Abstract
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) ecosystem faces increased risks and vulnerabilities due to adopting Industry 4.0 standards. Integrating data from various places and converging several systems have heightened the need for robust security measures beyond fundamental connection encryption. However, it is difficult to provide adequate security due to the IIoT ecosystem’s distributed hardware and software. The most effective countermeasures must be suggested together with the crucial vulnerabilities, linked threats, and hazards in order to protect industrial equipment and ensure the secure functioning of IIoT systems. This paper presents a thorough analysis of events that target IIoT systems to alleviate such concerns. It also offers a comprehensive analysis of the responses that have been advanced in the most recent research. This article examines several kinds of attacks and the possible consequences to understand the security landscape in the IIoT area. Additionally, we aim to encourage the development of effective defenses that will lessen the hazards detected and secure the privacy, accessibility, and reliability of IIoT systems. It is important to note that we examine the issues and solutions related to IIoT security using the most recent findings from research and the literature on this subject. This study organizes and evaluates recent research to provide significant insight into the present security situation in IIoT systems. Ultimately, we provide outlines for future research and projects in this field.
1. Introduction
The widespread adoption of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) devices has revolutionized industrial environments, enabling enhanced efficiency, automation, and data-driven decision making. However, this rapid integration also exposes these systems to an increased risk of cyber threats and attacks. This article, “A Comprehensive Survey of Cybersecurity Threats, Attacks, and Effective Countermeasures in Industrial Internet of Things”, addresses the critical issue of IIoT security. It comprehensively analyzes various attack vectors that target industrial systems while proposing effective countermeasures to mitigate these risks. By thoroughly examining the evolving threat landscape and identifying potential vulnerabilities, this study serves as a valuable resource for organizations aiming to protect their critical infrastructure and ensure the secure operation of their IIoT networks.
Cyber-physical infrastructures serve as vital elements inside these partially structured facilities if intelligent factories, as described by the industry 4.0 standards [1], have to maximize their manufacturing cycle. Their job entails monitoring and managing natural processes while making independent, decentralized decisions. The operational network of the IIoT is crucial since it makes it possible for logical systems to collaborate and communicate instantaneously. Thus, it is possible to execute the administrative services, operational procedures, and creative manufacturing solutions required for the smooth completion of the production chain [2].
This “IIoT” refers to an extensive collection of linked sensors, tools, and gadgets that, once incorporated into industrial sectors like manufacturing and energy management, produce a high-tech architecture of services. Figure 1 [3] illustrates how this interrelated structure makes it possible to deploy automation at an advanced level, reducing costs and increasing manufacturing procedure productivity.
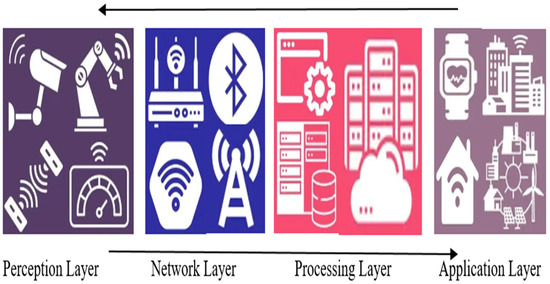
Figure 1.
Generalized architecture of Industrial Internet of Things systems.
The interconnectedness of the IIoT enables seamless data collection, analysis, and exchange, thereby facilitating the optimization of production chain performance. This enhanced connectivity also opens up new possibilities for the industrial sector, allowing the realization of previously impractical operations and driving significant innovation and progress in the industry.
The constant and seamless interchange of information across all production stages is essential for successfully transforming the supply chain into a fully automated operation powered by the IIoT. Utilizing a tiered architecture inside IIoT systems is frequently required to achieve this level of connectivity. Physical elements, including sensors, actuators, control systems, and security methods, are considered at the hardware level. The physical networking medium, such as cable and wireless technologies, are included at the network level. Finally, the architecture’s upper levels contain protocols that gather and send data throughout the communication stack, ensuring efficient and dependable data transport.
The requirement to defend critical industrial systems from cybersecurity threats is highlighted by the growing interconnectedness and adoption of standard communication protocols, as outlined in the Industry 4.0 specifications [4]. Factory automation systems (ICSs), which manage the manufacturing process and the functioning of intelligent factories, constantly have access to critical corporate data in addition to the internet and industrial networks [5]. Sensors employed in control loops for data collecting and process automation are two typical examples of such systems [6]. Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems (SCADA) are another example of the same environment. The IIoT network’s interconnected technologies allow for the remote monitoring and control of processes from any location. While connectivity and networking improve operational effectiveness, they also pose severe problems to infrastructure security [7]. Considerations for privacy, reliability, and accessibility become critical.
Moreover, the initial design focus of industrial machines and devices is functionality rather than security, rendering them particularly vulnerable to cyberattacks. Exploiting flaws in commonly used Industrial IoT communication protocols, as well as inadequacies in their management of operations and consumption, can result in the compromising of crucial devices, the denial of vital functions, and possibly the total or partial demise of those items, with likely disastrous results [8]. Although several studies have explored security risks in IoT systems in general, there is currently limited extensive research specifically focused on the Industrial IoT environment. In addition, the seriousness of assaults and the hazards that accompany them, which can cause substantial harm and even fatalities, are frequently not appropriately highlighted in current studies.
By undertaking a thorough analysis of popular attack techniques used in industrial applications and researching pertinent literature, this essay seeks to fill the following gaps.
- The objective is to promote a resilient industrial environment and provide a more efficient, cybersecurity-focused strategy.
- This study’s main contribution is to offer a thorough analysis of security hazards to manufacturing machinery and the most recent solutions to protect the infrastructure for researchers and organizations working with Industrial IoT technologies.
- It addresses these structures’ essential qualities and shortcomings and thoroughly analyzes all potential solutions to overcome the vulnerabilities, as recommended in recent research.
- The supplied evaluation and analytic paradigm set this research effort apart from other IIoT studies.
- It provides a thorough, current, and reliable standard for detecting and evaluating risks in the constantly changing workplace.
- This article offers a comprehensive analysis of the countermeasures that have been advanced in the most recent research articles.
- We examine many types of attacks and their possible consequences to understand the security landscape in the IIoT area.
This study is organized as follows: While Section 3 thoroughly explains the significant dangers in the Industrial IoT ecosystem, the second part reviews relevant studies. The next part additionally looks at how these risks operate and discusses practical fixes suggested in recent studies. The main conclusions regarding our investigation are presented in the fourth part. The last part summarizes the research and highlights potential directions for further investigation.
2. Related Literature
This part analyzes research studies that concentrate on the risks posed by Industrial IoT systems. The critical security threats are covered, as well as potential solutions. The contributions of these works are also examined, and issues that need additional research and study are noted. Many contemporary attacks and threats on critical infrastructure networks, such as power grids [9], exploit specific control systems like SCADA devices or compromise actuators or sensors in the physical layers of the network or attack links between devices in the data-link layer. Industrial automation control and telemetry systems depend on SCADA products, which use local controllers to connect to an Industrial IoT network. Contemporary cyber assaults [10,11] frequently use tactics to disconnect actuators or sensors, enabling the manipulation of sensor readings and changing how cyber-physical structures function in industrial settings. For example, cyber-attacks on a SCADA water supply and decontamination plant might cause crucial operations, including water treatment and production, flow meters, level and conductivity analysis, pH analysis, and chemical dosing pumps, to be compromised. Such assaults may have grave effects on public health. One specific paper skips over a detailed analysis of assaults on the physical layer and only lists the parts of a viable SCADA system. The paper’s authors address five attack types and attack vectors, including the use of cross-site scripting (XSS), overflowing buffers, injection of SQL queries, and source code design and implementation. However, they do not offer detailed explanations or methodological approaches for mitigation or prevention. Moreover, the study fails to provide substantial insights into attacks on the software 4.7 or raise awareness about the severity of attacks against SCADA systems, which can result in substantial destruction and human casualties.
In comparison, [8] presents a more thorough strategy for tackling vulnerabilities connected to Industrial IoT systems. The Industrial IoT’s functional levels classify the first three probable attacks as operational technology (OT), and the final two are classified as information technology (IT) in Table 1 by the authors. The first functional layer covers the physical IIoT processes involving embedded devices, sensors, actuators, transmitters, and motors. Attacks at this level demand in-depth familiarity with the IIoT system architecture, access to device specifications and engineering blueprints, and a comprehensive understanding of installation and operational functioning. The second functional layer consists of specialized hardware, such as distributed control systems (DCSs), programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and gateways, facilitating communication and control between components in the first functional layer. This assault aims to influence the information flow and obstruct appropriate communication between the two layers. The third functionality stage consists of IP-based data acquisition devices, master stations, human–machine interfaces, SCADA systems, and relevant industrial automation control and surveillance systems. Many SCADA-level attacks use IP packet manipulation techniques to conceal the sender’s identity by faking attributes like the source address. Thanks to this alteration, the recipient is duped into thinking the packet came from an authorized network user. Business planning services, including office applications, intranet, web, and mail services, are included in the fourth level of service. Threats at this stage use known or unidentified weaknesses in the attacked services.

Table 1.
Layered IIoT architecture and possible attacks.
Many tools like analysis, information extraction techniques used by enterprise applications, and cloud computing services are all included in the fifth level of functionality within the IIoT framework. Attacks at this level can take a variety of forms, including confrontational assaults as well as complex ones like surveillance and manipulation. A demilitarized zone between levels three and four, which includes service servers accessed by users from unknown networks, is introduced by the authors of the cited paper. It is essential to note. Even while the study provides insightful information about how the IIoT operates and the risks connected to it, its absence of particular instances of related attacks or preventative measures makes it insufficient. Instead, it acts as an overview of recognized attack types, including little data beyond what are already available in the existing literature.
Manuscript [17] presents a thorough framework for IIoT security based on standardized and commercial design. In a three-tier design, the study looks at the security needs for industrial connection and communication protocols and evaluates the type of safety these standards offer at each layer. The study starts by outlining a three-tier, generic IIoT architecture, which effectively classifies the core elements of most IIoT advances, as depicted in Figure 2. The edge tier comprises endpoints and edge-based gateway devices that interconnect actuators, control systems, and sensor equipment in a vicinity connection. Gateway units act as aggregating indications, allowing layered connections with the upper structure tier alongside internal inter-level connectivity. The system layer leverages web or mobile network connections as a conduit for data and control exchange between the various levels. It includes software 4.7 and services applications for integrating data, transforming data, and analyses. The third and highest level’s link with the organizational tier is formed via an intranet infrastructure driven mainly by the World Wide Web. The corporate tier provides specialized protocols for customer interface and enables suitable offers, including specialized apps for enterprise, domain services, and hosting cloud computing. Gebremichael et al. offer a set of interconnection procedures appropriate to each tier and explain the security characteristics of secure device implementation in IIoT networks based on this architectural framework. These deployment solutions improve the security posture by dispersing security needs across various network regions and building backup protection in widespread attacks.
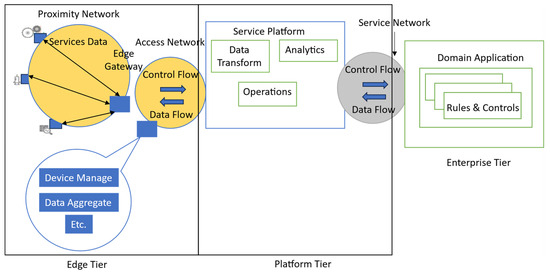
Figure 2.
Three-Tier Architectural Model for IIoT Connectivity and Communication Standards.
Lastly, researchers [18] have given a thorough analysis of SCADA attacks. The primary hardware of the IIoT ecosystem, SCADA devices, are employed to track different industrial processes. They are made up of several entities that are arranged in a tiered framework. They include methods for integrating human–machine interfaces (HMIs), data transmission, and data collecting systems. An HMI is an operator contact that links a human to a device and is mainly used for displaying information, tracking operation time, and viewing machine input and output data. The master station unit or master terminal unit (MSU/MTU) operates as the principal control facility for a SCADA network, while the sub-MSU/sub-MTU functions as an auxiliary control site. The most frequent assaults on SCADA systems, their occurrence patterns, and the techniques typically employed are listed in this paper. The ensuing modes of attack are discussed in further detail.
- Intercepting communications on a wired or wireless network [19] between master terminal units (MTUs), sub-MTUs, or remote terminal units (RTUs) is known as passive or active monitoring. To exploit the collected data, an attacker with network access can install malware [20]. A man-in-the-middle (MitM) attack [21] is when an individual observes and intercepts network traffic to modify and deliver data to the intended recipient [22,23]. When a breach is successful, the attacker seizes control of the session and keeps the connection going while using a fake IP address to evade detection [24,25].
- Masquerading assaults happen when a hacker adopts an alias and uses a fake IP address to pretend to be an authorized network client to take data from the system or network [26,27]. Brute force attacks may use stolen credentials to access critical data without authorization [28]. After conducting MitM or hybrid assaults, intruders may use infectious agents, Trojan horses, or worms [29,30,31]. Unauthorized people may gain access to the compromised system through malicious code, maybe exploiting it to launch more attacks on other infrastructure. Alternatively, the code may infect more MSUs/MTUs across the network, leading to unstable behavior or system failure [32,33].
- Rogue RTUs overwhelm the MTU with arbitrary IP addresses during denial of service (DoS) or distributed denial of service (DDoS) threats, draining the framework’s resources and making it unusable [1,34,35,36,37,38,39]. These threats make use of internet packet-based fragmentation flaws. The MSU/MTU is unable to manage data transmissions that are larger than the maximum transmission unit size, which results in a loss of connectivity and system breakdown [3,40,41,42].
- A Cinderella-like attack happens when an evil individual modifies the system’s intrinsic schedule after gaining unauthorized access to a machine. The computer system’s vulnerability is increased by this early expiration of security software 4.7 [43,44]. Doorknob rattling entails preparations, including legal methods for system testing. To assess the readiness and responsiveness of security measures, for instance, a small number of efforts to enter the network using randomized criteria are attempted [45,46].
Given the wide variety of systems with SCADA structures and associated designs, Ghosh and S. Sampalli performed thorough research on standards of current security (IEEE 1402, ISO 17799, ISO 15408, NERC security guidelines, NERC 1200, API 1164), detection mechanisms for SCADA (comprising some machine learning (ML)-based models like the Bayes algorithm, probabilistic forests, and choice trees), and avoiding a SCADA system assault. Adapting key management protocols like cryptography (SCADA Key Establishment (SKE), SCADA Key Management Architecture (SKMA)), and logical key hierarchy (LKH) are among the prevention techniques. [Source: Sampalli, S.; Ghosh, A. (2019). a thorough investigation of SCADA system security norms and key management protocols. Network and Computer Applications Journal [42,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59].
3. Security Attacks with Countermeasures
Remote administration and robotics can now improve the efficiency and caliber of services in critical infrastructures [47]. However, accuracy, dependability, and safety are of the utmost significance to effectively administer IIoT systems. Although the IIoT ecosystem incorporates digital technologies to increase efficiency, these technologies also present substantial hurdles because of the ongoing threats to digital security [48]. As a result, defending crucial national infrastructure, such as information technology, water and electricity networks, and public utilities, has come to be related to preserving the IIoT. These devices are excellent targets for extensive assaults since they are directly connected to the IIoT ecosystem. We divide IIoT risks into five broad categories in the following provisions: attacks involving phishing, ransomware infections, protocol assaults, supply chain attacks, and system attacks [49]. This categorization makes it easier to communicate security concerns thoroughly and comprehensively, along with the related solutions that are especially suitable for the Industrial Internet of Things environment.
3.1. Attacks by Phishers
Phishing attacks are a popular technique for collecting critical data from customers. In this kind of assault, the perpetrator assumes the identity of a trustworthy organization [50] and tricks people into disclosing personal information on phoney websites or via infected attachments. This might lead to the installation of malware or the unintentional revealing of private data. Specialized phishers deploy sophisticated methods known as compromised assaults on critical infrastructures, which combine social engineering techniques with the exploitation of lax user awareness and the absence of active security mechanisms in systems. These methods could include website forgeries, logo obfuscation, link manipulation, filter evasion, covert redirects, and zero-day spyware. The primary targets are often vendor or remote websites, aiming to breach IIoT systems and gain control over their linked operational systems. Having a final objective of breaking IIoT networks and gaining control over operational systems connected to them, the primary targets are frequently vendors or distant services.
The front-office stage usually occurs when a hacker tries to enter or use the IIoT. Analysts trace the system during the investigation phase, look for weaknesses, and decide when an extensive attack would be most effective. Pivoting, which is the act of switching from one system to another to apply the necessary exploits and compromise Industrial Control Systems (ICSs), may be involved. The problem of malicious website crawling employing specific techniques has been covered in several studies. A brand-new method named PHONEY, presented by Madhusudhanan et al. [51], allows for automated detection and analysis of phishing attacks. A web browser extension that informs users about the caliber of websites, their security certificates, and whether they have been found to contain dangerous code or misleading URLs is the basic idea behind PHONEY. Figure 3 depicts PHONEY’s entire structure.
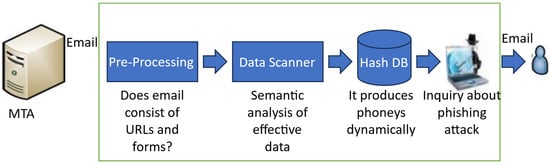
Figure 3.
PHONEY Architecture’s Block Diagram [51].
Using PHONEY tokens, the article [52] provided an innovative technique for spotting website phishing material. In the paper [53], authors devised a technique for ranking, detecting, and phishing sites based on association rules and categorization, creating correlations between objects and association criteria. In the sense of precision, their approach outperformed more sophisticated standardizations like the SVM algorithm. The authors in [54] built a prototype web browser as an agent for processing data from phishing attacks, enabling users to access emails securely and receive alerts if an attack is discovered. The Intelligence Web Application Firewall (IWAF), an automated active security tool for identifying phishing assaults in crucial infrastructure, is a cutting-edge ML technique suggested by [55]. To improve the ability of critical infrastructure to respond, IWAF uses an updating Izhikevich spiking neuron model to recognize phishing websites and convert the information into firewall rules. The Industrial IoT device network traffic is parsed for features of interest, and the Izhikevich spiking model algorithm classifies and recognizes phishing assaults. Creating and converting indicators of compromise (IoCs) into group policy objects (GPOs), which are then applied to Windows Active Directory, establishes rules to stop and restrict phishing assaults.
The URL Encoding (UE) technique, which analyzes relationships between various domain names and computes correlation coefficients among URLs, was first described in the publication [56]. The technique entails utilizing a network of neural networks to translate dispersed visualizations of URLs and then storing the mapping to handle spatial complexity. The authors suggest using clever machine-learning techniques to recognize malicious website addresses in DNS queries before they are executed. By mapping a sequence model based on extracting URLs from spam emails, the publication authors [57] created a method for identifying botnets. In [58], writers investigated various machine-learning techniques for categorizing websites according to their features and content. They used information, including IP addresses, WHOIS records, and lexical characteristics of phishing URLs, to filter emails connected to phishing and identify questionable domain registrations in the paper [59]. By building regular signatures based on expressions from a set of spam address data, Xie et al. [60] concentrated on identifying spamming botnets. By examining DNS queries, including multiple addresses (As) and NS records, IP ranges, time-to-leave (TTL), and alphanumeric characters from domains, the author developed a method [61] for identifying and reducing botnet infection.
Furthermore, the study suggested by [55] presents a ground-breaking defense mechanism against fast-flux botnets, which use domains created using the domain generation algorithm (DGA) method. The system builds a Smart URL Filter within a zone-based policy firewall to find harmful domain names generated by algorithms. The third and most sophisticated generation of neural networks, also known as the evolving spiking neural network (eSNN), which mimics how the human brain operates, is used in this system. Comparing it to other developing and bio-inspired learning techniques, the suggested method showed improved prediction accuracy and generalization to fresh data.
3.2. Attacks by Ransomware
In this form of attack, malware is introduced into the IIoT system to cause a denial of service (DoS) or access to private files, and the users are then required to pay a fee to regain access. Unlike traditional ransomware, which is generally disseminated, IIoT ransomware is typically targeted, i.e., it focuses on essential system components to cause as much harm as possible. Due to this restriction, IIoT ransomware research cannot be considered transferable to conventional ransomware. The authors of [62] present a comprehensive and methodical examination of the hazards posed by IIoT ransomware and offer some viable suggestions for remedies. According to their findings, IIoT edge gateways are particularly susceptible to ransomware assaults in IIoT networks. The IIoT gateways have some features in an industrial setting, despite different variations in their working as well as architecture. In a typical IIoT edge gateway, input/output (I/O) or program logic controller (PLC) devices act as a conduit between the outside globe and crucial IIoT infrastructure. The attacker can take complete control of an IIoT gateway after successfully attacking it with ransomware by changing its password and then replacing the current firmware with malicious code. Although the individual succeeds in reaching the surroundings of locking, the hacker is still capable of encryption and accession of all customers and their data, including those achieved from the PLCs and input/output devices as well as those exchanged across the internet and the business. The attacker can then threaten to slowly remove the victim’s data in case of unpaid ransom or demand payment to gain access to the information. To assess the vulnerabilities in IIoT edge frameworks, M. Al-Hawawreh and colleagues constructed a functional testbed for an IIoT framework in compliance with the Industrial Internet Reference Architecture (IIRA), as depicted in Figure 4 [31].
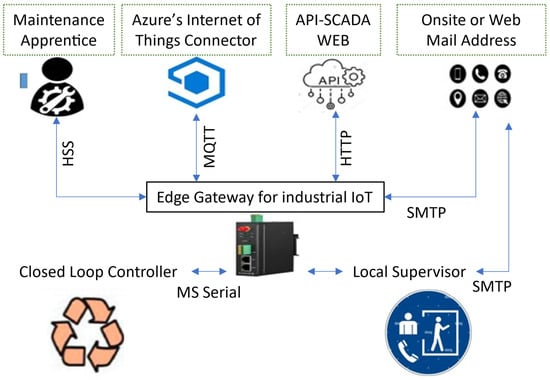
Figure 4.
The Evaluation Platform (Testbed) for IIoT Systems.
Their setup consists of three main elements: IIoT channels, input-output devices (like IoT actuators, controllers, and sensors), digital actors (such as maintenance personnel, email, and cloud servers for handling IoT data, and SCADA real-time monitoring devices). They employed Python code similar to the Erebus Linux Ransomware attack to execute proof-of-concept (PoC) ransomware attacks on this framework. This targeted ransomware attack affected various web services, databases, and multimedia files from a web hosting service [60]. Reference [63] description outlines the primary stages of the attack, which also include scanning for data and system files in specified directories of the IT/OT edge gateway, encrypting data and identifying original files, transmitting the pilfered data as an email attachment via Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) to a fabricated email account, and notifying the user about the ransom demand. M. AlHawawreh and team collected and analyzed data related to system performance, such as CPU usage, memory load, I/O device utilization, and CPU processing demands, and compared these metrics to data collected when the system was malware-free. Their findings show that compared to a similar attack on a desktop, the targeted ransom attack on the IIoT edge gateway considerably increased system resource utilization and processing power. These findings led the authors to conclude that keeping an eye on kernel-related activity characteristics can serve as a valuable predictor of crypto-ransomware attacks on IIoT edge gateways. M. Al-Hawawreh advocated adopting advanced security measures to fortify IIoT architectures against such attacks. These measures include the implementation of Next-Generation Firewalls equipped with sophisticated traffic filtering capabilities, the deployment of monitoring solutions like Intrusion Detection Systems (IDSs) for prompt recognition of malicious activities, and the strategic segregation of the IIoT edge gateway by positioning it in a specially designated secure area. These precautionary steps aim to substantially improve the resilience of IIoT systems to threats of this nature.
Numerous research studies have used machine and deep learning (DL) techniques in different domains alongside traditional methods [64,65,66,67]. For improving the detection of ransomware outbreaks to consistently detect Windows ransomware network attacks, the authors of [68] presented a detection model using dynamic ML approaches, specifically conversation-based network traffic features. Their tests showed that the feature database performed exceptionally well in accuracy. Two independent classifiers running concurrently at the packet and flow levels were used by the authors of [69] to create a network-based intrusion detection system to find Locky ransomware. The suggested methodology demonstrated high tracking efficiency and good detection precision for ransomware attacks. To minimize data dimensions and provide accurate activity visualizations, also suggested was a hybrid detection model that combines classical auto-encoding (CAE) [70] and variational auto-encoding (VAE) DL approaches [71]. A deep neural network (DNN) classifier was trained using a new vector created from extracted characteristics. The proposed approach performed the highest concerning detection rate (DR), false negative rate (FNR), and support vector machine (SVM) [72,73] efficiency when compared to other models, such as random forest [61], decision trees [68], logistic regression (LR), SVM, and DNN [73].
3.3. Attacks on Protocols
The OSI network framework for the Internet of Things (IoT) consists of five hierarchical layers: physical, data-link, network, transport, and application. In the context of IIoT devices, the first four layers often employ the same protocols utilized in conventional IoT systems, such as IEEE 802.15.4 6LoWPAN, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), IEEE 802.11 (commonly used by WiFi), Long-Term Evolution (LTE), and UDP/TCP protocols. This analysis emphasizes the significance of the application layer, which is vital for IIoT solutions, and provides a summary of potential risks and countermeasures applicable to the foundational four layers. These six layers—application layer, transport layer, network later, adaptation layer, MAC layer as well as physical layer—constitute the OSI network’s tiered structure for IoT, as delineated in Table 2 [74].

Table 2.
Comparison of IoT Protocol Stack and TCP/IP Stack [69].
3.3.1. Attacks on Physical and Data-Link Layers
Numerous studies have focused on attacks targeting different layers of IoT systems and have proposed corresponding countermeasures [74,75,76,77]. At the physical and data-link layers, denial-of-service (DoS) assaults are among the most prevalent dangers. In these assaults, rogue devices reduce the nodes’ processing power to turn off the system. The most common techniques used in DoS assaults include jamming, collision, exhaustion, and unfairness [77]. While tinkering, DoS assaults include physically altering sensor nodes, such as wiring on the electrical board or joining cables and buzzing. DoS threats entail transmitting signals at the same frequency to interfere with conversation. Cross-layer security detection and a jammed area mapping model (JAM) are two surveillance technologies created to identify buzzing DoS attacks and decrease their consequences [75,76,77,78]. Tampering risks in wireless sensor networks (WSN) and RFID sensor networks (RRSN) can be found and avoided by physical inspection or by using particular instruments.
When a malicious device transmits data on the victim’s frequency, it launches an interference DoS assault that results in subsequent signal transmissions and crashes. A fatigue assault is when the collision attack continues until the targeted node’s energy resources are depleted [79]. Injustice assaults take advantage of the system’s decreased functionality brought on by fatigue threats for their advantage. Frequency-hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) is one method of protection versus buzzing and crash assaults [80,81]. Assaults on data transfer that target IoT systems’ physical and data-link layers, such as packet sniffing and man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks, are common. Data encryption technologies such as the asymmetric encryption standard (AES) in IEEE 802.15.4 and 6LoWPAN networks [82], wired equivalent privacy (WEP), and WiFi Protected Access II (WPA2) in WiFi and LTE networks [83] are some of the countermeasures for these dangers. Encrypting data using technologies such as the asymmetric encryption standard (AES) in IEEE 802.15.4 and 6LoWPAN networks [82], wiring equivalent private (WEP), and WiFi Protected Access II (WPA2) in WiFi and LTE networks [83] are some of the solutions for these risks.
Numerous studies have discussed assaults on the layers and offer suitable defenses [74,75,76,77]. Denial of service (DoS) assaults constitute one of the most prevalent dangers at the physical and data-link levels. This kind of threat causes the system to become unavailable by reducing the nodes’ processing power. The four most significant DoS attack techniques are jamming, collision, exhaustion, and unfairness [77]. In contrast to node sensor manipulation, which involves physically taking control of the sensor node by connecting to the computer board or adding wires to the motherboard of the circuit, a DoS assault involves the attacker transmitting at the same frequencies to interfere with the transmitted signal. To identify jamming DoS attacks, the researchers of [75,76,77,78,79,80,81] propose a jamming area mapping model (JAM) that bypasses the crowded region of the wireless sensor network (WSN) by rerouting the packets to alternate channels. By physically inspecting the WSN with the naked eye or with specialized equipment, tampering hazards can be recognized and eliminated.
When an attacker’s device begins transmitting messages on the target device’s frequency, collisions, and packet retransmissions result. This is known as an interference DoS assault. A fatigue attack is one in which the impact attack lasts until the intended node’s resources for energy run out [82]. If an exhaustion attack compromises a system’s capability to benefit hostile users, this is known as an injustice assault. Frequency-hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) technology is used for efficient protection versus jamming and crash attacks [83,84,85,86,87]. Information transportation assaults, such as sniffing of packets and man in the middle (MitM) attacks, are highly prevalent at both the physical and data-link levels of IoT systems involving wireless sensor networks (WSN) and RFID sensor networks (RRSN). Encrypting information technologies such as the asymmetric encryption standard (AES) in IEEE 802.15.4 and 6LoWPAN systems [88,89,90], wired equivalent privacy (WEP), and WiFi Protected Access II (WPA2) in WiFi and LTE networks [91] are used as solutions against this kind of danger.
3.3.2. Attacks on Network Layer
Routing and DoS attacks, transmission of data assaults, and threats on the neighbor discovery protocol (NDP) are the most often seen threats at the network layer of IoT devices [75]. In routing attacks, the malicious device transmits the active signals to the incorrect routes, and in denial-of-service assaults (DoS), it overwhelms the network’s resources and clogs up data. Evacuation sorting, authorization, and control technologies, such as IoT-specific intrusion detection system (IDS) solutions like SVELTE, are efficient defenses against these attacks [92,93,94]. Information transfer threats impact data integrity and confidentiality. Datagrams Transport Layer Security (DTLS) is one of the condensed transport protocols that can be used as safeguards [89,90]. Work [85] discusses the dangers to the neighbor discovery protocol (NDP). This work thoroughly overviews the operation and the most frequent assaults against NDP. This article also includes a complete analysis of tunneling (IPSec) and secure neighbor discovery (SEND) procedures, two NDP security techniques. The study results show that SEND is a highly effective defense against DNP protocol attacks for NDP, although most operating systems still do not provide enough assistance.
Common risks to IoT devices at their network layer involve DoS and router assaults, assaults on data transport, and attacks on the neighbor discovery protocol (NDP) [70]. Routing assaults include illegal devices passing active data to the wrong pathways, whereas DoS attacks overwhelm the network’s resources and generate traffic congestion. Egress filtering, authorization, and monitoring technologies like IoT-specific intrusion detection system (IDS) solutions like SVELTE are effective defenses against these threats [84]. Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS), among other condensed transfer procedures, can be used to reduce the impact of information transit assaults on data integrity and secrecy [77]. In [85], which additionally examines defense techniques, including tunneling (IPSec) and secure neighbor discovery (SEND) standards, the dangers to the NDP are detailed in detail. Deliver is the most effective defense against NDP assaults despite most operating systems failing to embrace it entirely.
3.3.3. Attacks on Transport Layer
IoT systems’ transport layers are frequently targeted by attacks, including desynchronization, SYN flooding, and MQTT exploiting assaults [75]. Desynchronization threats interfere with terminal synchronization by inserting messages with fictitious command flag number sequences. A strong defense against desynchronization assaults is the authentication of messages [86,87,88]. SYN flooding attacks involve inundating the target with many SYN messages, which clogs the target’s queue and prevents it from processing valid SYN inquiries. By improving memory and queue management within the transport protocols and bolstering network security with packet screening and intermediary methods, SYN flooding assaults can be mitigated [84]. Work [85] lists the MQTT protocol’s shortcomings. Because it lacks built-in data encryption and authentication measures, the simple communication system MQTT, created for IoT applications with limited bandwidth, is open to assaults. Developing safe MQTT protocols that use attribute-based encryption (ABE) for scalable and reliable security is offensive against MQTT exploitation. An essential component of IoT applications, secure message delivery to numerous recipients, is supported by ABE [91]. Table 1 lists the most frequent protocol assaults in the IIoT, their hazards, and any suggested defenses.
Desynchronization, SYNflooding, and message queue telemetry transport (MQTT) make assaults among the most common IoT vulnerabilities at the transport layer [95]. Desynchronization assaults cause destinations to become out of sync by injecting messages with fictitious control flag sequence numbers. Message authentication is a valuable countermeasure [96,97,98,99]. In SYN-flooding assaults, the malicious device floods the target with many SYN packets. The faked device does not send acknowledgments (ACKs) in response to the victim’s SYN-ACKs.
Consequently, the target cannot receive valid requests for SYN because of a total backlog. To defend against SYN-flooding assaults, transport protocols must be modified and optimized. Memory and queue management must also be made to handle SYN packets more efficiently, and network security must be strengthened using packet filtering and proxy techniques [100,101,102]. The writers of [103] outline the shortcomings of the message queue telemetry transport (MQTT) protocol. A simple communication protocol called MQTT is tailored for remote equipment management with bandwidth restrictions, such as IoT applications. MQTT modifies the publish-and-subscribe communication strategy. However, because MQTT does not, by design, include any confidentiality or identity method, it is highly susceptible to assaults. Implementing scalability and reliable safety methods, such as the safe MQTT procedure that upholds the attribute-based encryption (ABE) method’s security, is critical to protection against MQTT attacks. ABE offers broadcasting encoding, a preferred capability in IoT gadgets [104,105,106], and enables secure message delivery to multiple intended receivers. Table 3 provides a comprehensive overview of the most frequently encountered protocol attacks in IIoT, outlining the associated risks and suggested mitigation strategies.

Table 3.
General attacks in the primary four layers of the IoT stack and probable countermeasures.
3.3.4. Attacks on Application Layer
Threats aimed at the SCADA protocol, frequently employed in SCADA networks, often target the application layer of IIoT systems. The writers of [107] focused on sensor assaults against loops of control for collecting SCADA infrastructure information, especially in gas pipelines and water tank storage implementations. The sensors themselves are PLCs (programmable logic controllers), acting as the operational devices in a network linked to provide remote monitoring and control of high-speed reaction processes, even across dispersed locations. The widely used SCADA Modbus messaging protocol that enables client–server connection over multiple bus or network types, generally via serial lines, makes it possible to communicate among these gadgets.
In the operated computer simulation, the research’s attention was directed toward Modbus master’s gadgets, which provide queries for details to facilitate discrete or analog IO communication and data recording by the slave, Modbus. Every transaction uses a simple demand–response method in which the master gadget sends the request, and the agent device answers appropriately. After realizing several flaws in the Modbus protocol implementations, they continued to mimic those weaknesses in a monitored setting. They were able to perform this to document and assess the different kinds of attacks that might take place. The lack of identification of a fake slave–master IP address within the SCADA network is a flaw in Modbus technology. By submitting requests with the wrong IP addresses, an unauthorized remote intrusive can use this security hole to launch a man-in-the-middle (MitM) assault. An intruder can learn more about the MSUs and MTUs of the network by examining the emails that are delivered.
An additional flaw results from insufficient safety measures and identity/certification inspections that jeopardize verifying the Modbus master and agent device connection. Using a Modbus master, this weakness permits outsiders to send random commands to any slave equipment without authenticating themselves. The SCADA Modbus system is also vulnerable to abuse due to development problems in handling request messages and separate input read responses. As a result, a remote attacker with malicious request or response parameters who targets susceptible Modbus programs can start a denial of service (DoS) or distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack on a SCADA network.
Last, Modbus TCP is the most widely used protocol for process control in SCADA systems. To allow communication via a serial RS-485 interface, the protocol being used sets a size restriction of 253 bytes for the protocol data unit (PDU). The Modbus protocol header is extended by 7 bytes by Modbus TCP, significantly limiting the permitted package size. An attacker can take advantage of this restriction by crafting a custom packet with more than 260 bytes and sending it to a Modbus master-slave. A successful buffer overflow attack may occur if the devices are not correctly set up to reject such packets. Using systems to detect and prevent intrusions with deep packet inspection capabilities or industrial firewalls is a frequent countermeasure to reduce such security threats. Such networks are able to recognize as well as avoid exact threats that are concealed within the communication flow [108]. In this regard, Liang et al. suggest a multi-feature data clustering optimization model-based corporate system intrusion detection system that achieves a detection rate of 97.8% and reduces false positives by 8.8% [109]. An autonomous progressive neural network and the support vector machine are combined in Constantinides et al.’s novel network intrusion prevention system based on incremental ML frameworks and exhibit robust and scalable accomplishment appropriate for industrial uses as Table 4 shows the overall main threats with possible solutions in case of application layer protocols [110,111].

Table 4.
Main security threats and required solutions in application layer protocols [110,111].
Modbus protocols, such as TCP design, also use ML-based intrusion detection techniques. A data preprocessing technique is presented by Deng et al. based on the frequency of coils and function codes for the Modbus protocol that are seen in Modbus TCP traffic. They used a support vector machine model to identify aberrant Modbus TCP traffic patterns [112]. In addition, intrusion detection and prevention technologies based on the cloud can potentially protect industry networks. An exact cloud-based design that makes use of software-defined networking, network function virtualization, and service function chaining is proposed by Brugman et al. This method uses a virtual private cloud hosted on Amazon Web Services to send messages to a public cloud for assessment, offering scalability, resilience, and visibility in identifying and preventing cybersecurity threats [108].
3.4. Attacks by Supply-Chain
Threats on supply chains carry a significant danger, particularly when the IIoT is integrated into the Industry 4.0 supply chain. In this way, cybersecurity presents a significant difficulty. Malicious code implanted within hardware chips can be highly evasive and run unnoticed for an extended time. Safety concerns result from the IIoT environment’s complexity and the involvement of several parties. The devices’ many parts are produced by numerous suppliers, assembled by another vendor, and then delivered by another party. This difficult-to-avoid circumstance frequently results in safety flaws, like installing backdoors that could endanger a whole manufacturing range, as depicted in Figure 5. Risk management has given more consideration to other parties’ involvement in the supply chain. They [113] studied supply chain hazards and suggested methods for managing risk in their study. They offer perceptions of the IoT supply chain risk landscape, highlighting its extreme diversity.
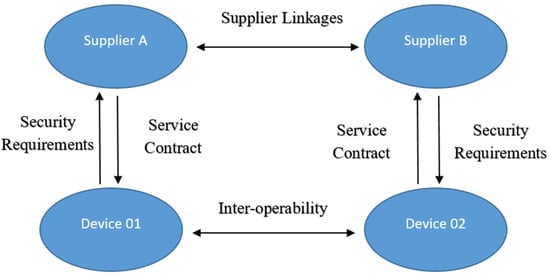
Figure 5.
Meaningful connections among many participants in the IoT supply chain ecosystem [113].
Given the identical protocols and traits, the description of supply chain risks associated with IoT also applies to the Industrial IoT context. Vendors can insert viruses, backdoor channels, or defective chips into their products. Identifying and managing supply chain risks might be difficult since they grow and spread throughout the intricate IoT ecosystem. It is challenging to analyze how gadgets and vendors communicate. Therefore, addressing hazards calls for a supply-chain approach. A distributed system and a centralized, top-down approach are both suggested. Although this work helps readers comprehend the hazards associated with supply chains, it fails to suggest any concrete technological protections for environments already exposed to such dangers that are unwilling to change their comprehensive risk mitigation approach.
A further contribution in the article [114,115] provides a dynamic and self-adapting supply chain system that AI, ML, and genuine expertise drive4. This strategy intends to create a blueprint for Industry 4.0 supply chains of small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs), who frequently do not have the assets to manage digital security risks successfully. Table 5 shows the research emphasizes the limitations of current methods for assessing the impact of cyber risk on supply chain infrastructure. Industry 4.0′s supply chain processes are poorly understood, which results in uneven measurements of supply chain security risks. Risk Analysis of IoT Supply chain Threats (RIoTS), a risk analysis technique for connected technologies like the Internet of Things, has been described in a separate paper [116]. Their strategy switches from focusing on vulnerabilities to modeling suppliers and components as a system. They suggest modifying attack tree approaches to consider vendor dangers and potential provider collaboration, exposing concealed dangers inside the IoT ecosystem. Numerous investigations primarily focus on supply chain attack risk prevention strategies.

Table 5.
The preventive measures of IIoT supply chain attacks [112,113,114,115,116].
3.5. Attacks by Whole System
Given their broad use and importance, attacks on SCADA systems are frequent in many industrial facilities worldwide. Addressing the security of SCADA systems is crucial due to the complexity and variety of these devices and their implementation in vital industries like water and energy. A detailed analysis of SCADA device attacks is provided in Reference [117], along with a particular solution for their prompt and efficient detection. The emphasis is on situations wherein assailants use a man-in-the-middle (MitM) assault on an Ethernet connections circle using the device’s root level ring (RLR) procedure, followed by a sneaky sensor threat, to exploit the fieldbus communication within the industrial EtherNet/IP protocol. A commercial computer network called Fieldbus is used for global control that operates in real-time and supports different network structures, including daisy-chain, stars, rings, branches, and trees. Gadgets use IO variables and communications that do not have particular formats and dimensions in fieldbus communication using the industrial EtherNet/IP protocol since the controller’s manufacturer decides these. 4–20 mA measurements are also used for encoding analog sensor command signals. Therefore, to understand the shared information and utilize the advantages of the instruments, a hacker needs a thorough understanding of the system’s architecture and access to device specs, engineering documents, and implementation designs.
Utilizing multiplexed EtherNet/IP connections employing the User Datagram Protocol, also known as (UDP), sensors and control devices in the system are able to communicate wirelessly with one another. Multicast functions at the IP level, so all UDP messages with an identified target IP will be allowed, even though only gadgets adhering to a particular multicast address receive the multicast frames. Despite other datagrams inside the Class A to Class C address spaces, IPv4 multicast, which uses the Class D address space (224.0.0.0–239.255.255.255), does not guarantee accurate delivery of this data to the information receivers. Each address in the Class D address space designates a group of recipients interested in receiving the data via the IPv4 multicast data delivery method. A host can join a group by delivering a JOIN Internet Group Message Protocol (IGMP) message, enabling involvement with no time constraints or group ownership.
Additionally, sending data to the group does not need a membership or the monitoring of transmitted data, making it extremely simple for an intrusive party to position itself as a man-in-the-middle (MItM). The assailant launches a covert sensor assault after determining the MItM placement. To change the behavior of specific processes without being detected by the system’s tracking devices, this assault requires changing the settings of the sensors and actuators. Think about an instance where an untreated water storage reservoir has a sensor to monitor the level of water, an opening that opens when the sensor detects a level below 0.5 m and closes when the level exceeds 0.8 m, and a pump whose operation is based on the Ultrafiltration (UF) process, where pressure or concentration gradients enable separation through a semipermeable membrane. The safety system requires that the pump be promptly turned off if the water level in the tank drops below 0.25 m.
The intruder wants to change the depth of the water without being detected by traditional anomaly-based monitoring systems. In order to update the functioning of the gadgets in accordance, this is accomplished by creating the proper packets that modify the sensor and actuator information while still assuring compliance with the Fieldbus communication. F. Mercaldo et al. has created an intelligent and straightforward method using time logic and high-level capabilities unique to SCADA architecture. To describe the behavior of the SCADA system and assess its resilience to an assault, they simulate the system logs using a network of synchronous automata. Beginning with separating SCADA system logs from other logs. The procedure records values that correspond to real-world measurements made by network controllers. Then, those notable results are divided into three groups: high, baseline, and low. The data is supplied into an automated system that employs automata, which are mathematical constructs that preserve machines with abstract finite states that can be used to solve challenging issues. An automated system changes states based on the input symbol and the transition function. An automaton is implemented and synchronized with a particular clock for each discrete scenario. A status table displays the system statuses in a temporal format for every situation evolution. The machines are randomly checked to find excess or underflow. Any divergence from the status table that is discovered denotes a system threat.
Although several clever methods are being put out for effectively examining web traffic among gadgets in the IIoT [118,119,120], particular standards are suggested in the paper “Blockchain Security Architecture for IIoT” [121]. This design, built on DL smart contracts, aims to improve the security and usefulness of industrial applications by giving SCADA equipment access to a decentralized, dependable peer-to-peer network. It closes a significant hole in the functionality of IIoT systems, especially regarding heterogeneous infrastructures built on blockchain. In order to perform sophisticated anomaly detection functions through smart contracts and enable secure network connection across trade devices within the system, the architecture uses the blockchain system’s characteristics. A complex deep automatic encoding is incorporated into the suggested deep neural network intelligent instrument’s code, providing a smart way to classify hazardous abnormalities in IIoT transactions, which frequently contain sophisticated cyberattacks. An auto-encoder is a coupled neural network architecture comprising an encoder and a decoder. Input data, such as network traffic between master and agent devices, is transformed into a compact and more dense representation known as a latent representation by the encoder network. The decoder network then reconstructs the original input using this hidden information. An automatic encoder’s job is to accurately recreate input data from a compressed and abstract representation it has learned. Using an autoencoder, the network can effectively compress the original data, filter out noise, and identify potential vulnerabilities associated with attacks in the SCADA Modbus protocol.
Assault against industrial control systems, also known as ICS, frequently entails changing the programming language of programmable logic controller (PLC) devices or influencing the regulation of centrifuges to interfere with industrial machinery’s operation. The optimal power flow (OPF) algorithm, frequently employed in power plant controllers to find the best power systems management method while reducing expenditures and preserving the system’s safety, is maliciously applied in one attack scenario described in [122]. Power line power and the permitted generator frequency span, for example (59.5–21.1 Hz for a 60 Hz rated power grid in the US), are two factors that are generally subject to constraints. The PLC’s programmable logic controller (PLC) transmits control signals to sensors responsible for power generation, system security margins, on/off commands, and other functions. Luis et al. maliciously alters the PLC’s optimal power flow (OPF) control algorithm in this research. Three changes are made: the safety margin state is eliminated, the cost minimization algorithm is changed to increase the hostile impact, and hidden conditions are added to prevent operators and SCADA devices from detecting malicious behavior. Various anomaly detection strategies have been implemented to handle behavioral aberrations by attacks. Even when the type of assault is unresolved, such efforts are made to detect aberrations. This entails contrasting the framework’s performance as it currently stands with a model or a set of parameters that describe typical functioning [123,124]. Network factors like operating conditions and average electrical power throughout periods are taken into account by behavioral analysis. Heuristic evaluation is one of the further investigation techniques used to find trends and recognize irregularities with no set of unfounded alarms [125,126,127].
System behavior can be abnormal in many ways, including individual, situational, aggregate, and protocol abnormalities. These anomalies display behavior that differs from the anticipated patterns and can be classified according to their traits and consequences. A simple anomaly detection strategy may not be sufficient when extremely sophisticated threats occur, like those discussed by Luis et al. There is a need for more intricate and advanced techniques. However, [128] suggests a straightforward yet efficient system capable of precisely identifying sophisticated attacks. The Cumulative Sum (CUSUM) algorithm, which intuitively accumulates the difference between a variable and its predicted value over time, is the foundation of the technique. Change occurs when the cumulative amount rises above a specific threshold. Equation (1) is used by the CUSUM method to identify changes. Sn stands for the cumulative value at sample n, xn for the observed data at sampling n, and wn for the anticipated mean of the observed data in the formula. A change is identified whenever Sn rises beyond a predefined threshold based on the relative size of the change and the noise in x.
while
In the research run by Luis et al., the anomaly detection algorithm, based on the CUSUM approach, was successfully employed and validated for recognizing abnormalities. In this case, the algorithm continuously tracked the deterministic PLC control initiative’s execution duration and produced alerts whenever adjustments were found. The program was successful in spotting early anomalies frequently linked to assaults. It obtained exceptionally accurate stages, identifying the majority of irregularities in a matter of moments and up to five minutes in the event of a crisis. The quick discovery considerably reduces the assailants’ capacity to harm the equipment. Additionally, the methodology’s ease of use makes it appropriate for integration into PLCs with limited resources, serving as an essential security safeguard for the entire IIoT environment.
In overall Section 3, the fundamental idea of comprehensive cybersecurity connects several security attack categories. Our evaluated work and the publications we cited most likely emphasize the need for a multifaceted approach to security that takes into account both specific modes of attack and an entity’s overall security posture. Furthermore, studies and actual examples are likely to highlight the value of ongoing surveillance, the exchange of threat intelligence, and teamwork among cybersecurity experts and businesses in order to recognize, hinder, and counter developing attacks.
In conclusion, our comprehensive approach to cybersecurity encompass various attack vectors, recognizing that attackers often exploit vulnerabilities across different layers and parts of the system. It requires ongoing vigilance, adaptation, and a strategic blend of technical, organizational, and human-centric countermeasures to safeguard against diverse and evolving security threats.
4. Discussion
The widespread use of infrastructure protection and the viability of the offered solutions should not be taken for granted, given that the cyber security of the IIoT ecosystem is a complex issue, as previously discussed [129]. The intricate nature of the components engaged in the IIoT and the broad spectrum of weaknesses that may arise from the visible major obstacles while referring to complicated patterns, systems, or processes that might not develop simultaneously over time and become possible shortcomings of the overall networks. [130]. For older, un-upgraded systems in the high-complexity environment under study, the complicated relationship descriptions and the minute distinctions that set them apart exhibit multivariate standardization systems while maintaining high heterogeneity [7]. The intricacy and secrecy of supply chain attacks, which make them difficult to combat effectively, have made them stand out among the other dangers as a considerable worry [131,132]. Approaches to risk management are frequently used to lessen such attacks. However, the existence of older industrial systems not initially developed with security as a precondition is a significant problem. This weakness significantly increases the risk of assaults, even if access control or encryption methods are later included [133,134,135]. Additionally, there are serious issues about the mechanisms for standardizing and harmonizing with already-instituted norms. Due to the dependence of many existing IIoT systems on their development businesses, it is challenging to modify or adapt their mechanisms, including the functions they support [7]. Due to its real-time operation and rapid evolution, the IIoT also encounters challenges in managing data with time discrepancies and considering correlations and interdependencies with other devices in the data flow sequence [98,100,105]. In manuscript [136], the authors investigated malicious attacks in underwater wireless sensor networks (UWSNs) by using a lightweight key management framework. An elliptic-curve-based algorithm was utilized for the key distribution, while a certificate-revocation-list-based algorithm was used for key revocation. This method provides high security with small amount of communication overhead compared to already existing methods.
To ensure the security, reliability, and accuracy of the data, these factors introduce new requirements. Encryption [113] and critical management strategies have been proposed and implemented in the IIoT context, providing strong security standards. They are constrained, nevertheless, in their ability to create procedures that are rapid and simple to use, making them appropriate for usage in low-resource devices. One major conclusion of this research is that their ML methods depend on device or network traffic data [106,116]. In manuscript [137,138], a novel method is proposed to investigate as well as identify the anomalous behavior of attacks in IIoT technology, called the transformer-based method. This method has good performance compared to conventional ML methods as well as deep learning approaches based on accuracy, precision, and recall.
There is an advanced and important framework called the reference technique. It was proposed with the purpose of providing security against different outsourcing flaws in the current era including side channels as well as state preparation flaws, which are created by mode dependencies and some attacks like Trojan horses and pulse correlations. In manuscript [131], the authors adopted the reference technique for proving the security of four-phase measurement device quantum key distribution (QKD) by using laser pulses to fight against potential attacks. One of the advanced security objectives of information is cryptography, which has subobjectives including confidentiality, non-repudiation, integrity, and authenticity. In manuscript [132], the authors proposed a highly efficient quantum digital signature (QDS) protocol that uses asymmetric quantum keys. The authors successfully completed the demonstration of the complete function of a quantum security network, which met all required objectives of information security.
Although the learned parameters lack certain variables from different usage or behavioral elements in the overall design due to the limited methods, the smoothing is insignificant. The main problems originate from the inappropriate sharing of current statistics with all automatic internal looping updates, since it is mistakenly assumed that the original model and all of its updated replicates have similar feature distributions. As mentioned, a more effective method is to progressively save analyses in stages and read the optimization parameters for each internal loop.
5. Conclusions
This study provides a comprehensive description of attacks on Industrial IoT systems. It addresses these structures’ essential qualities and shortcomings and thoroughly analyzes all potential solutions to alleviate these vulnerabilities, as recommended in recent research. As a result, our attempt serves as an accurate framework for comparison and a valuable scientific instrument for identifying and assessing risks in the dynamic industrial environment. Its insights significantly improve IIoT security and could assist in developing effective defenses against risks posed by the Internet of Things to industrial infrastructures. When considering the future development of this study, one important topic to look at is the analysis of new attack vectors or complex attack tactics that combine fresh attacks, including zero-day attacks. IIoT systems must keep informed of new attack vectors and actively respond to threats. Another significant development in this research is expanding the analysis of strategies with self-improvement and self-adaptation abilities to handle particular and undiscovered threats in IIoT contexts. Artificial intelligence and machine-learning-driven solutions can increase IIoT systems’ resistance to shifting cyber threats. To ensure overall safety, looking into and evaluating additional protection measures designed especially for Industrial IoT systems would be helpful. Given the notable aspects of the IIoT, such as real-time operation, resource constraints, and various device types, customizable security solutions can offer more effective defenses against possible faults and attacks. By focusing on these research topics, the study could be expanded further and contribute to ongoing initiatives to improve the safety and resilience of Industrial IoT infrastructure in the face of emerging cyber threats.
Future research can examine novel attack pathways and sophisticated attack strategies, such as zero-day assaults, to better understand the changing dangers to IIoT systems. Additionally, IIoT security can be strengthened against dynamic cyber threats by researching solutions that incorporate self-improvement and self-adaptation using artificial intelligence and machine learning. Given their distinctive qualities, such as real-time operation and resource limitations, Industrial IoT systems require specialized protective measures that must be carefully evaluated. Security systems that can be customized may provide stronger defenses. This study contributes to ongoing, existing initiatives targeted at bolstering the safety and resilience of Industrial IoT infrastructure in the face of rising cyber threats by delving into these research topics.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.I. and A.M.A.; methodology, S.M.T.; software, S.H.; M.I.; validation, A.M.A., F.A. and S.H.; formal analysis, M.I.; investigation, S.M.T.; resources, A.M.A.; M.I.; data curation, F.A; writing—original draft preparation, F.A.; writing—review and editing, A.M.A.; M.I., S.H., S.M.T. and F.A.; visualization, M.I. and S.H.; supervision, M.I.; project administration, A.M.A.; funding acquisition, A.M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not Applicable.
Acknowledgments
The researchers would like to thank the Deanship of Scientific Research, Qassim University for funding the publication of this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors confirm that no known financial conflict or personal connections might have swayed the findings presented in this paper.
References
- Alcácer, V.; Cruz-Machado, V. Scanning the Industry 4.0: A Literature Review on Technologies for Manufacturing Systems. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2019, 22, 899–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banafa, A. The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): Challenges, requirements and benefits. In Secure and Smart Internet of Things (IoT): Using Blockchain and AI; River Publishers: Gistrup, Denmark, 2018; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Soori, H.; Arezoo, B.; Dastres, R. Internet of things for smart factories in industry 4.0, a review. Internet Things Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2023, 3, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ani, U.P.D.; He, H.; Tiwari, A. Review of cybersecurity issues in industrial critical infrastructure: Manufacturing in perspective. J. Cyber Secur. Technol. 2016, 1, 32–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.-M. Impact of Industry 4.0 on Inventory Systems and Optimizations; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Gooi, H.B.; Liu, Y.; Chan, E.K. Internet-based SCADA display system, Computer Applications in Power. IEEE Comput. Appl. Power 2002, 15, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, P.; Dutta, I.K.; Daoud, H.; Bayoumi, M. A survey on security in internet of things with a focus on the impact of emerging technologies. Internet Things 2022, 19, 100564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perwej, Y.; Abbas, S.Q.; Dixit, J.P.; Akhtar, N.; Jaiswal, A.K. A Systematic Literature Review on the Cyber Security. Int. J. Sci. Res. Manag. 2021, 9, 669–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-W.; Rong, L.-L. Robustness of the western United States power grid under edge attack strategies due to cascading failures. Saf. Sci. 2011, 49, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, M.; Mahmood, A.; Chowdhury, M.J.M. SCADA vulnerabilities and attacks: A review of the state-of-the-art and open issues. Comput. Secur. 2023, 125, 103028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farman, H.; Khalil, A.; Ahmad, N.; Albattah, W.; Khan, M.A.; Islam, M. A Privacy Preserved, Trust Relationship (PTR) Model for Internet of Vehicles. Electronics 2021, 10, 3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, A.C.; Khadse, V.M.; Mahalle, P.N. Security issues in IIoT: A comprehensive survey of attacks on IIoT and its countermeasures. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Global Conference on Wireless Computing and Networking (GCWCN), Lonavala, India, 23–24 November 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 124–130. [Google Scholar]
- Ghori, M.R.; Wan, T.C.; Sodhy, G.C. Bluetooth low energy mesh networks: Survey of communication and security protocols. Sensors 2020, 20, 3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.; Paul, K. Architecture and security of SCADA systems: A review. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. Prot. 2021, 34, 100433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekala, S.H.; Baig, Z.; Anwar, A.; Zeadally, S. Cybersecurity for industrial IoT (IIoT): Threats, countermeasures, challenges and future directions. Comput. Commun. 2023, 208, 294–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhaib, M.; Shaikh, F.A.; Tanweer, W.; Alnajim, A.M.; Alyahya, S.; Khan, S.; Usman, M.; Islam, M.; Hasan, M.K. Faults Feature Extraction Using Discrete Wavelet Transform and Artificial Neural Network for Induction Motor Availability Monitoring—Internet of Things Enabled Environment. Energies 2022, 15, 7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerodimos, A.; Maglaras, L.; Ferrag, M.A.; Ayres, N.; Kantzavelou, I. IoT: Communication protocols and security threats. Internet Things Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2023, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, S.; Yearwood, J.; Hassan, M.M.; Almogren, A. Securing the operations in SCADA-IoT platform based industrial control system using ensemble of deep belief networks. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 71, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliatsios, D.; Sarigiannidis, P.; Lagkas, T.; Sarigiannidis, A.G. A Survey on SCADA Systems: Secure Protocols, Incidents, Threats and Tactics. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 1942–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, D. Fighting Computer Crime; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998; ISBN 0471163783. [Google Scholar]
- Spafford, E. Quotable Spaf, Gene Spafford’s Personal Pages. Available online: http://spaf.cerias.purdue.edu/quotes.html (accessed on 13 June 2023).
- Zhu, B.; Joseph, A.; Sastry, S. A taxonomy of cyber-attacks on SCADA systems. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Internet of Things and 4th International Conference on Cyber Physical and Social Computing, Dalian, China, 19–22 October 2011; pp. 380–388. [Google Scholar]
- Majeed, A.; Alnajim, A.M.; Waseem, A.; Khaliq, A.; Naveed, A.; Habib, S.; Islam, M.; Khan, S. Deep Learning-Based Symptomizing Cyber Threats Using Adaptive 5G Shared Slice Security Approaches. Future Internet 2023, 15, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiadi, F.; Putra, P.H.; Sucahyo, Y.G.; Hasibuan, Z.A. Determining components of national cyber security framework using Grounded Theory. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Informatics and Computing, Jayapura, Indonesia, 1–3 November 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Trifonov, R.; Manolov, G.; Yoshinov, R.; Pavlova, G. A survey of artificial intelligence for enhancing the information security. Int. J. Dev. Res. 2017, 7, 16866–16872. [Google Scholar]
- Takiddin, A.; Ismail, M.; Zafar, U.; Serpedin, E. Deep autoencoder-based anomaly detection of electricity theft cyberattacks in smart grids. IEEE Syst. J. 2022, 16, 4106–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podder, P.; Bharati, S.; Mondal, M.; Paul, P.K.; Kose, U. Artificial neural network for cybersecurity: A comprehensive review. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.01185. [Google Scholar]
- Albattah, W.; Khel, M.H.K.; Habib, S.; Islam, M.; Khan, S.; Abdul Kadir, K. Hajj Crowd Management Using CNN-Based Approach. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2020, 66, 2183–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnajim, A.M.; Habib, S.; Islam, M.; Albelaihi, R.; Alabdulatif, A. Mitigating the Risks of Malware Attacks with Deep Learning Techniques. Electronics 2023, 12, 3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.; Grier, C.; Ma, J.; Paxson, V.; Song, D. Design and evaluation of a real-time url spam filtering service. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), Oakland, CA, USA, 22–25 May 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 447–462. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, K.; Khan, R.U.; Albattah, W.; Nayab, D.; Qamar, A.M.; Habib, S.; Islam, M. Crowd Counting Using End-to-End Semantic Image Segmentation. Electronics 2021, 10, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, K.E.; Humphries, J.W.; Andel, T.R. Developing a virtualization platform for courses in networking, systems administration and cyber security education. In Proceedings of the 2009 Spring Simulation Multiconference, San Diego, CA, USA, 22–27 March 2009; SpringSim, Society for Computer Simulation International: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Stringhini, G.; Thonnard, O. That Aint You: Blocking Spearphishing through Behavioral Modelling. In Detection of Intrusions and Malware, and Vulnerability Assessment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 78–97. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, K.; Alnajim, A.M.; Naveed Malik, A.; Waseem, A.; Alyahya, S.; Islam, M.; Khan, S. Entice to Trap: Enhanced Protection against a Rate-Aware Intelligent Jammer in Cognitive Radio Networks. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Statistical Techniques for Network Security, Modern StatisticallyBased Intrusion Detection and Protection; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, D.; Nicol, D.M.; Yan, G. An event buffer flooding attack in DNP3 controlled SCADA systems. In Proceedings of the 2011 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 11–14 December 2011; pp. 2614–2626. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, I.; Abdullah, A.B.; Alghamdi, A.S. Evaluating neural network intrusion detection approaches using Analytic Hierarchy Process. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Symposium on Information Technology, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 15–17 June 2010; Volume 2, pp. 885–890. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Usynin, A.; Hines, J.W. Anomaly-Based Intrusion Detection for SCADA Systems; Technical Meeting on Cyber Security, Idaho; International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Vienna, Austria, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Linda, O.; Manic, M.; McQueen, M. Improving Control System Cyber-State Awareness using Known Secure Sensor Measurements. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Critical Information Infrastructure Security, CRITIS 2012, Lillehammer, Norway, 17–18 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Joshi, M.; Rose, C.P.; Fischer, F.; Weinberger, A.; Stegmann, K. Context Based Classification for Automatic Collaborative Learning Process Analysis; Artificial Intelligence in Education; IOS Press: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Papp, D.; Ma, Z.; Buttyan, L. Embedded systems security: Threats, vulnerabilities, and attack taxonomy. In Proceedings of the IEEE 13th Annual Conference on Privacy, Security and Trust (PST), Izmir, Turkey, 21–23 July 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, C.; Stavrou, I.; Dimmock, S.; Jhonson, C. Introducing a Forensics Data Type Taxonomy of Acquirable Artefacts from Programmable Logic Controllers; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Sampalli, S. A Survey of Security in SCADA Networks: Current Issues and Future Challenges. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 135812–135831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglaras, L.A.; Jiang, J. Intrusion detection in SCADA systems using machine learning techniques. In Proceedings of the Science and Information (SAI) Conference 2014, London, UK, 27–29 August 2014; pp. 626–631. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, Z.; Ali, H.; Badawy, M. Internet of Things (IoT): Definitions, Challenges, and Recent Research Directions. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2015, 128, 975–8887. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Christie, R.; Manjula, R. Scalability in Internet of Things: Features, Techniques and Research Challenges. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Res. 2017, 13, 1617–1627. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Guo, H. A Survey on IIoT Security. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE VTS Asia Pacific Wireless Communications Symposium (APWCS), Singapore, 28–30 August 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rondanini, C.; Carminati, B.; Ferrari, E. Confidential Discovery of IoT Devices through Blockchain. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Congress on Internet of Things (ICIOT), Milan, Italy, 8–13 July 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Shang, B.; Song, H.; Huang, Y.; Fan, P. Reliability versus Latency in IIoT Visual Applications: A Scalable Task Offloading Framework. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 16726–16735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorga, M.; Feldman, L.; Barton, R.; Martin, M.J.; Goren, N.; Mahmoudi, C. Fog Computing Conceptual Model; Technical Report; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran, M.; Chinchani, R.; Upadhyaya, S. PHONEY: Mimicking user response to detect phishing attacks. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Symposium on a World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks(WoWMoM’06), Buffalo-Niagara Falls, NY, USA, 26–29 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Basit, A.; Zafar, M.; Liu, X.; Javed, A.R.; Jalil, Z.; Kifayat, K. A comprehensive survey of AIenabled phishing attacks detection techniques. Telecommun. Syst. 2020, 76, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khonji, M.; Iraqi, Y.; Jones, A. Phishing Detection: A Literature Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 15, 2091–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, N.; Thabtah, F.; Abdel-jaber, H. Phishing detection: A recent intelligent machine learning comparison based on models content and features. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Intelligence and Security Informatics (ISI), Beijing, China, 22–24 July 2017; pp. 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Liu, Q.; Zou, L.; Yang, H.; Zhou, D.; Yu, F. A Content-Based Phishing Email Detection Method. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Software Quality, Reliability and Security Companion (QRS-C), Prague, Czech Republic, 25–29 July 2017; pp. 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.S.; Ali, S.T. PhishShield: A Desktop Application to Detect Phishing Webpages through Heuristic Approach. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 54, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuzzocrea, A.; Martinelli, F.; Mercaldo, F. A machine-learning framework for supporting intelligent web-phishing detection and analysis. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Database Applications & Engineering Symposium on-IDEAS ‘19, Athens, Greece, 10–12 June 2019; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadollahi, M.M.; Shoeleh, F.; Serkani, E.; Madani, A.; Gharaee, H. An Adaptive Machine Learning Based Approach for Phishing Detection Using Hybrid Features. In Proceedings of the 2019 5th International Conference on Web Research (ICWR), Tehran, Iran, 24–25 April 2019; pp. 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonowal, G.; Kuppusamy, K.S. PhiDMA–A phishing detection model with multi-filter approach. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2020, 32, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.B.; Jain, A.K. Phishing Attack Detection using a Search Engine and Heuristicsbased Technique. J. Inf. Technol. Res. 2020, 13, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavarsky, M.P.; Lindskog, D. Experimental Analysis of Ransomware on Windows and AISLAMndroid Platforms. Evol. Charact. 2016, 94, 465–472. [Google Scholar]
- Skrzewski, M. Monitoring Malware Activity on the LAN Network; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Alliance for Community Empowerment. Lucrative Ransomware Attacks: Analysis of the CryptoWall Version 4 Threat; Cryptowall Version 4 Threat Report; Alliance for Community Empowermen: Bridgeport, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yar, H.; Hussain, T.; Khan, Z.A.; Koundal, D.; Lee, M.Y.; Baik, S.W. Vision sensor-based real-time fire detection in resource-constrained IoT environments. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 5195508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yar, H.; Hussain, T.; Agarwal, M.; Khan, Z.A.; Gupta, S.K.; Baik, S.W. Optimized Dual Fire Attention Network and Medium-Scale Fire Classification Benchmark. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 6331–6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Farman, H.; Yar, H.; Khan, Z.; Habib, S.; Ammar, A. Deep learning-based election results prediction using Twitter activity. Soft Comput. 2021, 26, 7535–7543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yar, H.; Khan, Z.A.; Ullah, F.U.M.; Ullah, W.; Baik, S.W. A modified YOLOv5 architecture for efficient fire detection in smart cities. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 231, 120465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trend Micro. Ransomware Recap: New Families and Updated Variants in June; Trend Micro Incorporated Labs Report; Trend Micro: Tokyo, Japan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yorkdale. Criminals Continue to Defraud and Extort Funds from Victims Using CryptoWall Ransomware Schemes; Federal Bureau of Investigation: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z.A.; Hussain, T.; Ullah, F.U.M.; Gupta, S.K.; Lee, M.Y.; Baik, S.W. Randomly Initialized CNN with Densely Connected Stacked Autoencoder for Efficient Fire Detection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 116, 105403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorca, D.; Mercaldo, F.; Giacinto, G.; Visaggio, C.A.; Martinelli, F. R-PackDroid: API package-based characterization and detection of mobile ransomware. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Applied Computing, Marrakech, Morocco, 3–7 April 2017; pp. 1718–1723. [Google Scholar]
- Sgandurra, D.; Muñoz-González, L.; Mohsen, R.; Lupu, E.C. Automated Dynamic Analysis of Ransomware: Benefits, Limitations and Use for Detection. ArXiv160903020 Cs. September 2016. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1609.03020 (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Tseng, A.; Chen, Y.; Kao, Y.; Lin, T. Deep learning for ransomware detection. IEICE Tech. Rep. 2016, 116, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Abolhasan, M.; Wysocki, T.; Dutkiewicz, E. A review of routing protocols for mobile ad hoc networks. Ad. Hoc. Netw. 2004, 2, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.C.; Perrig, A.; Johnson, D.B. Ariadne: A Secure On-Demand Routing Protocol for Ad Hoc Networks. Wirel. Netw. 2005, 11, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albattah, W.; Habib, S.; Alsharekh, M.F.; Islam, M.; Albahli, S.; Dewi, D.A. An Overview of the Current Challenges, Trends, and Protocols in the Field of Vehicular Communication. Electronics 2022, 11, 3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojetunde, B.; Shibata, N.; Gao, J. Securing Link State Routing for Wireless Networks against Byzantine Attacks: A Monitoring Approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE 41st Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), Torino, Italy, 4–8 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, A.; Ibidun, O.; Nureni, A. Mitigation of Denial of Service Attacks in Fog-Based Wireless Sensor Networks Using Deep Neural Networks Techniques. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4372752 (accessed on 13 June 2023).
- Esmaeili, M.; Goki, S.H.; Masjidi, B.H.K.; Sameh, M.; Gharagozlou, H.; Mohammed, A.S. ML-DDoSnet: IoT Intrusion Detection Based on Denial-of-Service Attacks Using Machine Learning Methods and NSL-KDD. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmi, S.; Oughdir, L. Performance evaluation of deep learning techniques for DoS attacks detection in wireless sensor network. J. Big Data 2023, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.R.; Chan, K.S. RTT-TC: A topological comparison based method to detect wormhole attacks in MANET. In Proceedings of the IEEE 12th International Conference on Communication Technology, Nanjing, China, 11–14 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Antonopoulos, A.; Verikoukis, C.; Skianis, C.; Akan, O.B. Energy efficient network coding-based MAC for cooperative ARQ wireless networks. Ad. Hoc. Netw. 2013, 11, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B. Internet of Things (IoT), Three-Layer Architecture, Security Issues and Counter Measures. In ICT Analysis and Applications; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Fong, S., Dey, N., Joshi, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; Volume 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, G.; Simpson, S.V.; Minu, R.I. Chapter Thirteen-Edge computing security: Layered classification of attacks and possible countermeasures. In Advances in Computers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 127, pp. 359–377. ISSN 0065-2458. ISBN 9780128245064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, E.; Haseeb-Ud-Din, M.; Malik, A.J.; Khan, T.K.; Abbasi, A.A.; Kadry, S.; Khan, M.A.; Rho, S. Intrusion detection based on machine learning in the internet of things, attacks and counter measures. J. Supercomput. 2022, 78, 8890–8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouaatamid, O.E.; Lahmer, M.; Belkasmi, M. Internet of Things Security: Layered Classification of Attacks and Possible Countermeasures. Electron. J. Inf. Technol. 2016, 9, 24–37. Available online: http://www.webmail.revue-eti.net/index.php/eti/article/view/98 (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Usman, M.; Raponi, S.; Qaraqe, M.; Oligeri, G. KaFHCa: Key-Establishment via Frequency Hopping Collisions. arXiv201009642 Cs. October 2020. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2010.09642 (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Furstenau, L.B.; Rodrigues, Y.P.R.; Sott, M.K.; Leivas, P.; Dohan, M.S.; López-Robles, J.R.; Cobo, M.J.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Choo, K.-K.R. Internet of things: Conceptual network structure, main challenges and future directions. Digit. Commun. Networks 2023, 9, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrif, F.F.; Sundarajan, E.A.; Ahmed, R.; Hasan, M.K. SLAE6: Secure and Lightweight Authenticated Encryption Scheme for 6LoWPAN Networks. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Sensor Networks (SENSORNETS 2023), Online, 23–24 February 2023; pp. 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Hennebert, C.; Santos, J.D. Security protocols and privacy issues into 6LoWPAN stack: A synthesis. IEEE Internet Things J. 2014, 1, 384–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, A.H.; Abdirazak, M.; Shamsuzzaman Sadi, A.B.M.; Anam, T.; Khan, S.Z.; Rahman, M.M.; Omar, M.M. A comparative study of WLAN security protocols: WPA, WPA2. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Advances in Electrical Engineering (ICAEE), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 17–19 December 2015; pp. 165–169. [Google Scholar]
- Venkat, Y.; Chand, K.P.; Preethiya, T. An intrusion detection system for the Internet of Things based on machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Recent Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Ubiquitous Communication, and Computational Intelligence (RAEEUCCI), Chennai, India, 19–21 April 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Syed Ali, M.; Hussain, S.Z. Survey on intrusion detection system in iot network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovative Computing and Communications: Proceedings of ICICC 2022, Delhi, India, 19–20 February 2022; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, S.; Wallgren, L.; Voigt, T. SVELTE: Real-Time intrusion detection in the internet of things. Ad. Hoc. Netw. 2013, 11, 2661–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.S.A.M.S.; Hassan, R.; Othman, N.E. IPv6 neighbor discovery protocol specifications, threats and countermeasures: A survey. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 18187–18210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsal, E.; Çebi, Y. Denial of Service Attacks in WSN. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Computing in Science & Engineering, Izmir, Turkey, 4–6 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrag, M.A.; Maglaras, L.A.; Janicke, H.; Jiang, J.; Shu, L. Authentication protocols for internet of things: A comprehensive survey. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2017, 2017, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, R.; Zeng, S.; Wang, Z.; Shang, J.; Chen, W.; Huang, T.; Wang, S.; Yu, F.R.; Liu, Y. A Comprehensive Survey on Blockchain in Industrial Internet of Things: Motivations, Research Progresses, and Future Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2022, 24, 88–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiker Mohamed, M.; Matthew Alofe, O.; Ajmal Azad, M.; Singh Lallie, H.; Fatema, K.; Sharif, T. A comprehensive survey on secure software-defined network for the Internet of Things. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2022, 33, e4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-hajj, M.; Chamoun, M.; Fadlallah, A.; Serhrouchni, A. Analysis of authentication techniques in Internet of Things (IoT). In Proceedings of the 2017 1st Cyber Security in Networking Conference (CSNet), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 18–20 October 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Eddy, W.M. Defenses against TCP SYN flooding attacks. Internet Protoc. J. 2006, 9, 2–16. [Google Scholar]
- Toyeer-E-Ferdoush, R.H.; Hasan, M. A convenient way to mitigate DDoS TCP SYN flood attack. J. Discret. Math. Sci. Cryptogr. 2022, 25, 2069–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, M.E.; Demirci, M. ConPoolUBF: Connection pooling and updatable Bloom filter based SYN flood defense in programmable data planes. Comput. Netw. 2023, 231, 109802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán-Gómez, J.; Carrillo-Mondéjar, J.; Gómez, J.M.C.; Martínez, J.L.M. Security Assessment of the MQTT-SN Protocol for the Internet of Things. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2022; Volume 2224. [Google Scholar]
- Zeghida, H.; Boulaiche, M.; Chikh, R. Securing MQTT protocol for IoT environment using IDS based on ensemble learning. Int. J. Inf. Secur. 2023, 22, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, S.; Minhas, Q.A.; Ahmed, S.; Habib, S.; Hasan, M.K.; Islam, M.; Khan, S. An improved iBAT-COOP protocol for cooperative diversity in FANETs. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 67, 2527–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.A.; Ghadim, A.D.; Balador, A.; Alimadadi, Z.; Papadimitratos, P. Digital twin-based intrusion detection for industrial control systems. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops and other Affiliated Events (PerCom Workshops), Atlanta, GA, USA, 21–25 March 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wolsing, K.; Wagner, E.; Saillard, A.; Henze, M. IPAL: Breaking up silos of protocol-dependent and domain-specific industrial intrusion detection systems. In Proceedings of the 25th International Symposium on Research in Attacks, Intrusions and Defenses, Limassol, Cyprus, 26–28 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Xue, Q.; Feng, J.; Bai, D. Internet of things intrusion detection model and algorithm based on cloud computing and multi-feature extraction extreme learning machine. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2023, 9, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyamfi, E.; Jurcut, A.D. Novel online network intrusion detection system for industrial iot based on oi-svdd and as-elm. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 10, 3827–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Plaza-Hernández, M.; Prieto, J.; Corchado, J.M. Security in the Internet of Things Application Layer: Requirements, Threats, and Solutions. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 97197–97216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaei Khoei, T.; Kaabouch, N. A Comparative Analysis of Supervised and Unsupervised Models for Detecting Attacks on the Intrusion Detection Systems. Information 2023, 14, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, U.; Rishiwal, V.; Tanwar, S.; Chaudhary, R.; Sharma, G.; Bokoro, P.N.; Sharma, R. Blockchain technology for secure supply chain management: A comprehensive review. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 85493–85517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, S.E.; Nozari, H.; Edalatpanah, S.A. Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT) and Industry 4.0–Based Supply Chain (FMCG Industry). In A Roadmap for Enabling Industry 4.0 by Artificial Intelligence; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y. A Machine Learning Algorithm for Supplier Credit Risk Assessment Based on Supply Chain Management. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2022, 2022, 4766597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, S.; Zavrak, S.; Eken, S. Real-time monitoring and scalable messaging of scada networks data: A case study on cyber-physical attack detection in water distribution system. In International Congress of Electrical and Computer Engineering; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Karasmanoglou, A.; Antonakakis, M.; Zervakis, M. ECG-Based Semi-Supervised Anomaly Detection for Early Detection and Monitoring of Epileptic Seizures. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demertzis, K.; Iliadis, L.; Pimenidis, E.; Kikiras, P. Variational restricted Boltzmann machines to automated anomaly detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 15207–15220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.; Hussain, A.; Albattah, W.; Islam, M.; Khan, S.; Khan, R.U.; Khan, K. Abnormal Activity Recognition from Surveillance Videos Using Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors 2021, 21, 8291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, T.; Yuen, K.-V. Construction site information decentralized management using blockchain and smart contracts. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2022, 37, 1450–1467. [Google Scholar]
- Rrushi, J.L. Physics-Driven Page Fault Handling for Customized Deception against CPS Malware. ACM Trans. Embed. Comput. Syst. 2022, 21, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, R.; Aljuhani, A. Anomaly Detection for Industrial Internet of Things Cyberattacks. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2022, 44, 2361–2378. [Google Scholar]
- Chander, N.; Kumar, M.U. Metaheuristic feature selection with deep learning enabled cascaded recurrent neural network for anomaly detection in Industrial Internet of Things environment. Clust. Comput. 2022, 26, 1801–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgueglia, A.; Di Sorbo, A.; Visaggio, C.A.; Canfora, G. A systematic literature review of IoT time series anomaly detection solutions. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2022, 134, 170–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Samara, M.; Bennis, I.; Abouaissa, A.; Lorenz, P. A survey of outlier detection techniques in IoT: Review and classification. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2022, 11, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullahi, M.; Baashar, Y.; Alhussian, H.; Alwadain, A.; Aziz, N.; Capretz, L.F.; Abdulkadir, S.J. Detecting cybersecurity attacks in internet of things using artificial intelligence methods: A systematic literature review. Electronics 2022, 11, 198. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, B.; Wang, C. A Survey on Programmable Logic Controller Vulnerabilities, Attacks, Detections, and Forensics. Processes 2023, 11, 918. [Google Scholar]
- Marković-Petrović, J.D. A Model for Dynamic Cyber Security Risk Assessment in the Industrial IOT Environment. In Proceedings of the Sinteza 2022-International Scientific Conference on Information Technology and Data Related Research, Belgrade, Serbia, 16 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, G.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y. A Comprehensive Review of Blockchain Technology-Enabled Smart Manufacturing: A Framework, Challenges and Future Research Directions. Sensors 2022, 23, 155. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Cao, X.Y.; Fu, Y.; He, Z.W.; Yin, Z.J.; Yin, H.L.; Chen, Z.B. Experimental measurement-device-independent type quantum key distribution with flawed and correlated sources. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 2167–2175. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.-L.; Fu, Y.; Li, C.-L.; Weng, C.-X.; Li, B.-H.; Gu, J.; Lu, Y.-S.; Huang, S.; Chen, Z.-B. Experimental quantum secure network with digital signatures and encryption. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwac228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Ru, B.; Esperança, P.M.; Li, Z. On redundancy and diversity in cell-based neural architecture search. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.08887. [Google Scholar]
- Sangkhro, R.; Agrawal, A.K. Cybersecurity in Industrial Control Systems: A Review of the Current Trends and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2023 10th International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom), New Delhi, India, 15–17 March 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, S.R.; Wadhawan, S.; Goel, R. mrmr-pso: A hybrid feature selection technique with a multiobjective approach for sign language recognition. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 10365–10380. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.; Munir, A.; Waheed, A.; Alabrah, A.; Mukred, M.; Amin, F.; Salam, A. Enhancing Security and Efficiency in Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks: A Lightweight Key Management Framework. Symmetry 2023, 15, 1484. [Google Scholar]
- Salam, A.; Ullah, F.; Amin, F.; Abrar, M. Deep Learning Techniques for Web-Based Attack Detection in Industry 5.0: A Novel Approach. Technologies 2023, 11, 107. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.; Dukyil, A.S.; Alyahya, S.; Habib, S. An IoT Enable Anomaly Detection System for Smart City Surveillance. Sensors 2023, 23, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.; Alyahya, S.; Islam, M.; Alnajim, A.M.; Alabdulatif, A.; Alabdulatif, A. Design and Implementation: An IoT-Framework-Based Automated Wastewater Irrigation System. Electronics 2023, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).