Structural Integrity Assessment of Stainless Steel Fabricated by GMAW-Assisted Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing
Abstract
1. Introduction
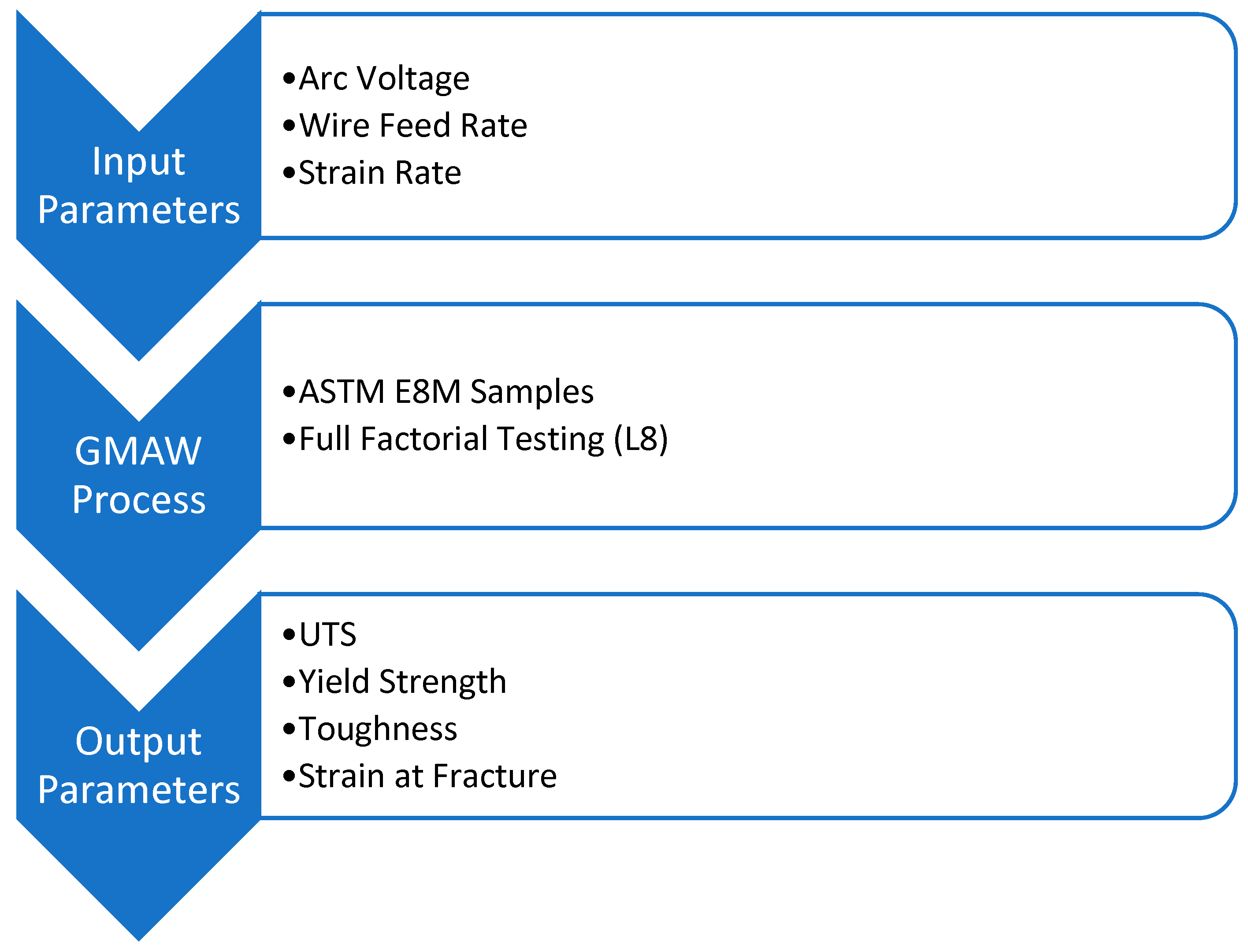
2. Experimental Design and Methodology
2.1. Design of Experiments
2.2. Postprocessing and Testing
3. Results and Discussion
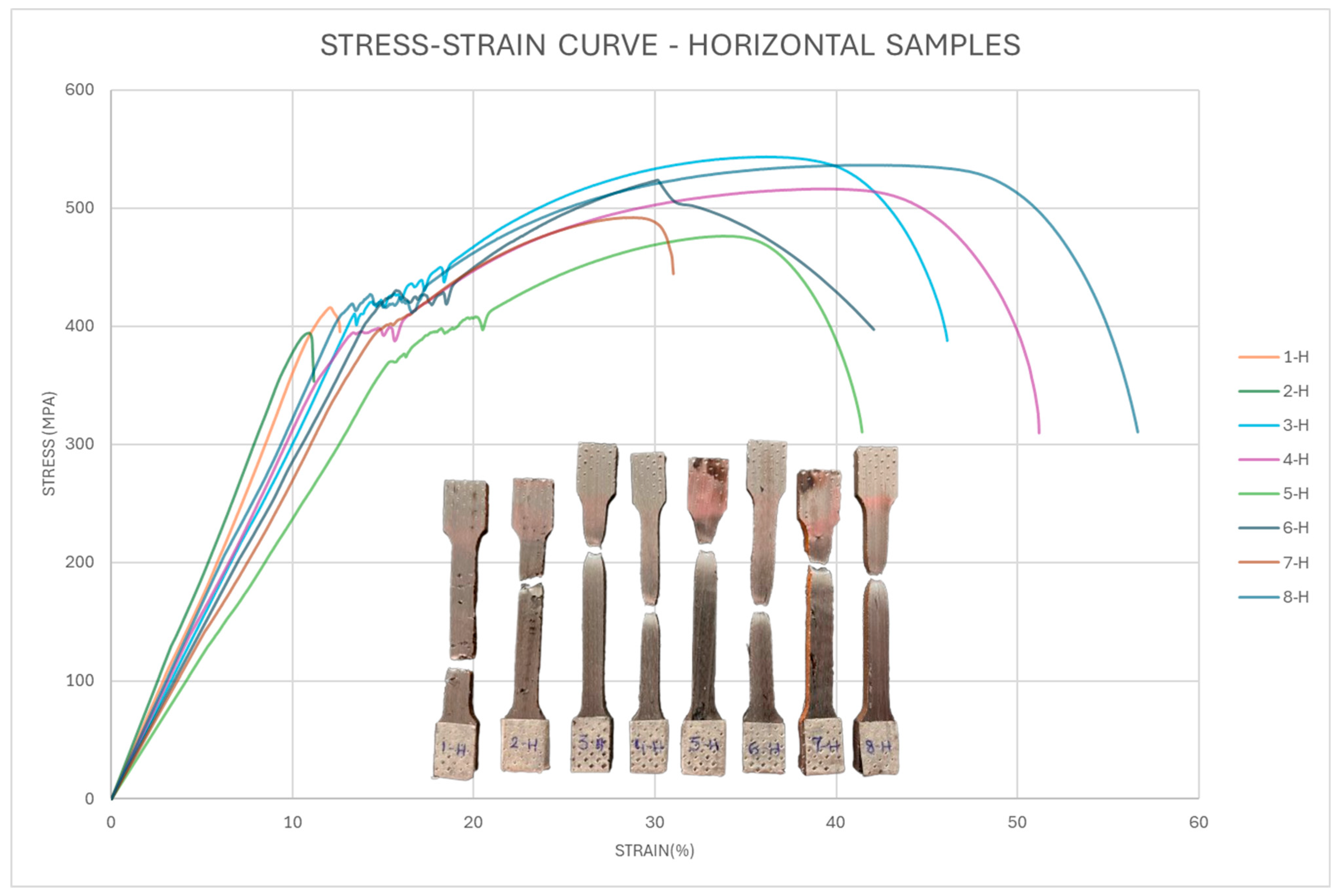
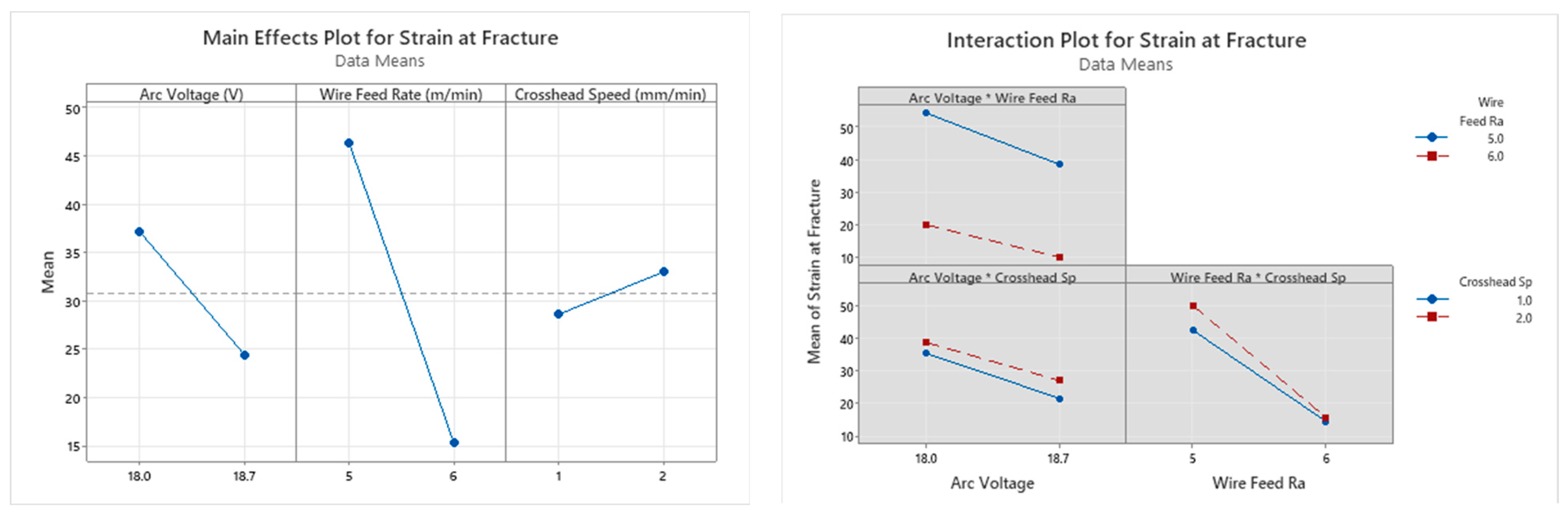
3.1. Horizontal Samples
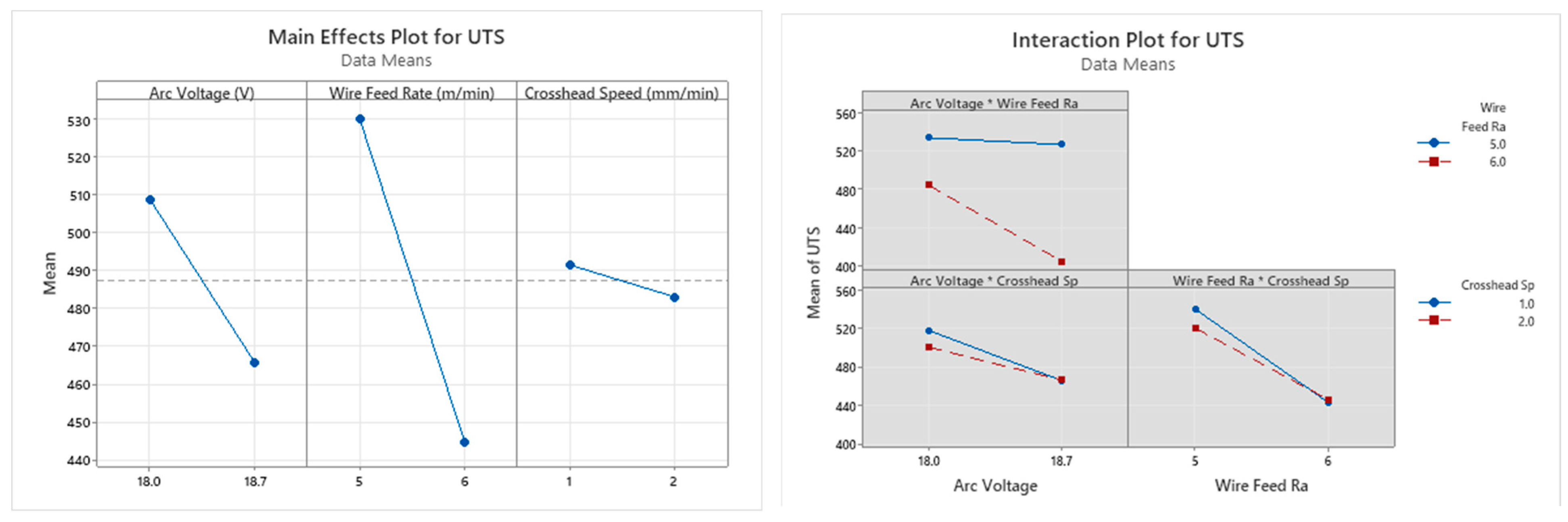
3.1.1. Analysis of Variance and Interaction Plots for Horizontal Samples
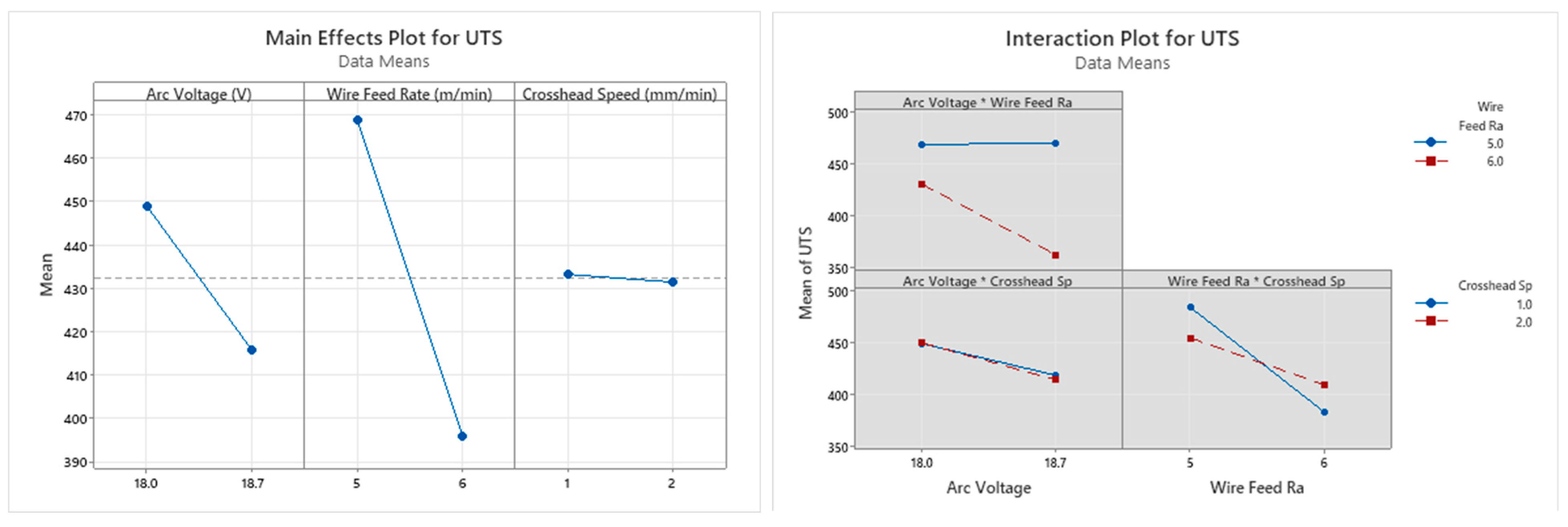
Ultimate Tensile Stress (UTS)
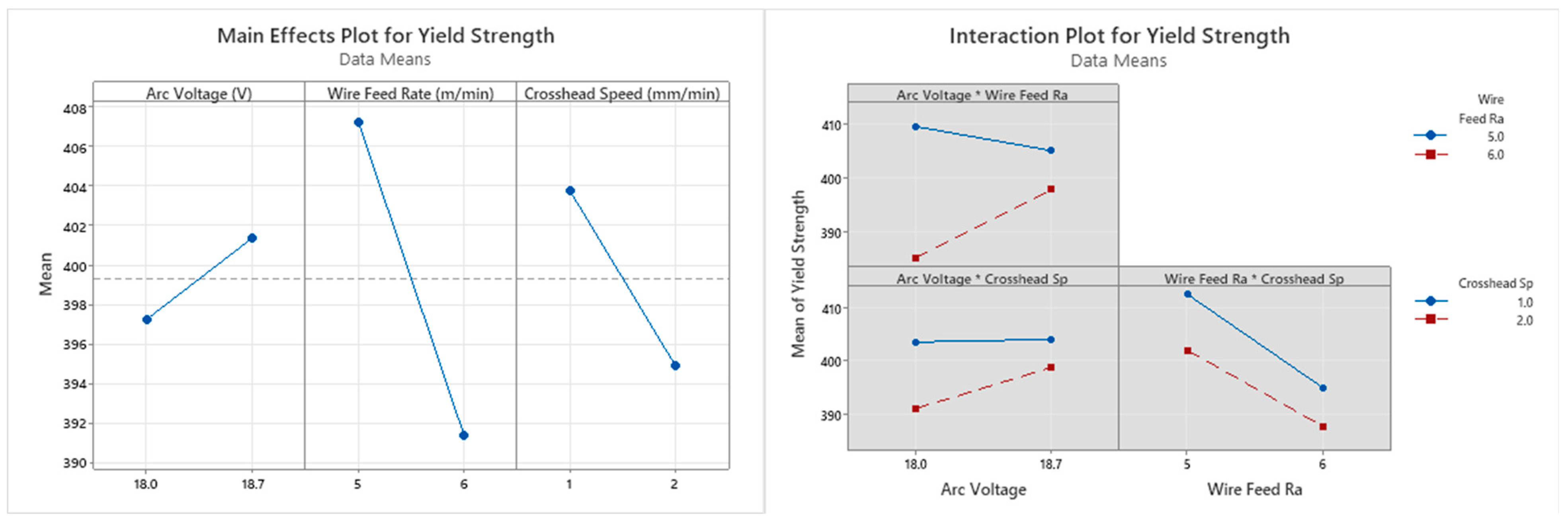
Yield Strength
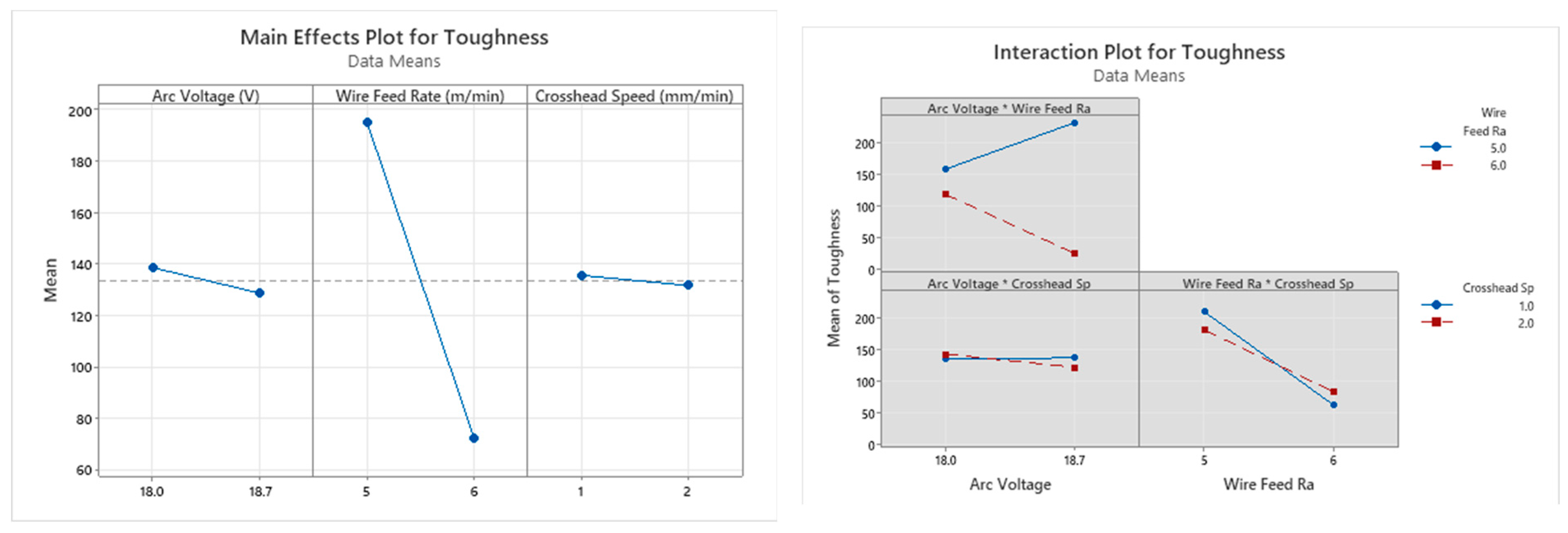
Toughness
Percentage Elongation
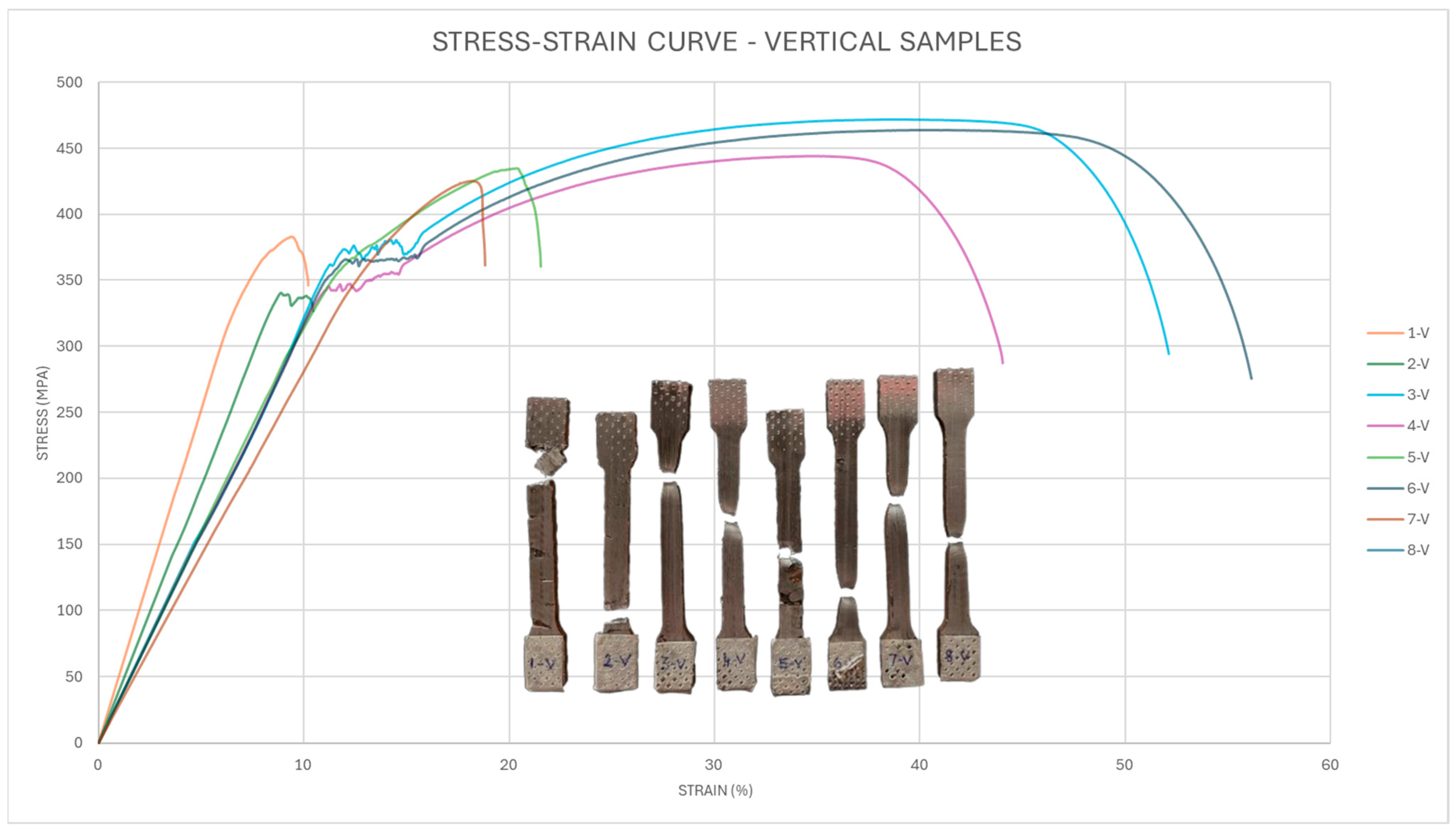
3.2. Vertical Samples
3.2.1. Analysis of Variance and Interaction Plots for Vertical Sample
Ultimate Tensile Stress (UTS)
Yield Strength
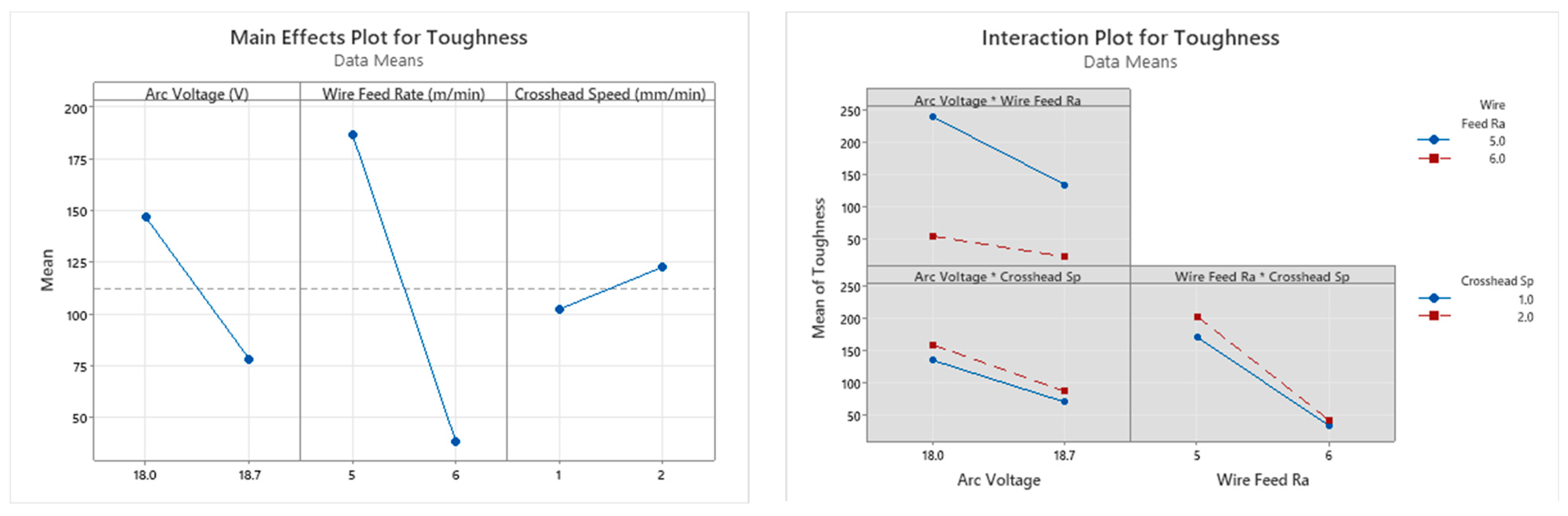
Toughness
Percent Elongation
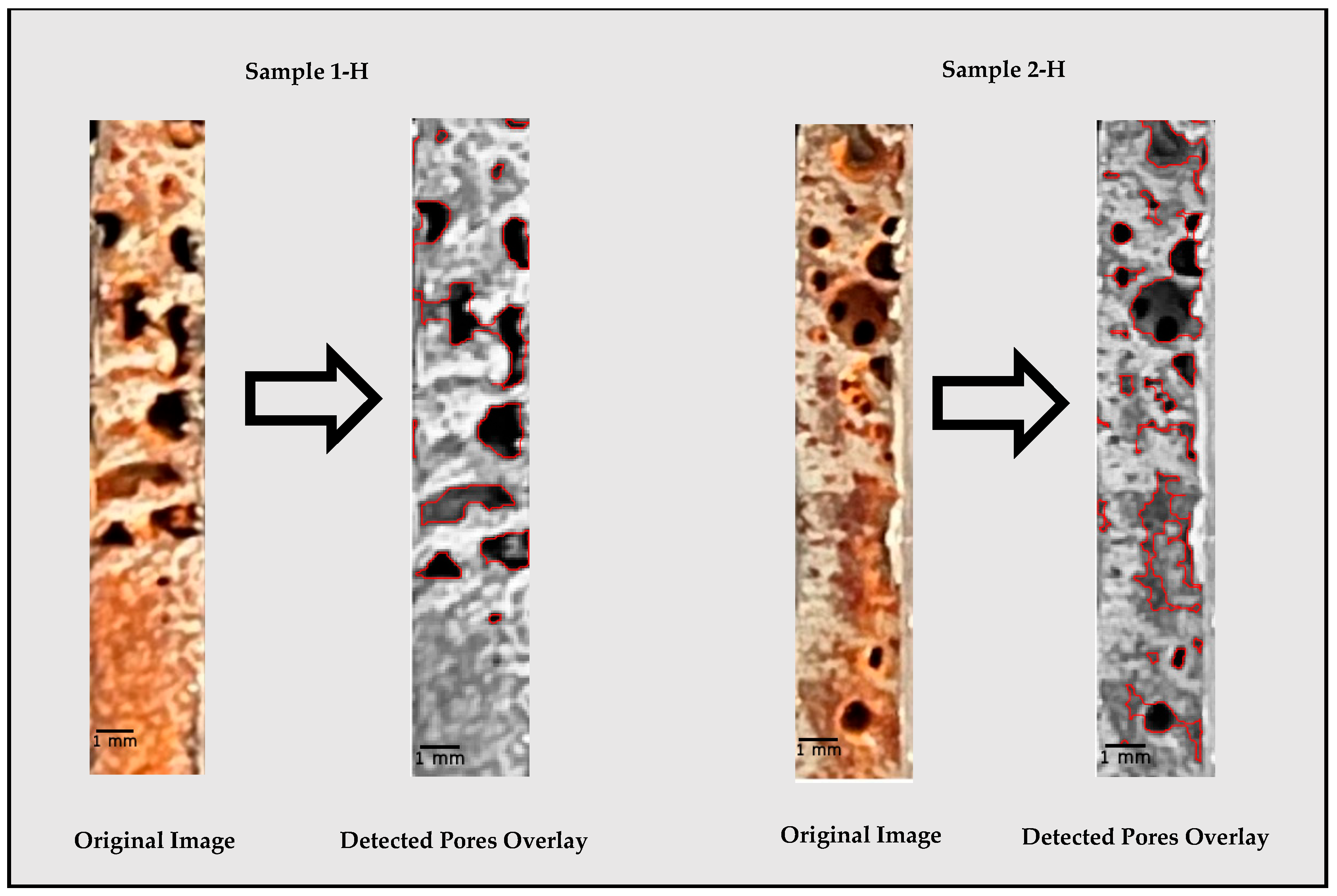
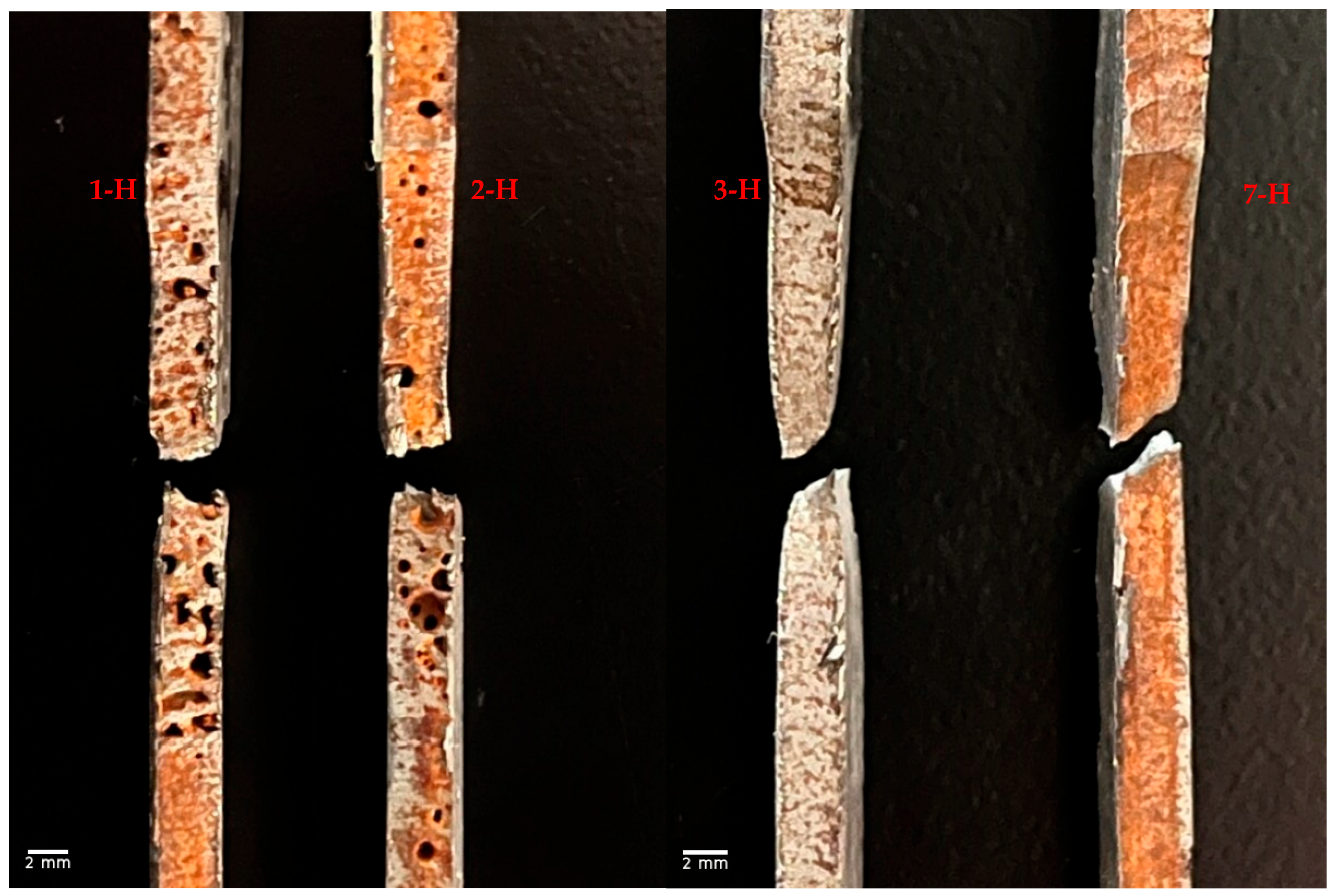
3.3. Porosity in Horizontal and Vertical Samples
4. Conclusions and Future Work
- Samples printed with an arc voltage of 18.7 V and a wire feed rate of 6 m/min showed the lowest mechanical properties, with certain output parameters being lower than the norm. This anomaly was seen because of the presence of high levels of porosity within the structure when printed with this particular combination of input parameters. The presence of porosity will facilitate faster fracture and also affect the quality of the final part.
- The influence of the wire feed rate was seen to be the highest for all output parameters across both the horizontal and vertical samples, except for the yield strength of the vertical samples. For the yield strength of the vertical samples, the arc voltage had the dominant significance, followed by the wire feed rate.
- The strain rate had a very low influence on the mechanical properties of both the vertical and horizontal samples.
- Samples taken out from the horizontal direction had higher tensile mechanical properties because of the favorable grain orientation. The vertical samples showed marginally lower mechanical properties.
- The highest UTS (543 ± 4 MPa) was observed in horizontal samples printed with an arc voltage of 18 V and a wire feed rate of 5 m/min tested at a strain rate of 1 mm/min. The highest YS (418 ± 7 MPa), toughness (248 ± 4 MPa) and %EL (57 ± 1%) were observed in horizontal samples printed with an arc voltage of 18.7 V and a wire feed rate of 5 m/min tested at a strain rate of 1 mm/min. Using this combination gave a UTS of 537 ± 4 MPa, which is very close to the highest UTS observed (543 ± 4 MPa).
- Overall, samples from the horizontal direction, printed with an arc voltage of 18 V and a wire feed rate of 5 m/min, showed the best results in this study.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, L.; Miller, J.; Vezza, J.; Mayster, M.; Raffay, M.; Justice, Q.; Al Tamimi, Z.; Hansotte, G.; Sunkara, L.D.; Bernat, J. Additive Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Review. Sensors 2024, 24, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM/ISO 52900; Additive Manufacturing—General Principles—Fundamentals and Vocabulary. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 2021.
- Rooney, K.; Dong, Y.; Pramanik, A.; Basak, A.K. Additive Manufacturing in Australian Small to Medium Enterprises: Vat Polymerisation Techniques, Case Study and Pathways to Industry 4.0 Competitiveness. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2023, 7, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alami, A.H.; Ghani Olabi, A.; Alashkar, A.; Alasad, S.; Aljaghoub, H.; Rezk, H.; Abdelkareem, M.A. Additive manufacturing in the aerospace and automotive industries: Recent trends and role in achieving sustainable development goals. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 14, 102516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkaseer, A.; Chen, K.J.; Janhsen, J.C.; Refle, O.; Hagenmeyer, V.; Scholz, S.G. Material jetting for advanced applications: A state-of-the-art review, gaps and future directions. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 60, 103270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Zhou, R.; Vivegananthan, P.; See Wu, M.; Gao, H.; Zhou, K. Recent progress in gradient-structured metals and alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 140, 101194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev Singh, D.; Mahender, T.; Reddy, A.R. Powder bed fusion process: A brief review. In Materials Today: Proceedings; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleff, A.; Küster, B.; Stonis, M.; Overmeyer, L. Process monitoring for material extrusion additive manufacturing: A state-of-the-art review. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 6, 705–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Cook, O.J.; Argüelles, A.P.; Beese, A.M. Review of Process–Structure–Property Relationships in Metals Fabricated Using Binder Jet Additive Manufacturing. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2023, 12, 883–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarzyński, B.; Śnieżek, L.; Grzelak, K. Metal Additive Manufacturing (MAM) Applications in Production of Vehicle Parts and Components—A Review. Metals 2024, 14, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Pan, Z.; Ding, D.; Cuiuri, D.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; Norrish, J. A review of the wire arc additive manufacturing of metals: Properties, defects and quality improvement. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 35, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yu, R.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, H.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, Y.M. Real-time sensing of gas metal arc welding process—A literature review and analysis. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 70, 452–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boillot, P.; Peultier, J. Use of stainless steels in the industry: Recent and future developments. In Procedia Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Schino, A. Manufacturing and applications of stainless steels. Metals 2020, 10, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubaldini, A.; Telloli, C.; Rizzo, A.; Gessi, A.; Marghella, G.; Bruni, S.; Calistri, S.; Gennerini, F.; Pintilei, G. A Study of Accelerated Corrosion of Stainless Steels under Highly Oxidizing Conditions. Coatings 2024, 14, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backhouse, A.; Baddoo, N. Recent developments of stainless steels in structural applications. Ce/Papers 2021, 4, 2349–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, V.K.; Silori, P.; Paradkar, P.; Niauzorau, S.; Sharstniou, A.; Hasib, A.; Villalobos, S.; Azeredo, B. 3d printing of stainless steel 316L and its weldability for corrosive environments. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 833, 142439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, H.S.; Seikh, A.H.; Alharbi, H.F.; Mohammed, J.A.; Soliman, M.S.; Fouly, A.; Ragab, S.A. Tribo-behavior and corrosion properties of welded 304l and 316l stainless steel. Coatings 2021, 11, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Zhang, C.; Jin, S.; Tian, Y.; Wellmann, D.; Liu, W. Wire arc additive manufacturing of stainless steels: A review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekis, M.; Tawfik, M.; Egiza, M.; Dewidar, M. Challenges and developments in wire arc additive manufacturing of steel: A review. Results Eng. 2025, 26, 104657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokare, S.; Shen, J.; Fonseca, P.P.; Lopes, J.G.; Machado, C.M.; Santos, T.G.; Oliveira, J.P.; Godina, R. Wire arc additive manufacturing of a high-strength low-alloy steel part: Environmental impacts, costs, and mechanical properties. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 134, 453–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6507-1:2023; Metallic Materials—Vickers Hardness Test—Part 1: Test Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Ermakova, A.; Mehmanparast, A.; Ganguly, S.; Razavi, N.; Berto, F. Investigation of mechanical and fracture properties of wire and arc additively manufactured low carbon steel components. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2020, 109, 102685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nabulsi, Z.; Mottram, J.T.; Gillie, M.; Kourra, N.; Williams, M.A. Mechanical and X ray computed tomography characterisation of a WAAM 3D printed steel plate for structural engineering applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 274, 121700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BS EN 10002-1:1992; Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing—Part 1: Method of Test at Ambient Temperature. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 1992.
- Hadjipantelis, N.; Weber, B.; Buchanan, C.; Gardner, L. Description of anisotropic material response of wire and arc additively manufactured thin-walled stainless steel elements. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 171, 108634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN ISO 6892-1:2019; Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing—Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Kyvelou, P.; Slack, H.; Mountanou, D.D.; Wadee, M.A.; Britton, T.B.; Buchanan, C.; Gardner, L. Mechanical and microstructural testing of wire and arc additively manufactured sheet material. Mater. Des. 2020, 192, 108675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmeira Belotti, L.; van Dommelen, J.A.W.; Geers, M.G.D.; Goulas, C.; Ya, W.; Hoefnagels, J.P.M. Microstructural characterisation of thick-walled wire arc additively manufactured stainless steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 299, 117373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, K.U.; Kumar, R.; Mahapatra, M.M.; Mulik, R.S.; Świerczyńska, A.; Fydrych, D.; Pandey, C. Wire Arc Additive Manufactured Mild Steel and Austenitic Stainless Steel Components: Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Residual Stresses. Materials 2022, 15, 7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E8/E8M-22; Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Sharma, S.K.; Sharma, C. Processing Techniques, Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Wire Arc Additive Manufactured Stainless Steel: A Review. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. C 2022, 103, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, N.; Anwar, M.N. Optimising 3D printing parameters through experimental techniques and ANOVA-Based statistical analysis. SPE Polym. 2024, 5, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.; Devjani, D.; Ali, S.; Abdallah, S.; Pervaiz, S. Optimization of 3D printed polylactic acid structures with different infill patterns using Taguchi-grey relational analysis. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2023, 6, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.V.; Gary Harlow, D. Statistical Modeling of Wire and Arc Additive Manufactured Stainless Steel 304: Microstructure and Fatigue. Int. J. Reliab. Qual. Saf. Eng. 2019, 26, 1950016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
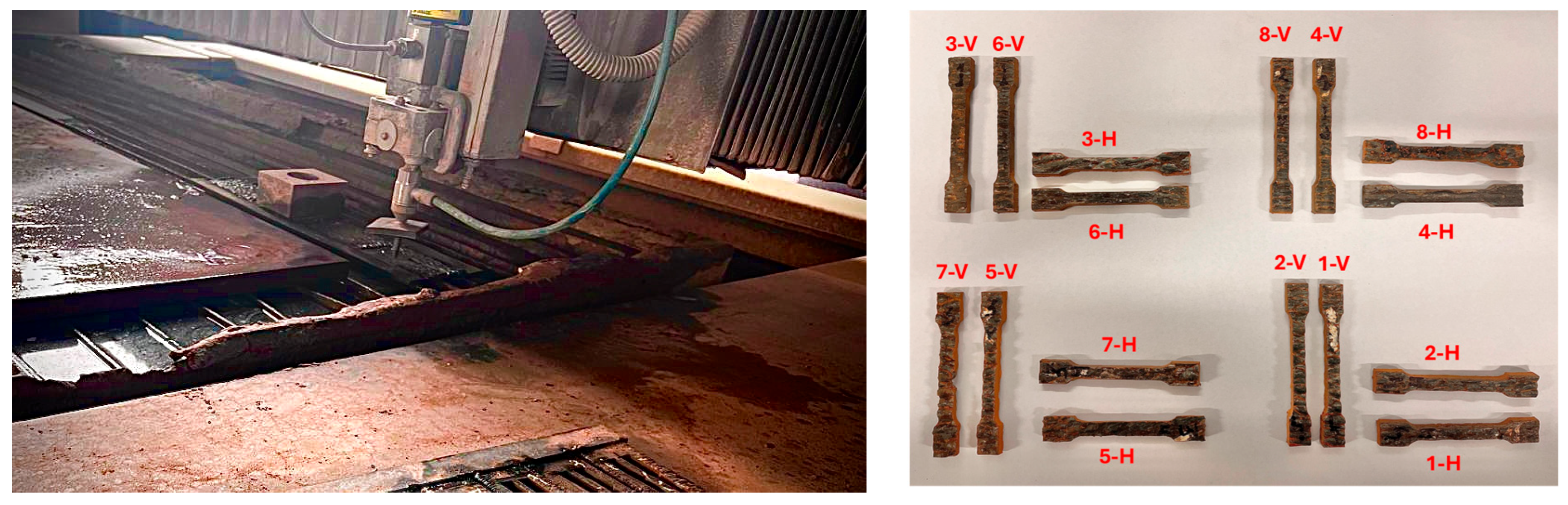
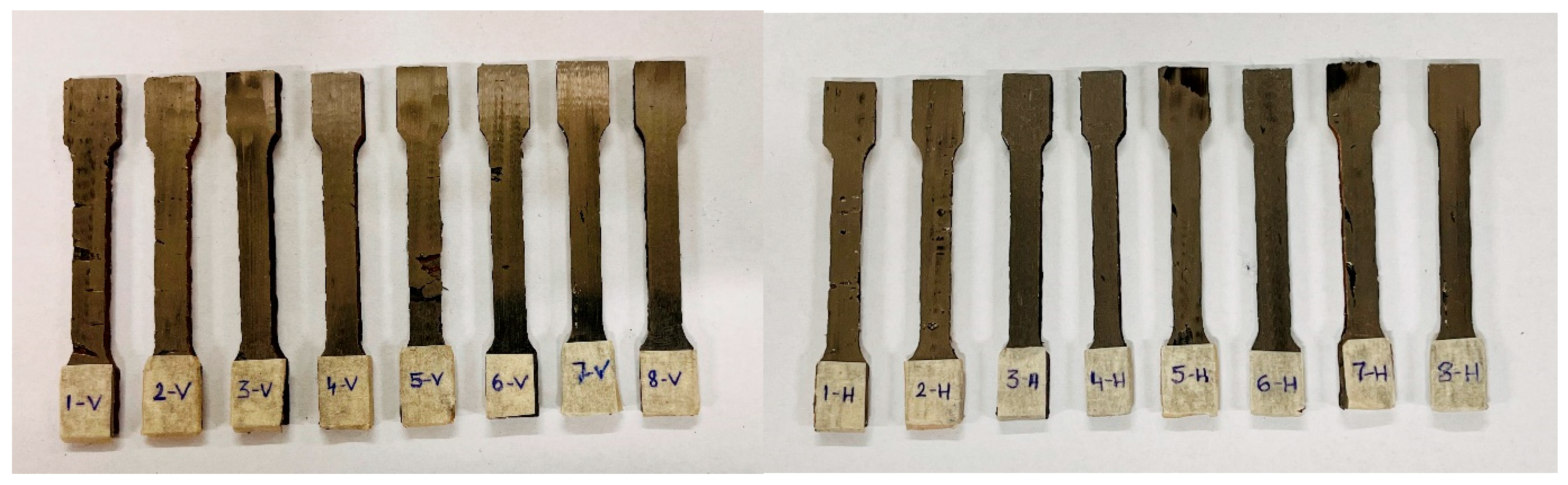
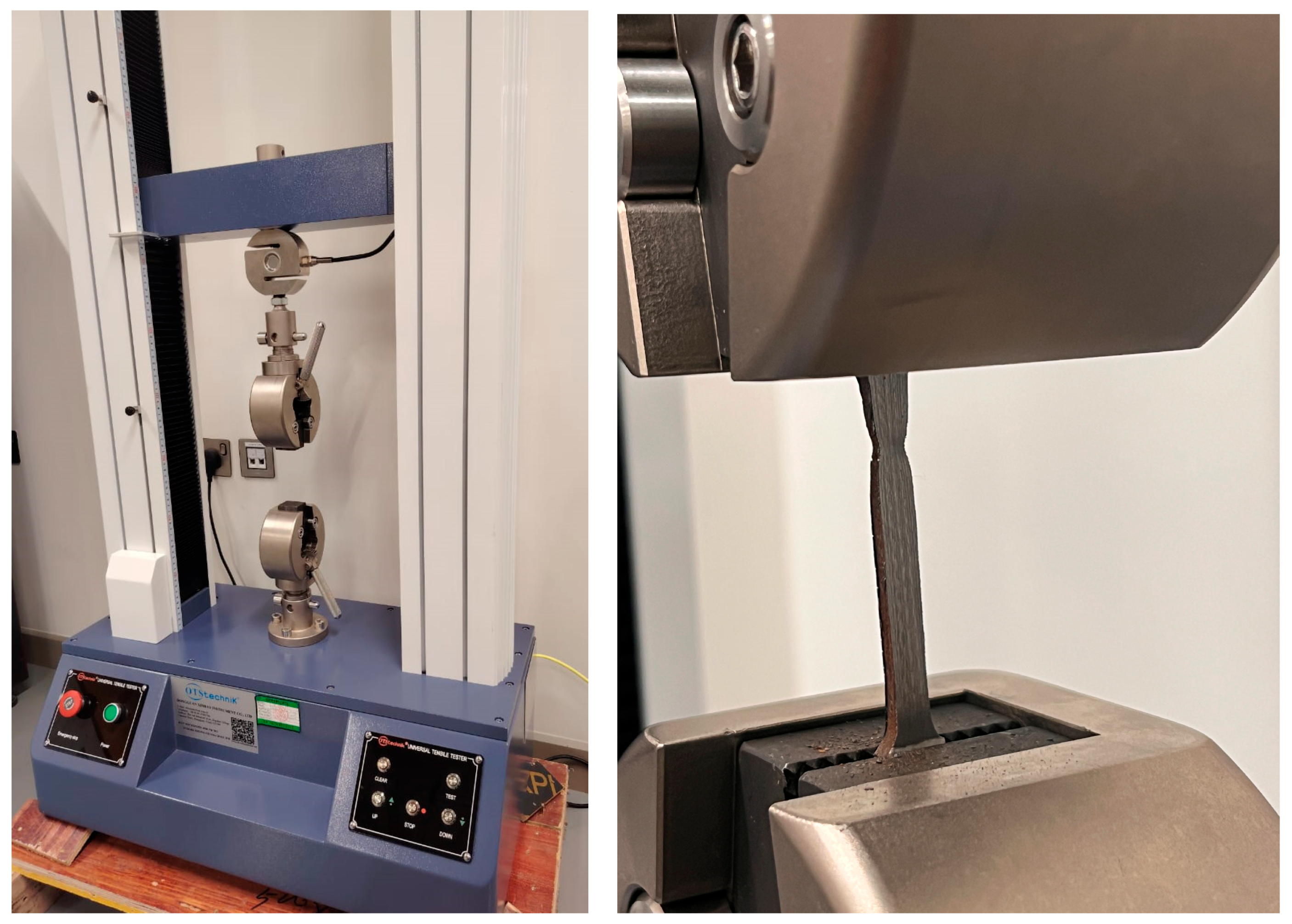
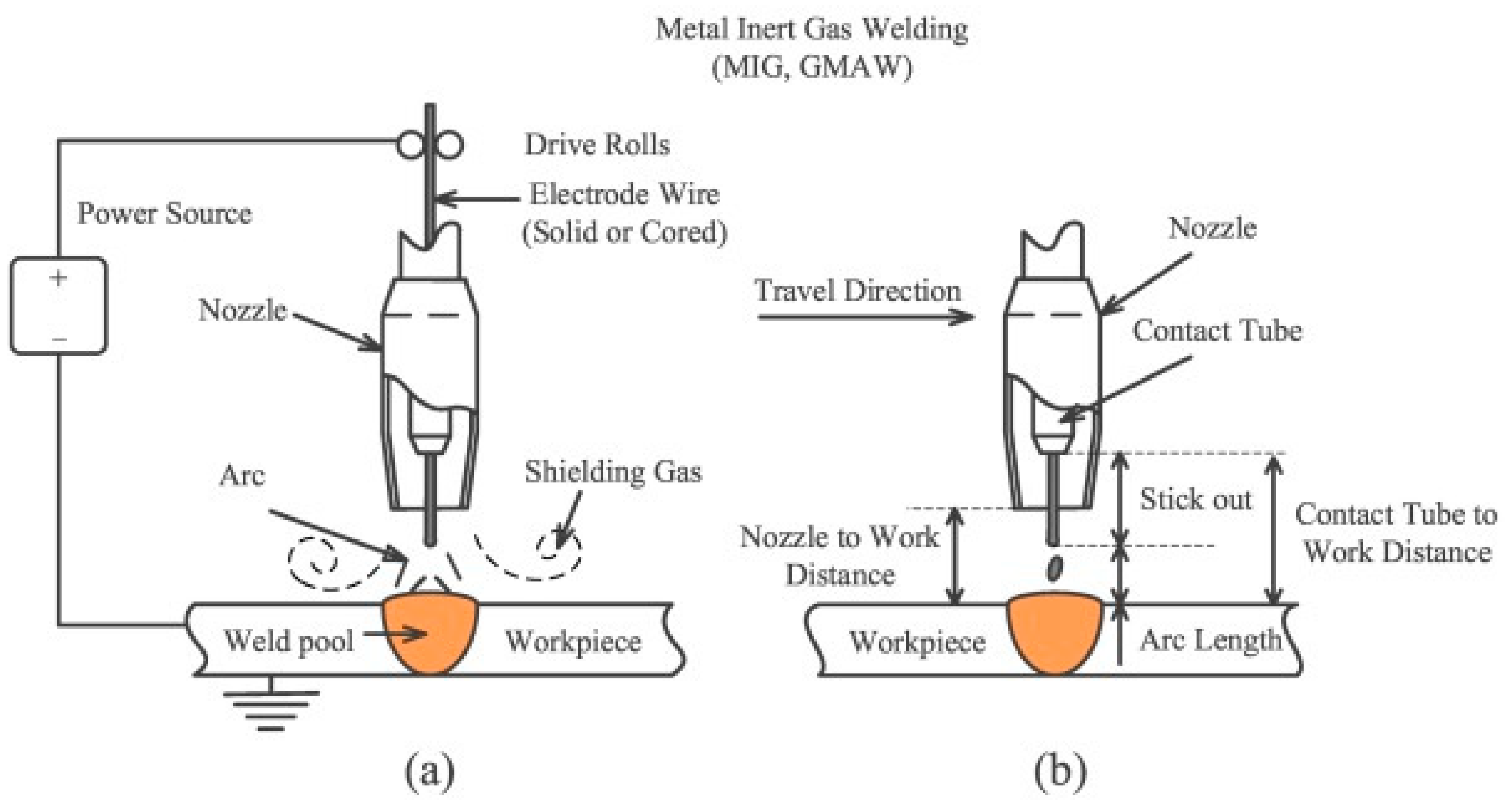
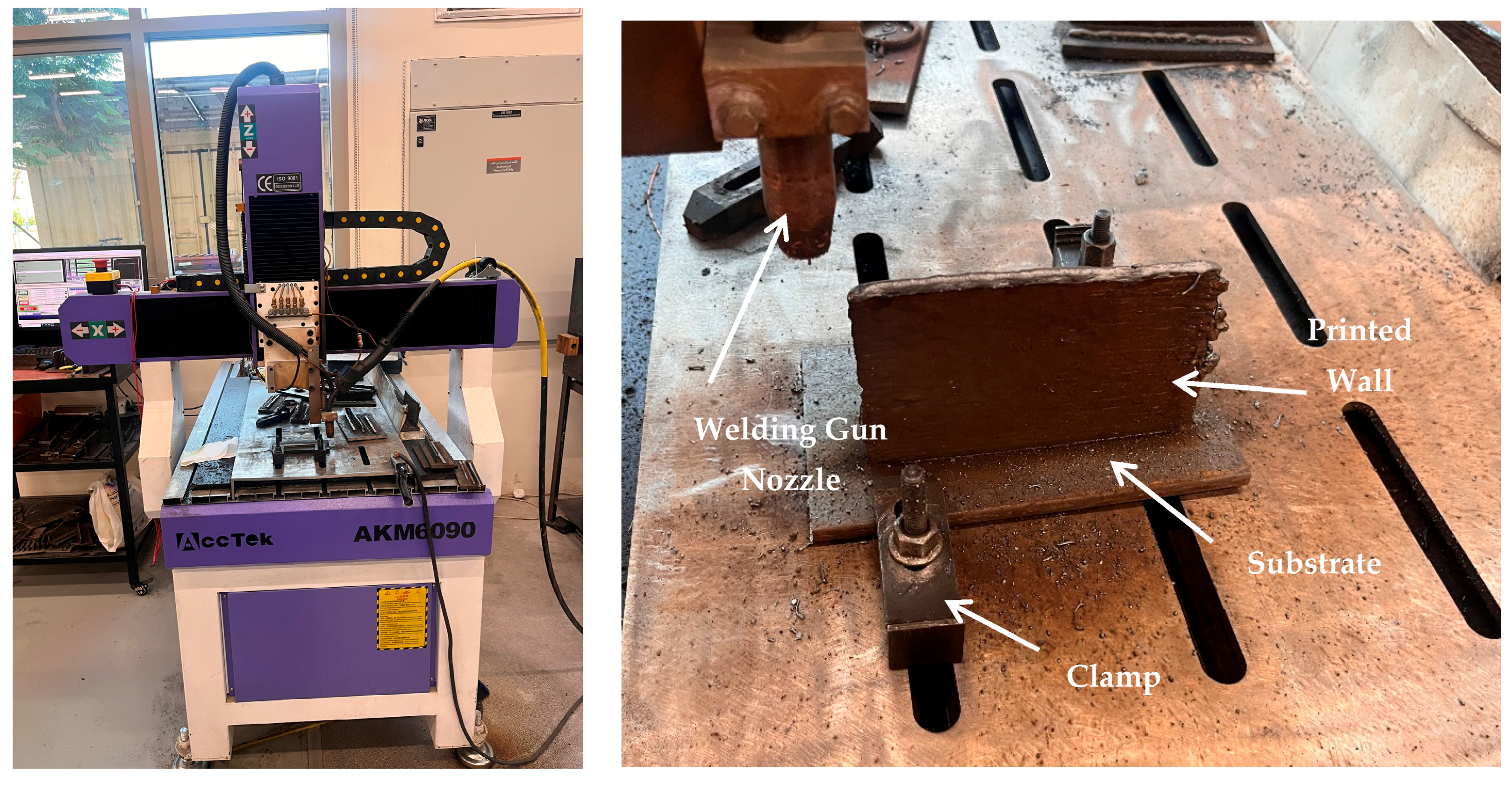









| Parameters | Set Values |
|---|---|
| Printing Parameters | |
| Printing Speed | 600 mm/min |
| Layer Height | 1.5 mm |
| Dwell Time | 60 s |
| Shielding Gas Composition | 100% Argon |
| Gas Flow Rate | 20 L/min |
| Arc Mode | Short Circuit |
| Print Material Information | |
| Material | Stainless-Steel ER316LSi |
| Standard | AWS A5.9 |
| Diameter | 1 mm |
| Parameters | Set Values |
|---|---|
| Current | 197 A, 189 A, 162 A, 156 A |
| Arc Mode | Short Circuit |
| CTWD | 15 mm |
| Torch Angle | 90 degrees to plate |
| Interpass Temperature | <140 °C |
| Carbon (C) | Silicone (Si) | Manganese/Magnesium (Mn) | Chromium (Cr) | Nickel (Ni) | Molybdenum (Mo) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.02 | 0.80 | 1.6 | 18.5 | 11.5 | 2.2 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Impact Strength (ISO-V/+20 °C) |
|---|---|---|
| Min. 400 | 550–700 | Min. 63 J |
| Parameter Investigated | Values |
|---|---|
| Arc Voltage | 18 V and 18.7 V |
| Wire Feed Rate | 5 m/min and 6 m/min |
| Crosshead Speed | 1 mm/min and 2 mm/min |
| Sample No. | Run Order | Arc Voltage (V) | Wire Feed Rate (m/min) | Crosshead Speed (mm/min) | Current (A) | HI (kJ/mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 18.7 | 6 | 2 | 197 | 0.37 |
| 2 | 2 | 18.7 | 6 | 1 | 197 | 0.37 |
| 3 | 3 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 156 | 0.28 |
| 4 | 4 | 18.7 | 5 | 2 | 162 | 0.30 |
| 5 | 5 | 18 | 6 | 2 | 189 | 0.34 |
| 6 | 6 | 18 | 5 | 2 | 156 | 0.28 |
| 7 | 7 | 18 | 6 | 1 | 189 | 0.34 |
| 8 | 8 | 18.7 | 5 | 1 | 162 | 0.30 |
| Horizontal Specimen No. | Arc Voltage (V) | Wire Feed Rate (m/min) | Crosshead Speed (mm/min) | UTS (MPa) | Yield Strength (Offset = 0.2%) (MPa) | Toughness (MPa) | %EL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18.7 | 6 | 2 | 416 ± 5 | 406 ± 6 | 27 ± 2 | 13 ± 1 |
| 2 | 18.7 | 6 | 1 | 394 ± 4 | 390 ± 4 | 24 ± 2 | 11 ± 1 |
| 3 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 543 ± 4 | 407 ± 5 | 170 ± 4 | 46 ± 1 |
| 4 | 18.7 | 5 | 2 | 516 ± 4 | 392 ± 4 | 215 ± 3 | 51 ± 2 |
| 5 | 18 | 6 | 2 | 476 ± 8 | 370 ± 6 | 138 ± 3 | 41 ± 1 |
| 6 | 18 | 5 | 2 | 524 ± 6 | 412 ± 4 | 146 ± 4 | 42 ± 2 |
| 7 | 18 | 6 | 1 | 492 ± 3 | 400 ± 7 | 100 ± 4 | 31 ± 1 |
| 8 | 18.7 | 5 | 1 | 537 ± 4 | 418 ± 7 | 248 ± 4 | 57 ± 1 |
| Source | DF | Seq SS | Contribution | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arc Voltage (V) | 1 | 3728.2 | 17.21% | 3728.2 | 3728.2 | 4.66 | 0.097 |
| Wire Feed Rate (m/min) | 1 | 14,594.9 | 67.37% | 14,594.9 | 14,594.9 | 18.26 | 0.013 |
| Crosshead Speed (mm/min) | 1 | 143.7 | 0.66% | 143.7 | 143.7 | 0.18 | 0.693 |
| Error | 4 | 3197.4 | 14.76% | 3197.4 | 799.3 | ||
| Total | 7 | 21,664.0 | 100.00% |
| Source | DF | Seq SS | Contribution | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arc Voltage (V) | 1 | 34.03 | 2.12% | 34.03 | 34.03 | 0.15 | 0.719 |
| Wire Feed Rate (m/min) | 1 | 504.03 | 31.36% | 504.03 | 504.03 | 2.21 | 0.211 |
| Crosshead Speed (mm/min) | 1 | 157.53 | 9.80% | 157.53 | 157.53 | 0.69 | 0.453 |
| Error | 4 | 911.87 | 56.73% | 911.87 | 227.97 | ||
| Total | 7 | 1607.47 | 100.00% |
| Source | DF | Seq SS | Contribution | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arc Voltage (V) | 1 | 196.8 | 0.43% | 196.8 | 196.8 | 0.05 | 0.833 |
| Wire Feed Rate (m/min) | 1 | 30,122.9 | 65.73% | 30,122.9 | 30,122.9 | 7.78 | 0.049 |
| Crosshead Speed (mm/min) | 1 | 30.8 | 0.07% | 30.8 | 30.8 | 0.01 | 0.933 |
| Error | 4 | 15,479.8 | 33.78% | 15,479.8 | 3870.0 | ||
| Total | 7 | 45,830.3 | 100.00% |
| Source | DF | Seq SS | Contribution | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arc Voltage (V) | 1 | 105.04 | 5.23% | 105.04 | 105.04 | 0.64 | 0.470 |
| Wire Feed Rate (m/min) | 1 | 1244.61 | 61.91% | 1244.61 | 1244.61 | 7.54 | 0.052 |
| Crosshead Speed (mm/min) | 1 | 0.72 | 0.04% | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.00 | 0.951 |
| Error | 4 | 659.86 | 32.83% | 659.86 | 164.96 | ||
| Total | 7 | 2010.22 | 100.00% |
| Vertical Specimen No. | Arc Voltage (V) | Wire Feed Rate (m/min) | Crosshead Speed (mm/min) | UTS (MPa) | Yield Strength (Offset = 0.2%) (MPa) | Toughness (MPa) | %EL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18.7 | 6 | 2 | 383 ± 4 | 340 ± 2 | 24 ± 1 | 10 ± 1 |
| 2 | 18.7 | 6 | 1 | 340 ± 3 | 330 ± 4 | 21 ± 1 | 10 ± 1 |
| 3 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 472 ± 5 | 362 ± 4 | 222 ± 4 | 52 ± 1 |
| 4 | 18.7 | 5 | 2 | 444 ± 4 | 342 ± 3 | 149 ± 2 | 44 ± 2 |
| 5 | 18 | 6 | 2 | 435 ± 3 | 325 ± 4 | 61 ± 2 | 22 ± 1 |
| 6 | 18 | 5 | 2 | 464 ± 3 | 365 ± 5 | 256 ± 4 | 56 ± 1 |
| 7 | 18 | 6 | 1 | 425 ± 4 | 350 ± 4 | 47 ± 1 | 19 ± 2 |
| 8 | 18.7 | 5 | 1 | 495 ± 4 | 320 ± 4 | 119 ± 2 | 33 ± 2 |
| Source | DF | Seq SS | Contribution | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arc Voltage (V) | 1 | 2207.1 | 12.54% | 2207.1 | 2207.1 | 1.86 | 0.245 |
| Wire Feed Rate (m/min) | 1 | 10,637.6 | 60.43% | 10,637.6 | 10,637.6 | 8.95 | 0.040 |
| Crosshead Speed (mm/min) | 1 | 6.3 | 0.04% | 6.3 | 6.3 | 0.01 | 0.945 |
| Error | 4 | 4752.9 | 27.00% | 4752.9 | 1188.2 | ||
| Total | 7 | 17,603.9 | 100.00% |
| Source | DF | Seq SS | Contribution | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arc Voltage (V) | 1 | 614.25 | 32.03% | 614.25 | 614.25 | 2.34 | 0.200 |
| Wire Feed Rate (m/min) | 1 | 243.10 | 12.68% | 243.10 | 243.10 | 0.93 | 0.390 |
| Crosshead Speed (mm/min) | 1 | 12.25 | 0.64% | 12.25 | 12.25 | 0.05 | 0.839 |
| Error | 4 | 1047.96 | 54.65% | 1047.96 | 261.99 | ||
| Total | 7 | 1917.56 | 100.00% |
| Source | DF | Seq SS | Contribution | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arc Voltage (V) | 1 | 9361.2 | 16.37% | 9361.2 | 9361.2 | 12.48 | 0.024 |
| Wire Feed Rate (m/min) | 1 | 43,979.8 | 76.93% | 43,979.8 | 43,979.8 | 58.65 | 0.002 |
| Crosshead Speed (mm/min) | 1 | 829.9 | 1.45% | 829.9 | 829.9 | 1.11 | 0.352 |
| Error | 4 | 2999.4 | 5.25% | 2999.4 | 749.8 | ||
| Total | 7 | 57,170.3 | 100.00% |
| Source | DF | Seq SS | Contribution | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arc Voltage (V) | 1 | 324.64 | 13.87% | 324.64 | 324.64 | 25.12 | 0.007 |
| Wire Feed Rate (m/min) | 1 | 1926.53 | 82.28% | 1926.53 | 1926.53 | 149.07 | 0.000 |
| Crosshead Speed (mm/min) | 1 | 38.47 | 1.64% | 38.47 | 38.47 | 2.98 | 0.160 |
| Error | 4 | 51.70 | 2.21% | 51.70 | 12.92 | ||
| Total | 7 | 2341.33 | 100.00% |
| Vertical Specimen No. | Porosity % | Horizontal Specimen No. | Porosity % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30% | 1 | 18.57% |
| 2 | 42% | 2 | 21.12% |
| 3 | 1.81% | 3 | 0.13% |
| 4 | 3.61% | 4 | 2.84% |
| 5 | 6.23% | 5 | 5.12% |
| 6 | 2.94% | 6 | 1.17% |
| 7 | 5.4% | 7 | 4.85% |
| 8 | 0.85% | 8 | 0.28% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
John, J.S.; Pervaiz, S. Structural Integrity Assessment of Stainless Steel Fabricated by GMAW-Assisted Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing. Technologies 2025, 13, 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13090392
John JS, Pervaiz S. Structural Integrity Assessment of Stainless Steel Fabricated by GMAW-Assisted Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing. Technologies. 2025; 13(9):392. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13090392
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohn, Joel Sam, and Salman Pervaiz. 2025. "Structural Integrity Assessment of Stainless Steel Fabricated by GMAW-Assisted Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing" Technologies 13, no. 9: 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13090392
APA StyleJohn, J. S., & Pervaiz, S. (2025). Structural Integrity Assessment of Stainless Steel Fabricated by GMAW-Assisted Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing. Technologies, 13(9), 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13090392







