Proximate Composition, Extraction, and Purification of Theobromine from Cacao Pod Husk (Theobroma Cacao L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Preparation of Dried Samples
2.4. Analysis of Proximate Composition of Cacao Pod Husk
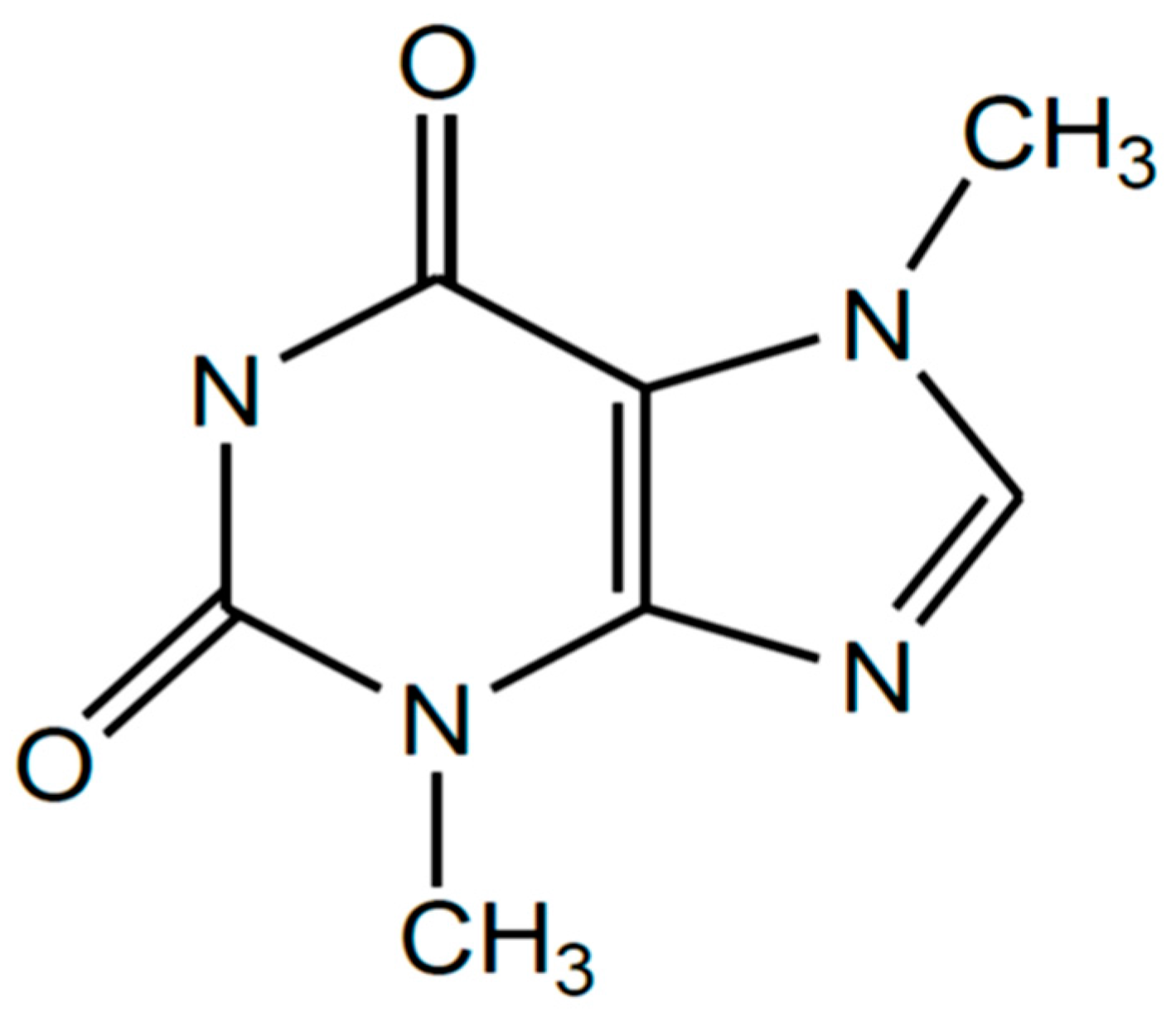
2.5. Extraction of Theobromine from Cacao Pod Husk
2.6. Purification of Crude Extracts from Cacao Pod Husk
2.7. Analysis of Theobromine Content
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proximate Composition of Cacao Pod Husk
3.2. Effect of Extraction Conditions on Theobromine Content from Cacao Pod Husk
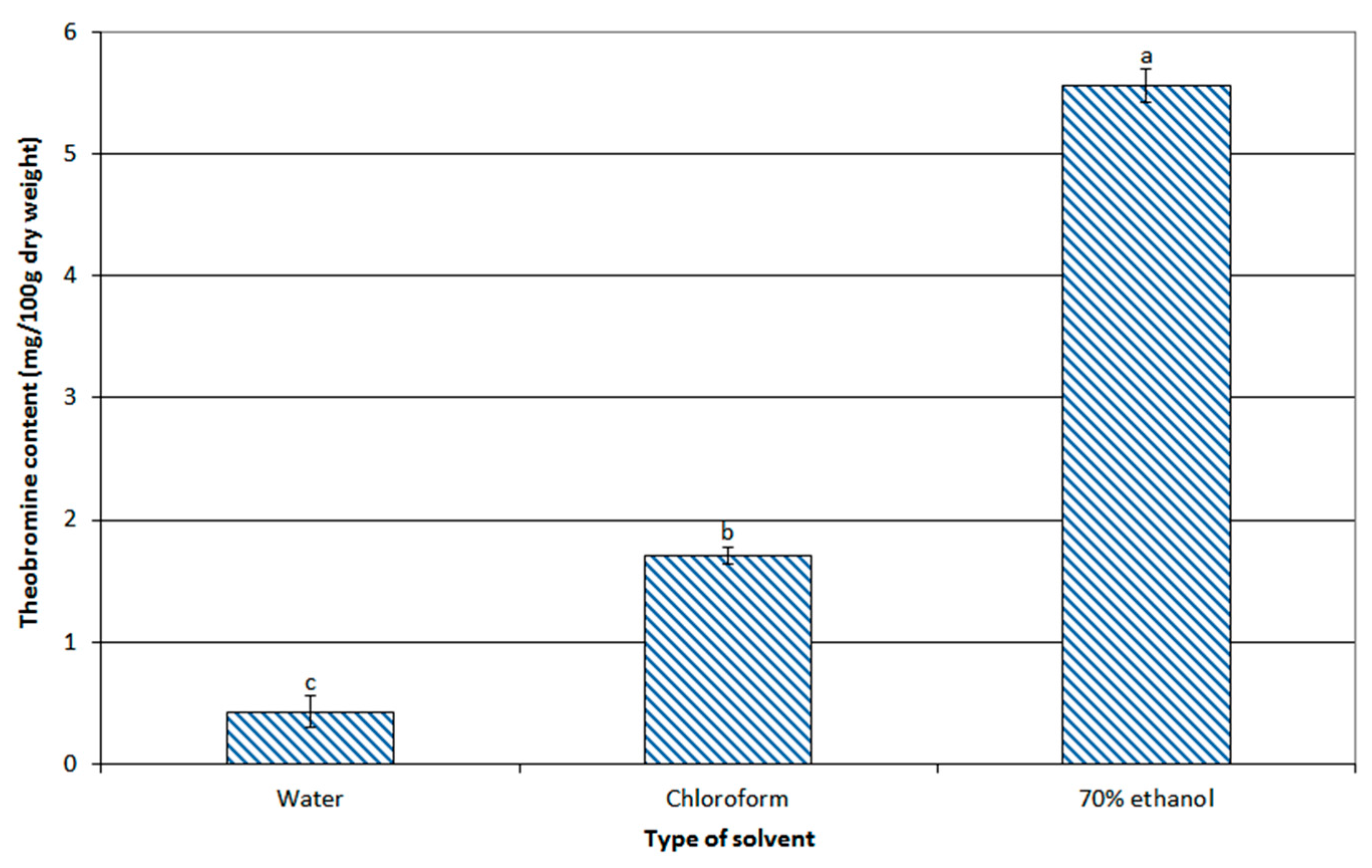
3.2.1. Effect of Various Solvents on Theobromine Content
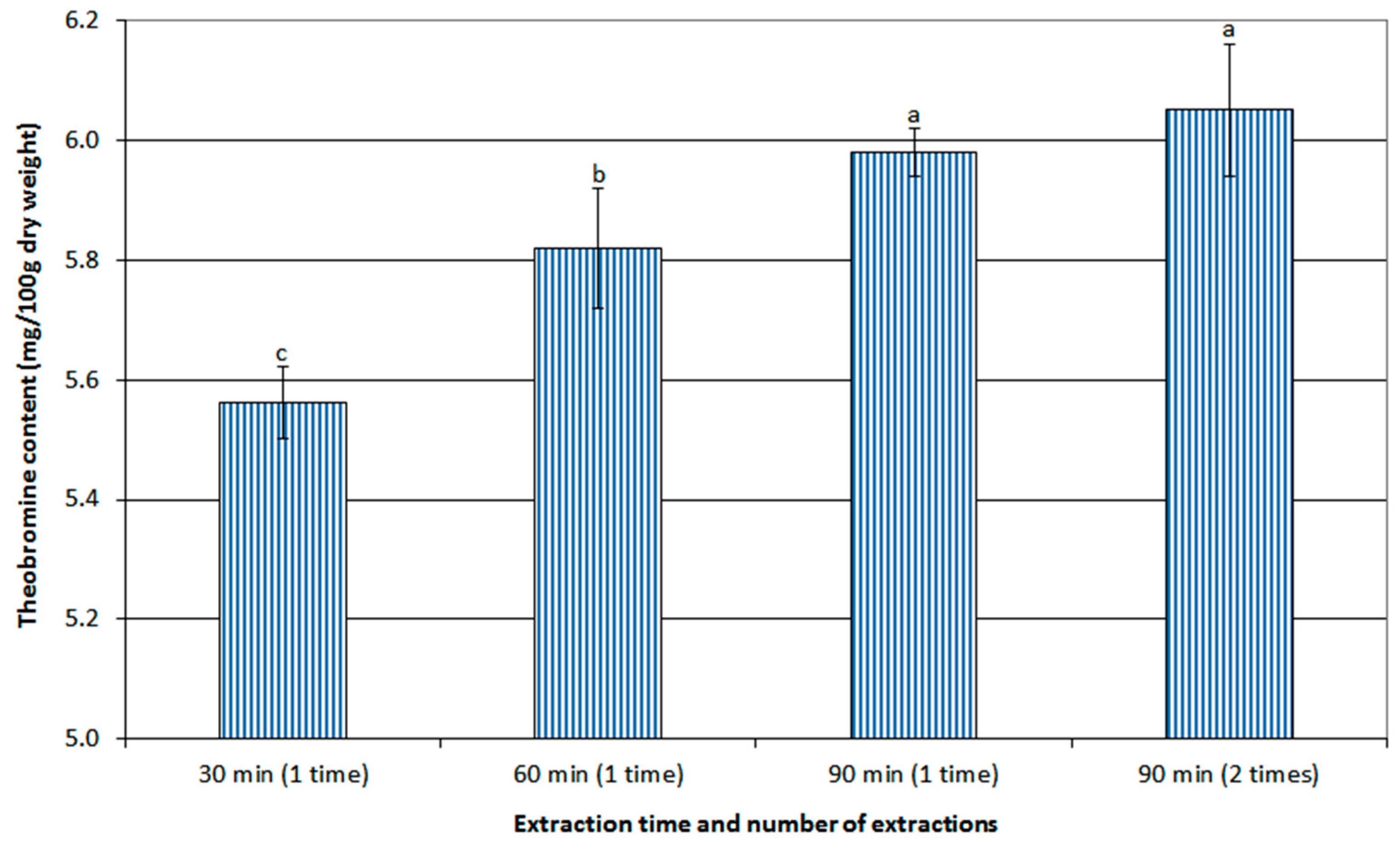
3.2.2. Effect of Extraction Time and Number of Extractions on Theobromine Content
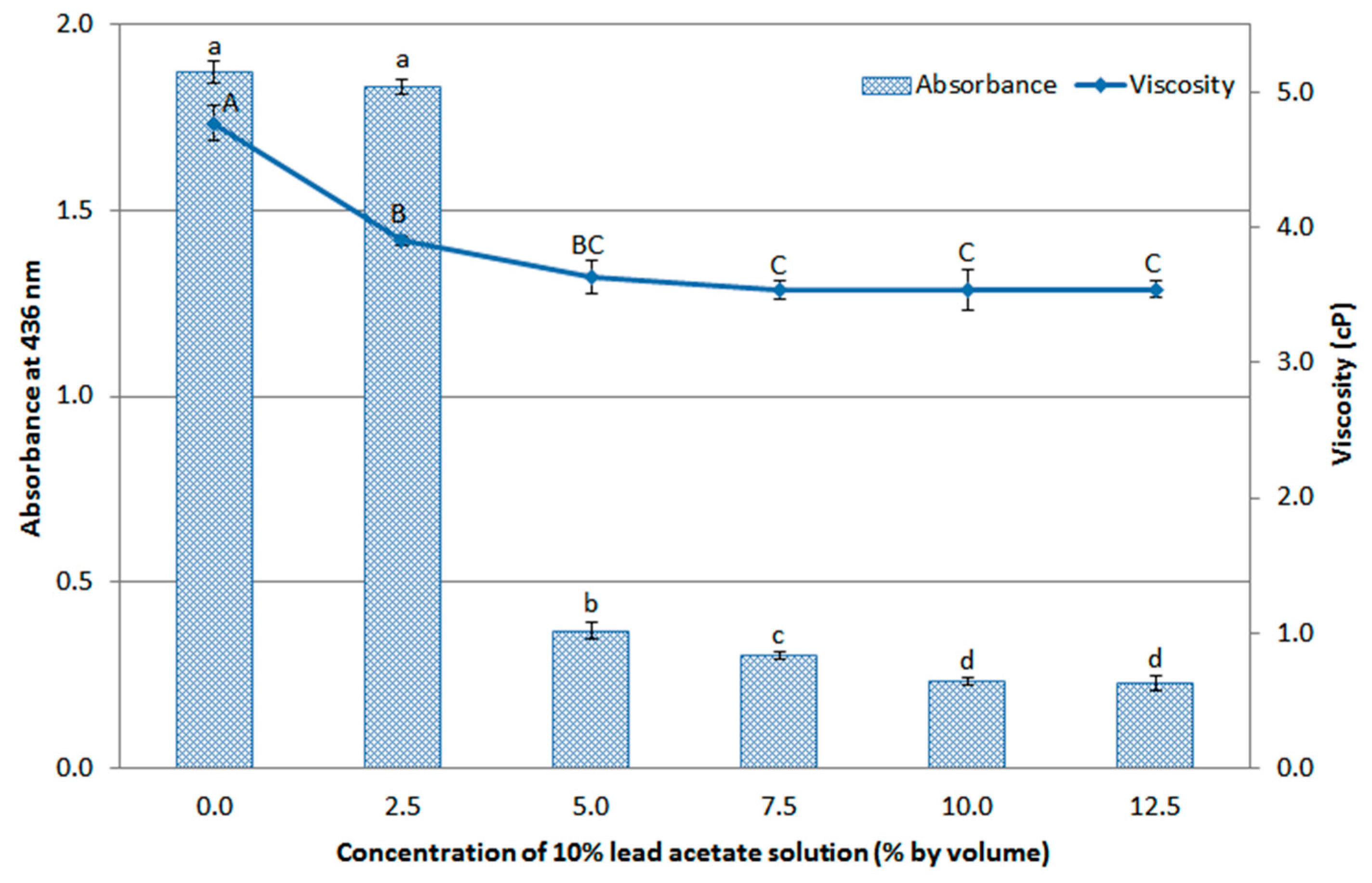
3.3. Effect of Purification on Physicochemical Properties of Extracts and Theobromine Content from Cacao Pod Husk
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAOSTAT. FAO Statistic Division. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: http://faostat3.fao.org/home/E (accessed on 31 December 2015).
- Nguyen, V.T. Mass proportion, proximate composition and effects of solvents and extraction parameters on pigment yield from cacao pod shell (Theobroma cacao L.). J. Food Process. Preserv. 2014, 39, 1414–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sena, A.R.; de Assis, S.A.; Branco, A. Analysis of theobromine and related compounds by reversed phase high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection: An update (1992–2011). Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2011, 49, 413–423. [Google Scholar]
- Kasabe, A.J.; Badhe, G.B. Extraction and estimation of theobromine in marketed tea by HPTLC and UV method. Int. J. Appl. Biol. Pharm. Technol. 2010, 1, 367–373. [Google Scholar]
- Arlorio, M.; Coisson, J.; Travaglia, F.; Varsaldi, F.; Miglio, G.; Lombardi, G.; Martelli, A. Antioxidant and biological activity of phenolic pigments from Theobroma cacao hulls extracted with supercritical CO2. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerstone, J.; Chimel, M. Methods for Extracting Cocoa Procyanidins and Extracts Thereof. U.S. Patent 0309991 A1, 17 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Peralta-Jiménez, L.; Cañizares-Macías, M. Ultrasound-assisted method for extraction of theobromine and caffeine from cacao seeds and chocolate products. Food Biol. Technol. 2013, 6, 522–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munier, F.; Hartadi, H. Theobromine content in cocoa pod husk (Theobroma cacao) fermented by Aspergillus spp. in different of chop sizes and fermentation times. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Seminar on Animal Industry, Jakarta, Indonesia, 5–6 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Adamafio, A. Theobromine toxicity and remendiation of cacao by-products: An overview. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 13, 570–576. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Wan, X.; Bal, R.; Yang, H. Theobromine and caffeine recovery with solvent extraction. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2003, 38, 3609–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Sánchez, B.; Sattayasamitsathit, S.; Gao, W.; Santos, L.; Fedorak, Y.; Singh, V.V.; Orozco, J.; Galarnyk, M.; Wang, J. Self-propelled activated carbon janus micromotors for efficient water purification. Small 2015, 11, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, D.B.; Roberto, B.; Allan, S.H. Optimization of Bleaching Process in Edible Oil Processing. AOCS Lipid Library. Available online: http://lipidlibrary.aocs.org/OilsFats/content.cfm?ItemNumber=40321 (accessed on 8 June 2016).
- Nguyen, V.T.; Vuong, Q.V.; Bowyer, M.C.; van Altena, I.A.; Scarlett, C.J. Effects of different drying methods on bioactive compound yield and antioxidant capacity of Phyllanthus amarus. Dry. Technol. J. 2015, 33, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Pham, Q.T. Effect of raw material and processing factors on the production of effervescent artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) tea tablets. Int. J. Food Eng. 2011, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Ueng, J.P.; Tsai, G.J. Proximate composition, total phenolic content, and antioxidant activity of Seagrape (Caulerpa lentillifera). J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, C950–C958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcel, B.K.G.; Andre, K.B.; Theodore, D.; Eeraphin, K.C. Waste and by-products of cocoa in breeding: Research synthesis. Int. J. Agron. Agric. Res. 2011, 1, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Bowyer, M.C.; Vuong, Q.V.; van Altena, I.A.; Scarlett, C.J. Phytochemicals and antioxidant capacity of Xao tam phan (Paramignya trimera) root as affected by various solvents and extraction methods. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 67, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.P.; Stathopoulos, C.; Parks, S.; Roach, P. An optimised aqueous extract of phenolic compounds from bitter melon with high antioxidant capacity. Antioxidants 2014, 3, 814–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlader, S.I.; Rahman, M.; Khalipha, A.B.R.; Rahman, M.; Ahmed, F. Antioxidant and antidiarrhoeal potentiality of Diospyros blancoi. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 8, 403–409. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, K.Y.; Lakshmi, S.M. Pharmacognostical and phytochemical investigation of whole plant of Oxalis corniculata L. Int. J. Phytother. 2012, 2, 34–53. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Pham, H.N.T.; Bowyer, M.C.; van Altena, I.A.; Scarlett, C.J. Influence of solvents and novel extraction methods on bioactive compounds and antioxidant capacity of Phyllanthus amarus. Chem. Pap. 2016, 70, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, L.; Marszalek, K.; Skąpska, S. Extraction of phenolic compounds from sour cherry pomace with supercritical carbon dioxide: Impact of process parameters on the composition and antioxidant properties of extracts. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Proximate Composition | Fresh Weight (%) | Dry Weight (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture | 87.06 ± 0.58 * | - |
| Crude protein (protein factor: 6.25) | 0.31 ± 0.21 | 2.42 ± 0.37 |
| Crude lipid | 0.12 ± 0.12 | 0.93 ± 0.34 |
| Ash | 1.48 ± 0.31 | 11.44 ± 0.41 |
| Carbohydrate (include crude fiber) | 11.03 ± 0.21 | 85.21 ± 0.29 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, V.T.; Nguyen, N.H. Proximate Composition, Extraction, and Purification of Theobromine from Cacao Pod Husk (Theobroma Cacao L.). Technologies 2017, 5, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies5020014
Nguyen VT, Nguyen NH. Proximate Composition, Extraction, and Purification of Theobromine from Cacao Pod Husk (Theobroma Cacao L.). Technologies. 2017; 5(2):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies5020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Van Tang, and Nghia Huu Nguyen. 2017. "Proximate Composition, Extraction, and Purification of Theobromine from Cacao Pod Husk (Theobroma Cacao L.)" Technologies 5, no. 2: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies5020014
APA StyleNguyen, V. T., & Nguyen, N. H. (2017). Proximate Composition, Extraction, and Purification of Theobromine from Cacao Pod Husk (Theobroma Cacao L.). Technologies, 5(2), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies5020014