Explainable AI (XAI) Applied in Machine Learning for Pain Modeling: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Scope of Review
3. Pain Measurement and Variation
3.1. Pain Measurement
3.2. Pain Variation
4. Explainability in Pain Models
4.1. Chest Pain
4.2. Back Pain
4.3. Shoulder Pain
4.4. Headache Pain
4.4.1. Primary Headaches
4.4.2. Secondary Headaches
4.5. Surgical/Postoperative Pain
5. Explainable AI Models
5.1. AlexNet
5.2. VGGNet
5.3. ResNet
5.4. DenseNet
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matheny, M.; Sonoo, T.I.; Mahnoor, A.; Danielle, W. (Eds.) Artificial Intelligence in Health Care: The Hope, the Hype, the Promise, the Peril; NAM Special Publication; National Academy of Medicine: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bohr, A.; Memarzadeh, K. The rise of artificial intelligence in healthcare applications. Artif. Intell. Healthc. 2020, 25–60. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128184387000022 (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Aniek, F.M.; Jan, A.K.; Peter, R.R. The role of explainability in creating trustworthy artificial intelligence for health care: A comprehensive survey of the terminology, design choices, and evaluation strategies. J. Biomed. Inform. 2021, 113, 103655. [Google Scholar]
- Rajkomar, A.; Oren, E.; Chen, K.; Dai, A.M.; Hajaj, N.; Hardt, M.; Liu, P.J.; Liu, X.; Marcus, J.; Sun, M.; et al. Scalable and accurate deep learning with electronic health records. NPJ Digit. Med. 2018, 1, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.Y.; Majeed, A.; Kuo, K.N. An overview of the healthcare system in Taiwan. Lond. J. Prim. Care 2010, 3, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Chun, C.B.; Lee, Y.G.; Seo, N.K. The National Health Insurance system as one type of new typology: The case of South Korea and Taiwan. Health Policy 2008, 85, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, B.K.; Yang, C.T. The equality of resource allocation in health care under the National Health Insurance System in Taiwan. Health Policy 2011, 100, 203–210. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, C.; Lee, J.L.; Schoon, R. Assessing Health Information Technology in a National Health Care System—An Example from Taiwan. Adv. Health Care Manag. 2012, 12, 75–109. [Google Scholar]
- Tonekaboni, S.; Joshi, S.; McCradden, M.D.; Goldenberg, A. What Clinicians Want: Contextualizing Explainable Machine Learning for Clinical End Use. In Proceedings of the 4th Machine Learning for Healthcare Conference, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 9–10 August 2019; Volume 106, pp. 359–380. [Google Scholar]
- Qinghan, X.; Mooi, C.C. Explainable deep learning based medical diagnostic system. Smart Health 2019, 13, 100068. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnie, B.D.; Jessica, L.; Jaime, L.N.; Qiana, B.; Daniel, A.; Robert, J.N. Use of Electronic Medical Records for Health Outcomes Research: A Literature Review. Med. Care Res. Rev. 2009, 66, 611–638. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, E.C.; Mowat, F.S.; Kelsh, M.A.; Legg, J.C.; Engel-Nitz, N.M.; Watson, H.N.; Collins, H.L.; Nordyke, R.J.; Whyte, J.L. Use of electronic medical records (EMR) for oncology outcomes research: Assessing the comparability of EMR information to patient registry and health claims data. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 3, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shuo, T.; Wenbo, Y.; Jehane, M.L.G.; Peng, W.; Wei, H.; Zhewei, Y. Smart healthcare: Making medical care more intelligent. Glob. Health J. 2019, 3, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Tjoa, E.; Guan, C. A Survey on Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Toward Medical XAI. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 4793–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzyeh, G.; Luke, O.R.; Andrew, L.B. The false hope of current approaches to explainable artificial intelligence in health care. Lancet Digit. Health 2021, 3, 745–750. [Google Scholar]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Irvin, J.; Zhu, K.; Yang, B.; Mehta, H.; Duan, T.; Ding, D.; Bagul, A.; Langlotz, C.; Shpanskaya, K.; et al. CheXNet: Radiologist-Level Pneumonia Detection on Chest X-rays with Deep Learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.05225. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Liu, X. The challenges of explainable AI in biomedical data science. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 22, 443–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, D.; Het, N.; Smiti, S.; Pankesh, P. Explainable AI meets Healthcare: A Study on Heart Disease Dataset. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.03195. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Sengupta, S.; Mohammed, A.R.; Faruq, I.; Jayakumar, V.; Zelek, J.; Lakshminarayanan, V. What is the Optimal Attribution Method for Explainable Ophthalmic Disease Classification. In Ophthalmic Medical Image Analysis; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 12069, pp. 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Abbod, M.; Shieh, J.-S. Pain and Stress Detection Using Wearable Sensors and Devices—A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myles, P.S.; Christelis, N. Measuring pain and analgesic response. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2011, 28, 399–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, B.; Clark, D.; Meldrum, M.; Ten Have, H.; Seymour, J.; Winslow, M.; Paz, S. The measurement of pain, 1945–2000. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2005, 29, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virrey, R.A.; Liyanage, C.D.S.; Petra, M.I.B.P.H.; Abas, P.E. Visual data of facial expressions for automatic pain detection. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2019, 61, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Tong, S.; Bordallo, M.; Boutellaa, E.; Peng, J.; Feng, X.; Hadid, A. On pain assessment from facial videos using spatio-temporal local descriptors. In Proceedings of the 2016 Sixth International Conference on Image Processing Theory, Tools and Applications (IPTA), Oulu, Finland, 12–15 December 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sourav, D.R.; Mrinal, K.B.; Priya, S.; Anjan, K.G. An Approach for Automatic Pain Detection through Facial Expression. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 84, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, A.B.; Lucey, S.; Cohn, J.F.; Chen, T.; Ambadar, Z.; Prkachin, K.M.; Solomon, P.E. The painful face—Pain expression recognition using active appearance models. Image Vis. Comput. 2009, 27, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyas, C.; Haque, M.; Rehm, M.; Nasrollahi, K.; Moeslund, T. Facial Expression Recognition for Traumatic Brain Injured Patients. In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2018), Funchal, Portugal, 27–29 January 2018; Volume 4, pp. 522–530. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, H.; Flanagan, C.; Zeng, L.; Lei, Y. Future of Artificial Intelligence in Anesthetics and Pain Management. J. Biosci. Med. 2019, 7, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Garcia-Chimeno, Y.; Garcia-Zapirain, B.; Gomez-Beldarrain, M.; Fernandez-Ruanova, B.; Garcia-Monco, J.C. Automatic migraine classification via feature selection committee and machine learning techniques over imaging and questionnaire data. BMC Med. Inf. Decis Mak. 2017, 17, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Cheng, D.; Houle, T.T.; Chen, L.; Zhang, W.; Deng, H. Machine learning methods for automatic pain assessment using facial expression information: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Med. 2018, 97, e13421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pranti, D.; Nachamai, M. Facial Pain Expression Recognition in Real-Time Videos. J. Healthc. Eng. 2018, 2018, 7961427. [Google Scholar]
- Lucey, P.; Cohn, J.F.; Matthews, I.; Lucey, S.; Sridharan, S.; Howlett, J.; Prkachin, K.M. Automatically Detecting Pain in Video Through Facial Action Units. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B 2011, 41, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jörn, L.; Alfred, U. Machine learning in pain research. Pain 2018, 159, 623–630. [Google Scholar]
- Keight, R.; Aljaaf, A.J.; Al-Jumeily, D.; Hussain, A.J.; Özge, A.; Mallucci, C. An Intelligent Systems Approach to Primary Headache Diagnosis. In Intelligent Computing Theories and Application; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 10362, pp. 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Evan, C.; Angkoon, P.; Erik, S. Feature Extraction and Selection for Pain Recognition Using Peripheral Physiological Signals. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 437. [Google Scholar]
- Rasha, M.A.-E.; Hend, A.-K.; AbdulMalik, A.-S. Deep-Learning-Based Models for Pain Recognition: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5984. [Google Scholar]
- Holzinger, A. From Machine Learning to Explainable AI. In Proceedings of the 2018 World Symposium on Digital Intelligence for Systems and Machines (DISA), Košice, Slovakia, 23–25 August 2018; pp. 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Arrieta, A.B.; Díaz-Rodríguez, N.; Del Ser, J.; Bennetot, A.; Tabik, S.; Barbado, A.; García, S.; Gil-López, S.; Molina, D.; Benjamins, R.; et al. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI. Inf. Fusion 2020, 58, 82–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Koh, Z.X.; Goh, J.; Lin, Z.; Haaland, B.; Ting, B.P.; Ong, M.E.H. Prediction of adverse cardiac events in emergency department patients with chest pain using machine learning for variable selection. BMC Med. Inf. Decis. Mak. 2014, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Six, A.J.; Backus, B.E.; Kelder, J.C. Chest pain in the emergency room: Value of the HEART score. Neth. Heart J. 2008, 16, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, J.; Lu, J.; Goudie, A.; Bennamoun, M.; Sprivulis, P.; Sanfillipo, F.; Dwivedi, G. Applications of machine learning to undifferentiated chest pain in the emergency department: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepinska, J.; Lettino, M.; Ahrens, I.; Bueno, H.; Garcia-Castrillo, L.; Khoury, A.; Lancellotti, P.; Mueller, C.; Muenzel, T.; Oleksiak, A.; et al. Diagnosis and risk stratification of chest pain patients in the emergency department: Focus on acute coronary syndromes. A position paper of the Acute Cardiovascular Care Association. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 9, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsterdam, E.A.; Kirk, J.D.; Bluemke, D.A.; Diercks, D.; Farkouh, M.E.; Garvey, J.L.; Kontos, M.C.; McCord, J.; Miller, T.D.; Morise, A.; et al. Testing of Low-Risk Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department with Chest Pain: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010, 17, 1756–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backus, B.E.; Six, A.J.; Kelder, J.C.; Bosschaert, M.A.R.; Mast, E.G.; Mosterd, A.; Veldkamp, R.F.; Wardeh, A.J.; Tio, R.; Braam, R.; et al. A prospective validation of the HEART score for chest pain patients at the emergency department. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 2153–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.I.; Hsu, C.C.; Kao, Y.; Chen, C.J.; Kuo, Y.W.; Hsu, S.L.; Liu, T.L.; Lin, H.J.; Wang, J.J.; Liu, C.F.; et al. Real-time AI prediction for major adverse cardiac events in emergency department patients with chest pain. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2020, 28, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kafri, A.S.; Sudirman, S.; Hussain, A.J.; Fergus, P.; Al-Jumeily, D.; Al-Jumaily, M.; Al-Askar, H. A Framework on a Computer Assisted and Systematic Methodology for Detection of Chronic Lower Back Pain Using Artificial Intelligence and Computer Graphics Technologies. Intell. Comput. Theor. Appl. 2016, 9771, 843–854. [Google Scholar]
- Tagliaferri, S.D.; Angelova, M.; Zhao, X.; Owen, P.J.; Miller, C.T.; Wilkin, T.; Belavy, D.L. Artificial intelligence to improve back pain outcomes and lessons learnt from clinical classification approaches: Three systematic reviews. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, H.; Kavitha, P.T.; Loy, F.L.; Ng, S.H.; Wang, C.; Phua, K.S.; Tjan, S.Y.; Yang, S.Y.; Guan, C. Scalp EEG-Based Pain Detection Using Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimi, P.; Yazdanian, T.; Benzel, E.C.; Aghaei, H.N.; Azhari, S.; Sadeghi, S.; Montazeri, A. A Review on the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Spinal Diseases. Asian Spine J. 2020, 14, 543–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, P.; Ashar, Y.; Tesarz, J.; Kazgan, M.; Cetin, B.; Wager, T.D. Emerging Clinical Technology: Application of Machine Learning to Chronic Pain Assessments Based on Emotional Body Maps. Neurotherapeutics 2020, 17, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitish, A. Prediction of low back pain using artificial intelligence modeling. J. Med. Artif. Intell. 2021, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Abelin-Genevois, K. Sagittal Balance of the Spine. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2021, 107, 102769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikulkaew, K.; Boonchieng, E.; Boonchieng, W.; Chouvatut, V. Pain Detection Using Deep Learning with Evaluation System. Proceedings of Fifth International Congress on Information and Communication Technology. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2020, 1184, 426–435. [Google Scholar]
- Lucey, P.; Cohn, J.F.; Prkachin, K.M.; Solomon, P.E.; Chew, S.; Matthews, I. Painful monitoring: Automatic pain monitoring using the UNBC-McMaster shoulder pain expression archive database. Image Vis. Comput. 2012, 30, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazal, B.; Xujuan, Z.; Ravinesh, C.D.; Jeffrey, S.; Frank, W.; Hua, W. Ensemble neural network approach detecting pain intensity from facial expressions. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 109, 101954. [Google Scholar]
- Guglielmo, M.; Zhanli, C.; Diana, J.W.; Rashid, A.; Yasemin, Y.; Çetin, A.E. Pain Detection from Facial Videos Using Two-Stage Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 11–14 November 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Straube, A.; Andreou, A. Primary headaches during lifespan. J. Headac. Pain 2019, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.L. Common Primary and Secondary Causes of Headache in the Elderly. Headache 2018, 58, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.; William, J.M. Headache. Am. J. Med. 2018, 131, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yamani, N.; Olesen, J. New daily persistent headache: A systematic review on an enigmatic disorder. J. Headac. Pain 2019, 20, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HIS Classification ICHD-3. Available online: https://ichd-3.org/classification-outline/ (accessed on 18 January 2022).
- Hansen, J.M.; Charles, A. Differences in treatment response between migraine with aura and migraine without aura: Lessons from clinical practice and RCTs. J. Headac. Pain 2019, 20, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vij, B.; Tepper, S.J. Secondary Headaches. In Fundamentals of Pain Medicine; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 291–300. [Google Scholar]
- Keight, R.; Al-Jumeily, D.; Hussain, A.J.; Al-Jumeily, M.; Mallucci, C. Towards the discrimination of primary and secondary headache: An Intelligent Systems Approach. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Anchorage, AK, USA, 14–19 May 2017; pp. 2768–2775. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Sanchez, P.A.; García-González, J.R.; Rúa Ascar, J.M. Automatic migraine classification using artificial neural networks. F1000Research 2020, 9, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Cai, J.; Fan, S.Z.; Abbod, M.F.; Shieh, J.S.; Kung, Y.; Lin, L. Spectrum Analysis of EEG Signals Using CNN to Model Patient’s Consciousness Level Based on Anesthesiologists’ Experience. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 53731–53742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ma, L.; Fan, S.Z.; Abbod, M.F.; Ai, Q.; Chen, K.; Shieh, J.S. Frontal EEG Temporal and Spectral Dynamics Similarity Analysis between Propofol and Desflurane Induced Anesthesia Using Hilbert-Huang Transform. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4939480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi–Xiao, W.; Faiyaz, D.; Yan-Xin, L.; Shou-Zen, F.; Jiann-Shing, S. An Optimized Type-2 Self-Organizing Fuzzy Logic Controller Applied in Anesthesia for Propofol Dosing to Regulate BIS. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 28, 1062–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Yi-Feng, C.; Shou-Zen, F.; Maysam, F.A.; Jiann-Shing, S.; Mingming, Z. Electroencephalogram variability analysis for monitoring depth of anesthesia. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 066015. [Google Scholar]
- Lötsch, J.; Kringel, D.; Ultsch, A. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) in Biomedicine: Making AI Decisions Trustworthy for Physicians and Patients. BioMedInformatics 2022, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alex, K.; Ilya, S.; Geoffrey, E.H. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Community 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Awwal, M.D.; Kamil, Y.; Huseyin, O. Application of Deep Learning in Neuroradiology: Brain Haemorrhage Classification Using Transfer Learning. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2019, 2019, 4629859. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Horry, M.J.; Chakraborty, S.; Paul, M.; Ulhaq, A.; Pradhan, B.; Saha, M.; Shukla, N. COVID-19 Detection Through Transfer Learning Using Multimodal Imaging Data. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 149808–149824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiming, H.; Xiangyu, Z.; Shaoqing, R.; Jian, S. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Weijun, H.; Yan, Z.; Lijie, L. Study of the Application of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in Processing Sensor Data and Biomedical Images. Sensors 2019, 19, 3584. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; van der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 2017, 2261–2269. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Shen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, T.-Q. Classification of breast cancer histopathological images using interleaved DenseNet with SENet (IDSNet). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.K.; Chen, Y.F.; Pham, T.; Chang, W.; Hsieh, M.Y. Artificial Intelligence in Medical Applications. J. Healthc. Eng. 2018, 2018, 4827875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemouri, R.; Zerhouni, N.; Racoceanu, D. Deep Learning in the Biomedical Applications: Recent and Future Status. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, J.L.; Rocha, M.X.; Vasconcelos, G.G.; Vasconcelos Filho, J.E.; De Albuquerque, V.H.C.; Alexandria, A.R. Advances in Photopletysmography Signal Analysis for Biomedical Applications. Sensors 2018, 18, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.W.; Torres Soto, J.; Glicksberg, B.S.; Shameer, K.; Miotto, R.; Ali, M.; Ashley, E.; Dudley, J.T. Artificial Intelligence in Cardiology. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2668–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronato, A.; Naeem, M.; De Pietro, G.; Paragliola, G. Reinforcement learning for intelligent healthcare applications: A survey. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 109, 101964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, L.; Bednarz, T. Explainable AI and Reinforcement Learning—A Systematic Review of Current Approaches and Trends. Front. Artif. Intell. 2021, 4, 550030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Pain Types | Pain-Affected Organs | AI/ML Techniques Used | Explainable Features in the Pain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chest pain | Heart | Random forest (RF), support vector machine (SVM), artificial neural network (ANN), linear regression (LR), gradient boosting. | ECG, Vitals, HEART Score, Troponin, Labs, Exam, PMHx, Sx, HRV |
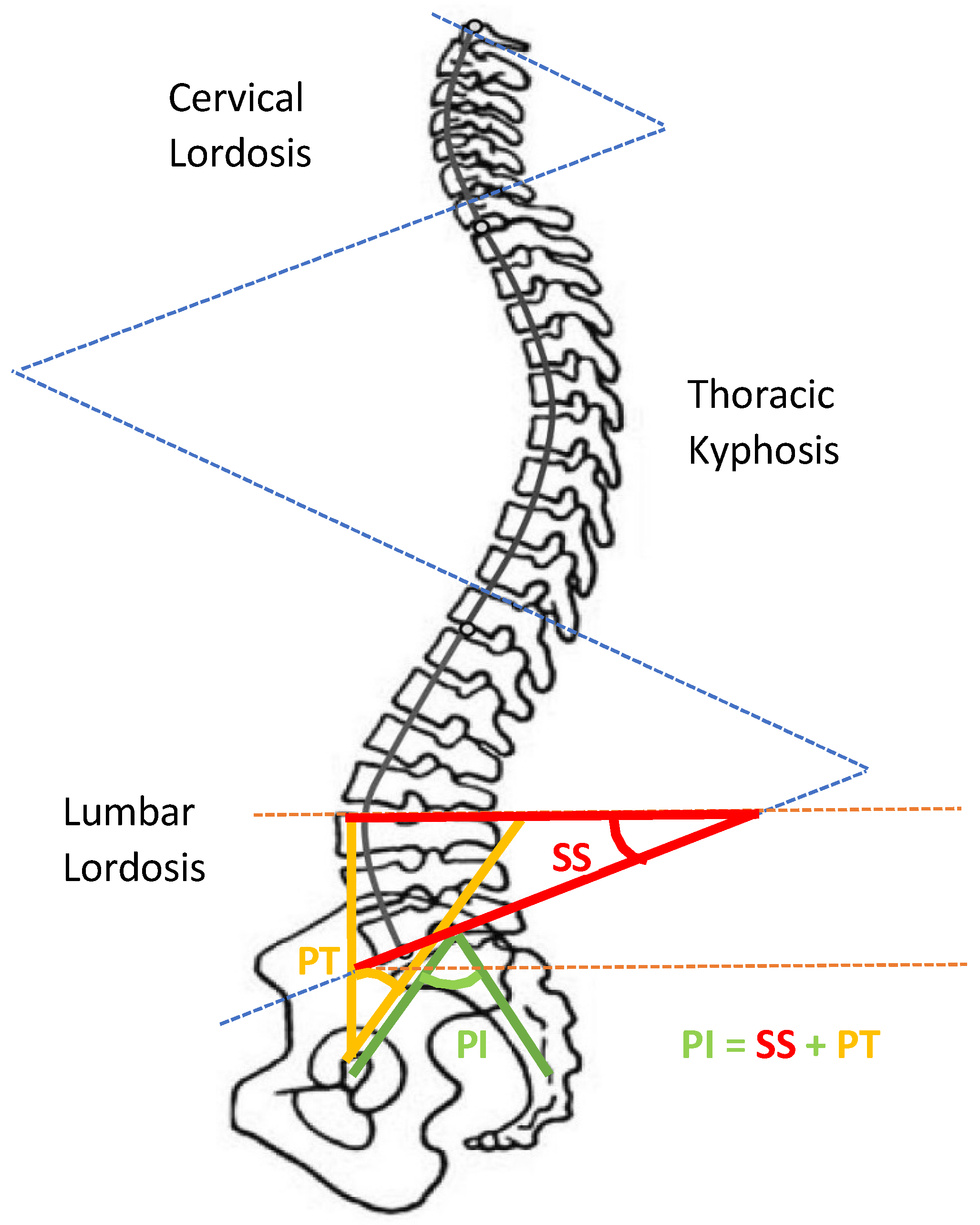
| Back pain | Back bone | K-nearest neighbor (K-NN), principal component analysis (PCA), random forest (RF), ANN, SVM, multilayer perceptron (MLP), LR, stochastic gradient boosting (SGM), naïve Bayes (NB). | EMG, HRV, pelvic incidence, pelvic tilt, lumbar lordosis angle, sacral slope, direct tilt, pelvic radius, degree spondylolisthesis, pelvic slope, thoracic slope, cervical tilt, sacrum angle and scoliosis slope, gait features, data from pressure sensors to assess sitting posture, erector spine muscle activity. |
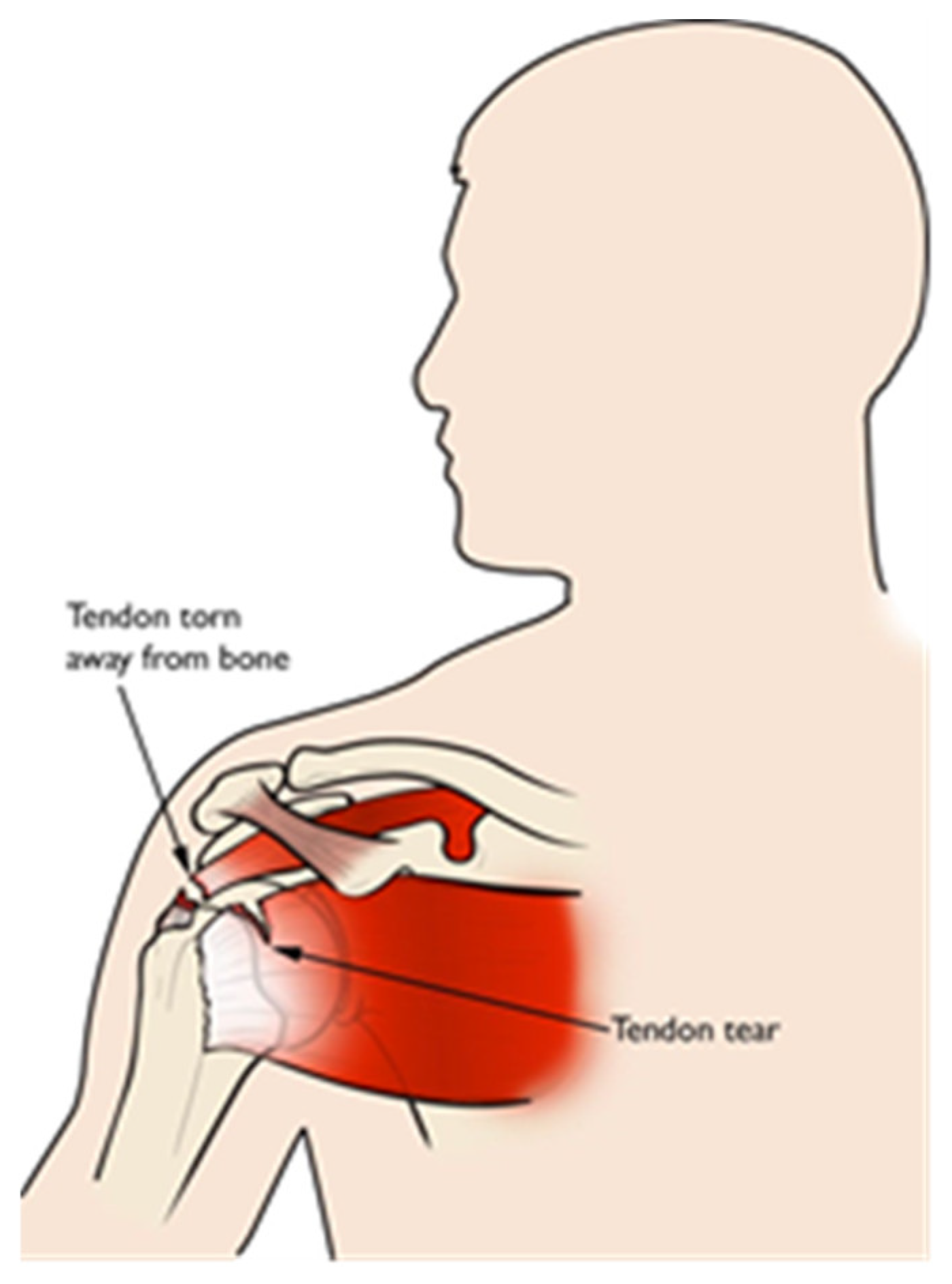
| Shoulder pain | Shoulder joint/muscle | SVM, ResNet | Facial images, landmarks. |
| Headache pain | Brain | Random oracle model (ROM), linear neural network (LNN), SVM, K-NN, ANN | Age, visual analog scale rating, duration of pain, facial images, landmarks. |
| Surgical/post-operative pain | Body cells | AlexNet, VGGNet, CifarNet, ResNet, DenseNet | Electroencephalogram (EEG) |
| HEART Score Points | MACE Occurrence | Hospitalization |
|---|---|---|
| 0–3 | 2.5% | Not Necessary |
| 4–6 | 20.3% | Necessary |
| ≥7 | 72.7% | Immediate |
| Primary Headache Type | Duration of Symptoms | Occurrence |
|---|---|---|
| Cluster-type | 15 min to 3 h | Frequent |
| Migraine with Aura | ≥5 min to 60 min | Frequent |
| Migraine without Aura | 4 to 72 h | Rare |
| NDPH | 24 h | Rare |
| Pain Type | High Variable Importance Features | Less Variable Importance Features |
|---|---|---|
| Chest pain | ECG, Vitals, HEART Score, PMHx, Sx, HRV | Troponin, Labs, Exam. |
| Back pain | Pelvic incidence, pelvic tilt, lumbar lordosis angle, sacral slope, direct tilt, pelvic radius, degree spondylolisthesis, pelvic slope, thoracic slope, cervical tilt, sacrum angle and scoliosis slope, gait features. | EMG, HRV, data from pressure sensors to assess sitting posture, Erector spine muscle activity. |
| Shoulder pain | Facial images, landmarks. | - |
| Headache pain | Facial images, landmarks. | Age, visual analog scale rating, duration of pain. |
| Surgical/postoperative pain | Electroencephalogram (EEG) | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madanu, R.; Abbod, M.F.; Hsiao, F.-J.; Chen, W.-T.; Shieh, J.-S. Explainable AI (XAI) Applied in Machine Learning for Pain Modeling: A Review. Technologies 2022, 10, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies10030074
Madanu R, Abbod MF, Hsiao F-J, Chen W-T, Shieh J-S. Explainable AI (XAI) Applied in Machine Learning for Pain Modeling: A Review. Technologies. 2022; 10(3):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies10030074
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadanu, Ravichandra, Maysam F. Abbod, Fu-Jung Hsiao, Wei-Ta Chen, and Jiann-Shing Shieh. 2022. "Explainable AI (XAI) Applied in Machine Learning for Pain Modeling: A Review" Technologies 10, no. 3: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies10030074
APA StyleMadanu, R., Abbod, M. F., Hsiao, F.-J., Chen, W.-T., & Shieh, J.-S. (2022). Explainable AI (XAI) Applied in Machine Learning for Pain Modeling: A Review. Technologies, 10(3), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies10030074








