Crustal Strain Observation Using a Two-Color Interferometer with Accurate Correction of Refractive Index of Air
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Refractive Index of Air
3. Principle of Two-Color Measurement


4. Two-Color Interferometer
4.1. Optical Configuration
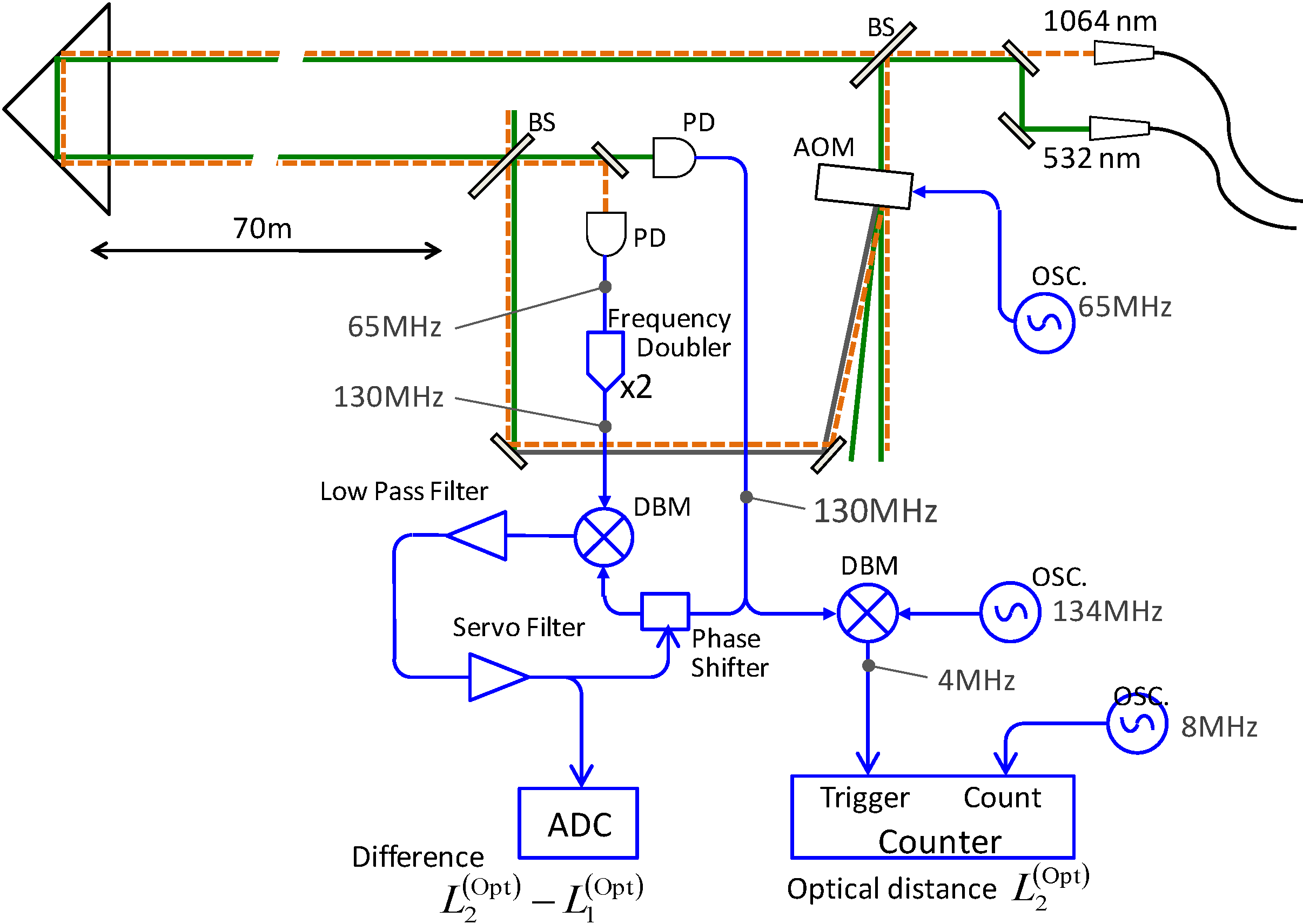

4.2. Measurement System
5. Calibration

6. Observation in the Shallow AIST Tunnel

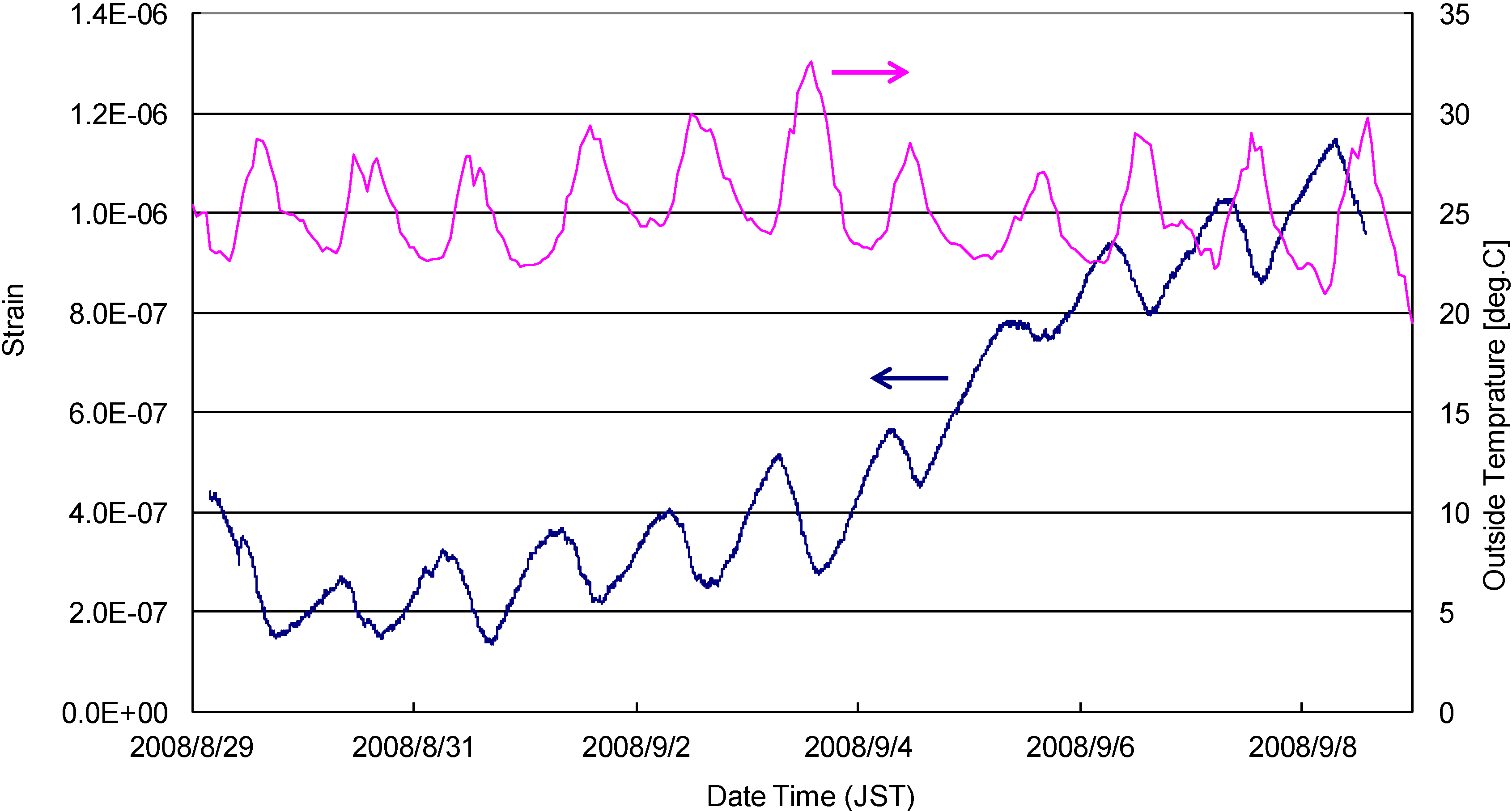
7. Observation at a Deep Underground Site in Kamioka

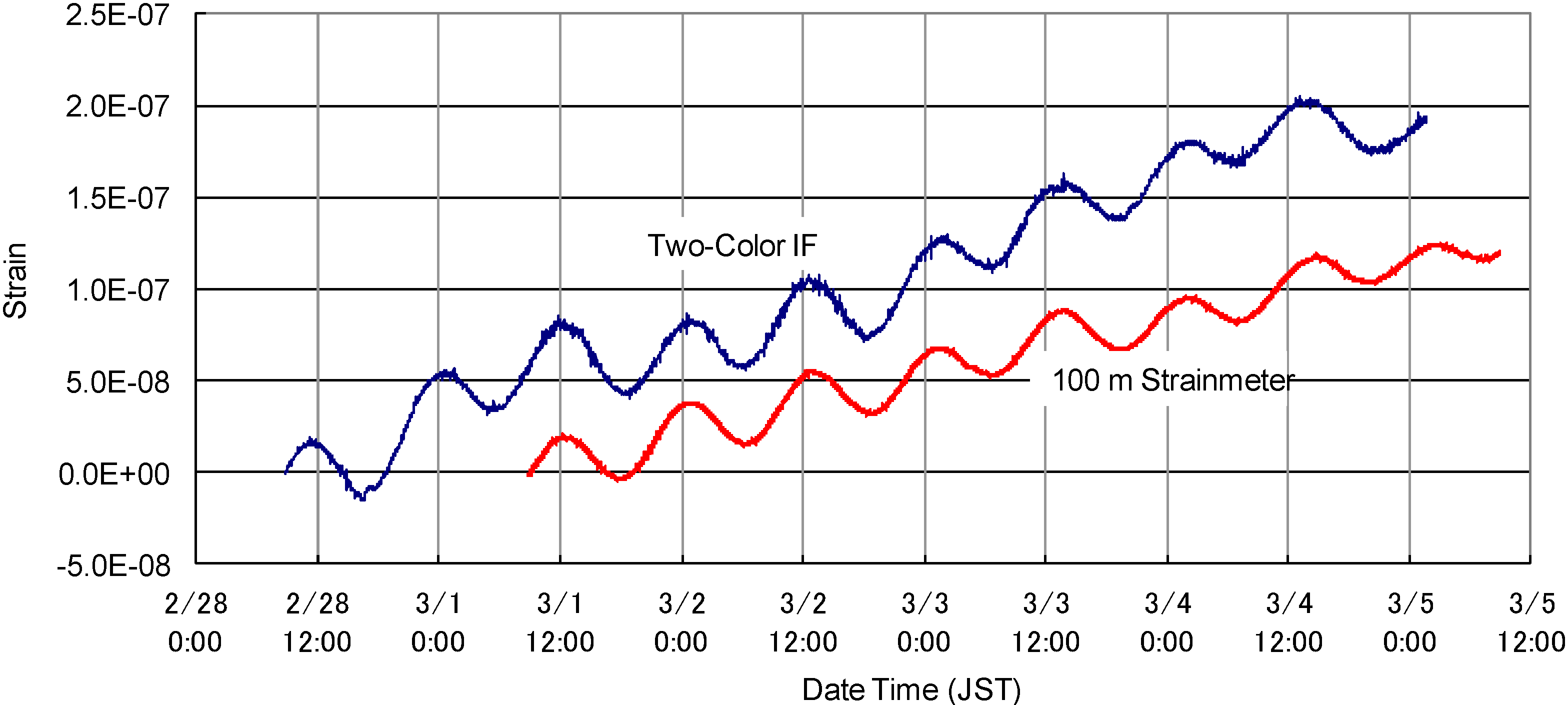
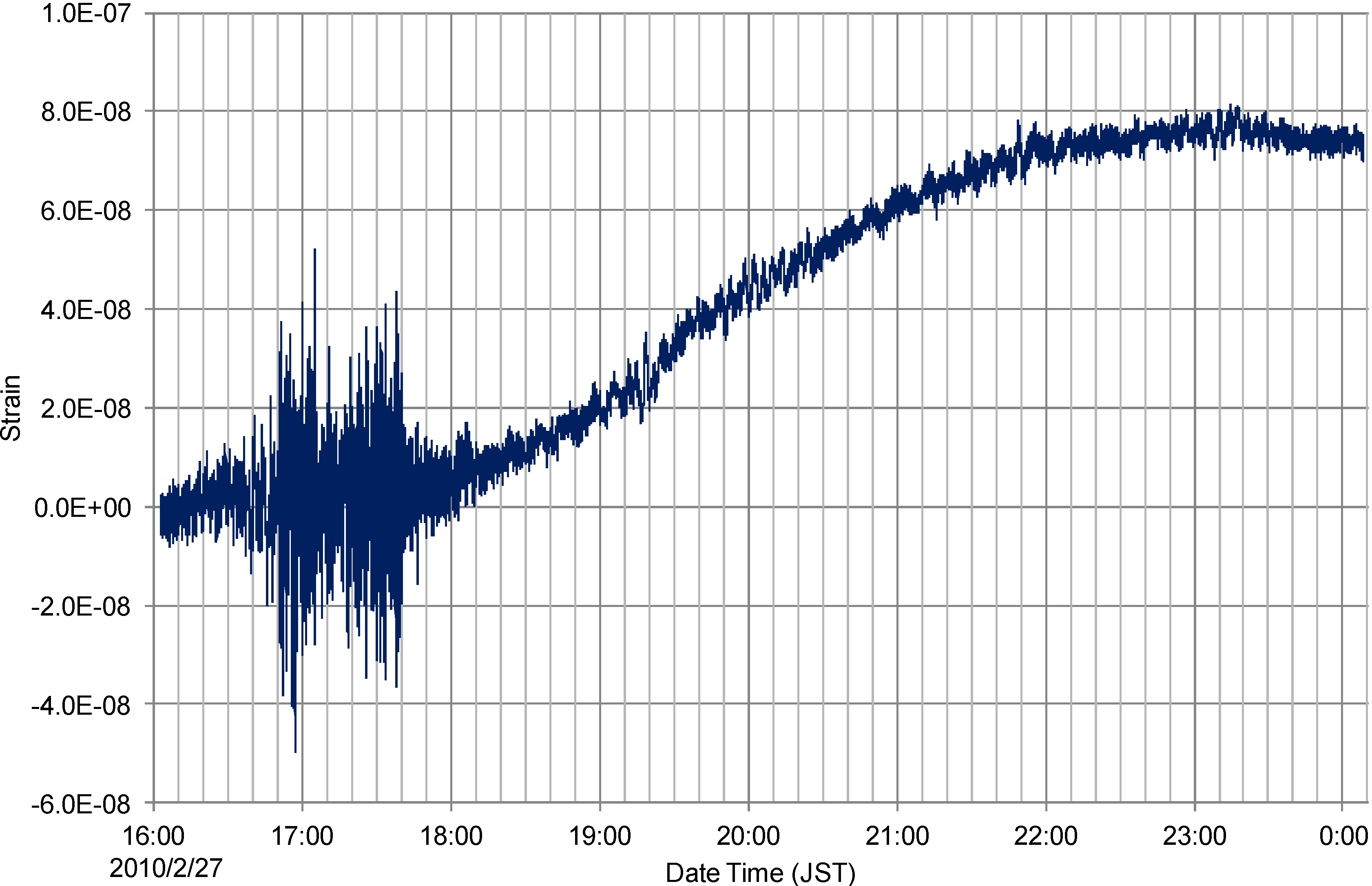
8. Discussion and Conclusions
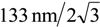 ), due to the continuous uniform distribution. This resolution corresponds to temperature measurements with 2 mK accuracy, if conventional one-color interferometer is used. Measurements of the temperature with such high accuracy are practically impossible in long-distance measurements. If we construct a longer two-color interferometer, the displacement resolution will have little dependence on the baseline, therefore the accuracy of the strain measurement will improve. The baseline can easily be extended because of the in-air optical path with low-cost guide pipes. This is a major advantage of using the two-color interferometer in geophysical applications to form a number of long-baseline strainmeters as a sensitive observation network. The long-baseline system also provides a long-distance standard in metrological application.
), due to the continuous uniform distribution. This resolution corresponds to temperature measurements with 2 mK accuracy, if conventional one-color interferometer is used. Measurements of the temperature with such high accuracy are practically impossible in long-distance measurements. If we construct a longer two-color interferometer, the displacement resolution will have little dependence on the baseline, therefore the accuracy of the strain measurement will improve. The baseline can easily be extended because of the in-air optical path with low-cost guide pipes. This is a major advantage of using the two-color interferometer in geophysical applications to form a number of long-baseline strainmeters as a sensitive observation network. The long-baseline system also provides a long-distance standard in metrological application.Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray-Moraleda, J. GPS: Applications in Crustal Deformation Monitoring. In Extreme Environmental Events; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 589–622. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, L.C. Synthetic interferometer radar for topographic mapping. Proc. IEEE 1974, 62, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeber, G. Satellite Geodesy, 2nd ed.; Walter de Gruyter Inc.: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bergstrand, E. Distance measuring by means of modulated light. Bull. Geod. 1952, 24, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasi, P.; Rioja, M.J.; Sarti, P. The European VLBI Network activity in geodesy: Crustal deformation in Europe. New Astron. Rev. 1999, 43, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benioff, H. Fuzed quartz extensometer for secular, tidal, and seismic strains. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1959, 70, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Lovberg, R. Earth strain measurements with a laser interferometer. Science 1970, 170, 296–303. [Google Scholar]
- Vali, V.; Bostrom, R.C. One thousand meter laser interferometer. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1968, 39, 1304–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Tokunaga, T.; He, Z. Sub-Nano resolution fiber-optic static sensor using a sideband interrogation technique. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 434–436. [Google Scholar]
- Araya, A.; Kunugi, T.; Fukao, Y.; Yamada, I.; Suda, N.; Maruyama, S.; Mio, N.; Moriwaki, S. Iodine-stabilized Nd:YAG laser applied to a long-baseline interferometer for wideband earth strain observations. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2001, 73, 2434–2439. [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto, S.; Araya, A.; Akamatsu, J.; Morii, W.; Momose, H.; Ohashi, M.; Kawasaki, I.; Higashi, T.; Fukuda, Y.; Miyoki, S.; et al. A 100 m laser strainmeter system installed in a 1 km deep tunnel at Kamioka, Gifu, Japan. J. Geodyn. 2004, 38, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, A.; Morii, W.; Hayakawa, H.; Takamori, A.; Uchiyama, T.; Ohashi, M.; Yamada, I.; Telada, S.; Takemoto, S. Broadband observation with laser strainmeters and a strategy for high resolution long-term strain observation based on quantum standard. J. Geod. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 53, 81–97. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, H.; Honda, T. High-accuracy length-measuring interferometer using the two-color method of compensating for the refractive index of air. Meas. Sci. Technol. 1992, 3, 1084–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Telada, S.; Seta, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Iwasaki, S. A weight average method to improve the uncertainty of length measurement in a two-color interferometer. Opt. Commun. 2001, 187, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujima, I.; Xie, G.; Seta, K. Precise measurement of the difference of the air refractive indices between visible and near-infrared wavelength using two-color interferometer. Proc. SPIE 1999, 3897, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlen, B. The refractive index of air. Metrologia 1966, 2, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciddor, P.E. Refractive index of air: New equations for the visible and the near infrared. Appl. Opt. 1996, 35, 1566–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohishi, T.; Seino, S.; Sakurai, Y. Vacuum-pipeless laser earth strainmeter. Appl. Opt. 1981, 20, 1329–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Super-Kamiokande Collaboration. The Super-Kamiokande detector. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. 2003, A501, 418–462. [Google Scholar]
- Araki, T.; Enomoto, S.; Furuno, K.; Gando, Y.; Ichimura, K.; Ikeda, H.; Inoue, K.; Kishimoto, Y.; Koga, Y.; Koseki, Y.; et al. Experimental investigation of geologically produced antineutrinos with KamLAND. Nature 2005, 436, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, M.; Kuroda, K.; Miyoki, S.; Uchiyama, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Kasahara, K.; Shintomi, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Haruyama, T.; Saito, Y.; et al. Design and construction status of CLIO. Class. Quantum Grav. 2003, 20, S599–S608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, T.; Miyoki, S.; Telada, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Ohashi, M.; Agatsuma, K.; Arai, K.; Fujimoto, M-K.; Haruyama, T.; Kawamura, S.; et al. Reduction of thermal fluctuations in a cryogenic laser interferometric gravitational wave detector. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 141101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, A.; Takamori, A.; Morii, W.; Hayakawa, H.; Uchiyama, T.; Ohashi, M.; Telada, S.; Takemoto, S. Analyses of far-field coseismic crustal deformation observed by a new laser distance measurement system. Geophys. J. Int. 2010, 181, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Telada, S.; Araya, A.; Takamori, A. Crustal Strain Observation Using a Two-Color Interferometer with Accurate Correction of Refractive Index of Air. Technologies 2014, 2, 115-128. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies2030115
Telada S, Araya A, Takamori A. Crustal Strain Observation Using a Two-Color Interferometer with Accurate Correction of Refractive Index of Air. Technologies. 2014; 2(3):115-128. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies2030115
Chicago/Turabian StyleTelada, Souichi, Akito Araya, and Akiteru Takamori. 2014. "Crustal Strain Observation Using a Two-Color Interferometer with Accurate Correction of Refractive Index of Air" Technologies 2, no. 3: 115-128. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies2030115
APA StyleTelada, S., Araya, A., & Takamori, A. (2014). Crustal Strain Observation Using a Two-Color Interferometer with Accurate Correction of Refractive Index of Air. Technologies, 2(3), 115-128. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies2030115



