Design for Assembly of a Confocal System Applied to Depth Profiling in Biological Tissue Using Raman Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Instrumental Test
2.3. Anatomy and Optical Characteristics of the Index Fingernail and Fingertip
3. Results
3.1. Confocal Volume
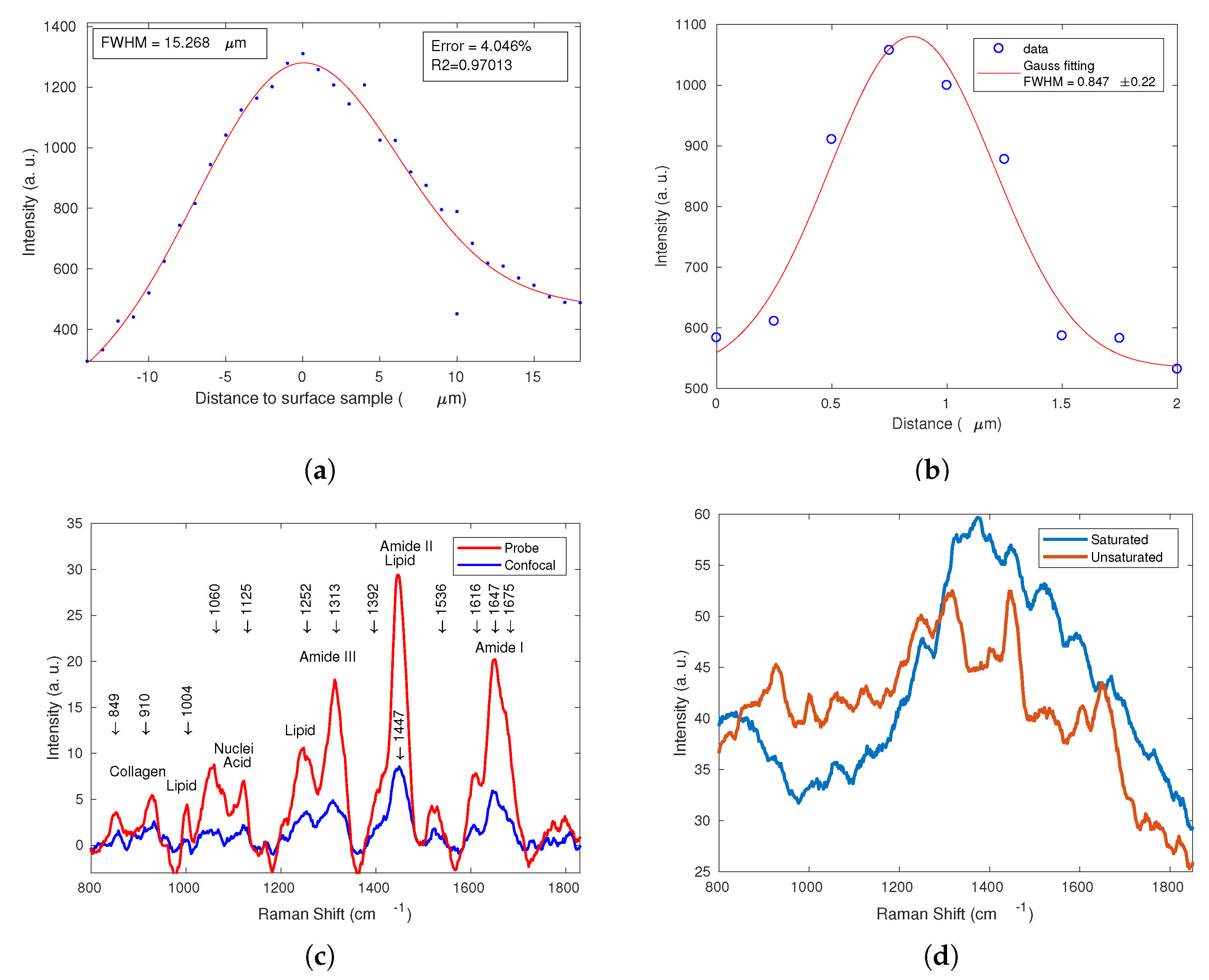
3.1.1. Spatial Resolution
3.1.2. Lateral Resolution
3.2. Comparison of Raman Spectra: RPB-785 vs. CRS System
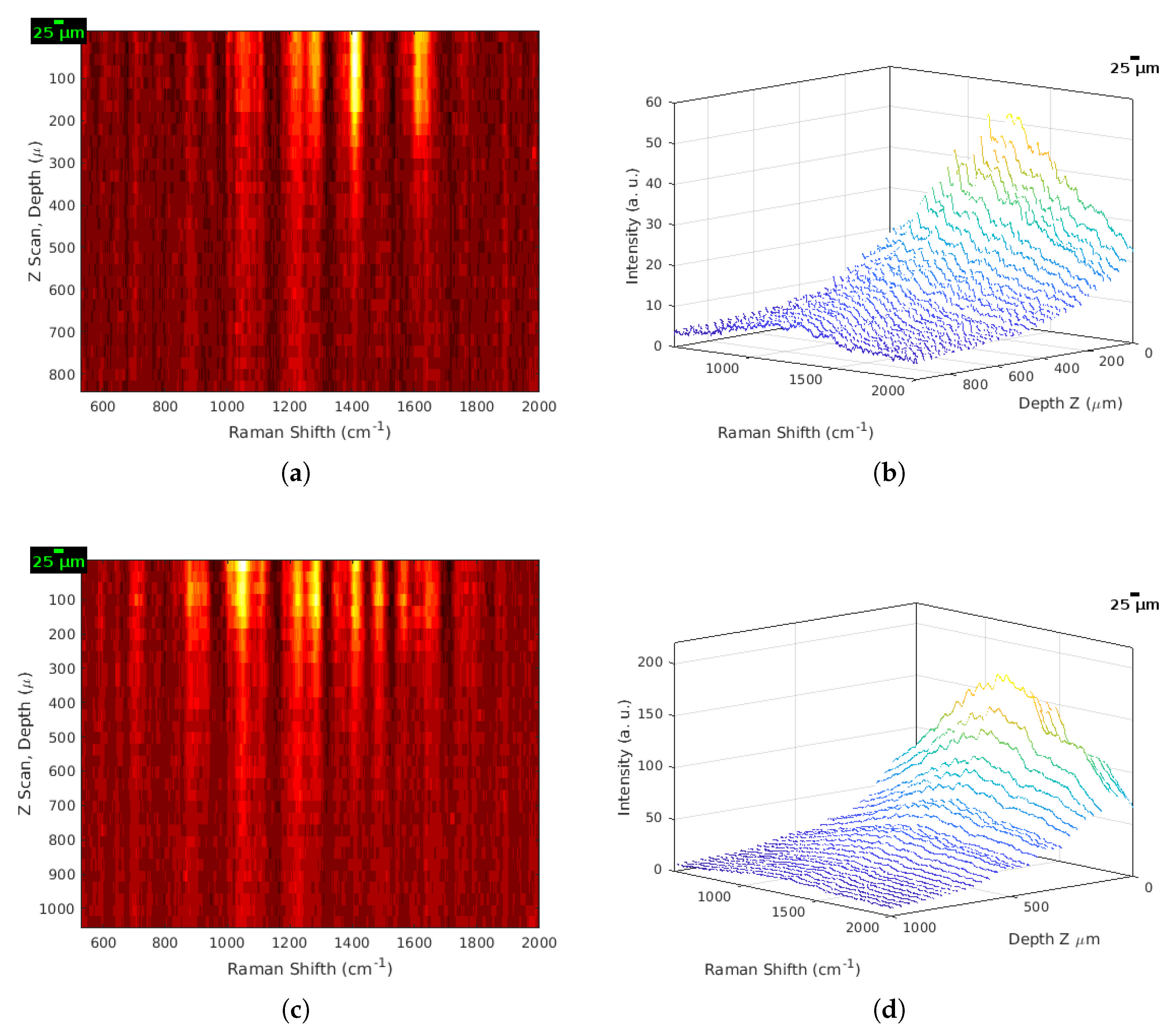
3.3. Protocol for the Acquisition of Raman Spectra In Vivo
- Laser power was limited to 30 mW for each acquired spectrum.
- Exposure time per spectrum was set to 25 s.
- The volunteers remained motionless, relaxed and breathing gently.
- The index finger was placed on a pad to ensure stability.
- The maximum intensity recorded was defined as the signal from the sample surface (Z = 0).
- At Z = 0, three consecutive spectra were acquired to estimate variability, yielding 5.75%.
- Only one spectrum was acquired at each depth step to avoid prolonged exposure at the same focal point.
- If a volunteer moved and the laser spot shifted from the target area then the measurement was interrupted and resumed only after the subject had relaxed.
3.4. Processing of Spectral Data
3.5. Generation of 2D and 3D Images from Raw Raman Spectra
Amide I Secondary Components as Biomarkers for Distinguishing Healthy and Diabetic Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CRS | Confocal Raman Spectroscopy |
| RPB | Raman Probe |
| LWD | Long Working Distance |
| ANSI | American National Standards Institute |
| RS | Raman Spectroscopy |
| CCD | Charge Coupled Device |
| SRS | Standard Raman System |
| FWHM | Full Width at Half Maximum |
| CNTs | Carbon Nanotubes |
References
- Smith, E.; Dent, G. Modern Raman Spectroscopy: A Practical Approach, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briancon, S.; Bolzinger, M.-A.; Chevalier, Y. Confocal Raman Spectroscopy as a Tool to Investigate the Action of Penetration Enhancers Inside the Skin. In Percutaneous Penetration Enhancers Drug Penetration Into/Through the Skin: Methodology and General Considerations; Dragicevic, E.N., Maibach, H.I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toporski, J.; Dieing, T.; Hollricher, O. (Eds.) Confocal Raman Microscopy; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.F.M.; Rodrigues, B.V.M.; Neto, L.P.M.; Lopes, L.d.; da Costa, A.L.F.; Santos, A.S.; Viana, B.C.; Tosato, M.G.; Silva, G.C.d.; Gusmão, G.O.M.; et al. Confocal Raman spectroscopy as a tool to assess advanced glycation end products on solar-exposed human skin. Vib. Spectrosc. 2021, 114, 103234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, M.G.; Wilson, B.C. Development of an In Vivo Raman Spectroscopic System for Diagnostic Applications. J. Raman Spectrosc. 1997, 28, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrit, L.; Hadjur, C.; Morel, S.; Sockalingum, G.D.; Lebourdon, G.; Leroy, F.; Manfait, M. In vivo chemical investigation of human skin using a confocal Raman fiber optic microprobe. J. Biomed. Opt. 2005, 10, 044007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Elías, M.G.; González, F.J. Raman Spectroscopy for In Vivo Medical Diagnosis. In Raman Spectroscopy; InTech: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdala, J.M.d.; Lemos, F.R.; Almeida, R.M.d.; Tippavajhala, V.K.; da Silva, G.C.; Neto, L.P.M.; Fávero, P.P.; Martin, A.A. Noninvasive in vivo application of confocal Raman spectroscopy in identifying age-related biochemical changes in human stratum corneum and epidermis. Vib. Spectrosc. 2024, 130, 103627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghita, A.; Pascut, F.C.; Sottile, V.; Notingher, I. Monitoring the mineralisation of bone nodules in vitro by space- and time-resolved Raman micro-spectroscopy. Analyst 2013, 139, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://static.horiba.com/fileadmin/Horiba/Application/Health_Care/Pharmaceuticals_and_Medicine_Manufacturing/Cosmetics/In_Vivo_Raman_measurements_of_Human_Skin.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Darvin, M.E.; Schleusener, J.; Parenz, F.; Seidel, O.; Krafft, C.; Popp, J.; Lademann, J. Confocal Raman microscopy combined with optical clearing for identification of inks in multicolored tattooed skin in vivo. Analyst 2018, 143, 4990–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tfayli, A.; Piot, O.; Manfait, M. Confocal Raman microspectroscopy on excised human skin: Uncertainties in depth profiling and mathematical correction applied to dermatological drug permeation. J. Biophotonics 2008, 1, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, C.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. Depth profiles of hydrogen bound water molecule types and their relation to lipid and protein interaction in the human stratum corneum in vivo. Analyst 2016, 141, 6329–6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, C.; Schleusener, J.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. Keratin-water-NMF interaction as a three layer model in the human stratum corneum using in vivo confocal Raman microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippavajhala, V.K.; de Oliveira Mendes, T.; Martin, A.A. In Vivo Human Skin Penetration Study of Sunscreens by Confocal Raman Spectroscopy. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspers, P.J.; Bruining, H.A.; Puppels, G.J.; Lucassen, G.W.; Carter, E.A. In Vivo Confocal Raman Microspectroscopy of the Skin: Noninvasive Determination of Molecular Concentration Profiles. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 116, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocean Optics. Raman Lasers. Available online: https://www.oceanoptics.com/accessories/light-sources/raman-lasers/ (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- InPhotonics. Low-Cost Laboratory Fiber Optic Raman Probe (Datasheet). Available online: https://www.inphotonics.com/probeRPB.htm (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Ocean Optics. Legacy Spectrometers: A Historical Archive of Ocean Optics Spectrometers. Available online: https://www.oceanoptics.com/resources/legacy-spectrometers/ (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- BoliOptics. 20X Infinity-Corrected Plan Achromatic POL Polarizing Microscope Objective Lens Working Distance 2.71 mm with Black Finish. Available online: https://bolioptics.com/20x-infinity-corrected-plan-achromatic-pol-polarizing-microscope-objective-lens-working-distance-2-71mm-with-black-finish/ (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- BestScope. BS-5070BTR Binocular Polarizing Microscope. Available online: https://www.bestscope.net/bs-5070btr-polarizing-microscope/ (accessed on 24 July 2025).
- Moll, R.; Divo, M.; Langbein, L. The human keratins: Biology and pathology. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 129, 705–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conejo-Mir, J.; Jiménez, J.C.M.; Martínez, F.M.C. Manual de Dermatología; Grupo Aula Médica S.L.: Madrid, Spain, 2018; Available online: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/libro?codigo=762726 (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Shin, M.K.; Kim, T.I.; Kim, W.S.; Park, H.; Kim, K.S. Changes in nail keratin observed by Raman spectroscopy after Nd:YAG laser treatment. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2017, 80, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowther, J.M.; Matts, P.J. Molecular Concentration Profiling in the Skin Using Confocal Raman Spectroscopy. In Textbook of Aging Skin; Farage, E.M.A., Miller, K.W., Maibach, H.I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 1171–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Shin, M.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Seo, J.-E.; Lee, Y.M.; Park, C.-H.; Chung, J.H. Effects of Infrared Radiation and Heat on Human Skin Aging in vivo. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2009, 14, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, B.H.; Ruvolo, E.; Hexsel, C.L.; Liu, Y.; Owen, M.R.; Kollias, N.; Lim, H.W.; Hamzavi, I.H. Impact of Long-Wavelength UVA and Visible Light on Melanocompetent Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 2092–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, E.J.; Roy, S.; Sharbirin, A.S.; Ranz, L.-G.; Dieing, T.; Kim, J. Measurement of lateral and axial resolution of confocal Raman microscope using dispersed carbon nanotubes and suspended graphene. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2020, 20, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, N. Comparison of Lateral Resolutions Obtained by Different Methods for Confocal Raman Microscopes. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2025, 56, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSI Z136.1-2022; American National Standard for Safe Use of Lasers. The American National Standards Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. Available online: https://webstore.ansi.org/ (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Veras, J.M.d.M.F.; Coelho, L.d.S.; Neto, L.P.M.; de Almeida, R.M.; da Silva, G.C.; de Santana, F.B.; Garcia, L.A.; Martin, A.A.; Favero, P.P. Identification of biomarkers in diabetic nails by Raman spectroscopy. Clin. Chim. Acta 2023, 544, 117363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kast, R.E.; Serhatkulu, G.K.; Cao, A.; Pandya, A.K.; Dai, H.; Thakur, J.S.; Naik, V.M.; Naik, R.; Klein, M.D.; Auner, G.W.; et al. Raman spectroscopy can differentiate malignant tumors from normal breast tissue and detect early neoplastic changes in a mouse model. Biopolymers 2008, 89, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourkoumelis, N.; Gaitanis, G.; Velegraki, A.; Bassukas, I.D. Nail Raman spectroscopy: A promising method for the diagnosis of onychomycosis. An ex vivo pilot study. Med. Mycol. 2018, 56, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, K.M.; Sastry, T.P.; Mandal, A.B. Comparative study on secondary structural changes in diabetic and non-diabetic human finger nail specimen by using FTIR spectra. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chu, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S. In vivo Raman spectroscopy for non-invasive transcutaneous glucose monitoring on animal models and human subjects. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2025, 329, 125584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azin, S.; Joye, I.J. Peak Fitting Applied to Fourier Transform Infrared and Raman Spectroscopic Analysis of Proteins. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Téllez-Soto, C.A.; Silva, M.G.P.; dos Santos, L.; de OMendes, T.; Singh, P.; Fortes, S.A.; Favero, P.; Martin, A.A. In vivo determination of dermal water content in chronological skin aging by confocal Raman spectroscopy. Vib. Spectrosc. 2021, 112, 103196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, R.; Rajarahm, P.; Zhang, S.; Attia, A.B.E.; Bi, R.; Olivo, M. Simultaneous Dual-Wavelength Source Raman Spectroscopy with a Handheld Confocal Probe for Analysis of the Chemical Composition of In Vivo Human Skin. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 5240–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabasz, T.; Szymańska, N.; Bąk-Drabik, K.; Damasiewicz-Bodzek, A.; Nowak, A. Is Raman Spectroscopy of Fingernails a Promising Tool for Diagnosing Systemic and Dermatological Diseases in Adult and Pediatric Populations? Medicina 2024, 60, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, N.-H.; Griffiths, F.; Mann, C.; Dawes, H.; van Arkel, R.; Bukhari, M.; Kerns, J.G. Raman spectroscopy identified fingernail compositional differences between sexes and age-related changes but not handedness or fingers in a healthy cohort. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0329092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, J.C.; Wang, Z.; Huang, S. Unveiling brain disorders using liquid biopsy and Raman spectroscopy. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 11879–11913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Component | Specification | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| Laser source | 785 nm power adjustable 1–550 mW | Ocean Optics [17] |
| Raman Probe RPB | portable fiber-coupled | InPhotonics [18] |
| Spectrograph | QE65000 SMA connector; high quantum efficiency 90%; CCD detector spectral range 400–1800 cm−1; spectral resolution in 14 cm−1 | Ocean Optics [19] |
| Optical fiber | 50 μm multimode fiber used as pinhole | Ocean Optics |
| Microscope objective | wide field of view; LWD = 1.2 cm (experimental); 20x/0.4; and spot size = 2.39 μm | BestScope BS-5070BTR [20,21] |
| XYZ CNC | 50 μm precision step | Custom-built |
| 1-axis stage | mechanical movement | Used to build a quartz response curve and CNT response curve. |
| Parameters | |
|---|---|
| Confocal Volume | Spatial resolution Z (FWHM) = 15.268 μm |
| Lateral resolution XY (FWHM) = 0.847 μm | |
| Area (XY × XY) = 0.717 μm2 | |
| Volume = Z × Area = 10.953 μm3 |
| Peak | Fingernail | Molecular Characteristic | Fingertip | Molecular Characteristic | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Center (cm−1) |
Intensity (a.u.) |
Center (cm−1) |
Intensity (a.u.) | |||
| 1 | 856.5 | 47.7 | tyrosine | 855.2 | 219.6 | tyrosine |
| 2 | 926.8 | 7.9 | C-C skeleton vibration | 856.3 | 320.3 | (C-C) skeleton vibration |
| 3 | 937.9 | 7.5 | stretch C-C skeletal -helix keratin | — | — | — |
| 4 | 1005.2 | 35.0 | aromatic ring of phenylalanine | 1017.2 | 276.5 | keratin |
| 5 | 1057.7 | 222.3 | C-H phenylalanine | 1054.0 | 452.8 | C-H phenylalanine |
| 6 | 1069.3 | 315.2 | CC skeletal, trans-conformation | — | — | — |
| 7 | 1119.2 | 62.6 | (C-C) of lipids segments and (C-N) of proteins | 1121.0 | 135.2 | (C-C) of lipids segments and (C-N) of proteins |
| 8 | 1254.7 | 236.9 | amide IIIβ | 1216.1 | 66.4 | small contribution keratin |
| 9 | 1314.4 | 353.3 | CH2, Cα-H | 1317.0 | 329.0 | amide III, CH3, CH2 wagging lipids |
| 10 | 1447.1 | 358.8 | (CH2) and as CH3) in proteins (around 1449) and lipids (around 1438) | 1447.0 | 324.4 | deformation (CH2) and as (CH3) in proteins (around 1449) and lipids (around 1438) |
| 11 | 1528.1 | 59.7 | skeletal vibration carotenoids | 1525.8 | 205.5 | skeletal vibration carotenoids |
| 12 | 1616.2 | 152.9 | aromatic vibration of phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan | 1602.1 | 120.8 | (C=C)vinyl, heme |
| 13 | 1648.7 | 299.6 | (C=0) amide I -sheet | 1645.7 | 123.7 | amide I |
| 14 | — | — | — | 1674.4 | 162.9 | (C=0) amide I -sheet, heme |
| 15 | 1650.0 | 44.6 | (C=0) amide I -helix -helix | 1672.0 | 28.4 | (C=0) amide I -sheet |
| 16 | 1659.0 | 44.6 | amide I -helix | 1644.0 | 2.365 | -sheet conformation |
| 17 | 1666.0 | 62.06 | (C=0) amide I -helix | 1680.0 | 16.22 | -turn conformation |
| Amide I secondary structures at Z = 0 μm | ||
| volunteer | Nail | Tip |
| (-s) (-h) (-s) | (-s) (-t) | |
| 1 | 1645 1673 | 1635 1686 |
| 2 | 1641 1672 | 1644 1697 |
| 3 | 1648 1676 | 1643 1685 |
| Amide I secondary structures at Z = 350 μm | ||
| volunteer | Nail | Tip |
| (-s) (-h) (-s) | (-s) (-t) | |
| 1 | 1644 1678 | 1647 1681 |
| 2 | 1638 1672 | 1628 1672 |
| 3 | 1628 1659 1666 | 1644 1680 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urrieta Almeida, E.; de la Cruz May, L.; Benavides, O.; Bandala Garces, M.; Flores Gil, A. Design for Assembly of a Confocal System Applied to Depth Profiling in Biological Tissue Using Raman Spectroscopy. Technologies 2025, 13, 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13100440
Urrieta Almeida E, de la Cruz May L, Benavides O, Bandala Garces M, Flores Gil A. Design for Assembly of a Confocal System Applied to Depth Profiling in Biological Tissue Using Raman Spectroscopy. Technologies. 2025; 13(10):440. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13100440
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrrieta Almeida, Edgar, Lelio de la Cruz May, Olena Benavides, Magdalena Bandala Garces, and Aaron Flores Gil. 2025. "Design for Assembly of a Confocal System Applied to Depth Profiling in Biological Tissue Using Raman Spectroscopy" Technologies 13, no. 10: 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13100440
APA StyleUrrieta Almeida, E., de la Cruz May, L., Benavides, O., Bandala Garces, M., & Flores Gil, A. (2025). Design for Assembly of a Confocal System Applied to Depth Profiling in Biological Tissue Using Raman Spectroscopy. Technologies, 13(10), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13100440










