higashi, O. A SVM-based method to extract urban areas from DMSP-OLS and SPOT VGT data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2205–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Masek, J.; Schwaller, M.; Hall, F. On the blending of the Landsat and MODIS surface reflectance: Predicting daily Landsat surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Gao, F.; Chen, X.; Masek, J.G. An enhanced spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model for complex heterogeneous regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Helmer, E.H.; Gao, F.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Lefsky, M.A. A flexible spatiotemporal method for fusing satellite images with different resolutions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 172, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wang, J.; Song, H.; Fu, D.; Wong, K. Generating High Spatiotemporal Resolution Land Surface Temperature for Urban Heat Island Monitoring. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Song, H. Spatiotemporal Reflectance Fusion via Sparse Representation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3707–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Schaaf, C.; Seto, K.C. The Vegetation Adjusted NTL Urban Index: A new approach to reduce saturation and increase variation in nighttime luminosity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.; Yan, F. Urban structural evolution over a century in Changchun city, Northeast China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 1877–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Tian, H.; Zhou, G.; Ge, H. Regional mapping of human settlements in southeastern China with multisensor remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3668–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.H.; Lu, D.S.; Schubring, J. Estimation of land surface temperature-vegetation abundance relationship for urban heat island studies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C. Estimation of urban vegetation abundance by spectral mixture analysis. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 1305–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, P.C. A scale-adjusted measure of “Urban sprawl” using nighttime satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Schneider, A.; Friedl, M.A. Mapping sub-pixel urban expansion in China using MODIS and DMSP/OLS nighttime lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Pozzi, F.; Elvidge, C.D. Spatial analysis of global urban extent from DMSP-OLS night lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; He, S.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, H.; Kong, H. Effects of the socio-economic influencing factors on SO2 pollution in Chinese cities: A spatial econometric analysis based on satellite observed data. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, R.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Guo, X.; Niu, Z.; Liu, H. Investigation of Urbanization Effects on Land Surface Phenology in Northeast China during 2001–2015. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Wan, H. Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of Urban Heat Island and Their Relationship with Land Cover Changes in Urbanization Process: A Case Study in Suzhou, China. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2010, 38, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Cai, C. Regional Urban Extent Extraction Using Multi-Sensor Data and One-Class Classification. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7671–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcik, F.B. Determining the impact of urban components on land surface temperature of Istanbul by using remote sensing indices. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 859–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morabito, M.; Crisci, A.; Messeri, A.; Orlandini, S.; Raschi, A.; Maracchi, G.; Munafo, M. The impact of built-up surfaces on land surface temperatures in Italian urban areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.P.; Quattrochi, D.A.; Luvall, J.C. Application of high-resolution thermal infrared remote sensing and GIS to assess the urban heat island effect. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Ripley, D.A. On the relation between NDVI, fractional vegetation cover, and leaf area index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; He, C.; Zhang, Q.; Han, L.; Du, S. Timely and accurate national-scale mapping of urban land in China using Defense Meteorological Satellite Program’s Operational Linescan System nighttime stable light data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the normalized difference water index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberg, A.J.; Park, J.W.; Hager, B.W.; Brock, M.V.; Diener-West, M. The use of “overall accuracy” to evaluate the validity of screening or diagnostic tests. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2004, 19, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Zhang, P. Simulation analysis on spatial pattern of urban population in Shenyang City, China in Late 20th century. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Ye, X.; Zheng, Z.; Li, D.; Sun, L.; Li, R.; Benya, S. Modeling Polycentric Urbanization Using Multisource Big Geospatial Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Duan, P.; Wang, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, B. The Extraction of Built-up Areas in Chinese Mainland Cities Based on the Local Optimal Threshold Method Using NPP-VIIRS Images. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2021, 49, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chen, Y. A Genetic Algorithm-Based Urban Cluster Automatic Threshold Method by Combining VIIRS DNB, NDVI, and NDBI to Monitor Urbanization. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Gao, D. Street-Scale Analysis of Population Exposure to Light Pollution Based on Remote Sensing and Mobile Big Data-Shenzhen City as a Case. Sensors 2020, 20, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Cheng, G.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, H. City Grade Classification Based on Connectivity Analysis by Luojia I Night-Time Light Images in Henan Province, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Liu, D.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Friedl, M.A. Enhancing MODIS land cover product with a spatial-temporal modeling algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
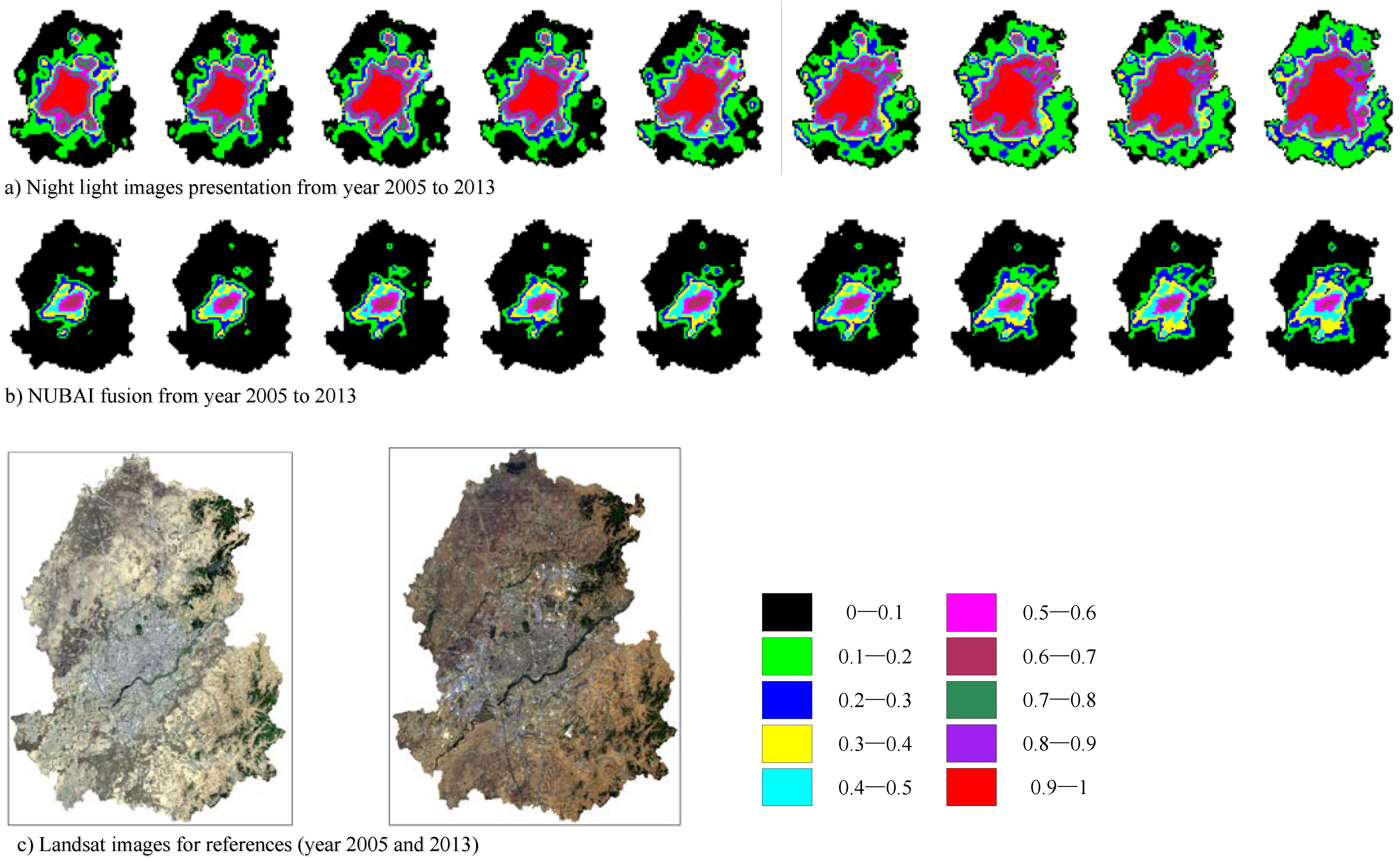




| Years | Statistical Area Sizes/km2 | Extraction Results by Night Light Data | Extraction Results by NUBAI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area Sizes/km2 | Error Rate | Area Sizes/km2 | Error Rate | ||
| 2005 | 310 | 307 | −0.97% | 312 | 0.65% |
| 2006 | 325 | 326 | 0.31% | 322 | −0.92% |
| 2007 | 347 | 351 | 1.15% | 351 | 1.15% |
| 2008 | 370 | 368 | −0.54% | 374 | 1.08% |
| 2009 | 395 | 410 | 3.80% | 388 | −1.77% |
| 2010 | 412 | 410 | −0.49% | 408 | −0.97% |
| 2011 | 430 | 462 | 7.44% | 426 | −0.93% |
| 2012 | 455 | 504 | 10.77% | 449 | −1.32% |
| 2013 | 455 | 504 | 10.77% | 450 | −1.10% |
| Years | Night Light Data | NUBAI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Omitted/km2 | Misidentified/km2 | Omitted /km2 | Misidentified /km2 | |
| 2005 | 35.00 | 31.91 | 9.82 | 11.73 |
| 2010 | 43.24 | 41.23 | 23.35 | 19.33 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, G.; Ma, Y.; Hu, J. A Fused Variable by Night Light Images and MODIS Products for Improving Urban Built-Up Area Extraction. Technologies 2021, 9, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies9020040
Yang G, Ma Y, Hu J. A Fused Variable by Night Light Images and MODIS Products for Improving Urban Built-Up Area Extraction. Technologies. 2021; 9(2):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies9020040
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Guang, Yuntao Ma, and Jiaqi Hu. 2021. "A Fused Variable by Night Light Images and MODIS Products for Improving Urban Built-Up Area Extraction" Technologies 9, no. 2: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies9020040
APA StyleYang, G., Ma, Y., & Hu, J. (2021). A Fused Variable by Night Light Images and MODIS Products for Improving Urban Built-Up Area Extraction. Technologies, 9(2), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies9020040





