Abstract
The combination of Chemical Looping Combustion (CLC) with Calcium Looping (CaL) using integrated pellets is an alternative CO2 capture process to the current amine-based sorbent processes, but the pellets lose sorption capacity over time. In this paper, the deactivation behavior of CaO, CuO and CuO/CaO integrated pellets used for multiple (16–20) cycles in a thermogravimetric analyzer was studied. The impact of thermal treatment and the presence of steam on the deactivation were also investigated. Nitrogen physisorption and scanning electron microscopy/energy-dispersive X-ray analysis were used to characterize the pellets. The analysis revealed significant migration of the copper to the surface of the composite pellets, which likely suppressed carbonation capacity by reducing the accessibility of the CaO. While thermal pre-treatment and steam addition enhanced the performance of the base CaO pellets, the former led to cracks in the pellets. In contrast, thermal pretreatment of the CuO/CaO composite pellets resulted in worse CLC and CaL performance.
1. Introduction
Multiple solutions have been developed to economically capture carbon dioxide. Among these, absorption using amine-based sorbents remains the most extensively-employed commercial scale technology [1]. Due the inherent economics and energy penalty of amine based solvents, however, alternative technologies may be more suitable depending on the process situation [2]. For instance, CO2 capture applications, such as flue gases from fossil fuel power plants (post-combustion) [3] and biomass gasifiers (pre-combustion) [4], with calcium looping (CaL) and chemical looping combustion (CLC) have been shown to be promising. One of the remaining challenges, however, is the deactivation (i.e., loss of reactivity, Equation (1)) of CaO based pellets used in this process. CaL consists of two stages: the forward reaction, Equation (1) to capture CO2 is named carbonation while the reverse reaction to release CO2, is named calcination. The carbonation is exothermic, and characterized by an initial rapid rate, which is kinetically controlled, followed by an abrupt transition to a slow reaction rate, which is diffusion controlled [5,6]. The reverse endothermic calcination to regenerate the CaO sorbent can be carried out in an oxyfuel combustor at high temperatures (up to 900 °C) to produce a concentrated stream of CO2 for compression and storage [7]. The integration of chemical looping combustion (CLC) within CaL was proposed by Abanades et al. [8], and Manovic and Anthony [3] to offset the energy penalty from oxyfuel combustion (air separation) units. The irreversibility of the reaction in Equation (1) is often ascribed to sorbent sintering or agglomeration [3,9,10,11], as inferred by pore size measurements and microscopy.
In CLC, metal oxides act as oxygen carriers and transfer the oxygen from the air to the fuel, thus avoiding direct contact and combustion [12]. CuO is a suitable oxygen carrier due to its high oxygen-carrying capacity (0.20 g O2/g CuO), high reactivity, and relatively low cost compared to metals such as NiO and CoO [3]. Since the reduction of the metal oxide is an exothermic reaction, it can supply the necessary heat energy to release CO2 from the sorbent via calcination, which in turn avoids the energy penalties inherent to technologies, such as oxyfuel combustion [13]. Once the combustion reaction Equation (2) is complete, the oxygen carrier is regenerated by exposure to air Equation (3).
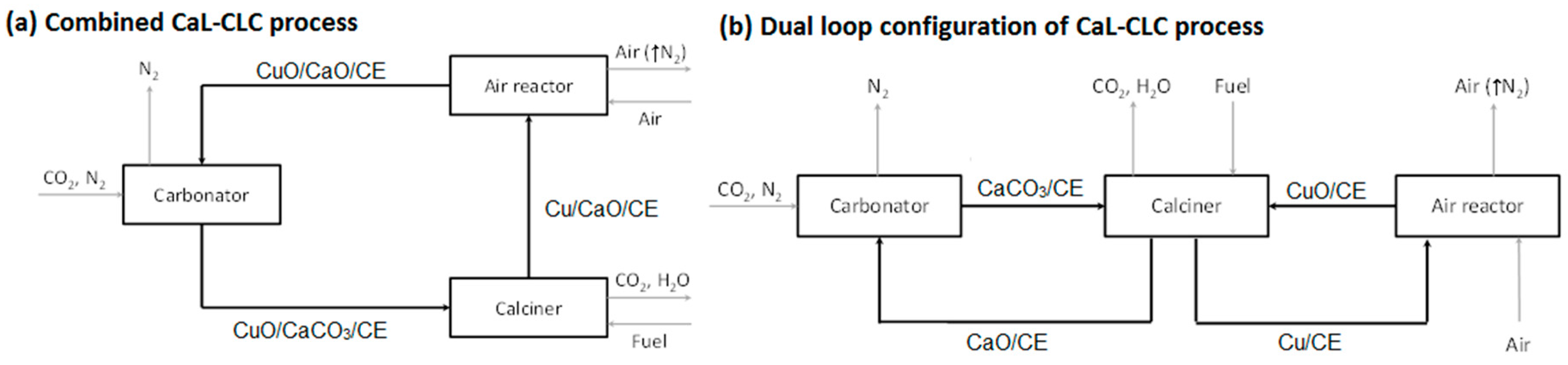
The stream obtained after the combustion of the fuel contains mainly CO2, possibly some unreacted alkanes from the fuel (e.g., natural gas), and steam that can be easily separated by condensation to produce a stream of CO2, which can be subsequently compressed and transported for storage [14]. The viability of various options of using CaL/CLC for post combustion CO2 capture has been investigated via process simulation [15]: Namely, integrated CaL/CLC using single CuO/CaO pellets (Figure 1a), and a dual-loop process with decoupled CuO and CaO pellets (Figure 1b). The simulation results showed that both configurations of CaL/CLC process had similar energy penalty reductions up to 40% as compared to just CaL process from the elimination of an air separation unit, but at the cost of increased solids circulation and process complexity. The dual-loop process required 10% to 20% less solids circulation to achieve similar energy efficiency as compared to the single-loop process. It is possible to offset the difference in the solids circulation between the two configurations if the carbonation capacity of the combined CaL/CLC is substantially improved which was part of the objective of this study.
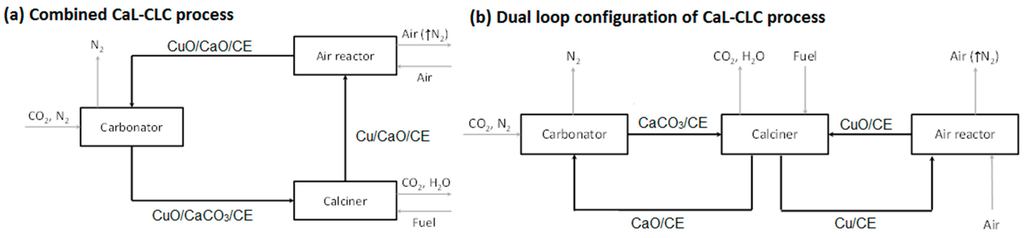
Figure 1.
Schematic of the CaL-CLC process in a (a) combined configuration; or (b) dual loop configuration. Black and gray arrows represent flow of solids and gases, respectively.
Several researchers have proposed combining CaL and CLC functions in a single composite pellet but all reported decreased carbonation performance relative to pure CaO sorbents [3,8,16]. Different strategies have been proposed to improve the performance. For example, Qin et al. [17] studied various heat pre-treatment procedures with CaO/CuO pellet mixing to overcome the loss of performance and found that certain thermal treatments improved the multi-cycle CaL stability. Steam, which is present in post combustion flue gas, has also been demonstrated to have a positive effect on the stability of pure CaO pellets to capture CO2 over multiple cycles [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. Several theories have been proposed to explain how steam improves the CaL process. Manovic et al. [19] suggested that the presence of steam promotes carbonation by enhancing the solid-state diffusion of CO2 through the CaCO3 layer forming over the CaO. Dou et al. [24] suggested that steam promotes the formation of Ca(OH)2 that will react with CO2 to form Ca(HCO3)2 and increase the amount of carbonation. In contrast, Yang and Xiao [22] reported that the performance of CaO was improved even without the formation of Ca(OH)2. Arias et al. [25] reported that the kinetic-controlled part of the carbonation reaction was not affected by the presence of steam, but the diffusion-controlled part was enhanced.
In an effort to better understand the deactivation and promotion processes, both individual CuO and CaO pellets, as well as integrated CuO/CaO pellets, were characterized after multiple CaL and/or CLC cycles. The impact of the two reported methods to reduce deactivation—thermal pretreatment and exposure to steam during carbonation—on the characteristics of the pellets has also been investigated. The CLC and/or CaL performance was measured with a thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA) using carbonation at 650 °C, calcination/reduction at 875 °C, and oxidation at 900 °C. The pellets were characterized with physisorption to determine surface area and pore volume, and scanning electron microscopy with field emission imaging to determine the distribution of components. The rates of deactivation were fit to an exponential decay model.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
Pellets containing CaO, CuO or a combination of CaO and CuO, and held together with a calcium aluminate-based cement (CE) binder were used in simulated dual loop (CaO/CE and CuO/CE) or single loop (CuO/CaO/CE) configurations (Figure 1). The CaO in the pellets originated from powdered (< 45 µm) Cadomin limestone (Cadomin, AB, Canada), while the CuO powder (Sigma-Aldrich Corporation, St. Louis, MO, USA) consisted of particles less than 5 µm in size. The calcium aluminate binder was a commercially available cement with the majority of particles (> 80%) of sizes less than 45 µm (CA-14, 71% Al2O3, and 28% CaO, Almatis Inc., Rotterdam, The Netherlands). The components were mixed together and pressed into pellets with sizes of 250–650 µm and the compositions given in Table 1. The compositions were chosen based on previous studies [3].

Table 1.
Composition, surface area and pore volume of the three types of pellets.
2.2. Characterization
Physisorption analysis with N2 adsorption was carried out at −196 °C using a Tristar 3000 adsorption instrument (Micromeritics Instrument Corporation, Norcross, GA, USA). Prior to analysis, the received samples were degassed under vacuum at 300 °C for 3 h. The reported values are the averages of measurements on three different samples.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images were obtained using a Quanta 250 FEG field emission scanning electron microscope (FEI Company, Hillsboro, OR, USA). This instrument also had energy-dispersive X-ray analysis capabilities for element detection and mapping. The samples were not sputter coated prior to imaging analysis because surface charging was minimal.
2.3. CaL/CLC Cyclic Reactivity Measurement
The performance of the pellets was studied using two different thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA) instruments. CaL/CLC experiments without steam were performed on a Cahn Thermax 500 instrument (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Rockford, IL, USA) at the University of Calgary; while experiments with steam were performed using a Cahn 1000 TGA at Canmet Energy National Laboratory, Ottawa. Sample sizes of approximately 25–30 mg were used for each experiment, and the gas flow rates were 300 mL/min.
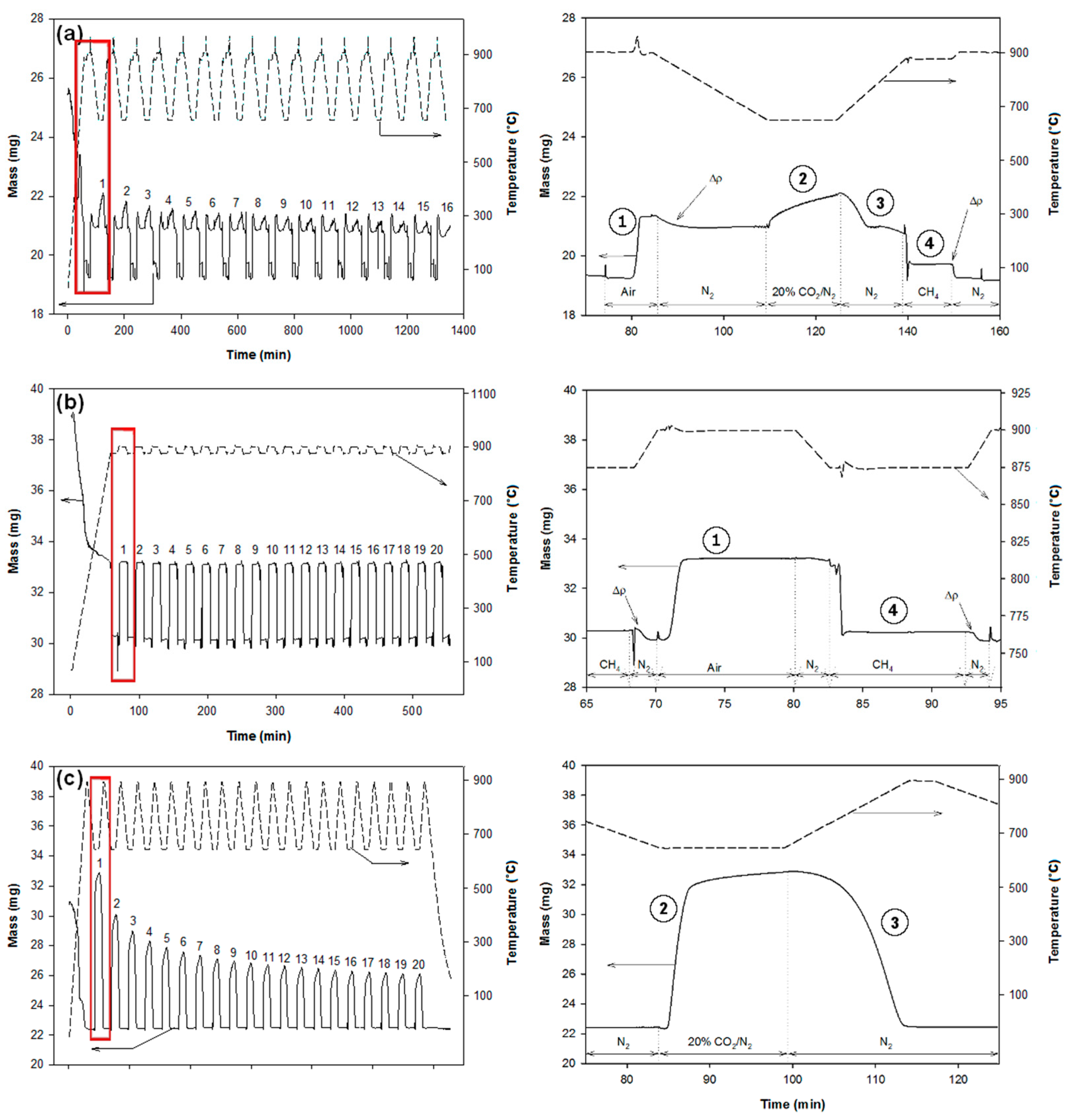
According to their composition, the pellets were cycled as shown in Figure 2. Each cycle of CaL and CLC (for 50% CuO/CaO/CE samples) consisted of the following steps: (1) oxidation in flowing air (Praxair Inc., Danbury, CT, USA) at 900 °C for 10 min; (2) carbonation in flowing of CO2 (20%, balance N2, Praxair) at 650 °C to simulate a coal-fired flue gas environment for 15 min; (3) calcination in flowing N2 (Praxair, 99.999%) while heating from 650 °C to 875 °C; and (4) reduction in flowing CH4 (Praxair, 99.7%) at 875 °C for 10 min. The standard heating and cooling rates were 15 °C/min and 10 °C/min, respectively. Experiments with the CaO/CE samples required only calcination and carbonation steps while those with the CuO/CE samples required only oxidation and reduction steps, all at the conditions given for the integrated pellets (as shown in Figure 2b,c). A maximum of 16 cycles was performed with the CuO/CaO/CE samples while 20 cycles were performed with the CaO/CE and CuO/CE samples according to the limits of the TGA software (Thermal Analyst, version 1.3.2.2). Typical TGA data for each of the samples are given in Figure 2. Each reported experiment was performed three times to check the reproducibility, and determine standard errors.
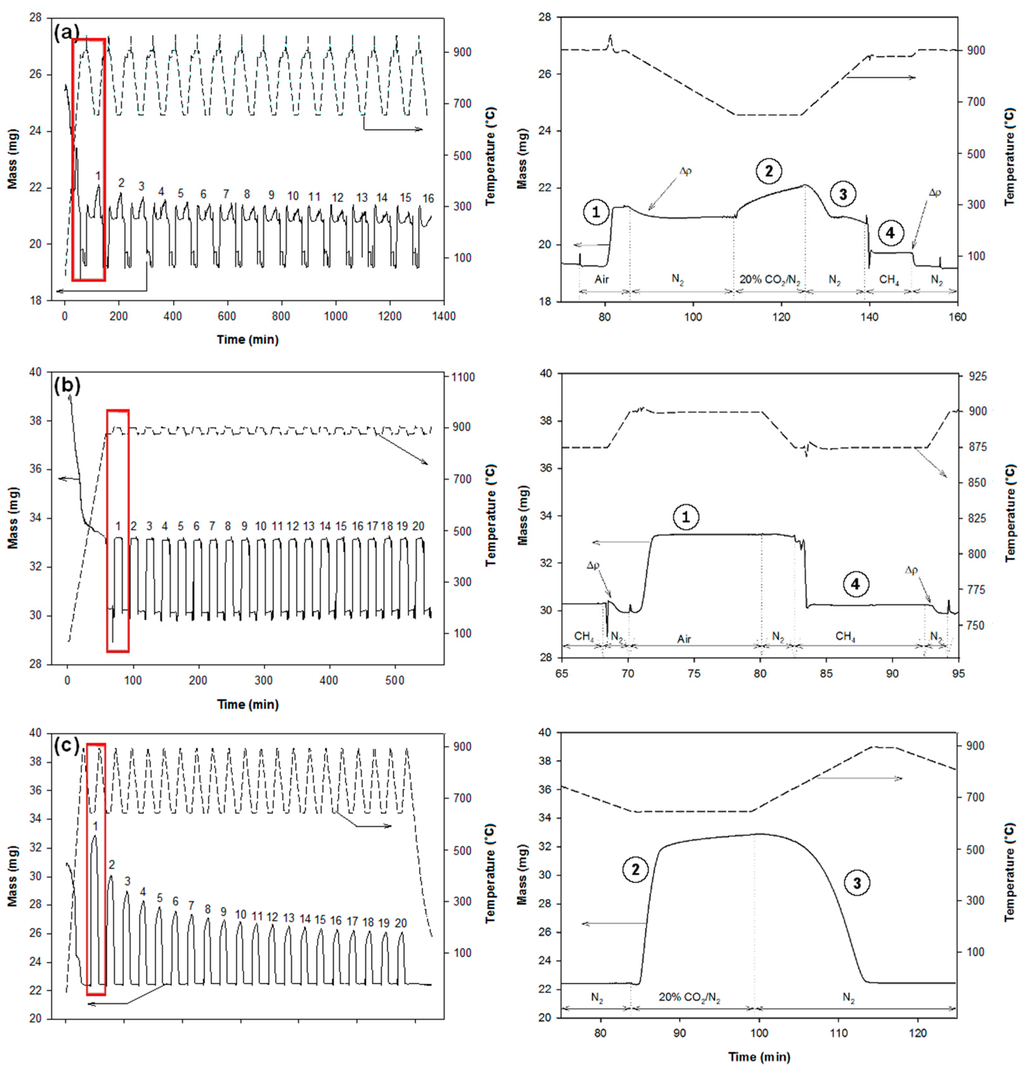
Figure 2.
Mass (left axis) and temperature (right axis) profiles recorded by TGA during multiple CaL and/or CLC cycles for (a) CaO/CuO/CE pellets; (b) CuO/CE pellets; and (c) CaO/CE pellets. The graphs in the right column are magnifications of the highlighted sections of each respective graph. ① oxidation, ② carbonation, ③ calcination, ④ reduction. Δρ are differences of buoyancies due to either the change of temperature or change of gas.
The recorded mass change during carbonation was attributed only to CaCO3 formation as given in Equation (1), such that the CO2 capacity and conversion for carbonation, were calculated as follows:
where is the mass of carbonated pellets, is the mass of oxidized pellets, is the mass fraction of CaO in the pellets, is the molecular weight of CaCO3 and is the molecular weight of CaO.
To test the effects of thermal pretreatment, some pellets were heated in an ex-situ reactor at rates of 1.5 °C/min or 7.5 °C/min to 900 °C in either flowing N2 or air (50 mL/min) and then held for 2 h. After 2 h, the samples were cooled in flowing N2 (50 mL/min). In these cases, the heating rate and atmosphere have been appended to the sample names. For example, CaO/CE-1.5N2 refers to CaO/CE pellets heated at 1.5 °C/min in N2.
3. Results and Discussion
The surface areas and pore volumes of the pellets are small (Table 1). The CuO/CE pellets had the highest surface area of 34 m2/g, while the CaO/CE pellets had the highest pore volume of 0.11 cm3/g. These results are consistent with those reported previously [26]. The higher proportion of cement, which contains high surface area alumina [18] in the CuO/CE pellets is consistent with their higher surface area.
3.1. Performance of Pellets over Multiple CaL and/or CLC Cycles
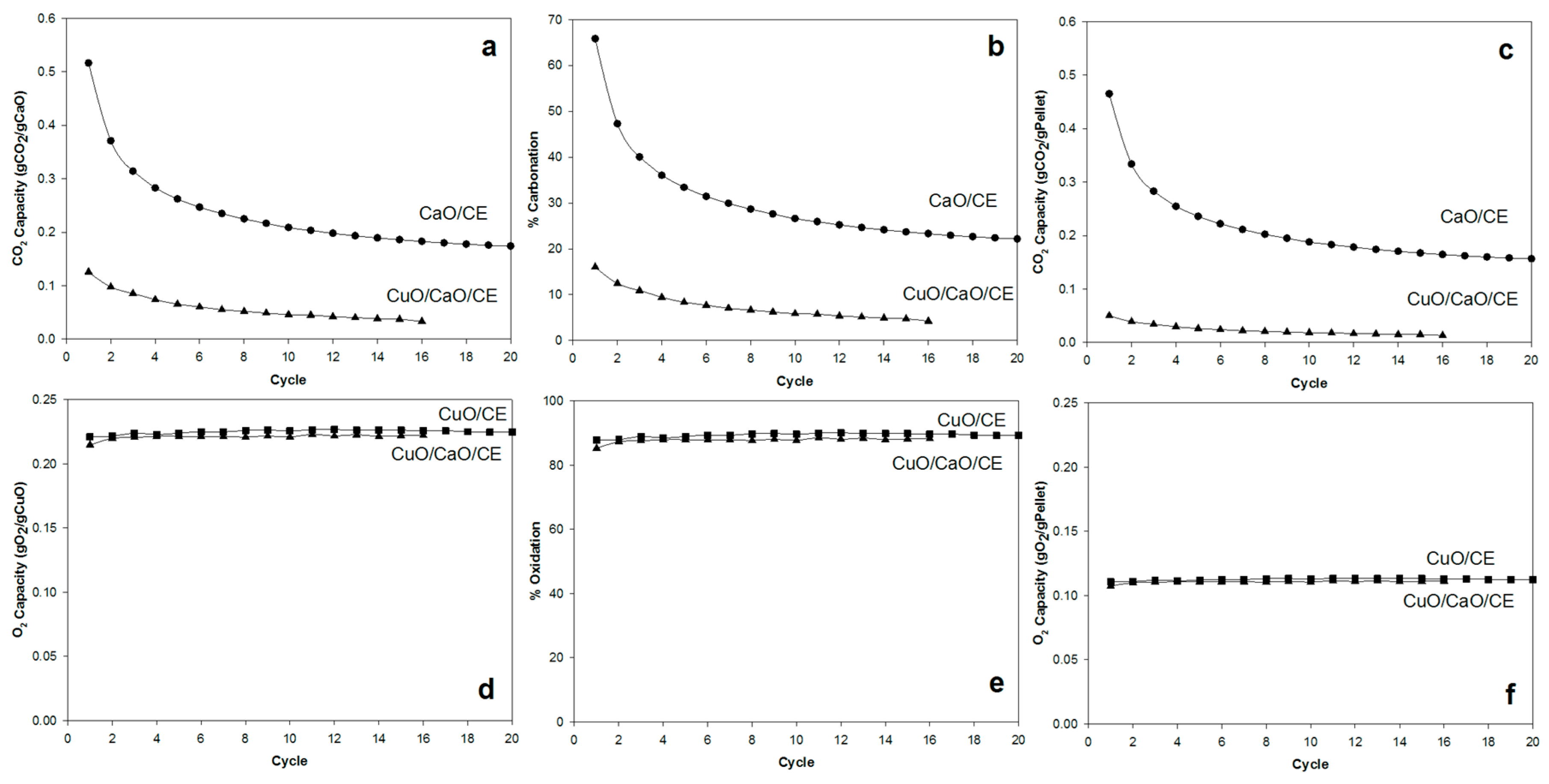
Figure 3 compares the performance of the CuO/CaO/CE, CaO/CE, and CuO/CE pellets. The CaL performance is shown based on both the CO2 capacity Equation (4), which is the amount of CO2 captured per theoretical amount of CaO (gCO2/gCaO, Figure 3a), and the percent carbonation, Equation (5), which is the actual amount of CO2 divided by the theoretical amount of CO2 capacity based on the carbonizable/available CaO (Figure 3b); while, the CLC performance is shown in terms of the O2 capacity (gO2/gCuO, Figure 3c) and % oxidation (Figure 3d).
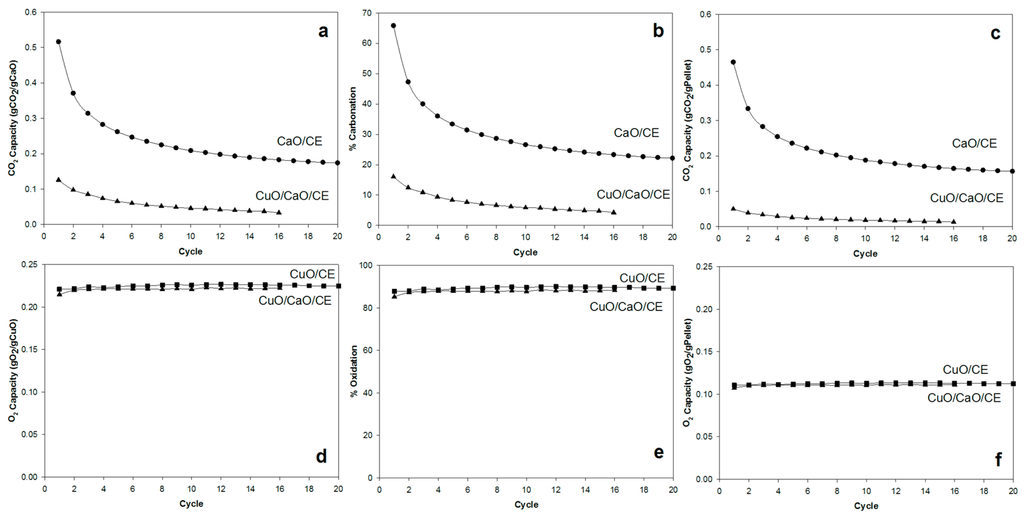
Figure 3.
Performance of CaO/CuO/CE, CuO/CE, and CaO/CE pellets over multiple cycles in terms of (a) CO2 capacity per gram of CaO; (b) % Carbonation; (c) CO2 capacity per gram of pellets; (d) O2 capacity per gram of CuO; (e) % Oxidation; and (f) O2 capacity per gram of pellets.
For both CuO/CaO/CE and CuO/CE pellets, the oxidation capacity remained essentially constant −0.22 gO2/gCuO (Figure 3c) and ~90% oxidation (Figure 3d)—over multiple cycles, suggesting its suitability as an oxygen carrier under the conditions of the tests. Using similar pellets, Rahman et al. [4] observed a ~15% loss in oxygen conversion after 15 cycles with reduction with syngas (10% H2 and 20% CO) in pre-combustion CO2 capture. In contrast, the capacity for CO2 (carbonation) decreased with increasing cycle number (Figure 3a,b) and the CO2 capacity was significantly lower for the CuO/CaO/CE pellets than for the CaO/CE pellets. More specifically, the initial CO2 capacity of the CuO/CaO/CE pellets was approximately 25% of that of the CaO/CE pellets. Given that the capacity has been normalized to the amount of CaO in each type of pellets, this result indicates that the presence of CuO is hindering the accessibility of the CaO. The carbonation capacity of the CuO/CaO/CE pellets decreased exponentially, losing more than 50% capacity after 6 cycles and more than 70% capacity after 16 cycles. Similarly, the carbonation capacity of the CaO/CE pellets decreased exponentially with a loss of 66% after 20 cycles. The loss in capacity for CaO/CE was similar to that of the CuO/CaO/CE pellets comparing at 16 cycles (~64%). Fitting the carbonation data to a two-parameter exponential decay equation gave decay constants of 0.5 and 0.2 for the CaO/CE and CuO/CaO/CE pellets, respectively. Thus, the decay rate of the CaO/CE pellets was approximately 2.5 times higher than that of the CuO/CaO/CE pellets. The initial CO2 capacity of the former pellets, however, was 4 times higher than that of the latter pellets, and so there was more capacity to lose.
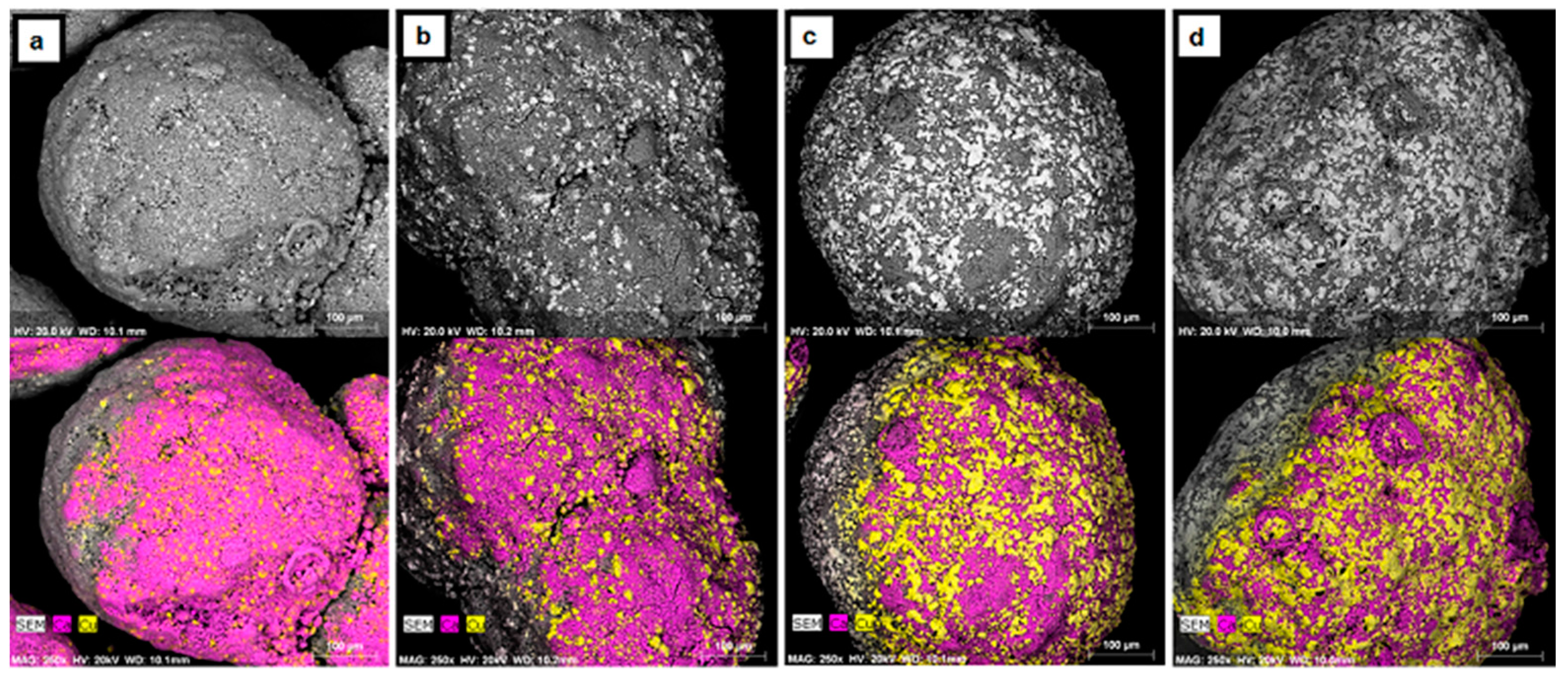
A decrease in the CO2 carrying capacity of the pellets with cycling has been observed previously, and sintering of Cu has been suggested as the main cause for the deactivation [3,9,10,11]. To verify that Cu is sintering, the pellets were examined with SEM/EDX as shown in Figure 4. The images shown are typical of all pellets without pretreatment. The “wrapping effect” of CuO over CaO with cycling is evident in these images, which shows the migration of Cu to the surface of the pellets with increased cycling. The melting points of Cu and CuO are 1084 °C and 1336 °C, respectively [16]. Although these melting points are several hundreds of degrees above the calcination/reduction (875 °C) and oxidation (900 °C) temperatures, the metal and metal oxide phases will soften and be mobile at the Tamman temperature of Cu and CuO (405 °C and 527 °C, respectively). Furthermore, the presence of CaCO3 has been shown to lower the melting points of other minerals including Cu and CuO [16].
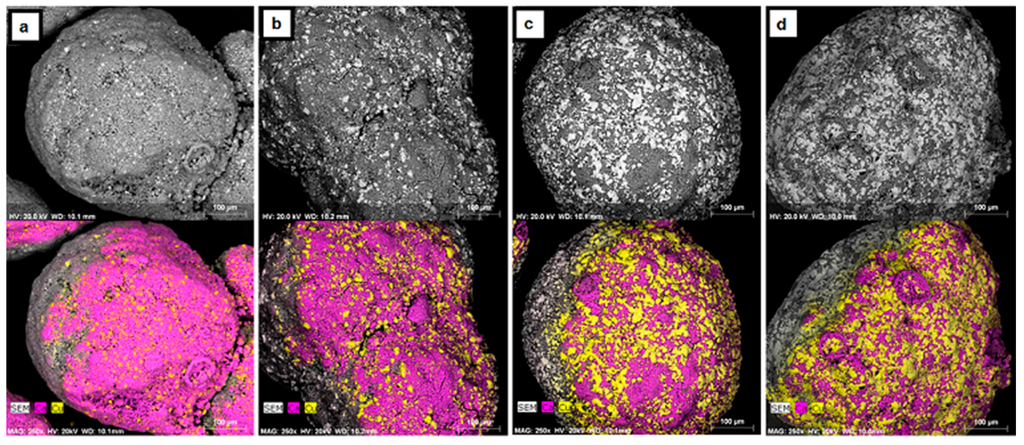
Figure 4.
SEM micrographs with corresponding EDX maps of CaO/CuO pellets after (a) 0; (b) 5; (c) 10; and (d) 15 cycles of CaL and CLC. The elements Ca and Cu are represented in purple and yellow, respectively.
3.2. Effect of Thermal Pre-Treatments on CO2 Capacity
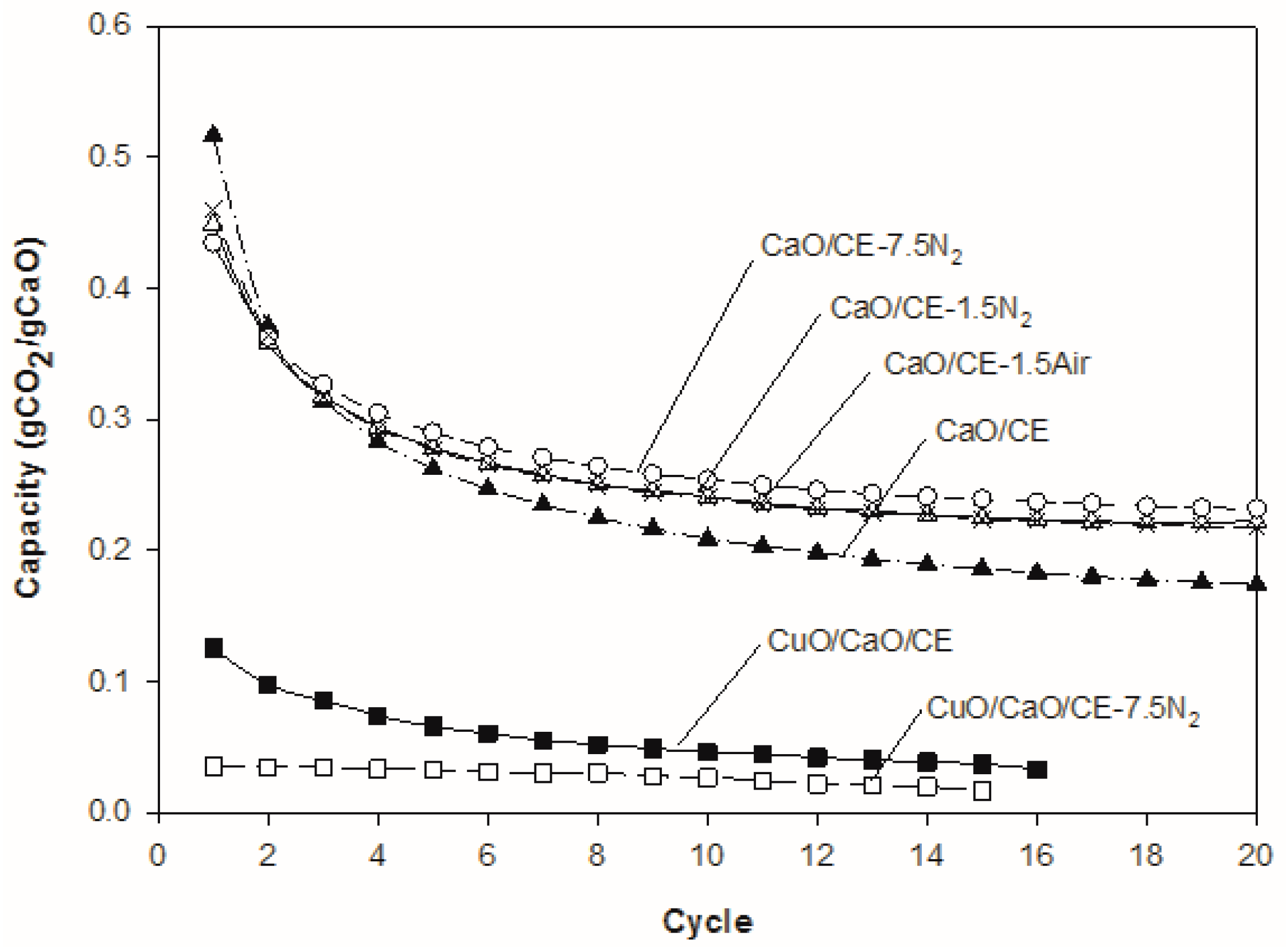
The CO2 capacity was higher in the first cycle for the untreated CaO/CE pellets than for CaO/CE pellets that were thermally treated (Figure 5). After three cycles, however, all thermally treated pellets had higher capacities, suggesting that the thermal treatment stabilized the pellets. At the end of 20 cycles, the capacity of the untreated CaO/CE pellets was 0.17 gCO2/gCaO which is less than 0.22 gCO2/gCaO for the pellets treated at 1.5 °C/min in either air or N2 and 0.23 gCO2/gCaO for the pellets heated at the higher rate of 7.5 °C/min in N2. The corresponding percent decreases in capacity over 20 cycles for these pellets were 65%, 53%, 51% and 46%, respectively. Since there were no noticeable differences in the results based on the use of air or N2 as a medium during the thermal pretreatment, it can be concluded that oxygen does not exert any significant effect on the state of the pellets.
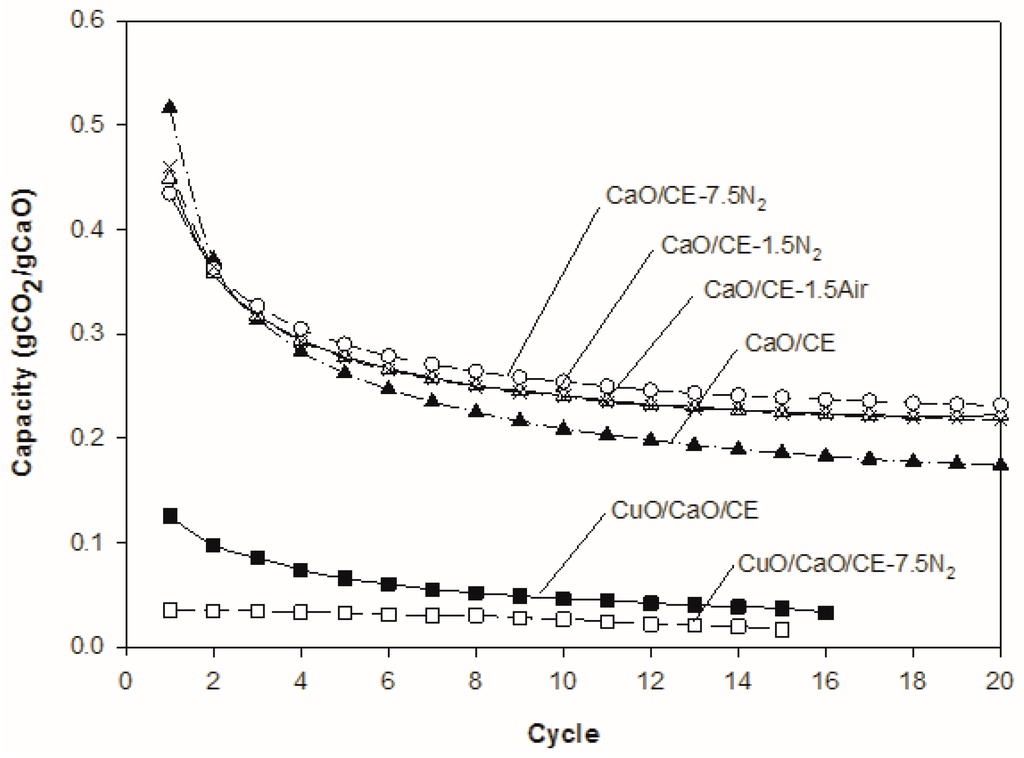
Figure 5.
Impact of different thermal pretreatments on the performance of CaO/CE pellets over multiple CaL cycles, and of CuO/CaO/CE pellets over multiple CaL and CLC cycles. Each curve is the average of three runs.
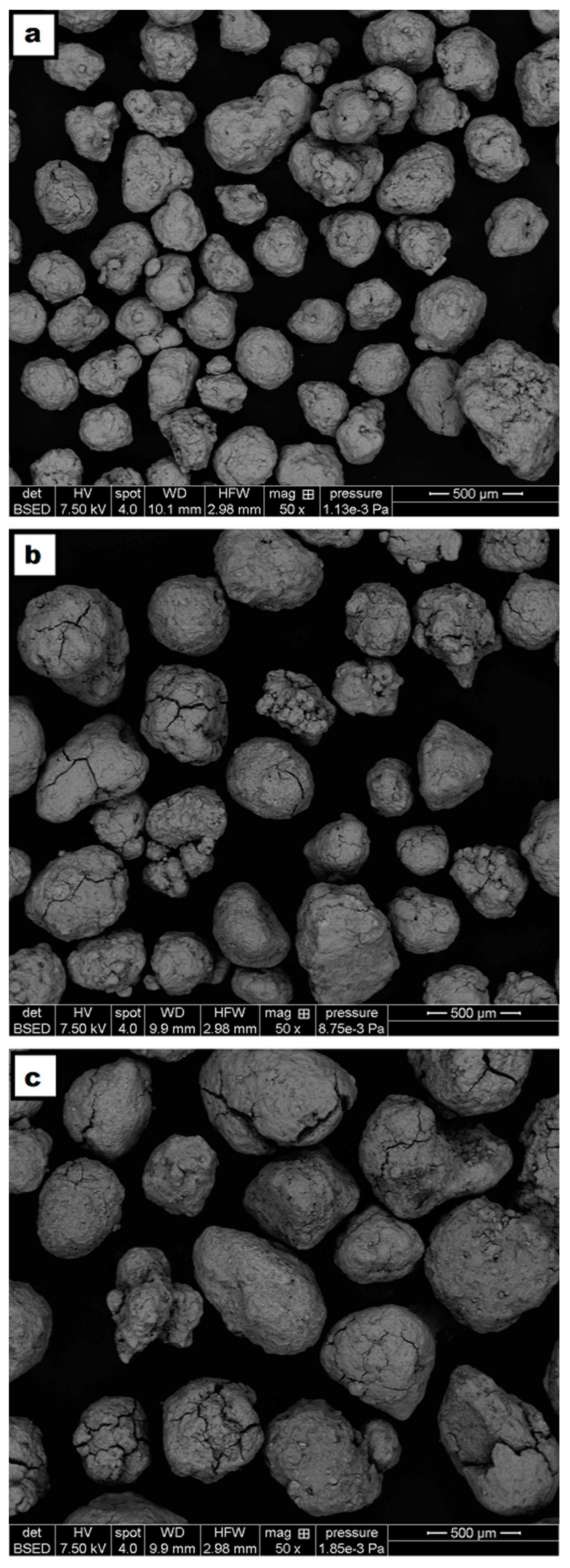
A faster heating rate (7.5 °C/min versus 1.5 °C/min) during the pretreatment may be beneficial; the confidence intervals for the CaO/CE-7.5N2 and CaO/CE-1.5N2 samples overlap and so further testing is required to confirm the optimal heating rate. A t-test with 95% confidence interval confirmed a significant improvement of CaO/CE-7.5N2 over CaO/CE at the 20th cycle. Other authors have used different temperatures and holding times [10,27] than those in the study herein (i.e., 900 °C and 2 h) but also saw an improvement in the stability of the CaO after thermal treatment. SEM micrographs of the CaO/CE pellets as received, after heating at 7.5 °C/min but before use, and after heating at 7.5 °C/min and 20 cycles are shown in Figure 6. There is a distribution of particles sizes in the as-received pellets (Figure 6a). The pellets heat-treated at 7.5 °C/min in flowing N2 had evidence of fractures /fissures on most pellets (Figure 6b). Although these fractures will be beneficial for diffusion, the particles will be less mechanically stable within the process. The CaO/CE-7.5N2 pellets in Figure 6c (after 20 cycles) were obtained at the end of a cycle (i.e., after carbonation) and so these pellets are larger than those in Figure 6b (at 0 cycles).
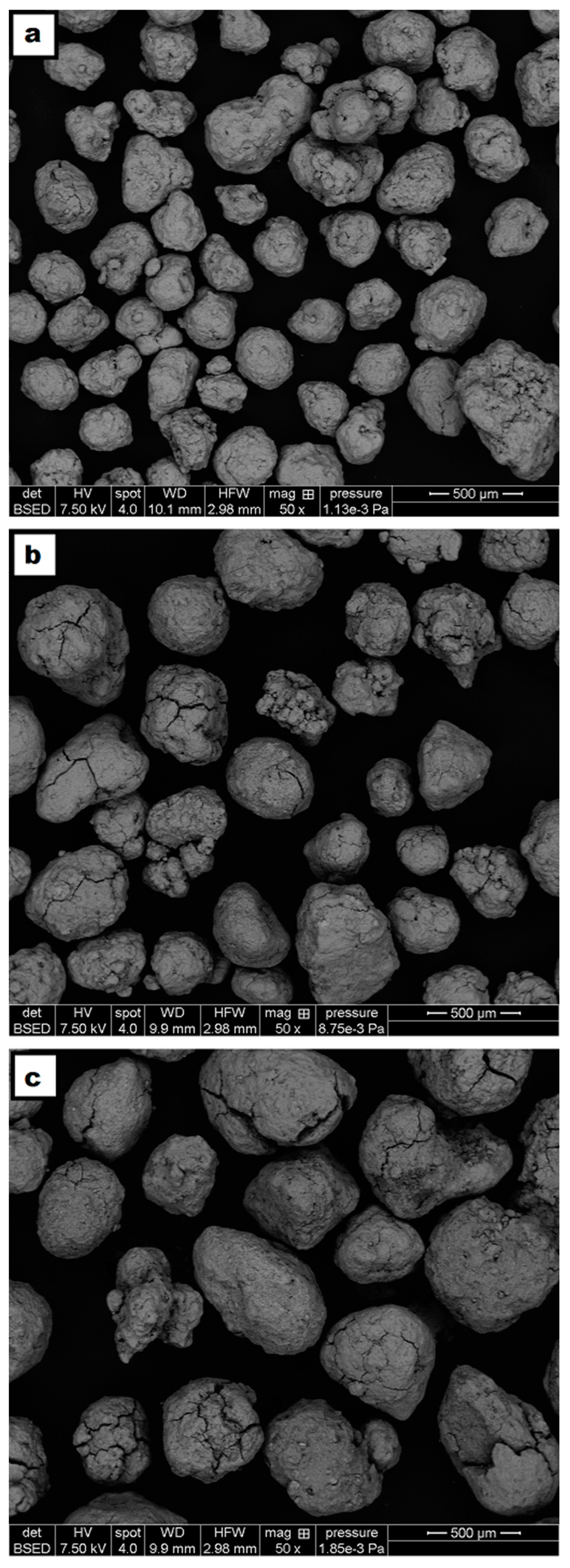

Figure 6.
SEM micrographs of (a) CaO/CE as received; (b) CaO/CE-7.5N2 at 0 cycle; and (c) CaO/CE-7.5N2 at 20 cycles (carbonated).
For the CuO/CaO/CE pellets, a thermal pretreatment with a heating rate of 7.5 °C/min in flowing N2 was tested because this treatment gave the best results for the CaO/CE pellets. For the integrated pellets, the thermal treatment resulted in more stable performance but the CO2 capacity was less than that of the untreated CuO/CaO/CE pellets (Figure 5). The additional heat treatment may have enhanced the sintering of the Cu. When applied before mixing with the CaO, heat treatment has been shown to improve the carbonation stability over 40 cycles [17]. Specifically, Qin et al. [17] used a heat pretreatment (800–1000 °C, 0.5–8 h) with the copper precursor (copper acetate) and observed a 50% increase in the carbonation capacity of their CuO/CaO/MgO pellets after 40 cycles. The authors suggested that this approach allowed the majority of the Cu/CuO components to form stable clusters that would not coat the CaO active surfaces during carbonation. Their wet impregnation method likely produced much smaller (nanometer-sized) Cu particles than the dry mixing of micron-sized CaO and CuO particles used herein.
3.3. Effect of Steam Addition on CO2 Capacity
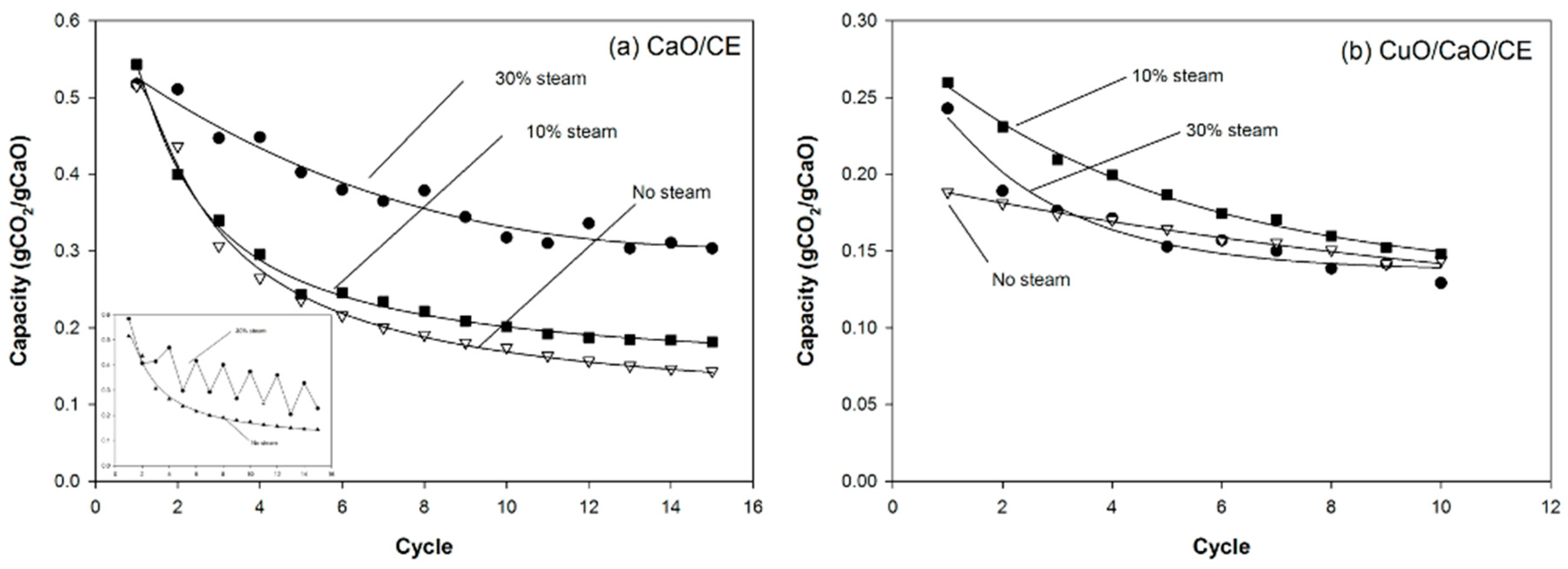
The addition of steam enhanced the performance of both the CaO/CE (Figure 7a) and CuO/CaO/CE pellets (Figure 7b). The capacity of the CaO/CE pellets after 15 cycles was 0.142 gCO2/gCaO without steam, 0.169 gCO2/gCaO with 10% steam, and 0.237 gCO2/gCaO with 30% steam. The results without steam and with 10% steam are not significantly different (t-test) even at the 15th cycle. With a higher level of steam (30%), there was a significant improvement in the performance of the CaO/CE pellets. At 30% steam, however, the carbonation conversion of CaO/CE pellets fluctuated between cycles. Five, instead of three, experiments were performed to confirm that this behavior was reproducible. The averages of the minimum and maximum capacities for each cycle in the five runs are plotted in Figure 7a. The inset graph shows representative data from one of the five runs. Even with the fluctuations, the capacity with 30% steam was always higher than with no steam. The reason for the fluctuations is not known.
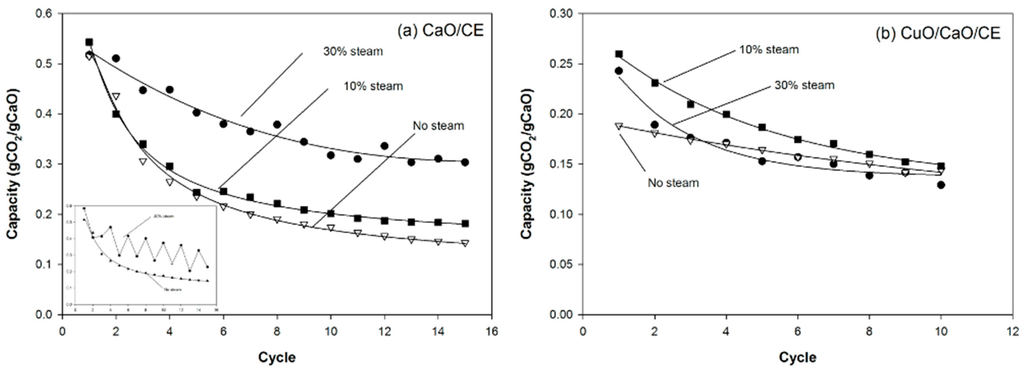
Figure 7.
Impact of different steam concentrations during carbonation on the performance of (a) CaO/CE pellets over multiple CaL cycles; and (b) CuO/CaO/CE pellets over multiple CaL and CLC cycles. The inset in Figure 7a demonstrates the fluctuations in performance when using 30% steam with the CaO/CE pellets.
For the CuO/CaO/CE pellets, a higher level of steam was not beneficial (Figure 7b). That is, the performance with 10% steam was better than 30% steam. The 30% steam addition resulted in a rapid loss in capacity and after 4 cycles the CO2 capacities were approximately 0.170 gCO2/gCaO with 30% steam or without steam. A fluctuation pattern similar to the experiment with the CaO/CE pellets and 30% steam, but with a smaller amplitude, was observed.
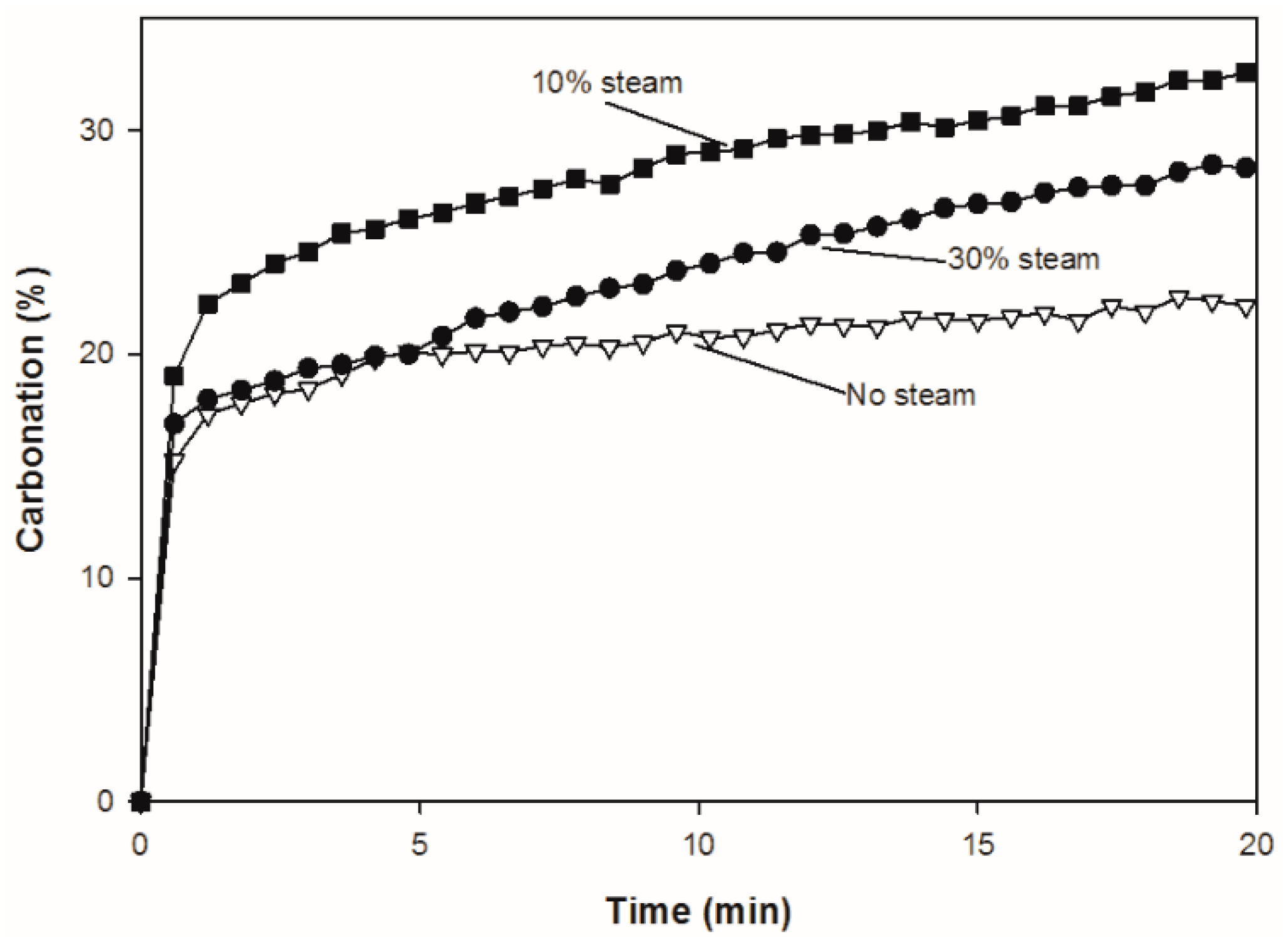
Figure 8 compares the carbonation of CuO/CaO/CE pellets in the first cycle with and without steam over 20 min. During carbonation, it has been suggested that there is a transition from kinetic to diffusion control, which is evident in the change in slope at approximately 1 min. The rates of carbonation are higher in the presence of steam, which supports the theory that steam enhances solid-state diffusion [19]. Unlike typical CaO based pellets which exhibited higher carbonation conversion with increasing steam concentration [19,25], the carbonation conversion of the CuO/CaO/CE pellets studied herein was higher with 10% steam than 30% steam (Figure 7b and Figure 8). This result could be due to side reactions catalyzed by the presence of Cu, which inhibit the carbonation of CaO.
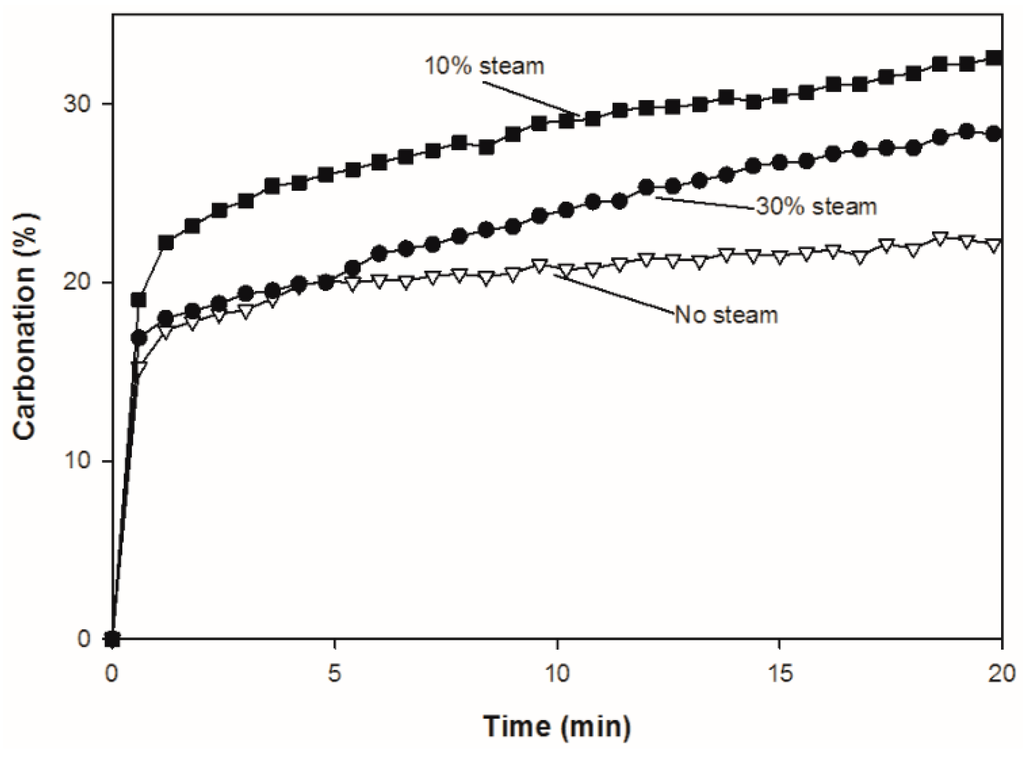
Figure 8.
Comparison of carbonation conversion (%) over one cycle for CuO/CaO/CE pellets with 0, 10% and 30% steam.
4. Conclusions
In this work, the performance of integrated CuO/CaO/CE pellets was evaluated against CaO/CE and CuO/CE pellets in a multi-cycle CaL and CLC process. The oxidation capacity of the integrated pellets remained constant and on par with the CuO pellets after 16 cycles. However, the carbonation capacity was significantly decreased with the addition of CuO to the pellets. SEM/EDX images showed an increasing surface enrichment of Cu on the integrated pellets with cycle number. Thermal pretreatments with either air or N2 stabilized the performance of the CaO/CE pellets but also caused fractures. Pretreatment with heating at 7.5 °C/min also stabilized the CuO/CaO/CE pellets but reduced the CO2 capacity and so was not beneficial. The addition of steam improved the performance of both CaO/CE and CuO/CaO/CE pellets. For the CaO/CE pellets, the initial CO2 capacity was unchanged by the addition of steam but there was significantly less loss in capacity with 30% steam, while only a minor improvement with 10% steam. In contrast, the initial CO2 capacity was enhanced for the CuO/CaO/CE pellets in the presence of steam but after 10 cycles the capacities were comparable with or without steam. The performance of the integrated pellets was better in 10% steam than 30% steam.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge funding from Carbon Management Canada (Project A346).
Author Contributions
All authors collaborated on the design of the experiments for this study as part of a collaborative project entitled “Pre- and post-combustion CO2 capture using novel composite CaO/CuO sorbents”. Alvaro Recio and Sip Chen Liew carried out the TGA experiments and characterization of the pellets; Dennis Lu, Ryad Rahman, and Arturo Macchi assisted Alvaro Recio with the experiments in the presence of steam; Ryad Rahman prepared the pellets; Alvaro Recio, Sip Chen Liew and Josephine M. Hill prepared the manuscript with input and feedback from Dennis Lu, Ryad Rahman, and Arturo Macchi.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, L.; Zhao, N.; Wei, W.; Sun, Y. A review of research progress on CO2 capture, storage, and utilization in Chinese academy of sciences. Fuel 2013, 108, 112–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adanez, J.; Abad, A.; Garcia-Labiano, F.; Gayan, P.; de Diego, L.F. Progress in chemical-looping combustion and reforming technologies. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2012, 38, 215–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manovic, V.; Anthony, E.J. Integration of calcium and chemical looping combustion using composite CaO/CuO-based materials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 10750–10756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, R.A.; Mehrani, P.; Lu, D.Y.; Anthony, E.J.; Macchi, A. Investigating the use of CaO/CuO sorbents for in situ CO2 capture in a biomass gasifier. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 3808–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.W.; Lim, C.J.; Grace, J.R. CO2 capture capacity of CaO in long series of pressure swing sorption cycles. Chem. Eng. Res. Design 2011, 89, 1794–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, K.R.; Fermoso, J.; Chen, D.; Jakobsen, H.A. Kinetic rate of uptake of a synthetic Ca-based sorbent: Experimental data and numerical simulations. Fuel 2014, 120, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blamey, J.; Anthony, E.J.; Wang, J.; Fennell, P.S. The calcium looping cycle for large-scale CO2 capture. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2010, 36, 260–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abanades, J.C.; Murillo, R.; Fernandez, J.R.; Grasa, G.; Martínez, I. New CO2 capture process for hydrogen production combining Ca and Cu chemical loops. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6901–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazi, S.S.; Aranda, A.; Meyer, J.; Mastin, J. High performance CaO-based sorbents for pre- and post- combustion CO2 capture at high temperature. Energy Procedia 2014, 63, 2207–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manovic, V.; Anthony, E.J. Lime-based sorbents for high-temperature CO2 capture—A review of sorbent modification methods. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 3129–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manovic, V.; Wu, Y.; He, I.; Anthony, E.J. Core-in-shell CaO/CuO-based composite for CO2 capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 12384–12391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattisson, T.; Järdnäs, A.; Lyngfelt, A. Reactivity of some metal oxides supported on alumina with alternating methane and oxygen application for chemical-looping combustion. Energy Fuels 2003, 17, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Labiano, F.; de Diego, L.F.; Adánez, J.; Abad, A.; Gayán, P. Temperature variations in the oxygen carrier particles during their reduction and oxidation in a chemical-looping combustion system. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leion, H.; Lyngfelt, A.; Mattisson, T. Solid fuels in chemical-looping combustion using a NiO-based oxygen carrier. Chem. Eng. Res. Design 2009, 87, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhoux, B. Combined Calcium Looping and Chemical Looping Combustion Process Simulation Applied to CO2 Capture. M.Sc. Thesis, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, NO, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, C.; Yin, J.; Liu, W.; An, H.; Feng, B. Behavior of CaO/CuO based composite in a combined calcium and copper chemical looping process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 12274–12281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Yin, J.; Luo, C.; An, H.; Liu, W.; Feng, B. Enhancing the performance of CaO/CuO based composite for CO2 capture in a combined Ca-Cu chemical looping process. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manovic, V.; Fennell, P.S.; Al-Jeboori, M.J.; Anthony, E.J. Steam-enhanced calcium looping cycles with calcium aluminate pellets doped with bromides. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 7677–7683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manovic, V.; Anthony, E.J. Carbonation of CaO-based sorbents enhanced by steam addition. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 9105–9110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, S.; Lu, D.Y.; Macchi, A.; Symonds, R.T.; Anthony, E.J. Influence of steam injection during calcination on the reactivity of CaO-based sorbent for carbon capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 2241–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobner, S.; Sterns, L.; Graff, R.A.; Squires, A.M. Cyclic calcination and recarbonation of calcined dolomite. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Design Dev. 1977, 16, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xiao, Y. Steam catalysis in cao carbonation under low steam partial pressure. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 4043–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symonds, R.T.; Lu, D.Y.; Macchi, A.; Hughes, R.W.; Anthony, E.J. CO2 capture from syngas via cyclic carbonation/calcination for a naturally occurring limestone: Modelling and bench-scale testing. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 3536–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, B.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Feng, C. High temperature CO2 capture using calcium oxide sorbent in a fixed-bed reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, B.; Grasa, G.; Abanades, J.C.; Manovic, V.; Anthony, E.J. The effect of steam on the fast carbonation reaction rates of CaO. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 2478–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Sithambaram, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Jin, L.; Joesten, R.; Suib, S.L. Novel urchin-like CuO synthesized by a facile reflux method with efficient olefin epoxidation catalytic performance. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, J.M.; Sanchez-Jimenez, P.E.; Perez-Maqueda, L.A. High and stable CO2 capture capacity of natural limestone at Ca-looping conditions by heat pretreatment and recarbonation synergy. Fuel 2014, 123, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).