Design Optimization of Long-Span Cold-Formed Steel Portal Frames Accounting for Effect of Knee Brace Joint Configuration
Abstract
1. Introduction
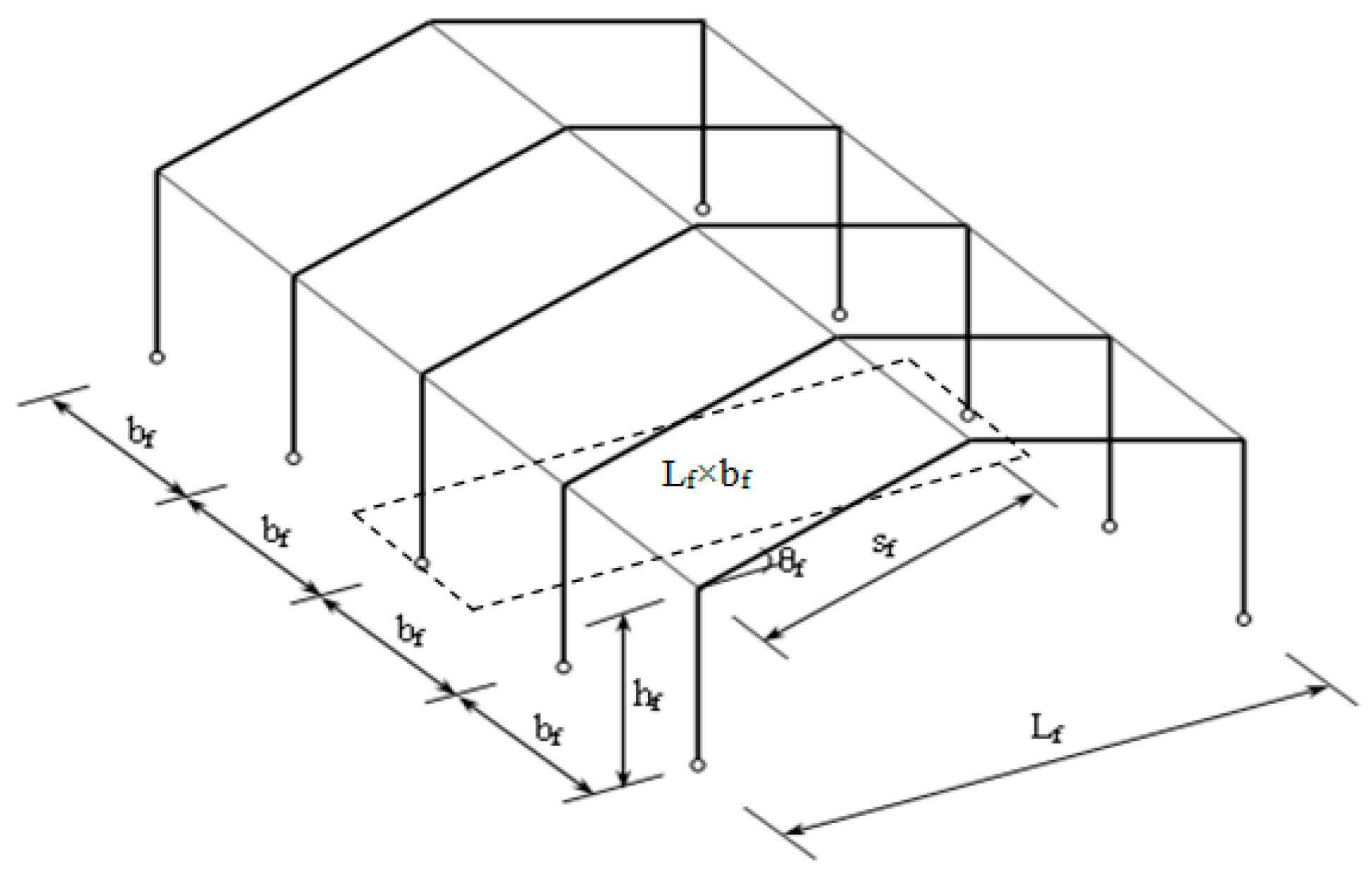
2. General Description of Long-Span Cold-Formed Steel Portal Frames
3. Design of Benchmark Frame Following Eurocode 3
- ULS is the ultimate limit state
- EHF is the equivalent horizontal forces
4. Design Optimization Model
- W is the weight of the frame per square meter of floor area
- wi are the weights per unit length of cold-formed steel sections for frame members
- li are the lengths of cold-formed steel frame members
- m is the number of structural members in the portal frame
- wbr is the total weight of the brackets
- G1.
- The size of cross sections designated for column, rafter and knee brace members
- G2.
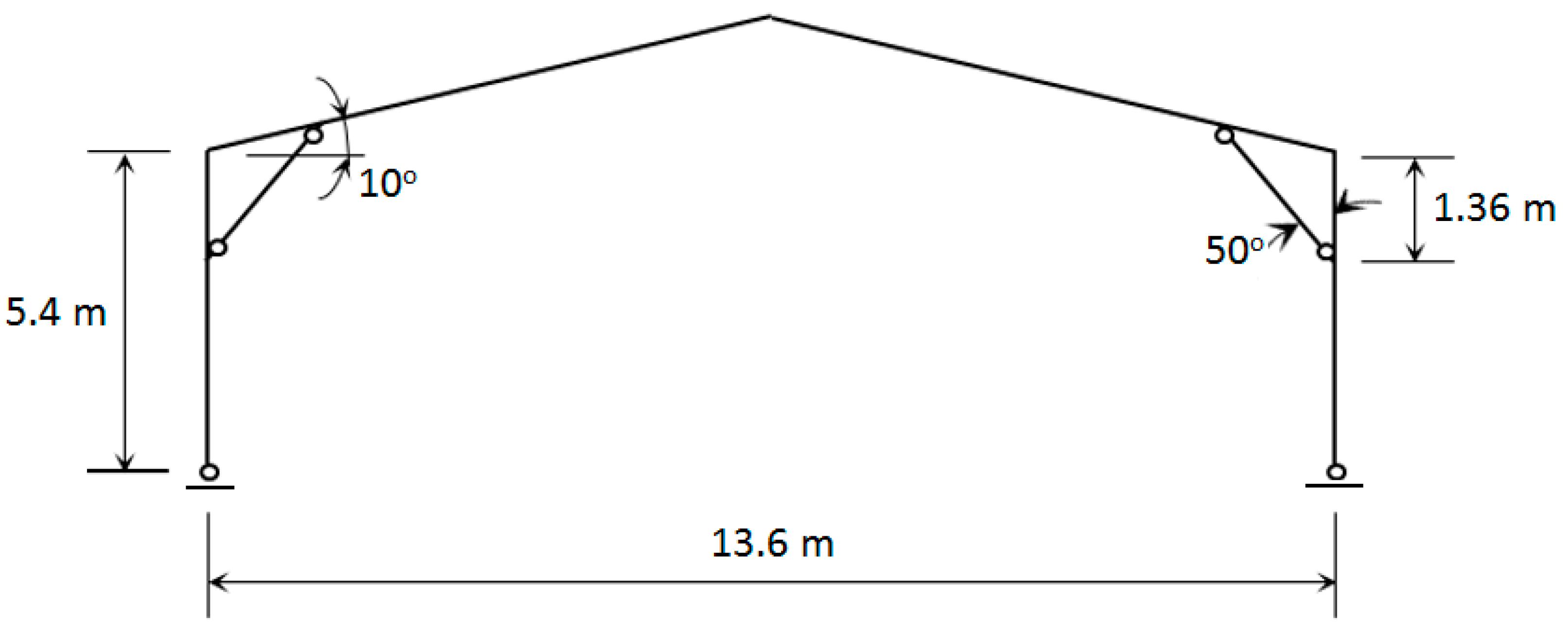
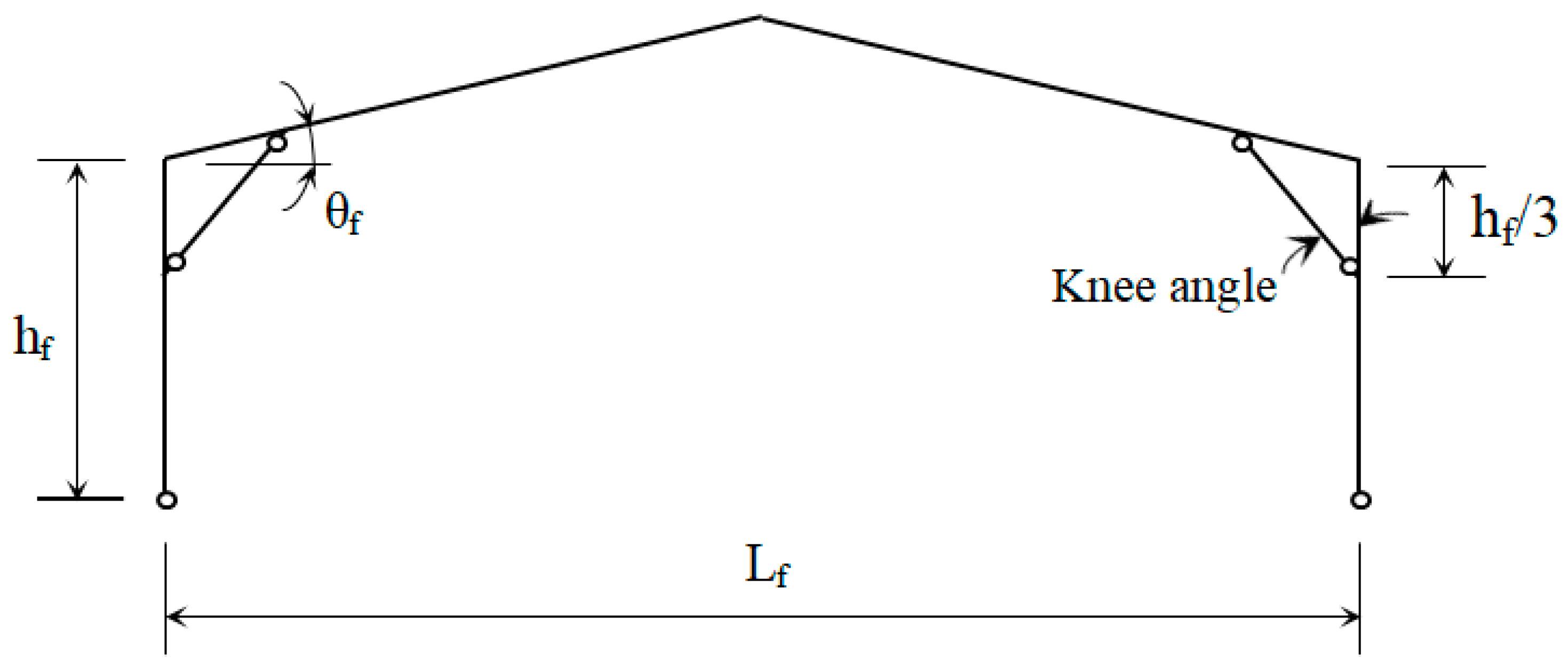
- Dimensions of knee brace joints: knee angle and position of knee brace connection from the top of column (vert. dist.), as shown in Figure 5.
- G3.
- Topology of framing system: frame spacing (bay) and rafter pitch
- G4.
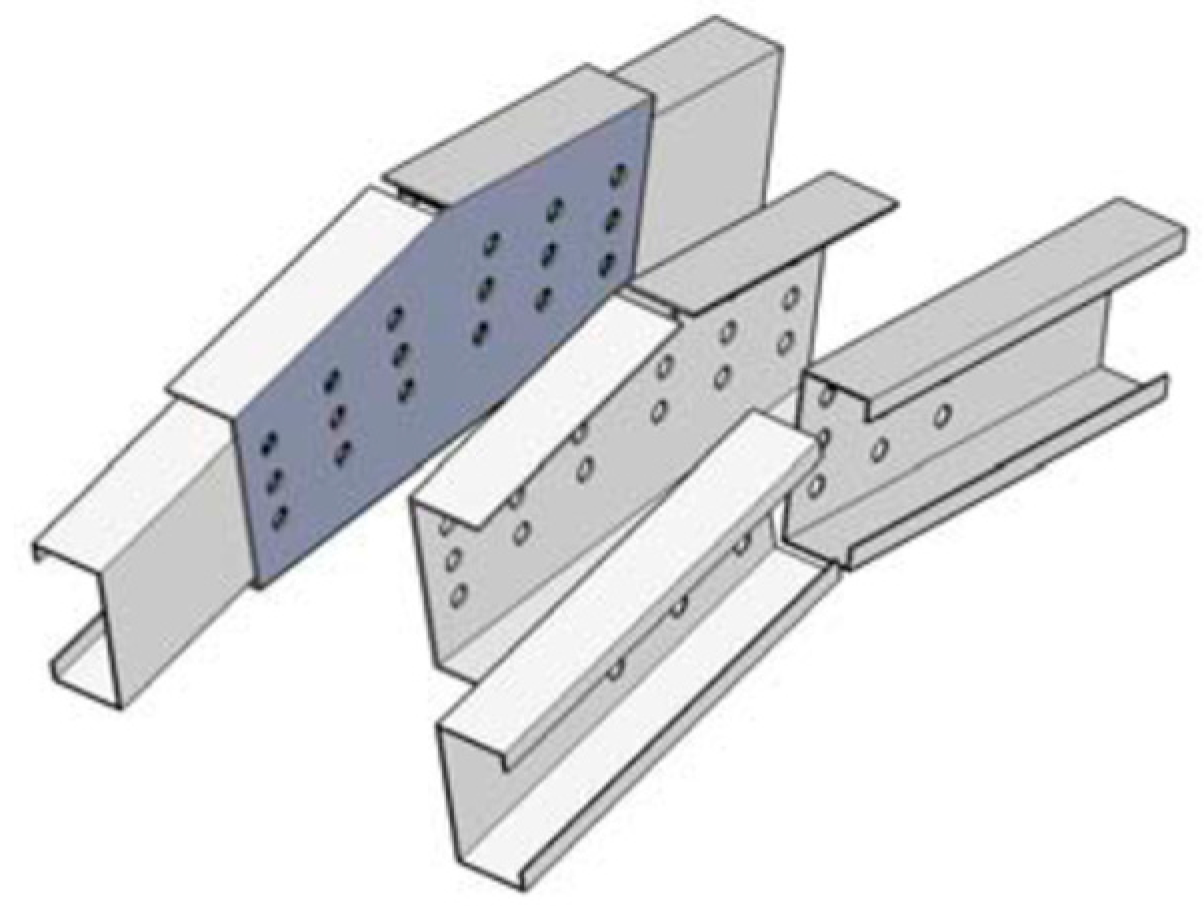
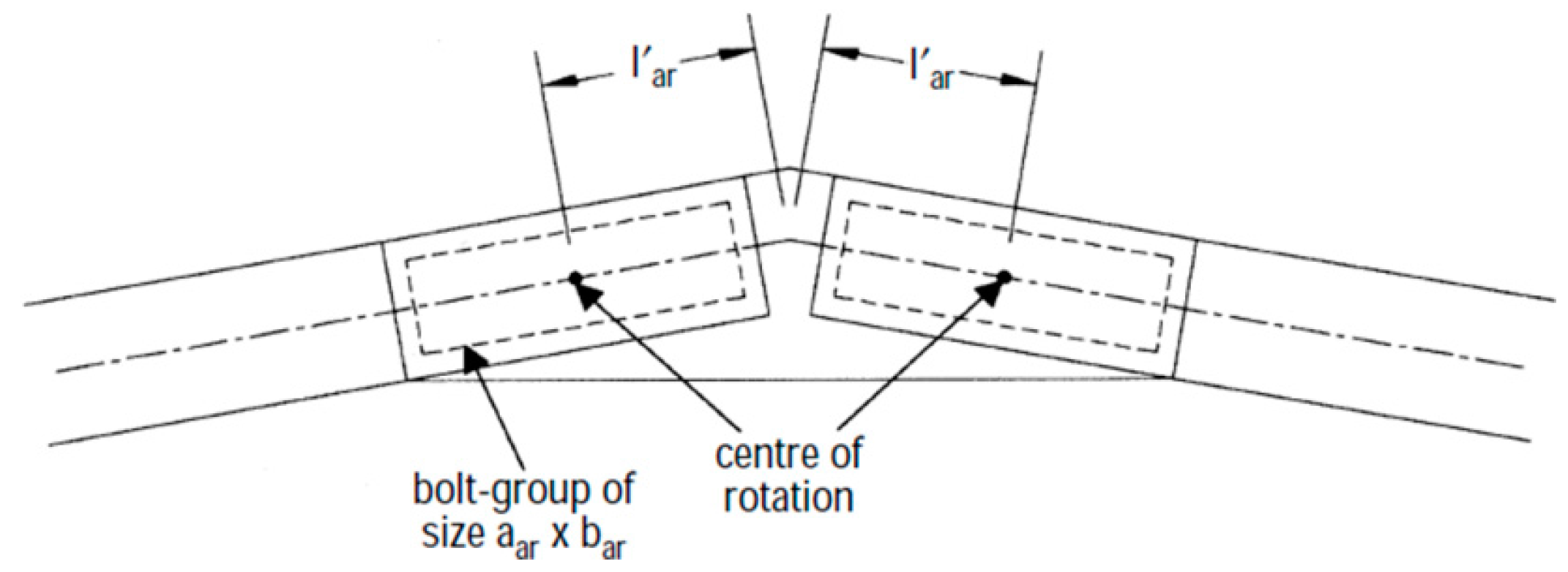
- Length of bolt-group of apex joint
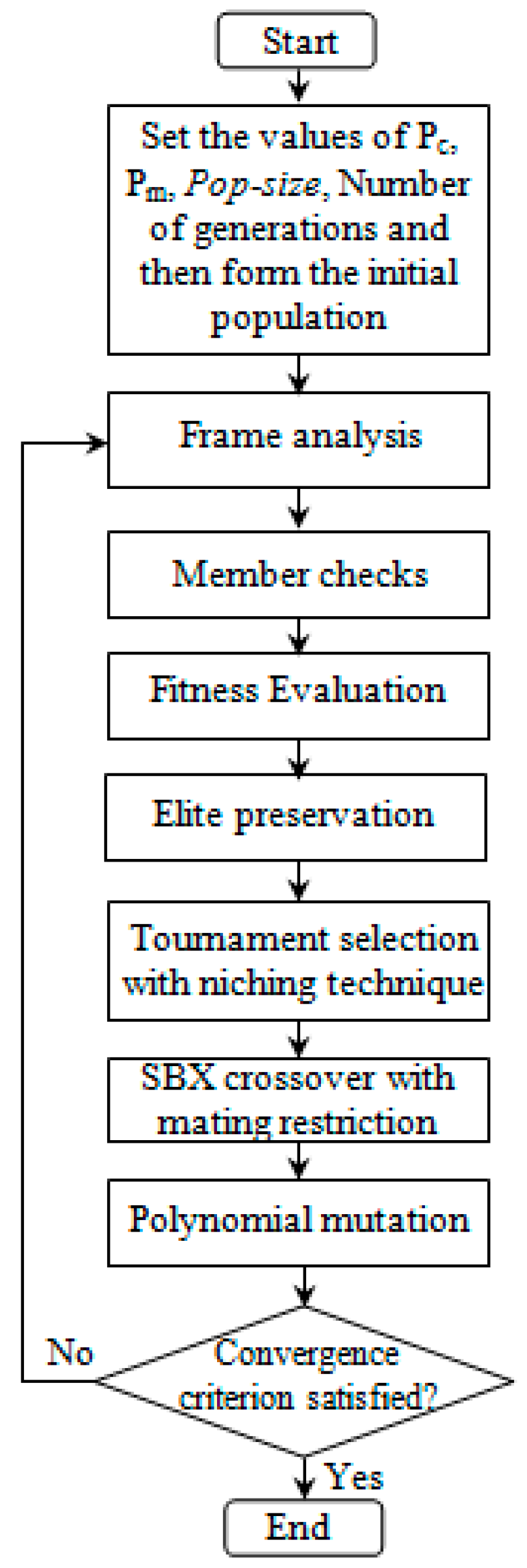
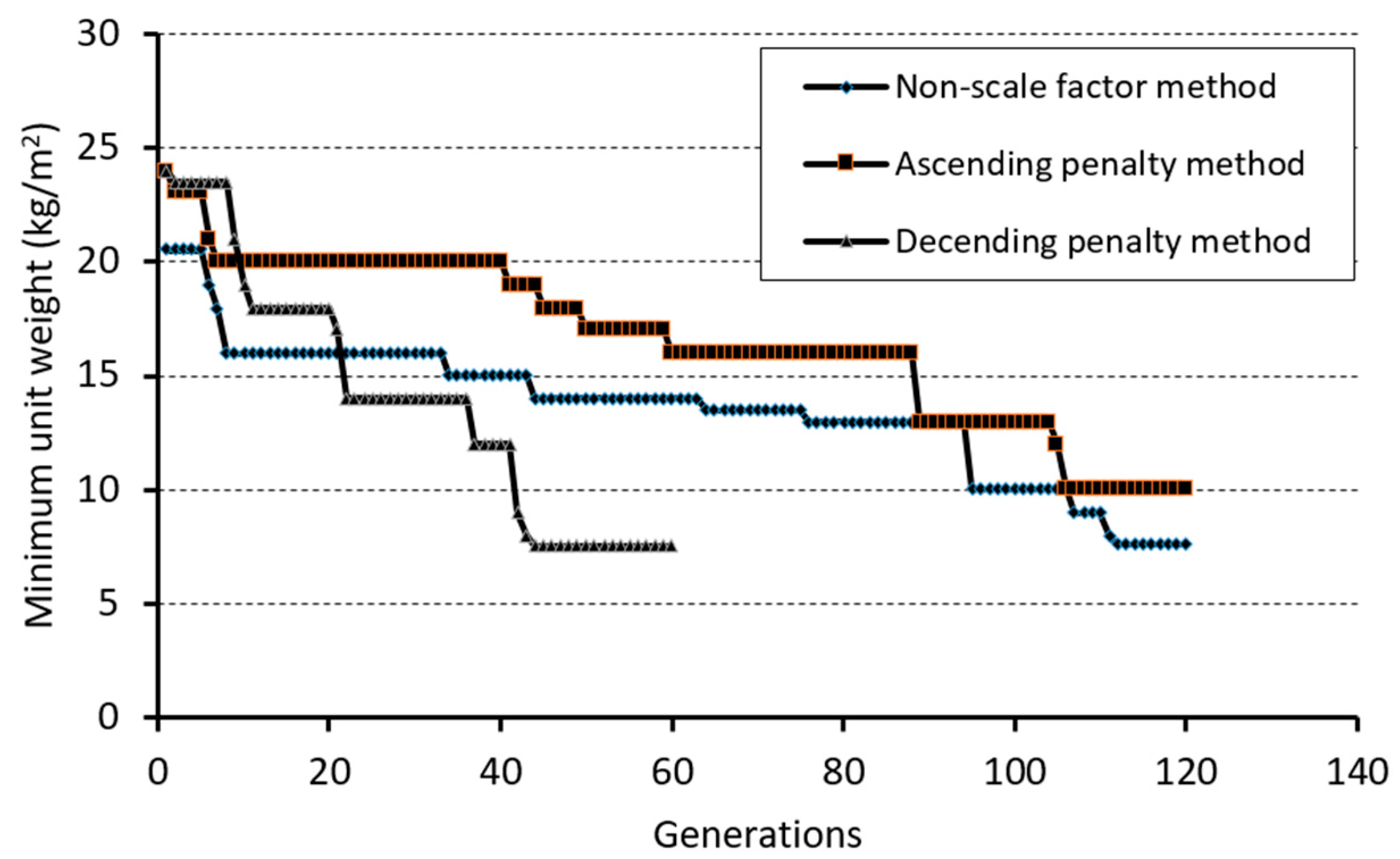
5. Fitness Function
6. Design Examples
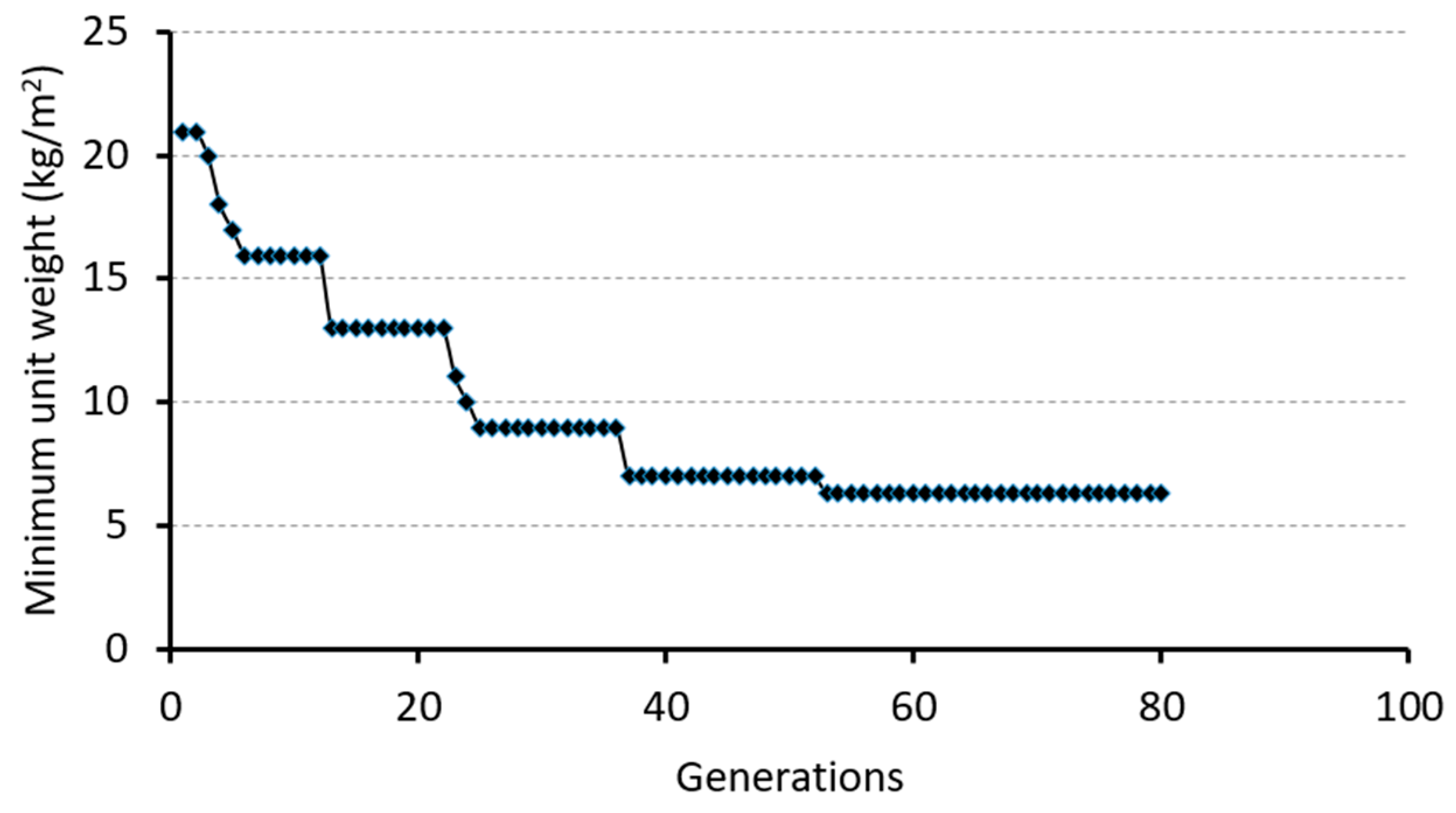
6.1. Optimum Design of Benchmark Frame with Full Rigidity for Apex Joint
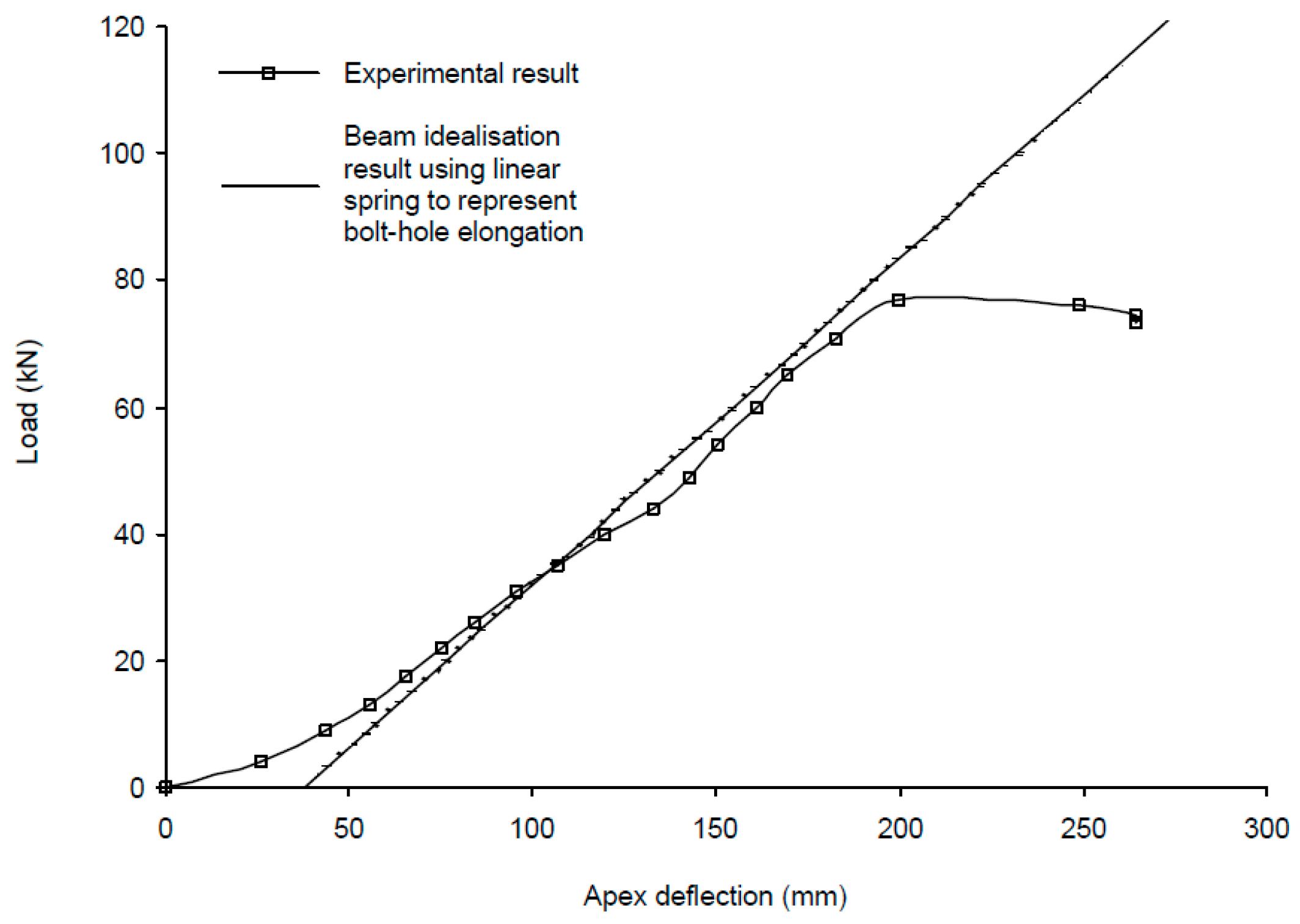
6.2. Optimum Design of Benchmark Frame Accounting for Semi-Rigidity of Apex Joint
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blum, H.B.; Rasmussen, K.J.R. Experiments on long-span cold-formed steel portal frames composed of double channels. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Coupled Instabilities in Metal Structures, Baltimore, MD, USA, 7–8 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dundu, M. Design approach of cold-formed steel portal frames. Int. J. Steel Struct. 2011, 11, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, B.W. Local, Distortional and Euler Buckling of Thin-Walled Columns. J. Struct. Eng. 2002, 128, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, M.; Lavacchini, G.; Ortolani, B.; Spinelli, P. Experimental capacity of perforated cold-formed steel open sections under compression and bending. Steel Compos. Struct. 2017, 24, 201–211. [Google Scholar]
- Bertocci, L.; Comparini, D.; Lavacchini, G.; Orlando, M.; Salvatori, L.; Spinelli, P. Experimental, numerical and regulatory P-Mx-My domains for cold-formed perforated steel uprights of pallet-racks. Thine-Walled Struct. 2017, 119, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.B.P.; Nethercot, D.A. Finite element idealization of a cold-formed steel portal frame. J. Struct. Eng. 2004, 130, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.T.; Lim, J.B.P.; Tanyimboh, T.T.; Sha, W. Effect of joints having semi-rigidity and finite connection-length in optimal design of cold-formed steel portal frames. Int. J. Steel Struct. 2017, 17, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toropov, V.V.; Mahfouz, S.Y. Design optimization of structural steelwork using genetic algorithm, FEM and a system of design rules. Eng. Comput. 2001, 18, 437–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, M.P. Optimum design of pitched roof steel frames with haunched rafters by genetic algorithm. Comput. Struct. 2003, 81, 1967–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, H.K.; Mohammad, F.A. Effect of mutation schemes on convergence to optimum design of steel frames. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2010, 66, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.T.; Lim, J.B.P.; Tanyimboh, T.T.; Lawson, R.M.; Martin, S.; Sha, W. Effect of serviceability limit on optimal design of steel portal frames. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2013, 86, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinstray, R.; Lim, J.B.P.; Tanyimboh, T.T.; Sha, W.; Phan, D.T. Optimal design of long-span steel portal frames using fabricated beams to Eurocode. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2015, 104, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.T.; Lim, J.B.P.; Sha, W.; Siew, C.; Tanyimboh, T.T.; Issa, K.H.; Mohammad, F.A. Design optimization of cold-formed steel portal frames taking into account the effect of topography. Eng. Optim. 2013, 45, 415–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autralian/New Zealand StandardTM. Cold-Formed Steel Structures; AS/NZS4600:2005; Standards Australia: Sydney, Australia, 2005. Available online: https://www.saiglobal.com/PDFTemp/Previews/OSH/as/as4000/4600/4600-2005.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2017).
- Wrzesien, A.M.; Phan, D.T.; Lim, J.B.P.; Lau, H.H.; Hajirasouliha, I.; Tan, C.S. Effect of stressed-skin action on optimal design of cold-formed steel square and rectangular-shaped portal frame buildings. Int. J. Steel Struct. 2016, 16, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.T.; Lim, J.B.P.; Tanyimboh, T.T.; Wrzesien, A.M.; Sha, W.; Lawson, R.M. Optimal design of cold-formed steel portal frames for stressed-skin action using genetic algorithm. Eng. Struct. 2015, 93, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.T.; Wrzesien, A.M.; Lim, J.B.P.; Hajirasouliha, I. Effects of Stressed-Skin Action on Optimal Design of a Cold-Formed Steel Portal Framing System. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Specialty Conference in Cold-Formed Steel Structures, Saint Louis, MO, USA, 5–6 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- British Standard. BS 5950–5: Structural Use of Steelworks in Building. Part 5. Code of Practice for Design of Cold-Formed Thin Gauge Sections; British Standards Institution: London, UK, 1998; Available online: https://shop.bsigroup.com/ProductDetail/?pid=000000000030155279 (accessed on 10 December 2017).
- Yeniay, O. Penalty function methods for constrained optimization with genetic algorithms. Math. Comput. Appl. 2005, 10, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K. An efficient constraint handling method for genetic algorithms. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2000, 186, 311–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshk, S.; Camp, C.V.; Chen, D. Design of nonlinear framed structures using genetic optimization. J. Struct. Eng. 2000, 126, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K. Multi-Objective Optimization Using Evolutionary Algorithms; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Erbatur, F.; Hasançebi, O.; Tutuncu, I.; Kiliç, H. Optimal design of planar and space structures with genetic algorithms. Comput. Struct. 2000, 75, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.B.P.; Nethercot, D.A. Stiffness prediction for bolted moment-connections between cold-formed steel members. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2004, 60, 85–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrzesien, A.M.; Lim, J.B.P.; Nethercot, D.A. Optimum Joint Detail for a General Cold-Formed Steel Portal Frame. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2012, 15, 623–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulak, G.L.; Fisher, J.W.; Struik, J.H.A. Guide to Design Criteria for Bolted and Riveted Joints, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, J.M. Connections for cold-formed steelwork. In Design of Cold-Formed Steel Members; Rhodes, J., Ed.; Elsevier Applied Science: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Zandanfarrokh, F.; Bryan, E.R. Testing and design of bolted connections in cold-formed steel sections. In Proceedings of the 11th International Specialty Conference on Cold-Formed Steel Structures, Saint Louis, MO, USA, 20–21 October 1992; pp. 625–662. [Google Scholar]
- British Standard BS EN 1993-1-1. Eurocode 3: Design of Steel Structures: Part 1—General Rules and Rules for Buildings; Committee European de Normalization: Brussels, Belgium, 2005; ISBN 0580460789. Available online: http://eurocodes.jrc.ec.europa.eu/showpage.php?id=133 (accessed on 11 December 2017).
- SAS IP, Inc. ANSYS: Release 14.5. 2012. Available online: http://www.ansys.com (accessed on 11 December 2017).
- Dubina, D.; Ungureanu, V.; Landolfo, R. Design of Cold-Formed Steel Structures; European Convention for Constructional Steelwork: Timisoara, Romania, 2012; ISBN 978-3-433-02979-4. Available online: http://as.wiley.com/WileyCDA/WileyTitle/productCd-3433029792.html (accessed on 11 December 2017).

| No. | Section | Depth (mm) | Width (mm) | Lip (mm) | Aeff (mm2) | Ieff (mm4) | kb (kN/mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C14014 | 140 | 62 | 13 | 204.0401 | 1,082,779 | 7.86 |
| 2 | C14015 | 140 | 62 | 13 | 232.1936 | 1,201,011 | 8.33 |
| 3 | C14016 | 140 | 62 | 13 | 261.3747 | 1,321,448 | 8.79 |
| 4 | C14018 | 140 | 62 | 13 | 322.529 | 1,563,576 | 9.67 |
| 5 | C14020 | 140 | 62 | 13 | 386.939 | 1,809,198 | 10.53 |
| 6 | C17014 | 170 | 62 | 13 | 203.7955 | 1,626,803 | 7.86 |
| 7 | C17015 | 170 | 62 | 13 | 229.7369 | 1,806,830 | 8.33 |
| 8 | C17016 | 170 | 62 | 13 | 258.3304 | 1,990,087 | 8.79 |
| 9 | C17018 | 170 | 62 | 13 | 320.1387 | 2,355,960 | 9.67 |
| 10 | C17020 | 170 | 62 | 13 | 385.4579 | 2,729,076 | 10.53 |
| 11 | C17025 | 170 | 62 | 13 | 547.9565 | 3,638,582 | 12.5 |
| 12 | C20014 | 200 | 70 | 15 | 211.0629 | 2,404,960 | 7.86 |
| 13 | C20015 | 200 | 70 | 15 | 238.186 | 2671228 | 8.33 |
| 14 | C20016 | 200 | 70 | 15 | 266.5817 | 2950971 | 8.79 |
| 15 | C20018 | 200 | 70 | 15 | 329.2035 | 3,524,825 | 9.67 |
| 16 | C20020 | 200 | 70 | 15 | 399.0659 | 4,101,795 | 10.53 |
| 17 | C20025 | 200 | 70 | 15 | 583.5274 | 5,555,008 | 12.50 |
| 18 | C24015 | 240 | 74 | 17 | 244.4894 | 4,054,743 | 8.33 |
| 19 | C24016 | 240 | 74 | 17 | 273.7871 | 4,486,942 | 8.79 |
| 20 | C24018 | 240 | 74 | 17 | 336.7747 | 5,374,958 | 9.67 |
| 21 | C24020 | 240 | 74 | 17 | 409.5579 | 6,283,747 | 10.53 |
| 22 | C24025 | 240 | 74 | 17 | 607.8716 | 8,585,415 | 12.50 |
| 23 | C24030 | 240 | 74 | 17 | 806.4516 | 1.08 × 107 | 14.28 |
| 24 | C30020 | 300 | 95 | 19 | 418.55 | 1.07 × 107 | 10.53 |
| 25 | C30025 | 300 | 95 | 19 | 617.1334 | 1.50 × 107 | 12.50 |
| 26 | C30030 | 300 | 95 | 19 | 862.1016 | 1.95 × 107 | 14.28 |
| Design Options | G1 (BBC Configuration) | G2 | G3 | Weight | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Column | Rafter | Knee | Vert.dist. | Knee Angle | Bay | Pitch | kg/m2 | |
| G1: varied G2,G3: fixed | C24030 | C24016 | C14014 | 1.36 m | 50° | 3.6 m | 10° | 7.76 |
| G1,G2 b: varied G2 a,G3: fixed | C24025 | C24020 | C14014 | 1.36 m | 37.4° | 3.6 m | 10° | 7.61 |
| G1,G2: varied G3: fixed | C24025 | C24018 | C14014 | 1.79 m | 38.2° | 3.6 m | 10° | 7.44 |
| All: varied | C30030 | C24025 | C14014 | 1.75 m | 41.2° | 6.0 m | 7.4° | 6.23 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Phan, T.D.; Lim, J.B.P.; Selowara Joo, M.; Lau, H.-H. Design Optimization of Long-Span Cold-Formed Steel Portal Frames Accounting for Effect of Knee Brace Joint Configuration. Technologies 2017, 5, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies5040081
Phan TD, Lim JBP, Selowara Joo M, Lau H-H. Design Optimization of Long-Span Cold-Formed Steel Portal Frames Accounting for Effect of Knee Brace Joint Configuration. Technologies. 2017; 5(4):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies5040081
Chicago/Turabian StylePhan, Thanh Duoc, James B. P. Lim, Meheron Selowara Joo, and Hieng-Ho Lau. 2017. "Design Optimization of Long-Span Cold-Formed Steel Portal Frames Accounting for Effect of Knee Brace Joint Configuration" Technologies 5, no. 4: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies5040081
APA StylePhan, T. D., Lim, J. B. P., Selowara Joo, M., & Lau, H.-H. (2017). Design Optimization of Long-Span Cold-Formed Steel Portal Frames Accounting for Effect of Knee Brace Joint Configuration. Technologies, 5(4), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies5040081






