A Real-Time and Online Dynamic Reconfiguration against Cyber-Attacks to Enhance Security and Cost-Efficiency in Smart Power Microgrids Using Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Literature Review
1.2. Contribution
- Proposing an online and real-time framework for SG reconfiguration against CPSs using neural networks and conventional recurrent neural networks based on the long short-term memory (LSTM) approach.
- Evaluating technical indicators of MGs such as voltage deviation and avoiding changes in short-circuit levels (to prevent disruption of protective settings) along with economic objectives in determining optimal dynamic reconfiguration.
- Assessing reliability indicators such as the expected energy not served (EENS) and load ability limit (LAL) of the system along with economic objectives after the CPS.
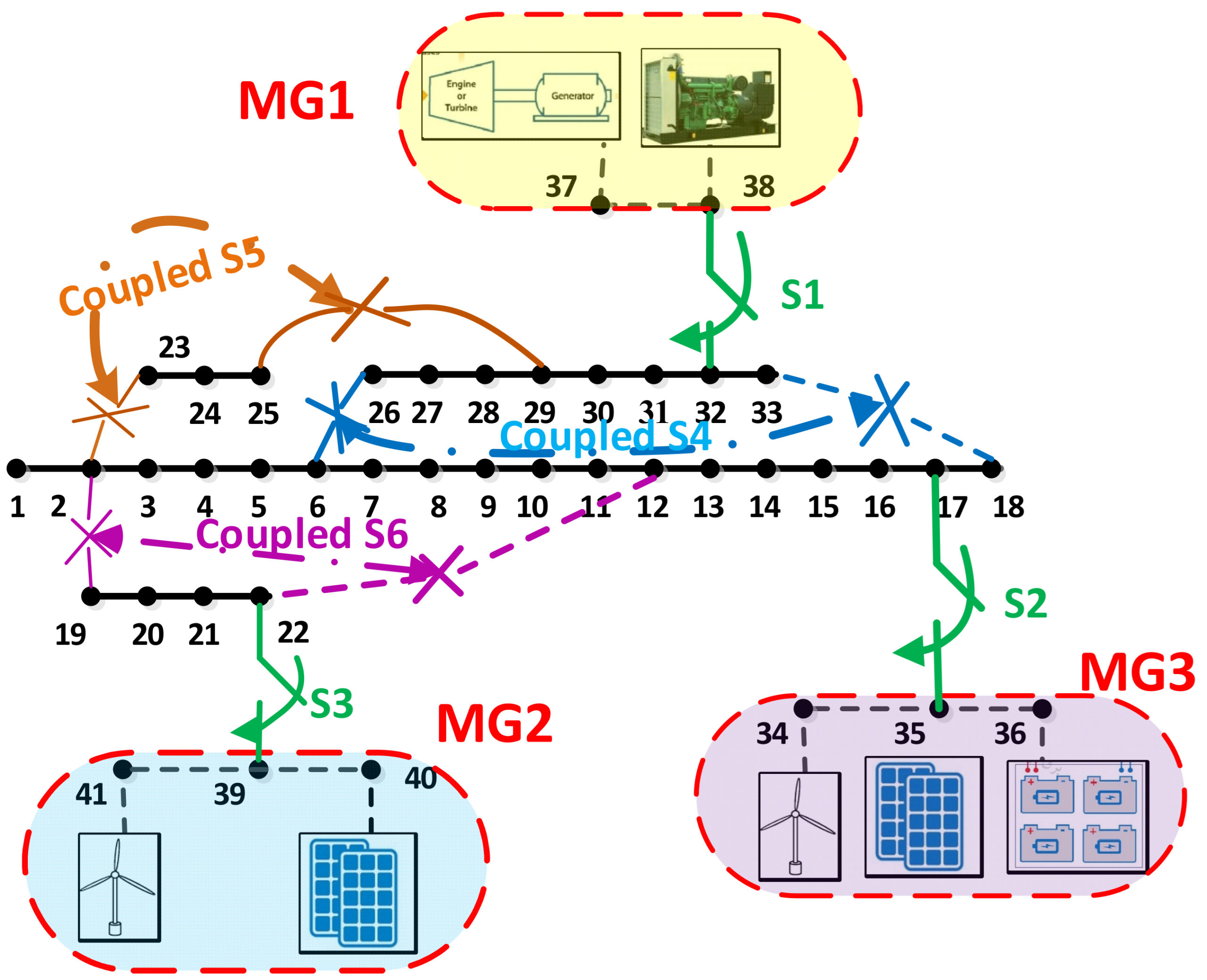
- Considering three different types of switching in the problem of dynamic reconfiguration:
- Switching of coupled lines in the main distribution network (regular reconfigurations).
- Switching of the lines between the MGs connected to the upstream network.
- Switching of the connection lines of MGs to the upstream distribution network.
1.3. Organization
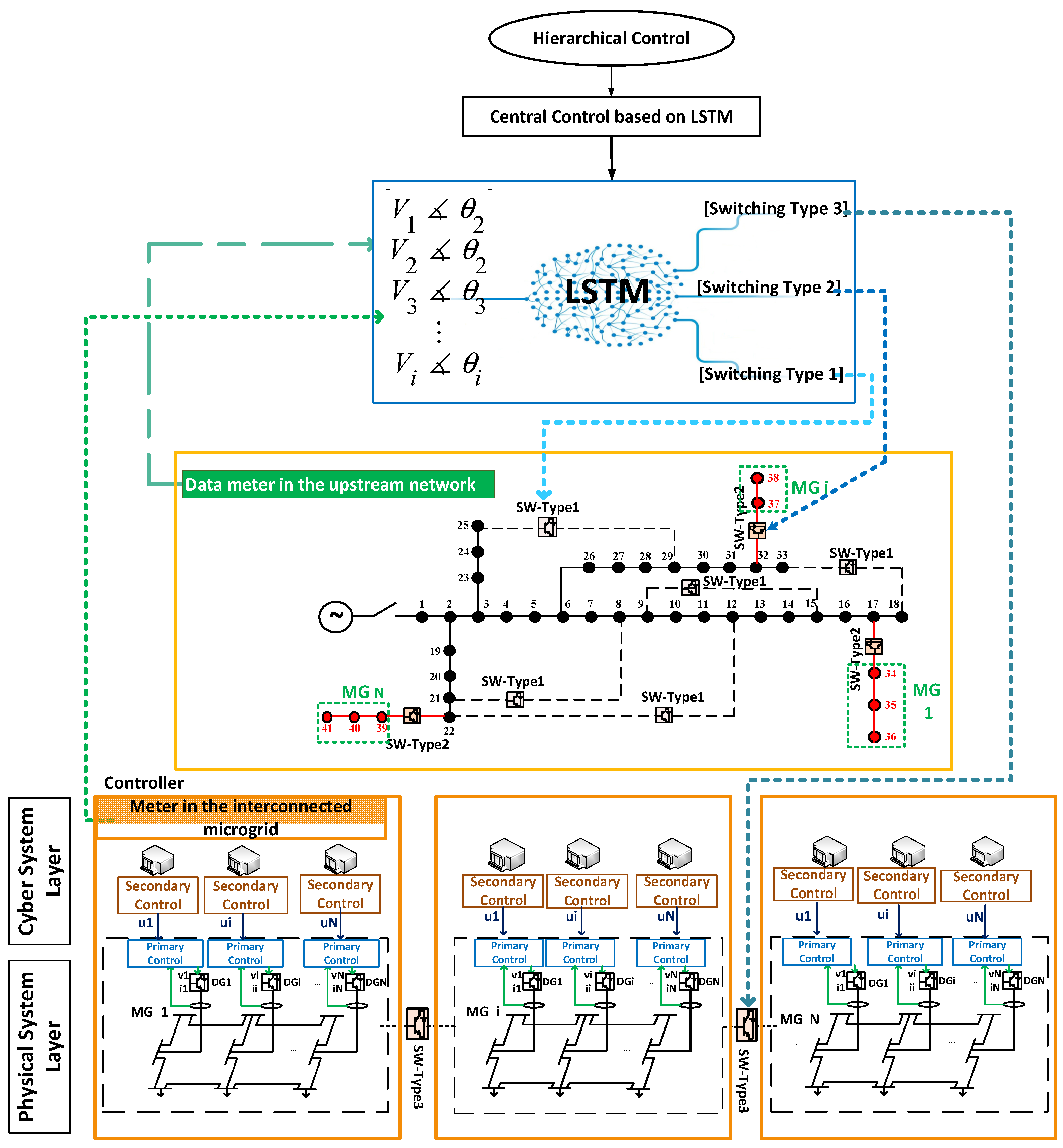
2. Proposed Framework
3. Mathematical Problem Formulations
| Algorithm 1: Real-time dynamic reconfigurations against the physical–cyberattacks. |
| Start 1. Calculate Required Parameters for Optimal Dynamic Reconfiguration: Input Data: ● Load Profile ● Electricity Price ● Initial Reconfiguration ● Initial DG Generation 2. Hierarchical Control System: Gather Required Data: ▪ Gather Required Data: ▪ Initial Losses Index ▪ Initial VD Index ▪ Initial EENS Index ▪ Initial SCL Index ▪ Initial LAL Index ▪ Initial SOC of ESS ▪ Initial DG Limits 3. Prepare Data for Optimization Algorithm For Each Parameter: ● Collect relevant data points ● Format data for the optimization algorithm End 4. Optimize Proposed Objective Function For Each Optimization Iteration: ● Apply the optimization algorithm to minimize/maximize the objective function ● Evaluate performance metrics (e.g., cost, losses) End 5. Train LSTM Neural Network for Optimal DR If Training Data is Sufficient: ● Use the optimized data to train the LSTM neural network ● Perform back-propagation and adjust weights Else: ● Collect additional data and retry training End 6. Select Optimal DR Using LSTM Neural Network For Each Real-Time Input: ● Utilize the trained LSTM neural network to predict the optimal DR based on current conditions End 7. Receive Real-Time Input Data from Online DMU: Input Data: ▪ Voltages Magnitude of Each Bus ▪ Voltage Angle of Each Bus ● Update the system state with the latest input data End Stop |
3.1. Cost Modelling of the Solar and Wind Generation Units
3.2. Cost Modelling of the Traditional Generation Units
3.3. Battery Energy Storage Unit Modeling
3.4. Demand Response Implementation
Consumption Management through Time-Based Rate and Incentive-DR Scheme
3.5. Modelling the Uncertainty in Loads and Renewable Energy Sources
3.6. Power Losses Formulation
3.7. Voltage Deviation Formulations
3.8. Dynamic Reconfiguration Modeling
3.9. Short-Circuit Level Criteria Modeling
3.10. Load Ability Limit Criteria
3.11. Expected Energy Not Served Criteria
3.12. Objective Function Formulation
4. Multi-Objective Optimization Method
5. Fast Decision-Making Using LSTM Neural Network
5.1. Inputs and Outputs of the LSTM Network
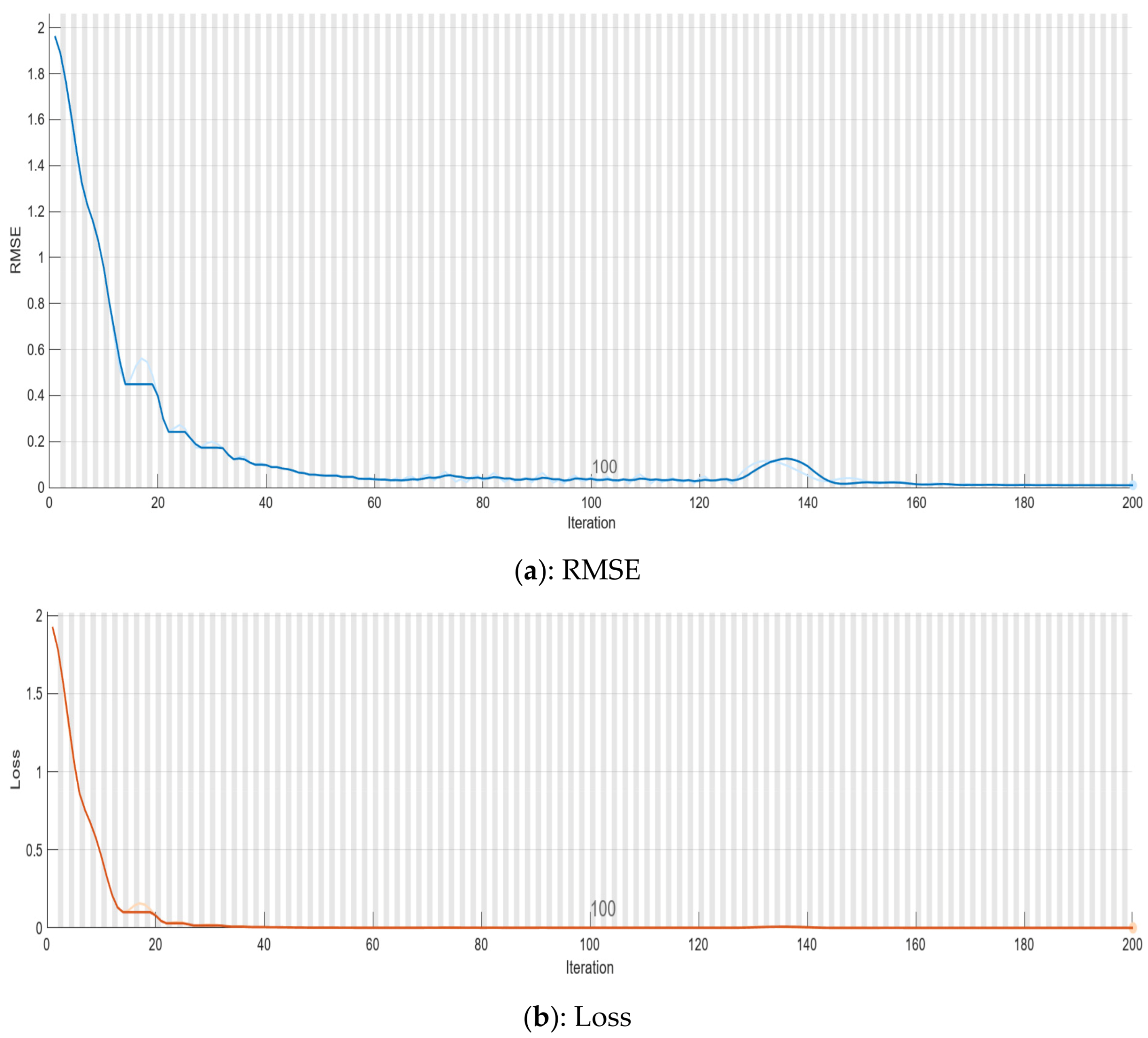
5.2. Optimization and Training Process
5.3. LSTM Architecture and Functionality
- The cell state section formulation:
- 2.
- The Input Gate section formulation:
- 3.
- The Forget Gate section formulation:
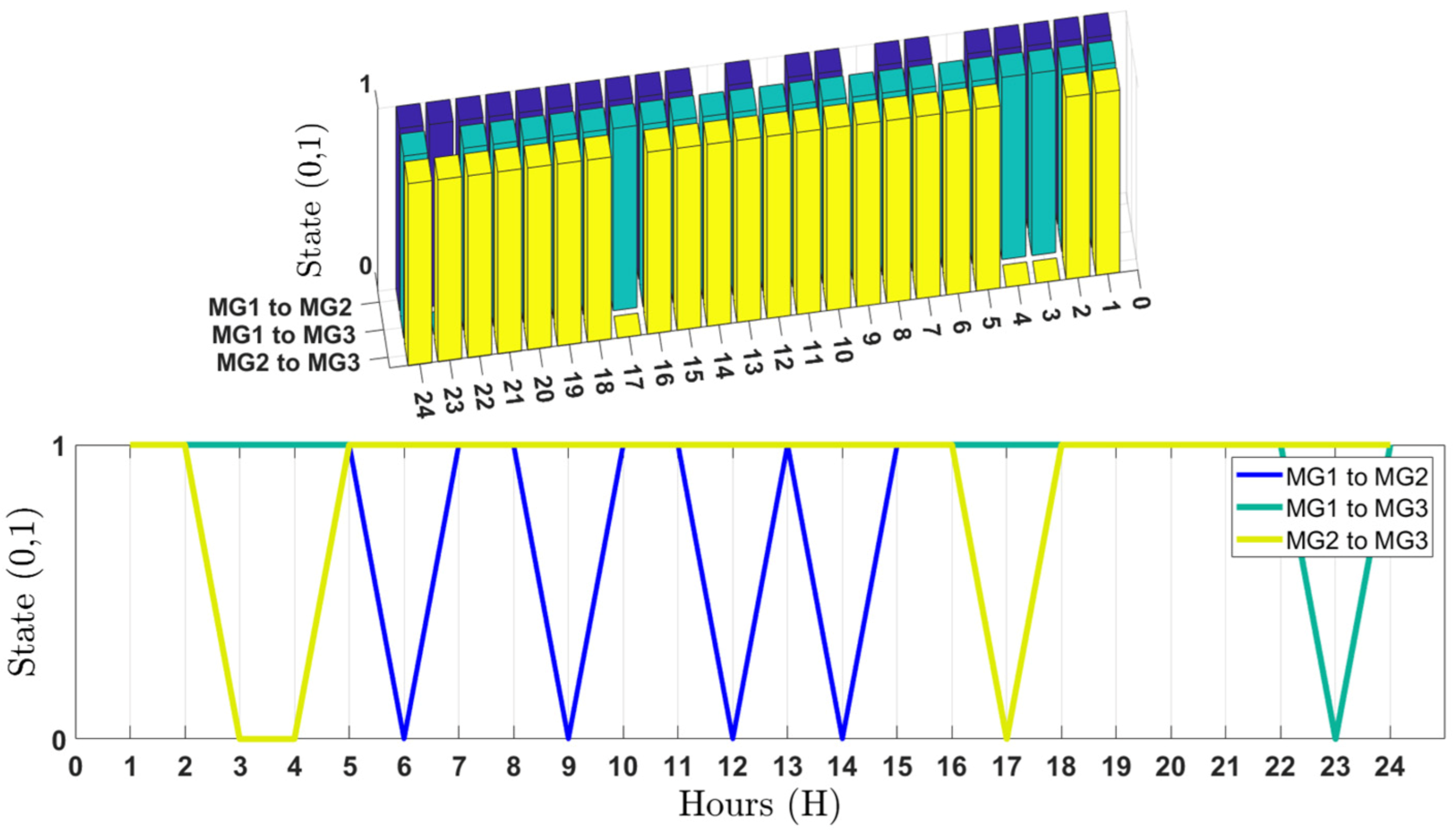
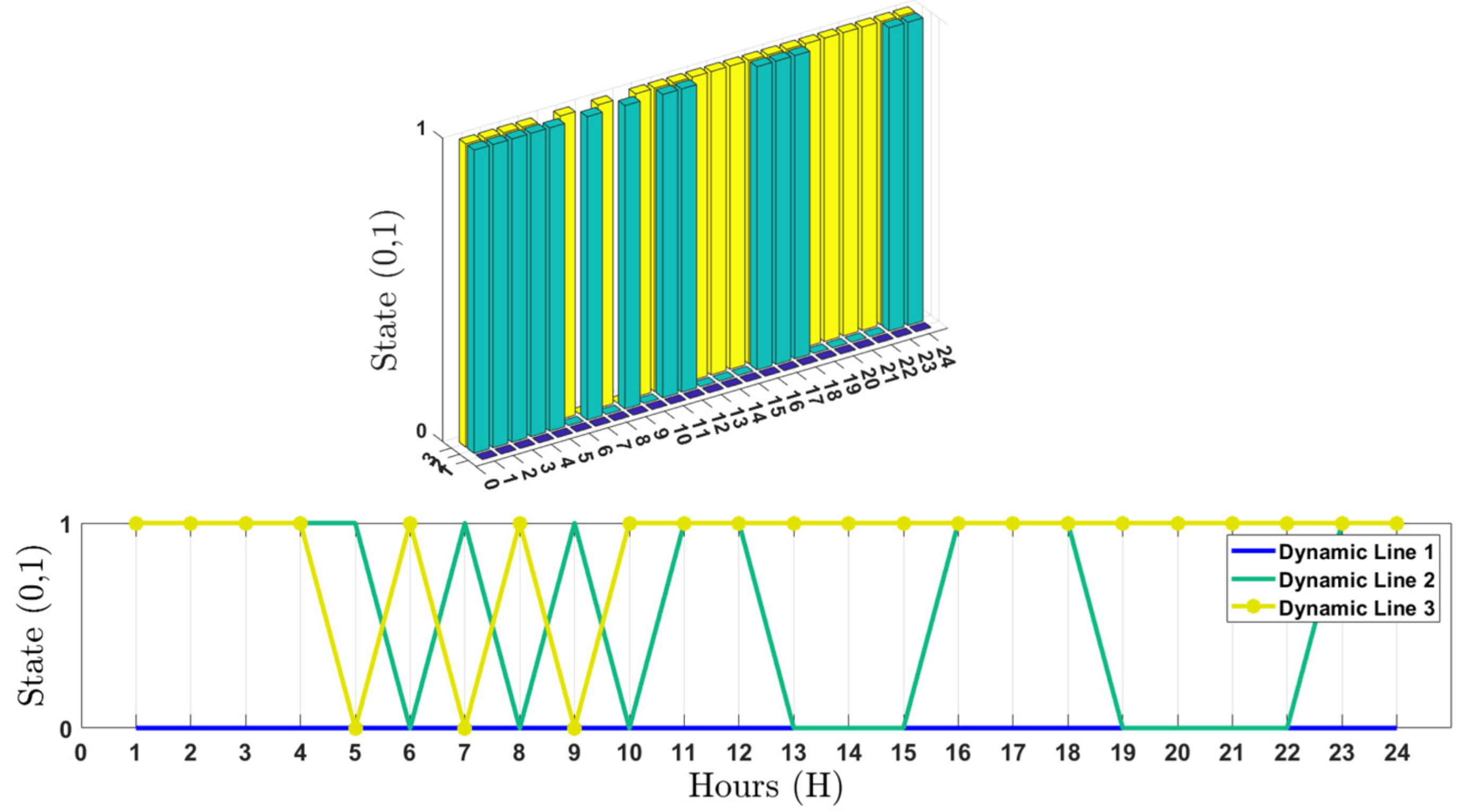
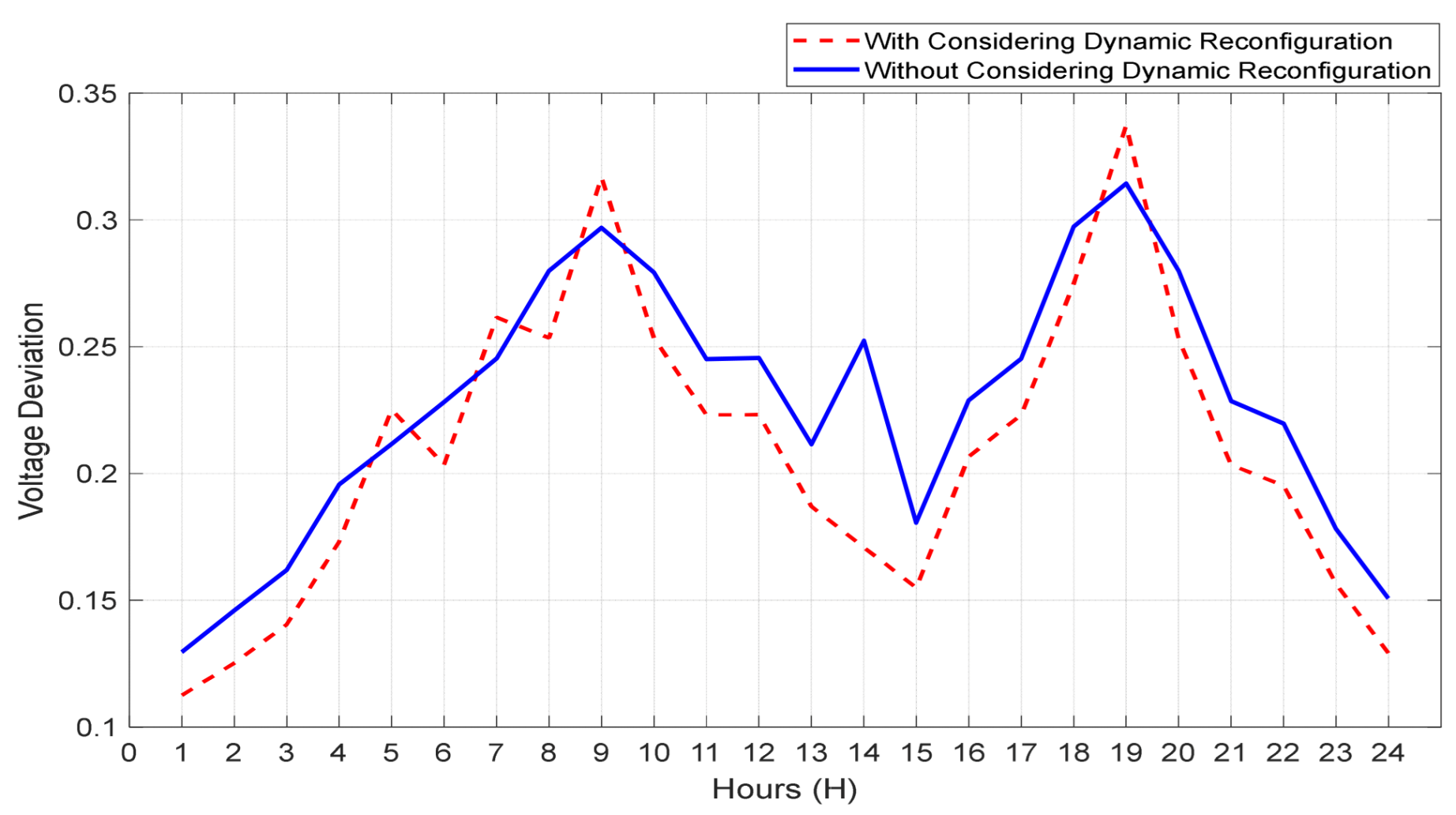
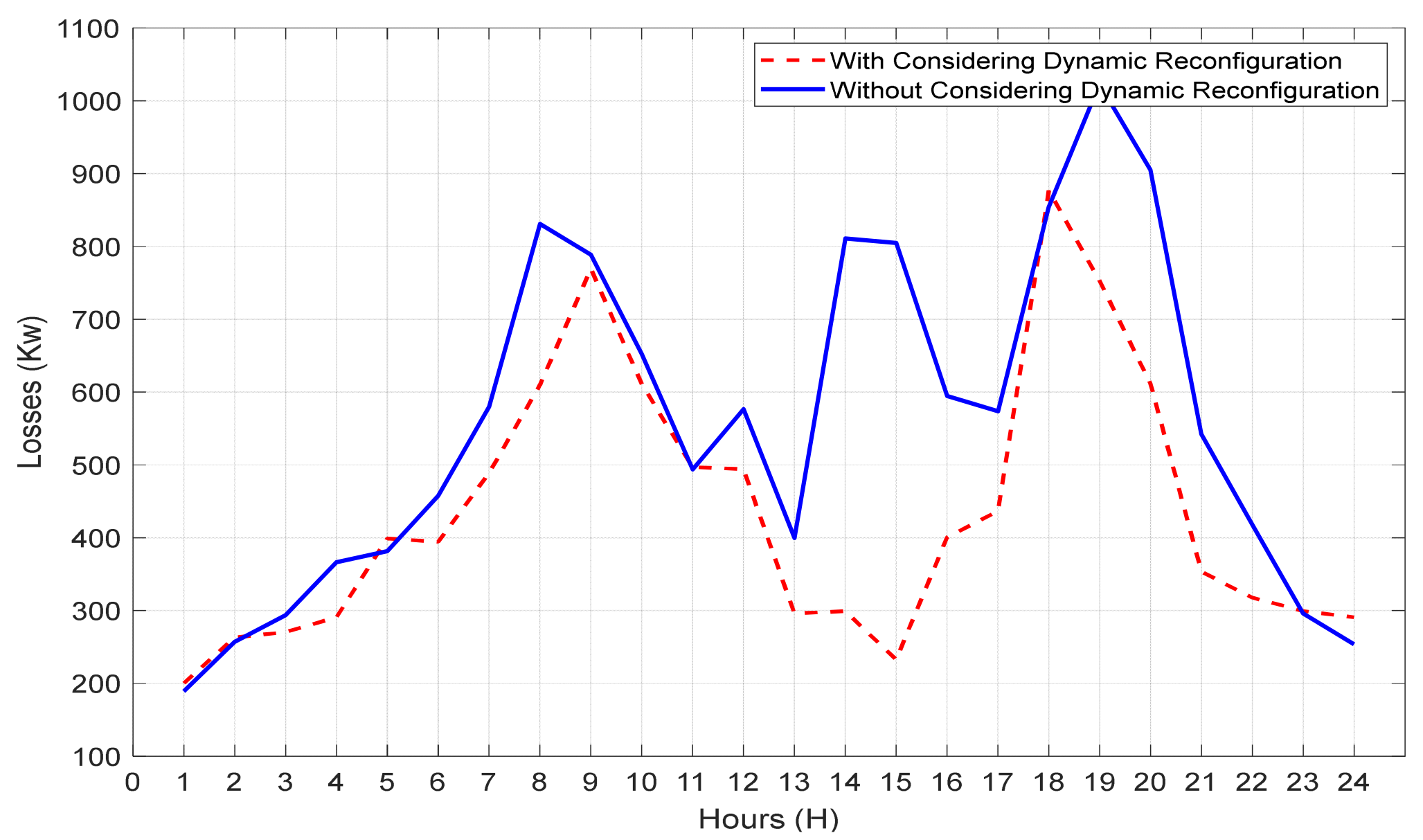
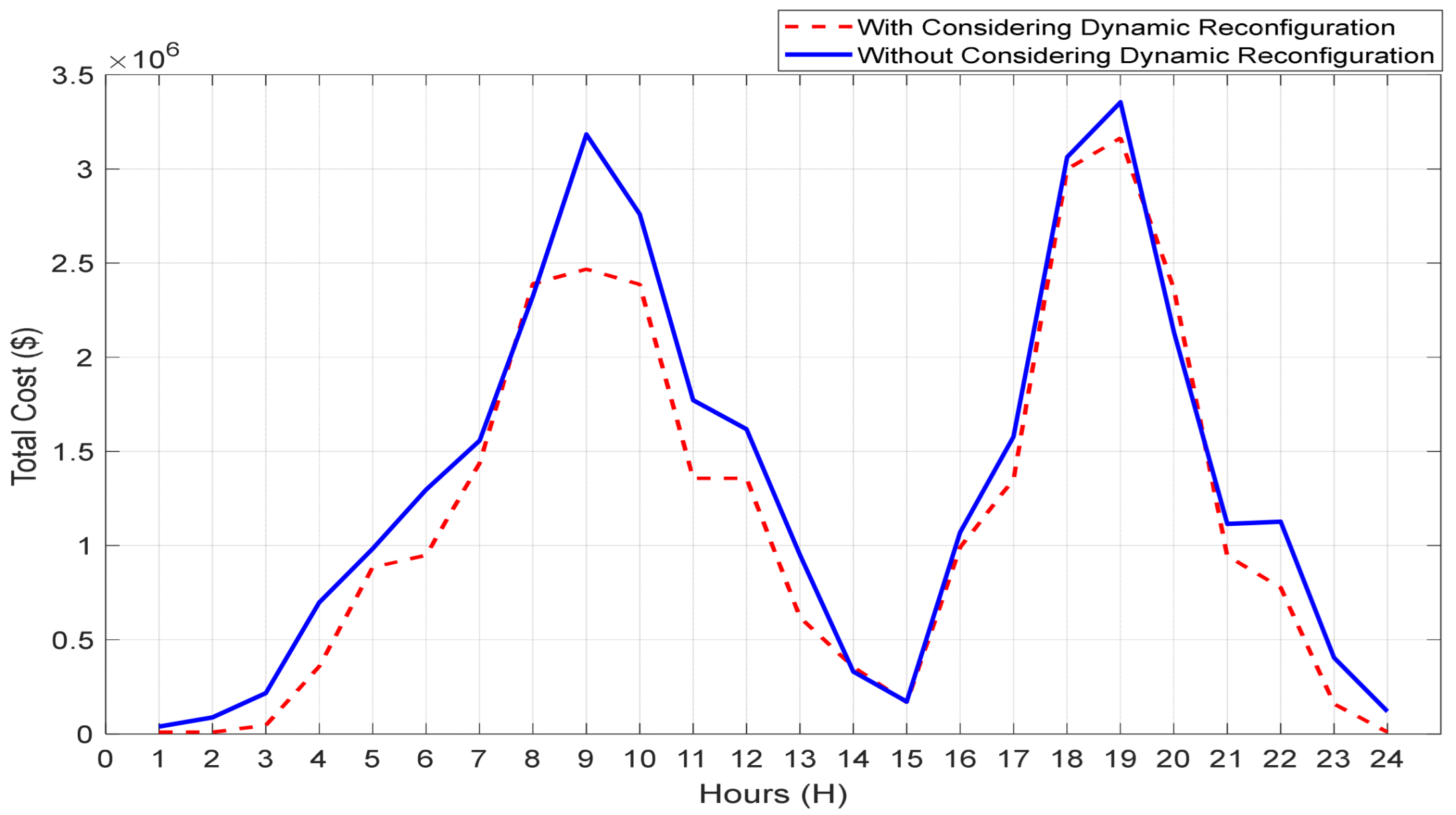
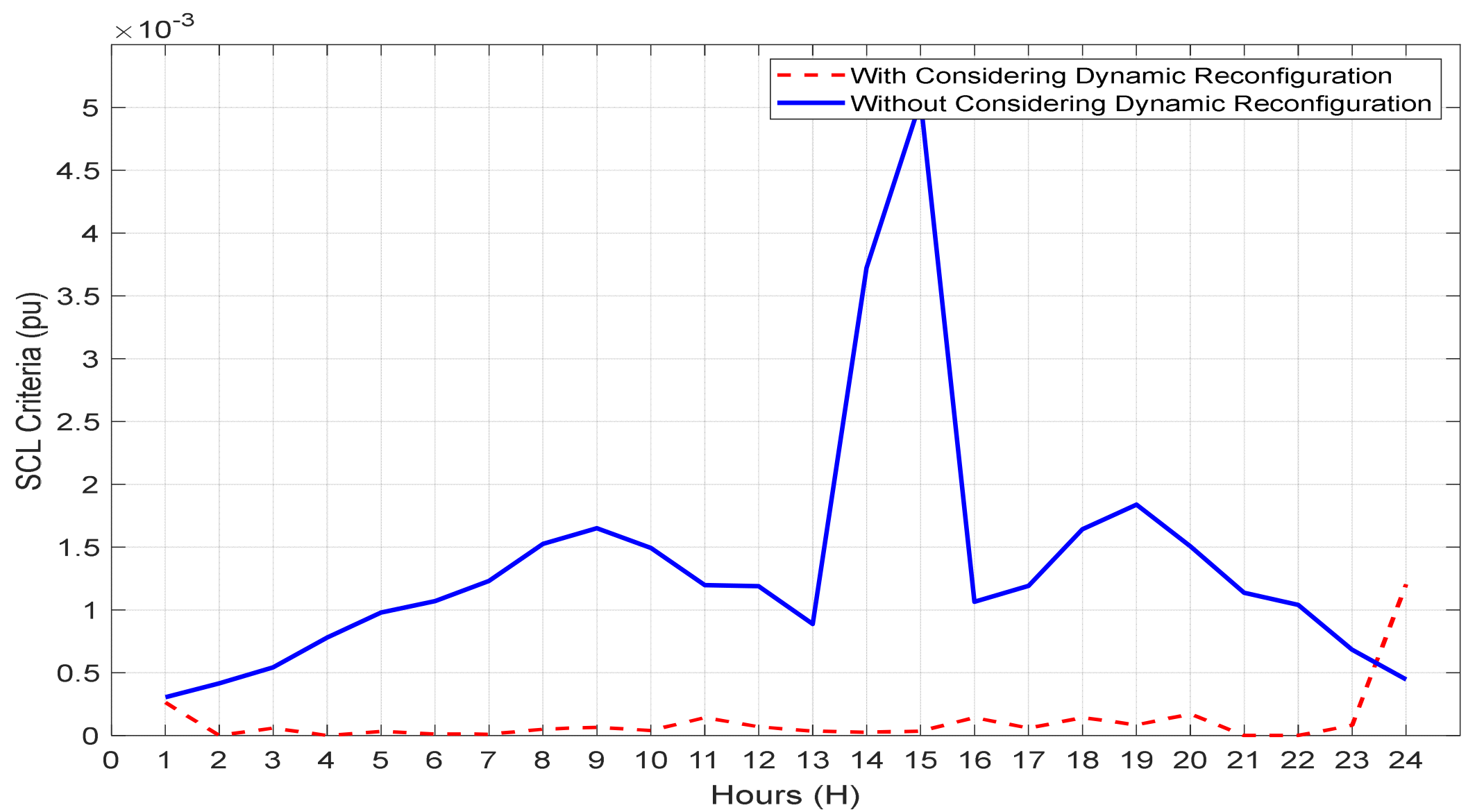
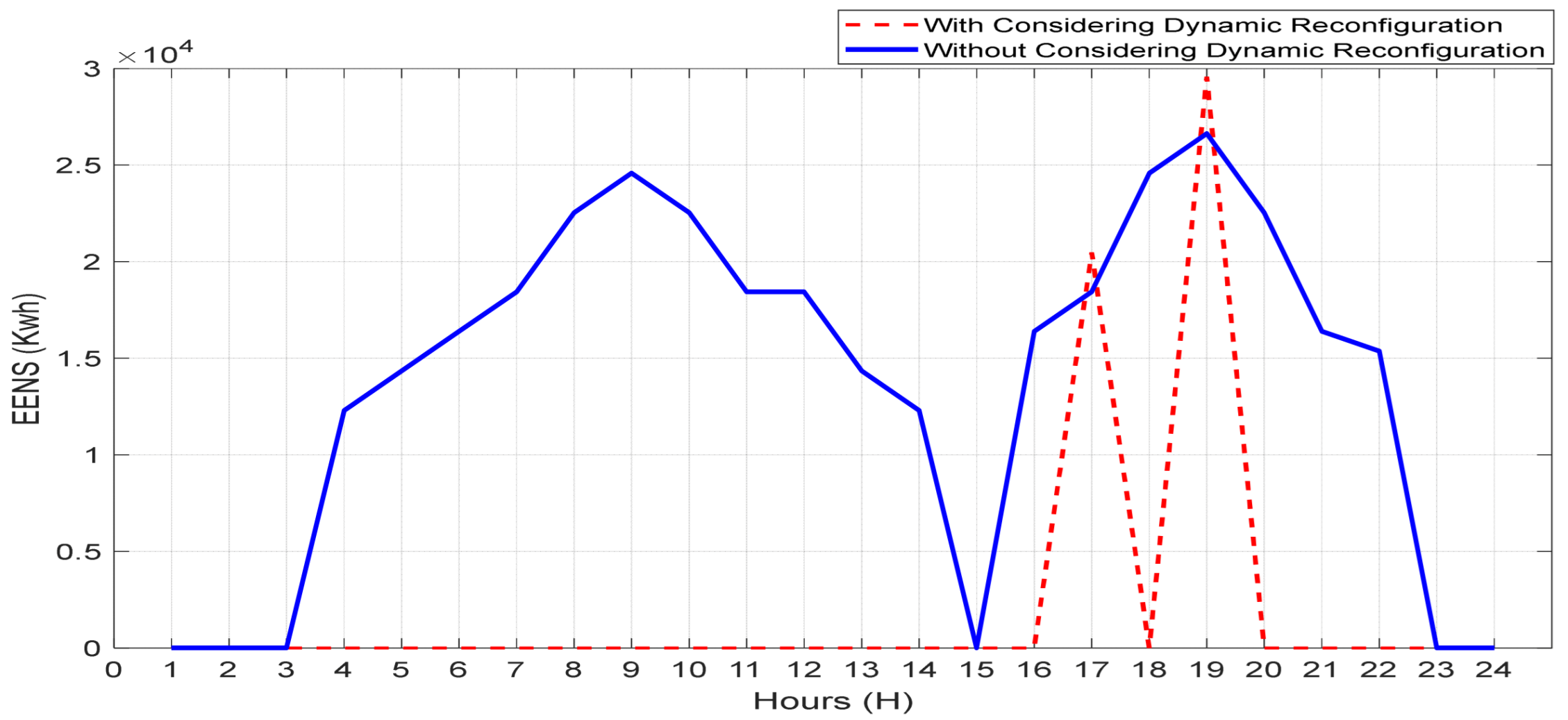
6. Simulation Results and Discussion
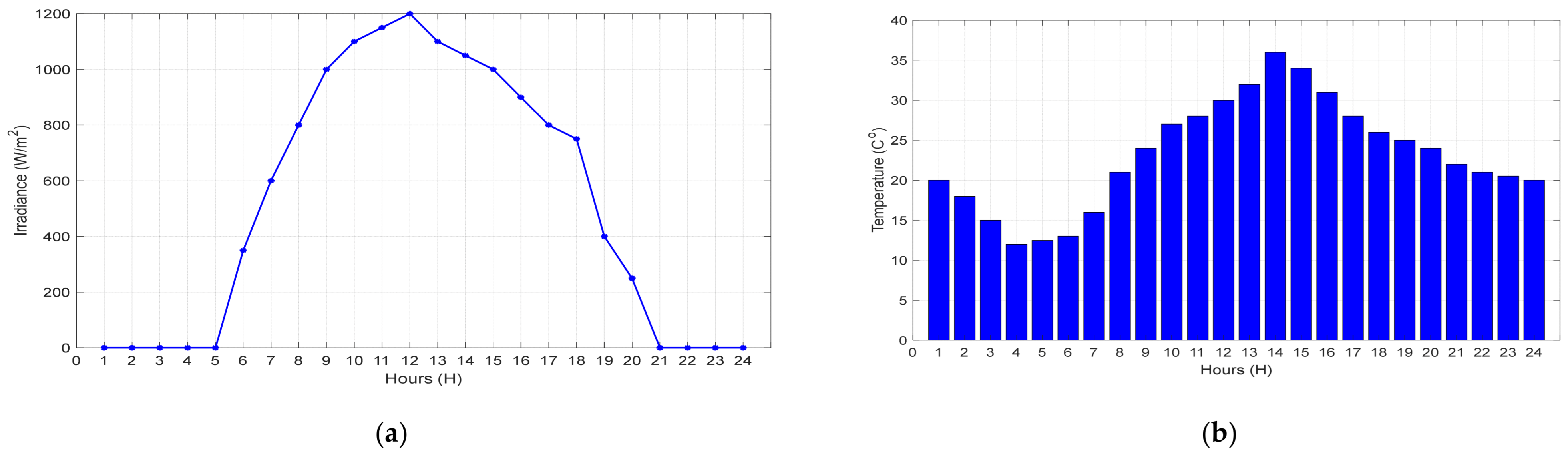
6.1. Input Parameters of the System
6.2. Results Analysis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, R.; Islam, N.; Das, S.K.; Muyeen, S.; Moyeen, S.I.; Ali, M.F.; Tasneem, Z.; Islam, M.R.; Saha, D.K.; Badal, M.F.R. Energy sustainability–survey on technology and control of microgrid, smart grid and virtual power plant. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 104663–104694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, M.; Niknam, T.; Wang, Z.; Mehrandezh, M.; Dehghani, M.; Ghadimi, N. A comprehensive review of cyber-attacks and defense mechanisms for improving security in smart grid energy systems: Past, present and future. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 215, 108975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafees, M.N.; Saxena, N.; Cardenas, A.; Grijalva, S.; Burnap, P. Smart Grid Cyber-Physical Situational Awareness of Complex Operational Technology Attacks: A Review. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Mombeshora, E.M.; Clark, K.P.; Mbavarira, T.S. Understanding of Cyber-Attack Vulnerabilities During Natural Disasters and Discussing A Cyber-Attack Resiliency Framework. In Proceedings of the SoutheastCon, Atlanta, GA, USA, 15–24 March 2024; pp. 466–471. [Google Scholar]
- Asrari, A.; Ansari, M.; Khazaei, J.; Cecchi, V. Real-time Blackout Prevention in Response to Decentralized Cyberattacks on a Smart Grid. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Texas Power and Energy Conference (TPEC), College Station, TX, USA, 6–7 February 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasi, M.; Dehghani, M.; Niknam, T.; Kavousi-Fard, A. Investigating overall structure of cyber-attacks on smart-grid control systems to improve cyber resilience in power system. Network 2020, 1, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Hui, H.; Ding, Y.; Ye, C.; Zheng, M. Operational reliability evaluation of urban multi-energy systems with equiv-alent energy storage. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 59, 2186–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, D.; Yu, L.; Yan, H. Dynamic Event-Triggered Output Feedback Control for Load Frequency Control in Power Systems with Multiple Cyber Attacks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2022, 52, 6246–6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghahadi, M.; Bosisio, A.; Merlo, M.; Berizzi, A.; Pegoiani, A.; Forciniti, S. Digitalization Processes in Distribution Grids: A Comprehensive Review of Strategies and Challenges. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariz, P.; Keivanimehr, M. Towards Electromobility: Challenges in Integrating Electric Vehicles and Charging Stations on Power systems. In Advanced Technologies in Electric Vehicles; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 505–520. [Google Scholar]
- Yaghoubi, E.; Yaghoubi, E.; Yusupov, Z.; Rahebi, J. Real-time techno-economical operation of preserving microgrids via optimal NLMPC considering uncertainties. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2024, 57, 101823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazaralizadeh, S.; Banerjee, P.; Srivastava, A.K.; Famouri, P. Battery Energy Storage Systems: A Review of Energy Man-agement Systems and Health Metrics. Energies 2024, 17, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Basumallik, S.; Banerjee, P.; Srivastava, A.K. Intrusion Detection in Cyber-Physical Grid using Incremental ML with Adaptive Moment Estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Cyber-Physical Syst. 2024, 2, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirunavukkarasu, G.S.; Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Jamei, E.; Horan, B.; Mekhilef, S.; Stojcevski, A. Role of optimization techniques in microgrid energy management systems—A review. Energy Strat. Rev. 2022, 43, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Samman, M.; Mokhlis, H.; Mansor, N.N.; Mohamad, H.; Suyono, H.; Sapari, N.M. Fast Optimal Network Reconfiguration with Guided Initialization Based on a Simplified Network Approach. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 11948–11963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, H.; Coelho, E.A.A.; Guerrero, J.M. MAS-Based Distributed Coordinated Control and Optimization in Microgrid and Microgrid Clusters: A Comprehensive Overview. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 33, 6488–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghikhani, M.A.; Khamseh, J. Multi-objective optimal energy management of storage system and distributed generations via water cycle algorithm concerning renewable resources uncertainties and pollution reduction. J. Energy Storage 2022, 52, 4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callenes, J.; Poshtan, M. Dynamic Reconfiguration for Resilient State Estimation Against Cyber Attacks. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2023, 12, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, A.V.; Li, X. Network Reconfiguration Impact on Renewable Energy System and Energy Storage System in Day-Ahead Scheduling. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Washington, DC, USA, 26–29 July 2021; pp. 01–05. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, C.; Wang, Y.; Wen, C.; Xu, Y.; Lin, P. Distributed resilient control for energy storage systems in cyber–physical mi-crogrids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Li, M.; Li, Z.S. Resilience-based optimal recovery strategy for cyber–physical power systems considering compo-nent multistate failures. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2020, 70, 1510–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.; Kazemi, A.; Gilani, M.A.; Shafie-Khah, M. A Stochastic Planning Model for Improving Resilience of Distribution System Considering Master-Slave Distributed Generators and Network Reconfiguration. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 78859–78872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilpoor, K.; Ameli, M.T.; Azad, S.; Sayadi, Z. Resilient energy management incorporating energy storage system and network reconfiguration: A framework of cyber-physical system. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2023, 17, 1734–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Lu, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, B.; Tu, H.; Lukic, S. Dynamic Microgrids in Resilient Distribution Systems with Reconfigurable Cyber-Physical Networks. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 9, 5192–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamari, M.; Amrane, Y.; Boudour, M.; Boussahoua, B. Multi-objective economic/emission optimal energy management system for scheduling micro-grid integrated virtual power plant. Energy Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 3057–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedighizadeh, M.; Fazlhashemi, S.S.; Javadi, H.; Taghvaei, M. Multi-objective day-ahead energy management of a mi-crogrid considering responsive loads and uncertainty of the electric vehicles. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 121562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, S.; Akbari, A.; Ghahremani, B.; Razban, A. Reliability-based energy scheduling of active buildings subject to re-newable energy and demand uncertainty. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2022, 28, 101149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keswani, R.; Verma, H.K.; Sharma, K.S. Optimal Power Flow Integrating Renewable Energy Sources in Microgrid Employing Hybrid Grey Wolf- Equilibrium Optimizer. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE IAS Global Conference on Emerging Technologies (GlobConET), Arad, Romania, 20–22 May 2022; pp. 14–720. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, F.; Hajjiah, A.; Jermsittiparsert, K.; Al-Sumaiti, A.S.; Elsayed, S.K.; Ghoneim, S.S.; Mohamed, M.A. A secured so-cial-economic framework based on PEM-blockchain for optimal scheduling of reconfigurable interconnected microgrids. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 40797–40810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyewole, P.A.; Jayaweera, D. Power System Security with Cyber-Physical Power System Operation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 179970–179982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Arefifar, S.A. Hybrid PSO-TS based distribution system expansion planning for system performance im-provement considering energy management. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 221599–221611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, H.; Shojaei, A.A. A dynamic model for multi-objective feeder reconfiguration in distribution network considering demand response program. Energy Syst. 2022, 14, 1051–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffonneau, Y.; Bacha, S.; Barruel, F.; Ploix, S. Optimal Power Flow Management for Grid Connected PV Systems With Batteries. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2011, 2, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghami, M.R.; Pasupuleti, J.; Ling, C.M. Impact of Photovoltaic Penetration on Medium Voltage Distribution Network. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghami, M.R.; Pasupuleti, J.; Ling, C.M. A Static and Dynamic Analysis of Photovoltaic Penetration into MV Distribution Network. Processes 2023, 11, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherian, A.; Tafreshi, S.M.M. A Developed Energy Management System for A Microgrid in the Competitive Electricity Market. In Proceedings of the IEEE Power Tech Conference, Bucharest, Romania, 28 June–2 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fardini, A.; Ahmadian, A.; Aliakbar Golkar, M. Optimal energy management of a distribution network connected to different microgrids based on game theory approach. Iran. Electr. Ind. J. Qual. Product. 2019, 7, 30–46. [Google Scholar]
- Azizi, A.; Jahromi, M.Z.; Dehghanian, P.; Chamorro, H.R.; Mírez, J.; Sood, V.K. Decentralized multi-objective energy management with dynamic power electronic converters and demand response constraints. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 146297–146312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzin, H.; Fotuhi-Firuzabad, M.; Moeini-Aghtaie, M. Role of Outage Management Strategy in Reliability Performance of Multi-Microgrid Distribution Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 33, 2359–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Botterud, A.; Bessa, R.; Keko, H.; Carvalho, L.; Issicaba, D.; Sumaili, J.; Miranda, V. Wind power forecasting un-certainty and unit commitment. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 4014–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bludszuweit, H.; Dominguez-Navarro, J.A.; Llombart, A. Statistical Analysis of Wind Power Forecast Error. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2008, 23, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinson, P.; Kariniotakis, G. Conditional Prediction Intervals of Wind Power Generation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, B.; Mustafa, M.W.; Sultana, U.; Bhatti, A.R. Review on reliability improvement and power loss reduction in distri-bution system via network reconfiguration. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 66, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Ali, I.; Thomas, M.S.; Singh, S. Imposing voltage security and network radiality for reconfiguration of distri-bution systems using efficient heuristic and meta-heuristic approach. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2017, 11, 2457–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qawaqzeh, M.; Al_Issa, H.A.; Buinyi, R.; Bezruchko, V.; Dikhtyaruk, I.; Miroshnyk, O.; Nitsenko, V. The assess reduction of the expected energy not-supplied to consumers in medium voltage distribution systems after installing a sectionalizer in optimal place. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2023, 34, 101035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, M.S.; Esmaeel Nezhad, A. Multi-objective, multi-year dynamic generation and transmission expansion planning-renewable energy sources integration for Iran’s National Power Grid. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2019, 29, e2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werbos, P. Backpropagation through time: What it does and how to do it. Proc. IEEE 1990, 78, 1550–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oruh, J.; Viriri, S.; Adegun, A. Long Short-Term Memory Recurrent Neural Network for Automatic Speech Recognition. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 30069–30079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, L. An improved TS algorithm for loss-minimum reconfiguration in large-scale distribution systems. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2007, 77, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, S.A.; Ahmarinejad, A.; Nematbakhsh, E.; Javadi, M.S.; Jordehi, A.R.; Catalão, J.P. Energy management in microgrids including smart homes: A multi-objective approach. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Zhu, X.; Gu, X.; Yang, F.; Mohammadi, M. Stochastic energy management and scheduling of microgrids in correlated environment: A deep learning-oriented approach. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamir, N.; Kamel, S.; Megahed, T.F.; Hori, M.; Abdelkader, S.M. Developing Hybrid Demand Response Technique for Energy Management in Microgrid Based on Pelican Optimization Algorithm. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 214, 8905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolurian, A.; Akbari, H.; Daemi, T.; Mirjalily, S.A.A.; Mousavi, S. Energy management in microgrids considering the de-mand response in the presence of distributed generation resources on the IoT platform. Energy Sources Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 2022, 17, 2038729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| DG | Distributed Generation | MOGA | Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithm |
| FDIA | False Data Injection Attacks | PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization |
| AMIs | Advanced Metering Infrastructures | ICA | Independent Component Analysis |
| FC | Fuel Cell | HHO | Harris Hawks Optimization |
| MT | Micro Turbine | PM | Proposed Method |
| ESS | Energy Storage System | EENS | Expected Energy Not Served |
| Factors | [7] | [11] | [12] | [13] | [14] | [15] | [16] | [18] | [19] | [20] | [21] | This Paper |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Management | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Uncertainty | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| Power Loss | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Voltage Profile | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| Network Reconfiguration | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Cost of Load | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Pollution Reduction | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| Optimal Switching | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| EENS | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Operation Cost of the MGs | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Voltage Deviation | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Real-Time or Fast Online | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| Dynamic Reconfiguration | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Cyber-Attacks | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| Stability and Reliability Indexes | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| Dynamic Reconfiguration with Three Types of Switching | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| Optimization Method | Best O.F. | Number of Iterations | CPU Times(s) | Operating Cost ($) | Power Losses (KW) | VD (pu) | EENS (kWh) | Load Ability Limit (KW) | Sum of SCL Changes (pu) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (PM) | 380.4826 | 15 | 19 | 27,557,510.40 | 10.46 | 5.0 | 58.62 | 2,079,887.87 | 0.0027 |
| (PSO) | 392.5123 | 21 | 22 | 2,796,6581.51 | 11.12 | 5.31 | 55.46 | 2,091,957.19 | 0.0045 |
| (MOGA) | 384.7896 | 18 | 21 | 27,855,164.43 | 10.74 | 5.21 | 54.82 | 2,088,287.52 | 0.0039 |
| (ICA) | 383.4212 | 19 | 23 | 27,697,412.74 | 10.46 | 5.01 | 50.18 | 2,088,254.54 | 0.0029 |
| (HHO) | 382.5893 | 17 | 20 | 27,594,718.87 | 10.48 | 5.0 | 58.62 | 2,080,917.73 | 0.0028 |
| Epoch | Iteration | Time Elapsed (hh:mm:ss) | Mini-Batch RMSE | Mini-Batch Loss | Base Learning Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 00:00:04 | 1.96 | 1.9 | 0.01 |
| 50 | 50 | 00:00:06 | 0.05 | 1.4 × 10⁻3 | 0.01 |
| 100 | 100 | 00:00:07 | 0.04 | 1.0 × 10⁻3 | 0.01 |
| 150 | 150 | 00:00:08 | 0.03 | 5.3 × 10⁻⁴ | 0.001 |
| 200 | 200 | 00:00:09 | 0.01 | 5.2 × 10⁻⁵ | 0.001 |
| Consideration Statues | Operating Cost ($) | Power Losses (kW) | VD (pu) | EENS (kWh) | Load Ability Limit (kW) | Sum of SCL Changes (pu) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM | 27,557,510.4 | 10.46 | 5.0 | 50.07 | 2,079,887.87 | 0.007 |
| [23,51] | 31,956,594.76 | 13.34 | 5.45 | 334.91 | 24,750.58 | 0.23 |
| [52] | 29,165,841.21 | 11.34 | 6.28 | 448.51 | 31,252.61 | 0.12 |
| [53,54] | 243,116,712.42 | - | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yaghoubi, E.; Yaghoubi, E.; Yusupov, Z.; Maghami, M.R. A Real-Time and Online Dynamic Reconfiguration against Cyber-Attacks to Enhance Security and Cost-Efficiency in Smart Power Microgrids Using Deep Learning. Technologies 2024, 12, 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12100197
Yaghoubi E, Yaghoubi E, Yusupov Z, Maghami MR. A Real-Time and Online Dynamic Reconfiguration against Cyber-Attacks to Enhance Security and Cost-Efficiency in Smart Power Microgrids Using Deep Learning. Technologies. 2024; 12(10):197. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12100197
Chicago/Turabian StyleYaghoubi, Elnaz, Elaheh Yaghoubi, Ziyodulla Yusupov, and Mohammad Reza Maghami. 2024. "A Real-Time and Online Dynamic Reconfiguration against Cyber-Attacks to Enhance Security and Cost-Efficiency in Smart Power Microgrids Using Deep Learning" Technologies 12, no. 10: 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12100197
APA StyleYaghoubi, E., Yaghoubi, E., Yusupov, Z., & Maghami, M. R. (2024). A Real-Time and Online Dynamic Reconfiguration against Cyber-Attacks to Enhance Security and Cost-Efficiency in Smart Power Microgrids Using Deep Learning. Technologies, 12(10), 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12100197







