Assessment of Cognitive Fatigue from Gait Cycle Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Computer vision-based system that uses gait sequence analysis to identify an individuals cognitive fatigue state.
- A dataset of gait sequences of individuals in non-cognitively fatigued and cognitively fatigued states.
- A 1D-CNN model based solution to classify cognitive fatigue in individuals.
2. Related Work
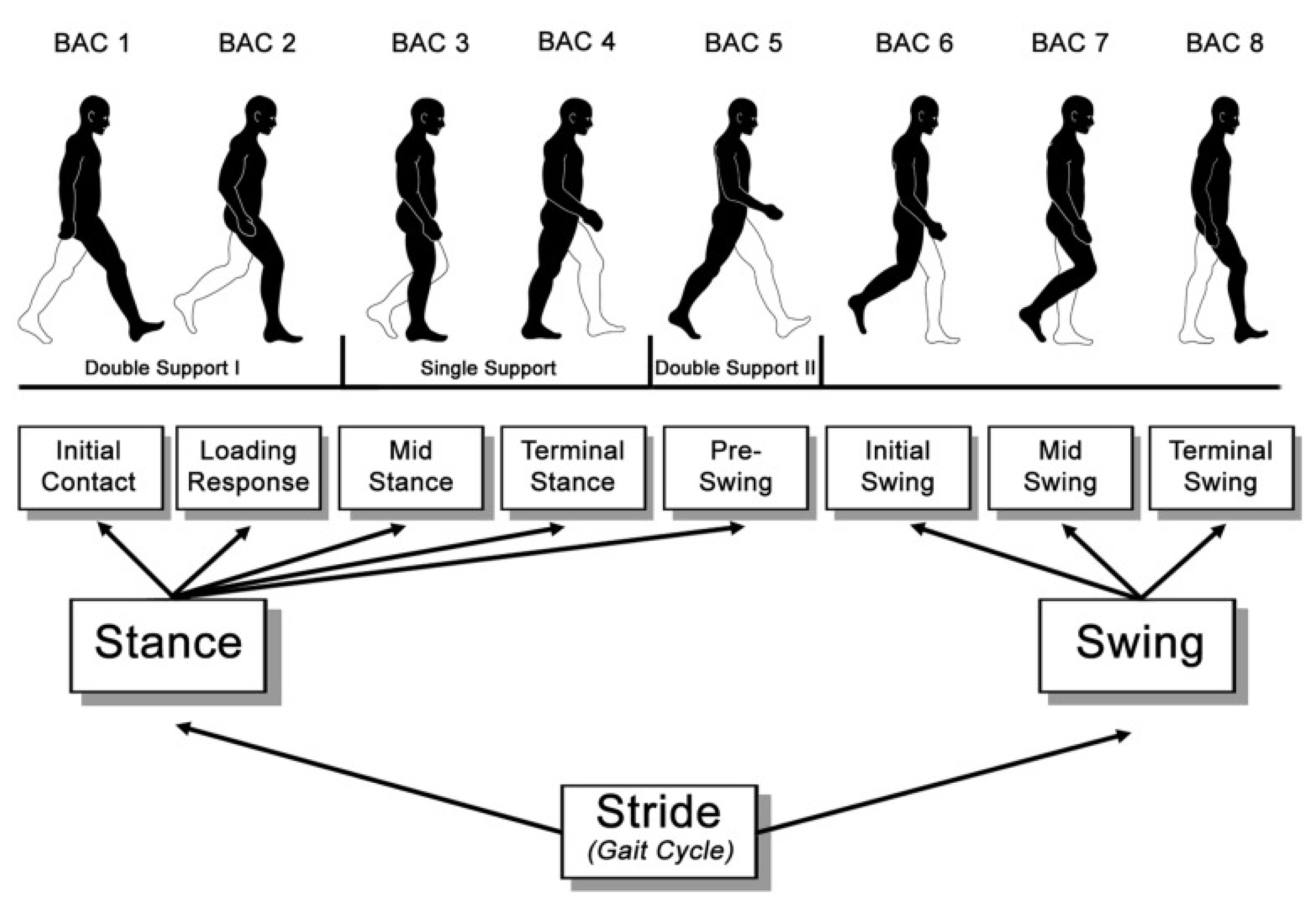
3. Experimental Setup, Dataset Collection and Annotation
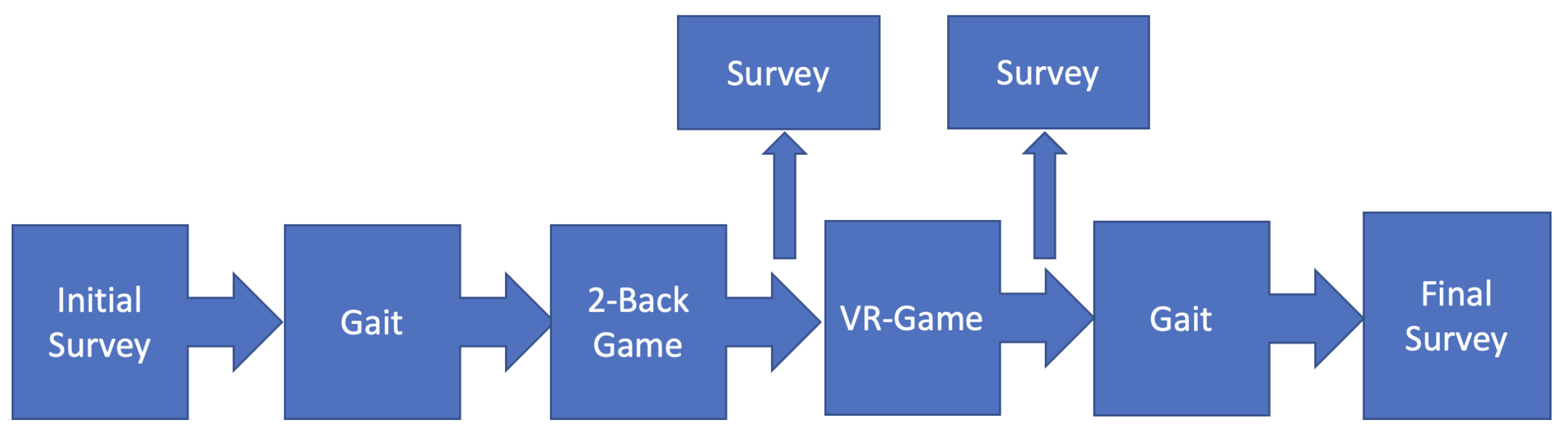
3.1. Experimental Setup
- Fill out an initial survey with the participants’ data and initial Cognitive Fatigue(CF) level.
- Collect walking (gait) data.
- Play multiple rounds of the 2-Back game. Fill out a survey mentioning CF level.
- Play multiple rounds of a VR game and fill out a survey mentioning CF level.
- Collect walking (gait) data and survey with CF level.
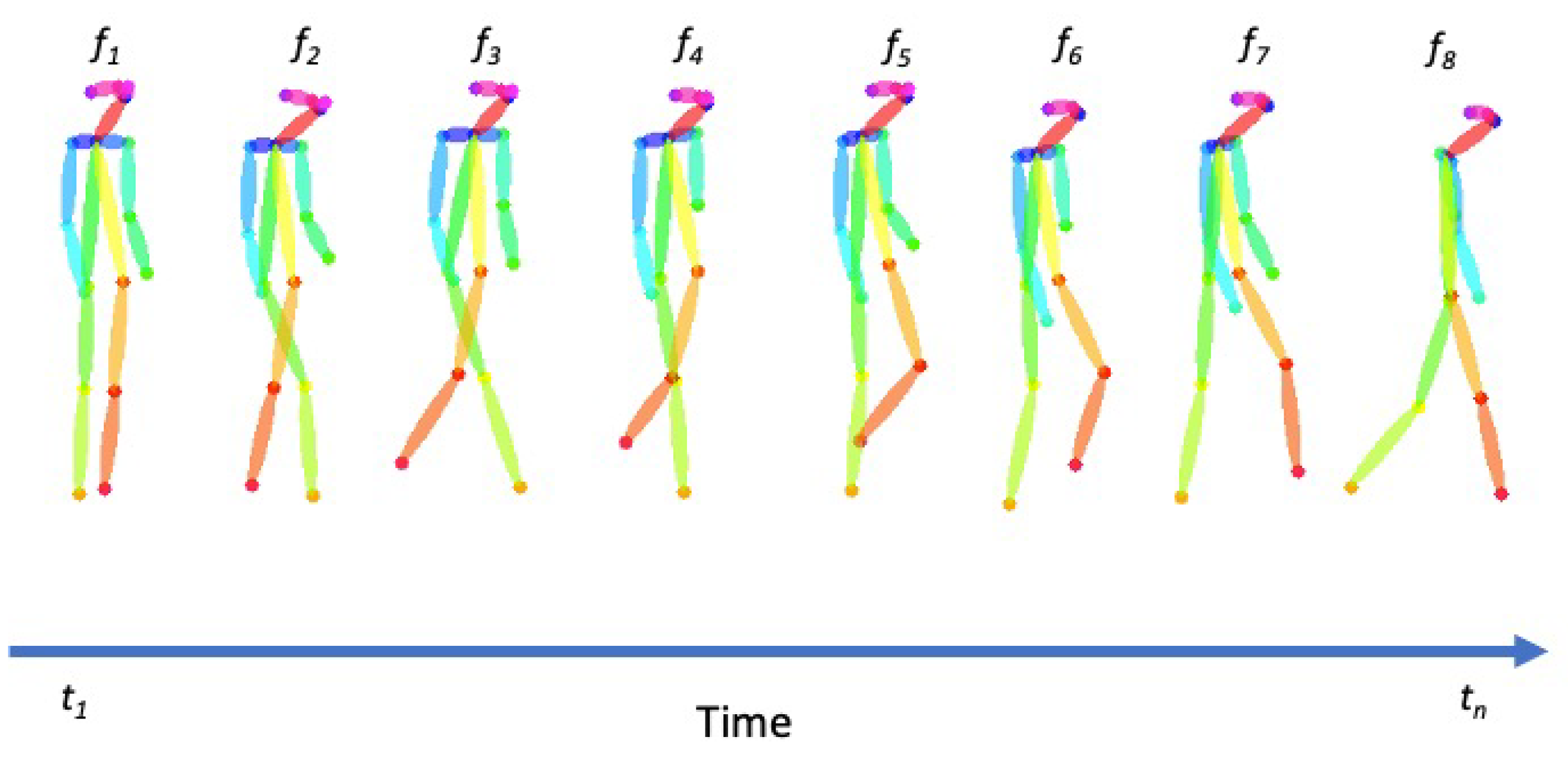
3.2. Data Collection and Annotation
4. Problem Formulation and Methods
4.1. Problem Statement
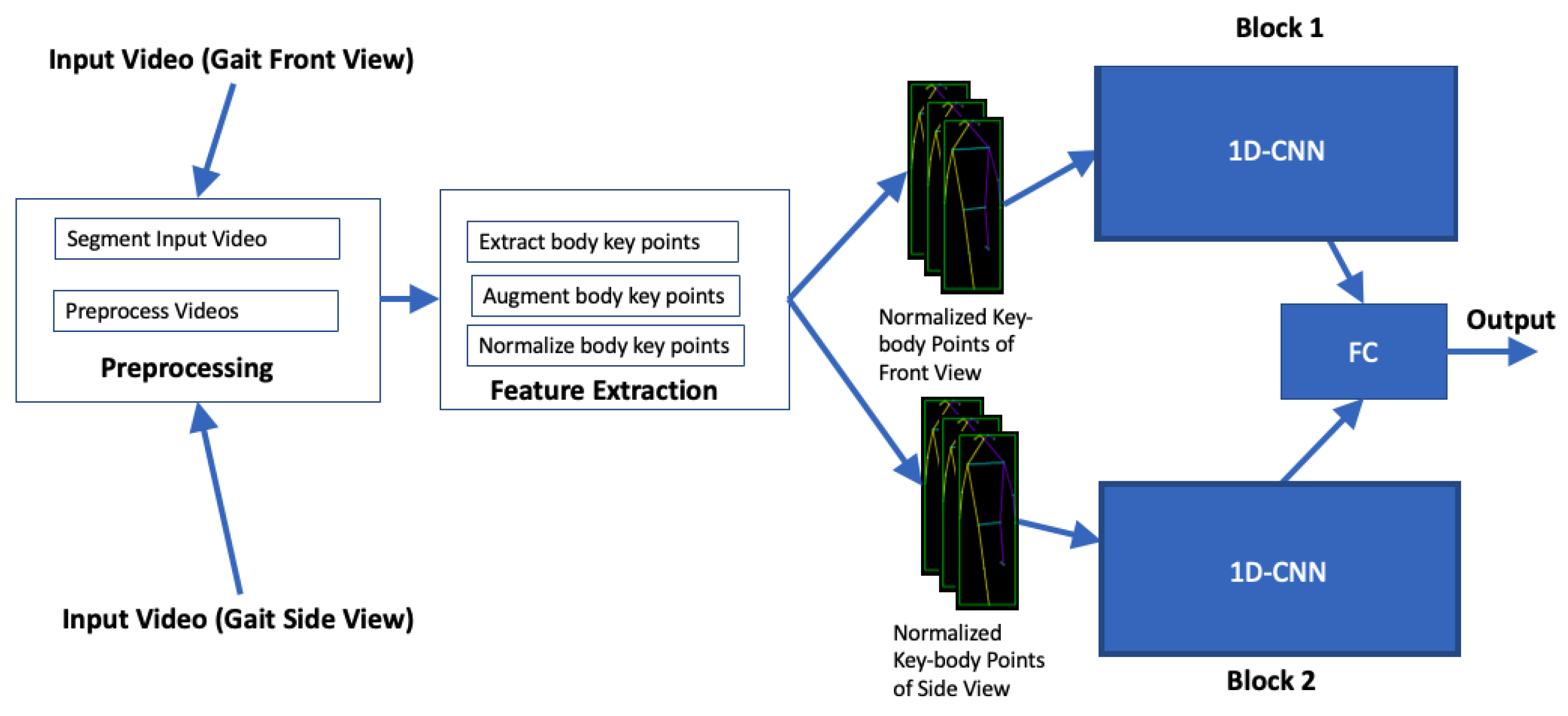
4.2. Proposed Method
5. Results
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mullette-Gillman, O.A.; Leong, R.L.; Kurnianingsih, Y.A. Cognitive fatigue destabilizes economic decision making preferences and strategies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievertsen, H.H.; Gino, F.; Piovesan, M. Cognitive fatigue influences students’ performance on standardized tests. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2621–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilsoul, J.; Libertiaux, V.; Collette, F. Cognitive fatigue in young, middle-aged, and older: Breaks as a way to recover. Appl. Psychol. 2022, 71, 1565–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.S.; Michael, J.; Austin, R.; Åkerstedt, T.; Van Dongen, H.; Watson, N.; Czeisler, C.; Pack, A.I.; Rosekind, M.R. Asleep at the wheel—The road to addressing drowsy driving. Sleep 2017, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinges, D.F. An overview of sleepiness and accidents. J. Sleep Res. 1995, 4, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, F.; Kadzielski, J.; Landrigan, C.P.; Evans, B.; Herndon, J.H.; Rubash, H.E. Surgeon fatigue: A prospective analysis of the incidence, risk, and intervals of predicted fatigue-related impairment in residents. Arch. Surg. 2012, 147, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Nishikawa, H.; Makihara, Y.; Muramatsu, D.; Takemura, N.; Yagi, Y. Physical Fatigue Detection From Gait Cycles via a Multi-Task Recurrent Neural Network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 127565–127575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbostad, J.L.; Leirfall, S.; Moe-Nilssen, R.; Sletvold, O. Physical fatigue affects gait characteristics in older persons. J. Gerontol. Ser. Biol. Sci. Med Sci. 2007, 62, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socie, M.J.; Sosnoff, J.J. Gait variability and multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Int. 2013, 2013, 645197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.; Tiwari, A.; Routray, A. Analysis of cognitive fatigue using EEG parameters. In Proceedings of the 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), IEEE, Jeju, Korea, 11–15 July 2017; pp. 2554–2557. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, M.Z.; Babu, A.R.; Lim, J.B.; Kyrarini, M.; Wylie, G.; Makedon, F. Towards cognitive fatigue detection from functional magnetic resonance imaging data. In Proceedings of the 13th ACM International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments, Corfu, Greece, 30 June–3 July 2020; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Sikander, G.; Anwar, S. Driver fatigue detection systems: A review. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 20, 2339–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöckel, T.; Jacksteit, R.; Behrens, M.; Skripitz, R.; Bader, R.; Mau-Moeller, A. The mental representation of the human gait in young and older adults. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Lal, S.K.; Kavanagh, D.; Rossiter, P. Applying neural network analysis on heart rate variability data to assess driver fatigue. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 7235–7242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjortskov, N.; Rissén, D.; Blangsted, A.K.; Fallentin, N.; Lundberg, U.; Søgaard, K. The effect of mental stress on heart rate variability and blood pressure during computer work. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 92, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Meziane, R.; Otis, M.J.D.; Ezzaidi, H.; Cardou, P. A Smart Safety Helmet using IMU and EEG sensors for worker fatigue detection. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Symposium on Robotic and Sensors Environments (ROSE) Proceedings, Timisoara, Romania, 16–18 October 2014; pp. 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotta, L.; Buurke, J.H.; van Beijnum, B.J.F.; Reenalda, J. Towards machine learning-based detection of running-induced fatigue in real-world scenarios: Evaluation of IMU sensor configurations to reduce intrusiveness. Sensors 2021, 21, 3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.; Li, X. Multi-task learning for gait-based identity recognition and emotion recognition using attention enhanced temporal graph convolutional network. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 114, 107868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, U.; Mittal, T.; Chandra, R.; Randhavane, T.; Bera, A.; Manocha, D. Step: Spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for emotion perception from gaits. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 1342–1350. [Google Scholar]
- Gribble, P.A.; Hertel, J. Effect of lower-extremity muscle fatigue on postural control. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 85, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, J.J.; Morrison, S.; Barrett, R.S. Lumbar and cervical erector spinae fatigue elicit compensatory postural responses to assist in maintaining head stability during walking. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 101, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, F.A.; dos Santos, P.C.R.; Vitório, R.; van Dieën, J.H.; Gobbi, L.T.B. Effect of muscle fatigue and physical activity level in motor control of the gait of young adults. Gait Posture 2013, 38, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobe, S.; Kakar, R.S.; Smith, M.L.; Mehta, R.; Baghurst, T.; Boolani, A. Impact of cognitive fatigue on gait and sway among older adults: A literature review. Prev. Med. Rep. 2017, 6, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Hidalgo Martinez, G.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.; Sheikh, Y.A. OpenPose: Realtime Multi-Person 2D Pose Estimation using Part Affinity Fields. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 43, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, G. Multi-stage HRNet: Multiple stage high-resolution network for human pose estimation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.05901. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, K.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.W.; Kim, M.S. Deep Learning-Based Multimodal Abnormal Gait Classification Using a 3D Skeleton and Plantar Foot Pressure. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 161576–161589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, V.; Manoghar, B.M.; Sashank Dorbala, V.; Manocha, D.; Bera, A. ProxEmo: Gait-based Emotion Learning and Multi-view Proxemic Fusion for Socially-Aware Robot Navigation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2021; pp. 8200–8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teepe, T.; Khan, A.; Gilg, J.; Herzog, F.; Hörmann, S.; Rigoll, G. Gaitgraph: Graph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-Based Gait Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Anchorage, AK, USA, 19–22 September 2021; pp. 2314–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, M.; Mahmood, A. Improved gait recognition based on specialized deep convolutional neural network. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2017, 164, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Bhanu, B. Individual recognition using gait energy image. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 28, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Gu, P.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, J.; Song, X. Abnormal gait recognition algorithm based on LSTM-CNN fusion network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 163180–163190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Q.; Bennamoun, M.; An, S.; Sohel, F.; Boussaid, F. A new representation of skeleton sequences for 3d action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3288–3297. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, A.; Channon, S.; Beaumont, J. The relationship between subjective fatigue and cognitive fatigue in advanced multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2007, 13, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskander, J.; Hossny, M.; Nahavandi, S. A Review on Ocular Biomechanic Models for Assessing Visual Fatigue in Virtual Reality. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 19345–19361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wewers, M.E.; Lowe, N.K. A critical review of visual analogue scales in the measurement of clinical phenomena. Res. Nurs. Health 1990, 13, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; et al. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Systems. 2015. Available online: tensorflow.org (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]



| Method | Overall Accuracy |
|---|---|
| Multi-Layer Perceptrons | 54.81% |
| Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) | 58.24% |
| Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) | 63.1% |
| 1D-CNN | 67.5% |
| Proposed Method | 81.64% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pavel, H.R.; Karim, E.; Jaiswal, A.; Acharya, S.; Nale, G.; Theofanidis, M.; Makedon, F. Assessment of Cognitive Fatigue from Gait Cycle Analysis. Technologies 2023, 11, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies11010018
Pavel HR, Karim E, Jaiswal A, Acharya S, Nale G, Theofanidis M, Makedon F. Assessment of Cognitive Fatigue from Gait Cycle Analysis. Technologies. 2023; 11(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies11010018
Chicago/Turabian StylePavel, Hamza Reza, Enamul Karim, Ashish Jaiswal, Sneh Acharya, Gaurav Nale, Michail Theofanidis, and Fillia Makedon. 2023. "Assessment of Cognitive Fatigue from Gait Cycle Analysis" Technologies 11, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies11010018
APA StylePavel, H. R., Karim, E., Jaiswal, A., Acharya, S., Nale, G., Theofanidis, M., & Makedon, F. (2023). Assessment of Cognitive Fatigue from Gait Cycle Analysis. Technologies, 11(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies11010018







