The Role of mPOS System in Process Change and Strategy Change: A Situated Change Perspective
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- What is the impact of mPOS on the process change under situated perspective?
- What is the impact of process change on the changes of IT strategy and service strategy under situated perspective?
2. Theoretical Background and Proposition Development
2.1. Theoretical Background
2.1.1. The Strategic Alignment Model
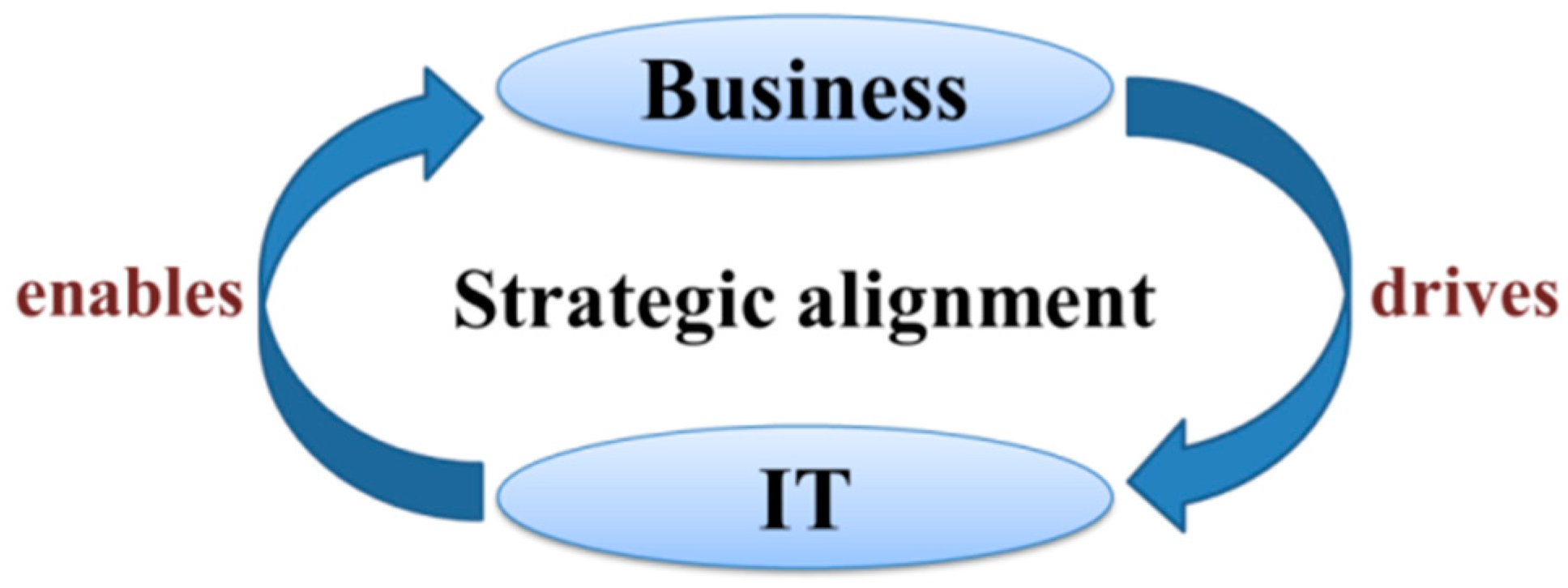
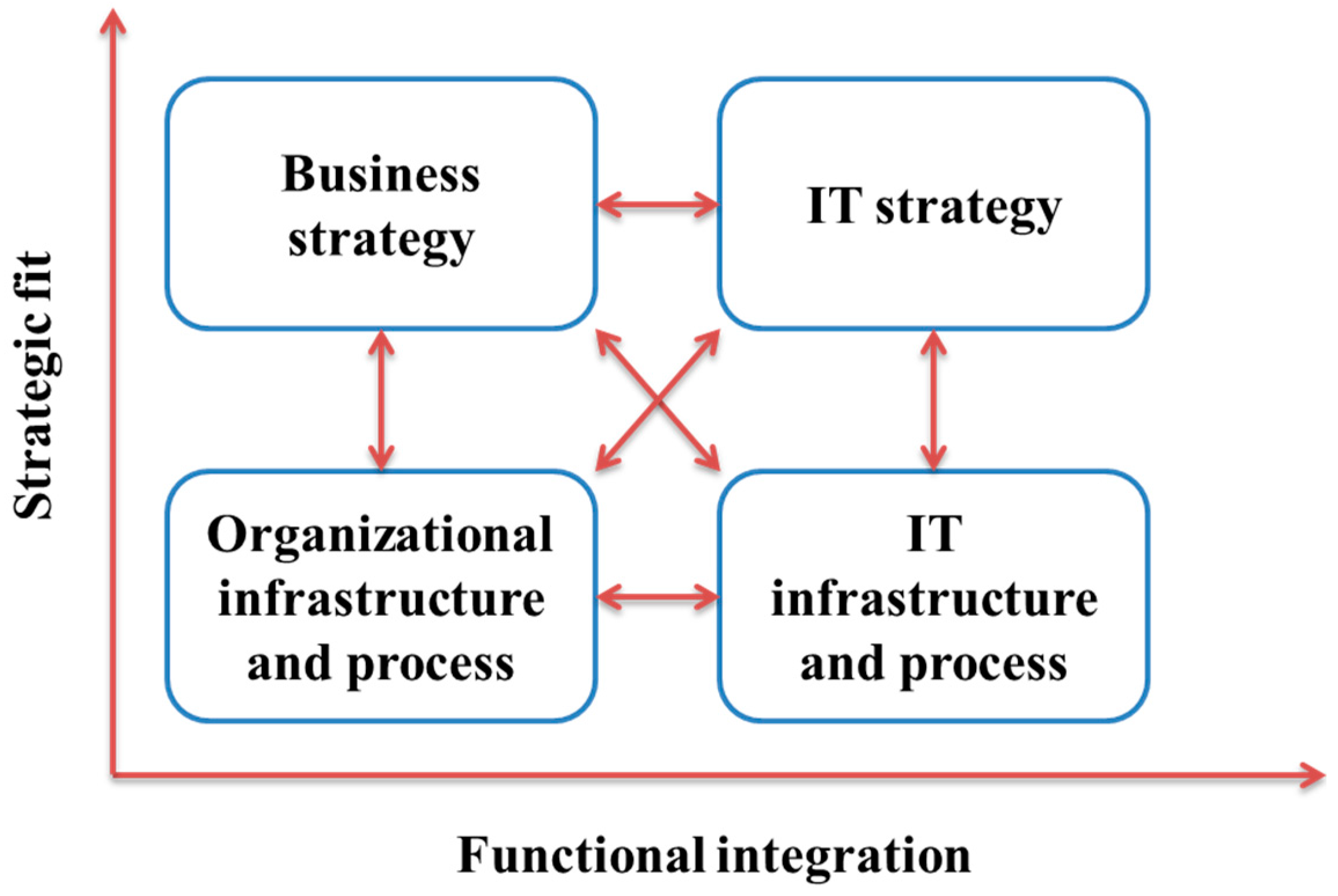
2.1.2. Organizational Change under Situated Change Perspective
2.2. Proposition Development
2.2.1. The mPOS System and Process Change
Therefore we propose Proposition 1: The changing of traditional POS system to mPOS creates more agile and efficient process in restaurants.
2.2.2. Strategy Changes
Therefore we propose Proposition 2: The agile and efficient process will lead to the changing of service strategy and IT strategy.
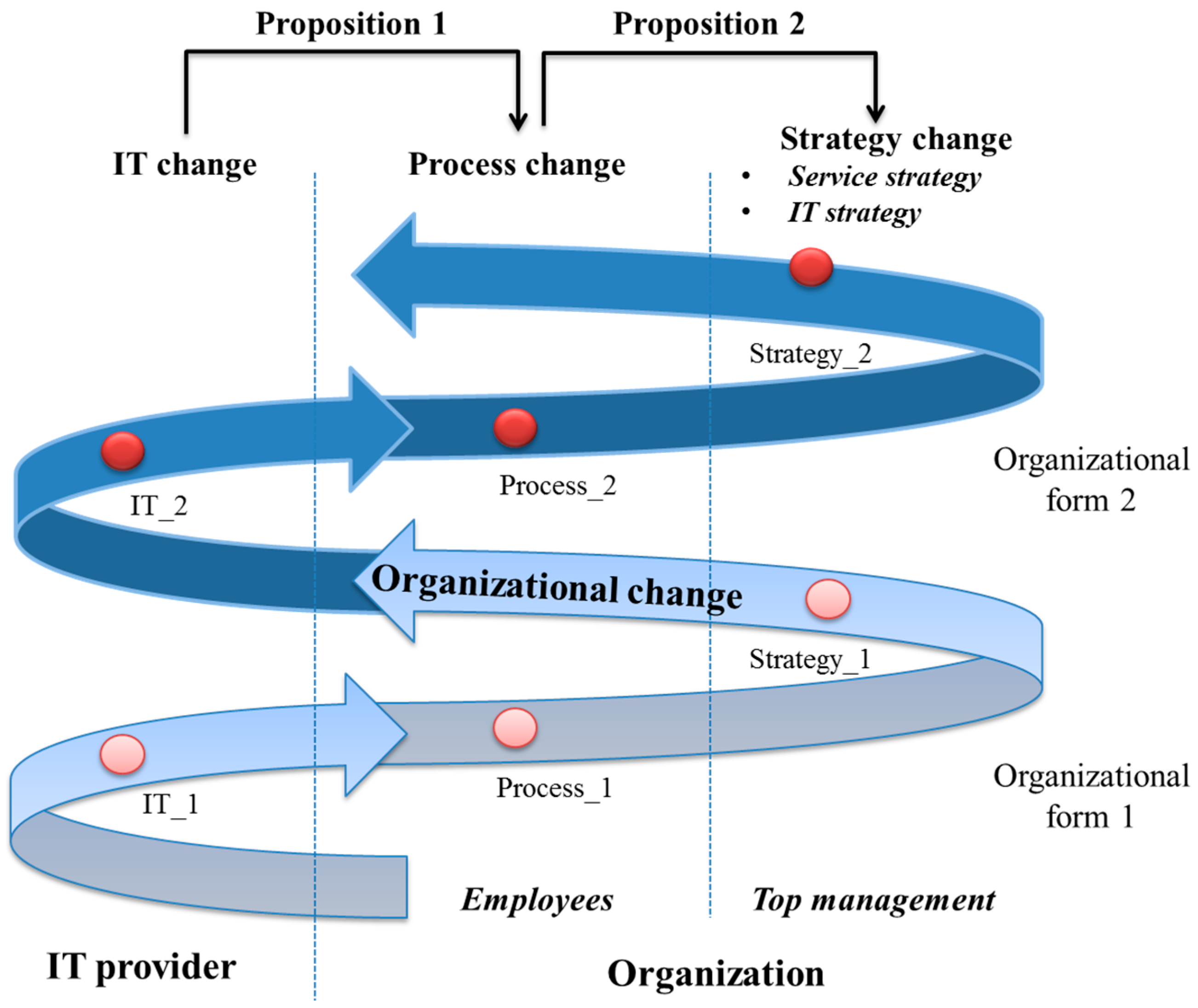
3. Research Design and Methodology
3.1. Case Selection
3.1.1. The mPOS System in this Study
3.1.2. Restaurants
| Features | Western Style | Eastern Style | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Café | Set Meal | Noodle | Group Dining | ||||||
| FR | CA | MAC | NO | GO | CY | HA | MAZ | KI1 | |
| iCHEF | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Equipment | 1 iPad 1Printer | 1 iPad 1Printer | 3 iPad 2 Printer | 1 iPad mini 1 iPad 2 Printer | 1 iPad mini 1 iPad 2 Printer | 2 iPad mini 1 iPad 3 Printer | 1 iPad mini 1 iPad 2 Printer | 2 iPad mini 1 iPad 2 Printer | 3 iPad mini 1 iPad 5 Printer |
| Size (seats) | 39 | 28 | 64 | 52 | 50 | 32 | 30 | 45 | 134 |
| Floor | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Waiting area | Y | N | Y | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y |
| Reservation form | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y |
| Employees (waiter/chef) | 6 | 6 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 3 | 10 | 17 |
| 2 out 4 in | 2 out 4 in | 4 out 6 in | 3 out 5 in | 2 out 5 in | 3 out 4 in | 2 out 1 in | 5 out 5 in | 7 out 10 in | |
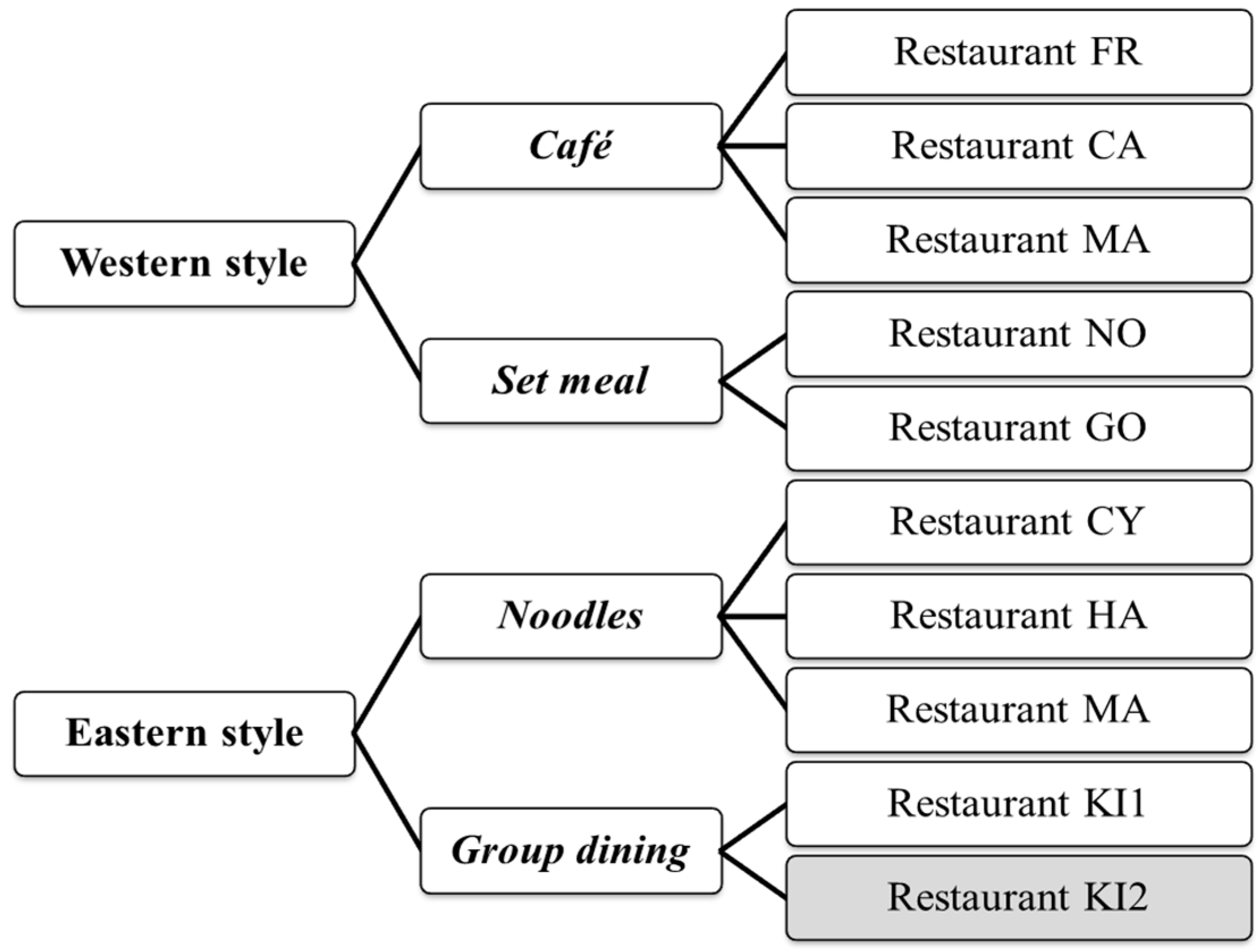
Restaurant FR
Restaurant CA
Restaurant MAC
Restaurant NO
Restaurant GO
Restaurant CY
Restaurant HA
Restaurant MAZ
Restaurant KI1
3.2. Data Collection and Analysis
4. Findings and Discussion
4.1. POS Change and Process Change
| Traditional | New | |
|---|---|---|
| Target merchant size | Medium to large | Small to medium |
| Pricing | Complex | Simple |
| Merchant account | Required | Included |
| Complexity | High | Low |
| Speed to market | Slow | Fast |
| Maintenance | Expensive | Cheap |
| Analytics | Available | Available |
| Aesthetics | Well | Slick |
| Business model | IC fees and support-based | IC fees and/or ad-based |
| Module | Process | Description | Activity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry (I) | Waiting line (1) | Start from customers come to restaurant, begin to line up until get inform of available seats | Customer | 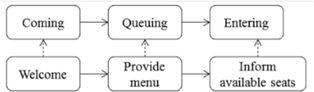 |
| Waiter | ||||
| Table arranging (2) | Start from customers enter restaurant and have seats until be ready for ordering | Customer | 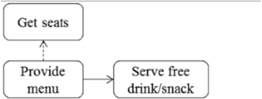 | |
| Waiter | ||||
| Ordering (II) | Ordering (3) | Start from customers check menu until finish ordering | Customer | 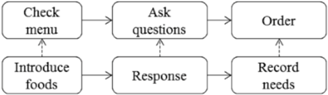 |
| Waiter | ||||
| Ordering handling (4) | Start from waiter get order until send it to relevant parties | Waiter | 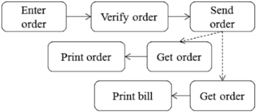 | |
| Kitchen/bar | ||||
| Receptionist | ||||
| Food serving (III) | Cooking (5) | Start from kitchen/bar prepare materials until finish cooking | Chefs | 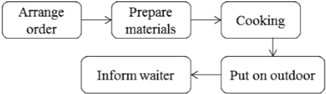 |
| Food delivering (6) | Start from waiter get food from kitchen/bar until put on customers tables | Waiter | 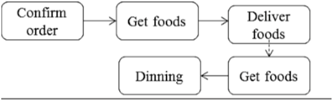 | |
| Customer | ||||
| Serving (7) | Start from customers get foods until finish dinning | Customer |  | |
| Waiter | ||||
| Exiting (IV) | Payment (8) | Start from customers get bill until make payment | Customer | 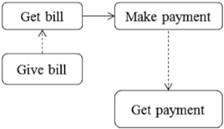 |
| Waiter | ||||
| Receptionist | ||||
| Clean-up (9) | Clean table, reset system from welcome new customers | Waiter |  | |
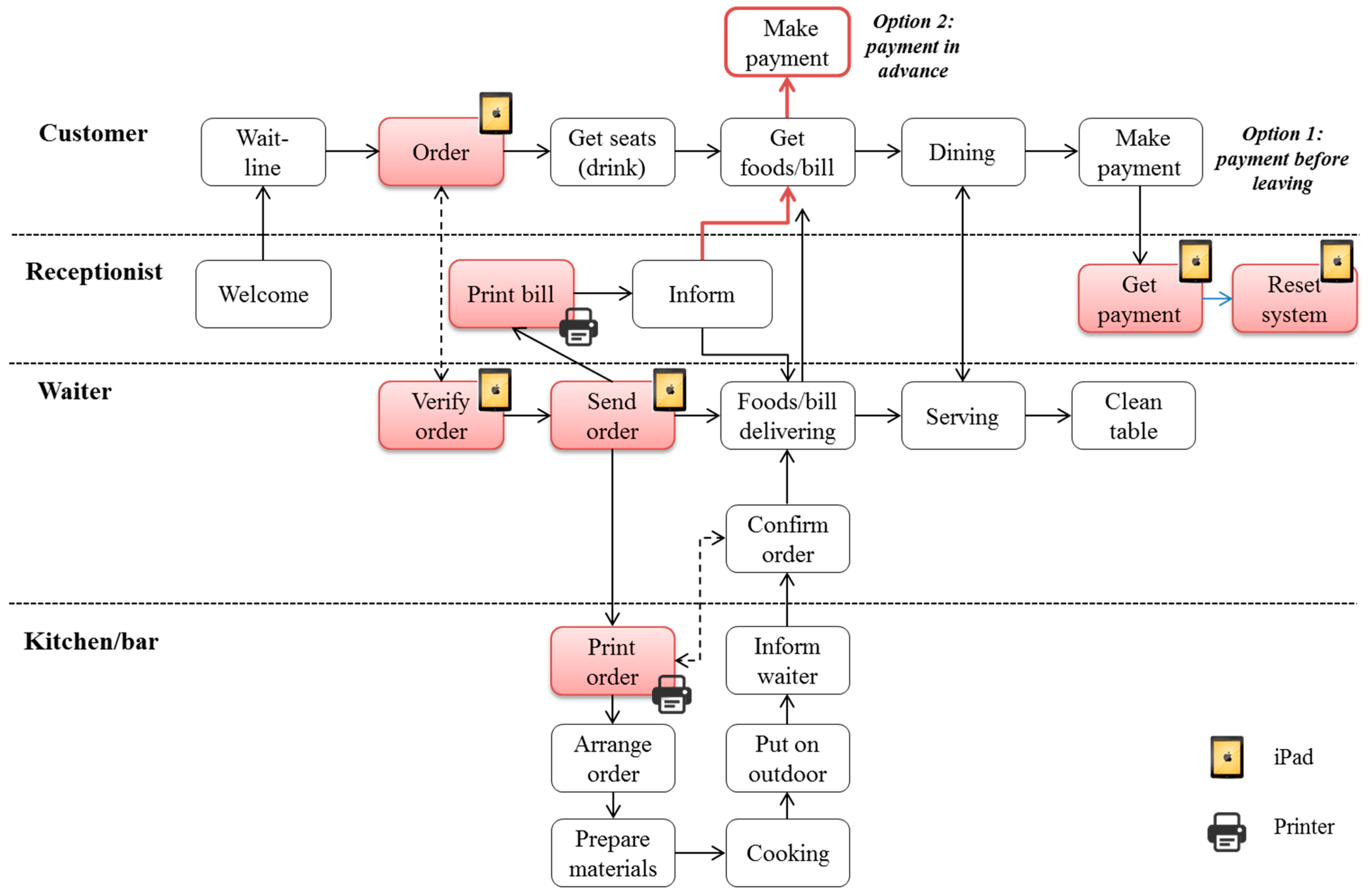

4.2. Process Change and Strategy Change
| Complicated Menu | New/Strange Food/Beverage | Multiple Serving Area | Multiple Cooking Area | Small Size | Professional Image Building | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR | √ | √ | ||||
| CA | √ | |||||
| MAR | √ | √ | ||||
| NO | √ | √ | ||||
| GO | √ | √ | ||||
| CY | √ | √ | ||||
| HA | √ | |||||
| MAZ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| KI1 | √ | √ | √ |
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Complicated menu | Foods have many ingredients that customers need to select (type of noodle, meat, source, spices, etc.) and sometimes they choose the wrong thing as it is not clear, and thus difficult for chefs to cook. Restaurant have many items to manage, not only food but extra items (gifts and souvenirs) |
| New/strange food/beverage | Foods are from other countries and have strange names, which need pictures to illustrate |
| Multiple serving area | Restaurants have many floors, many rooms, difficult to manage by observation, need to use screen |
| Multiple cooking area | Restaurants have the bar and kitchen in different areas and so need to receive order one time to save time, thus they should put printers in different area |
| Small size | Small restaurant with no place to put large machine |
| Professional image building | Bring a professional feeling to customers |
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marcovic, S.; Raspor, S.; Segaric, K. Does Restaurant Performance Meet Customers’ Expectations. An Assessment of Restaurant Service Quality Using a Modified Dineserv Approach. Tour. Horpitality Manag. 2010, 16, 181–195. [Google Scholar]
- Venard, B. Organisational change in service multinationals: From radical change to destabilisation. Serv. Ind. J. 2002, 22, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.G.; Eves, A.; Scarles, C. Building a model of local food consumption on trips and holidays: A grounded theory approach. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2009, 28, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, A.; Nath, B. The role of information technology in business process reengineering. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 1997, 50, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, G.R.; Cobanoglu, C. Hospitality Information Technology: Learning how to Use It; Kendall/Hunt Publishing: Dubuque, IA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, G. Selecting POS systems for table service restaurants. Hosp. Rev. 1991, 9. Article 5. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, T. “Echelon 2014: Run a restaurant? Let iChef take care of your orders” E27, 11 April 2014. Available online: http://e27.co/run-restaurant-let-ichef-take-care-orders-20150306/ (accessed on 23 September 2015).
- Ching, J. iCHEF sets the new standard for restaurant POS system. Vulcan Post. 2014. Available online: http://vulcanpost.com/3579/taiwans-iCHEF-sets-the-new-standard-for-restaurant-pos-system/ (accessed on 23 September 2015).
- Beheshti, H.M. The impact of IT on SMEs in the United States. Inf. Manag. Comput. Secur. 2004, 12, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roge, J.N.; Chakrabarty, S. Waiting for the other shoe to drop: Has information technology integrated marketing operations with marketing strategy? J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2003, 43, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron, F.; Raymond, L.; Rivard, S. Ideal patterns of strategic alignment and business performance. Inf. Manag. 2004, 41, 1003–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.E.; Huff, S.L.; Barclay, D.W.; Copeland, D.G. Business strategic orientation, information strategic orientation, and strategic alignment. Inf. Syst. Res. 1997, 8, 125–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallon, P.P. A process-oriented perspective on the alignment of information technology and business strategy. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2008, 24, 227–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaran, M. Exploring the relationship between information technology and business process reengineering. Inf. Manag. 2004, 41, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, T.H.; Short, J.E. The new industrial engineering: Information technology and business process redesign. In Operations Management: Critical Perspectives on Business and Management; Taylor & Francis US: Florence, KY, USA, 2003; pp. 97–123. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, T.H.; Khan, A.Q. Impact of Information Technology on BPR: A Study of Information Technology as BPR Enabler in Tractor Industry in Pakistan. J. Inf. Eng. Appl. 2014, 4, 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, T.J.; Magee, J.F.; Roussel, P.A.; Saad, K.N. Managing technology as a business strategy. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 1990, 31. Article 73. [Google Scholar]
- Reich, B.; Benbasat, I. Chapter 10 Measuring the Information Systems—Business Strategy Relationship. In Strategic Information Management; Butterworth-Heinemann: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013; p. 265. [Google Scholar]
- Kettinger, W.J.; Teng, J.T. Aligning BPR to strategy: A framework for analysis. Long Range Plan. 1998, 31, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnam, R.; Johnsen, J.; Wen, H.J. Alignment of business strategy and IT strategy: A case study of a fortune 50 financial services company. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2004, 45, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Orlikowski, W.J. Improvising organizational transformation over time: A situated change perspective. Inf. Syst. Res. 1996, 7, 63–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, V.C.; de Carvalho, M.M. Strategic alignment and performance: Brazilian companies in the medical diagnostics sector. Serv. Ind. J. 2011, 31, 1405–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Grembergen, W.; de Haes, S. Enterprise Governance of Information Technology: Achieving Strategic Alignment and Value; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, Y.J.; Kim, W.; Ham, S. Users’ intentions to employ a Point-Of-Sale system. Serv. Ind. J. 2014, 34, 901–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M. Poisoned POS-A Case Study in iOS Based Mobile Point-of-Sale Gone Wrong. Available online: https://owasp.confex.com/owasp/appsecusa13/webprogram/Session1206.html (accessed on 23 September 2015).
- Earl, M.J.; Sampler, J.L.; Short, J.E. Strategies for business process reengineering: Evidence from field studies. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 1995, 12, 31–56. [Google Scholar]
- Weick, K.E. The Social Psychology of Organizing (Topics in Social Psychology Series); McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Malone, T.W.; Crowston, K. The interdisciplinary study of coordination. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 1994, 26, 87–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschke, R.L. An Empirical Analysis of Business Process Agility: Examining the Relationship of IT on Business Process Agility and the Effects of Business Process Agility on Process Outcomes; Arizona State University: Tempe, AZ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, M.E. Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Analyzing Industries and Competitors; Simon and Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, S.S. IT Strategy and Management; PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd.: Delhi, India, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, J.C.; Venkatraman, N. Strategic alignment: Leveraging information technology for transforming organizations. IBM Syst. J. 1993, 32, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, P.N. Eroding grounded theory. In Critical Issues in Qualitative Research Methods; SAGE: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1994; pp. 212–223. [Google Scholar]
- McCutcheon, D.M.; Meredith, J.R. Conducting case study research in operations management. J. Oper. Manag. 1993, 11, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holsti, O.R. Content Analysis for the Social Sciences and Humanities; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.C.; Ha, N.-H.; Lin, K.-S. The Role of mPOS System in Process Change and Strategy Change: A Situated Change Perspective. Technologies 2015, 3, 198-218. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies3040198
Lin YC, Ha N-H, Lin K-S. The Role of mPOS System in Process Change and Strategy Change: A Situated Change Perspective. Technologies. 2015; 3(4):198-218. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies3040198
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yao Chin, Nhu-Hang Ha, and Kuo-Sung Lin. 2015. "The Role of mPOS System in Process Change and Strategy Change: A Situated Change Perspective" Technologies 3, no. 4: 198-218. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies3040198
APA StyleLin, Y. C., Ha, N.-H., & Lin, K.-S. (2015). The Role of mPOS System in Process Change and Strategy Change: A Situated Change Perspective. Technologies, 3(4), 198-218. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies3040198





