Abstract
We report on enhancing the photon-extraction efficiency (PEE) of deterministic quantum dot (QD) microlenses via anti-reflection (AR) coating. The AR-coating deposited on top of the curved microlens surface is composed of a thin layer of Ta2O5, and is found to effectively reduce back-reflection of light at the semiconductor-vacuum interface. A statistical analysis of spectroscopic data reveals, that the AR-coating improves the light out-coupling of respective microlenses by a factor of 1.57 ± 0.71, in quantitative agreement with numerical calculations. Taking the enhancement factor into account, we predict improved out-coupling of light with a PEE of up to 50%. The quantum nature of emission from QDs integrated into AR-coated microlenses is demonstrated via photon auto-correlation measurements revealing strong suppression of two-photon emission events with g(2)(0) = 0.05 ± 0.02. As such, these bright non-classical light sources are highly attractive with respect to applications in the field of quantum cryptography.
1. Introduction
Single self-assembled semiconductor quantum dots (QD) are of particular interest regarding quantum communication schemes [1]. They have been proposed to act as efficient quantum-light sources emitting indistinguishable [2] and entangled photons [3], constituting essential building blocks towards the physical realization of quantum communication networks [4]. Recent experiments utilizing self-assembled QDs have demonstrated a record-high photon indistinguishability of 99.5% [5], while a fidelity for polarization-entangled photon pairs of 88% has been achieved exploiting strain-tunable optoelectronic devices [6]. However, critical to such applications and to proceed towards multi-node quantum networks, is to combine the individual benefits, e.g., the purity of single-photon emission or the entangled-state fidelity, within a single device concept compatible with a high photon-extraction efficiency (PEE) and based on deterministic device processing. Huge progress has been achieved with respect to the realization of high PEEs in recent years by exploiting cavity quantum electrodynamics (cQED) effects in optically and electrically driven photonic microcavity structures to enhance the interaction between a QD and a light field via the Purcell-effect [7,8,9,10,11]. Drawbacks arising from the use of cQED effects, however, are the rather small spectral bandwidth, due to the required large Q-factors of the corresponding microcavities, as well as the need for highly sophisticated growth and processing techniques, often hindering a scalable device fabrication.
A well-known alternative technique to enhance the in- or out-coupling efficiency of light in various types of light emitting structures, which is also used in an industrial scale, is to apply anti-reflection (AR) coatings, which reduce parasitic reflections at material surfaces [12]. So far, AR-coatings have been used in solar cells [13], light-emitting diodes [14], single-photon detectors [15] and magnetic field imaging of an ensemble of nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond [16].
In this work, we present the application of an AR-coating in the field of nanophotonics by increasing the PEE of a single quantum emitter. In fact, we exploit the anti-reflective properties of a thin layer of Ta2O5 evaporated onto the curved surface of deterministic single-QD microlenses. Further, by demonstrating triggered single-photon emission with high single-photon purity and a high PEE using this novel approach, we merge the excellent quantum optical properties of single artificial atoms with industrial-scale fabrication techniques.
Our device concept is based on monolithic microlenses precisely aligned (with 24 nm accuracy [17]) to pre-registered single QDs, allowing for an increased PEE of single photons of up to 29% [18] and close to ideal quantum optical properties in terms of the multiphoton suppression and the photon indistinguishability [19]. An important advantage of the microlens concept is the broadband enhancement of the PEE (a bandwidth of ~50 nm has been calculated via finite-element method (FEM) simulations). This appealing feature offers the possibility to boost not only the emission of single photons, but also of bicolored polarization-entangled photon-pairs from the biexciton-exciton (XX-X) radiative cascade of QDs with diminishing fine-structure splitting [3,20] without the necessity for a complicated cavity structure. However, due to the refractive index contrast at the semiconductor-vacuum interface along the uncoated curved surface of the microlens, a significant portion of the incident light emitted by a quantum emitter is reflected back into the semiconductor, limiting the extraction-efficiency of the device. Considering a simplified model of a planar GaAs-vacuum interface and Fresnel’s equations this amount is estimated to ~30% of the incident light. In order to circumvent this issue, we apply an anti-reflective layer of Ta2O5 to the QD microlens surface and provide a detailed statistical analysis of its impact with respect to the enhancement of the PEE and the quantum-optical properties.
2. Device Fabrication and Experimental Setup
To prove the impact of an AR-coating on the PEE of QDs integrated into microlenses, we utilize two different sample layouts. For a fundamental investigation of the AR-coating, we exploit a semiconductor structure with InGaAs QDs in the active layer grown on GaAs (001) substrate by means of metal-organic chemical vapor deposition. In the first step, 530 nm GaAs and 20 nm AlGaAs were deposited, followed by a 300 nm GaAs layer including a low-density layer of self-assembled Stranski-Krastanov InGaAs-QDs in the center. Next, again 20 nm AlGaAs were grown and finally capped by 230 nm of GaAs. To obtain maximum PEE in Section 3.4 and Section 3.5 a second sample structure was grown. It includes a lower mirror based on a distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) consisting of 23 alternating λ/4-thick layers of AlGaAs (77.0 nm) and GaAs (65.7 nm). The DBR is followed by a GaAs spacer (65.0 nm), a low-density layer of Stranski-Krastanov self-assembled InGaAs-QDs, and a 400 nm thick GaAs capping layer [19]. This layout allows for the collection of QD-photons emitted into the lower hemisphere, thereby boosting the PEE of microlenses further.
The integration of pre-selected QDs into monolithic microlenses is based on three-dimensional (3D) in-situ electron-beam lithography (EBL) enabled by cathodoluminescence (CL) spectroscopy at cryogenic temperatures [21]. We utilize the EBL resist polymethyl-methacrylate (PMMA) which is spin-coated (thickness: 225 nm) onto the sample [22]. During the in-situ lithography process, the resist is gradually inverted by writing concentric circles with a carefully adjusted electron-dose centered at the positions of pre-selected QDs. Developing the resist at room temperature results in a 3D etch-mask of inverted, i.e., cross-linked, PMMA with hemispheric profiles. In the subsequent plasma-etching step this mask is directly transferred into the semiconductor material to form monolithic microlenses. More details on the fabrication process can be found in Ref. [19].
In contrast to planar sample structures, for which total internal reflection limits the PEE to less than 1% [23], the microlens design leads to significantly higher PEEs because of its curved surface. However, the device is still suffering from partial reflection at the semiconductor-vacuum interface. In order to reduce the associated detrimental back-reflection, a 110 nm thick λ/4 layer of Ta2O5 was evaporated onto both sample structures via electron beam sputtering with 1 nm thickness accuracy. A schematic of the entire microlens structure is depicted in Figure 1a. To investigate the optical quality of AR-coated QD-microlenses and to evaluate their potential to act as bright quantum-light sources with enhanced PEE, we performed statistical spectroscopic studies using micro-photoluminescence (µPL) spectroscopy at 10 K. Single QDs were optically excited using a continuous wave (cw) diode laser emitting at a wavelength of 657 nm or alternatively a pulsed Ti:Sapphire laser (f = 80 MHz) at a wavelength of 840 nm operated in picosecond mode. Photoluminescence of single QD microlenses is collected by a microscope objective (numerical aperture (NA) = 0.4) and analyzed by a double-grating spectrometer (25 µeV spectral resolution) with an attached liquid-nitrogen-cooled Silicon-based charge-coupled-device camera. The non-classical photon-statistics of the QD emission is investigated via a fiber-based Hanbury-Brown and Twiss (HBT) setup with Silicon-based single-photon counting modules (SPCMs) with a combined timing resolution of 350 ps.
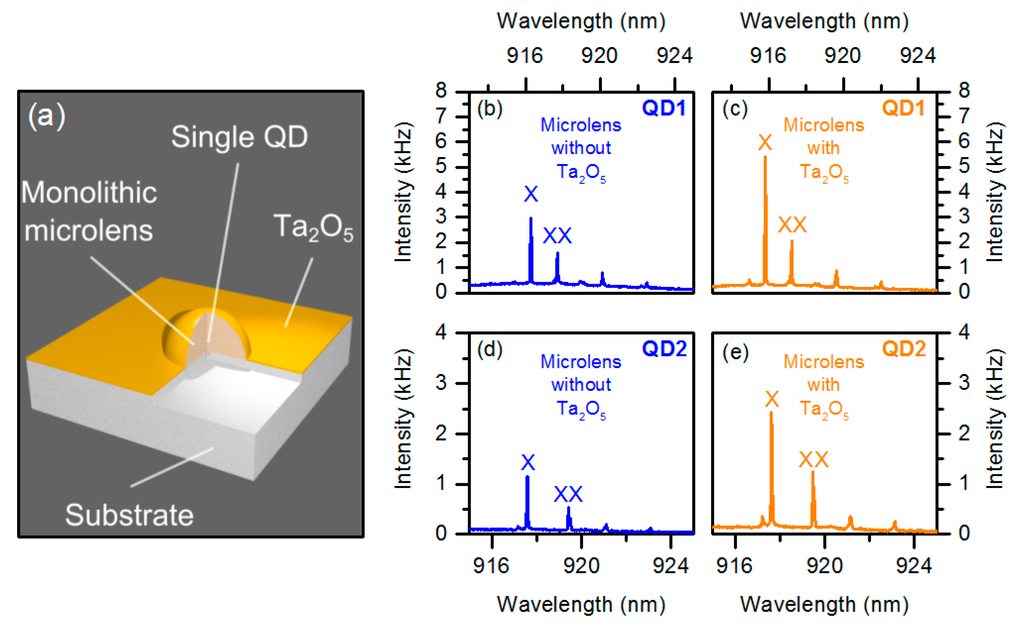
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic of a deterministic quantum dot (QD) microlens device. To enhance the photon-extraction efficiency (PEE) the microlens-surface is coated with a thin layer of Ta2O5 (n = 2.1) acting as anti-reflection (AR) coating; (b,c,d,e) micro-photoluminescence (µPL) spectra measured at saturation of X emission from two QD microlenses before and after coating with Ta2O5.
3. Methods and Materials
3.1. Deposition of Ta2O5 onto the Microlens Surface
To reduce partial back reflection at the microlens surface resulting from the refractive index contrast between GaAs and vacuum, both samples were coated with a layer of a third material that fulfills the condition ncoating × d = λ/4 with d being the thickness of the coating layer, ncoating its refractive index and λ the wavelength of the photons. This discussion neglects the possible effect of the curved microlens surface which will be addressed in Section 3.3 dealing with numerical simulations. Optimum optical impedance matching requires ncoating = (nvacuum × nGaAs)1/2 = 1.88 [24]. Based on these considerations we deposited a thin film of d = 110 nm Ta2O5, with a close to ideal refractive index of nTa2O5 = 2.1 at 930 nm, onto the samples. We confirm the deposition of a homogeneous layer of Ta2O5 even on the curved surface of the microlens (diameter of 2.4 µm) by scanning electron microscopy (SEM-) images (not shown here).
3.2. µPL Spectroscopy on AR-Coated Microlenses
We studied the impact of the AR-coating on the optical properties of deterministic QD-microlenses without backside mirror by µPL measurements at saturation pump power of the exciton. The latter ensures that we can rule out the influence of possibly different excitation efficiencies with and without AR-coating on the achieved PEE. Figure 1b,d present a µPL spectrum of QD1 and QD2 integrated into an uncoated microlens under above-band-gap excitation at 657 nm. Figure 1c,e show the spectrum of the corresponding QD after coating the microlens with Ta2O5. To compare the integrated µPL intensities of single QDs, we fitted the exciton emission line (X) with a Lorentzian profile. The effect of the AR-coating on the PEE is quantified by the ratio of the corresponding emission intensity after and before deposition of Ta2O5. In the present case this ratio is IInt,Ratio,QD1 = 1.64 ± 0.04 and IInt,Ratio,QD2 = 2.22 ± 0.15, which clearly demonstrates the positive impact of AR-coating on the extraction efficiency of the QD-microlens. Interestingly, the absolute spectral position of the emission lines observed in Figure 1 is blue-shifted by 1.28 nm for QD1 and 0.08 nm for QD2 after applying the AR-coating. A spectral shift has been observed consistently for all investigated AR-coated QD-microlenses. Thus, we can exclude that the blue-shift has a purely random character related, e.g., to varying charge configurations in the vicinity of the QD. We assign it to a modified quantum confined Stark shift arising from a different configuration of charge states at the semiconductor surface with and without AR coating. These surface states pin the Fermi level and thereby create an electric field, which in turn alters the emission energy of the QDs via the Stark-effect. We exclude that this effect affects significantly the outcoupling enhancement due to an increased electron-hole wavefunction overlap as we observe no correlation between the spectral shifts and the integrated intensity ratios.
We confirm the results obtained in the exemplary cases above by performing a statistical spectroscopic investigation on 19 QD-microlenses, where each structure was studied within a one-to-one comparison before and after applying the AR-coating. Figure 2 illustrates the statistical analysis performed on the brightest emission line in each spectrum in histogram representation. Here, (a) depicts the ratio of the integrated intensities IInt,Ratio; (b) the ratio of the saturation pump powers PSat,Ratio and (c) the spectral shifts Δλ. It reveals a mean value for the intensity ratio as high as 1.57 ± 0.71.
This finding confirms, that the observed increase in detected µPL intensity of the QD is due to an effective reduction of reflections by the AR-coating, which enhances the PEE. For the saturation power ratio a mean value of = 0.42 ± 0.27 is extracted, implying that the AR-coating enhances on average also the excitation efficiency. The spectral shift is determined to (1.30 ± 0.84) nm.
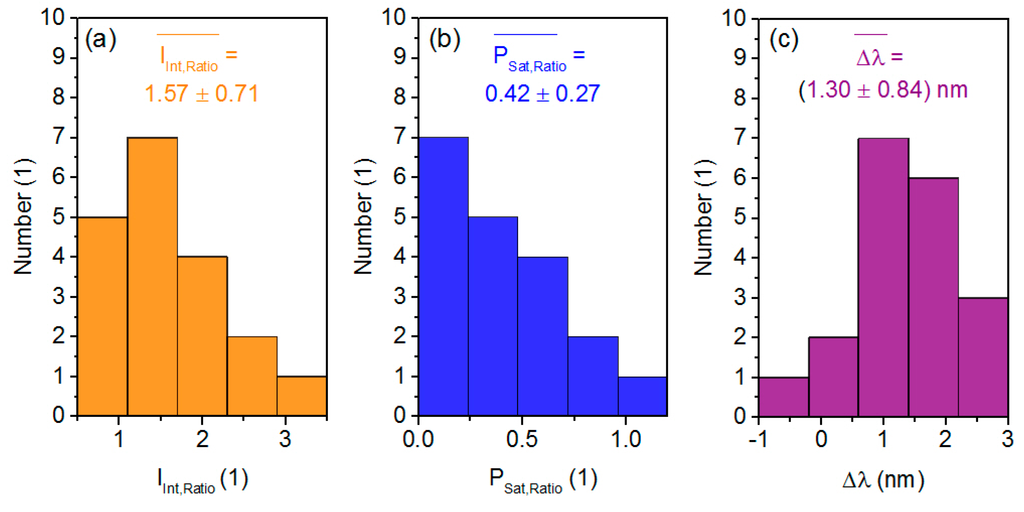
Figure 2.
Statistical analysis performed on 19 QDs for (a) the ratio of the integrated intensities ; (b) the ratio of saturation power; and (c) the spectral shift of the investigated QD emission line Δλ each before and after the coating with Ta2O5.
3.3. Simulation of Coated Microlenses Using Finite-Element Methods
Deeper insights into the outcoupling enhancement resulting from the AR-coating are obtained by performing numerical simulations of microlenses using a finite-element solver [25]. Here, a microlens structure was incorporated in a rotational symmetric (quasi two-dimensional) setting without backside reflector. Figure 3a displays the PEE as a function of the thickness d of the Ta2O5 coating for numerical apertures of the collection lens of 0.2, 0.4 and 1.0. The dependence of PEE(d) shows an oscillating behaviour resulting from interference effects caused by the coating. The first maximum at dsim = 160 nm is close to the thickness of the AR-coating used in our experiment (d = 110 nm). Figure 3b shows the enhancement of the PEE versus AR-coating thickness d, as derived from Figure 3a by calculating PEE(d)/PEE(d = 0) for each curve. At d = 110 nm an enhancement of ~1.8 is extracted, in agreement with the experimental data.
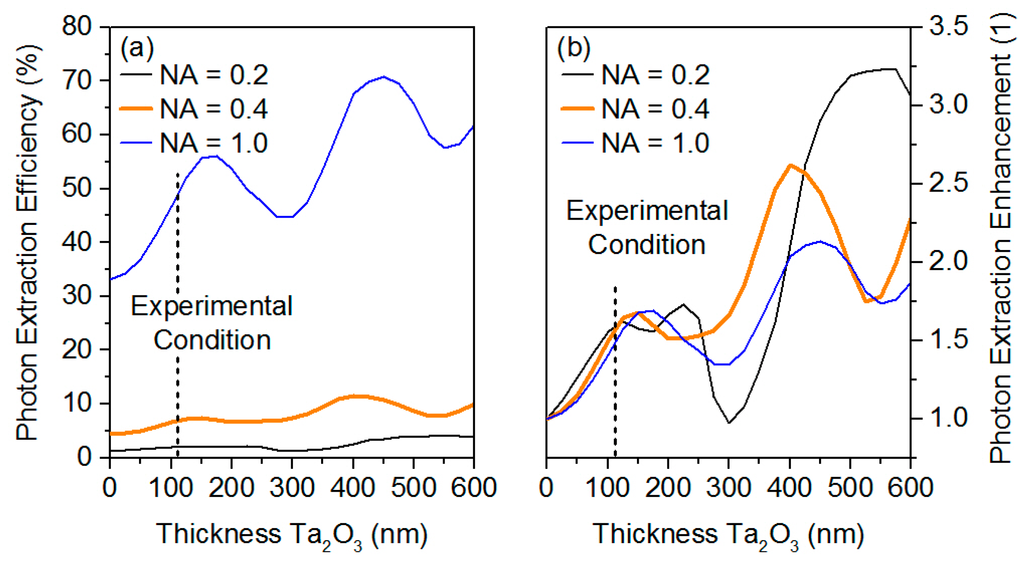
Figure 3.
(a) Finite element method simulation of the PEE based on solving Maxwell’s equations for a microlens without a backside distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) for numerical apertures of 0.2, 0.4 and 1.0 of the collecting optics as a function of Ta2O5 thickness; (b) Photon-extraction enhancement deduced from (a) as a function of Ta2O5 thickness.
3.4. PEE of AR-Coated Deterministic QD Microlenses with DBR
In addition to the bare lens design, we investigated the influence of a backside DBR on the outcoupling efficiency of AR-coated microlenses. Again, we performed a statistical µPL analysis of 14 QD-microlenses under saturation pump power of the exciton before and after applying the AR-coating. From the comparison we found a ratio of the integrated intensities of 2.19 ± 1.34, a ratio of the saturation pump power of = 0.96 ± 0.44 and a spectral shift of (1.18 ± 0.65) nm. Besides the observation of a further increase in intensity as compared to Section 3.2, we are able to estimate the PEE for the given microlens structure. Taking the PEE of 25%–29% found for uncoated microlenses with backside DBR in Refs. [18,19] using a microscope objective with NA of 0.4 and multiplying it with the integrated intensity ratio from above, we predict a PEE of up to 50% for the AR-coated microlenses with DBR. This enhancement of PEE clearly highlights the benefits of suitable AR-coatings for QD-based single-photon sources that normally suffer from Fresnel-reflections at the semiconductor-vacuum interface.
3.5. Triggered Single Photons from AR-Coated Deterministic QD Microlenses
The quantum nature of emission from an AR-coated QD microlens with DBR is investigated via measurements of the photon-autocorrelation function g(2)(τ) under pulsed non-resonant excitation at 840 nm. For this purpose the emission of the brightest QD state (X+) was spectrally filtered by the monochromator and coupled into the HBT setup. Taking the combined detection rate of the SPCMs and the setup efficiency into account, we are able to deduce the photon flux F emitted into the first lens of the setup to F = (12.5 ± 0.6) MHz. The resulting coincidence histogram of g(2)(τ) is presented in Figure 4. Triggered single-photon emission of the QD state is reflected in the strongly reduced number of coincidences at zero time delay (τ = 0). At finite time delay, coincidence maxima occur at a periodicity of 12.5 ns, corresponding to the 80 MHz pulse repetition rate of the Ti:Sapphire laser. To quantitatively evaluate the suppression of two-photon emission events, we fitted the experimental data with equidistant peaks, each represented by the convolution of a two-sided exponential function (decay time constant τD = (0.83 ± 0.01) ns) with a Gaussian accounting for the HBT’s timing resolution (350 ps). Assuming a constant area A of the pulses at finite time delay, g(2)(0) is expressed by the ratio A0/A, where A0 corresponds to the zero-delay peak-area. The fitted model function (orange curve in Figure 4) reveals an antibunching value of g(2)(0) = 0.05 ± 0.02, which unambiguously proves the emission of triggered single photons of the AR-coating-enhanced emission of the QD-microlens.
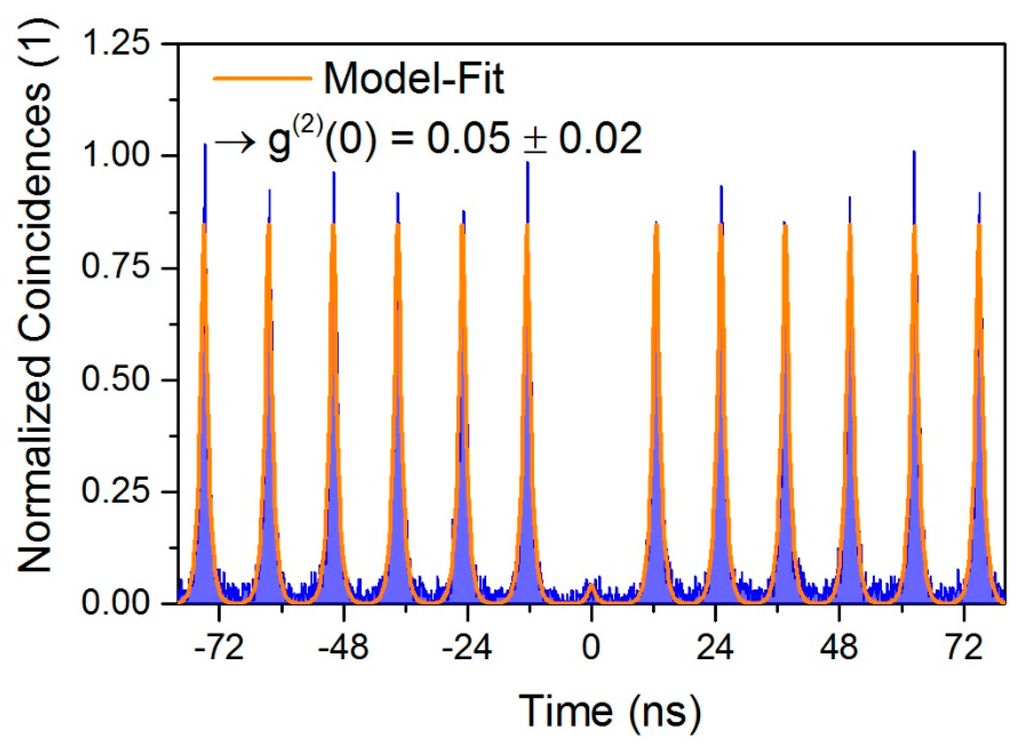
Figure 4.
Photon-autocorrelation measurement of the X+ emission-line under above-band pulsed excitation. Strong antibunching with g(2)(0) = 0.05 ± 0.02 is observed, clearly demonstrating triggered single-photon emission.
4. Conclusion
In summary, we have demonstrated a bright single-photon source by applying an AR-coating to monolithic microlenses containing single InGaAs-QDs. Depositing a Ta2O5 dielectric layer allows us to meet the λ/(4 × ncoating)-criterion to obtain destructive interference of the reflected rays. To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of an AR-coated micro-structure surface in the single-quantum emitter regime reducing partial back reflections and thereby enhancing the PEE to an estimated value of 50%. This technique can be easily extended to an advanced coating design comprising graded-index stacked layers with gradually decreasing refractive index similar to surfaces covered with nanostructures to further optimize the optical impedance matching [14,26].
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge expert sample preparation and sample coating by C. Scharfenorth. This work was financially supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) through SFB 787 “Semiconductor Nanophotonics: Materials, Models, Devices”, the BMBF VIP-project QSOURCE (Grant-No.: 03V0630) and from the German-Israeli-Foundation for Scientific Research and Development (Grant-No.: 1148-77.14/2011).
Author Contributions
Peter Schnauber, Christoph Vincent Heine and Manuel Gschrey performed the CL lithography and Peter Schnauber, Christoph Vincent Heine, Alexander Thoma, Liron Gantz, Alexander Schlehahn, Caspar Hopfmann and Tobias Heindel carried out the μPL investigations. Christoph Vincent Heine Peter Schnauber and Alexander Thoma analyzed the data. Benjamin Wohlfeil conducted the numerical modelling. Ronny Schmidt processed the samples in the clean room. Jan-Hindrik Schulze and André Strittmatter grew the samples. Alexander Thoma wrote the manuscript with input from all authors, Sven Rodt, David Gershoni, Ulrike Woggon and Stephan Reitzenstein initiated the research and supervised the project. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kiraz, A.; Atatüre, M.; Imamoğlu, A. Quantum-dot single photon sources: Prospects for applications in linear quantum-information processing. Phys. Rev. A 2004, 69, 032305. [Google Scholar]
- Santori, C.; Fattal, D.; Vučkovic, J.; Solomon, G.S.; Yamamoto, Y. Indistinguishable photons from a single photon device. Nature 2002, 419, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akopian, N.; Lindner, N.H.; Poem, E.; Berlatzky, Y.; Avron, J.; Gershoni, D.; Gerardot, B.D.; Petroff, P.M. Entangled Photon Pairs from Semiconductor Quantum Dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 130501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisin, N.; Thew, R. Quantum communication. Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.-M.; He, Y.; Wei, Y.-J.; Wu, D.; Atatüre, M.; Schneider, C.; Hoefling, S.; Kamp, M.; Lu, C.-Y.; Pan, J.-W. On-demand semiconductor single-photon source with near-unity indistinguishability. Nat. Nano 2013, 8, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotta, R.; Wildmann, J.S.; Zallo, E.; Schmidt, O.G.; Rastelli, A. Highly Entangled Photons from Hybrid Piezoelectric-Semiconductor Quantum Dot Devices. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 3439–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gérard, J.M.; Sermage, B.; Gayral, B.; Legrand, B.; Costard, E.; Thierry-Mieg, V. Enhanced Spontaneous Emission by Quantum Boxes in a Monolithic Optical Microcavity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 1110–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiraz, A.; Michler, P.; Becher, C.; Gayral, B.; Imamoğlu, A.; Zhang, L.; Hu, E.; Schoenfeld, W.V.; Petroff, P.M. Cavity-quantum electrodynamics using a single InAs quantum dot in a microdisk structure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 3932–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, D.J.P.; Bennett, A.J.; Dewhurst, S.J.; Nicoll, C.A.; Ritchie, D.A.; Shields, A.J. Cavity-enhanced radiative emission rate in a single-photon-emitting diode operating at 0.5 GHz. New J. Phys. 2008, 10, 043035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dousse, A.; Suffczyński, J.; Beveratos, A.; Krebs, O.; Lemaître, A.; Sagnes, I.; Bloch, J.; Voisin, P.; Senellart, P. Ultrabright source of entangled photon pairs. Nature 2010, 466, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heindel, T.; Schneider, C.; Lermer, M.; Kwon, S.H.; Braun, T.; Reitzenstein, S.; Höfling, S.; Kamp, M.; Forchel, A. Electrically driven quantum dot-micropillar single photon source with 34% overall efficiency. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 011107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayleigh, J.S. On the reflection of vibrations at the confines of two media between which the transition is gradual. Proc. London Math. Soc. 1880, 11, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, M.L.; Poxson, D.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Mont, F.W.; Kim, J.K.; Schubert, E.F.; Lin, S.Y. Realization of a near-perfect antireflection coating for silicon solar energy utilization. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 2527–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.J.; Chae, J.H.; Yi, G.-C.; Park, G.H. Enhanced light output of GaN-based light-emitting diodes with ZnO nanorod arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 121108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosfjord, K.; Yang, J.; Dauler, E.; Kerman, A.; Anant, V.; Voronov, B.; Gol’tsman, G.; Berggren, K. Nanowire single-photon detector with an integrated optical cavity and anti-reflection coating. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, T.K.; le Sage, D.; Pham, L.M.; Stanwix, P.L.; Walsworth, R.L. Anti-reflection coating for nitrogen-vacancy optical measurements in diamond. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 251111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschrey, M.; Schmidt, R.; Schulze, J.-H.; Strittmatter, A.; Rodt, S.; Reitzenstein, S. Resolution and alignment accuracy of low-temperature in situ electron beam lithography for nanophotonic device fabrication. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2015, 33, 021603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlehahn, A.; Gaafar, M.; Vaupel, M.; Gschrey, M.; Schnauber, P.; Schulze, J.-H.; Rodt, S.; Strittmatter, A.; Stolz, W.; Rahimi-Iman, A.; et al. Single-photon emission at a rate of 143 MHz from a deterministic quantum-dot microlens triggered by a mode-locked vertical-external-cavity surface-emitting laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 041105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschrey, M.; Thoma, A.; Schnauber, P.; Seifried, M.; Schmidt, R.; Wohlfeil, B.; Krüger, L.; Schulze, J.-H.; Heindel, T.; Burger, S.; et al. Highly indistinguishable photons from deterministic quantum-dot microlenses utilizing three-dimensional in situ electron-beam lithography. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, R.J.; Stevenson, R.M.; Atkinson, P.; Cooper, K.; Ritchie, D.A.; Shields, A.J. Improved fidelity of triggered entangled photons from single quantum dots. New. J. Phys. 2006, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschrey, M.; Gericke, F.; Schüßler, A.; Schmidt, R.; Schulze, J.-H.; Heindel, T.; Rodt, S.; Strittmatter, A.; Reitzenstein, S. In situ electron-beam lithography of deterministic single-quantum-dot mesa-structures using low-temperature cathodoluminescence spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 251113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschrey, M.; Schmidt, R.; Kaganskiy, A.; Rodt, S.; Reitzenstein, S. Study of high-resolution electron-beam resists for applications in low-temperature lithography. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2014, 32, 061601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, W.L.; Björk, G.; Gérard, J.M.; Jonsson, P.; Wasey, J.A.E.; Worthing, P.T.; Zwiller, V. Solid-state single photon sources: Light collection strategies. Eur. Phys. J. D 2002, 18, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, H.K.; Ganesh, V.A.; Nair, A.S.; Ramakrishna, S. Anti-reflective coatings: A critical in-depth review. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 3779–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JCMwave. JCMwave-Complete Finite Element Technology for Optical Simulations. Available online: http://www.jcmwave.com (accessed on 3 September 2015).
- Huang, Y.-F.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Jen, Y.-J.; Peng, C.-Y.; Liu, T.-A.; Hsu, Y.-K.; Pan, C.-L.; Lo, H.-C.; Hsu, C.-H.; Chang, Y.-H.; et al. Improved broadband and quasi-omnidirectional anti-reflection properties with biomimetic silicon nanostructures. Nat. Nano 2007, 2, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).