Numerical Study of the Influence of the Structural Parameters on the Stress Dissipation of 3D Orthogonal Woven Composites under Low-Velocity Impact
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Development of the Geometric Model
2.2. Damage Criterion
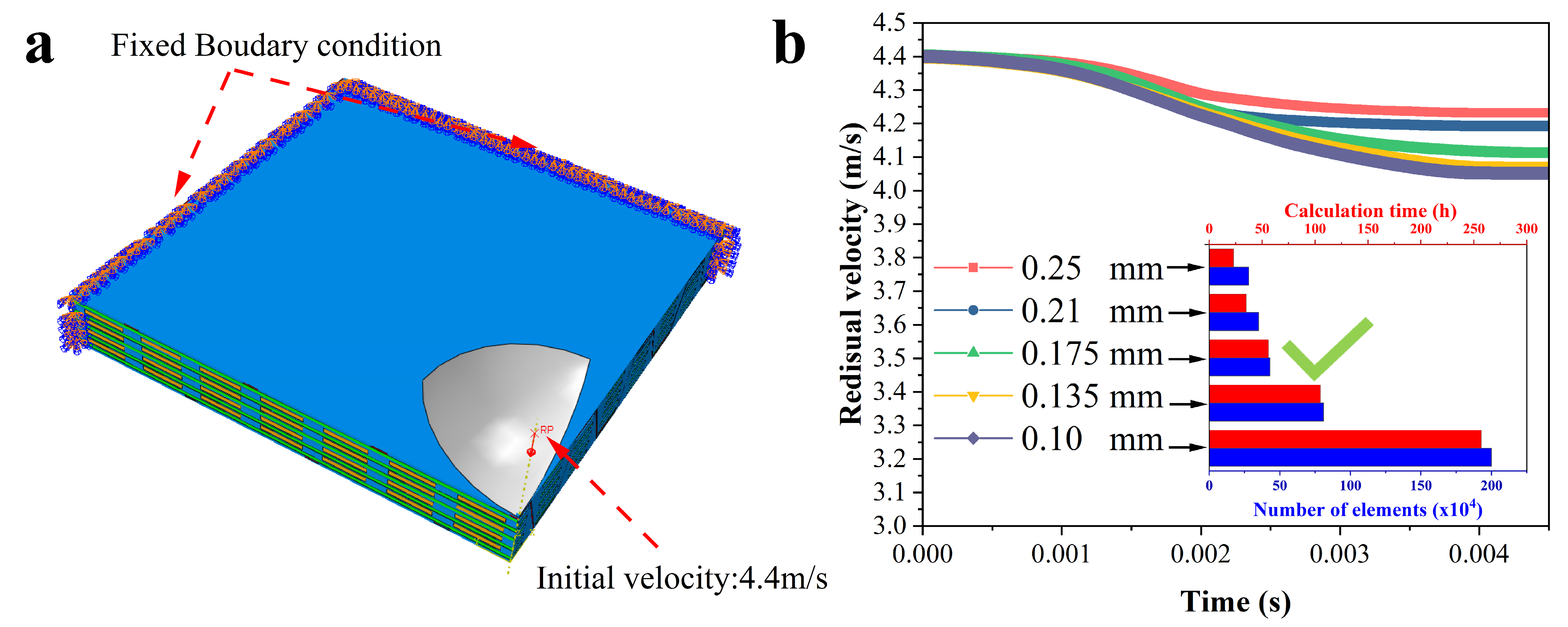
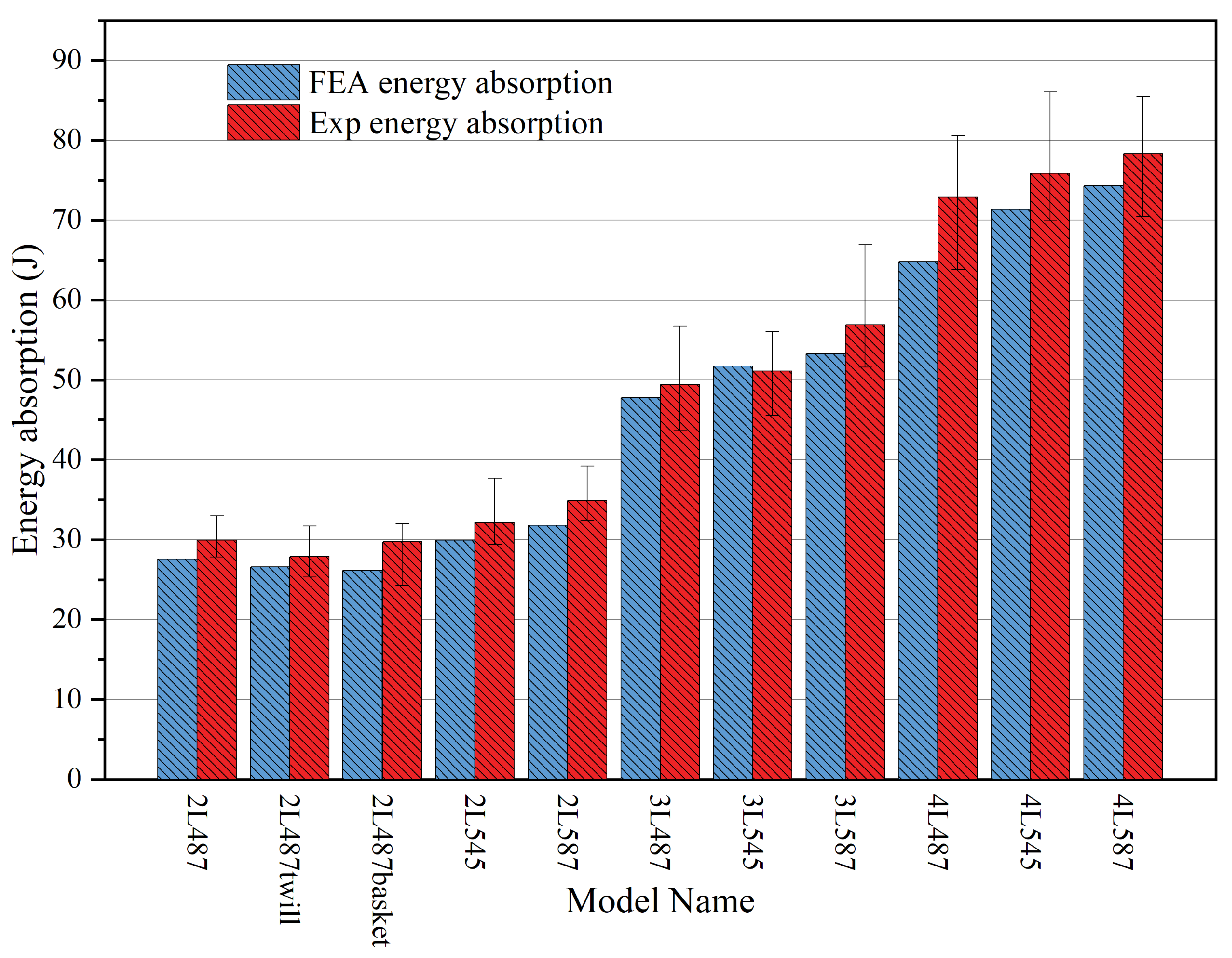
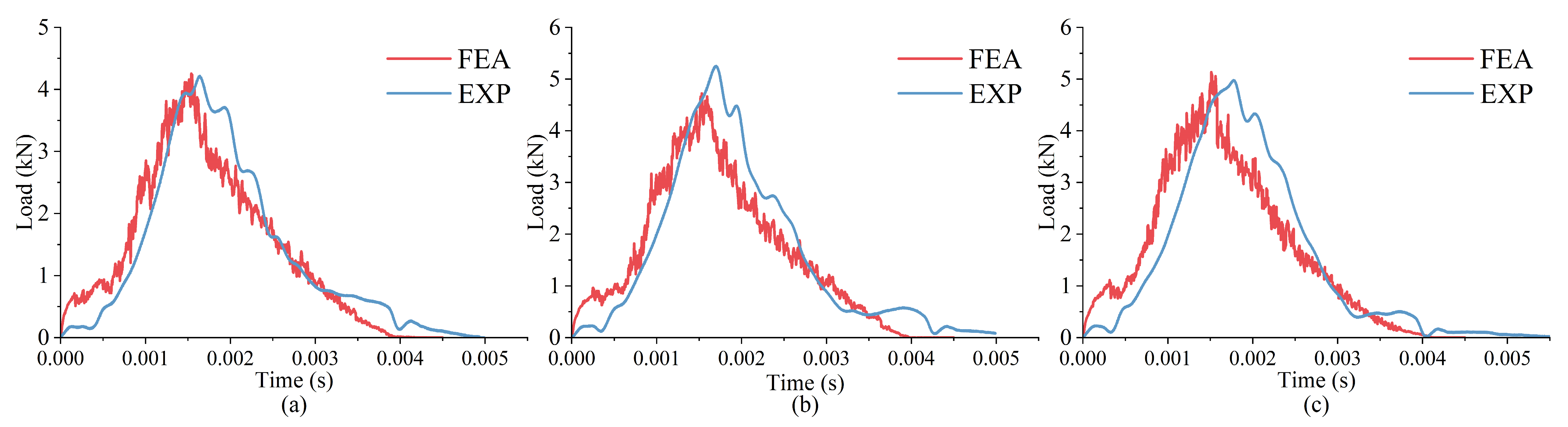
2.3. Model Set-Up and Validation
3. Results and Discussions
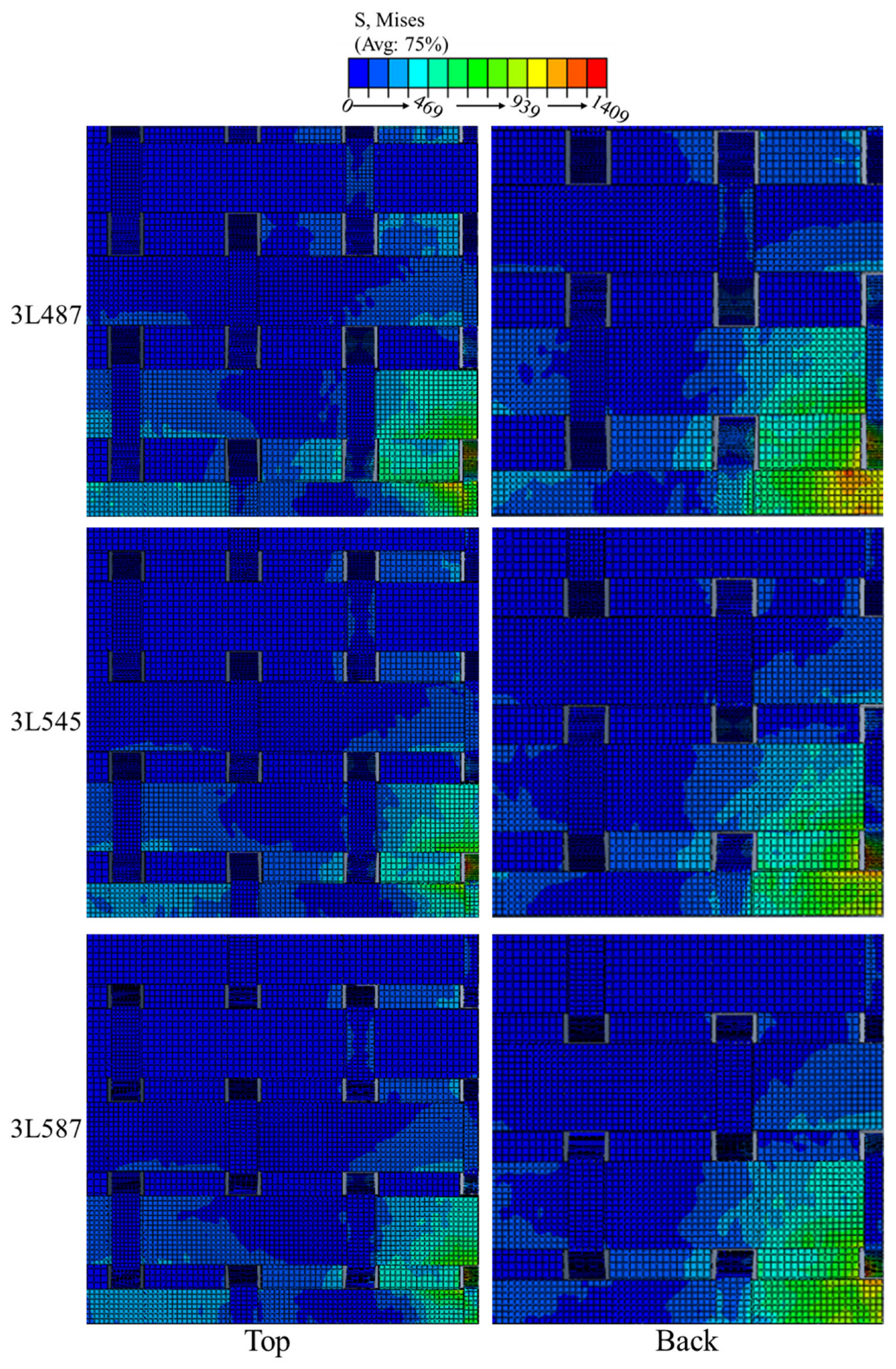
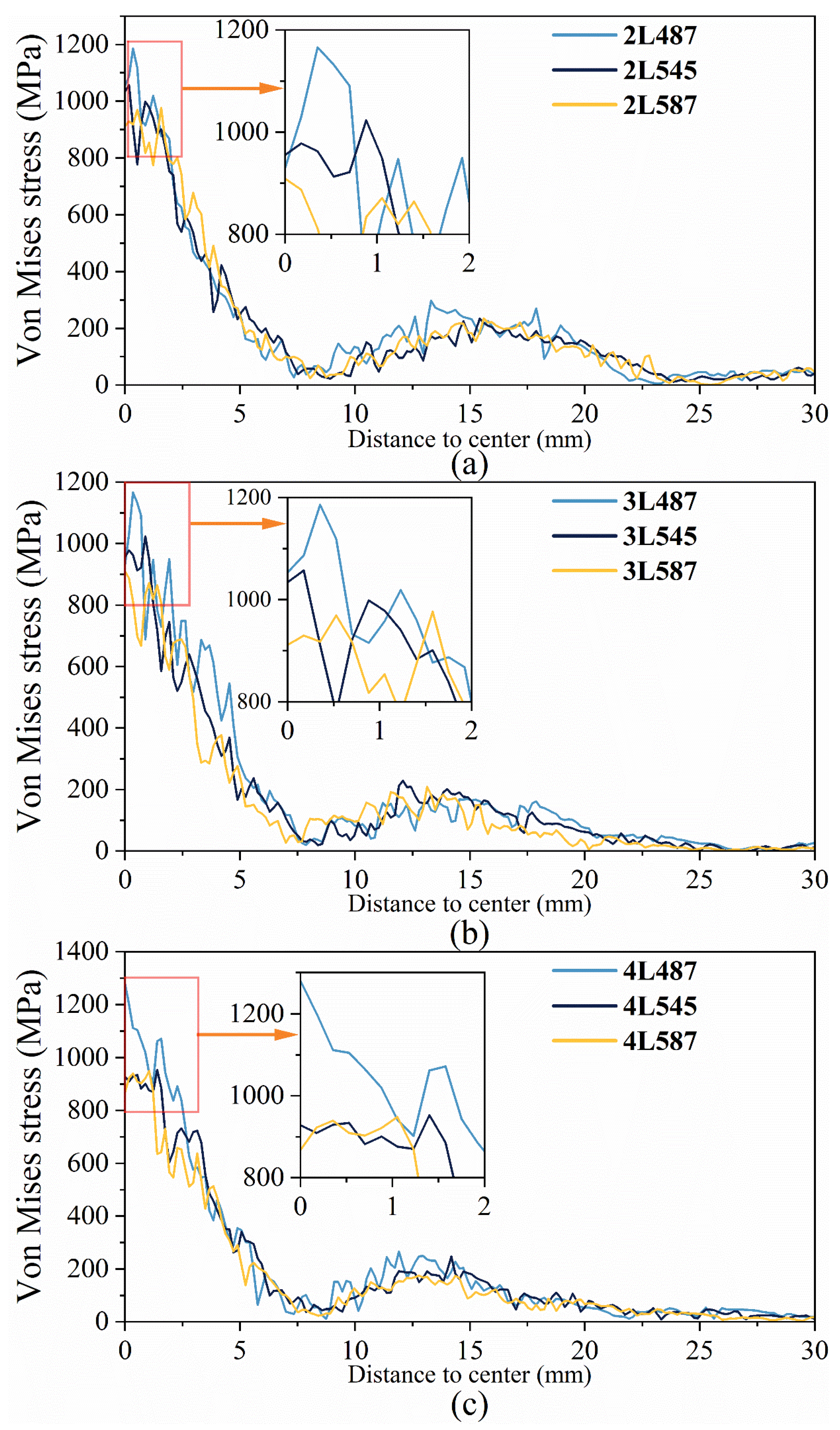
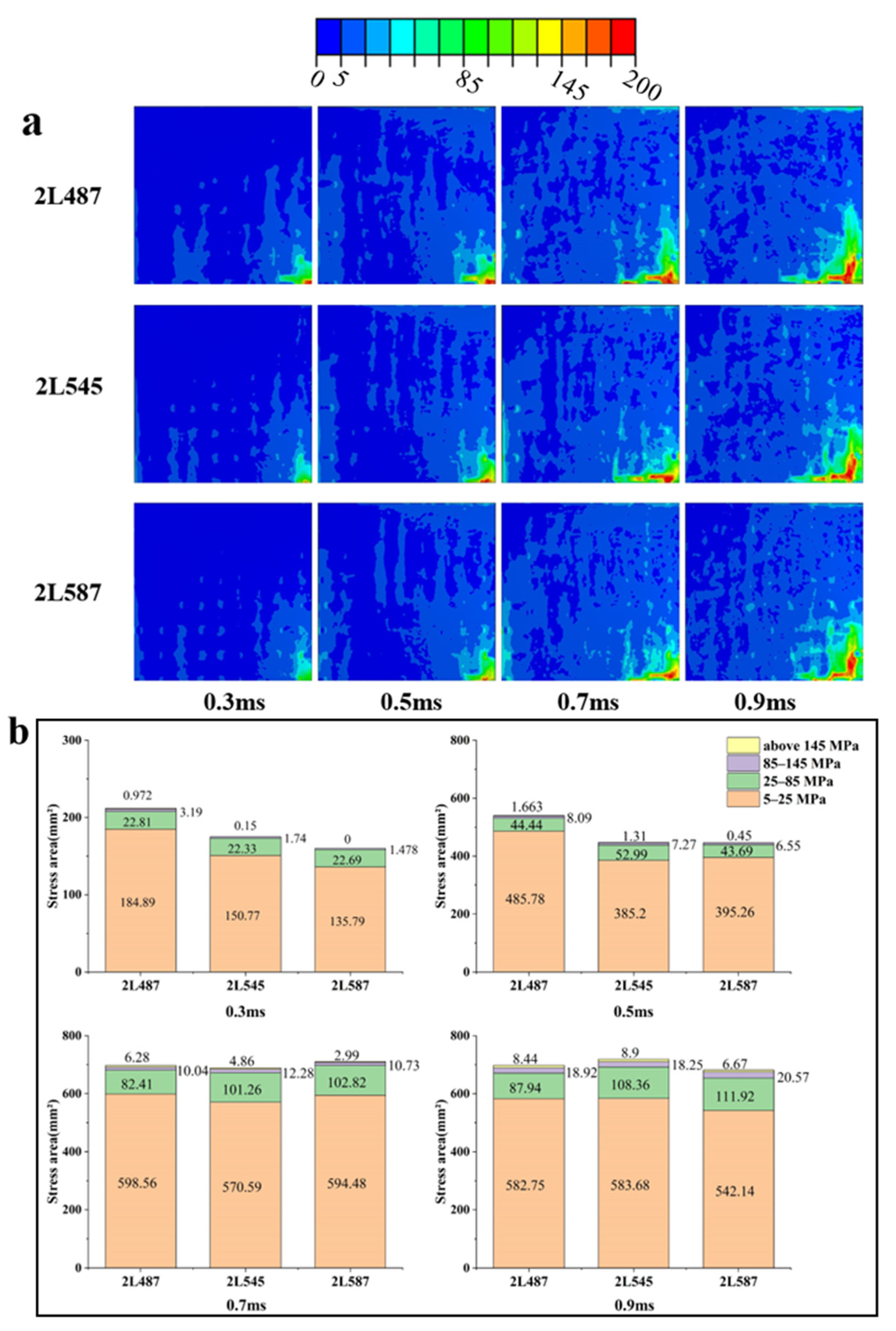
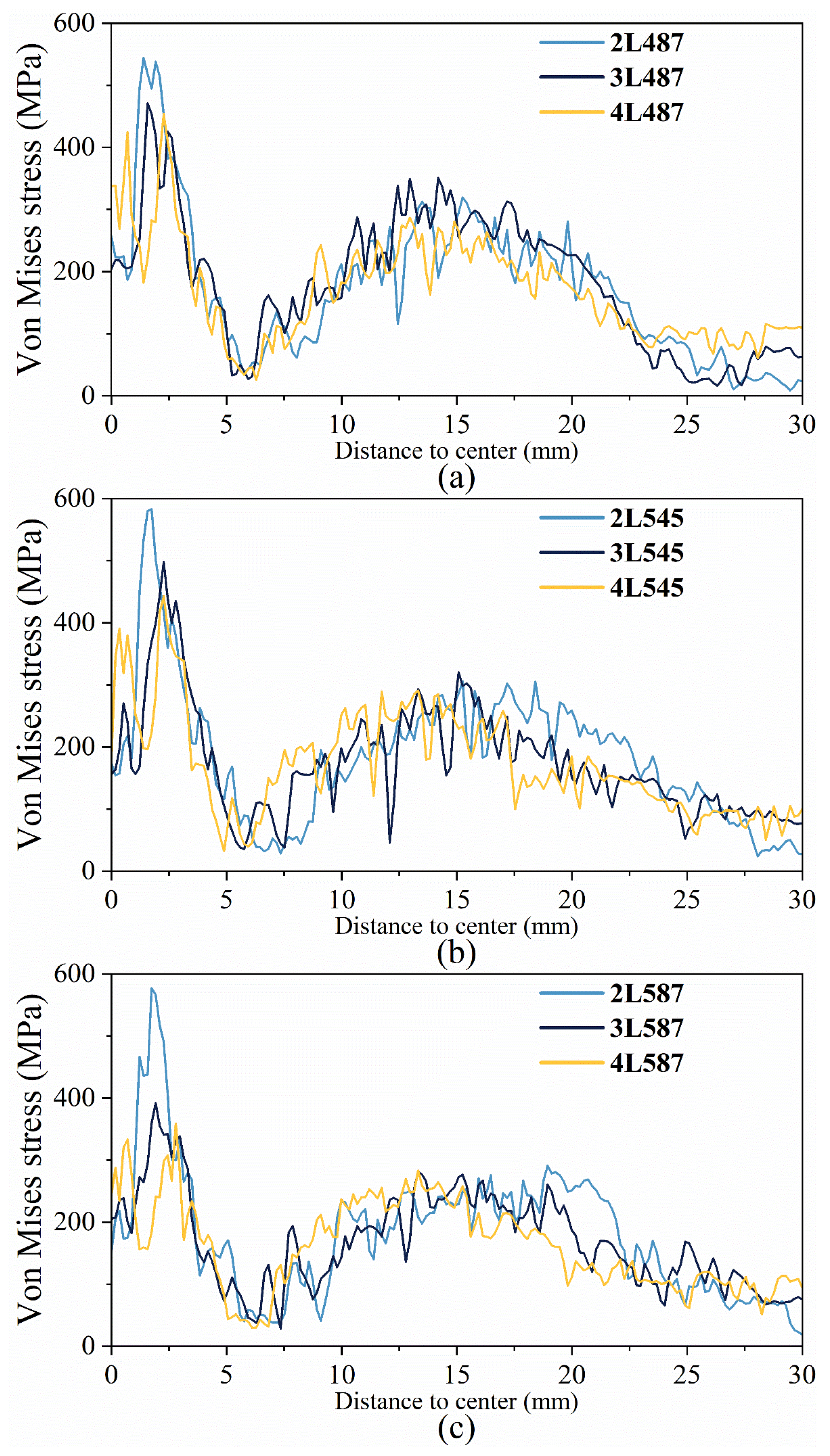
3.1. Effect of X-Yarn Density
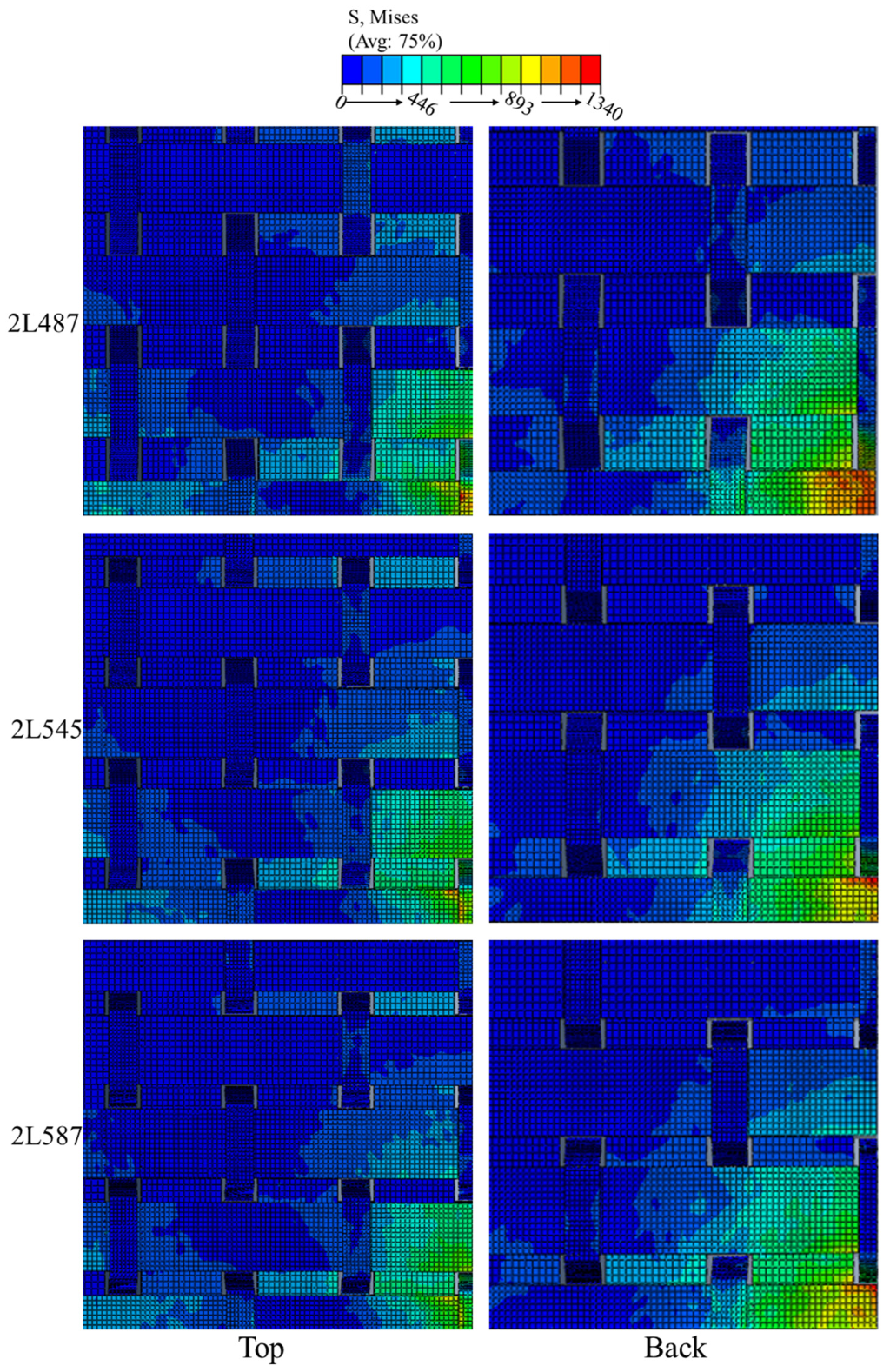
3.1.1. Effect of X-Yarn Density on Stress Distribution in the Reinforcement
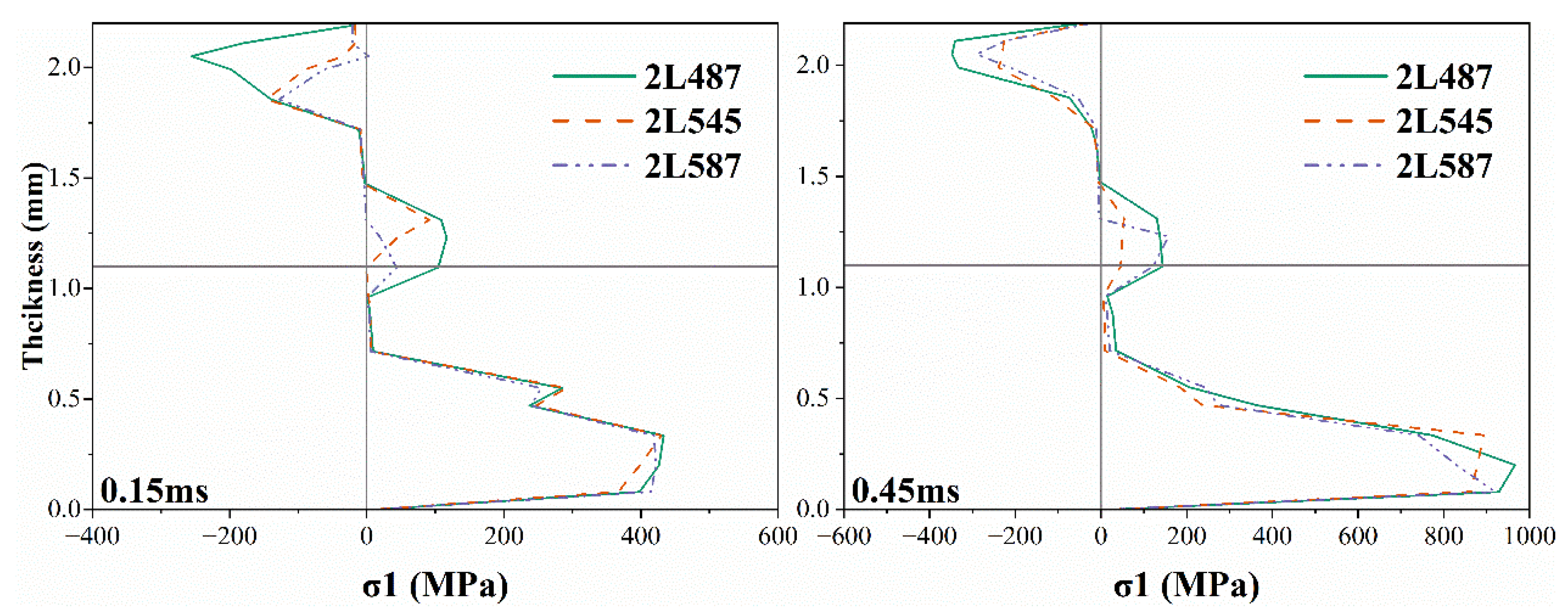
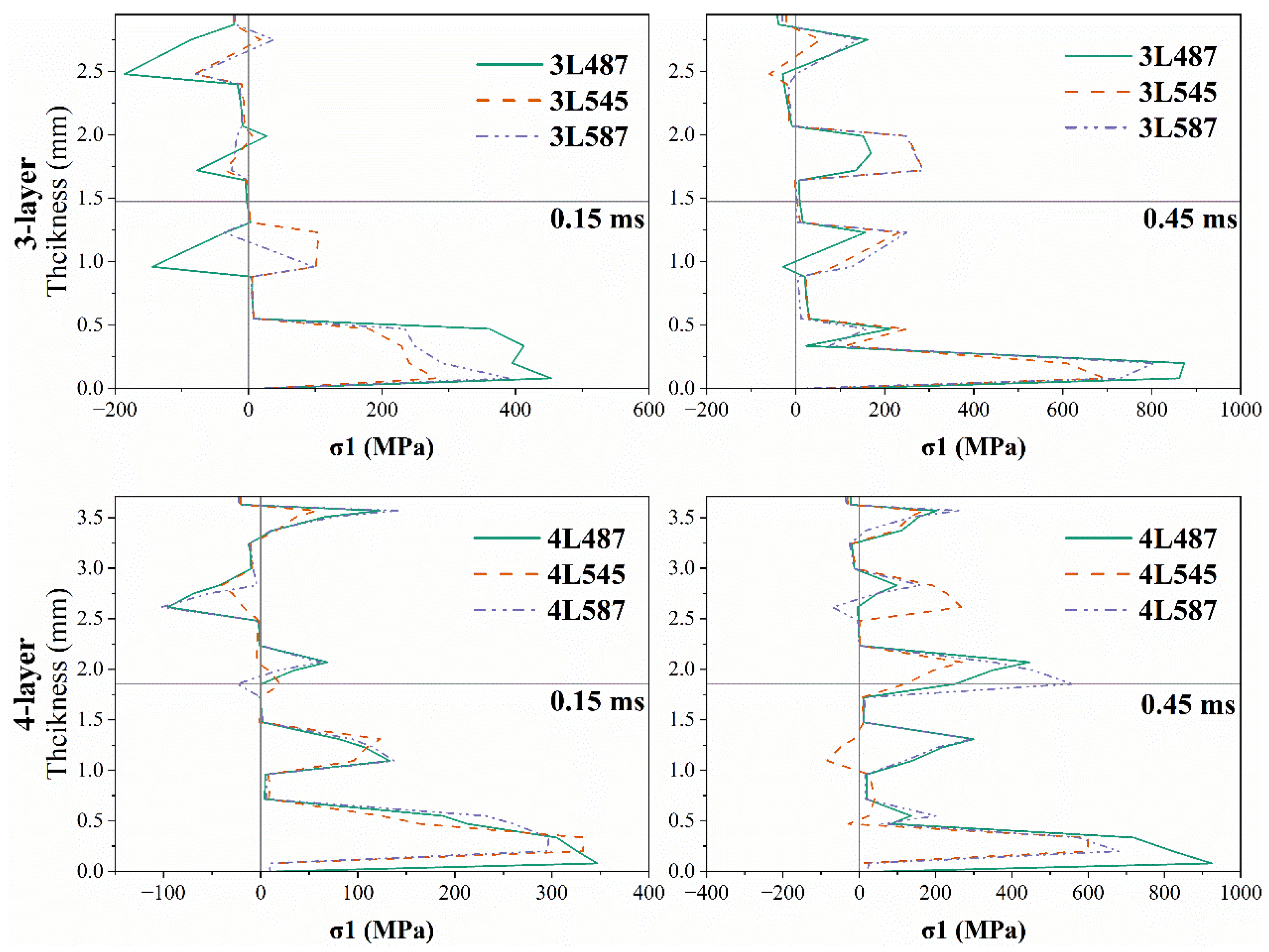
3.1.2. Axial Stress Distribution
3.1.3. Effect of X-Yarn Density on Stress Distribution in the Resin Matrix
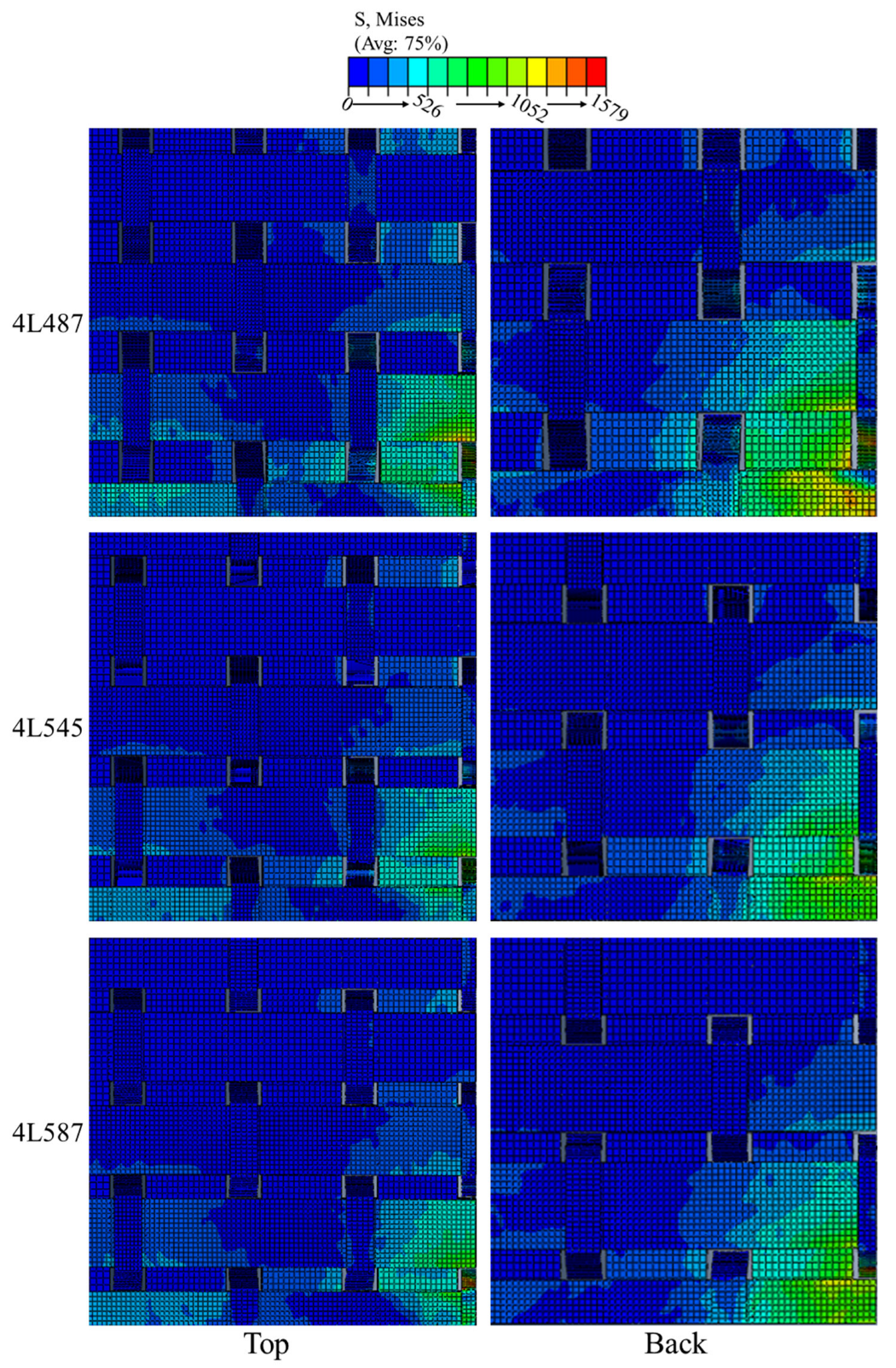
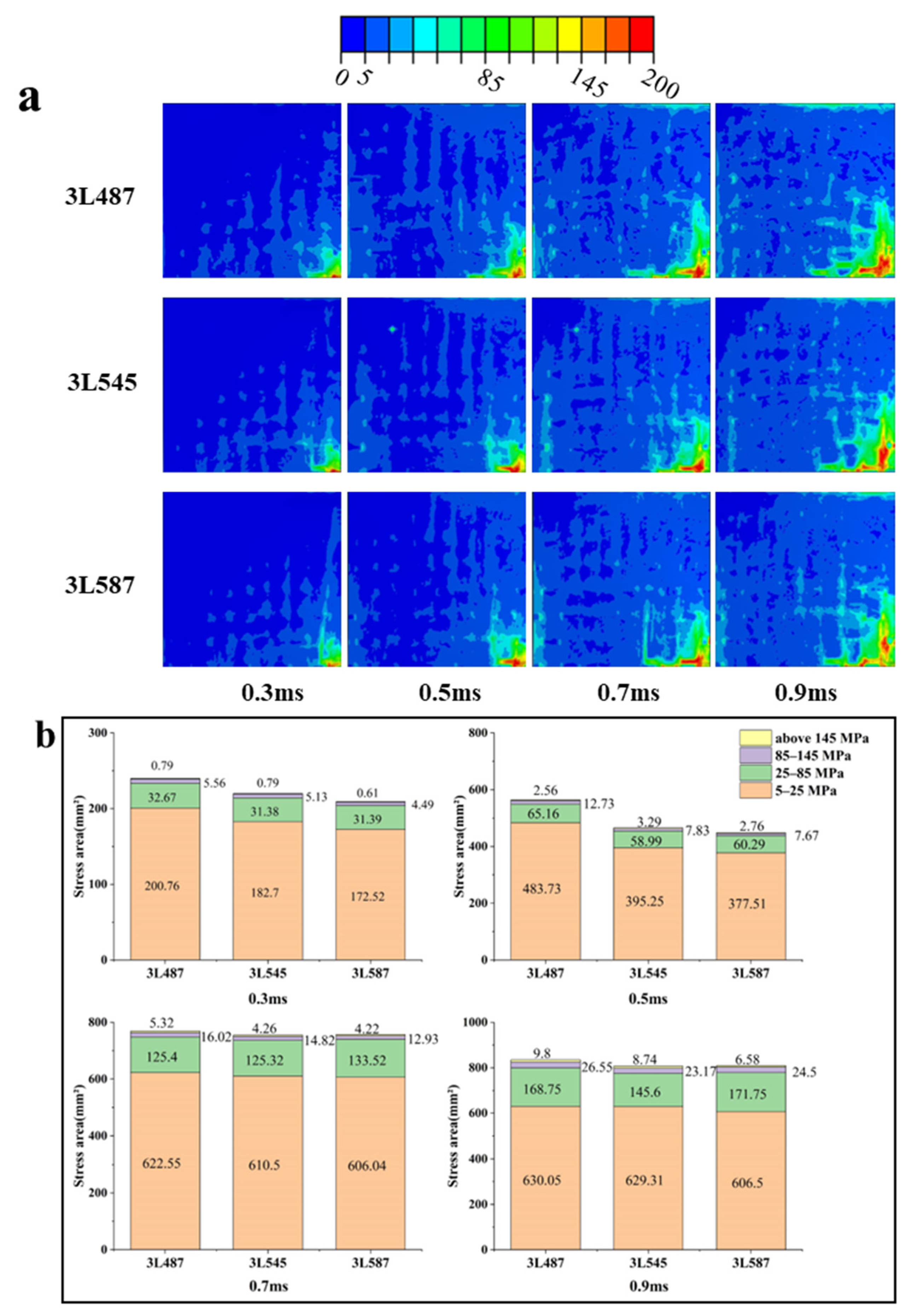
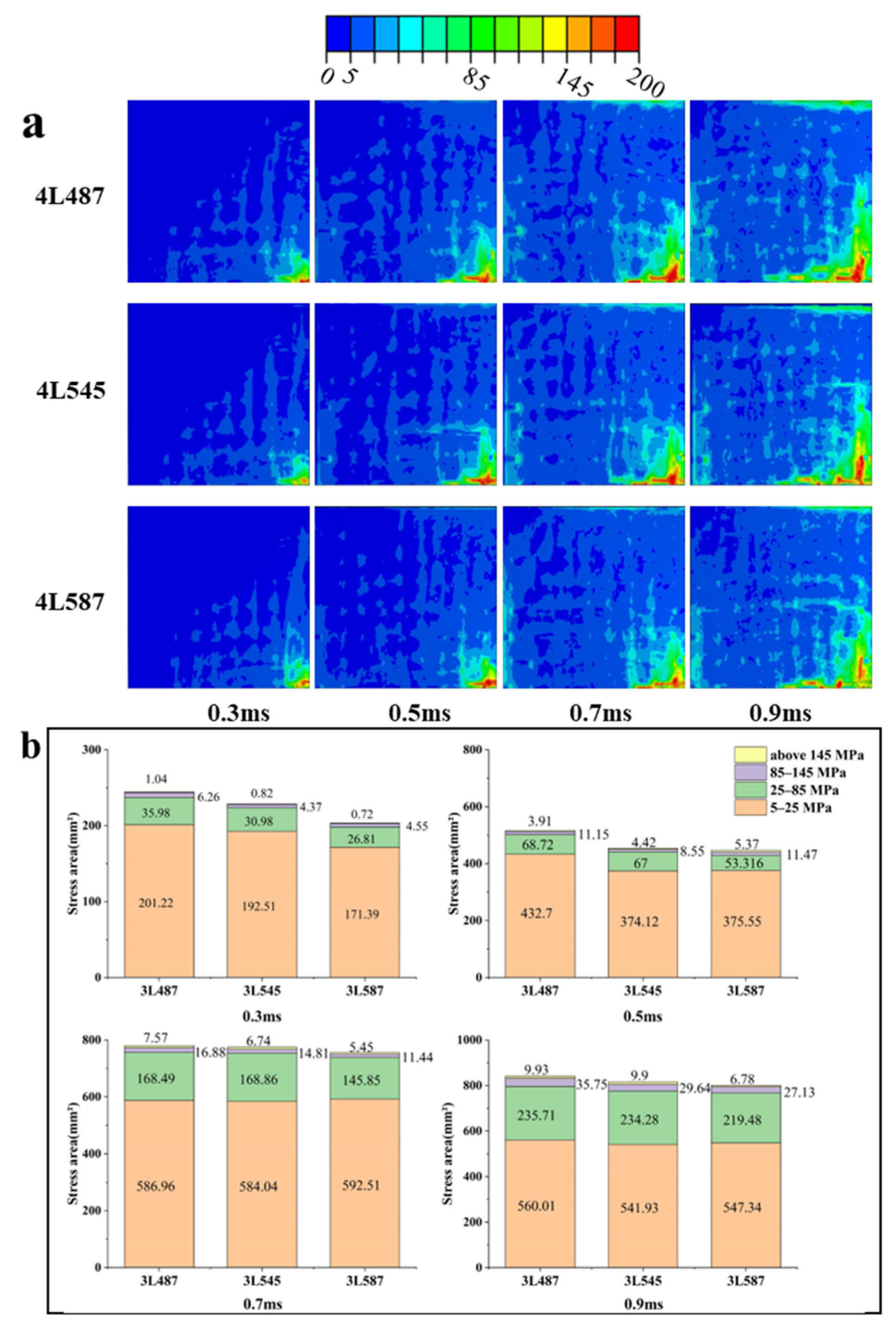
3.2. Effect of the Number of Layers
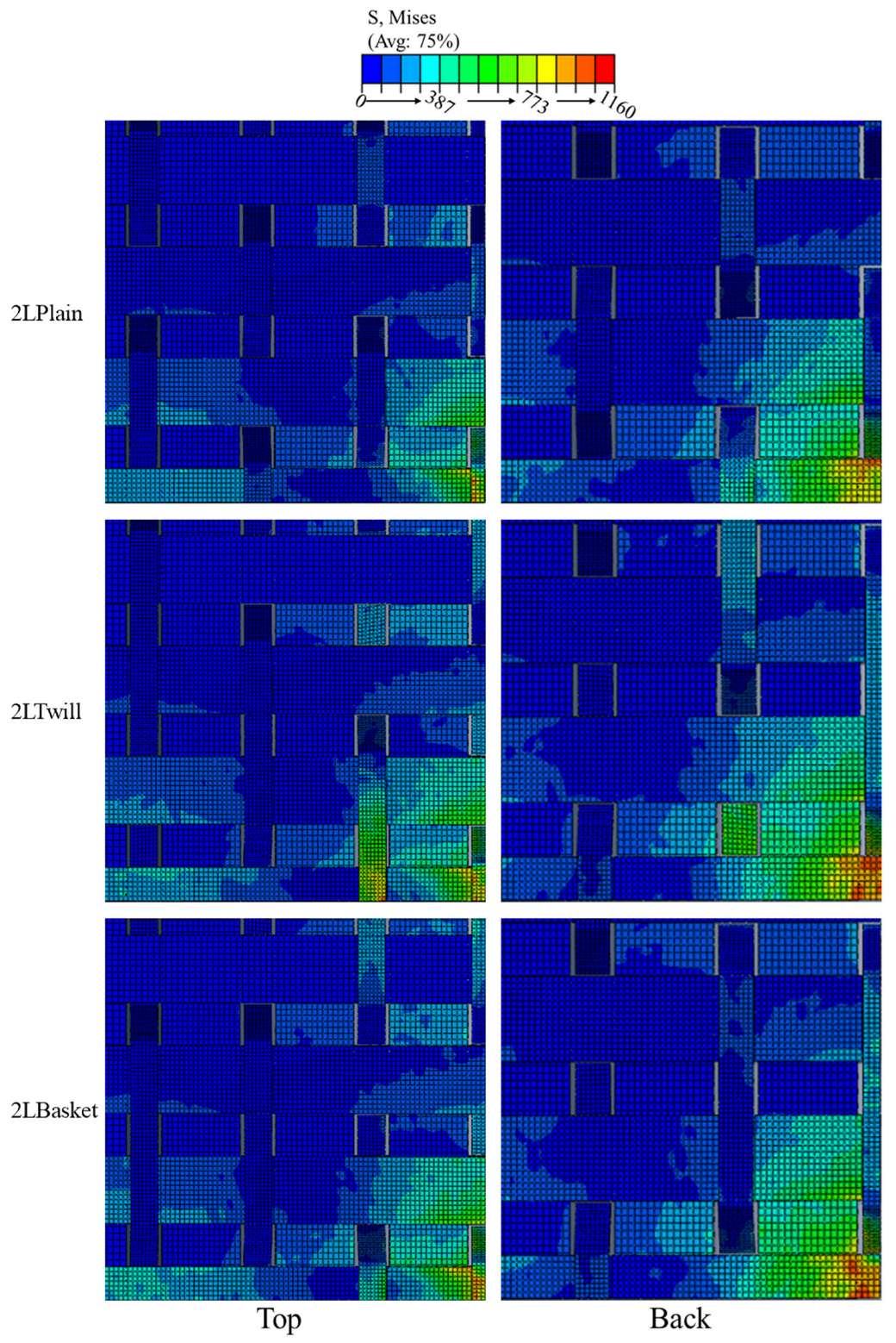
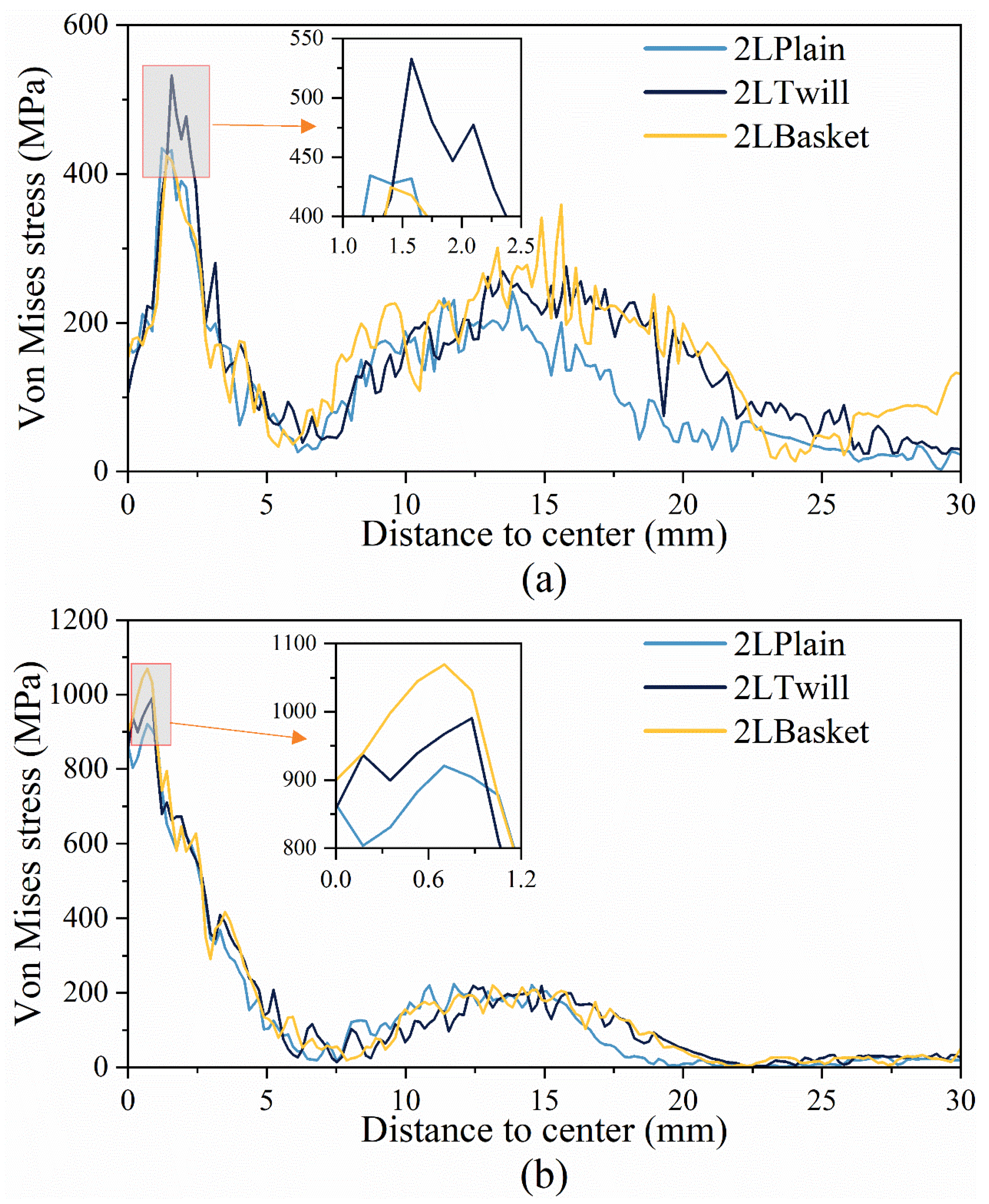
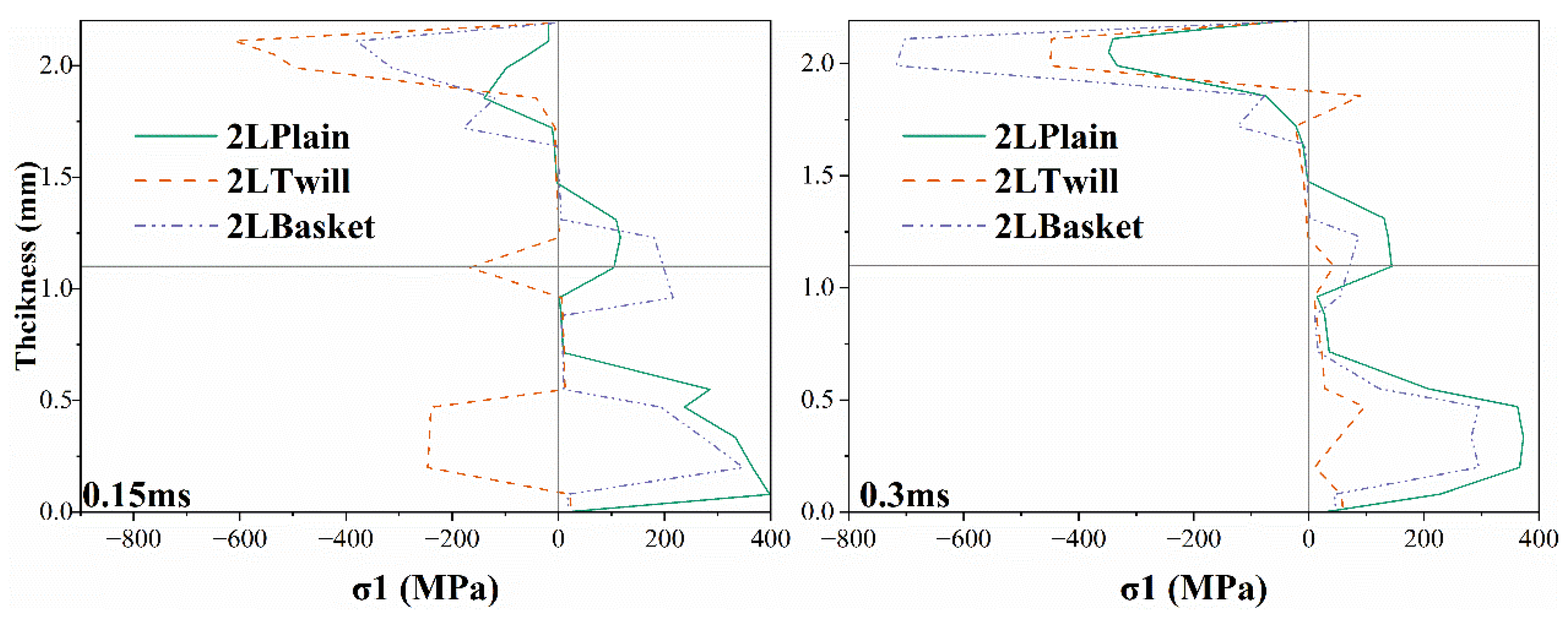
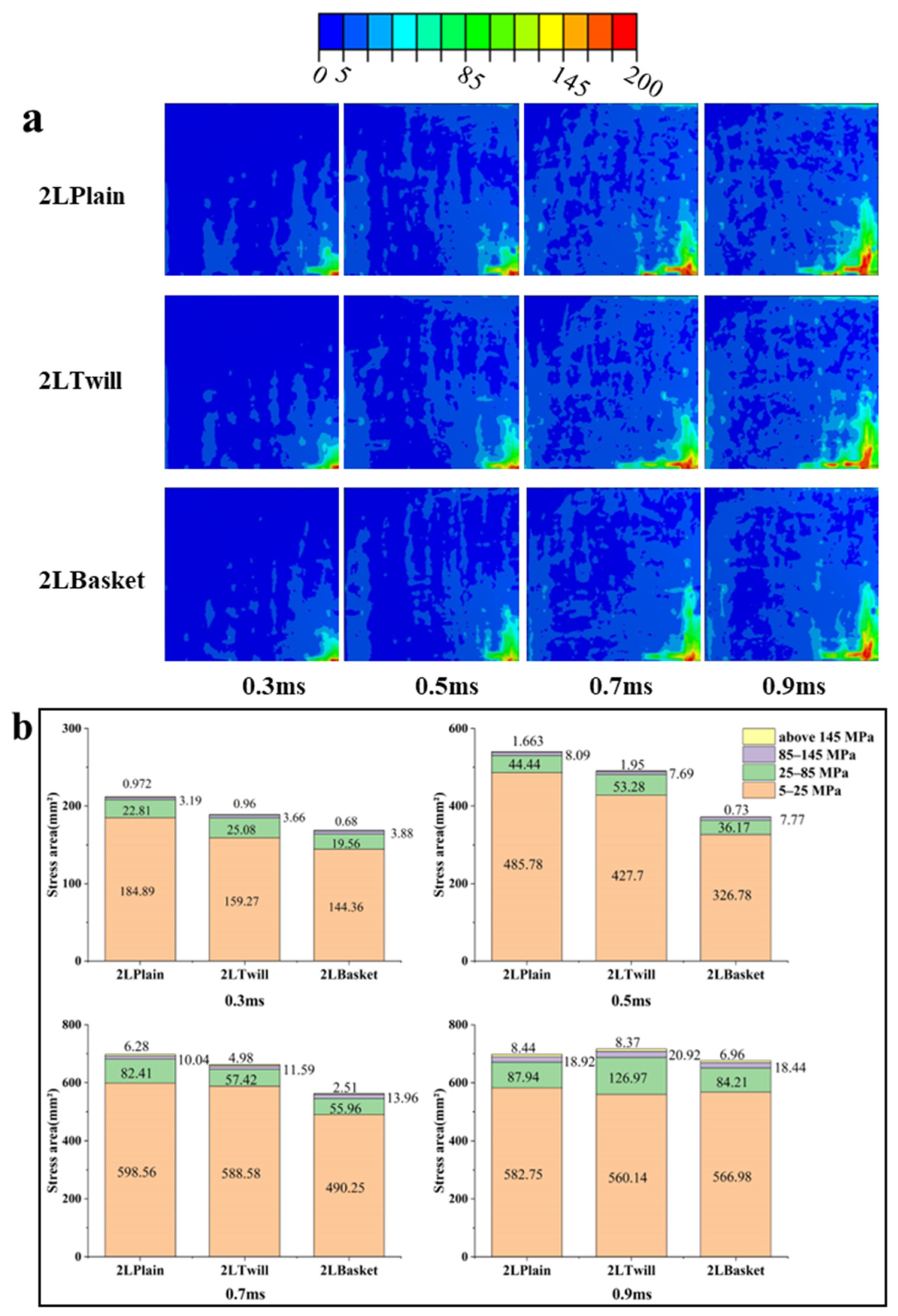
3.3. Effect of Z-Yarn Path
3.3.1. Effect of X-Yarn Density on Stress Distribution in the Reinforcement
3.3.2. Effect of X-Yarn Density on Stress Distribution in the Resin Matrix
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G. Review of the Mechanical Properties of a 3D Woven Composite and Its Applications. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2018, 57, 740–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtew, M.A. A comprehensive review on advancements, innovations and applications of 3D warp interlock fabrics and its composite materials. Compos. B Eng. 2024, 278, 111395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Qian, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lyu, L. 3D woven tubular composites with bamboo-structures for enhanced energy absorption: Designing, manufacturing and performance analysis. Polym. Compos. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.N.; Yudhanto, A.; Potluri, P.; Lubineau, G.; Soutis, C. Characterising the loading direction sensitivity of 3D woven composites: Effect of z-binder architecture. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 90, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilisik, K. Multiaxis 3D Woven Preform and Properties of Multiaxis 3D Woven and 3D Orthogonal Woven Carbon/Epoxy Composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2009, 29, 1173–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Memon, H.; Qiu, Y.; Wei, Y. The Failure Mechanism of Composite Stiffener Components Reinforced with 3D Woven Fabrics. Materials 2019, 12, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.; Zhao, Z.; Xia, X.; Cakmak, M.; Vogt, B.D. Enhanced Impact Resistance of Three-Dimensional-Printed Parts with Structured Filaments. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16087–16094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedifar, M.; Saleh, M.N.; El-Dessouky, H.M.; Teixeira De Freitas, S.; Zarouchas, D. Damage assessment of NCF, 2D and 3D woven composites under compression after multiple-impact using acoustic emission. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 132, 105833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewangan, M.K.; Panigrahi, S.K. Finite element analysis of hybrid 3D orthogonal woven composite subjected to ballistic impact with multi-scale modeling. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 964–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, A.; Devi, G.R.; Gupta, A.K. Preparation of 3D orthogonal woven C–SiC composite and its characterization for thermo-mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 6210–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Wang, M.; Ying, Z.; Cheng, X.; Wu, Z. Failure mechanism of Ω-shape 3D orthogonal woven composite component under transverse low-velocity impact and subsequent axial compression load. Int. J. Damage Mech. 2021, 31, 246–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Shao, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, G.; Luo, G.; Chen, W. Bird impact response and damage mechanism of 3D orthogonal woven composite aeroengine blades. Compos. Struct. 2023, 304, 116311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, Z.; Ji, J.; Chen, G.; Luo, G.; Chen, W. Development and experimental verification of a modified constitutive model for 3D orthogonal woven composite under bird impact. Compos. Struct. 2023, 303, 116305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, P.; Liu, T.; Zeng, X. Collapse of 3D orthogonal woven carbon fibre composites under in-plane tension/compression and out-of-plane bending. Compos. Struct. 2016, 142, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, N.; Wisner, B.; Cuadra, J.; Amini, S.; Kontsos, A. Investigation of the Z-binder role in progressive damage of 3D woven composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 98, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baucom, J.N.; Zikry, M.A. Evolution of Failure Mechanisms in 2D and 3D Woven Composite Systems under Quasi-Static Perforation. J. Compos. Mater. 2003, 37, 1651–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baucom, J.N.; Zikry, M.A. Low-velocity impact damage progression in woven E-glass composite systems. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2005, 36, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, A.; Neelakrishnan, S. An evaluation of the loading direction sensitivity of 3D woven composite with novel web-shaped Z-binder architecture. Mater. Res. Express 2022, 9, 075601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, D.; Yan, L. Impact Response of Carbon/Kevlar Hybrid 3D Woven Composite under High Velocity Impact: Experimental and Numerical Study. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2020, 27, 285–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Lv, L.; Sun, B.; Qiu, Y.; Gu, B. Transverse impact behavior and energy absorption of three-dimensional orthogonal hybrid woven composites. Compos. Struct. 2007, 81, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; De, S. Z-fiber influence on high speed penetration of 3D orthogonal woven fiber composites. Mech. Mater. 2014, 68, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Wu, Z.; Ying, Z.; Hu, X. The numerical and experimental investigation on low-velocity impact response of composite panels: Effect of fabric architecture. Compos. Struct. 2019, 227, 111343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midani, M.; Seyam, A.-F.; Saleh, M.N.; Pankow, M. The effect of the through-thickness yarn component on the in- and out-of-plane properties of composites from 3D orthogonal woven preforms. J. Text. Inst. 2019, 110, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Cunningham, P.R.; Marshall, S.; Silva, C. Influence of fibre architecture on the tensile, compressive and flexural behaviour of 3D woven composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 69, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Bijoya, D.; Behera, K.; Dash, A.K.; Behera, B.K. Role of weave design on the mechanical properties of 3D woven fabrics as reinforcements for structural composites. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 109, 952–960. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Dai, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, J. Micromechanisms and Characterization of Low-Velocity Impact Damage in 3D Woven Composites. Materials 2022, 15, 6636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrun, F.M.Z.; Yahya, M.F.; Ghani, S.A.; Ahmad, M.R. Effect of weft density and yarn crimps towards tensile strength of 3D angle interlock woven fabric. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1774. [Google Scholar]
- Kohri, Y.; Takebe, T.; Minami, Y.; Kanai, T.; Takarada, W.; Kikutani, T. Structure and properties of low-isotacticity polypropylene elastomeric fibers prepared by sheath-core bicomponent spinning: Effect of localization of high-isotacticity component near the fiber surface. J. Polym. Eng. 2014, 35, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, G.; Dahale, M.; Yoo, S.; Toso, N.; McGarrigle, C.; Quinn, J.; Kelly, J.; McIlhagger, A.; Archer, E.; Harkin-Jones, E. Improved crush energy absorption in 3D woven composites by pick density modification. Compos. B Eng. 2020, 192, 108007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.G.; Li, D.S.; Zhu, H.; Guo, Z.X.; Jiang, L. Mechanical properties prediction of 3D angle-interlock woven composites by finite element modeling method. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 22, 100769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, T.; Seyam, A.F.M.; Peters, K. Evaluation of the integrity of 3D orthogonal woven composites with embedded polymer optical fibers. Compos. B Eng. 2015, 78, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midani, M.; Seyam, A.F.; Pankow, M. The Effect of the Structural Parameters of 3D Orthogonal Woven Composites on their Impact Responses under Different Modes of Impact. Key Eng. Mater. 2018, 786, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, B.A.; Bogetti, T.A.; Gillespie, J.W., Jr. Progressive Damage Modeling of Plain-Weave Composites using LS-Dyna Composite Damage Model MAT162. In Proceedings of the 7th European LS-DYNA Conference, Salzburg, Austria, 14–15 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gama, B.A.; Gillespie, J.W. Finite element modeling of impact, damage evolution and penetration of thick-section composites. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2011, 38, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.R.; Gama, B.A.; Gillespie, J.W. Progressive damage and delamination in plain weave S-2 glass/SC-15 composites under quasi-static punch-shear loading. Compos. Struct. 2007, 78, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, M.E. Performance of Composites from 3D Orthogonal Woven Preforms in Terms of Architecture and Sample Location during Resin Infusion. Ph.D. Thesis, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.; Ma, W.; Xu, W.; Sun, Y.; Gu, B.; Chen, X. A numerical study on stress wave propagation in quasi-isotropic stacks of Dyneema® compliant composite laminates. Compos. Struct. 2023, 312, 116869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; He, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, P.; Lu, Z.; Xu, W. Estimating shear modulus of yarn on impact by lazy learning. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 270, 109074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, J.B.; Naito, C.J.; Haque, B.Z. Progressive damage modeling of plain weave E-glass/phenolic composites. Compos. B Eng. 2014, 61, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
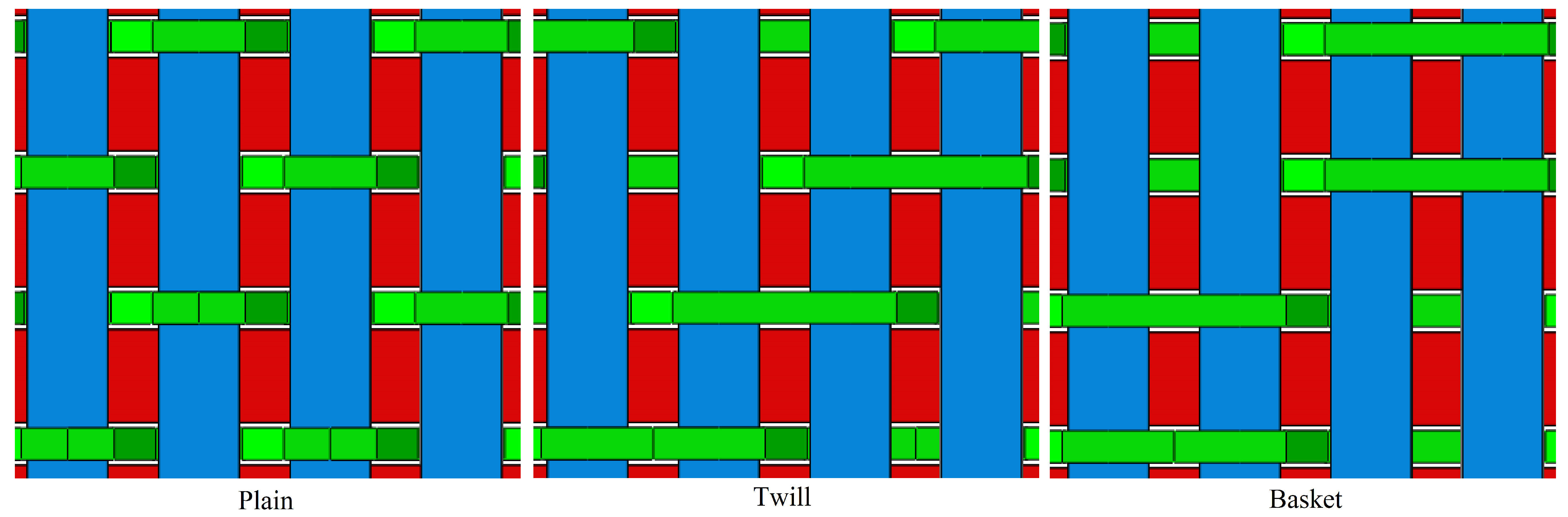
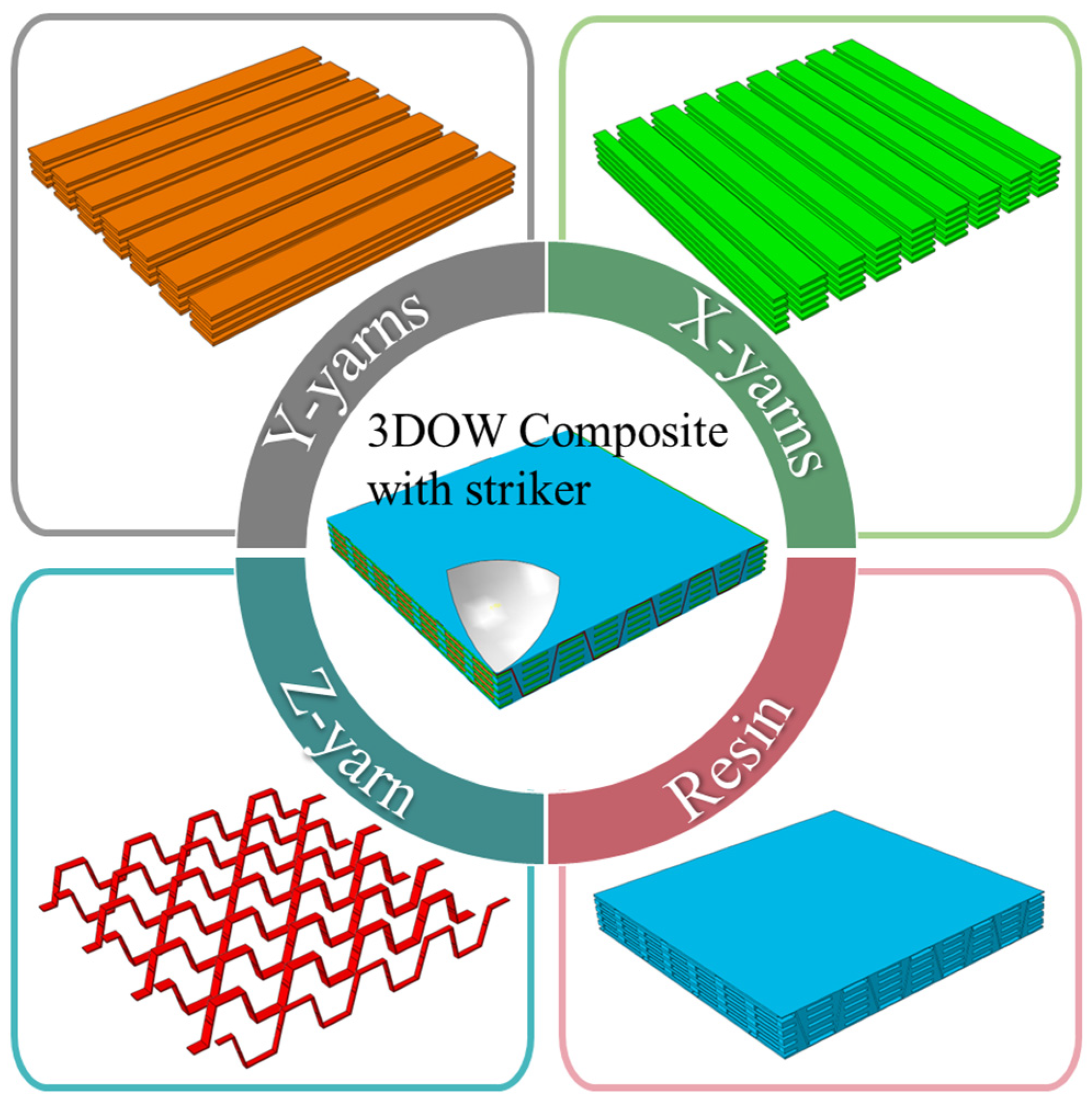
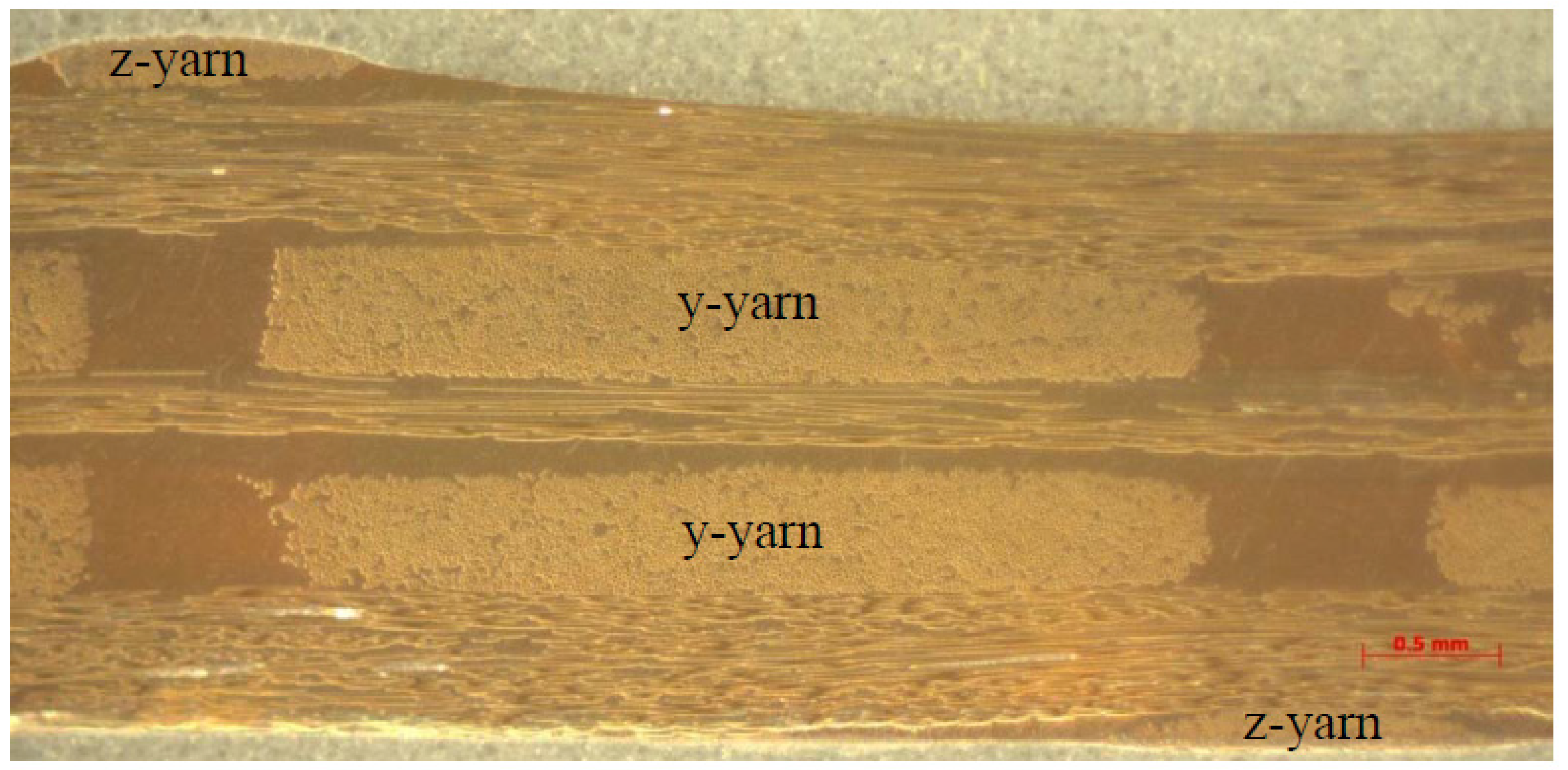
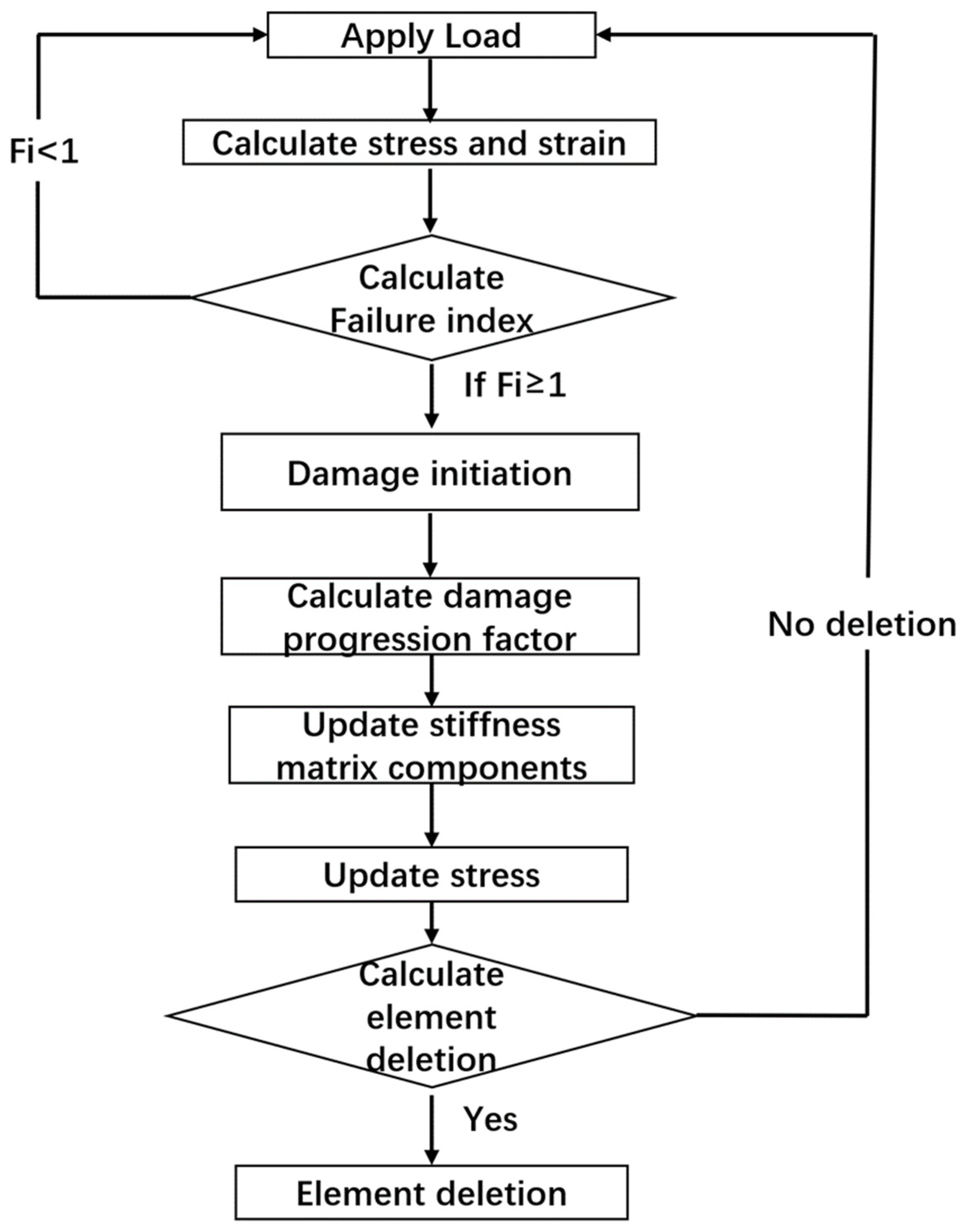
| Model ID | X-Yarn Density/Layer (cm−1) | Z-Yarn Path | Y-Yarn Density/Layer (cm−1) | Number of Layers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2L487 | 4.87 | Plain | 2.36 | 2 |
| 2L487twill | 4.87 | Twill | 2.36 | 2 |
| 2L487basket | 4.87 | Basket | 2.36 | 2 |
| 2L545 | 5.45 | Plain | 2.36 | 2 |
| 2L587 | 5.87 | Plain | 2.36 | 2 |
| 3L487 | 4.87 | Plain | 2.36 | 3 |
| 3L545 | 5.45 | Plain | 2.36 | 3 |
| 3L587 | 5.87 | Plain | 2.36 | 3 |
| 4L487 | 4.87 | Plain | 2.36 | 4 |
| 4L545 | 5.45 | Plain | 2.36 | 4 |
| 4L587 | 5.87 | Plain | 2.36 | 4 |
| Failure Modes | Criteria | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Fiber tension/shear failure mode | (1) | |
| (2) Fiber compression failure mode | (2) | |
| (3) Fiber crush failure mode | (3) | |
| (4) Matrix transverse failure mode | (4) | |
| (5) Matrix perpendicular failure mode | (5) | |
| Model | Exp E/Thickness (J/mm) | FEA E/Thickness (J/mm) | Difference (%) | Exp E/Areal Density (kJ/g/mm2) | FEA E/Areal Density (kJ/g/mm2) | Difference (%) | Exp E/Preform Areal Density (kJ/g/mm2) | FEA E/Preform Areal Density (kJ/g/mm2) | Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2L487 | 13.67 | 12.61 | 7.77 | 8.92 | 7.97 | 12.22 | 18.87 | 17.89 | 5.48 |
| 2L545 | 13.03 | 13.67 | −4.91 | 8.60 | 8.51 | 0.96 | 18.50 | 17.95 | 3.04 |
| 2L587 | 13.80 | 14.52 | −5.22 | 9.39 | 9.04 | 5.29 | 19.29 | 17.47 | 10.44 |
| 2L487twill | 13.34 | 11.95 | 9.97 | 8.60 | 7.65 | 12.07 | 16.86 | 17.32 | −2.62 |
| 2L487basket | 13.53 | 12.15 | 10.13 | 8.70 | 7.51 | 15.49 | 18.40 | 17.00 | 8.28 |
| 3L487 | 16.21 | 16.0 | 1.29 | 10.65 | 10.15 | 5.05 | 21.74 | 21.84 | −0.45 |
| 3L545 | 16.08 | 17.56 | 9.20 | 10.62 | 10.77 | −1.31 | 21.85 | 20.95 | 4.30 |
| 3L587 | 17.68 | 18.05 | 2.09 | 11.28 | 11.09 | 1.81 | 21.95 | 21.62 | 1.53 |
| 4L487 | 20.31 | 17.23 | 15.16 | 13.02 | 10.90 | 11.51 | 27.41 | 22.92 | 11.52 |
| 4L545 | 21.25 | 19.25 | 12.19 | 12.22 | 11.87 | 3.04 | 26.45 | 23.56 | 12.28 |
| 4L587 | 21.23 | 20.02 | 5.69 | 12.35 | 12.26 | 0.88 | 23.98 | 23.43 | 2.35 |
| Model ID | Damage Initiation (ms) | Failure (ms) |
|---|---|---|
| 2L487 | 0.75 | 1.65 |
| 2L545 | 0.8 | 1.7 |
| 2L587 | 0.81 | 1.76 |
| 2LTwill | 0.69 | 1.62 |
| 2LBasket | 0.6 | 1.58 |
| 3L487 | 0.63 | 1.7 |
| 3L545 | 0.72 | 1.74 |
| 3L587 | 0.77 | 1.76 |
| 4L487 | 0.66 | 1.79 |
| 4L545 | 0.69 | 1.89 |
| 4L587 | 0.74 | 1.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, W.; Zikry, M.; Seyam, A.-F.M. Numerical Study of the Influence of the Structural Parameters on the Stress Dissipation of 3D Orthogonal Woven Composites under Low-Velocity Impact. Technologies 2024, 12, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12040049
Xu W, Zikry M, Seyam A-FM. Numerical Study of the Influence of the Structural Parameters on the Stress Dissipation of 3D Orthogonal Woven Composites under Low-Velocity Impact. Technologies. 2024; 12(4):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12040049
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Wang, Mohammed Zikry, and Abdel-Fattah M. Seyam. 2024. "Numerical Study of the Influence of the Structural Parameters on the Stress Dissipation of 3D Orthogonal Woven Composites under Low-Velocity Impact" Technologies 12, no. 4: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12040049
APA StyleXu, W., Zikry, M., & Seyam, A.-F. M. (2024). Numerical Study of the Influence of the Structural Parameters on the Stress Dissipation of 3D Orthogonal Woven Composites under Low-Velocity Impact. Technologies, 12(4), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12040049








