Real-Time Prediction of Foot Placement and Step Height Using Stereo Vision Enhanced by Ground Object Awareness
Abstract
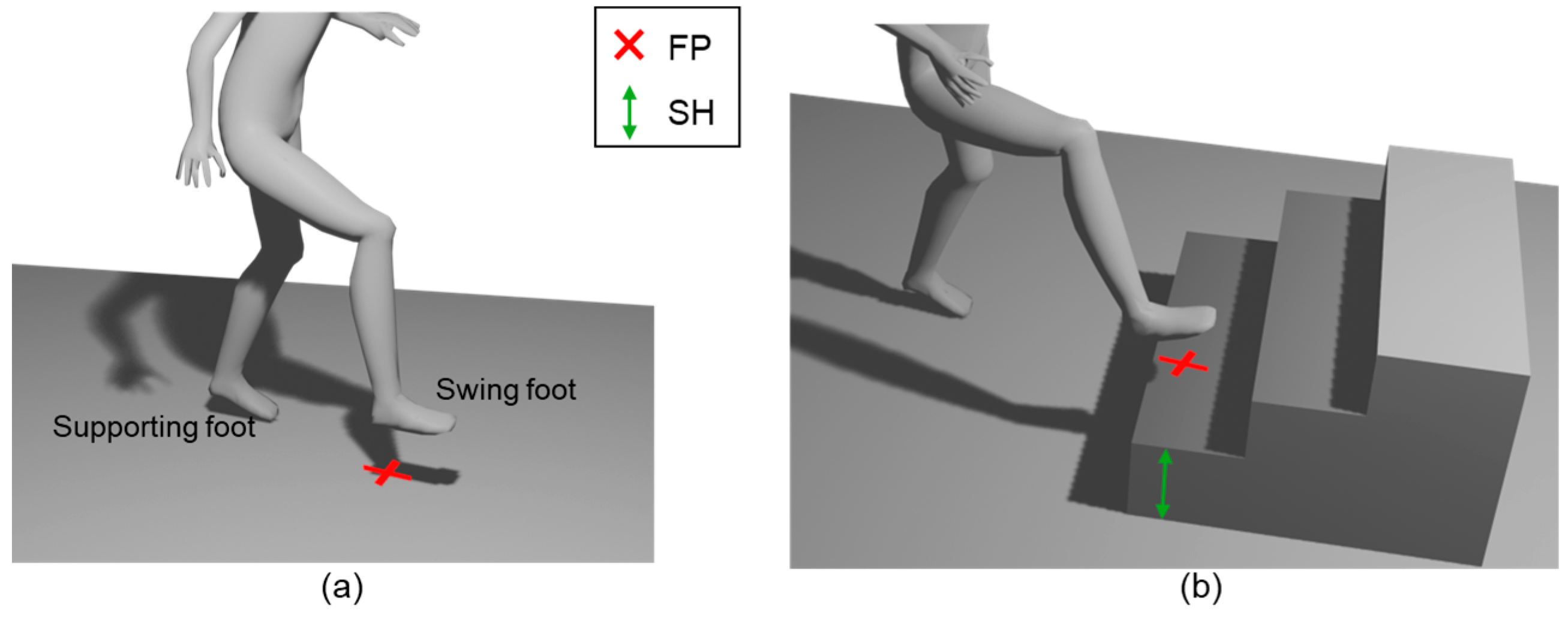
1. Introduction
- FP was predicted using a stereo camera and a camera-mounted IMU, without additional IMU or EMG sensors attached to the lower limbs, to minimize hardware and model complexity.
- SH was estimated from the FP height using an RGB-D stereo camera, which is essential for wearable robot control on irregular terrains.
- Both lower-limb motion and the environmental information were extracted from on-body RGB-D images and considered to increase FP prediction accuracy.
- Real-time inference was evaluated using an embedded system to verify its practical applicability.
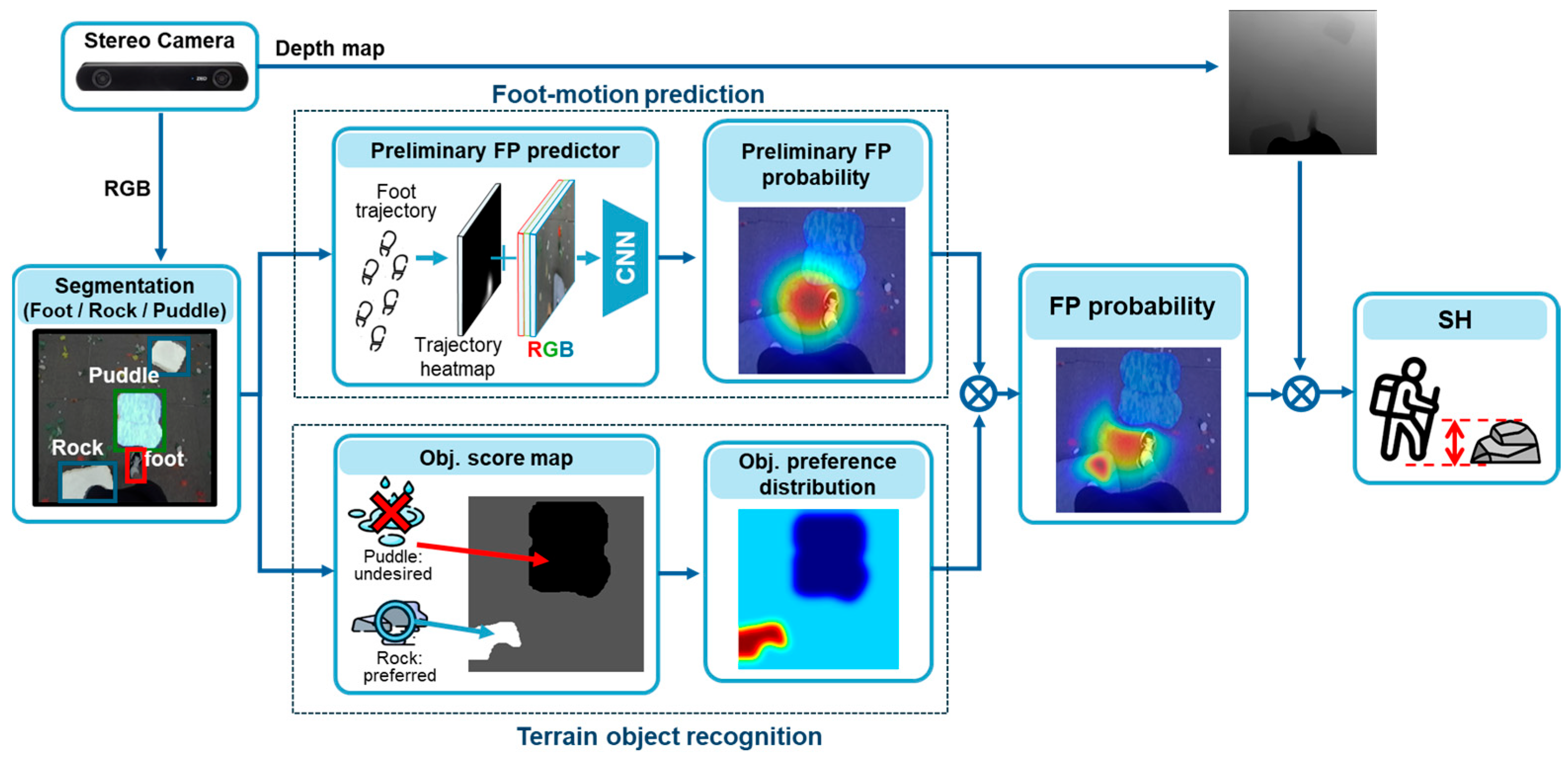
2. Materials and Methods
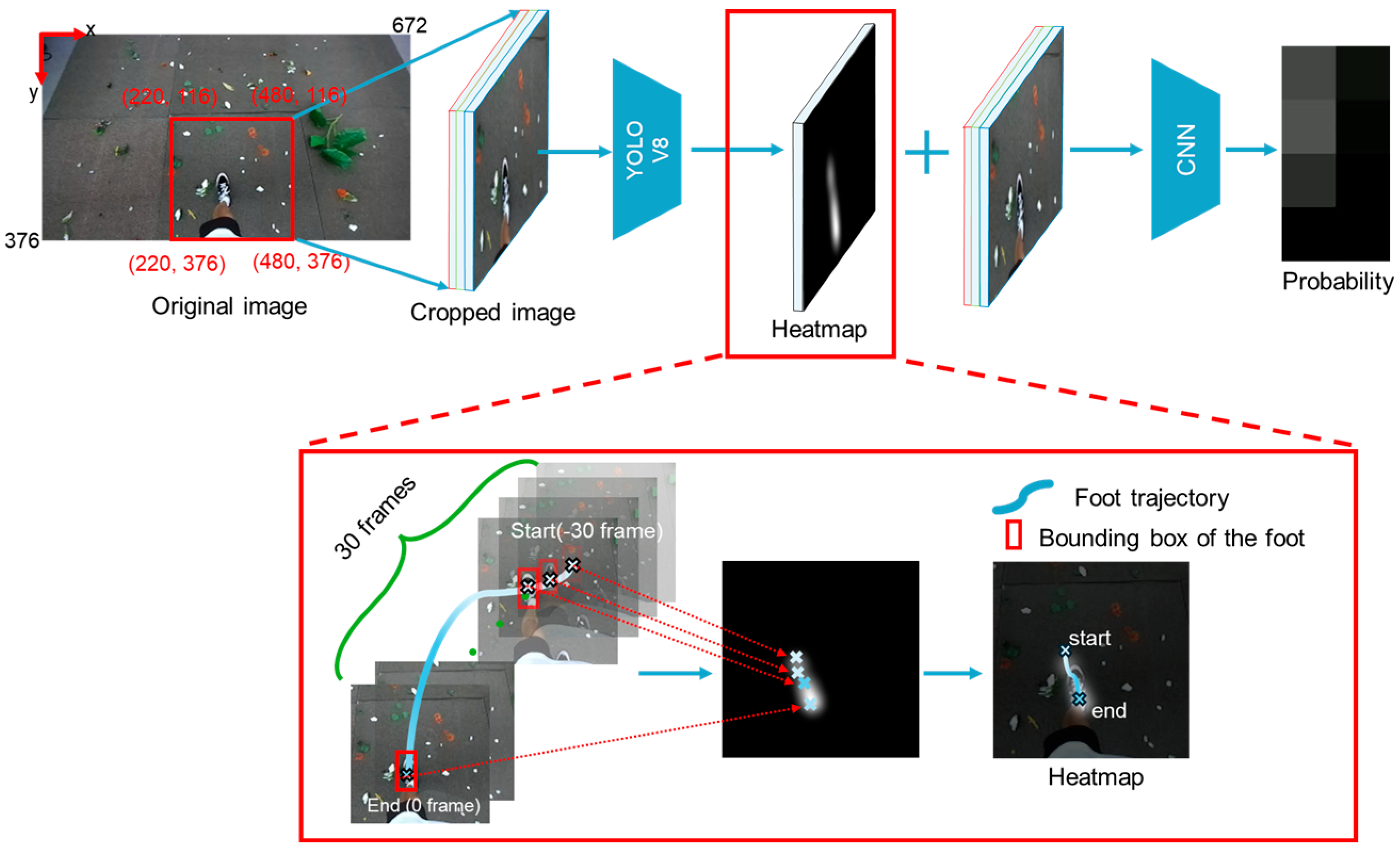
2.1. Foot-Motion Prediction
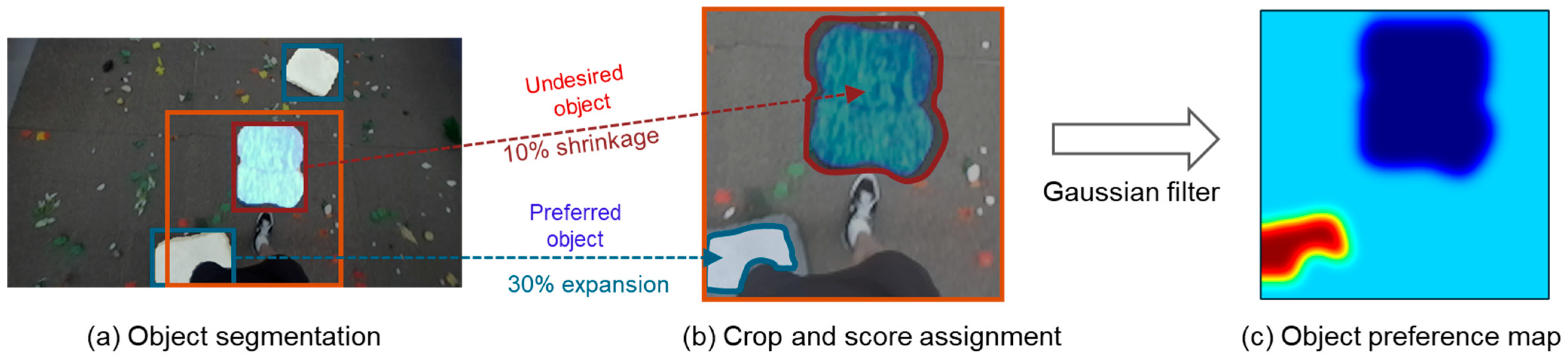
2.2. Terrain Object Recognition
2.3. FP Probability
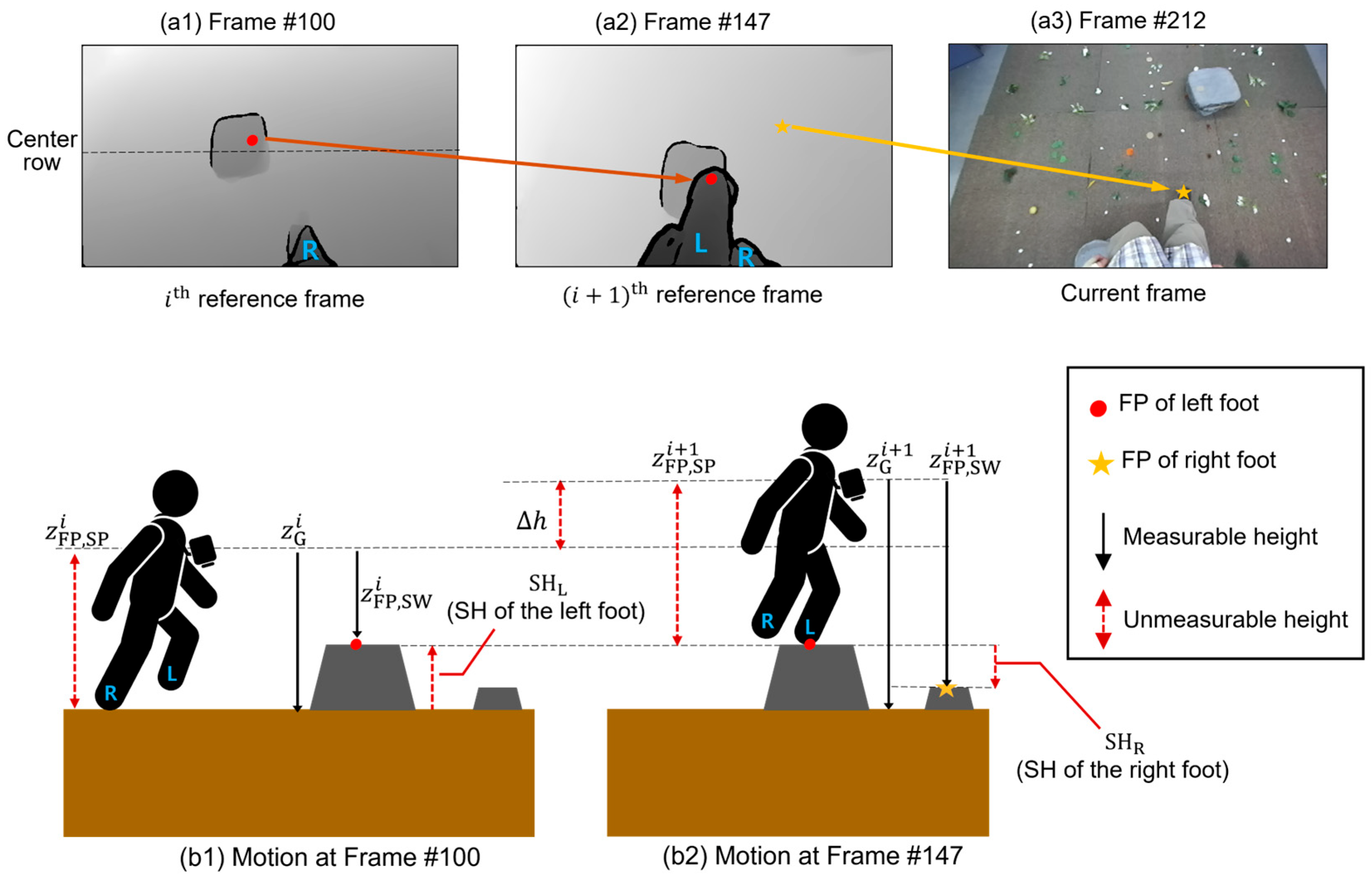
2.4. SH Calculation
3. Experiments and Dataset
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Effects of the Foot Trajectory Heatmap
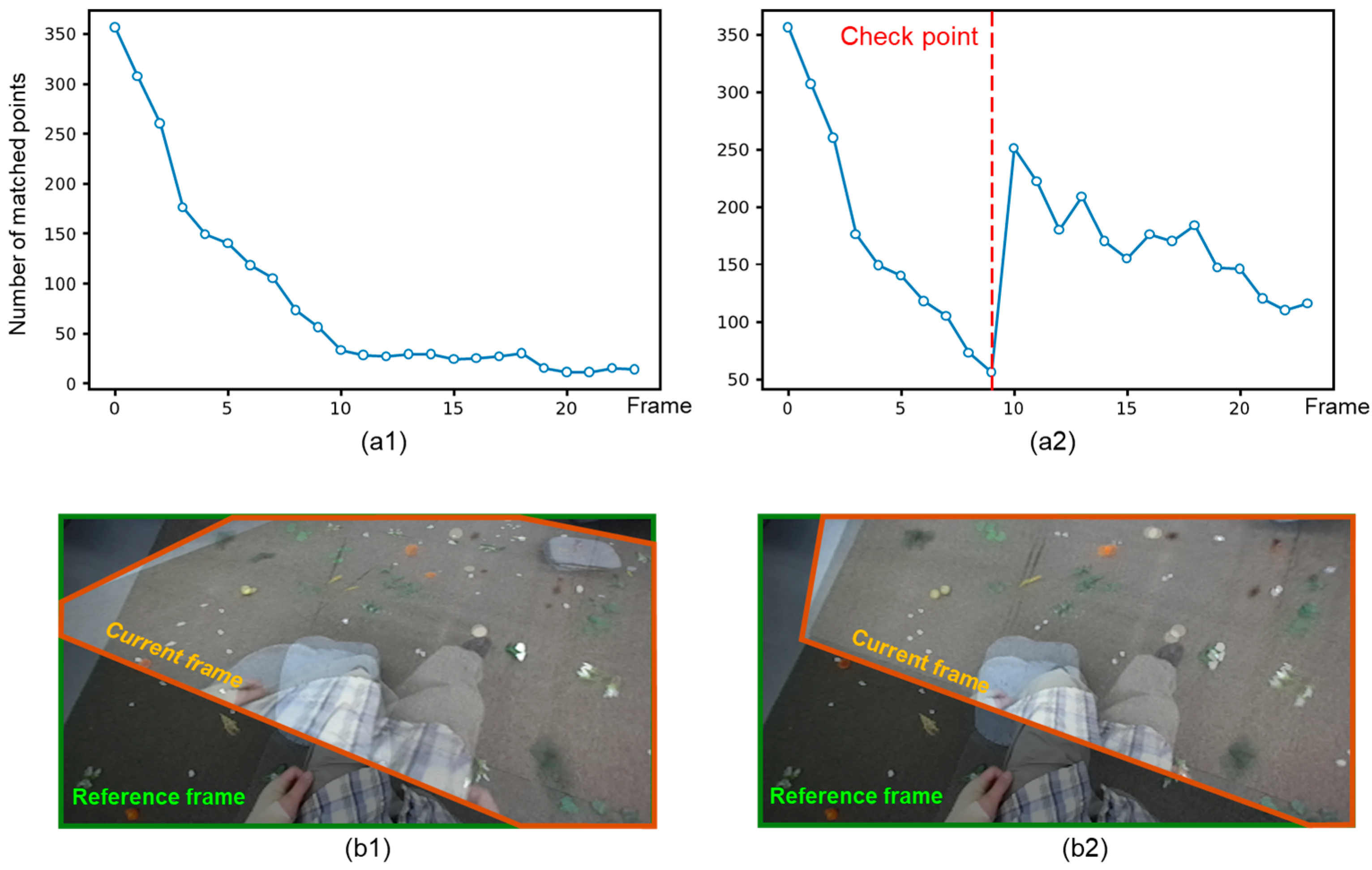
4.2. Effects of the Checkpoint Frame
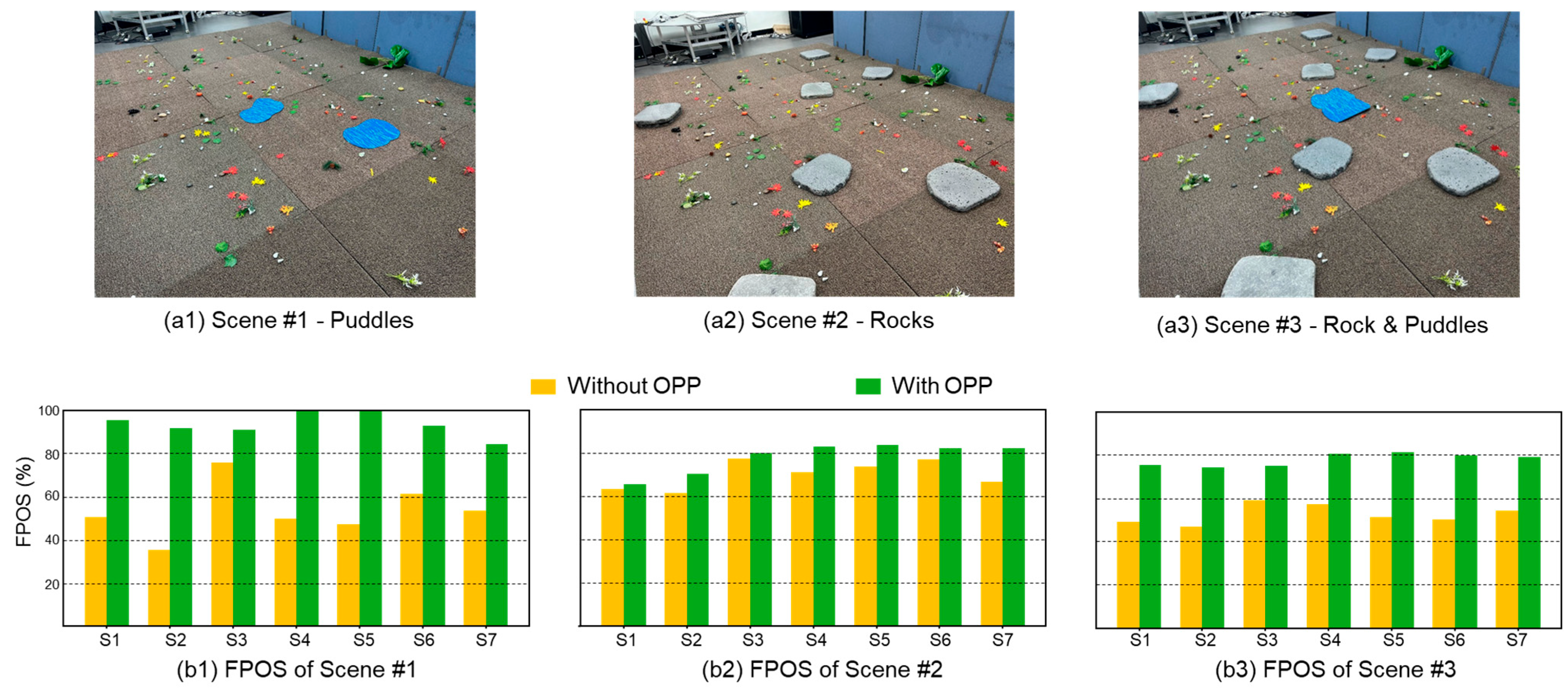
4.3. Effects of Object Preference
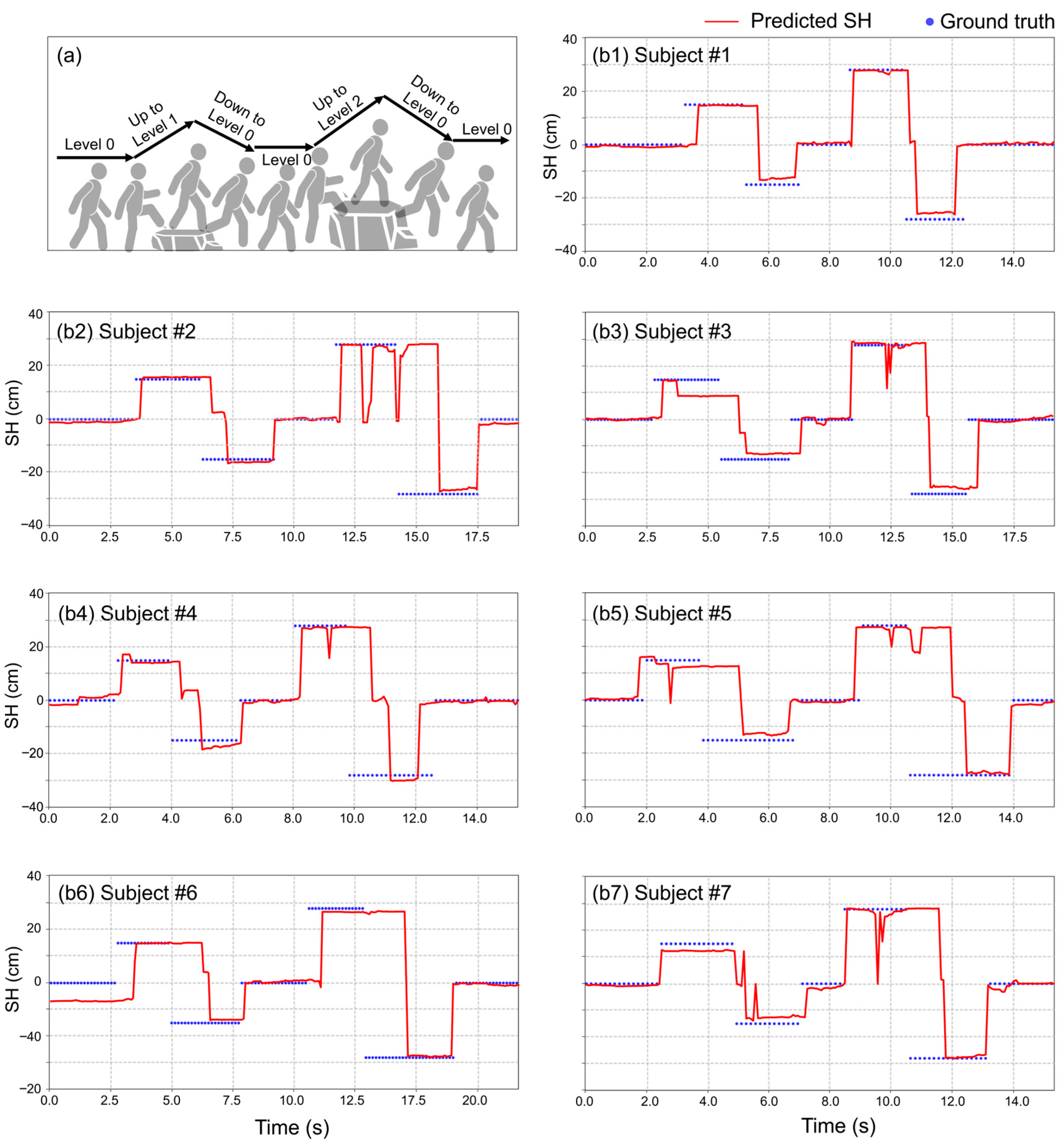
4.4. SH Prediction
4.5. Inference Speed in Embedded Systems
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mooney, L.M.; Rouse, E.J.; Herr, H.M. Autonomous exoskeleton reduces metabolic cost of human walking during load carriage. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2014, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malcolm, P.; Derave, W.; Galle, S.; De Clercq, D. A simple exoskeleton that assists plantarflexion can reduce the metabolic cost of human walking. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Nam, K.; Yun, J.; Moon, J.; Ryu, J.; Park, S.; Yang, S.; Nasirzadeh, A.; Nam, W.; Ramadurai, S.; et al. Effect of hip abduction assistance on metabolic cost and balance during human walking. Sci. Robot. 2023, 8, eade0876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-dabbagh, A.H.; Ronsse, R. A review of terrain detection systems for applications in locomotion assistance. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2020, 133, 103628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.-Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, S.-Q.; Sheng, M.; Jiang, J.; Xiang, K. A CNN-based method for intent recognition using inertial measurement units and intelligent lower limb prosthesis. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Li, W.; He, Y.; Zeng, T.; Li, B.; Song, G.; Qiu, J. Terrain slope parameter recognition for exoskeleton robot in urban multi-terrain environments. Complex Intell. Syst. 2024, 10, 3107–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, K.; Zheng, H.; Song, W.; Pei, Z.; Chen, W. Cross-Modality Self-Attention and Fusion-Based Neural Network for Lower Limb Locomotion Mode Recognition. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024, 22, 5411–5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbis, A.G.; Laschowski, B.; Mihailidis, A. Stair recognition for robotic exoskeleton control using computer vision and deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 25–29 July 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Laschowski, B.; McNally, W.; Wong, A.; McPhee, J. Preliminary design of an environment recognition system for controlling robotic lower-limb prostheses and exoskeletons. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2019; pp. 868–873. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, H.-H.; Le, T.-L.; Vuillerme, N. Real-Time Obstacle Detection System in Indoor Environment for the Visually Impaired Using Microsoft Kinect Sensor. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 3754918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Xiong, J.; Leng, Y.; Yu, H.; Fu, C. Predictive locomotion mode recognition and accurate gait phase estimation for hip exoskeleton on various terrains. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 6439–6446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-W.; Asbeck, A. A deep learning-based approach for foot placement prediction. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 4959–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Qian, Y.; Leng, Y.; Fu, C. A probability fusion approach for foot placement prediction in complex terrains. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2023, 31, 4591–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhong, B.; Lobaton, E.; Huang, H. Fusion of human gaze and machine vision for predicting intended locomotion mode. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ultralytics. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 26 August 2024).
- Devroye, L.; Györfi, L.; Lugosi, G. A Probabilistic Theory of Pattern Recognition; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.-C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Rublee, E.; Rabaud, V.; Konolige, K.; Bradski, G. ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 2564–2571. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- NVIDIA TensorRT. Available online: https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt/ (accessed on 4 March 2024).


| Subject | Age | Height (cm) | Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 26 | 170 | 62 |
| 2 | 27 | 178 | 82 |
| 3 | 26 | 176 | 73 |
| 4 | 27 | 175 | 68 |
| 5 | 24 | 184 | 78 |
| 6 | 27 | 169 | 58 |
| 7 | 24 | 183 | 71 |
| Model | FP RMSE (cm) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Mobilenet–v2 (RGB + H) | 17.70 | 0.0136 |
| Mobilenet–v2 (RGB) | 20.89 | |
| VGG16 (RGB + H) | 16.81 | 0.0251 |
| VGG16 (RGB) | 20.66 |
| Scene | Average FPOS (%) | Average FP RMSE (cm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without OPP | With OPP | Without OPP | With OPP | |
| 1 (Puddles) | 56.32 | 75.56 | 26.14 | 25.56 |
| 2 (Rocks) | 70.11 | 78.19 | 20.16 | 19.32 |
| 3 (Puddles + Rocks) | 52.57 | 78.01 | 25.55 | 23.70 |
| Average | 59.67 | 77.25 | 23.95 | 22.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, C.; Baek, J.; Han, J.; Lee, G.; Nam, W. Real-Time Prediction of Foot Placement and Step Height Using Stereo Vision Enhanced by Ground Object Awareness. Technologies 2025, 13, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13090399
Lim C, Baek J, Han J, Lee G, Nam W. Real-Time Prediction of Foot Placement and Step Height Using Stereo Vision Enhanced by Ground Object Awareness. Technologies. 2025; 13(9):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13090399
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Chulyong, Jaewon Baek, Junhee Han, Giuk Lee, and Woochul Nam. 2025. "Real-Time Prediction of Foot Placement and Step Height Using Stereo Vision Enhanced by Ground Object Awareness" Technologies 13, no. 9: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13090399
APA StyleLim, C., Baek, J., Han, J., Lee, G., & Nam, W. (2025). Real-Time Prediction of Foot Placement and Step Height Using Stereo Vision Enhanced by Ground Object Awareness. Technologies, 13(9), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13090399








