Segmentation of Retinal Blood Vessels Using Focal Attention Convolution Blocks in a UNET
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preprocessing
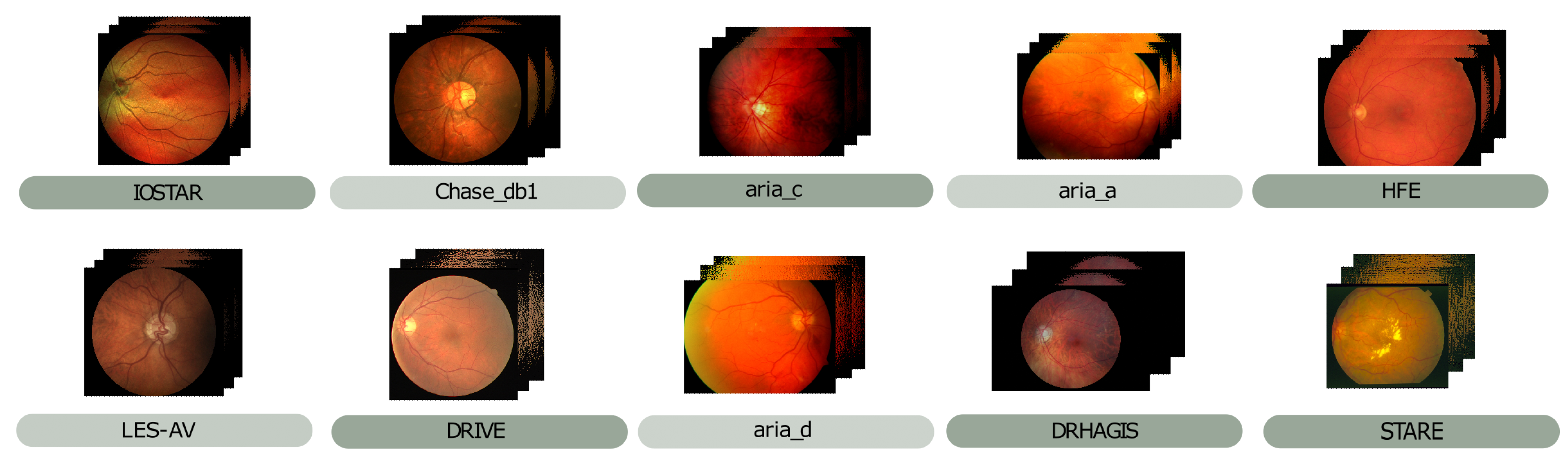
2.1.1. Data Cleaning
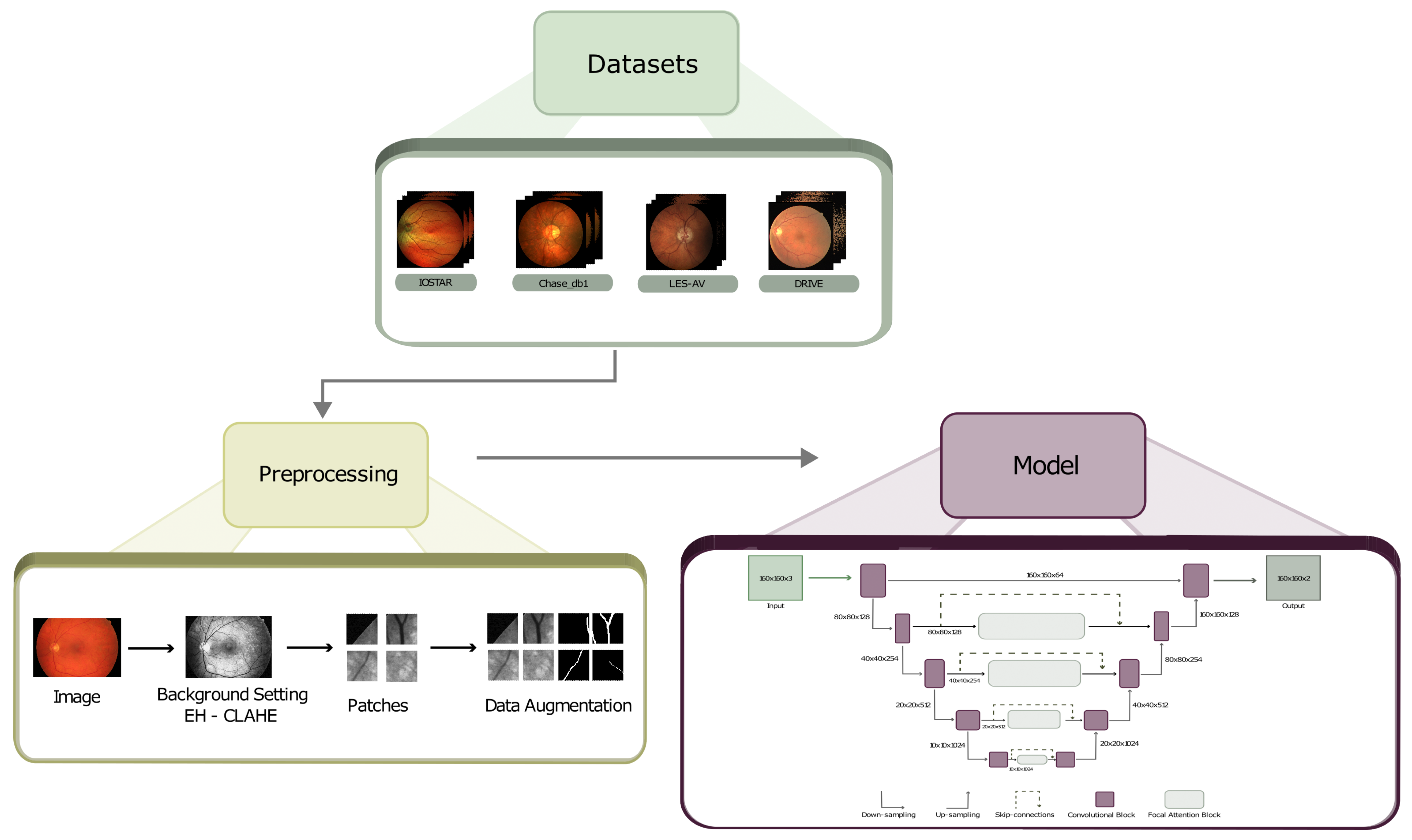
2.1.2. Data Augmentation
2.2. The Model
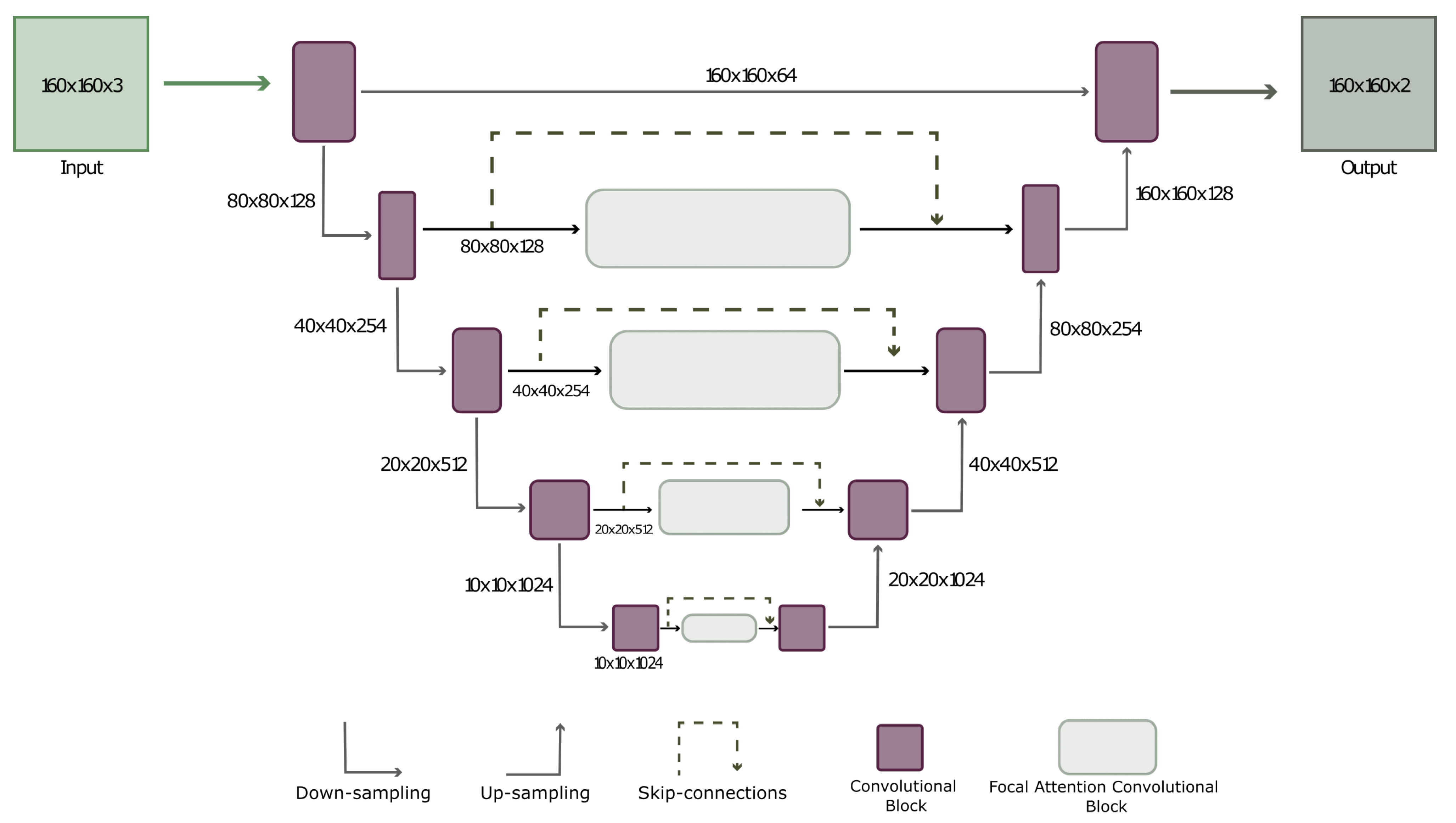
2.2.1. Model Overview
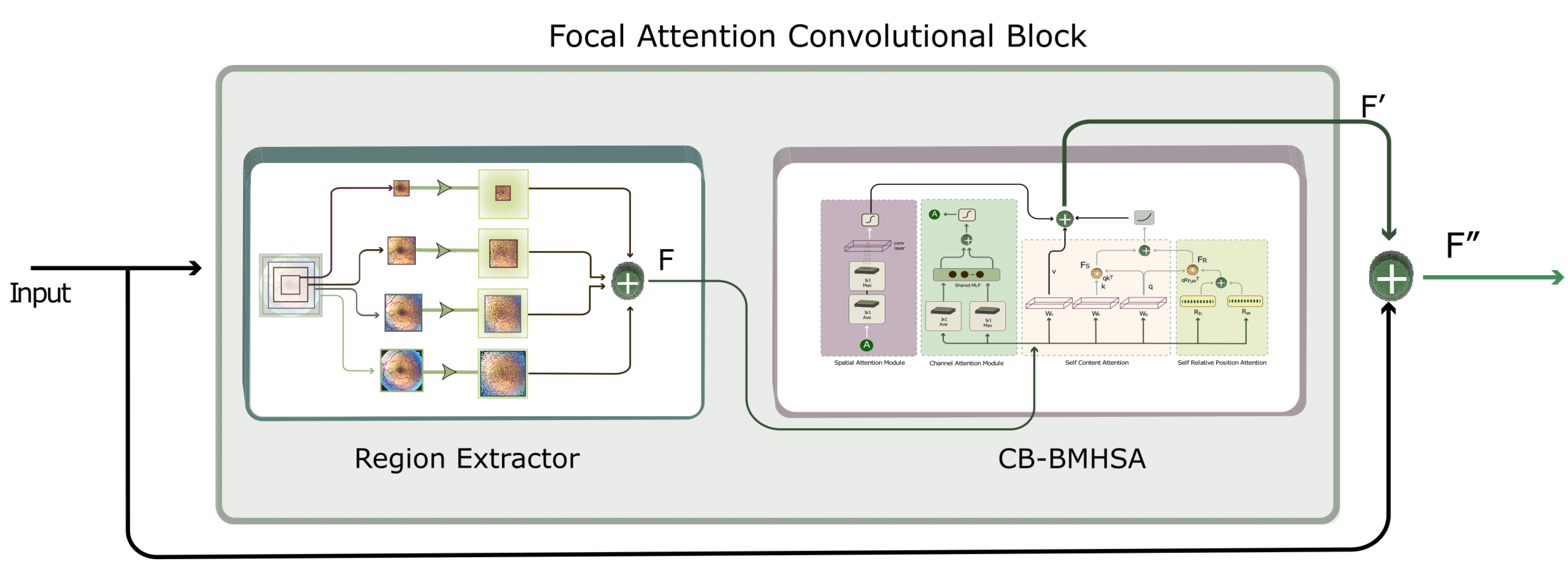
2.2.2. UNET with FACB
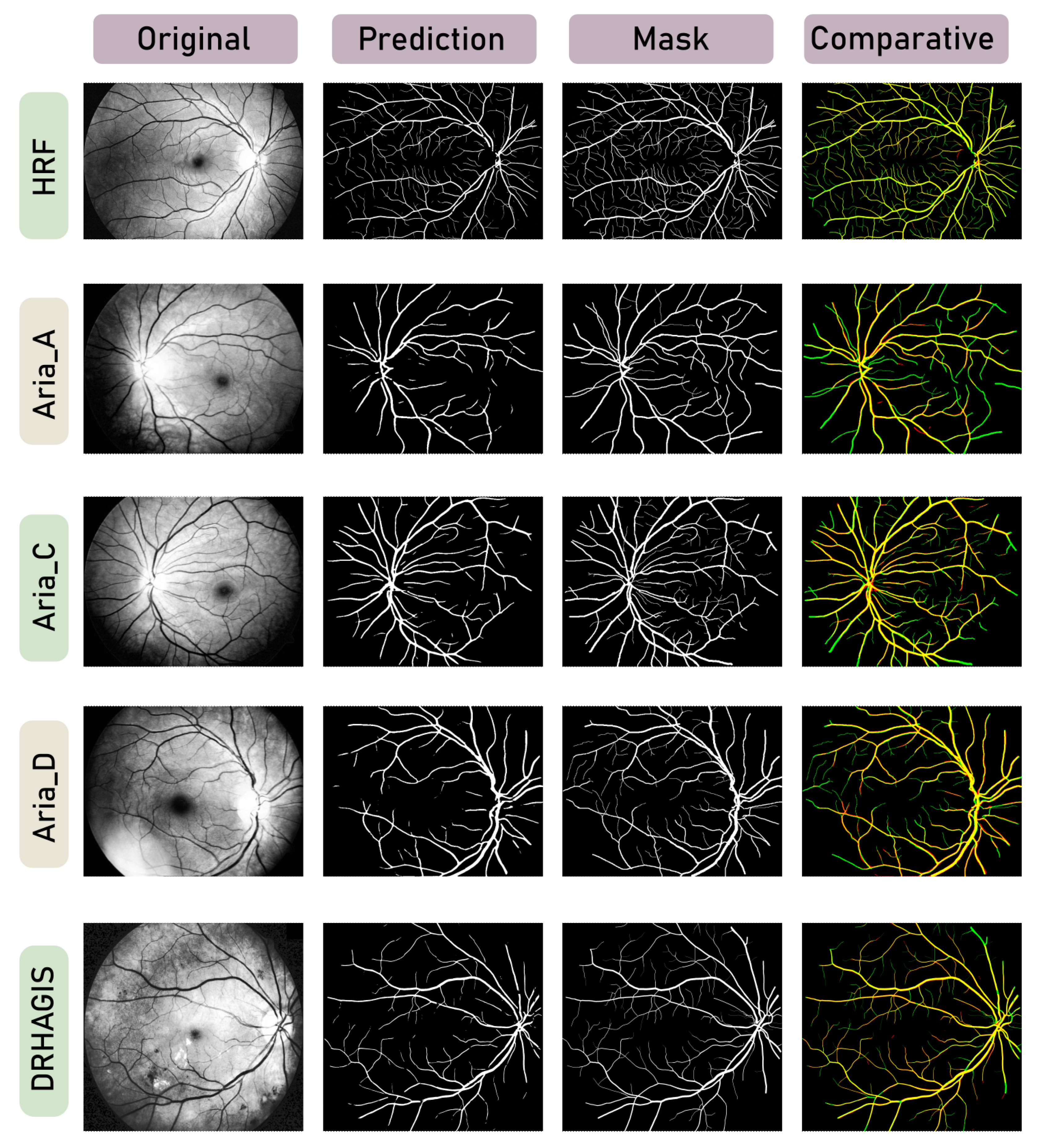
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dakhel, A.M.; Majdinasab, V.; Nikanjam, A.; Khomh, F.; Desmarais, M.C.; Jiang, Z.M. GitHub Copilot AI Pair Programmer: Asset or Liability? J. Syst. Softw. 2023, 203, 111734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly Accurate Protein Structure Prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, K.; Wan, Z.; Xie, S.; Lv, Z. Popular Deep Learning Algorithms for Disease Prediction: A Review. Clust. Comput. 2023, 26, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias-Garzón, D.; Alzate-Grisales, J.A.; Orozco-Arias, S.; Arteaga-Arteaga, H.B.; Bravo-Ortiz, M.A.; Mora-Rubio, A.; Saborit-Torres, J.M.; Serrano, J.Á.M.; De La Iglesia Vayá, M.; Cardona-Morales, O.; et al. COVID-19 Detection in X-ray Images Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Mach. Learn. Appl. 2021, 6, 100138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzubaidi, L.; Zhang, J.; Humaidi, A.J.; Al-Dujaili, A.; Duan, Y.; Al-Shamma, O.; Santamaría, J.; Fadhel, M.A.; Al-Amidie, M.; Farhan, L. Review of Deep Learning: Concepts, CNN Architectures, Challenges, Applications, Future Directions. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image Is Worth 16 × 16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale 2021. arXiv, 2020; arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Front Matter. In Computational Retinal Image Analysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. i–iii. ISBN 978-0-08-102816-2.
- Poplin, R.; Varadarajan, A.V.; Blumer, K.; Liu, Y.; McConnell, M.V.; Corrado, G.S.; Peng, L.; Webster, D.R. Prediction of Cardiovascular Risk Factors from Retinal Fundus Photographs via Deep Learning. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheloni, R.; Gandolfi, S.A.; Signorelli, C.; Odone, A. Global Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy: Protocol for a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e022188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambyal, N.; Saini, P.; Syal, R.; Gupta, V. Modified U-Net Architecture for Semantic Segmentation of Diabetic Retinopathy Images. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 40, 1094–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.U.; Cho, S.; Kim, J.H.; Chong, K.T. BU-Net: Brain Tumor Segmentation Using Modified U-Net Architecture. Electronics 2020, 9, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.U.; Cho, S.; Kim, J.; Chong, K.T. BrainSeg-Net: Brain Tumor MR Image Segmentation via Enhanced Encoder–Decoder Network. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, V.; Gupta, S.; Koundal, D.; Nayak, S.R.; Barsocchi, P.; Bhoi, A.K. Modified U-NET Architecture for Segmentation of Skin Lesion. Sensors 2022, 22, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, K.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, C. A Field Weed Density Evaluation Method Based on UAV Imaging and Modified U-Net. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Proceeding of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, H.; Lin, Y.; Yao, Z.; Xie, Z.; Wei, Y.; Ning, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, L.; et al. Swin Transformer V2: Scaling Up Capacity and Resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, F.; Qi, Z.; Duan, K.; Xi, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Xiong, H.; He, Q. A Comprehensive Survey on Transfer Learning. Proc. IEEE 2020, 109, 43–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, A.; Lin, T.-Y.; Parmar, N.; Shlens, J.; Abbeel, P.; Vaswani, A. Bottleneck Transformers for Visual Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 25 June 2021; IEEE: Piscatway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 16514–16524. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, P.; Dai, X.; Xiao, B.; Yuan, L.; Gao, J. Focal Self-Attention for Local-Global Interactions in Vision Transformers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.00641. [Google Scholar]
- Moccia, S.; De Momi, E.; El Hadji, S.; Mattos, L.S. Blood Vessel Segmentation Algorithms—Review of Methods, Datasets and Evaluation Metrics. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 158, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciecholewski, M.; Kassjański, M. Computational Methods for Liver Vessel Segmentation in Medical Imaging: A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurício, J.; Domingues, I.; Bernardino, J. Comparing Vision Transformers and Convolutional Neural Networks for Image Classification: A Literature Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, A.; Estrada, R. Dynamic Deep Networks for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. Front. Comput. Sci. 2020, 2, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gegundez-Arias, M.E.; Marin-Santos, D.; Perez-Borrero, I.; Vasallo-Vazquez, M.J. A New Deep Learning Method for Blood Vessel Segmentation in Retinal Images Based on Convolutional Kernels and Modified U-Net Model. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 205, 106081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdran, A.; Anjos, A. State-of-the-art retinal vessel segmentation with minimalistic models. Front. Nat. 2022, 12, 6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Liang, Q.; Yan, X.; Zhang, D.; Coppola, G.; Sun, W. Multi-Proportion Channel Ensemble Model for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 111, 103352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Duan, X.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Y. Retinal Vessel Segmentation by Deep Residual Learning with Wide Activation. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2020, 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuyet, V.T.H.; Binh, N.T. Improving Retinal blood vessels Segmentation via Deep Learning in Salient Region. SN Comput. Sci. 2020, 1, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-B.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, J.Y. M-GAN: Retinal Blood Vessel Segmentation by Balancing Losses Through Stacked Deep Fully Convolutional Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 146308–146322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Z.; Huang, J.; Lu, K.; Pan, D.; Feng, S. A Size-Invariant Convolutional Network with Dense Connectivity Applied to Retinal Vessel Segmentation Measured by a Unique Index. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 196, 105508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, S.A.; Hossain, K.F.; Tavakkoli, A.; Zuckerbrod, S.L.; Sanders, K.M.; Baker, S.A. RV-GAN: Segmenting Retinal Vascular Structure in Fundus Photographs Using a Novel Multi-Scale Generative Adversarial Network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 27 September 27–1 October 2021; Volume 12908, pp. 34–44. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, G.; Maheshwari, S.; Agarwal, A. Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization Based Enhancement for Real Time Video System. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), Delhi, India, 24–27 September 2014; IEEE: Piscatway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 2392–2397. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1905.11946. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going Deeper with Convolutions. arXiv, 2014; arXiv:1409.4842. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Yang, W.; Wang, L.; Tan, S.; Lin, J.; Bu, W. PCAT-UNet: UNet-like Network Fused Convolution and Transformer for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Szemenyei, M.; Yi, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y. Dense Residual Network for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020–2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1374–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Li, M.; Yin, S. Lightweight Attention Convolutional Neural Network for Retinal Vessel Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2021, 17, 1958–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Zhong, J.; Lei, B.; Wen, Z.; Qin, J. SCS-Net: A Scale and Context Sensitive Network for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 70, 102025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajbakhsh, N.; Lai, B.; Ananth, S.; Ding, X. ErrorNet: Learning Error Representations from Limited Data to Improve Vascular Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Iowa City, IA, USA, 3–7 April 2020. [Google Scholar]



| Dataset | Author | Accuracy | AUC | Precision | Recall | Specificity | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRIVE | Park, K.-B. et al. [29] | 97.06 | 98.68 | 83.02 | 83.46 | 98.36 | 83.24 |
| Galdran, A. et al. [25] | - | 98.1 | - | - | - | - | |
| Chen, D. et al. [40] | 96.22 | 98.78 | - | 85.76 | 99.32 | 81.60 | |
| UNET with FACB | 97.9 | 93.6 | 91.7 | 88.1 | 99.0 | 89.9 | |
| CHASEDB1 | Park, K.-B. et al. [29] | 97.36 | 98.59 | - | - | - | 81.1 |
| Galdran, A. et al. [25] | - | 98.47 | - | - | - | - | |
| Chen, D. et al. [40] | 98.12 | 99.25 | - | 84.93 | 99.66 | 82.73 | |
| UNET with FACB | 99.1 | 97.0 | 94.8 | 94.4 | 99.5 | 94.6 | |
| HRF | Park, K.-B. et al. [29] | 97.61 | 98.52 | 79.72 | - | - | 79.72 |
| Galdran, A. et al. [25] | - | 98.25 | - | - | - | - | |
| Tang, P. et al. [26] | 96.31 | 98.43 | - | 76.53 | 98.66 | 77 | |
| UNET with FACB | 97.7 | 91.3 | 87.2 | 83.8 | 98.9 | 85.4 | |
| STARE | Park, K.-B. et al. [29] | 98.76 | 99.73 | 84.17 | 83.24 | 99.38 | 83.7 |
| Galdran, A. et al. [25] | - | 98.28 | - | - | - | - | |
| Chen, D. et al. [40] | 97.96 | 99.53 | - | 87.93 | 99.37 | 88.36 | |
| UNET with FACB | 97.9 | 93.6 | 91.7 | 88.1 | 99 | 89.9 | |
| LES-AV | Galdran, A. et al. [25] | - | 97.34 | - | - | - | - |
| UNET with FACB | 99.3 | 97.1 | 94.7 | 94.6 | 99.6 | 94.6 | |
| IOSTAR | Guo, C. et al. [41] | 97.13 | 98.73 | - | 80.82 | 98.54 | - |
| Li, X. et al. [42] | 95.44 | 96.23 | - | 73.22 | 98.02 | - | |
| Wu, H. et al. [43] | 97.06 | 98.65 | - | 82.55 | 98.30 | - | |
| UNET with FACB | 99.3 | 97.1 | 94.7 | 94.6 | 99.6 | 94.6 | |
| ARIA (mean) | Tajbakhsh, N. et al. [44] | - | - | - | - | - | 72 |
| UNET with FACB | 97.3 | 89.9 | 86.4 | 81.4 | 96.1 | 83.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortiz-Feregrino, R.; Tovar-Arriaga, S.; Pedraza-Ortega, J.C.; Rodriguez-Resendiz, J. Segmentation of Retinal Blood Vessels Using Focal Attention Convolution Blocks in a UNET. Technologies 2023, 11, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies11040097
Ortiz-Feregrino R, Tovar-Arriaga S, Pedraza-Ortega JC, Rodriguez-Resendiz J. Segmentation of Retinal Blood Vessels Using Focal Attention Convolution Blocks in a UNET. Technologies. 2023; 11(4):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies11040097
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtiz-Feregrino, Rafael, Saul Tovar-Arriaga, Jesus Carlos Pedraza-Ortega, and Juvenal Rodriguez-Resendiz. 2023. "Segmentation of Retinal Blood Vessels Using Focal Attention Convolution Blocks in a UNET" Technologies 11, no. 4: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies11040097
APA StyleOrtiz-Feregrino, R., Tovar-Arriaga, S., Pedraza-Ortega, J. C., & Rodriguez-Resendiz, J. (2023). Segmentation of Retinal Blood Vessels Using Focal Attention Convolution Blocks in a UNET. Technologies, 11(4), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies11040097








