Synthesis and Sintering of ZnO Nanopowders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ZnO Nanopowders
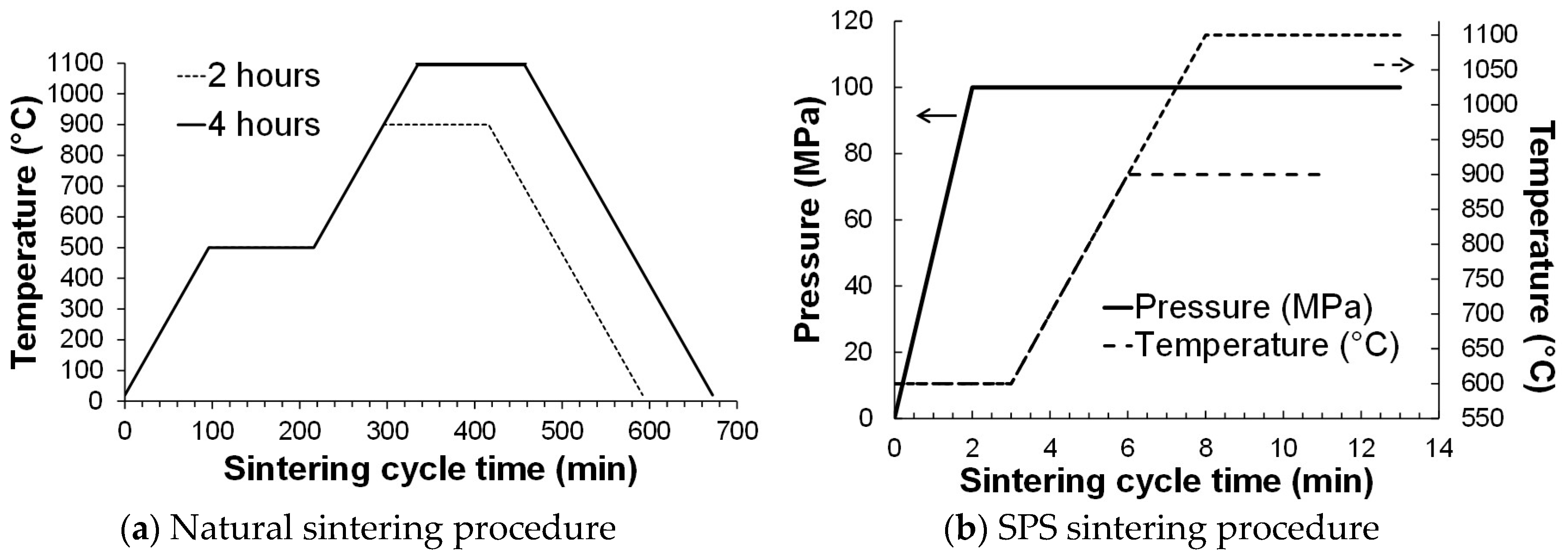
2.2. Sintering Procedure
2.3. Characterization Methods
3. Results
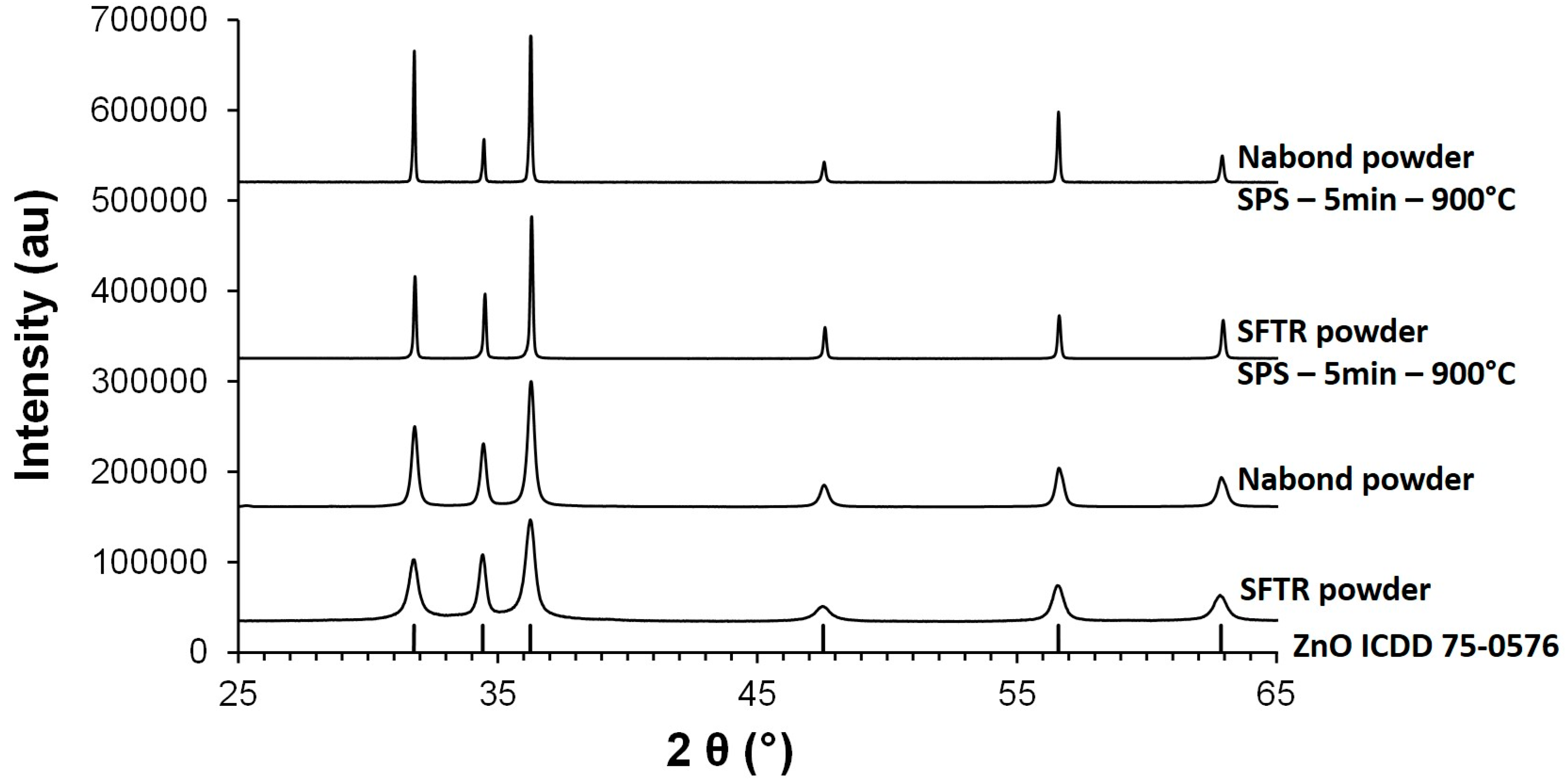
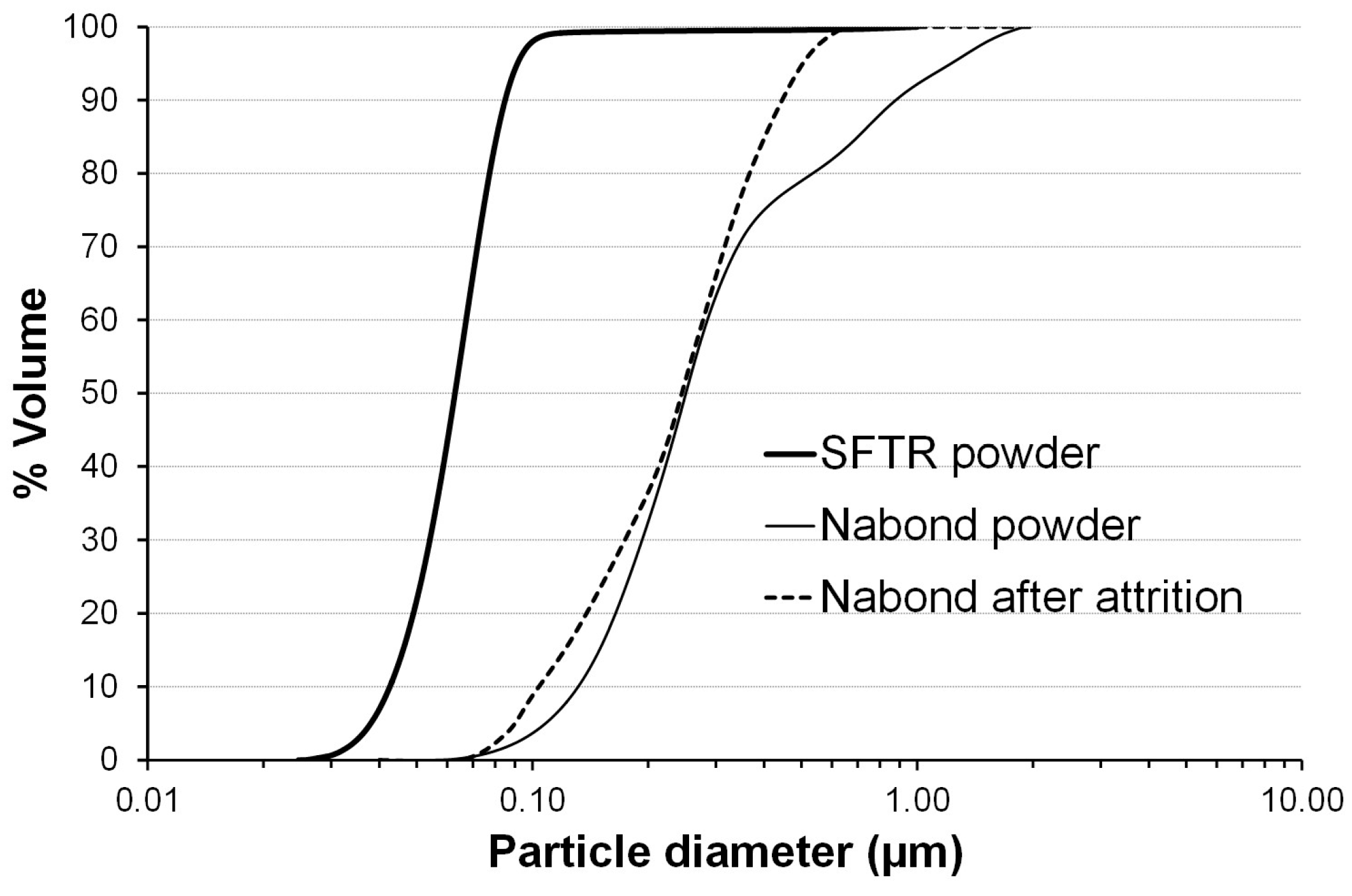
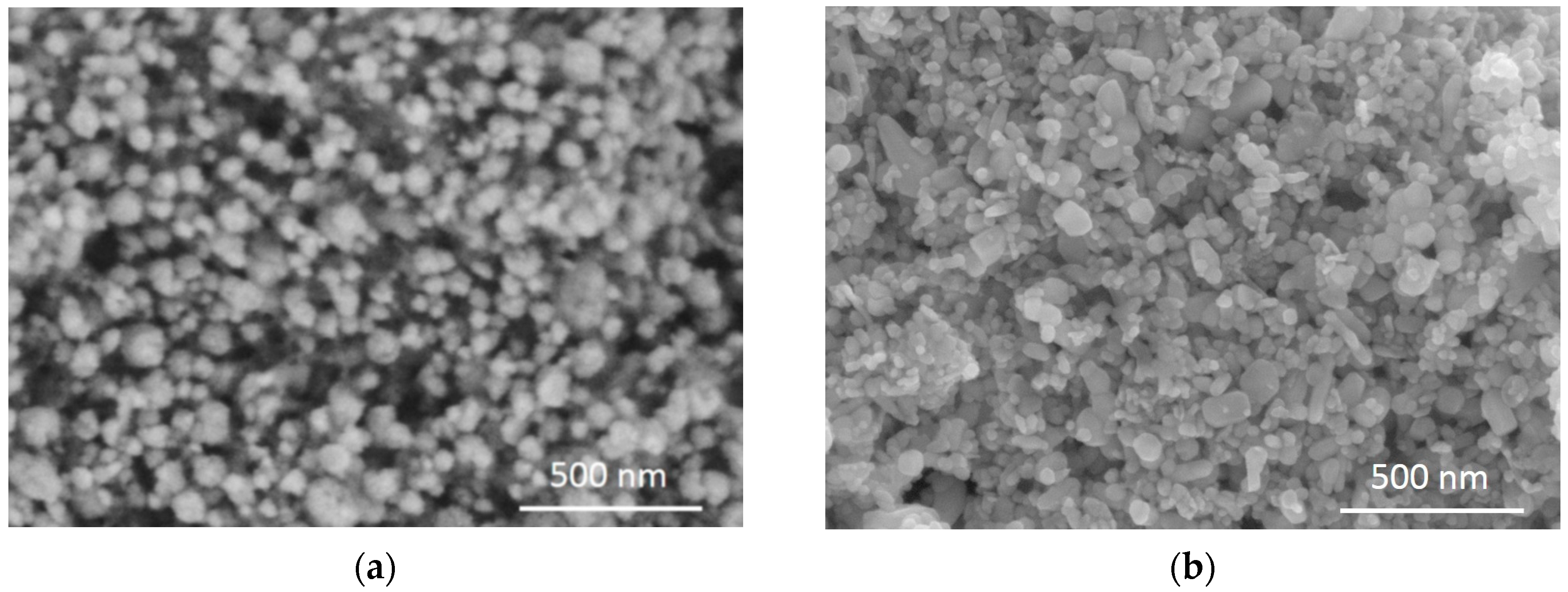
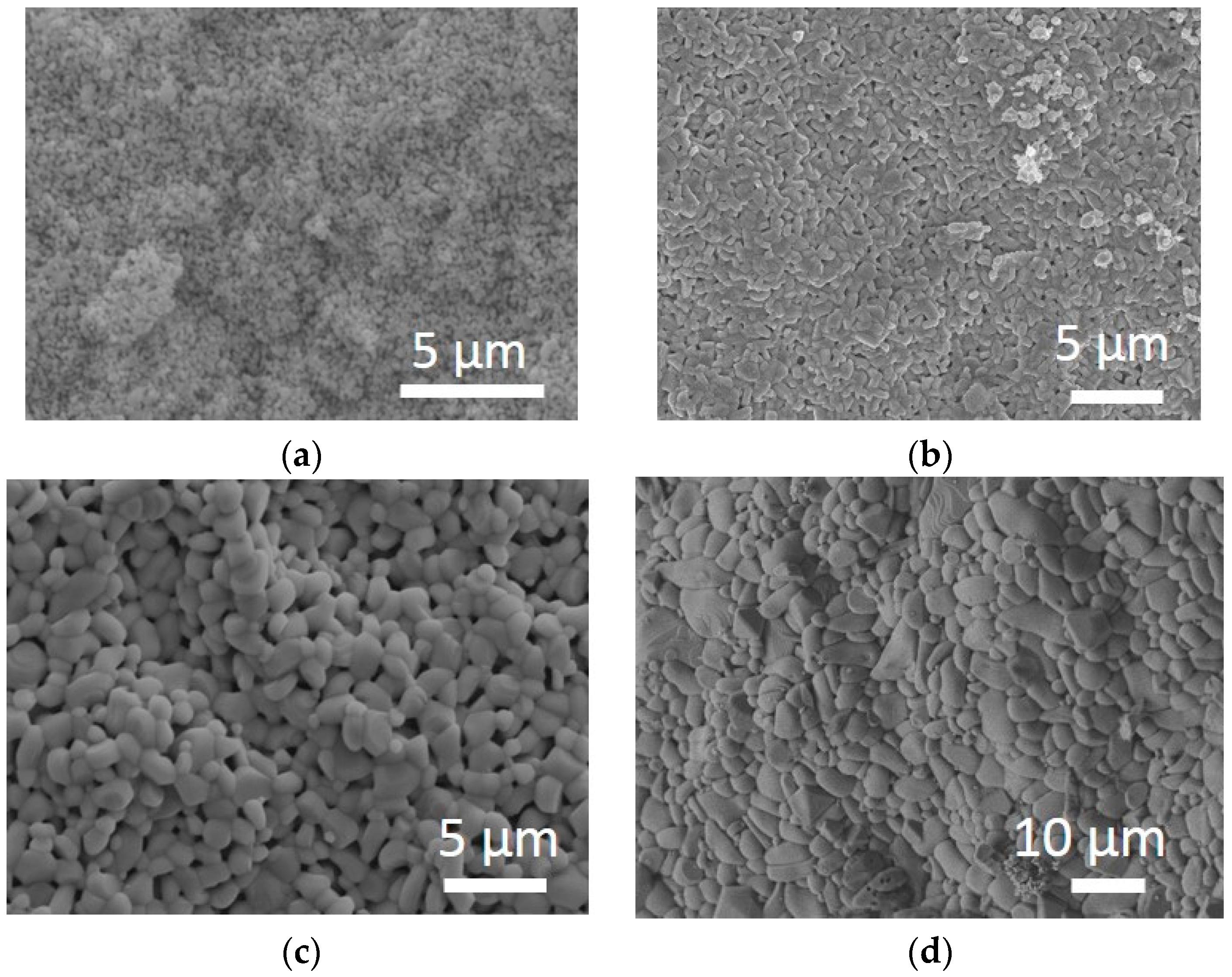
3.1. Characterization of ZnO Nanopowders
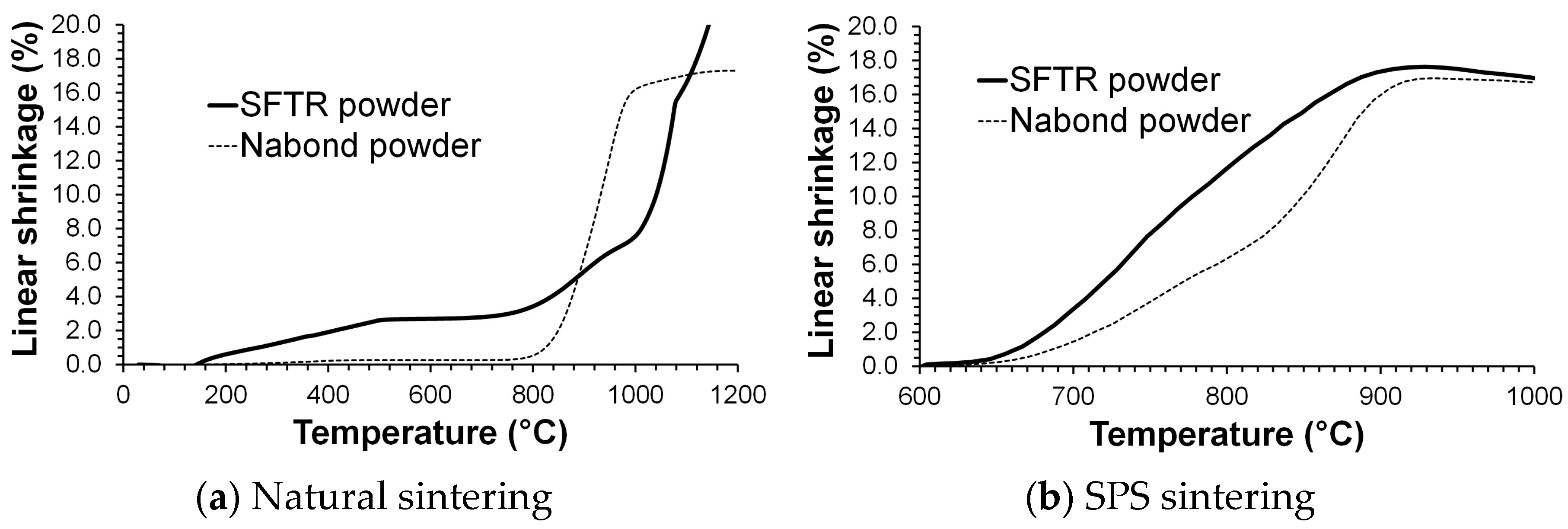
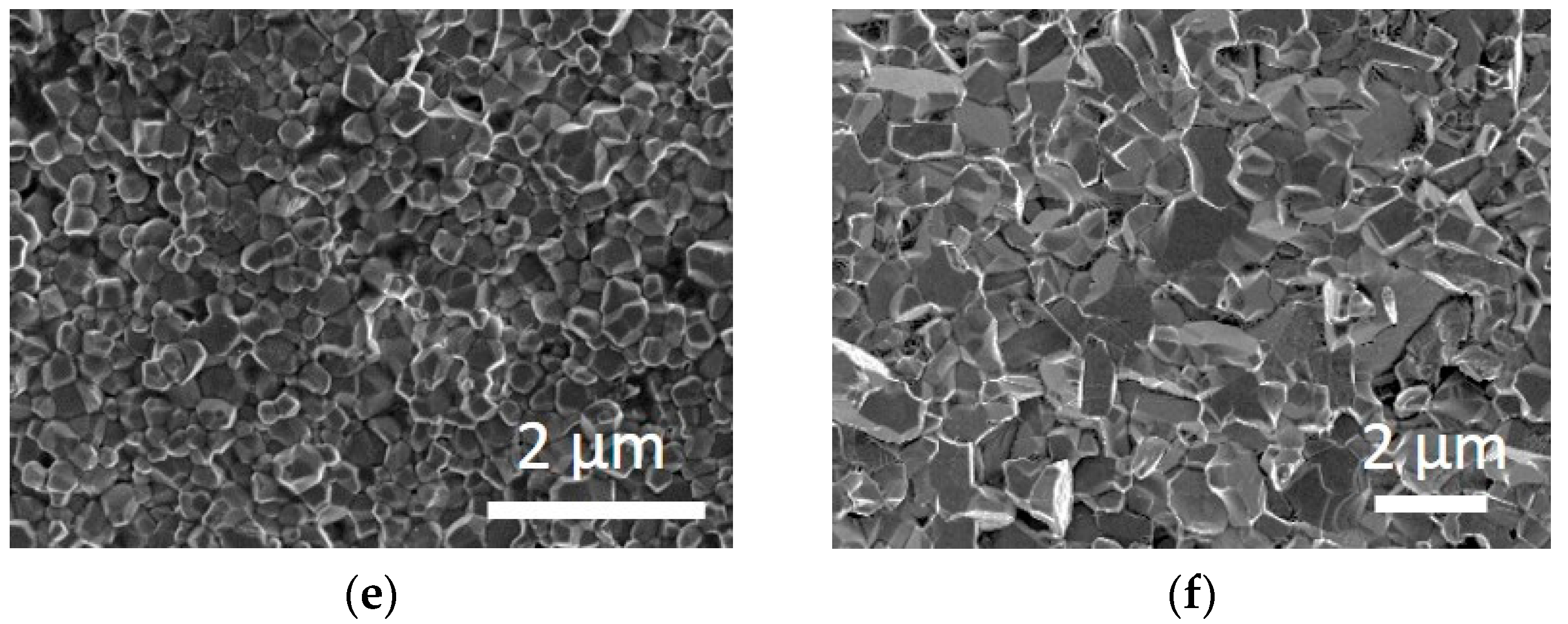
3.2. Sintering Behavior of ZnO Nanopowders
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lange, F.F. Powder Processing Science and Technology for Increased Reliability. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1989, 72, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwey, E.J.W.; Overbeek, J.T.G.; Overbeek, J.T.G. Theory of the stability of lyophobic colloids. In Courier Corporation; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, J.A. Colloidal Processing of Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2000, 83, 2341–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, L. Colloidal Processing of Ceramics. Available online: https://fr.scribd.com/document/259254918/Colloidal-Processing-of-Ceramics (accessed on 16 December 2016).
- Cameron, C.P.; Raj, R. Grain-Growth Transition During Sintering of Colloidally Prepared Alumina Powder Compacts. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1988, 71, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Zinc oxide nanostructures: Growth, properties and applications. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2004, 16, R829–R858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgur, U.; Alivov, Y.I.; Liu, C.; Teke, A.; Reshchikov, M.A.; Dogan, S.; Avrutin, V.; Cho, S.-J.; Morkoc, H. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, D.R. Varistor Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 82, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonoberov, V.A.; Balandin, A.A. ZnO Quantum Dots: Physical Properties and Optoelectronic Applications. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 2006, 1, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willander, M.; Nur, O.; Zhao, Q.X.; Yang, L.L.; Lorenz, M.; Cao, B.Q.; Pérez, J.Z.; Czekalla, C.; Zimmermann, G.; Grundmann, M.; et al. Zinc oxide nanorod based photonic devices: Recent progress in growth, light emitting diodes and lasers. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 332001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, P.R.; Varela, J.A.; Longo, E. SnO2, ZnO and related polycrystalline compound semiconductors: An overview and review on the voltage-dependent resistance (non-ohmic) feature. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 505–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, L.F.; Parravano, G. Sintering of Zinc Oxide. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1963, 46, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, G.C. Grain Growth in Zinc Oxide. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1965, 48, 214–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, T.K.; Coble, R.L. Sintering of ZnO: I Densification and Grain Growth. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1968, 51, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senda, T.; Bradt, R.C. Grain Growth in Sintered ZnO and ZnO-Bi2O3 Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1990, 73, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, S.C.; Kelly, J.M.; McCormack, D.E.; Ramesh, R. High performance ZnO varistors prepared from nanocrystalline precursors for miniaturised electronic devices. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 3926–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahm, C.-W. Low-temperature sintering effect on varistor properties of ZnO–V2O5–MnO2–Nb2O5–Bi2O3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 2117–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahraki, M.M.; Shojaee, S.A.; Sani, M.A.F.; Nemati, A.; Safaee, I. Two-step sintering of ZnO varistors. Solid State Ion. 2011, 190, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmi-Tamburini, U.; Garay, J.E.; Munir, Z.A. Fast low-temperature consolidation of bulk nanometric ceramic materials. Scr. Mater. 2006, 54, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren, M.; Shen, Z. Hot Pressing and Spark Plasma Sintering. In Ceramics Science and Technology; Riedel, R., Chen, I.-W., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 189–214. [Google Scholar]
- Anselmi-Tamburini, U.; Gennari, S.; Garay, J.E.; Munir, Z.A. Fundamental investigations on the spark plasma sintering/synthesis process: II. Modeling of current and temperature distributions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 394, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, Z.A.; Anselmi-Tamburini, U.; Ohyanagi, M. The effect of electric field and pressure on the synthesis and consolidation of materials: A review of the spark plasma sintering method. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, Z.A.; Quach, D.V.; Ohyanagi, M. Electric current activation of sintering: A review of the pulsed electric current sintering process. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 94, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, M.; Akimune, Y.; Furuya, K.; Hatano, M.; Yamanaka, M.; Uchiyama, M. Phase transition and electrical conductivity of scandia-stabilized zirconia prepared by spark plasma sintering process. Solid State Ion. 2005, 176, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Li, Q.; Luan, W.; Kawaoka, H.; Sekino, T.; Niihara, K. Preparation and Electric Properties of Dense Nanocrystalline Zinc Oxide Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 85, 1016–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.I.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, B.K. Spark plasma sintering behavior of nanocrystalline WC–10Co cemented carbide powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 351, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watari, F.; Yokoyama, A.; Omori, M.; Hirai, T.; Kondo, H.; Uo, M.; Kawasaki, T. Biocompatibility of materials and development to functionally graded implant for bio-medical application. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2004, 64, 893–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.W.; Loh, N.H.; Khor, K.A.; Tor, S.B.; Cheang, P. Spark plasma sintering of hydroxyapatite powders. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Li, J.-F.; Zhang, B.P.; Lin, Y.H.; Ren, L.R.; Chen, G.F. Microstructure and thermoelectric properties of Zn1−xAlxO ceramics fabricated by spark plasma sintering. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2010, 71, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuer, M.; Zhao, Z.; Aschauer, U.; Bowen, P. Transparent polycrystalline alumina using spark plasma sintering: Effect of Mg, Y and La doping. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 30, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beynet, Y.; Izoulet, A.; Guillemet-Fritsch, S.; Chevallier, G.; Bley, V.; Pérel, T.; Malpiece, F.; Morel, J.; Estournès, C. ZnO-based varistors prepared by spark plasma sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Fan, L.; Shi, Y.; Xie, J.; Lei, F.; Ren, D. Elaboration of translucent ZnO ceramics by spark plasma sintering under low temperature. Opt. Mater. (n.d.) 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacassy, R.; Jongen, N.; Bowen, P.; Lemaître, J.; Hofmann, H. Development of the new segmented flow tubular reactor for powder technology. Proc. World Congr. Part. Technol. 1998, 3, 196–197. [Google Scholar]
- Lemaitre, J.; Jongen, N.; Vacassy, R.; Bowen, P. Production of Powders. United States Patent 6458335, 1 October 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Vacassy, R.; Lemaitre, J.; Hofmann, H.; Gerlings, J.H. Calcium carbonate precipitation using new segmented flow tubular reactor. AIChE J. 2000, 46, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, P.; Donnet, M.; Testino, A.; Viviani, M.; Buscaglia, M.T.; Buscaglia, V.; Nanni, P. Synthesis of Barium Titanate Powders by Low-Temperature Aqueous Synthesis Using a New Segmented Flow Tubular Reactor. Key Eng. Mater. 2002, 206, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemet-Fritsch, S.; Aoun-Habbache, M.; Sarrias, J.; Rousset, A.; Jongen, N.; Donnet, M.; Bowen, P.; Lemaitre, J. High-quality nickel manganese oxalate powders synthesized in a new segmented flow tubular reactor. Solid State Ion. 2004, 171, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnet, M.; Jongen, N.; Lemaître, J.; Bowen, P. New morphology of calcium oxalate trihydrate precipitated in a segmented flow tubular reactor. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2000, 19, 749–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongen, N.; Donnet, M.; Bowen, P.; Lemaitre, J.; Hofmann, H.; Schenk, R.; Hofmann, C.; Aoun-Habbache, M.; Guillemet-Fritsch, S.; Sarrias, J. Development of a Continuous Segmented Flow Tubular Reactor and the Scale-out Concept—In Search of Perfect Powders. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2003, 26, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, P.; Testino, A.; Legagneur, V.; Donnet, M.; Hofmann, H.; Cobut, N. Proceedings of the Fifth World Congress on Particle Technology (WCPT5), Orlando, FL, USA, 23 April 2006.
- Aimable, A.; Jongen, N.; Testino, A.; Donnet, M.; Lemaître, J.; Hofmann, H.; Bowen, P. Precipitation of Nanosized and Nanostructured Powders: Process Intensification and Scale-Out Using a Segmented Flow Tubular Reactor (SFTR). Chem. Eng. Technol. 2011, 34, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimable, A.; Strachowski, T.; Wolska, E.; Lojkowski, W.; Bowen, P. Comparison of two innovative precipitation systems for ZnO and Al-doped ZnO nanoparticle synthesis. Process. Appl. Ceram. 2010, 4, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimable, A.; Buscaglia, M.T.; Buscaglia, V.; Bowen, P. Polymer-assisted precipitation of ZnO nanoparticles with narrow particle size distribution. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 30, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, J.I.; Wilson, A.J.C. Scherrer after sixty years: A survey and some new results in the determination of crystallite size. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1978, 11, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimable, A.; Bowen, P. Nanopowder metrology and nanoparticle size measurement—Towards the development and testing of protocols. Process. Appl. Ceram. 2010, 4, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| - | SBET | dBET | dXRD | dv10 | dv50 | dv90 | Span | Fagg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | (m²/g) | (nm) | (nm) | (nm) | (nm) | (nm) | - | - |
| SFTR powder | 78.2 | 14 | 24 | 42 | 63 | 85 | 0.68 | 4.5 |
| Nabond powder | 16.3 | 66 | 41 | 131 | 250 | 853 | 2.89 | 3.8 |
| Nabond after attrition | 23.8 | 45 | 41 | 102 | 248 | 415 | 1.26 | 5.5 |
| - | Relative Density (%) | |||||
| Green Body | Natural Sintering | SPS Sintering | ||||
| - | 900 °C | 1100 °C | 900 °C | |||
| - | 2 h | 4 h | 2 h | 4 h | 5 min | |
| SFTR powder | 44.0 | 49.2 | 51.3 | 60.0 | 64.7 | 99.5 |
| Nabond powder | 52.0 | 74.6 | 79.7 | 96.9 | 98.0 | 95.1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aimable, A.; Goure Doubi, H.; Stuer, M.; Zhao, Z.; Bowen, P. Synthesis and Sintering of ZnO Nanopowders. Technologies 2017, 5, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies5020028
Aimable A, Goure Doubi H, Stuer M, Zhao Z, Bowen P. Synthesis and Sintering of ZnO Nanopowders. Technologies. 2017; 5(2):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies5020028
Chicago/Turabian StyleAimable, Anne, Hervé Goure Doubi, Michael Stuer, Zhe Zhao, and Paul Bowen. 2017. "Synthesis and Sintering of ZnO Nanopowders" Technologies 5, no. 2: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies5020028
APA StyleAimable, A., Goure Doubi, H., Stuer, M., Zhao, Z., & Bowen, P. (2017). Synthesis and Sintering of ZnO Nanopowders. Technologies, 5(2), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies5020028






