Electrospinning of Chitosan–Halloysite Nanotube Biohybrid Mats for Clobetasol Propionate Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of Biocomposite Mats by Electrospinning Technique
2.3. Electrospun Mat Characterization
2.4. Drug Release Kinetics
2.5. In Vitro Study of Cytotoxicity and Anti-Inflammatory Activity on the THP-1 Cell Line Model
2.6. In Vitro Study of Cytotoxicity and Adhesion on the MSC Model
3. Results and Discussion
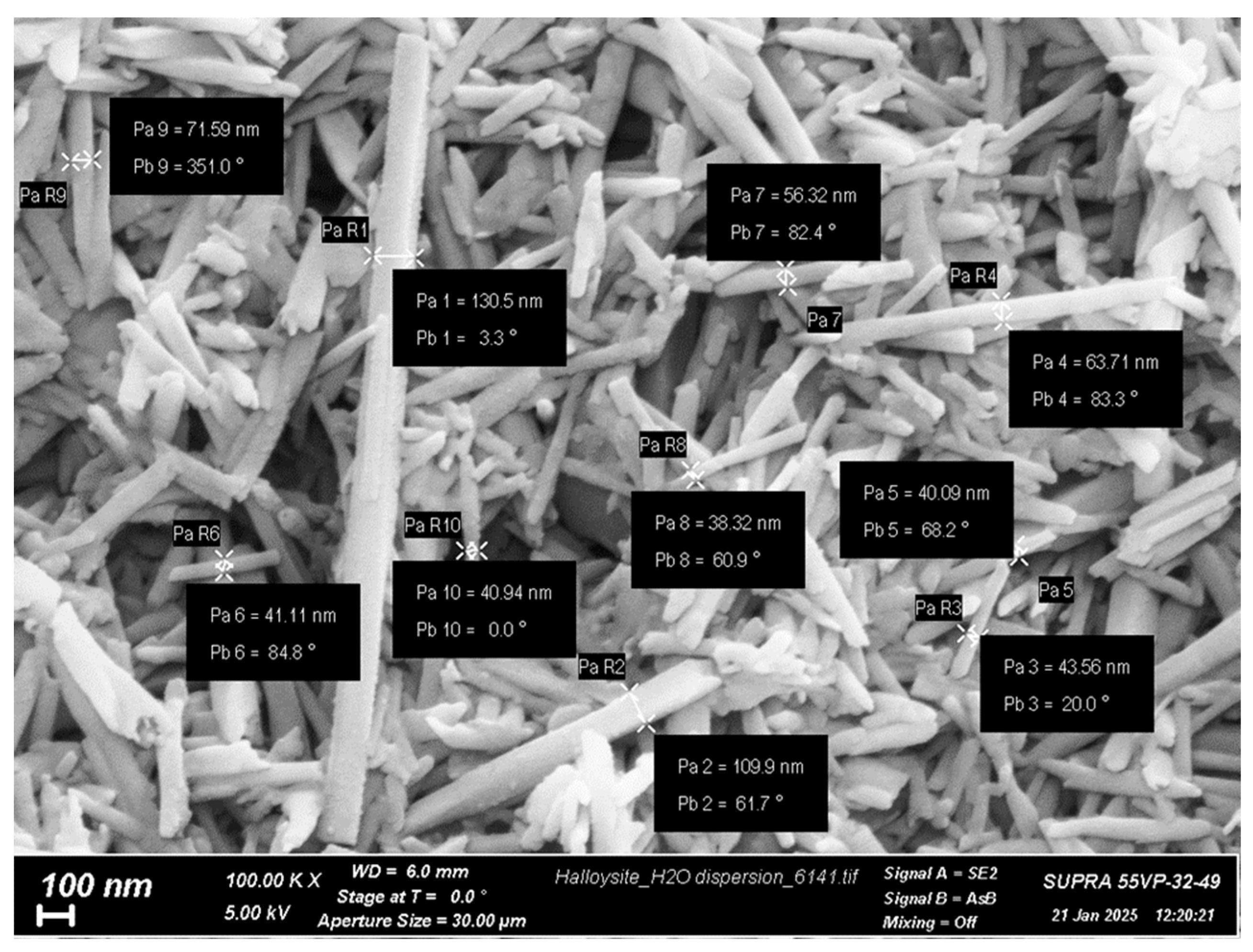
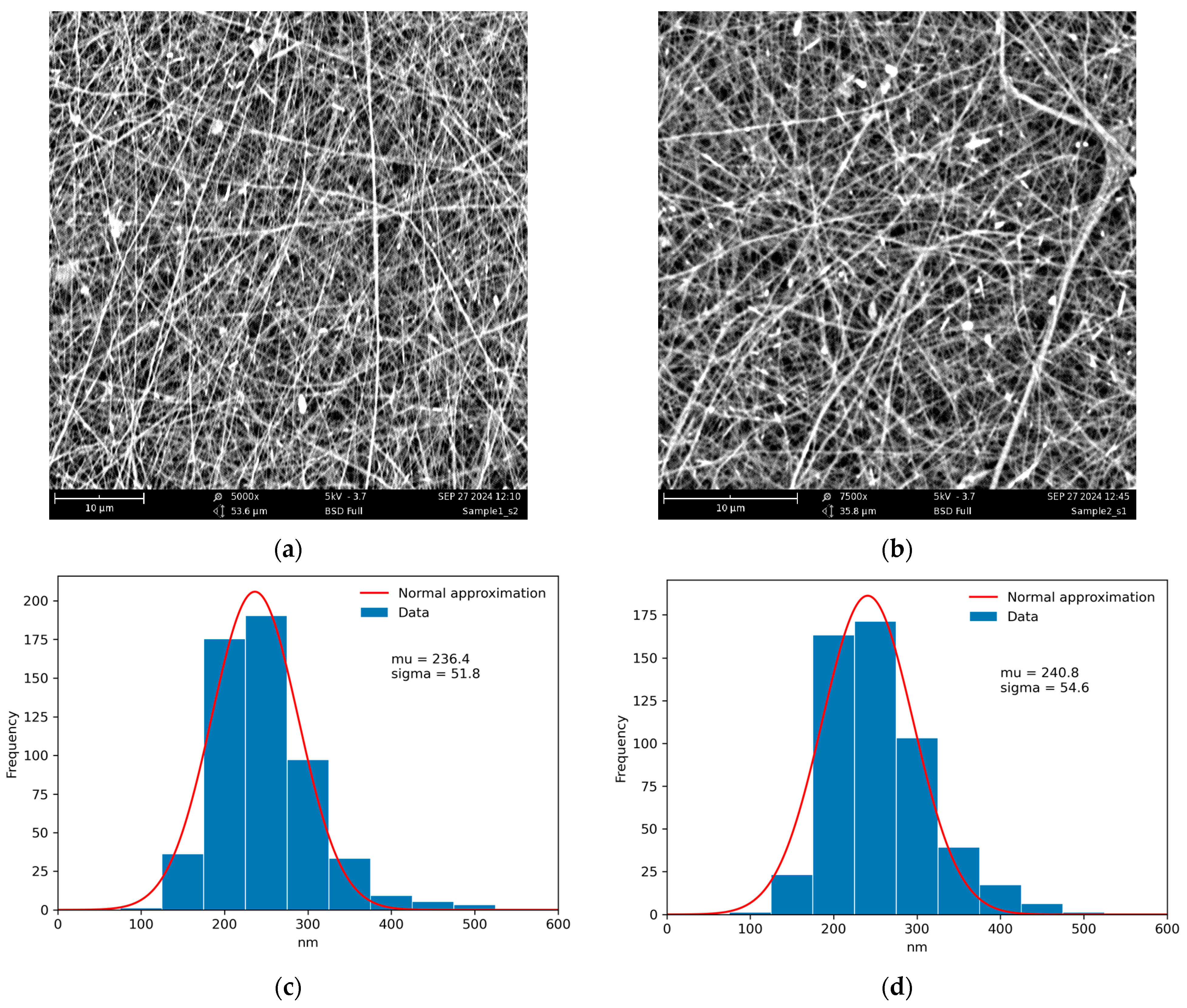
3.1. Electrospinning of Composite CS-HNT and CS-HNT-CP Mats
3.2. Swelling of Electrospun Mats
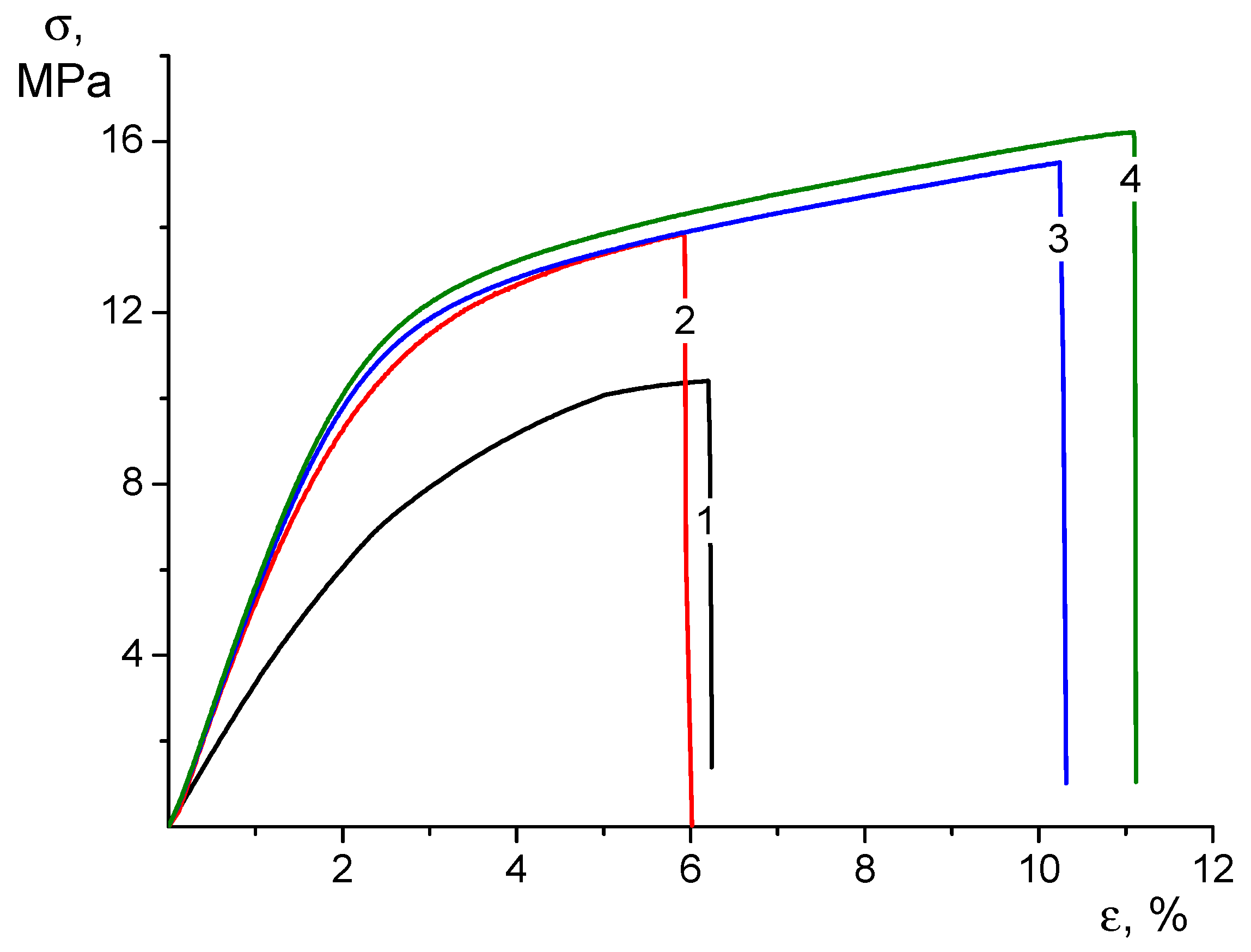
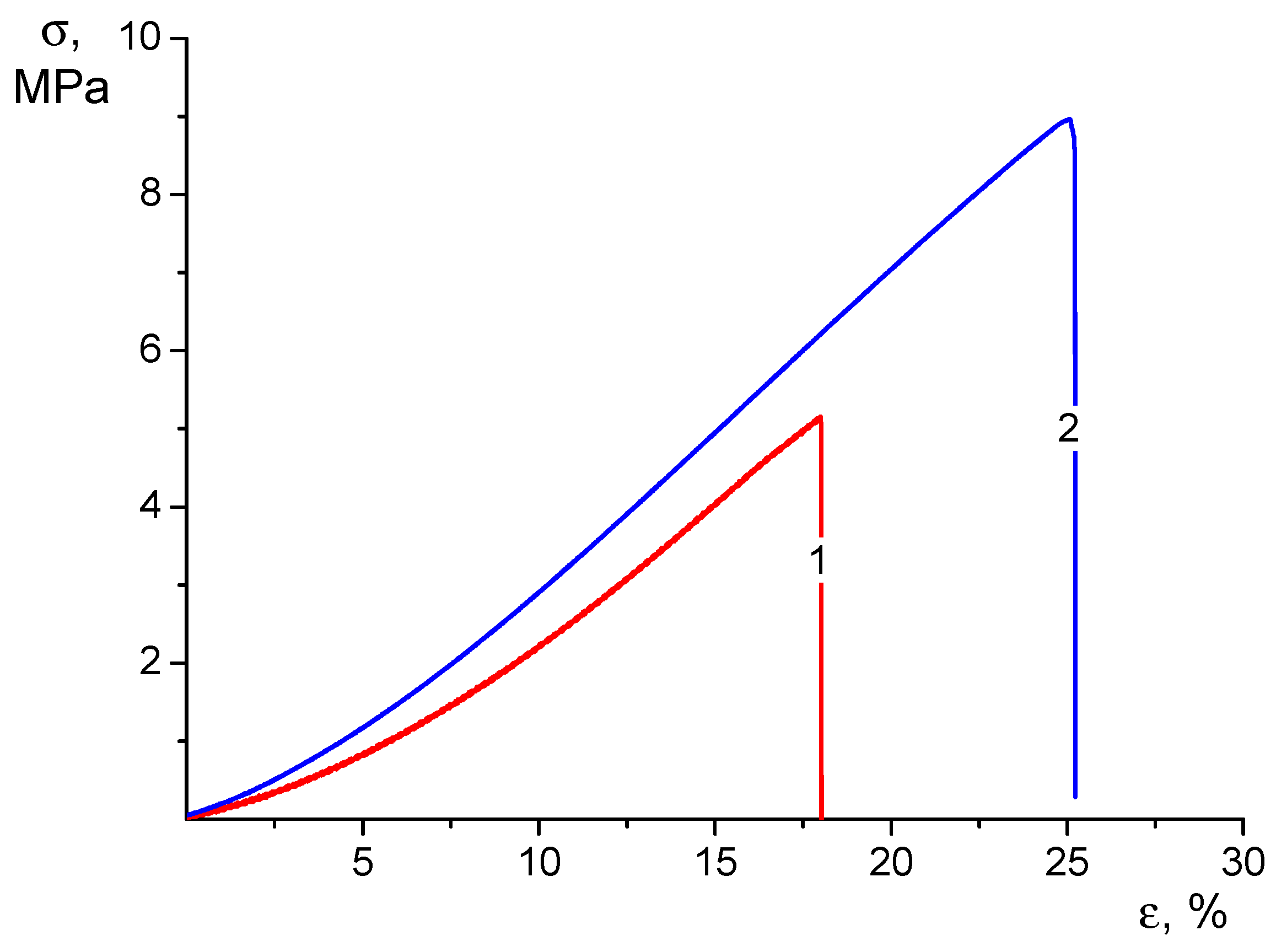
3.3. Mechanical Properties of Electrospun Mats
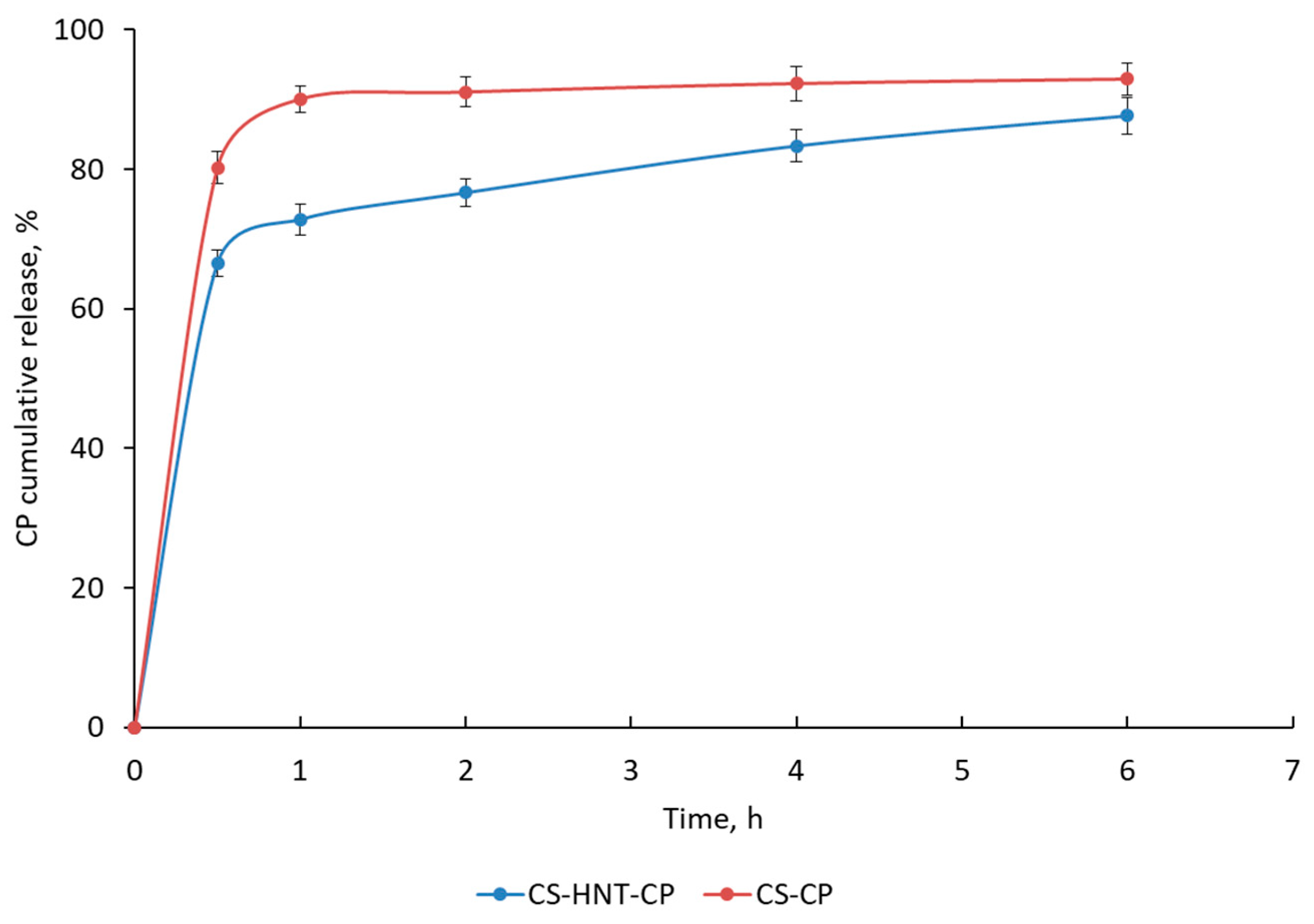
3.4. Release Kinetics of CP from the CS-HNT-CP Mat
3.5. In Vitro Study of Cytotoxicity and Anti-Inflammatory Activity
3.6. In Vitro Study of Cytotoxicity and Cell Adhesion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dott, C.; Tyagi, C.; Tomar, L.K.; Choonara, Y.E.; Kumar, P.; du Toit, L.C.; Pillay, V. A mucoadhesive electrospun nanofibrous matrix for rapid oramucosal drug delivery. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 924947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubashynskaya, N.V.; Petrova, V.A.; Skorik, Y.A. Biopolymer drug delivery systems for oromucosal application: Recent trends in pharmaceutical r&d. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega-Avila, A.L.; Perales-Perez, O.; Valentín Rullan, R. Biopolymers nanofibers for biomedical applications and environmental applications. In Electrospun Biomaterials and Related Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 109–147. [Google Scholar]
- Luraghi, A.; Peri, F.; Moroni, L. Electrospinning for drug delivery applications: A review. J. Control. Release 2021, 334, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanaswamy, R.; Torchilin, V.P. Hydrogels and their applications in targeted drug delivery. In The Road from Nanomedicine to Precision Medicine; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2020; pp. 1117–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Eslamian, M.; Khorrami, M.; Yi, N.; Majd, S.; Abidian, M.R. Electrospinning of highly aligned fibers for drug delivery applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Windbergs, M. Controlled dual drug release by coaxial electrospun fibers–impact of the core fluid on drug encapsulation and release. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 556, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikmaram, N.; Roohinejad, S.; Hashemi, S.; Koubaa, M.; Barba, F.J.; Abbaspourrad, A.; Greiner, R. Emulsion-based systems for fabrication of electrospun nanofibers: Food, pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 28951–28964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opriș, O.; Mormile, C.; Lung, I.; Stegarescu, A.; Soran, M.-L.; Soran, A. An overview of biopolymers for drug delivery applications. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, E.; Ridolfo, A.; Neri, G. Thermally activated noble metal nanoparticles incorporated in electrospun fiber-based drug delivery systems. Curr. Nanomater. 2019, 4, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Li, P.; Jin, X.; Su, F.; Shen, J.; Yuan, J. Poly (ε-caprolactone)/keratin/heparin/vegf biocomposite mats for vascular tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2020, 108, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, R.T.; Kraemer, R.; Lopez-Rubio, A.; Torres-Giner, S.; Ocio, M.J.; Lagarón, J.M. Extraction of microfibrils from bacterial cellulose networks for electrospinning of anisotropic biohybrid fiber yarns. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 4201–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somord, K.; Somord, K.; Suwantong, O.; Thanomsilp, C.; Peijs, T.; Soykeabkaew, N. Self-reinforced poly (lactic acid) nanocomposites with integrated bacterial cellulose and its surface modification. Nanocomposites 2018, 4, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.G.; Fajardo, A.R.; Gerola, A.P.; Rodrigues, J.H.; Nakamura, C.V.; Muniz, E.C.; Hsieh, Y.-L. First report of electrospun cellulose acetate nanofibers mats with chitin and chitosan nanowhiskers: Fabrication, characterization, and antibacterial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 250, 116954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseri, N.; Algan, C.; Jacobs, V.; John, M.; Oksman, K.; Mathew, A.P. Electrospun chitosan-based nanocomposite mats reinforced with chitin nanocrystals for wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 109, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalvandi, J.; White, M.; Truong, Y.B.; Gao, Y.; Padhye, R.; Kyratzis, I.L. Release and antimicrobial activity of levofloxacin from composite mats of poly (ɛ-caprolactone) and mesoporous silica nanoparticles fabricated by core–shell electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 7967–7974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, W.; Jia, Y.; Chang, A.; Mo, X.; Wang, H.; He, C. Electrospun nanofibers incorporating self-decomposable silica nanoparticles as carriers for controlled delivery of anticancer drug. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 65897–65904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, C.J.; Wright, C.J. The fabrication of iron oxide nanoparticle-nanofiber composites by electrospinning and their applications in tissue engineering. Biotechnol. J. 2017, 12, 1600693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, V.A.; Poshina, D.N.; Golovkin, A.S.; Mishanin, A.I.; Zhuravskii, S.G.; Yukina, G.Y.; Naumenko, M.Y.; Sukhorukova, E.G.; Savin, N.A.; Erofeev, A.S. Electrospun composites of chitosan with cerium oxide nanoparticles for wound healing applications: Characterization and biocompatibility evaluation in vitro and in vivo. Polymers 2024, 16, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zienkiewicz-Strzałka, M.; Deryło-Marczewska, A.; Skorik, Y.A.; Petrova, V.A.; Choma, A.; Komaniecka, I. Silver nanoparticles on chitosan/silica nanofibers: Characterization and antibacterial activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahimizadeh, M.; Wong, L.W.; Baifa, Z.; Sadjadi, S.; Auckloo, S.A.B.; Palaniandy, K.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Tan, J.B.L.; Singh, R.R.; Yuan, P. Halloysite clay nanotubes: Innovative applications by smart systems. Appl. Clay Sci. 2024, 251, 107319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledano-Magaña, Y.; Flores-Santos, L.; de Oca, G.M.; González-Montiel, A.; García-Ramos, J.-C.; Mora, C.; Saavedra-Ávila, N.-A.; Gudiño-Zayas, M.; González-Ramírez, L.-C.; Laclette, J.P.; et al. Toxicological evaluations in macrophages and mice acutely and chronically exposed to halloysite clay nanotubes functionalized with polystyrene. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 29882–29892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danyliuk, N.; Tomaszewska, J.; Tatarchuk, T. Halloysite nanotubes and halloysite-based composites for environmental and biomedical applications. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 309, 113077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobaraki, M.; Karnik, S.; Li, Y.; Mills, D.K. Therapeutic applications of halloysite. Appl. Sci. 2021, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.W.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Arabi, A.M.; Keeling, J.; Tan, J.B.L. Halloysite nanotubes from various geological deposits: New insights to acid etching and their impacts on products’ characteristics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohidi, S.; Ghaee, A.; Barzin, J. Preparation and characterization of poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid)/chitosan electrospun membrane containing amoxicillin-loaded halloysite nanoclay. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2016, 27, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.Y.; Prajapati, N.; DeCoster, M.A.; Lvov, Y. Tagged halloysite nanotubes as a carrier for intercellular delivery in brain microvascular endothelium. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CeCe, R.; Jining, L.; Islam, M.; Korvink, J.G.; Sharma, B. An overview of the electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for biomedical applications related to drug delivery. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2024, 26, 2301297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubashynskaya, N.V.; Skorik, Y.A. Patches as polymeric systems for improved delivery of topical corticosteroids: Advances and future perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofi, H.S.; Abdal-Hay, A.; Ivanovski, S.; Zhang, Y.S.; Sheikh, F.A. Electrospun nanofibers for the delivery of active drugs through nasal, oral and vaginal mucosa: Current status and future perspectives. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 111, 110756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wydro, P.; Krajewska, B.; Hac-Wydro, K. Chitosan as a lipid binder: A langmuir monolayer study of chitosan− lipid interactions. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2611–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzarelli, R.; Frega, N.; Miliani, M.; Muzzarelli, C.; Cartolari, M. Interactions of chitin, chitosan, n-lauryl chitosan and n-dimethylaminopropyl chitosan with olive oil. Carbohydr. Polym. 2000, 43, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeini, A.; Pedram, P.; Makvandi, P.; Malinconico, M.; d’Ayala, G.G. Wound healing and antimicrobial effect of active secondary metabolites in chitosan-based wound dressings: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 233, 115839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ju, J.; Yan, H.; Huang, X.; Tan, Y. Advances in halloysite nanotubes–polysaccharide nanocomposite preparation and applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, Z.; Murdoch, C.; Hansen, J.; Siim Madsen, L.; Colley, H.E. Corticosteroid delivery using oral mucosa equivalents for the treatment of inflammatory mucosal diseases. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2021, 129, e12761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colley, H.; Said, Z.; Santocildes-Romero, M.; Baker, S.; D’Apice, K.; Hansen, J.; Madsen, L.S.; Thornhill, M.; Hatton, P.; Murdoch, C. Pre-clinical evaluation of novel mucoadhesive bilayer patches for local delivery of clobetasol-17-propionate to the oral mucosa. Biomaterials 2018, 178, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Moles, M.A.; Morales, P.; Rodriguez-Archilla, A.; Isabel, I.R.-A.; Gonzalez-Moles, S. Treatment of severe chronic oral erosive lesions with clobetasol propionate in aqueous solution. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2002, 93, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvidzayi, M.; Rath, S.; Bon, C.; Abboo, S.; Kanfer, I. A novel approach to assess the potency of topical corticosteroids. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogodina, N.; Pavlov, G.; Bushin, S.; Mel’Nikov, A.; Lysenko, Y.B.; Nud’Ga, L.; Marsheva, V.; Marchenko, G.; Tsvetkov, V. Conformational characteristics of chitosan molecules as demonstrated by diffusion-sedimentation analysis and viscometry. Polym. Sci. USSR 1986, 28, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.R.; Loebenberg, R.; Almukainzi, M. Simulated biological fluids with possible application in dissolution testing. Dissolution Technol. 2011, 18, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubashynskaya, N.V.; Bokatyi, A.N.; Trulioff, A.S.; Rubinstein, A.A.; Kudryavtsev, I.V.; Skorik, Y.A. Development and bioactivity of zinc sulfate cross-linked polysaccharide delivery system of dexamethasone phosphate. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, V.A.; Khripunov, A.K.; Golovkin, A.S.; Mishanin, A.I.; Gofman, I.V.; Romanov, D.P.; Migunova, A.V.; Arkharova, N.A.; Klechkovskaya, V.V.; Skorik, Y.A. Bacterial cellulose (komagataeibacter rhaeticus) biocomposites and their cytocompatibility. Materials 2020, 13, 4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poshina, D.N.; Khadyko, I.A.; Sukhova, A.A.; Serov, I.V.; Zabivalova, N.M.; Skorik, Y.A. Needleless electrospinning of a chitosan lactate aqueous solution: Influence of solution composition and spinning parameters. Technologies 2019, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Sahlin, J.J. Hydrogels as mucoadhesive and bioadhesive materials: A review. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, N.; Dutta, J. Development and in vitro characterization of chitosan/starch/halloysite nanotubes ternary nanocomposite films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 127, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucard, N.; Viton, C.; Domard, A. New aspects of the formation of physical hydrogels of chitosan in a hydroalcoholic medium. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 3227–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darbasi, M.; Askari, G.; Kiani, H.; Khodaiyan, F. Development of chitosan based extended-release antioxidant films by control of fabrication variables. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalonek, J. Surface and thermal behavior of chitosan/poly (ethylene oxide) blends. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2016, 640, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luan, S.; Yuan, Z.; Lin, C.; Fan, S.; Wang, S.; Ma, C.; Wu, S. Therapeutic effect of platelet-rich plasma on glucocorticoid-induced rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 151. [Google Scholar]


| Solution Composition | HNTs, % (by Weight of CS) | Voltage, kV |
|---|---|---|
| 2% CS, 20% PEO (by CS mass), 50% acetic acid | 2 4 6 8 | 23 |
| 2% CS, 20% PEO (by CS mass), 50% acetic acid, 20% ethanol | 2 4 6 8 | 23 |
| 2% CS, 20% PEO (by CS mass), 5% acetic acid | 2 4 6 8 | not spinable |
| 2% CS, 20% PEO (by CS mass), 5% acetic acid, 20% ethanol | 2 4 6 8 | 45 25 35 44 |
| Sample | Swelling Capacity (g/g) | |
|---|---|---|
| In Water | In 0.9% NaCl Solution | |
| CS-CP | 3.7 | 3.5 |
| CS-HNT | 3.1 | 2.7 |
| CS-HNT-CP | 3.6 | 3.4 |
| Sample | E (MPa) | σy, (MPa) | σb (MPa) | εb (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS-0 | 398 ± 9 | 9.4 ± 0.4 | 10.1 ± 0.8 | 6.2 ± 0.8 |
| CS-HNT | 546 ± 65 | 12.1 ± 0.3 | 14.3 ± 0.9 | 5.9 ± 0.3 |
| CS-CP | 620 ± 85 | 11.9 ± 0.8 | 15.3 ± 0.7 | 10.3 ± 0.3 |
| CS-HNT-CP | 632 ± 56 | 12.2 ± 0.9 | 16.2 ± 1.2 | 11.0 ± 2.0 |
| Sample | E (MPa) | σy, (MPa) | σb (MPa) | εb (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS-CP | 13.3 ± 0.9 | - | 5.1 ± 0.5 | 18 ± 1 |
| CS-HNT-CP | 17.8 ± 0.9 | - | 7.1 ± 0.8 | 25 ± 1 |
| Sample | Without Addition of TNFα | With the Addition of 10 ng/mL TNFα |
|---|---|---|
| Negative control | 95.92 (95.23; 96.45) | 94.44 (94.30; 94.59) |
| CP | 95.57 (94.37; 96.66) | 93.90 (91.78; 95.89) |
| CS-HNT-CP | 96.14 (95.67; 96.63) | 94.75 (94.03; 95.64) |
| CS-HNT | 95.80 (94.65; 96.75) | 93.74 (91.55; 95.18) |
| Sample | Without Addition TNFα | With the Addition of 10 ng/mL TNFα |
|---|---|---|
| Negative control | 0.583 (0.543; 0.596) * | 1.929 (1.735; 2.420) * |
| CP | 0.616 (0.607; 0.657) | 0.931 (0.846; 1.090) |
| CS-HNT-CP | 0.566 (0.540; 0.574) | 0.933 (0.899; 1.015) ** |
| CS-HNT | 0.567 (0.565; 0.579) | 1.106 (0.986; 1.341) ** |
| Sample | Number of Cells |
|---|---|
| CS-HNT | 70.9 ± 4.0 |
| CS-HNT-CP | 13.1 ± 1.0 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dubashynskaya, N.V.; Petrova, V.A.; Kudryavtsev, I.V.; Trulioff, A.S.; Rubinstein, A.A.; Golovkin, A.S.; Mishanin, A.I.; Murav’ev, A.A.; Gofman, I.V.; Poshina, D.N.; et al. Electrospinning of Chitosan–Halloysite Nanotube Biohybrid Mats for Clobetasol Propionate Delivery. Technologies 2025, 13, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13030090
Dubashynskaya NV, Petrova VA, Kudryavtsev IV, Trulioff AS, Rubinstein AA, Golovkin AS, Mishanin AI, Murav’ev AA, Gofman IV, Poshina DN, et al. Electrospinning of Chitosan–Halloysite Nanotube Biohybrid Mats for Clobetasol Propionate Delivery. Technologies. 2025; 13(3):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13030090
Chicago/Turabian StyleDubashynskaya, Natallia V., Valentina A. Petrova, Igor V. Kudryavtsev, Andrey S. Trulioff, Artem A. Rubinstein, Alexey S. Golovkin, Alexander I. Mishanin, Anton A. Murav’ev, Iosif V. Gofman, Daria N. Poshina, and et al. 2025. "Electrospinning of Chitosan–Halloysite Nanotube Biohybrid Mats for Clobetasol Propionate Delivery" Technologies 13, no. 3: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13030090
APA StyleDubashynskaya, N. V., Petrova, V. A., Kudryavtsev, I. V., Trulioff, A. S., Rubinstein, A. A., Golovkin, A. S., Mishanin, A. I., Murav’ev, A. A., Gofman, I. V., Poshina, D. N., & Skorik, Y. A. (2025). Electrospinning of Chitosan–Halloysite Nanotube Biohybrid Mats for Clobetasol Propionate Delivery. Technologies, 13(3), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13030090









