Abstract
This article addresses the task of building personalized educational recommendations based on a heterogeneous knowledge graph that integrates data from university curricula, job vacancies, and online courses. To solve the problem of course recommendations by their relevance to a user’s competencies, a graph neural network (GNN)-based approach is proposed, specifically utilizing and comparing the Heterogeneous Graph Transformer (HGT) architecture, Graph Sample and Aggregate network (GraphSAGE), and Heterogeneous Graph Attention Network (HAN). Experiments were conducted on a heterogeneous graph comprising various node and relation types. The models were evaluated using regression and ranking metrics. The results demonstrated the superiority of the HGT-based recommendation model as a link regression task, especially in terms of ranking metrics, confirming its suitability for generating accurate and interpretable recommendations in educational systems. The proposed approach can be useful for developing adaptive learning recommendations aligned with users’ career goals.
Keywords:
graph neural network (GNN); ontology; domain integration; heterogeneous knowledge graph; personalized recommendations; link regression; link weight prediction; graph sample and aggregate network (GraphSAGE); heterogeneous graph transformer (HGT); heterogeneous graph attention network (HAN); course recommendation; meta-paths; meta-relations; skill embeddings 1. Introduction
In the context of rapid technological change and increasing labor market demands, aligning university educational programs, employer requirements, and online learning opportunities has become particularly relevant. Despite the availability of course recommendation systems, most do not account for the complex, multi-source nature of skill-related data represented in curricula, job postings, and Massive Open Online Courses’ (MOOCs) structures.
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are used in many recommender systems. There are a large number of GNNs, which are well covered in general surveys [1,2,3,4,5] with the construction of their taxonomy from different points of view. For example, four categories of GNNs are considered in [1] by their architectural features—recurrent, convolutional, autoencoders and spatiotemporal—and their limitations are discussed. The article [2] divides GNNs into four types in terms of imbalance, noise, privacy, and out-of-distribution attacks. A survey [3] classifies GNNs by tasks and analyzes several aspects of GNN robustness; a taxonomy of GNNs for time series is constructed in [4]. A review [5] is presented of the main key points: fundamental principles, popular GNN architectures, advantages and disadvantages, and areas of application. In [6,7], surveys consider the problems of oversquashing (difficulties in transmitting information between remote nodes) and oversmoothing (increasing the number of layers leads to homogeneity of nodes).
In addition to the general description of GNNs, there are several surveys of GNN-based recommender systems [8,9,10,11], which briefly show the evolution of the direction from basic GNN to advanced techniques at the junction with LLM. In [8], the authors identify five typical GNN frameworks and build taxonomies for four types of recommendations: user–item collaborative filtering, sequential recommendation, social recommendation, and knowledge graph-based recommendation. In their review, the authors of [9] provide a systematic and extensive analysis with the construction of a taxonomy and numerous examples of recommendation models on the main key perspectives: multi-stage architecture (matching, ranking, re-ranking), application scenarios (social, sequential, session-based, bundle, cross-domain and multi-behavior recommendations), goals of recommendation systems (accuracy/precision, diversity/novelty, explainability/interpretability, fairness, security, privacy), and types of application (product, point-of-interest, news, movie, video, job, food, music recommendation, and so on). The authors of [10] pay attention to some aspects of recommendations in addition to the usual accuracy: diversity, serendipity, fairness. Finally, paper [11] discusses the so-called Graph Foundation Models (GFMs), which combine GNNs and large language model (LLMs), forming a new paradigm in recommender systems by combining graph structure and language semantics. They distinguish three types of recommender systems: graph-augmented LLM, LLM-augmented graph, and LLM-graph harmonization.
Recent studies highlight the potential of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) for modeling complex inter-entity relationships in heterogeneous graphs. GNNs are most commonly applied to link prediction tasks, i.e., predicting the existence or likelihood of a connection between two nodes. Examples include predicting interactions in medical networks [12] and scientific literature networks [13]. These works have demonstrated the effectiveness of GNNs in uncovering hidden structural patterns and semantic relationships.
Notwithstanding, link prediction typically addresses a binary classification problem and does not reflect the degree of relevance between entities. In practical applications such as educational recommendation systems, there is a need for link regression or link weight prediction, which involves estimating the weight or importance of a connection on a continuous scale [14]. Link weight prediction is relatively new compared to traditional link prediction tasks [15]. The key difference between the two is that edge existence prediction is a classification task, while edge weight prediction is a regression task [14]. In some studies [15], the authors introduce a method that transforms the subgraph surrounding a target edge into a linear graph and then applies a Graph Convolutional Network (GCN) to learn features representing relationships in the original graph. Research on link weight prediction remains limited but is gaining momentum. For example, the authors of [16] propose a model using node embeddings obtained via various methods to predict edge weights. The authors of [17] develop a model based on convolutional neural networks and the Weisfeiler–Lehman algorithm to predict edge weights in graphs. Example of link weight prediction in heterogeneous graphs is [18], where two heterogeneous weighted graphs were used for social recommendations. However, most existing works focus on homogeneous graphs and do not capture the semantic complexity of heterogeneous graphs in educational contexts.
This study aims to fill these gaps by applying GNNs to the task of link regression in a heterogeneous knowledge graph that integrates competencies from university programs or user profiles, actual IT job postings from the hh.kz recruitment platform, and computer science courses from Coursera. A pointwise regression-based approach using GNNs is employed to train course recommendation models. Evaluation is conducted using both regression and ranking metrics, where each connection between a user’s competency and an online course is assigned a normalized relevance score [0, 1], based on the number of structural paths in the graph. The study compares three course recommendation architectures for personalized recommendations based on three types of GNNs: GraphSAGE (as a baseline), HANConv (meta-path-based attention model) [19], and HGTConv (meta-relation-based attention model) [20].
Key scientific contributions of this study include (a) development of curriculum–vacancy–course recommendation models trained via link regression using HANConv and HGTConv, adapted for heterogeneous graph structures and (b) comprehensive evaluation and comparison of the GraphSAGE-, HAN-, and HGT-based recommendation models using both regression and ranking quality metrics, demonstrating the models’ ability to generate semantically relevant recommendations based on the structural features of the graph.
The proposed methods can enable the construction of personalized learning paths based on the analysis of current competencies and labor market trends, thereby supporting continuous professional development through intelligent educational recommendations.
2. Methods
2.1. Dataset
In this study, three datasets were collected: competency maps from a university educational program, job vacancies from the online recruitment platform hh.kz, and MOOCs from Coursera (Mountain View, CA, USA).
The educational dataset includes phrases describing competencies, learning outcomes, and brief course descriptions for the Information Systems degree program in Russian, based on the 2022 academic curriculum [21].
The hh.kz dataset consists of job titles, company names, industry sectors, experience requirements, salary information, publication dates, vacancy links, skills, and partial descriptions of requirements and responsibilities in both Russian and English. The data was collected from the HeadHunter platform (https://hh.kz/) using the provided API (https://api.hh.ru/vacancies, 1 May 2025) and the Python 3.19 programming language. Job vacancies were selected for 25 IT professions across 177 localities in Kazakhstan during the period from 1 February 2024 to 31 March 2024, totaling 5248 job postings [21].
The Coursera dataset includes free online courses in English related to computer science, information technology, and data science as of 3 May 2024. The data includes course titles, difficulty levels, ratings, skill lists, module and lesson names with their durations, and short descriptions. The courses were scraped using the Beautiful Soup library, resulting in 953 course entries [21].
2.2. Methods
All three datasets were uploaded into the Neo4j graph database as separate knowledge graphs, each defined by its own ontology.
We defined [10] the ontological model of the knowledge graph of the subject area as a heterogeneous, labeled, directed graph G = {E, R, A, V, r, f, p}, where E is the set of entity classes; R is the set of relationship types; A is the set of attributes of entities or relationships; V is the set of attribute values; the function r: R → E × E means that each relationship type is assigned a pair of entity classes; the function f: E ∪ R → 2A means that each entity class or relationship type has an attribute from the set A; the function p: E ∪ R → 2A×V means the correspondence of an entity class or relationship type to a set of attribute–value pairs.
Three ontologies are designed manually: 1. The curriculum has phrases of competencies, units of study, and annotations (CUA) of disciplines: Euniversity = {Curriculum, CUA}, Runiversity = {HAS}, r(HAS) = (Curriculum, CUA), f(Curriculum) = {code, title}, f(CUA) = {code, description, embedding}; 2. The vacancy has skills, requirements, and responsibilities: ERecruitment = {Vacancy, Skill, Requirement, Responsibility}, RRecruitment = {REQUIRE, HAS_REQUIREMENT, HAS_RESPONSIBILITY}, r(REQUIRE) = (Vacancy, Skill), r(HAS_REQUIREMENT) = (Vacancy, Requirement), r(HAS_RESPONSIBILITY) = (Vacancy, Responsibility), f(Vacancy) = {title, profession, city, company, industry, experience, salary, url, publish_date}, f(Skill) = {name, embedding}, f(Requirement) = {description, embedding}, f(Responsibility) = {description, embedding}; 3. The MOOC courses consist of modules, the module consists of lessons, and skills are developed in MOOC courses: EMOOC = {MCourse, MSkill, Mmodule, MLesson}, RMOOC = {DEVELOPED_BY, CONSISTS_OF}, r(DEVELOPED_BY) = (Mskill, Mcourse), r(CONSISTS_OF) = (MCourse, Mmodule), r(CONSISTS_OF) = (Mmodule, Mlesson), f(MCourse) = {title, url, organization, certificate_type, rating, reviews_num, difficulty, students_enrolled}, f(MSkill) = {name, embedding}, f(Mmodule) = {title, description, duration, embedding}, f(MLesson) = {title, type, embedding}.
The ontologies of the three knowledge graphs were then integrated at the skill level by computing two types of cosine similarity using Equations (1) and (2) on skill embeddings across the sources:
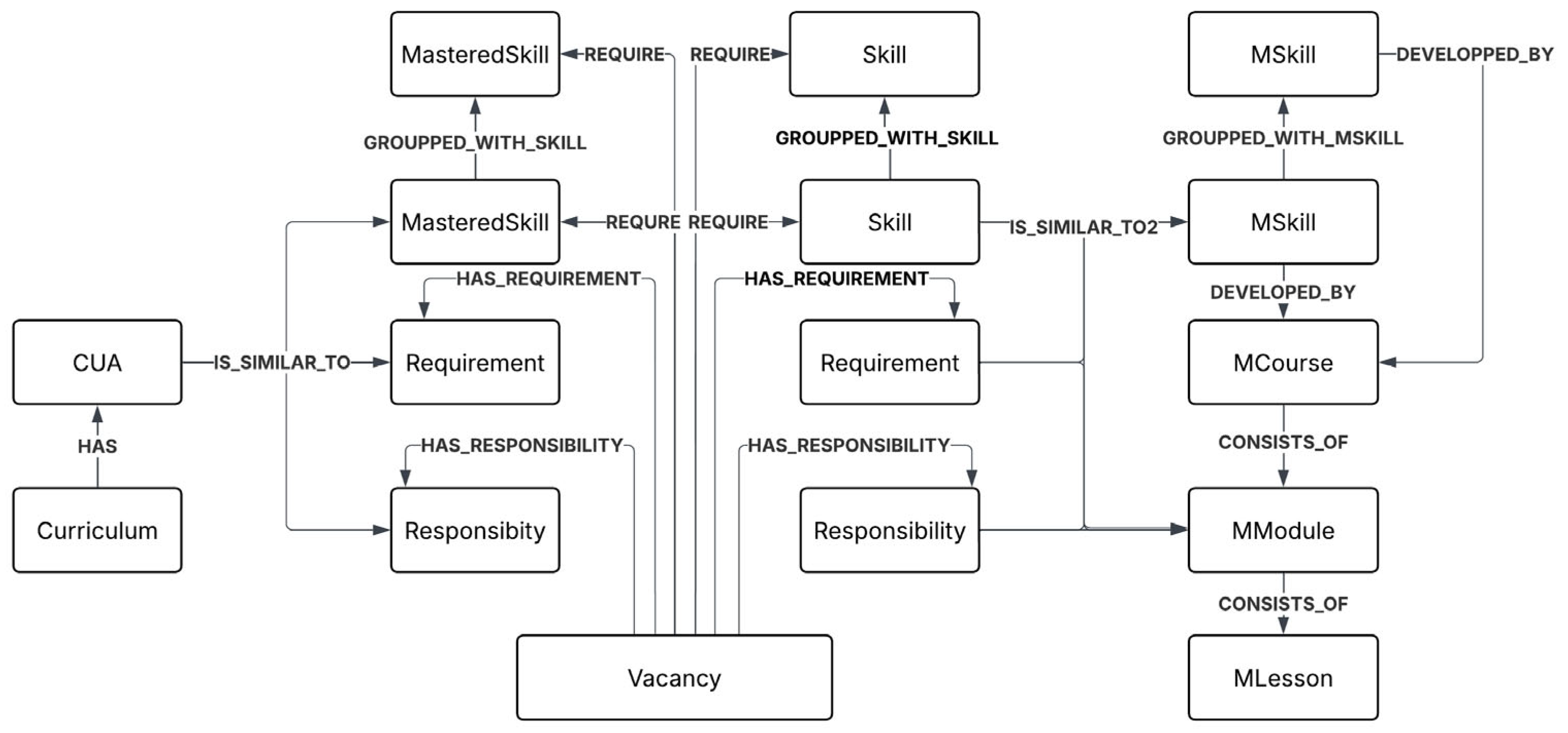
The whole curriculum–vacancy–course ontology was integrated via new relations: R = {IS_SIMILAR_TO, IS_SIMILAR_TO2} ∪ Runiversity ∪ RRecruitment ∪ RMOOC, E = Euniversity ∪ ERecruitment ∪ EMOOC, r(IS_SIMILAR_TO) = (CUA, Skill), r(IS_SIMILAR_TO2) = (Skill, MSkill), f(IS_SIMILAR_TO) = {similarity1} > threshold1, f(IS_SIMILAR_TO2) = {similarity2} > threshold2. Thresholds were determined experimentally. Skill embeddings were generated using the multilingual pre-trained model paraphrase-multilingual-mpnet-base-v2, which supports over 50 languages and was fine-tuned on job-related skills. The figure for ontology curriculum–vacancy–course is presented below in Figure 1.
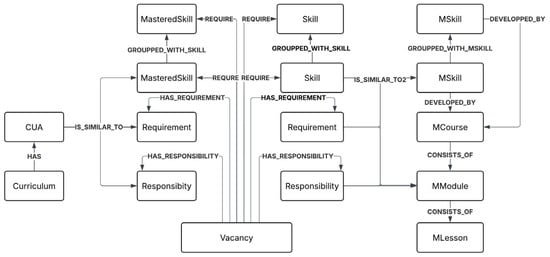
Figure 1.
Ontology of knowledge graph: curriculum–vacancy–course.
After that, two types of clusters of similar skills from the vacancy and course domains were formed using embeddings of the multilingual pre-trained model paraphrase-multilingual-mpnet-base-v2 and agglomerative clustering with a maximum of mean silhouette coefficient of all samples [−1, 1] at the skill-embedding level. Additional edges were created between the three types of skill nodes, when the similarity score between skills exceeded a defined threshold: R′ = R ∪ {GROUPPED_WITH_SKILL} ∪ {GROUPPED_WITH_MSKILL}, r(GROUPPED_WITH_SKILL) = (Skill, Skill); r(GROUPPED_WITH_MSKILL) = (Mskill, Mskill).
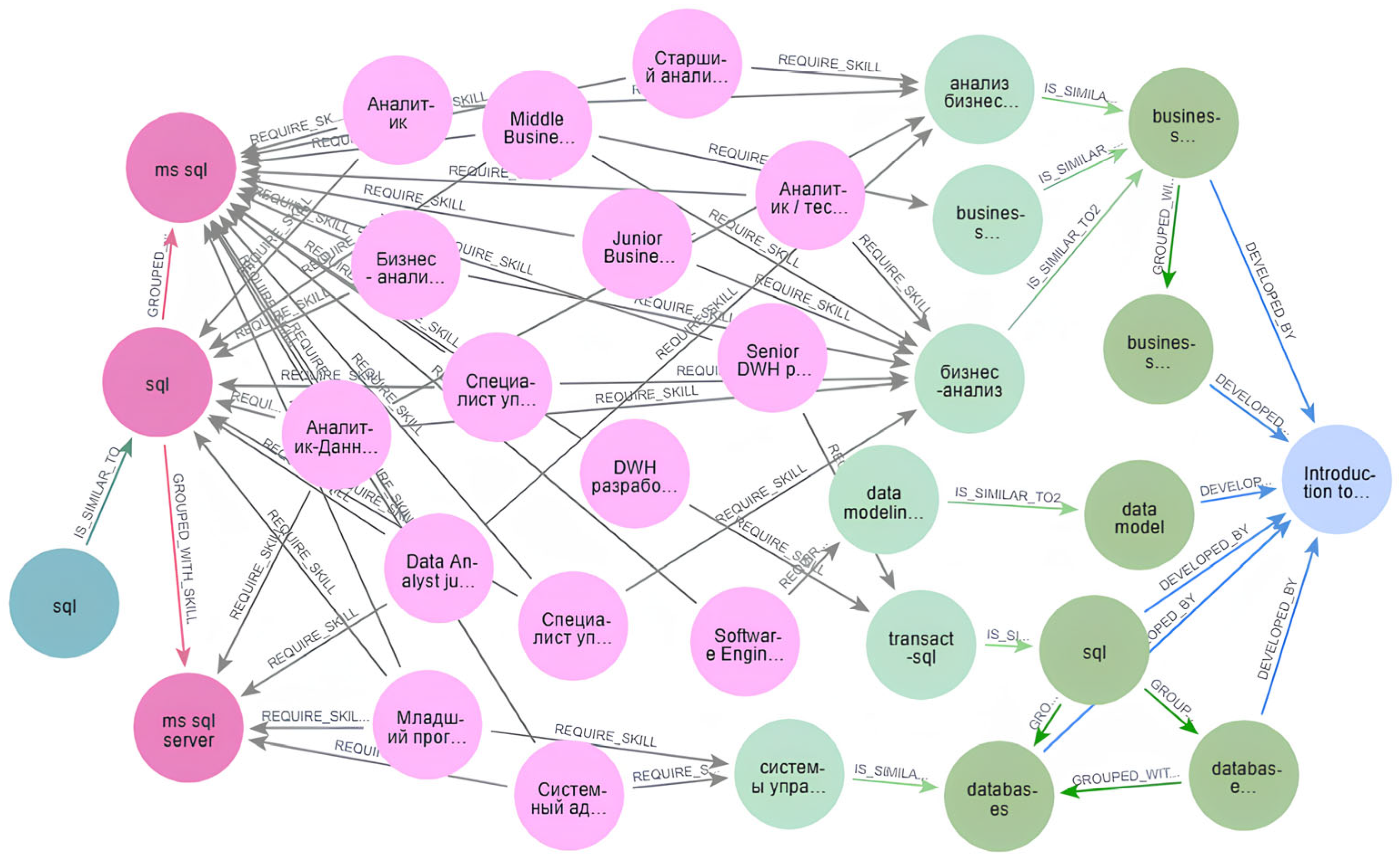
Furthermore (Figure 1), job skills that were matched with user competencies were transformed into a distinct node type to facilitate downstream processing: SkillMastered = {s ∈ Skill ∣ ∃ sg ∈ {Cluster(s)} ∪ {Skill}, ∃ c ∈ CUA: (c, sg) ∈ r(IS_SIMILAR_TO)}, where Cluster(s) = {s1 ∈ Skill|(s, s1) ∈ r(GROUPPED_WITH_SKILL) ∨ (s1, s) ∈ r(GROUPPED_WITH_SKILL)}; Skill′ = Skill\SkillMastered; E′Recruitment = ERecruitment\{Skill} ∪ {SkillMastered, Skill′}, r(IS_SIMILAR_TO) = (CUA, SkillMastered), r(GROUPPED_WITH_SKILL) = (SkillMastered, SkillMastered), r(GROUPPED_WITH_SKILL) = (Skill′, Skill′), r(IS_SIMILAR_TO2) = (SkillMastered, MSkill), r(IS_SIMILAR_TO2) = (Skill′, Mskill), r(REQUIRE) = (Vacancy, SkillMastered), r(REQUIRE) = (Vacancy, Skill′). An example of a subgraph is presented in Figure 2.
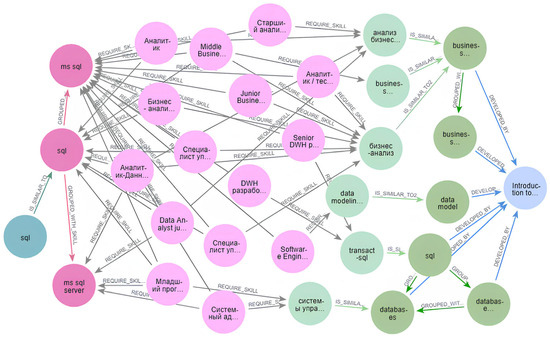
Figure 2.
Subgraph showing paths between the initial user competency node (CUA) and the target course node (MCourse). Node colors: CUA—emerald, MasteredSkill—bright pink, Vacancy—pink, Skill—light green, Mskill—bright green, Mcourse—blue.
To facilitate further processing, the graph was split based on user skill nodes (CUA): 80% were allocated to the training subgraph and 20% to the test subgraph. Each subgraph (train/test) was loaded into PyTorch version 1.13.1 Geometric as a separate HeteroData object, comprising six node types and eleven edge types, integrating data on users’ educational competencies, labor market demands, and online courses.
To enhance the expressiveness of the training set and to model semantic relations between users and courses, four meta-paths were constructed. Meta-paths are logical sequences of transitions through intermediate node types that reflect some base aspects of the relationship between source and target entities through similar skill clusters. The meta-paths were constructed manually using the AddMetaPaths transformation from PyTorch Geometric, which creates new CUA → MCourse edges if at least one path exists between them according to the specified schema: R″ = R′ ∪ {CONNECTED_TO, metapath_0, metapath_1, metapath_2, metapath_3}.
The newly constructed CONNECTED_TO edge type carries training labels ranging from 0 to 1, which are used to train the model based on existing meta-relations and meta-paths in order to rank recommended courses depending on the user’s initial skill: r(CONNECTED_TO) = (CUA, MCourse), f(CONNECTED_TO) = {score}.
The ground truth edge weights for CONNECTED_TO were generated by counting the number of paths between the initial node and all target course nodes in a query, followed by normalization to a [0, 1] scale: p(CONNECTED_TO) = {score: y}, where y ∈ [0, 1]. This was performed by dividing the number of paths k from a given competency to a course by the maximum number of paths kmax from that competency to any course within the same query: score = k/kmax. Thus, the CONNECTED_TO edge from a CUA node (user competency) to an MCourse node (MOOC) that had the highest number of connecting paths received a label of 1, while other course edges received values less than 1.

Table 1.
Node types in the heterogeneous graph.

Table 2.
Edge (relation) types in the heterogeneous graph.
In this study, we train and compare GraphSAGE-, HGTConv-, and HANConv- based recommendation models on a link regression task between user competencies (CUA) and online courses (MCourse) in a heterogeneous graph incorporating labor market vacancies.
GraphSAGE is a framework that uses node feature information (e.g., text attributes) to generate node embeddings for previously unseen data. The choice of GraphSAGE was justified by the simplicity and speed of processing large graphs.
The HGT convolutional layer operator introduces an adaptation of the multi-head attention mechanism from the transformer architecture to graphs with multiple node and edge types. The HGT architecture consists of three key components: (a) heterogeneous mutual attention, sensitive to meta-relations; (b) heterogeneous message passing from source nodes; (c) target-specific message aggregation. For each relation triplet («source node type»–«edge type»–«target node type»), HGT learns its own weight matrices and scaling coefficients, making attention weights semantically aware of the specific relation. By aggregating such type-dependent messages, the layer generates node representations that account for both the graph structure and the heterogeneity of its elements. To support training on web-scale graphs (e.g., 179 million nodes and 2 billion edges in the Open Academic Graph), HGT introduces the HGSampling strategy, which samples mini-batches based on type distributions, significantly reducing memory requirements. On tasks such as node classification, link prediction, and recommendation, HGT outperforms previous GNN baselines by 9–21% [20].
The HAN architecture follows a two-level attention mechanism adapted for heterogeneous graphs. First, the input features for each node type are linearly projected into a shared hidden space. Then, for each meta-path, node-level attention is applied: each edge receives an asymmetric attention weight, which is normalized via softmax and used to aggregate messages from neighboring nodes. The resulting embeddings for each relation are then combined through semantic-level attention, where a learnable query vector weighs the contribution of different meta-paths to form the final node representation. As a result, each node obtains a contextualized embedding that captures both structural connections of different types and their semantic relevance [19].
Both operators are designed for heterogeneous graphs, but their core difference lies in how they represent relational structure: HGT operates on meta-relations, while HAN operates on meta-paths, which are composed of sequences of relations.
The heterogeneous graph for the GraphSAGE and HGT-based recommendation models include six node types and ten directed edge types, representing both forward and reverse relations (e.g., IS_SIMILAR_TO and rev_IS_SIMILAR_TO). Each node stores 768-dimensional SBERT embeddings. Information about the nodes and edges is presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Nodes and edges for the recommendation model with the GraphSAGE and HGT layers.
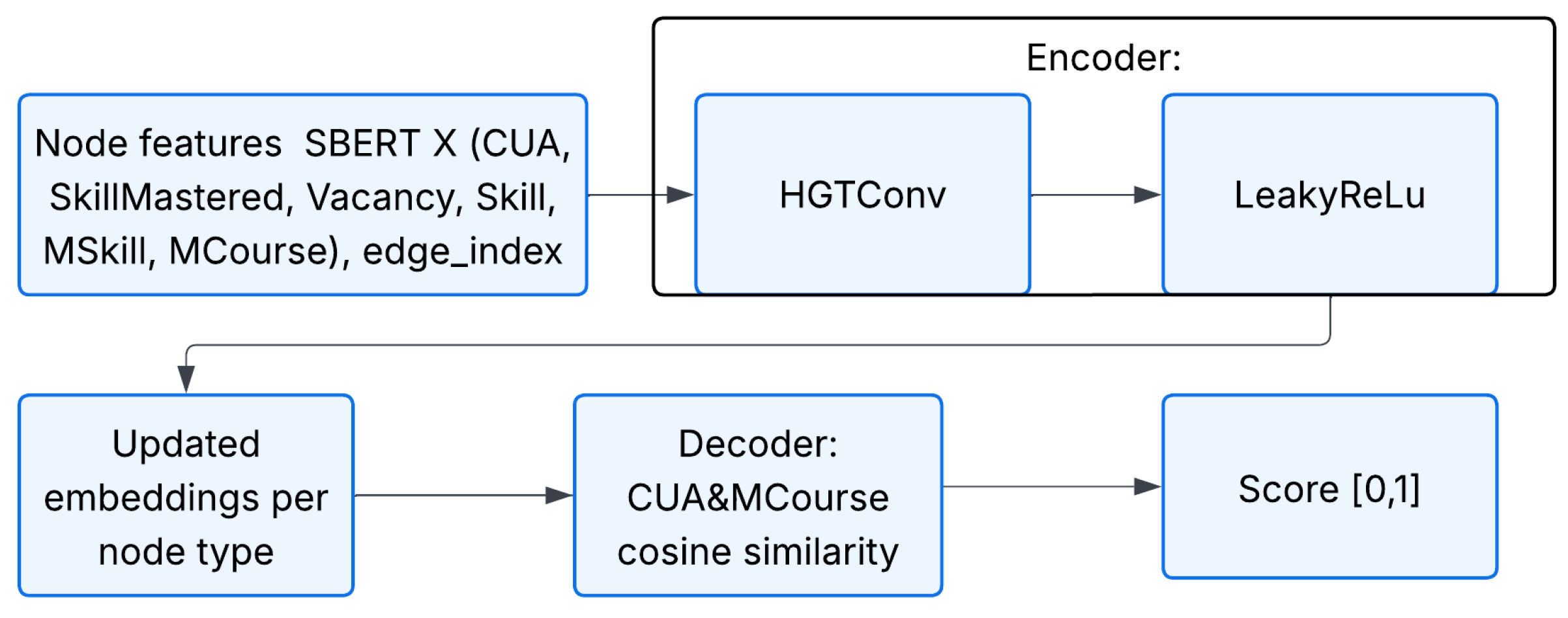
We consider the task of predicting continuous labels ∈ [0, 1] for the CONNECTED_TO edges in a heterogeneous graph: p(CONNECTED_TO) = {score: }. The proposed recommendation model adopts an encoder–decoder architecture. As the encoder for the first model, we employ the HGTConv operator from the Heterogeneous Graph Transformer (HGT) framework, implemented using PyTorch Geometric. HGTConv extends the multi-head attention mechanism to heterogeneous graphs by accounting for multiple node and edge types. In our configuration, the layer uses 768 hidden units and four attention heads, with a dropout rate of 0.2 applied to mitigate overfitting.
The HGTConv layer processes the graph metadata and input node features X and produces contextualized embeddings Z for the downstream regression Equation (3).
After message aggregation, the LeakyReLU activation function (α = 0.1) is applied to each relevant node type to prevent gradient vanishing. The activation function is defined by Equation (4) [22]:
The decoder is parameter-free: the final representations of the CUA and MCourse nodes are compared using cosine similarity, which is then rescaled from the interval [−1, 1] to [0, 1]. The standard formula for computing cosine similarity is given in Equation (5):
The rescaling is then performed as shown in Equation (6):
The workflow of the recommendation model is illustrated in Figure 3. The initial node features are passed through a single HGTConv layer followed by the LeakyReLU activation function. Updated embeddings are then extracted specifically for each CUA–MCourse node pair. The decoder, based on cosine similarity, outputs a final score in the range [0, 1].
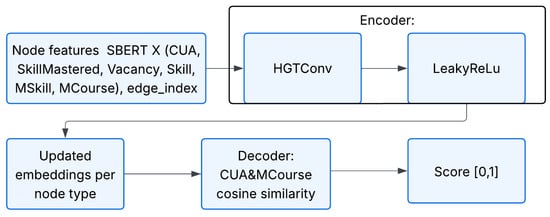
Figure 3.
Inference pipeline of the course recommendation model based on HGT with respect to the user’s competency.
The model is trained for 100 epochs using the Adam optimizer (learning rate = 0.005, weight decay = 0.0001) with mini-batches of 2000 edges. The loss function is the Mean Squared Error (MSE) Equation (7), computed between the predicted score and the ground truth weight of the CONNECTED_TO edge:
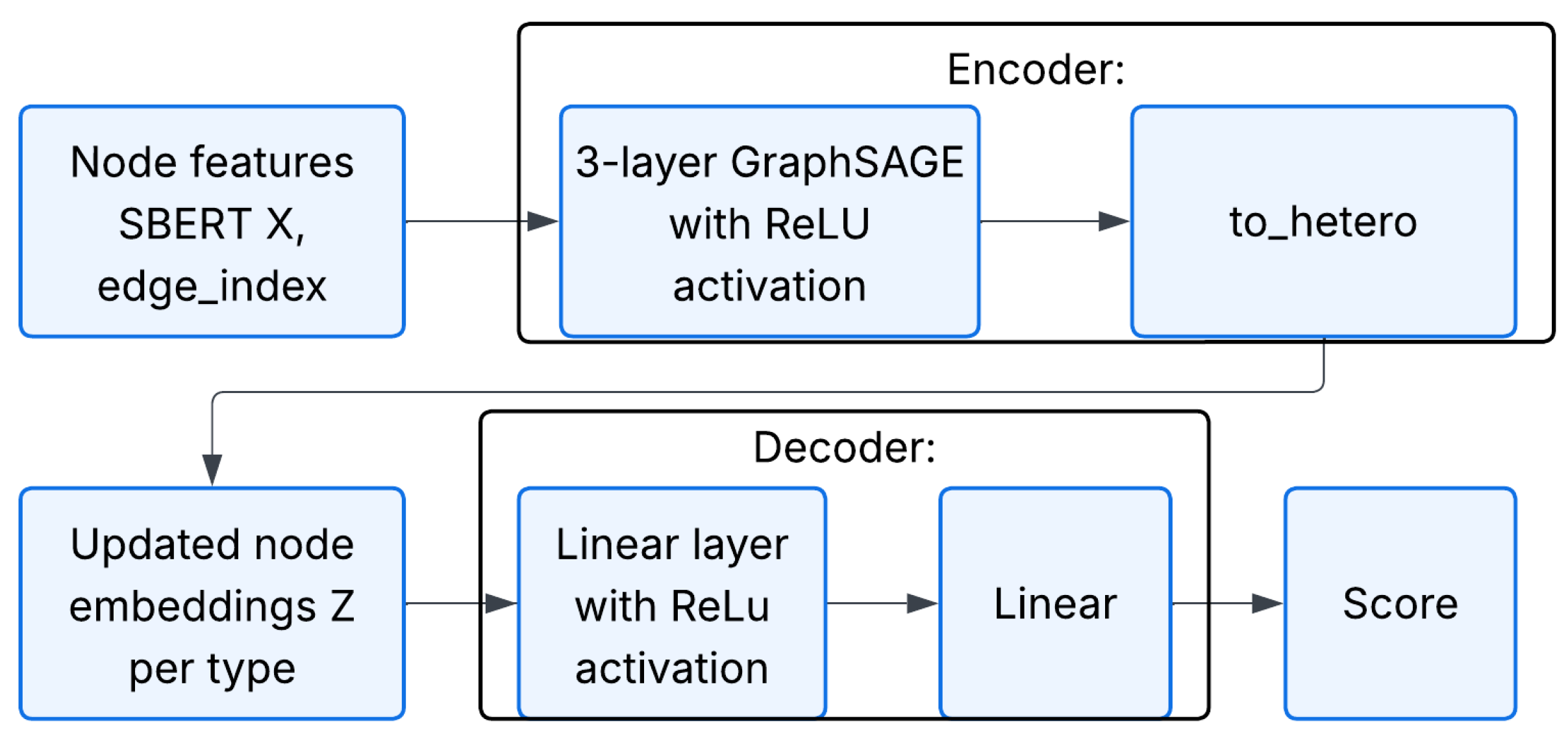
The encoder of the next GraphSAGE-based model (see Figure 4) is the three-layer graph neural network, Equation (8), adapted for heterogeneous graphs [23]:
with a rectified linear unit (ReLU), Equation (9), activation function after every SAGEConv:
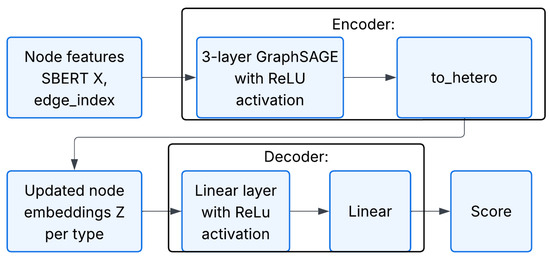
Figure 4.
Workflow of the course recommendation model based on SAGEConv.
At the output, a two-layer decoder is used, consisting of two linear layers, which transforms the combined embeddings of pairs into a final score, Equation (10), of their connection in the range of [0, 1]:
The model was trained for 100 epochs using the Adam optimizer (learning rate = 0.003) with mini-batches of 2000 edges. The loss function is the MSE.
The graph used for the third recommendation model consists of six node types and eighteen meta-path types, including ten forward and eight reverse edge types. Information about the nodes and edges is presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Nodes and edges for the recommendation model with the HAN layer.
The third recommendation model also consists of two key components: an encoder and a decoder. As the encoder, we use the HANConv attention operator from the Heterogeneous Graph Attention Network (HAN) architecture in PyTorch Geometric. This operator aggregates information across all specified meta-paths using a combination of multi-head node-level and semantic-level attention mechanisms. In our recommendation model, the HANConv layer is configured with an input dimensionality of 768 and sixteen attention heads.
The heterogeneous graph is first passed through the HANConv layer, Equation (11):
The output embeddings for each node type (CUA and MCourse) are then passed through the LeakyReLU activation function with α = 0.1 (see Equation (4)). To compute the strength of connection between each pair of nodes, the corresponding embeddings are selected and passed through a bilinear layer, Equation (12):
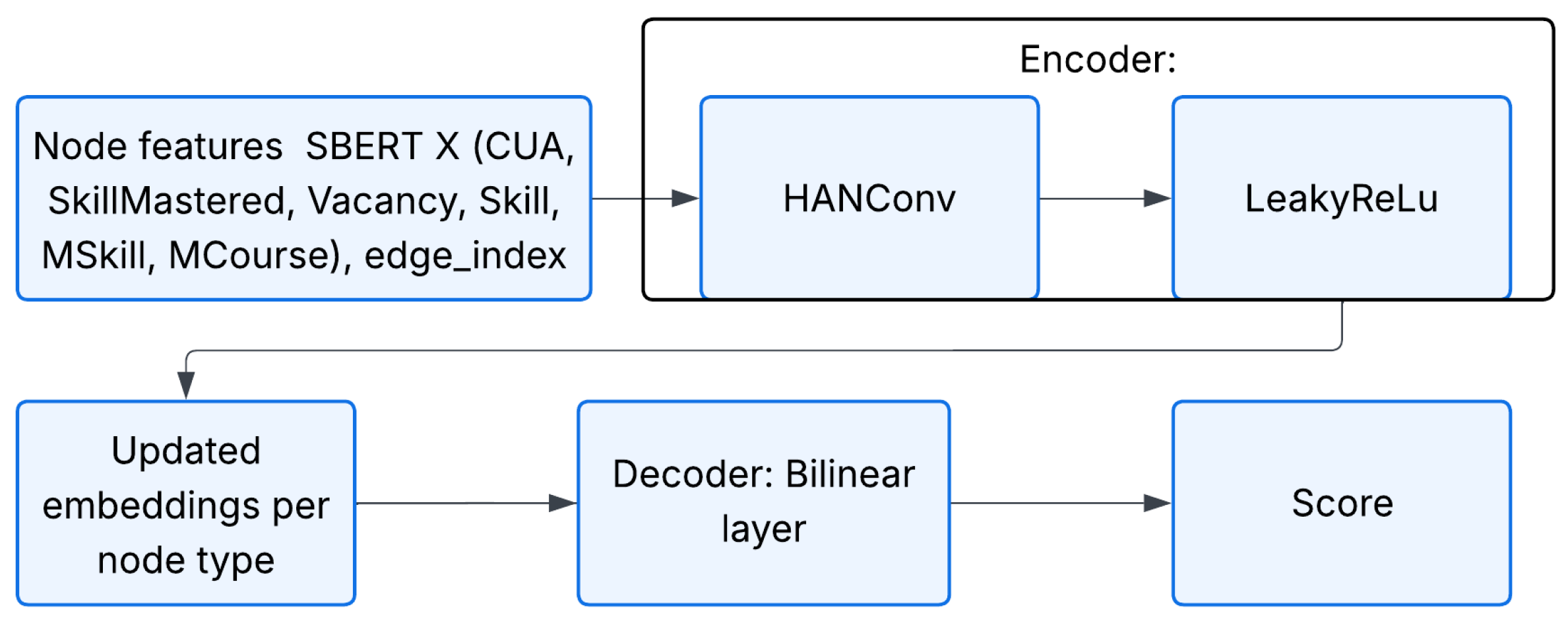
which produces a scalar raw score in the range of [−0.1, 1]. The overall architecture is illustrated in Figure 5.
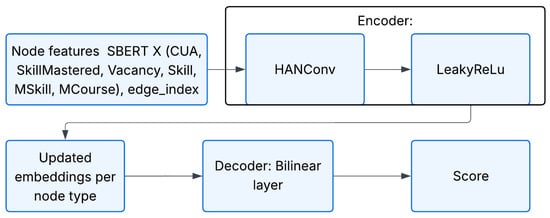
Figure 5.
Architecture of the second recommendation model based on HANconv.
The model was trained for 100 epochs using the Adam optimizer (learning rate = 0.002, weight decay = 0.001) with mini-batches of 2000 edges. The loss function is the Mean Squared Error (MSE), calculated between the predicted score and the ground truth weight of the CONNECTED_TO edge.
Since both recommendation models predict a continuous score for the connection CUA → MCourse and are designed to generate a ranked list of courses for each user competency, the evaluation includes both regression and ranking metrics. The models are evaluated on both the training and test subgraphs. In addition to Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), the following ranking metrics are computed: Precision@k, Recall@k, Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain at k (NDCG@k), and Mean Average Precision at k (MAP@k) [24]. To calculate these metrics, for each source node CUA, we generate relevance maps (where ground truth edge weights >0.5) and corresponding predictions. Evaluation metrics are then averaged across all source nodes.
We first computed RMSE [25] using the standard formulation shown in Equation (13), implemented via the PyTorch Geometric library:
Precision@k Equation (14) and Recall@k Equation (15) indicate how many truly relevant courses appear in the top-k positions and how completely the recommendation covers the relevant set, respectively.
where Rk denotes the number of relevant items among the top-k retrieved results [24].
where R is the total number of relevant items for a given query [24].
MAP calculates the average precision for each query and then averages the resulting values across all queries. The Average Precision (AP) for a single query is defined as follows in Equation (16):
where reli takes the value 0 or 1, indicating the relevance of position i [24]. Then, for a total number of queries Q, MAP@k is defined as shown in Equation (17):
NDCG evaluates the ranking quality of search results. This metric considers the positions of relevant documents in the output, providing a single score that balances both the relevance of the documents and their order. It heavily penalizes relevant documents that appear lower in the ranked list [24]. The metric is computed as follows in Equation (18):
where Discounted Cumulative Gain (DCG) is defined by Equation (19):
Ideal Discounted Cumulative Gain (IDCG) represents the DCG value for the ideal ranking, i.e., the best possible ordering of documents, using Equation (20):
where reli∗ denotes the relevance score of the document at position i in the ideal ranking list [24,26]. In our study, we used the standard implementation of NDCG provided by the scikit-learn library.
3. Results and Discussions
This section presents the experimental results aimed at evaluating the accuracy of course recommendation models based on HGT, GraphSAGE, and HAN for the link regression task in heterogeneous graphs. The experiments utilized both training and test datasets in the HeteroData format, loaded from the Neo4j graph database. Model performance was assessed using RMSE, Precision@k, Recall@k, MAP@k, and NDCG@k metrics.
The evaluation was conducted for k = 5, 10, 15, and 20. The comparison of the evaluation results of the HGT-, GraphSAGE- and HAN-Based recommendation models is presented in Table 5.

Table 5.
Comparison of evaluation results of the HGT-, GraphSAGE-, and HAN-based recommendation models on the training and test dataset.
The results demonstrate the satisfactory effectiveness of the HGT-based model in the link regression task on a heterogeneous graph, particularly when analyzing the MAP@k and NDCG@k metrics—two key indicators of ranking quality.
On the training set, the model achieves outstanding values for both MAP@k and NDCG@k. Specifically, MAP@5 reaches 0.8334, indicating a high precision in placing relevant items within the top-5 results. As k increases to 20, MAP@k slightly decreases to 0.8001 but remains at a high level, demonstrating the model’s consistent ability to maintain recommendation relevance as the list expands. Similarly, NDCG@k increases from 0.8911 to 0.9127, reflecting excellent positional relevance: the model ranks the most relevant items closer to the top of the list. On the test set, the model shows lower scores: MAP@5 is 0.5739 and NDCG@5 is 0.6973, indicating strong positional relevance, especially when compared to the HAN-based model. As k increases, both metrics show a natural upward trend, with MAP@20 reaching 0.5226 and NDCG@20 reaching 0.7388. This confirms the model’s robustness when handling longer recommendation lists.
Overall, the MAP and NDCG metrics confirm that the HGT-based model performs well in prioritizing relevant recommendations: it accurately identifies the most relevant links and ranks them at the top of the list. This is especially important in recommendation systems, where users typically interact only with the top-ranked results.
The difference between the training and testing metrics of the recommendation model based on the GraphSAGE layer is small, which indicates that the generalization ability of the model is good. The main metrics have low scores, only NDCG shows an acceptable ranking result.
Let us now examine the performance of the HAN-based model. On the training dataset, a positive trend is observed in both metrics as k increases: MAP@k rises from 0.3788 at k = 5 to 0.4096 at k = 20, indicating improved ranking quality as more recommendations are considered. Similarly, NDCG@k steadily increases from 0.5715 to 0.6632, confirming that relevant items are consistently positioned closer to the top of the recommendation list. To reduce the risk of overfitting the model, early stopping, regularization (weight decay, dropout) or cross-validation can be used. On the test dataset, the metrics show a similar trend; however, the values are consistently lower than those observed during training. MAP@k ranges from 0.3873 at k = 5 to 0.3400 at k = 20. NDCG@k increases from 0.5812 to 0.6523, indicating that the model maintains its ability to correctly rank relevant items, despite a decline in MAP precision. The relatively close NDCG values between the training and test sets suggest good generalization capability.
Overall, NDCG@k exhibits more stable behavior, reflecting the model’s robustness across different values of k. In contrast, MAP@k shows that the model loses some precision on the test set as the number of recommendations increases.
The experimental results highlight the differences in the recommendation performance of the HGT-, GraphSAGE-, and HAN-based models for the link regression task in a heterogeneous graph. The HGT-based model significantly outperforms the HAN model on both the training and test datasets across most evaluation metrics.
On the training set, the HGT model achieves high values for Precision@k, MAP@k, and NDCG@k at all levels of k, reaching up to 0.91 for NDCG@20. This indicates a strong ability to extract and leverage information about node and edge types within the heterogeneous structure. In contrast, the GraphSAGE- and HAN-based models yield noticeably lower scores.
On the test dataset, the HGT-based model demonstrates superior performance. For example, at k = 10, NDCG@10 reaches 0.7139 compared to 0.5900 for GraphSAGE- and 0.6140 for HAN, and MAP@10 is 0.5508 versus 0.3083 and 0.3446, respectively.
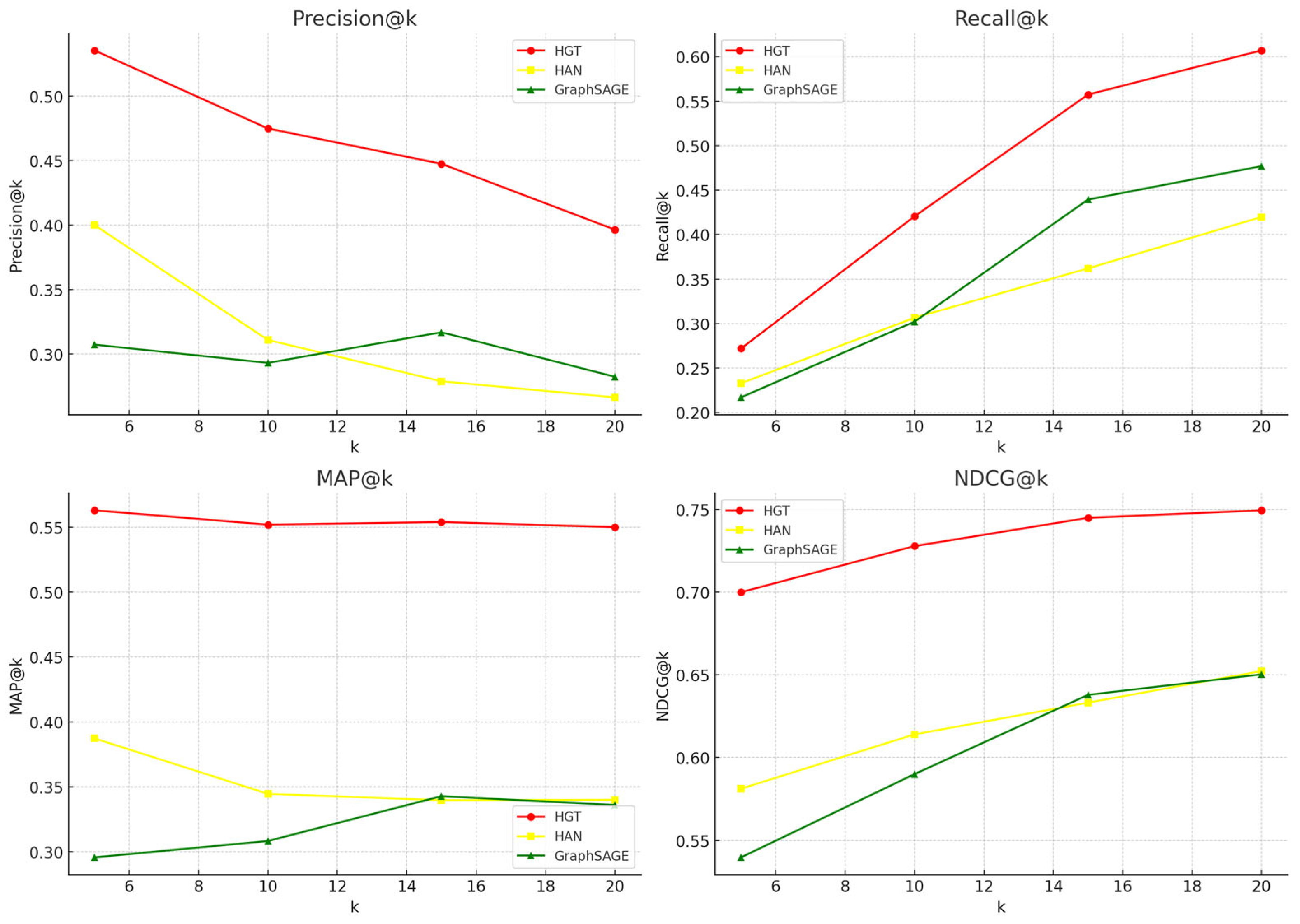
On the test dataset (Figure 6), the HGT model shows the best results. It consistently outperforms the HAN and GraphSAGE models on all key quality metrics.
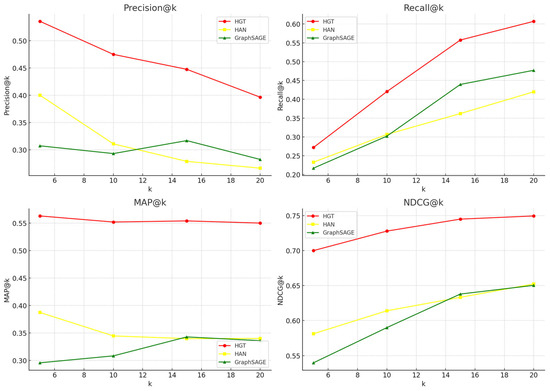
Figure 6.
Comparison of Precision@k, Recall@k, MAP@k and NDCG@k metrics for recommendation models based on GraphSAGE, HGT, and HAN layers on the test set.
GraphSAGE and HAN achieve lower RMSE values on the test set than HGT; that means that the HGT-based recommendation model exhibits a slightly higher degree of overfitting compared to the GraphSAGE- and HAN-based models. To reduce the risk of overfitting the HGT-based model, early stopping, regularization (weight decay, dropout) or cross-validation can be used. However, their quality metrics (Precision, Recall, MAP, NDCG) are significantly worse. This suggests that while GraphSAGE and HAN better predict the absolute edge weight values, they perform poorly in ranking them in descending order of relevance—a critical requirement in recommendation systems.
The overall evaluation results indicate that both models still require improvement. Enhancing the performance of the recommendation models may be possible by increasing the size of the experimental dataset.
The difference in the performance of the recommender models is due to the differences in the architecture of HGT, GraphSAGE, and HAN. HGT uses individual attention mechanisms at three levels: different types of source nodes, different types of relationships between the source node and the target node, and specific message aggregation for each type of target node. HAN uses attention mechanisms at two levels: at the level of features of neighboring nodes within a meta-path and at the level of different manually specified meta-paths. GraphSAGE aggregates and concatenates features of all neighboring nodes based on existing relations but does not distinguish their type. Obviously, HGT uses additional attention mechanisms at the meta-relationship level, which are not present in GraphSAGE and which are not limited by meta-paths as in HAN. Attention at the meta-relationship level in HGT is more flexible and refers to all neighboring node types that may not be included in the meta-paths specified for HAN. Thus, HGT overcomes the limitations of GraphSAGE and HAN.
This more fine-grained architecture helps HGT to capture the richer semantic nature of educational recommendations, where not only different types of nodes but also different types of relations play an important role.
Accordingly, the performance gap will be especially noticeable for recommendations that include several types of nodes and complex relation chains. For simpler recommendations consisting of low-type or short chains, the difference between the models will be minimal.
Table 6 shows the comparison of evaluation results for the recommendation model based on the three HGT layers for the short and long paths from «CUA–MasteredSkill–Vacancy», «Vacancy–Skill–Mskill-MCourse» and «CUA–MasteredSkill–Vacancy–Skill–Mskill-MCourse» over the heterogeneous graph.

Table 6.
Evaluation results of the trained recommendation model based on the three HGT layers for short and long paths.
Table 6 demonstrates that short meta-paths have least value of RMSE and maximum values of Precision@k, Recall@k, MAP@k, NDCG@k. Long meta-paths demonstrate worse values of RMSE and other metrics. The longer the meta-path, the greater the difference between the training and test sets, for example, Precision@5: 0.8372–0.5500, the more the model is overfitted and its generalization ability is weakened. Short meta-paths provide better ranking than long, for example, on the test set NDCG@k5: 0.9804–0.7159. As k increases, there is a decrease in Precision@k and an increase in Recall@k, MAP@k, and NDCG@k, but for long meta-paths, Precision@k decreases more smoothly. From these observations, we can conclude that short meta-paths demonstrate better results and are more suitable for recommendations based on HGT layers.
Thus, for the task of link regression and the development of a recommendation system over a heterogeneous graph, the HGT model is more favorable—particularly in terms of ranking performance and selecting the top-k most relevant links.
Table 7 presents a comparative analysis of link prediction and link weights prediction across homogeneous and heterogeneous graphs.

Table 7.
Comparison of link prediction and link weight prediction models across different types of graphs.
Table 7 shows link prediction problems typically use metrics to evaluate the quality of binary classification models, while regression evaluation metrics are used to evaluate link weight prediction models. As can be seen from MSE and RMSE, classical methods are more accurate for homogeneous graphs; however, using modern methods, comparable results can be achieved for predicting connections on short meta-paths between the source and destination nodes in heterogeneous graphs. Although the HAN and HGT architectures are known, the article demonstrates for the first time how to apply them to the problem of link regression in a heterogeneous graph combining such diverse sources as university competencies, vacancies from hh.kz, and Coursera courses in a multilingual context. Our work significantly expands the possibilities of applying GNNs in complex heterogeneous graphs.
Table 8 compares approaches using knowledge graphs in an educational context and integrating professional and educational skills.

Table 8.
Comparison of skills integration in knowledge graphs from different data sources in an educational context.
Table 8 shows that in the integration of educational and professional contexts based on knowledge graphs, the application of language models and recommendation engines evolves from the most classical to the advanced ones; for example, the classical language algorithms FastText and Word2Vec were successfully replaced by Bert, SBert, and LLM. However, some experts note that specifically trained language models sometimes outperform general LLMs in solving narrow tasks [35]. Recommendation engines also shift from simple semantic searches on knowledge graphs to advanced training of graph neural networks on meta-paths. Upon comparison with other approaches, it can be noted that other approaches mainly build graphs from one or two data sources, while our approach combines three sources. Our approach is multilingual and uses a multilingual language model and advanced architecture on HGT. Thus, our approach is distinguished by comprehensive content coverage, multilingualism, and advanced architecture based on HGT.
4. Conclusions
This study addressed the link weights prediction task between user competencies and online courses in the context of developing curriculum–vacancy–course recommendation models using heterogeneous knowledge graphs. Although the HAN and HGT architectures are known, how to apply them to the problem of link regression was demonstrated for the first time. The graph integrated data from a university curriculum, real job vacancies, and Coursera courses. To solve this task, three graph neural network–based recommendation models were developed and evaluated: HGTConv, SAGEConv, and HANConv.
Experimental results demonstrated that the HGTConv-based model achieved superior ranking quality on key metrics such as MAP@k and NDCG@k, on both the training and test subgraphs. The SAGEConv- and HANConv-based models showed lower performance. Comparison of short and long meta-paths demonstrated better results for short paths.
Future research will focus on further improving the HGT-based recommendation model, comparing the contribution of different meta-paths, and expanding the dataset with new data to improve training efficiency.
The obtained results confirm the potential of applying GNN models on heterogeneous graphs for more accurate and interpretable recommendations of educational content. Attention mechanisms sensitive to node and edge types allow for modeling the structural and semantic complexity of educational and career pathways. This approach opens up promising directions for the development of intelligent learning support systems that adapt to individual user needs and labor market demands.
Author Contributions
Methodology, A.Y. and G.K.; Software, V.R.; Validation, Z.S.; Data curation, M.S. and S.S.; Visualization, Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been funded by the Science Committee of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan (Grant No. AP22783030).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wu, Z.; Pan, S.; Chen, F.; Long, G.; Zhang, C.; Yu, P.S. A comprehensive survey on graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, W.; Wu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, T.; Chen, Q.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y. A survey of graph neural networks in real world: Imbalance, noise, privacy and OOD challenges. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.04468. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2403.04468 (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- Dai, E.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yu, P.S. A comprehensive survey on trustworthy graph neural networks: Privacy, robustness, fairness, and explainability. Front. Comput. Sci. 2024, 18, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, C.; Tao, D. A survey on graph neural networks for time series: Forecasting, classi-fication, imputation, and anomaly detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.03759. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.03759 (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- Khemani, B.; Patil, S.; Kotecha, K.; Tanwar, S. A review of graph neural networks: Concepts, architectures, techniques, challenges, datasets, applications, and future directions. J. Big Data 2024, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Xu, J. Rewiring techniques to mitigate oversquashing and oversmoothing in GNNs: A survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.17429. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2411.17429 (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- Akansha, S. Over-squashing in Graph Neural Networks: A comprehensive survey. Neurocomputing 2025, 642, 130389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Sun, F.; Zhang, W.; Xie, X.; Cui, B. Graph neural networks in recommender systems: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zheng, Y.; Li, N.; Li, Y.; Qin, Y.; Piao, J.; Quan, Y.; Chang, J.; Jin, D.; He, X.; et al. A survey of graph neural networks for recommender systems: Challenges, methods, and directions. ACM Trans. Recomm. Syst. 2023, 1, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duricic, T.; Kowald, D.; Lacic, E.; Lex, E. Beyond-accuracy: A review on diversity, serendipity, and fairness in recommender systems based on graph neural networks. Front. Big Data 2023, 6, 1251072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, J.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Yin, D.; Shi, C. Graph Foundation Models for Recommendation: A Comprehensive Survey. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.08346. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2502.08346 (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- Gharizadeh, A.; Abbasi, K.; Ghareyazi, A.; Mofrad, M.R.K.; Rabiee, H.R. HGTDR: Advancing drug repurposing with heterogeneous graph transformers. Bioinformatics 2024, 40, btae349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, C.; Han, Y.; Xu, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, K.; Su, Y. A community detection and graph-neural-network-based link prediction approach for scientific literature. Mathematics 2024, 12, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Yeung, D.-Y. Temporal link prediction: A unified framework, taxonomy, and review. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 56, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Pu, C.; Shu, X.; Xia, Y.; Xia, C. Line graph neural networks for link weight prediction. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2025, 661, 130406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Holder, L.B. Link weight prediction with node embeddings. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.07312. [Google Scholar]
- Zulaika, U.; Sánchez-Corcuera, R.; Almeida, A.; López-De-Ipiña, D. LWP-WL: Link weight prediction based on CNNs and the Weisfeiler-Lehman algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 120, 108657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Ma, Y.; Li, Q.; He, Y.; Zhao, E.; Tang, J.; Yin, D. Graph Neural Networks for Social Recommendation. In Proceedings of The World Wide Web Conference (WWW ‘19), New York, NY, USA, 13–17 May 2019; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 417–426. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ji, H.; Shi, C.; Wang, B.; Ye, Y.; Cui, P.; Yu, P.S. Heterogeneous graph attention network. In Proceedings of the World Wide Web Conference, New York, NY, USA, 13–17 May 2019; pp. 2022–2032. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Wang, K.; Sun, Y. Heterogeneous graph transformer. In Proceedings of the Web Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, 20–24 April 2020; pp. 2704–2710. [Google Scholar]
- Ramazanova, V.; Sambetbayeva, M.; Serikbayeva, S.; Sadirmekova, Z.; Yerimbetova, A. Development of a Knowledge Graph-Based Model for Recommending MOOCs to Supplement University Educational Programs in Line With Employer Requirements. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 193313–193331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, S.; Lerman, G. The effect of Leaky ReLUs on the training and generalization of overparameterized net-works. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.11942. [Google Scholar]
- Pytorch-Geometric. Link Regression on MovieLens. Available online: https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1N3LvAO0AXV4kBPbTMX866OwJM9YS6Ji2?usp=sharing#scrollTo=Ptk1J307IVn8 (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- Zhong, M.; Wu, Z.; Honda, N. Deep Learning Based Dense Retrieval: A Comparative Study. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.20315. [Google Scholar]
- Jakobs, M.; Liebig, T. AALF: Almost Always Linear Forecasting. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.10142. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, F.; Liang, T.; Liu, H. Service recommendation method based on text view and interaction view. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StellarGraph. HinSAGE Link Prediction Demonstration. Available online: https://stellargraph.readthedocs.io/en/stable/demos/link-prediction/hinsage-link-prediction.html (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- Giabelli, A.; Malandri, L.; Mercorio, F.; Mezzanzanica, M.; Seveso, A. Skills2Job: A recommender system that encodes job offer embeddings on graph databases. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 101, 107049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S. Graph-Community-Enabled personalized course-job recommendations with cross-domain data integration. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichselbraun, A.; Waldvogel, R.; Fraefel, A.; van Schie, A.; Kuntschik, P. Building knowledge graphs and recommender systems for suggesting reskilling and upskilling options from the web. Information 2022, 13, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fettach, Y.; Ghogho, M.; Benatallah, B. Knowledge graphs in education and employability: A survey on applications and techniques. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 80174–80183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troussas, C.; Krouska, A.; Tselenti, P.; Kardaras, D.K.; Barbounaki, S. Enhancing Personalized Educational Content Recommendation through Cosine Similarity-Based Knowledge Graphs and Contextual Signals. Information 2023, 14, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Henriksson, A.; Duneld, M.; Nouri, J.; Wu, Y. Evaluating Embeddings from Pre-Trained Language Models and Knowledge Graphs for Educational Content Recommendation. Futur. Internet 2024, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y. Enhancing Knowledge-Concept Recommendations with Heterogeneous Graph-Contrastive Learning. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamieh, I.; Zesch, T.; Giebermann, K. LLMs in Short Answer Scoring: Limitations and Promise of Zero-Shot and Few-Shot Approaches. In Proceedings of the 19th Workshop on Innovative Use of NLP for Building Educational Applications (BEA 2024), Mexico City, Mexico, 20 June 2024; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2024; pp. 309–315. Available online: https://aclanthology.org/2024.bea-1.25.pdf (accessed on 30 July 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).