Effect of Foreign Object Damage on Corrosion Fatigue Behavior in Surface-Strengthened EA4T Railway Axle Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
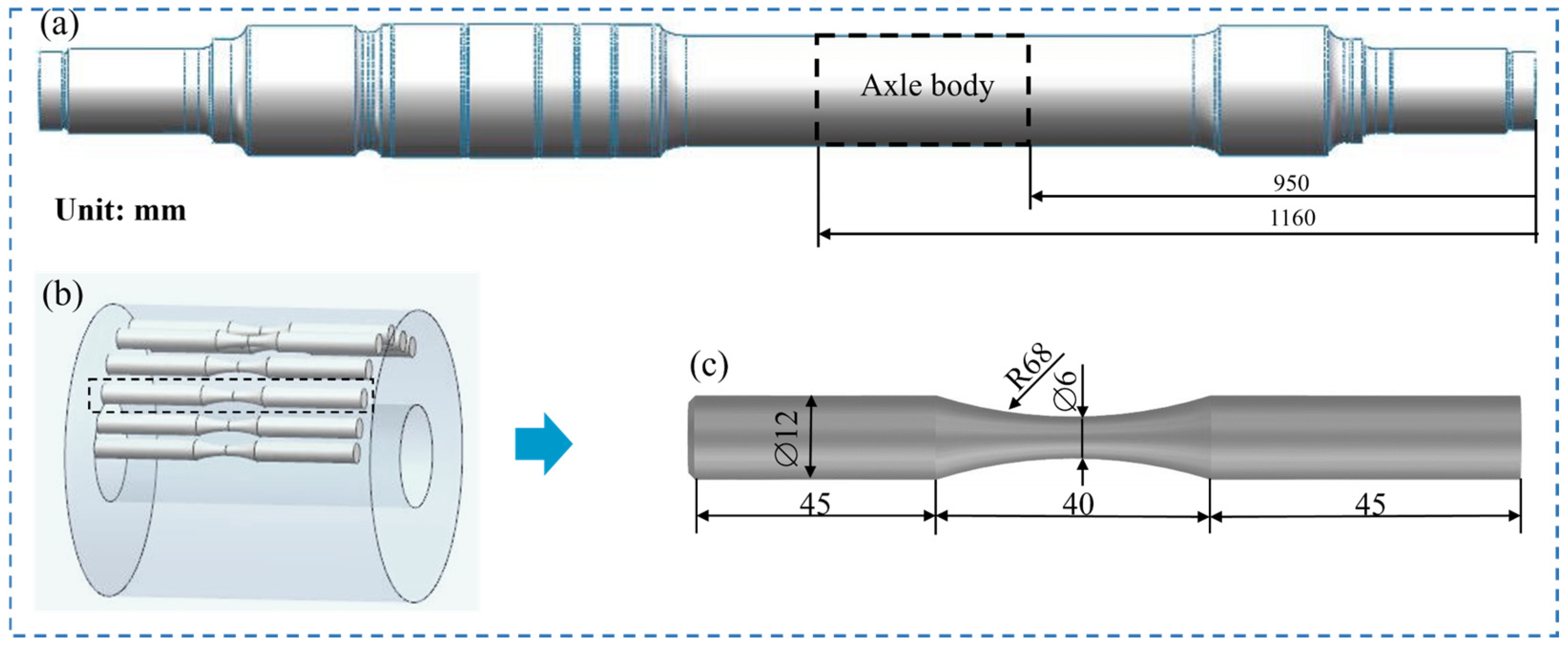
2.1. Specimen Preparation
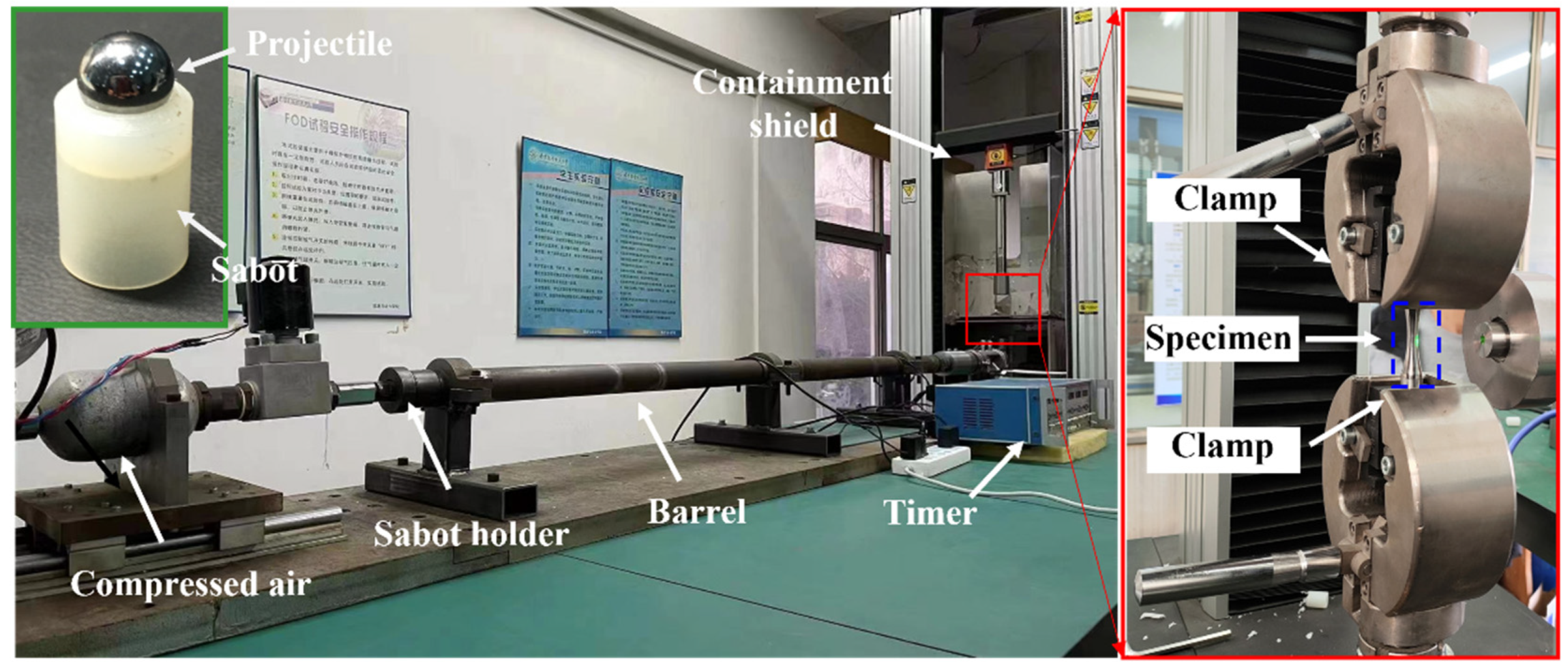
2.2. FOD Experiments
2.3. Surface Characterization
2.4. Electrochemical Testing
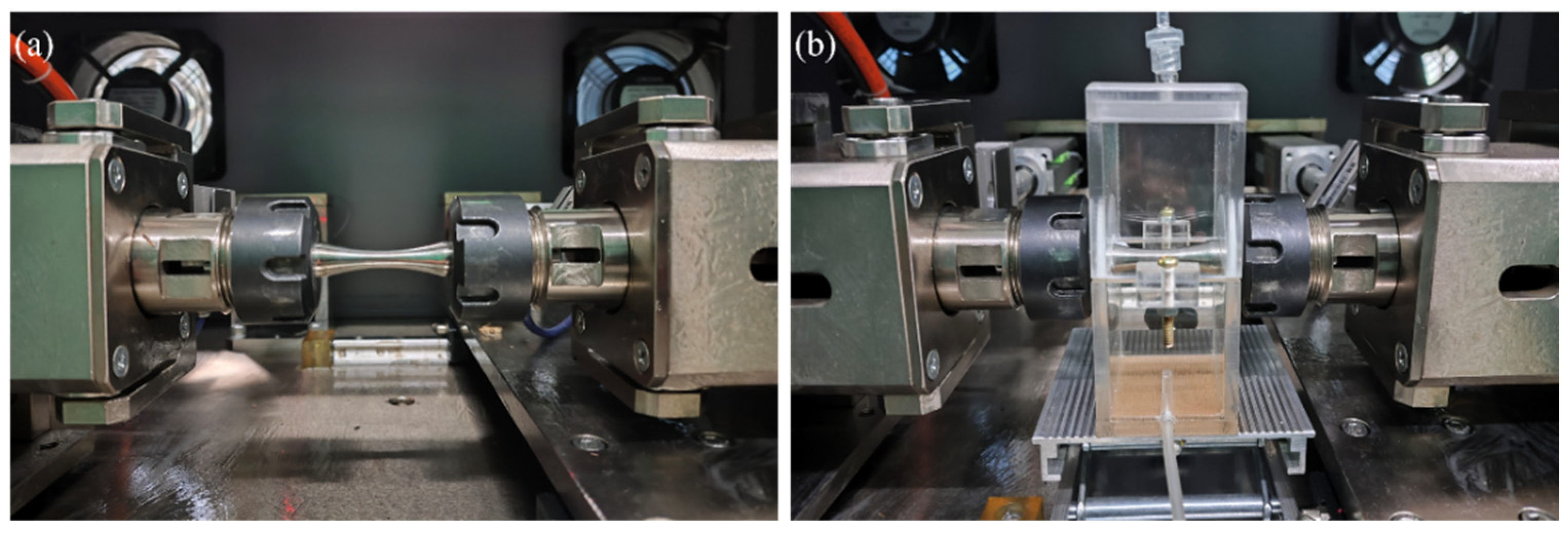
2.5. Fatigue Testing
3. Experimental Results
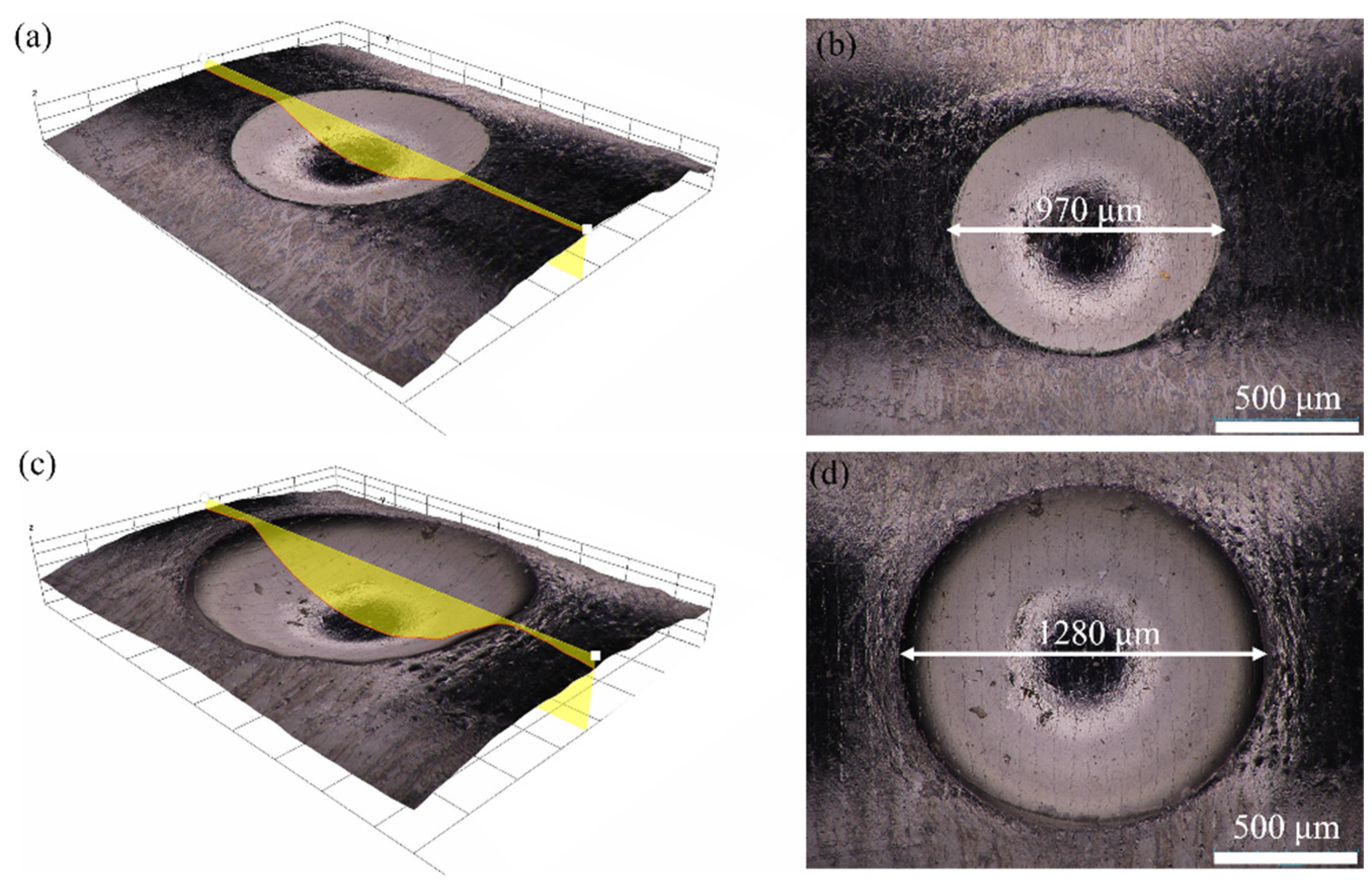
3.1. Morphologies of Impact Damage
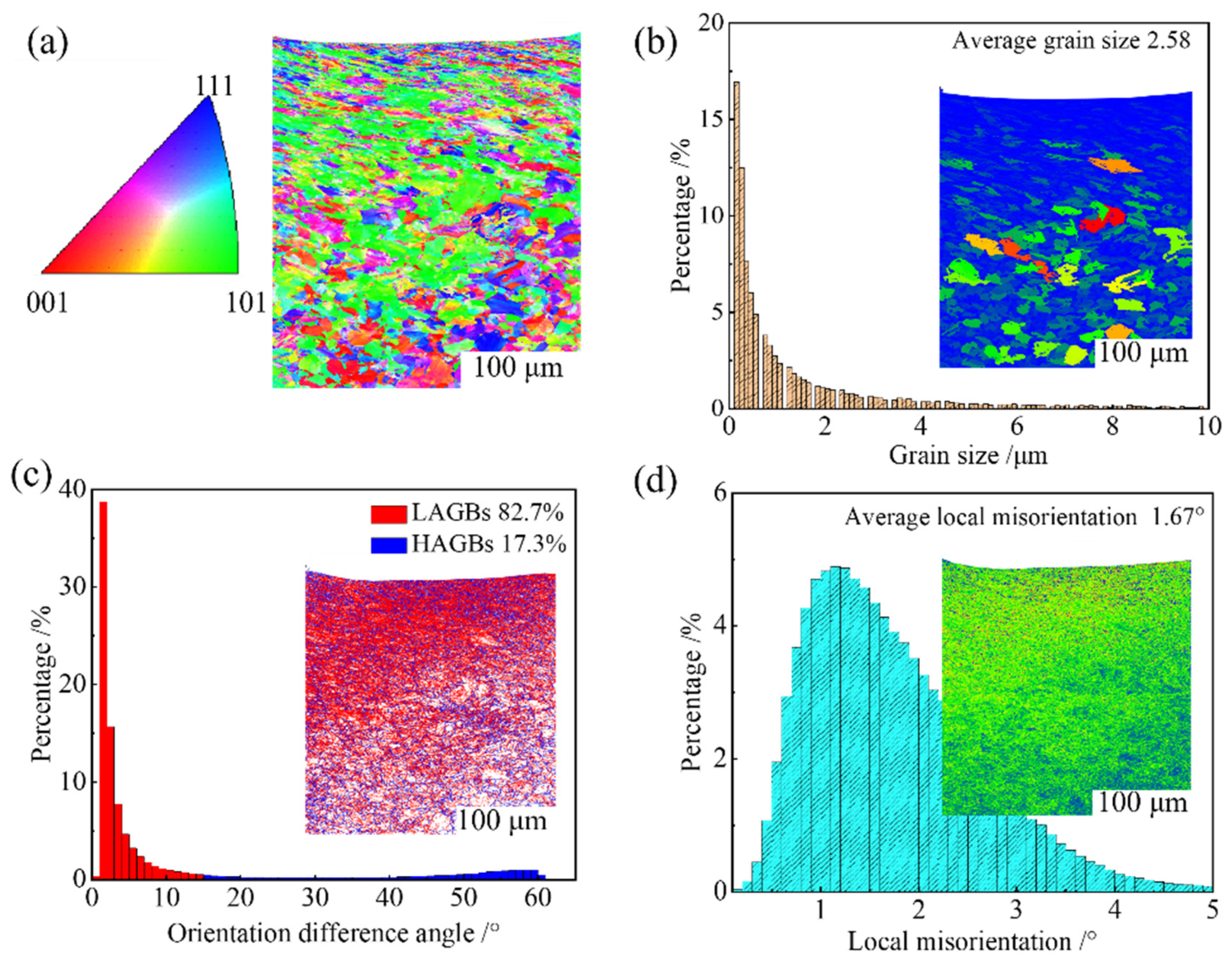
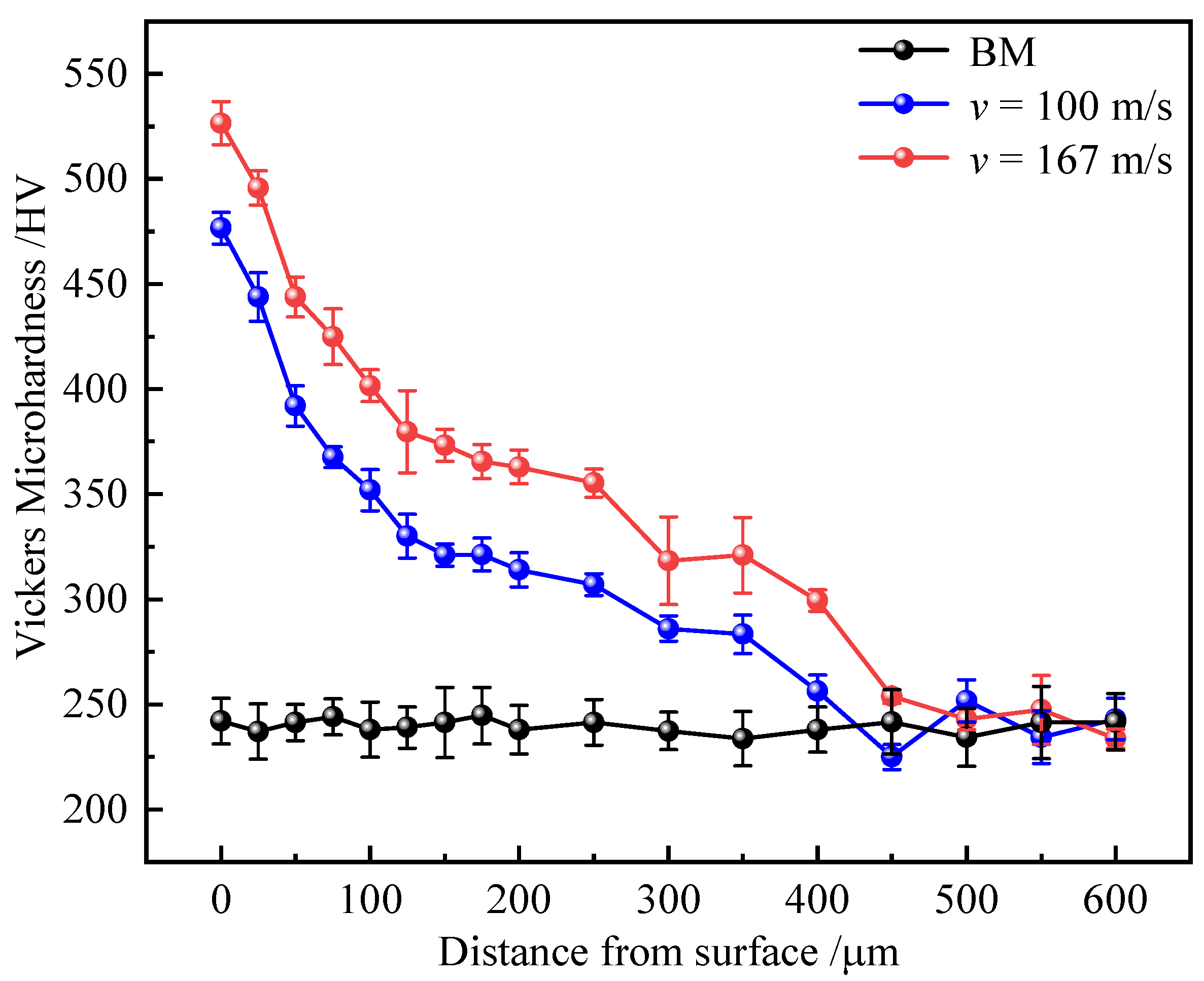
3.2. Microstructure and Hardness
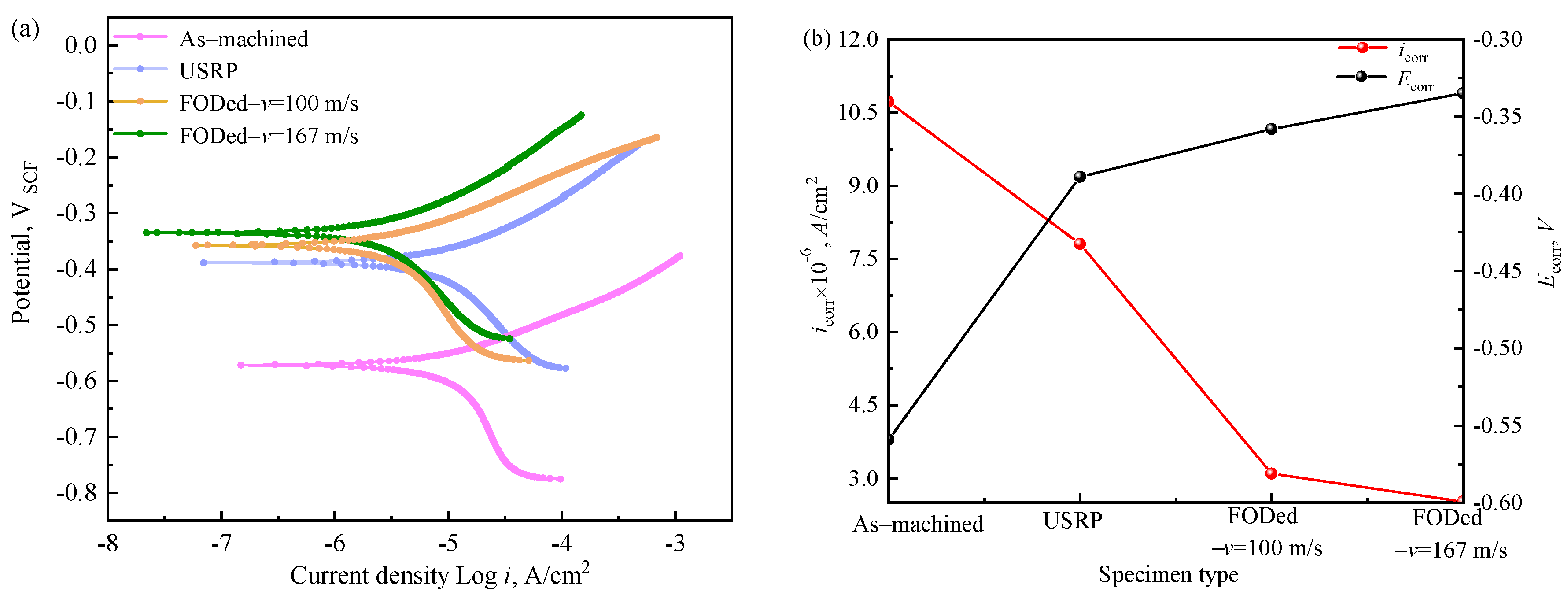
3.3. Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior
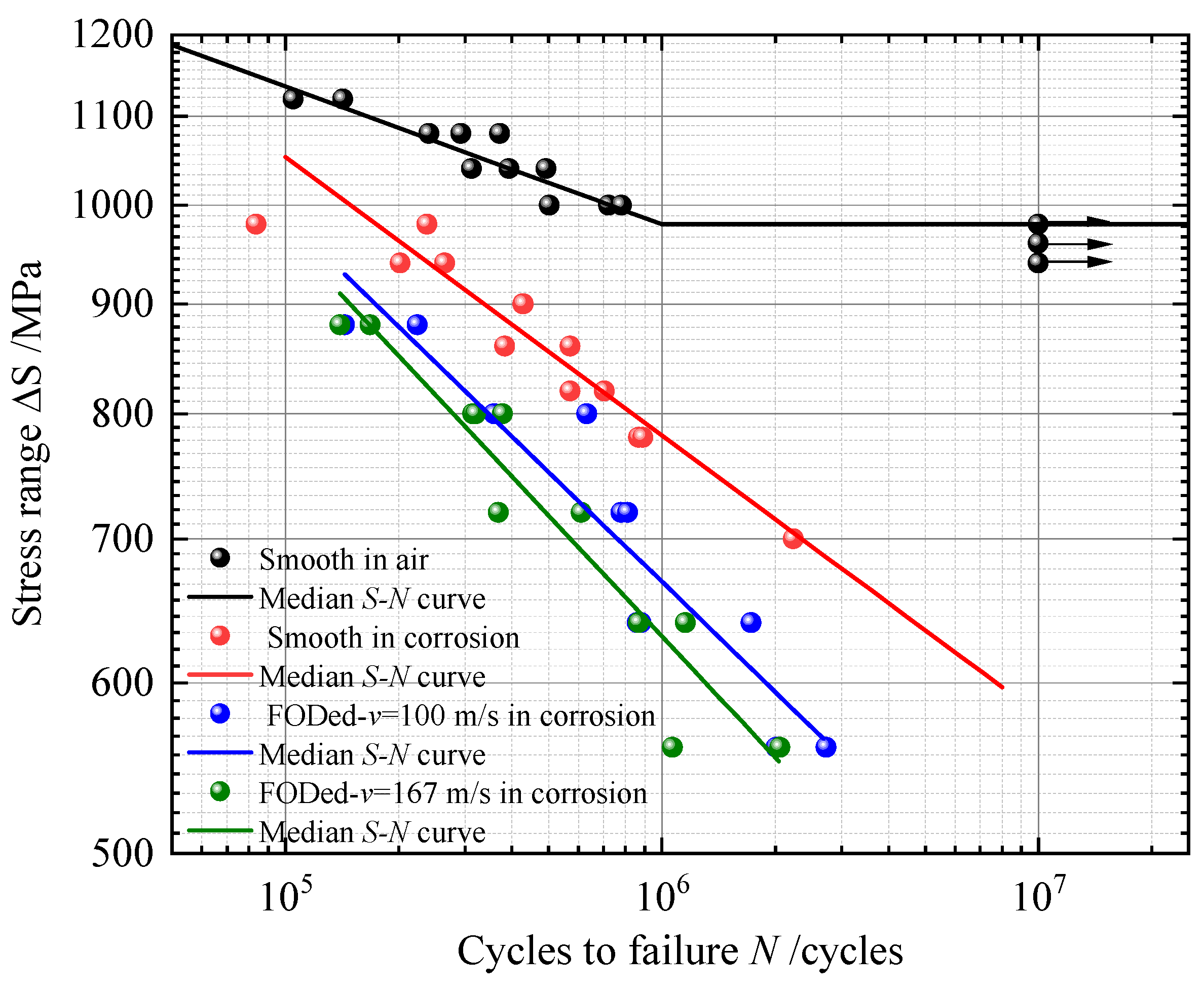
3.4. Corrosion Fatigue Performance
4. Discussion
4.1. Corrosion Electrochemical Behavior
4.2. Corrosion Fatigue Behavior
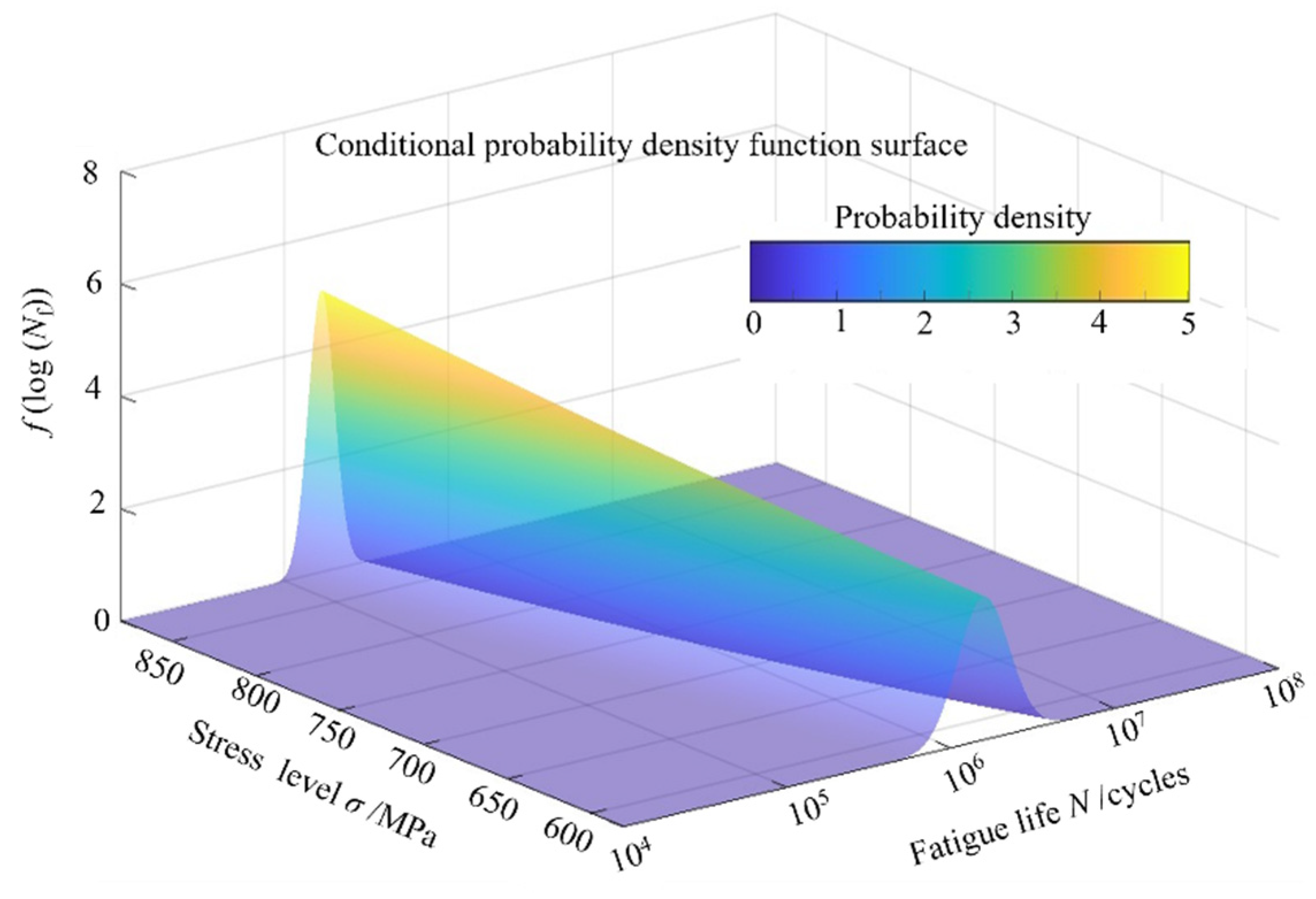
4.2.1. Corrosion Fatigue Strength Analysis
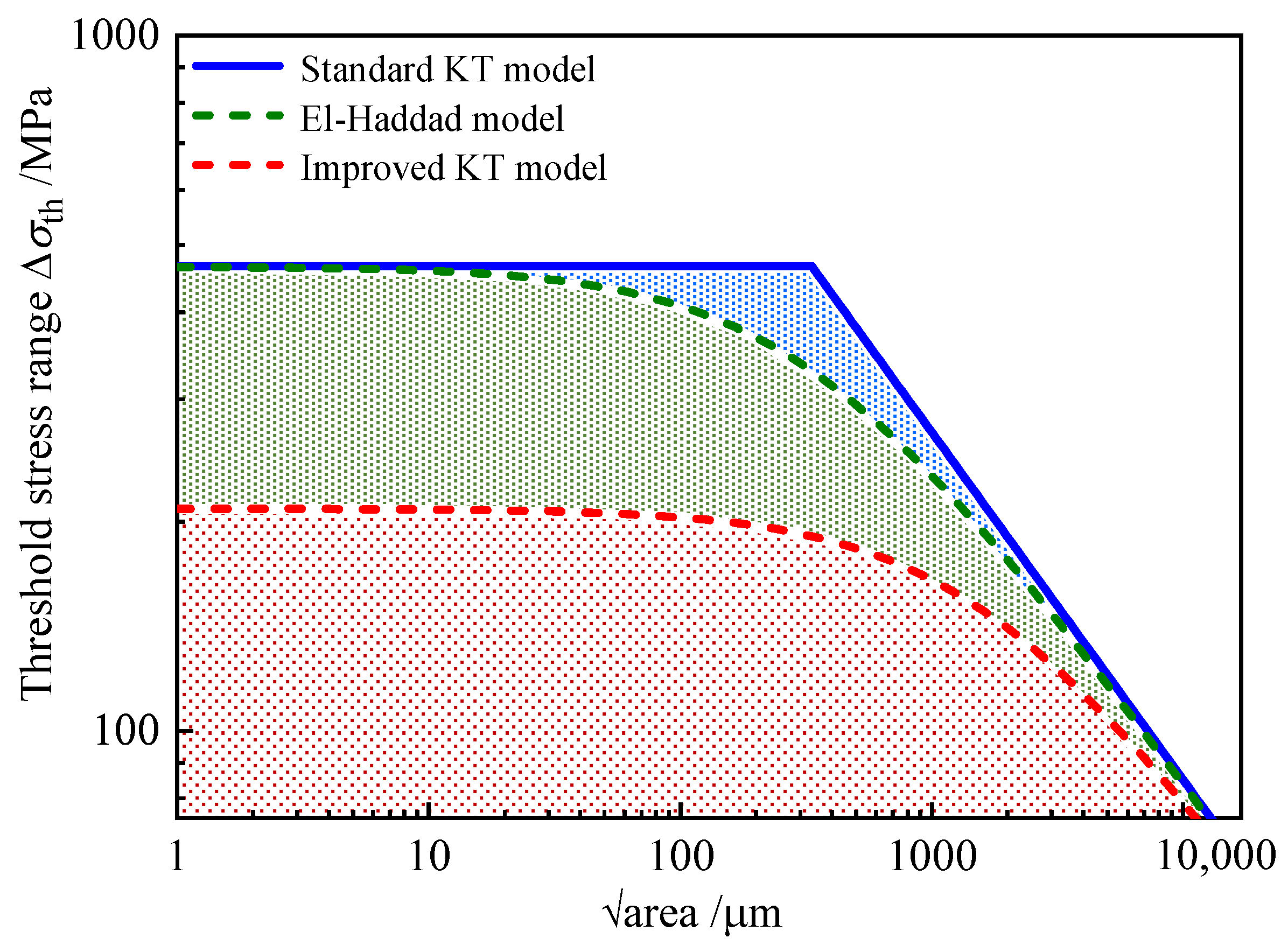
4.2.2. Defect Tolerance Evaluation
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Impact-induced surface hardening improves the corrosion resistance of EA4T steel, with higher impact speeds enhancing this effect. At 167 m/s, Ecorr increased by 13.88% and icorr decreased by 67.61% versus the smooth sample.
- (2)
- Corrosion fatigue strength decreased progressively with increasing defect size (√area: 265–580 μm). At the maximum defect size (√area = 580 μm, v = 167 m/s), the theoretical fatigue limit reached 270 MPa.
- (3)
- Environmentally induced cracks in smooth specimens preferentially initiated at localized corrosion pits. However, surface defects emerged as the primary determinant governing the initiation of corrosion fatigue cracks in foreign object damaged axle specimens.
- (4)
- In contrast to the conventional KT diagram derived from the fatigue limit of smooth specimens, the refined KT diagram integrating considerations of size effect and surface damage becomes smaller, thereby enabling the determination of operational safety boundaries for fatigue loading with enhanced reliability and accuracy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zerbst, U.; Beretta, S.; Köhler, G.; Lawton, A.; Vormwald, M.; Beier, H.T.; Klinger, C.; Černý, I.; Rudlin, J.; Heckel, T.; et al. Safe life and damage tolerance aspects of railway axles—A review. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2013, 98, 214–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.C.; Zhang, S.Q.; Xu, Z.W.; Kang, G.Z.; Cai, L.X. Cyclic plastic strain based damage tolerance for railway axles in China. Int. J. Fatigue 2016, 93, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinger, C.; Bettge, D. Axle fracture of an ICE3 high speed train. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2013, 35, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Han, R.P.; Gao, J.W.; Zhu, S.P.; Han, J. Fatigue performance evaluation of high-strength railway axles subjected to different surface defects. Alex. Eng. J. 2025, 127, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.C.; Xu, Z.W.; Kang, G.Z.; He, W.F. Probabilistic fatigue assessment for high-speed railway axles due to foreign object damages. Int. J. Fatigue 2018, 117, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, C.H.; Ren, X.Y.; Wu, S.C. Fatigue strength assessment of high-speed railway axle EA4T steel with foreign object damage. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 133, 205961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beretta, S.; Carboni, M.; Fiore, G.; Conte, A.L. Corrosion-fatigue of A1N railway axle steel exposed to rainwater. Int. J. Fatigue 2010, 32, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.W.; Dai, G.Z.; Li, Q.Z.; Zhang, M.N.; Zhu, S.P.; Correia, J.A.F.O.; Lesiuk, G.; Jesus, A.M.P.D. Fatigue assessment of EA4T railway axles under artificial surface damage. Int. J. Fatigue 2021, 146, 106157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.W.; Yu, M.H.; Liao, D.; Zhu, S.P.; Han, J.; Lesiuk, G.; Correia, J.A.F.O.; Jesus, A.M.P.D. Fatigue and damage tolerance assessment of induction hardened S38C axles under different foreign object. Int. J. Fatigue 2021, 149, 106276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, N.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H.H.; Wu, S.C.; Liu, D.; Xu, P.G.; Su, Y.H.; Kan, Q.H.; Kang, G.Z. Corrosion fatigue crack growth behavior of a structurally gradient steel for high-speed railway axles. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2023, 281, 109166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, J.W.; Ao, N.; Xu, J.S.; Ji, D.D. Influence of residual stress and its relaxation on the corrosion bending fatigue resistance of EA4T axle steel treated by ultrasonic surface rolling. Int. J. Fatigue 2023, 170, 107561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beretta, S.; Conte, A.L.; Rudin, J.; Panggabean, D. From atmospheric corrosive attack to crack propagation for A1N railway axles steel under fatigue: Damage process and detection. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2015, 47, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.L.; Liu, Z.Y.; Du, C.W.; Liu, C.; Xu, X.X.; Li, X.G. Modeling for corrosion fatigue crack initiation life based on corrosion kinetics and equivalent initial flaw size theory. Corros. Sci. 2018, 142, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.N.; Wu, S.C.; Withers, P.J.; Cao, H.T.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Y.J.; Shen, Z.; Vojtek, T.; Hutař, P. Corrosion fatigue lifetime assessment of high-speed railway axle EA4T steel with artificial scratch. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2021, 245, 107588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.W.; Dai, X.; Zhu, S.P.; Zhao, J.W.; Correia, J.A.F.O.; Wang, Q.Y. Failure causes and hardening techniques of railway axles-a review from the perspective of structural integrity. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 141, 106656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, T.P.; Liu, G. Investigations on the nanocrystallzation of 40Cr using ultrasonic surface rolling processing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 1824–1829. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, T.Y.; Ao, N.; Ren, X.Y.; Zhao, X.; Wu, S.C. Determination of optimal ultrasonic surface rolling parameters to enhance the fatigue strength of railway axle EA4T steel. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2022, 275, 108831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, G.; Ao, N.; Qi, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S. Effect of ultrasonic rolled material layer on the corrosion fatigue resistance of railway axle EA4T alloy steel. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 157, 107895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Retraint, D.; Baudin, T.; Helbert, A.L.; Brissset, F.; Chemkhi, M.; Zhou, J.; Kanouté, P. Experimental study of microstructure changes due to low cycle fatigue of a steel nanocrystallised by surface mechanical attrition treatment. Mater. Charact. 2017, 124, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Yang, M.; Jiang, Y.; Lei, L.; Zhang, Y. Achieving excellent corrosion resistance properties of 7075 Al alloy via ultrasonic surface rolling treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 911, 165009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Hu, X.T.; Jiang, R.; Song, Y.D.; Qu, S.D. Experimental investigation of small fatigue crack growth due to foreign object damage in titanium alloy TC4. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 739, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gok, A.; Inal, S.; Taspinar, F.; Gulbandilar, E.; Gok, K. Fatigue behaviors of different materials for schanz screws in femoral fracture model using finite element analysis. Optoelectron. Adv. Mat. 2014, 8, 576–580. [Google Scholar]
- Gok, K.; Ada, H.D.; Erdem, M.; Gök, A.; Topçuoğlu, K.; Alkan, M.A. Investigation of erosion corrosion caused by drinking water in the faucet with computational fluid dynamics. J. Met. Mater. Res. 2023, 6, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gok, K.; Ada, H.D.; Kilicaslan, N.; Gok, A. A review of CFD modeling of erosion-induced corrosion formation in water jets using FEA. J. Mech. Mater. Mech. Res. 2023, 6, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerit, M.; Genel, K.; Eksi, S. Numerical investigation on stress concentration of corrosion pit. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2009, 16, 2467–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Liu, C.C.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.C. Multiaxial fatigue behaviors of 2024-T4 aluminum alloy under different corrosion conditions. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 98, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruschau, J.; Thompson, S.R.; Nicholas, T. High cycle fatigue limit stresses for airfoils subjected to foreign object damage. Int. J. Fatigue 2003, 25, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.L.; Liu, Z.Y.; Du, C.W.; Dai, C.D.; Li, X.G.; Zhang, B.W. Corrosion fatigue crack initiation and initial propagation mechanism of E690 steel in simulated seawater. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 708, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Cui, C.Y.; Lu, J.Z.; Lu, Y.F. Effect of coverage layer on the electrochemical corrosion behaviour of Mg-Al-Mn alloy subjected to massive laser shock peening treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 782, 1058–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.X.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhao, T.L.; Cui, Q.Q.; Zhang, T.Y.; Li, X.G. Corrosion fatigue behavior of Fe-16Mn-0.6C-1.68Al twinning-induced plasticity steel in simulated seawater. Corros. Sci. 2021, 182, 109282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.; Song, G.L.; Yang, S.; Outeiro, J.C.; Dillon, O.W., Jr.; Puleo, D.A.; Jawahir, I.S. Grain refined and basal textured surface produced by burnishing for improved corrosion performance of AZ31B Mg alloy. Corros. Sci. 2012, 57, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.H.; Nie, X.F.; Zhou, L.C.; Li, Y.; He, W. High cycle fatigue performance in laser shock peened TC4 Titanium alloys subjected to foreign object damage. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiijve, J. Fatigue of Structures and Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, J.W.; Wu, S.C.; Zhang, H.O.; Fu, Y.N. Corrosion fatigue mechanism and life prediction of railway axle EA4T steel exposed to artificial rainwater. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 138, 106319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y. Metal Fatigue: Effects of Small Defects and Nonmetallic Inclusions; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, J.O.; Boyce, B.L.; Chen, X.; McNaney, J.M.; Hutchinson, J.W.; Ritchie, R.O. On the application of the Kitagawa-Takahashi diagram to foreign-object damage and high-cycle fatigue. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2002, 69, 1425–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Haddad, M.H.; Topper, T.H.; Smith, K.N. Prediction of non-propagation cracks. Eng. Fract. Mech. 1979, 11, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.M.; Li, X.Y. A methodology to determine a conditional probability density distribution surface from S-N data. Int. J. Fatigue 2012, 44, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.L.; Pan, J.; Hathaway, R.B.; Barkey, M.E. Fatigue Testing and Analysis: Theory and Practice; Elsevier: Burlington, VT, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]


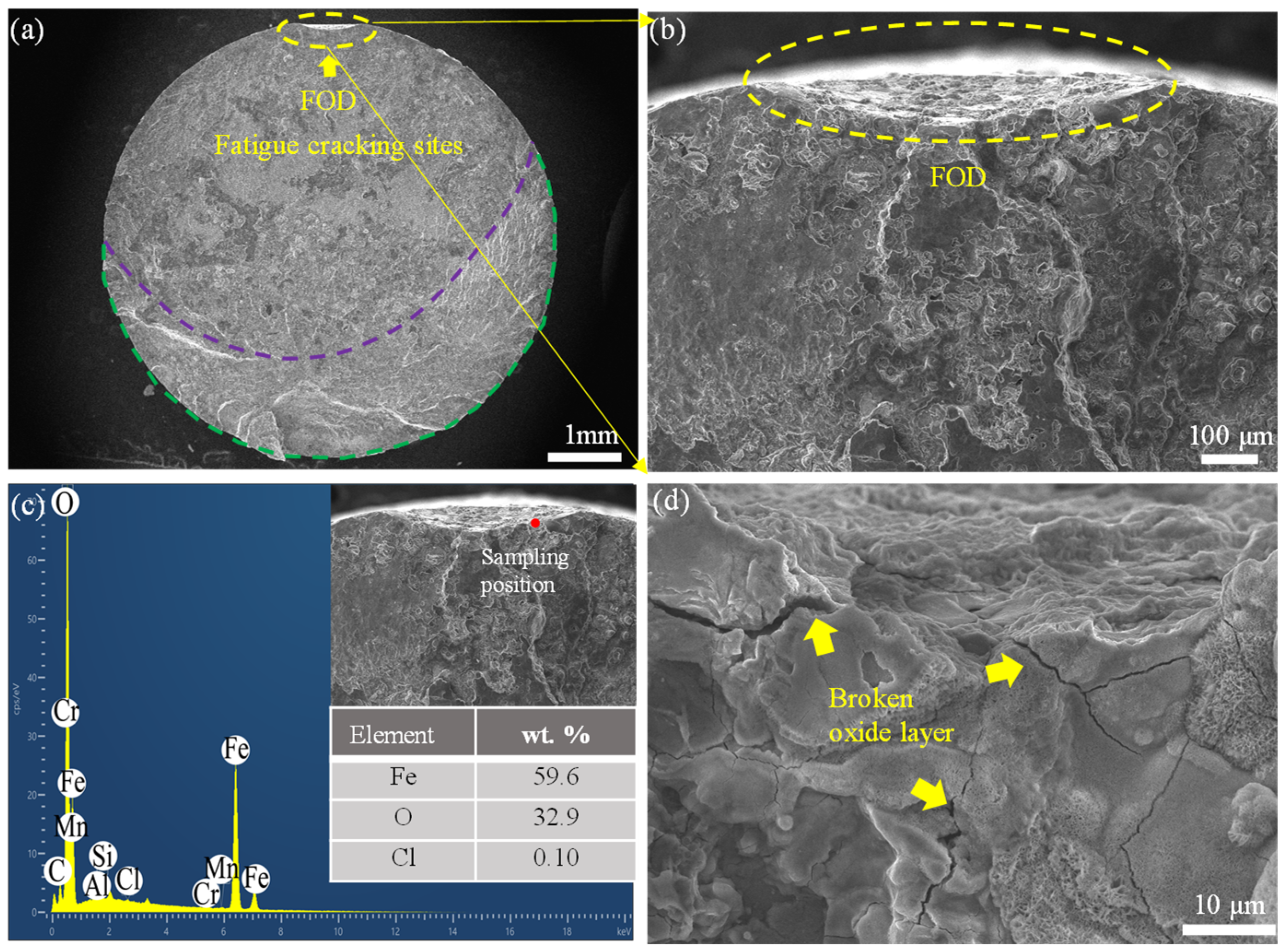
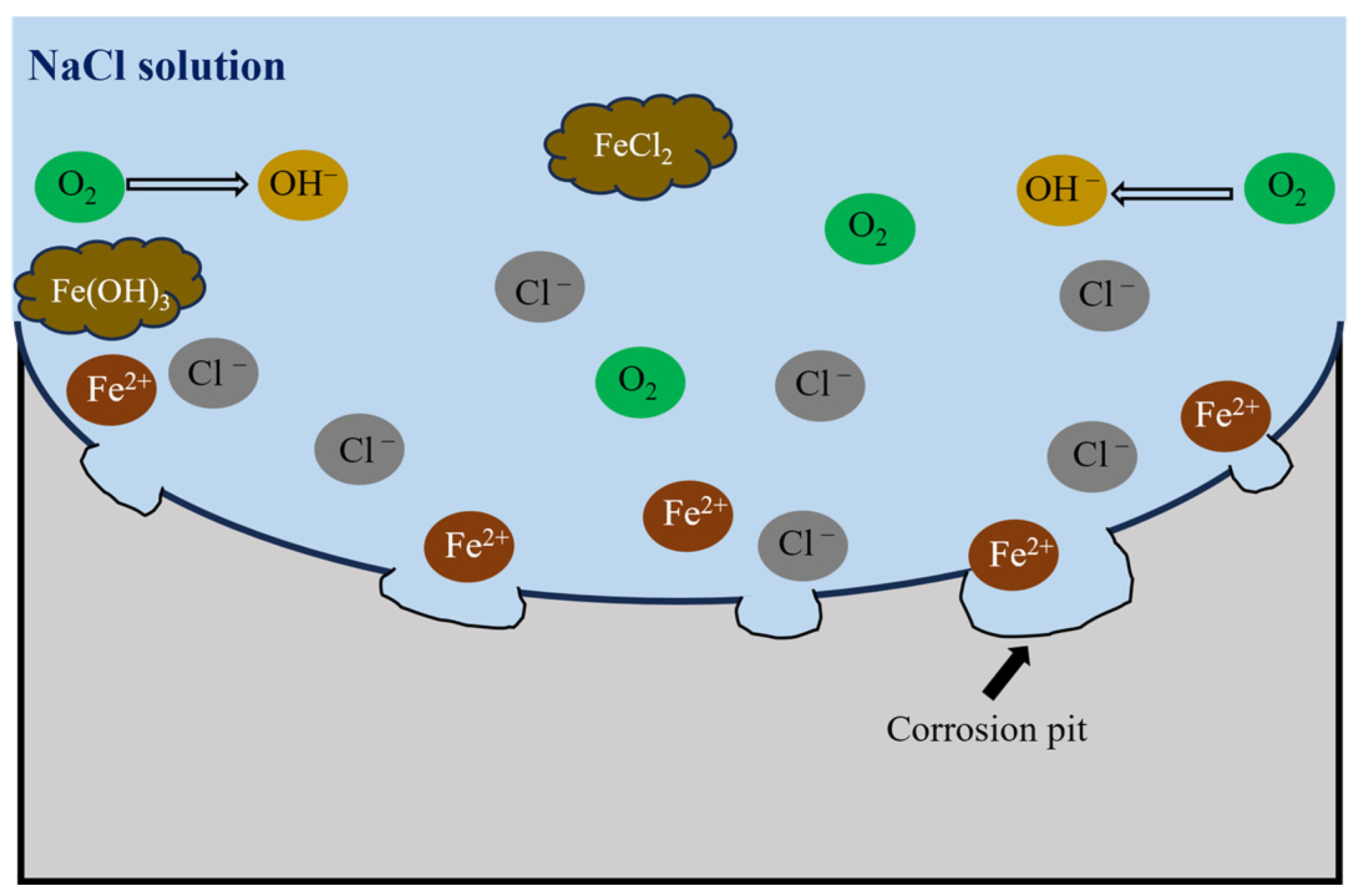
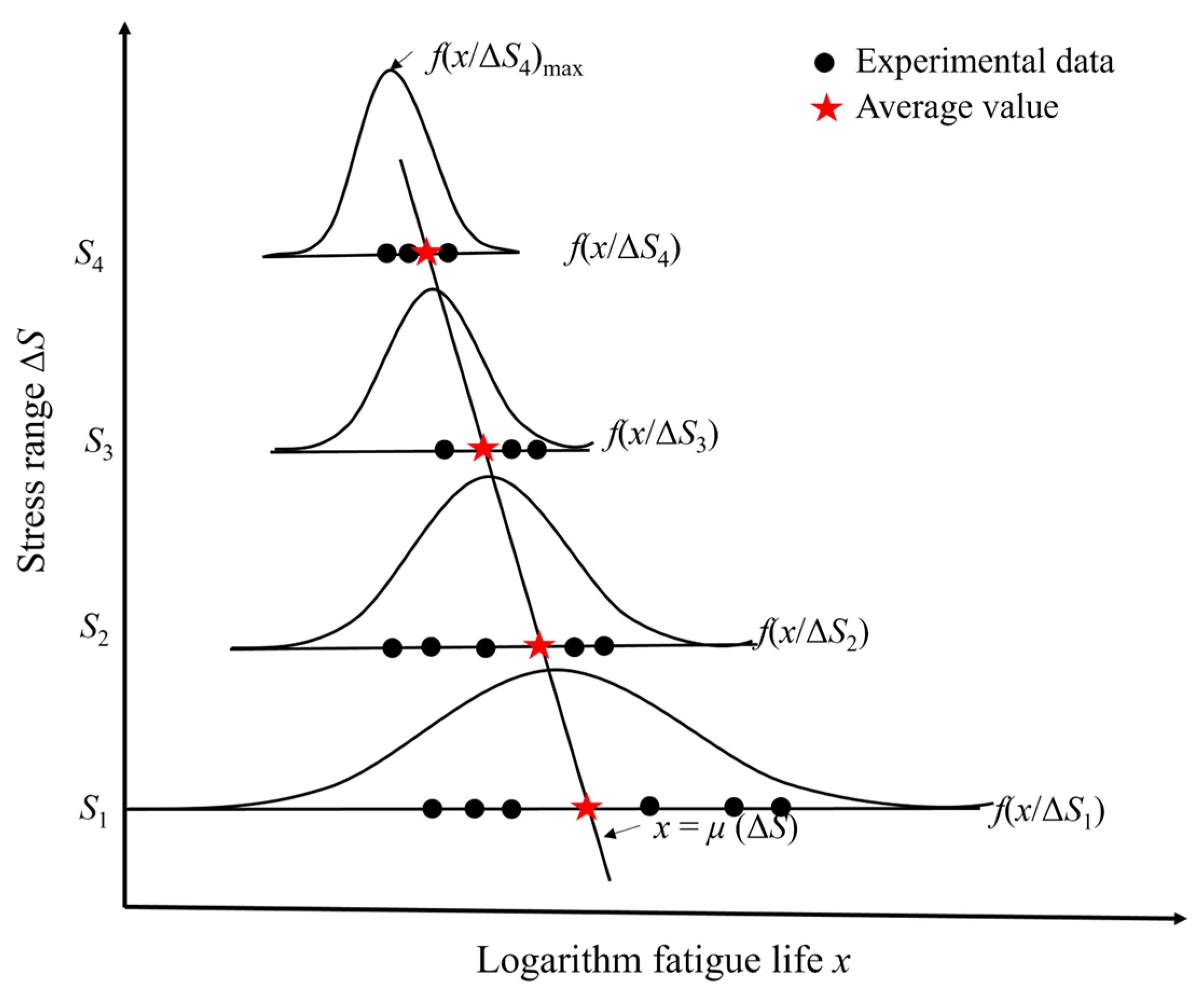
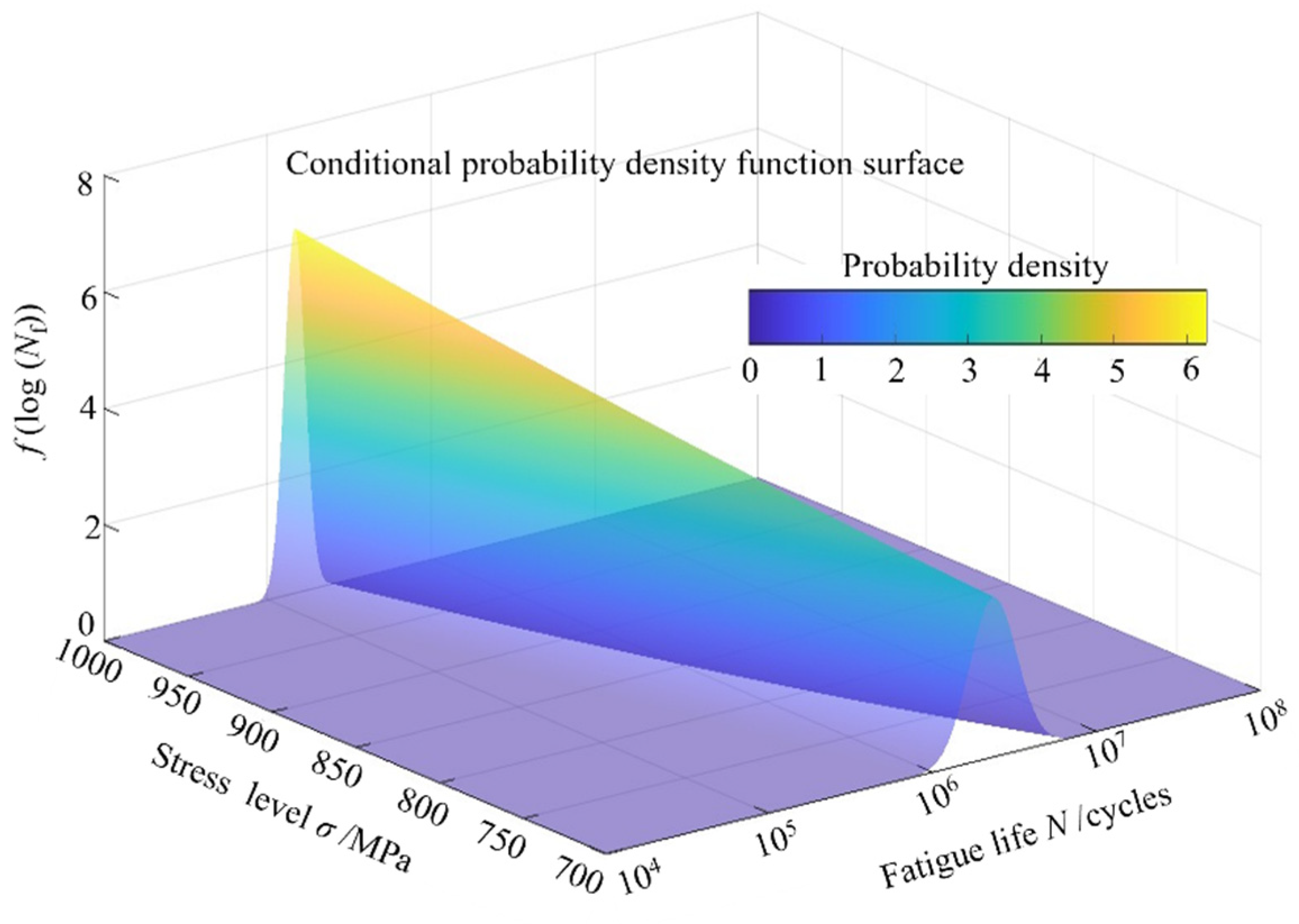
| Element | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Cu | Ni | Mo | Fe |
| wt.% | 0.27 | 0.39 | 0.72 | 0.0075 | 0.0013 | 1.11 | 0.01 | 0.25 | 0.25 | balance |
| Stress Range ΔS/MPa | Fatigue Life Nf/Cycles | Log (Nf) | Mean Value μ(ΔS) | STD σ(ΔS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 980 | 83,808 | 4.92 | 5.24 | 0.062 |
| 238,176 | 5.38 | |||
| 940 | 201,717 | 5.30 | 5.38 | 0.073 |
| 264,785 | 5.42 | |||
| 900 | 427,864 | 5.63 | 5.53 | 0.082 |
| 428,581 | 5.63 | |||
| 860 | 383,250 | 5.58 | 5.68 | 0.092 |
| 570,113 | 5.76 | |||
| 820 | 703,257 | 5.85 | 5.84 | 0.101 |
| 570,113 | 5.76 | |||
| 780 | 868,309 | 5.94 | 6.01 | 0.111 |
| 889,715 | 5.95 | |||
| 700 | 2,233,640 | 6.35 | 6.37 | 0.131 |
| Stress Range ΔS/MPa | Fatigue Life Nf/Cycles | Log (Nf) | Mean Value μ(ΔS) | STD σ(ΔS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 880 | 167,900 | 5.23 | 5.22 | 0.076 |
| 139,854 | 5.15 | |||
| 800 | 315,157 | 5.50 | 5.45 | 0.095 |
| 377,152 | 5.58 | |||
| 320,329 | 5.51 | |||
| 720 | 368,061 | 5.57 | 5.69 | 0.115 |
| 611,697 | 5.79 | |||
| 640 | 866,623 | 5.94 | 5.96 | 0.135 |
| 1,155,430 | 6.06 | |||
| 560 | 2,055,190 | 6.31 | 6.28 | 0.154 |
| 1,068,370 | 6.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Y.; Li, G.; Li, C.; Qi, C.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, P. Effect of Foreign Object Damage on Corrosion Fatigue Behavior in Surface-Strengthened EA4T Railway Axle Steel. Technologies 2025, 13, 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13080368
Luo Y, Li G, Li C, Qi C, Hu Y, Yuan P. Effect of Foreign Object Damage on Corrosion Fatigue Behavior in Surface-Strengthened EA4T Railway Axle Steel. Technologies. 2025; 13(8):368. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13080368
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Yan, Gang Li, Cunhai Li, Chuanqi Qi, Yongxu Hu, and Ping Yuan. 2025. "Effect of Foreign Object Damage on Corrosion Fatigue Behavior in Surface-Strengthened EA4T Railway Axle Steel" Technologies 13, no. 8: 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13080368
APA StyleLuo, Y., Li, G., Li, C., Qi, C., Hu, Y., & Yuan, P. (2025). Effect of Foreign Object Damage on Corrosion Fatigue Behavior in Surface-Strengthened EA4T Railway Axle Steel. Technologies, 13(8), 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13080368






