Electrospinning for the Modification of 3D Objects for the Potential Use in Tissue Engineering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- -
- Filaflex 82A (Recreus, Elda, Spain)
- -
- Conductive PLA (Proto-pasta, Vancouver, Canada)
- -
- XT-CF20 (Colorfabb, Belfeld, The Netherlands)
- -
- Bronzefill (Colorfabb, Belfeld, The Netherlands)
- -
- Growlay brown (Lay-Filaments, Cologne, Germany)
- -
- Carbon X2–85 (3DXTech, Grand Rapids, MI, USA)
- -
- CarbonFil (Formfutura, Nijmegen, The Netherlands)
- -
- Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) (Filamentworld, Neu-Ulm, Germany)
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arkoun, M.; Daigle, F.; Heuzey, M.-C.; Ajji, A. Antibacterial electrospun chitosan-based nanofibers: A bacterial membrane perforator. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 5, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalcinkaya, F. A review on advanced nanofiber technology for membrane distillation. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2019, 14, 1558925018824901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer 2008, 49, 5603–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cengiz, F.; Krucinska, I.; Gliscinska, E.; Chrzanowski, M.; Göktepe, F. Comparative analysis of various electrospinning methods of nanofibre formation. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2009, 72, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Electrospinning: A fascinating method for the preparation of ultrathin fibers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5670–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of nanofibers: Reinventing the wheel? Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1151–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertocchi, M.J.; Simbana, R.A.; Wynne, L.H.; Lundin, J.G. Electrospinning of tough and elastic liquid crystalline polymer-polyurethane composite fibers: Mechanical properties and fiber alignment. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1900186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazrafshan, Z.; Stylios, G.K. A novel approach to enhance the spinnability of collagen fibers by graft polymerization. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 94, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storck, J.L.; Grothe, T.; Mamun, A.; Sabantina, L.; Klöcker, M.; Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Orientation of electrospun magnetic nanofibers near conductive areas. Materials 2020, 13, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, D.N.; Hwang, Y.; Moon, W. Electrospinning of well-aligned fiber bundles using an end-point control assembly method. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 77, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellert, C.; Storck, J.L.; Grothe, T.; Kaltschmidt, B.; Hütten, A.; Ehrmann, A. Positioning and aligning electrospun PAN fibers by conductive and dielectric substrate patterns. Macromol. Symp. 2021, 395, 2000213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, V.; Iannotti, V.; Ausanio, G.; Ambrosio, L.; Lanotte, L. Elastomagnetic nanofiber wires by magnetic field assisted electrospinning. Express Polym. Lett. 2019, 13, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.D.L.; Ganguly, D.; Zuidema, J.M.; Cardina, T.J.; Ziemba, A.M.; Kearns, K.R.; McCarthy, S.M.; Thompson, D.M.; Ramanath, G.; Borca-Tasciuc, D.A.; et al. Injectable, magnetically orienting electrospun fiber conduits for neuron guidance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 356–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, A.; Oldinski, R.; Ma, H.; Bryers, J.D.; Zhang, M. Chitosan-based nanofibrous membranes for antibacterial filter applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ehrmann, A. Non-toxic crosslinking of electrospun gelatin nanofibers for tissue engineering and biomedicine—A review. Polymers 2021, 13, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.; Huang, Y.; Agarwal, S.; Lannutti, J. Materials selection and residual solvent retention in biodegradable electrospun fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatih Canbolat, M.; Tang, C.; Bernacki, S.H.; Pourdeyhimi, B.; Khan, S. Mammalian cell viability in electrospun composite nanofiber structures. Macromol. Biosci. 2011, 11, 1346–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortmann, M.; Frese, N.; Sabantina, L.; Petkau, R.; Kinzel, F.; Gölzhäuser, A.; Ehrmann, A. New polymers for needleless electrospinning from low-toxic solvents. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plamus, T.; Savest, N.; Viirsalu, M.; Harz, P.; Tarasova, E.; Krasnou, I.; Krumme, A. The effect of ionic liquids on the mechanical properties of electrospun polyacrylonitrile membranes. Polym. Test. 2018, 71, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasonu, I.; Tarassova, E.; Malmberg, S.; Vassiljeva, V.; Krumme, A. Preparation of fibrous electrospun membranes with activated carbon filler. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 500, 012022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehlage, D.; Blattner, H.; Mamun, A.; Kutzli, I.; Diestelhorst, E.; Rattenholl, A.; Gudermann, F.; Lütkemeyer, D.; Ehrmann, A. Cell growth on electrospun nanofiber mats from polyacrylonitrile (PAN) blends. AIMS Bioeng. 2020, 7, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehlage, D.; Blattner, H.; Sabantina, L.; Böttjer, R.; Grothe, T.; Rattenholl, A.; Gudermann, F.; Lütkemeyer, D.; Ehrmann, A. Sterilization of PAN/gelatin nanofibrous mats for cell growth. Tekstilec 2019, 62, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.X.; Hua, S.; Yang, M.K.; Fu, Z.Z.; Teng, S.S.; Niu, K.; Zhao, Q.H.; Yi, C.Q. Fabrication and characterization of electrospinning/3D printing bone tissue engineering scaffold. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 110557–110565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muerza-Cascante, M.L.; Shokoohmand, A.; Khosrotehrani, K.; Haylock, D.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Loessner, D. Endosteal-like extracellular matrix expression on melt electrospun written scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2017, 52, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Mori, A.; Pena Fernández, M.; Blunn, G.; Tozzi, G.; Roldo, M. 3D Printing and Electrospinning of Composite Hydrogels for Cartilage and Bone Tissue Engineering. Polymers 2018, 10, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trabelsi, M.; Mamun, A.; Klöcker, M.; Sabantina, L.; Großerhode, C.; Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Increased mechanical properties of carbon nanofiber mats for possible medical applications. Fibers 2019, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Böttjer, R.; Grothe, T.; Wehlage, D.; Ehrmann, A. Electrospraying poloxamer/(bio-) polymer blends using a needleless electrospinning machine. J. Text. Fibrous Mater. 2018, 1, 2515221117743079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabantina, L.; Rodríguez Mirasol, J.; Cordero, T.; Finsterbusch, K.; Ehrmann, A. Investigation of needleless electrospun PAN nanofiber mats. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1952, 020085. [Google Scholar]
- Grothe, T.; Storck, J.L.; Dotter, M.; Ehrmann, A. Impact of solid content in the electrospinning solution on the physical and chemical properties of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofibrous mats. Tekstilec 2020, 63, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerker, E.; Steinhäußer, D.; Mamun, A.; Trabelsi, M.; Fiedler, J.; Sabantina, L.; Juhász Junger, I.; Schiek, M.; Ehrmann, A.; Kaschuba, R. Spectroscopic investigation of highly-scattering nanofiber mats during drying and film formation. Optik 2020, 208, 164081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grothe, T.; Böhm, T.; Habashy, K.; Abdullaeva, O.S.; Zablocki, J.; Lützen, A.; Dedek, K.; Schiek, M.; Ehrmann, A. Optical Index Matching, Flexible Electrospun Substrates for Seamless Organic Photocapacitive Sensors. Phys. Status Solidi B 2021, 258, 2000543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, H.C.; Schmelzeisen, D.; Gries, T. 4D textiles made by additive manufacturing on pre-stressed textiles—An overview. Actuators 2021, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrmann, G.; Ehrmann, A. 3D printing of shape memory polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
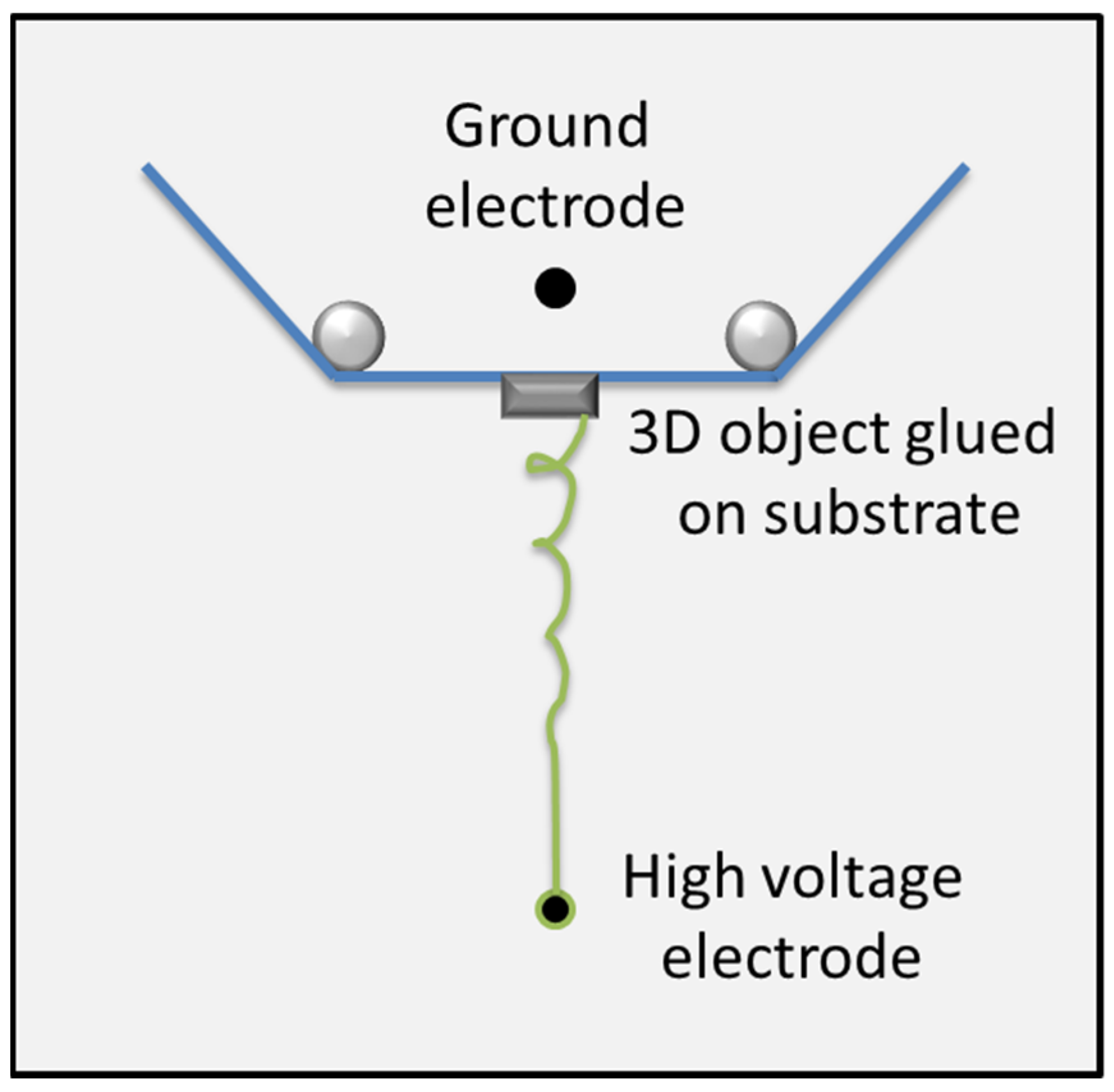
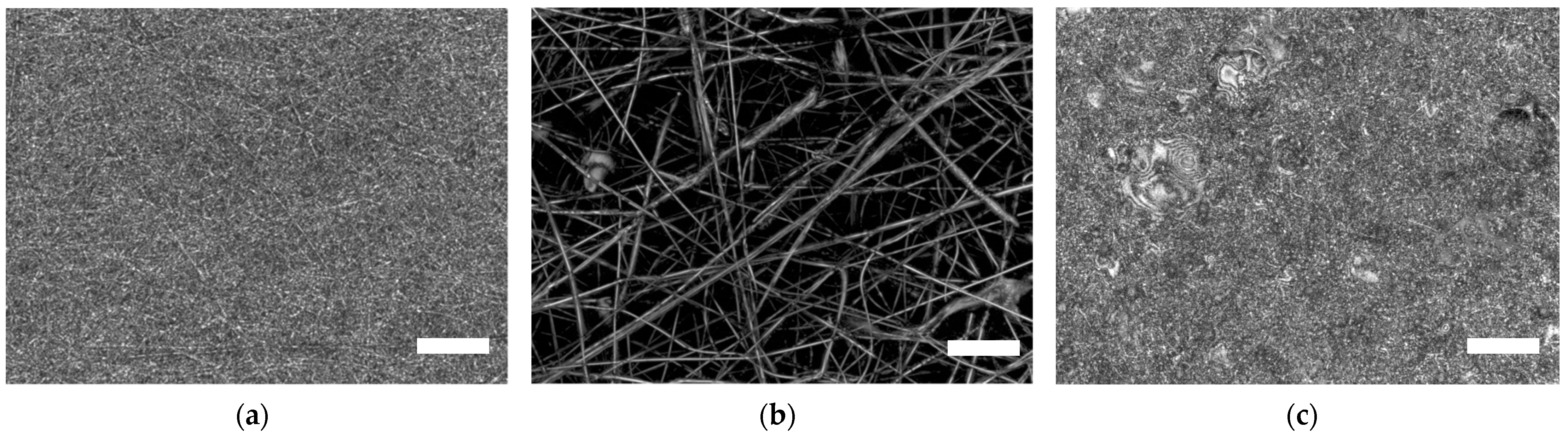
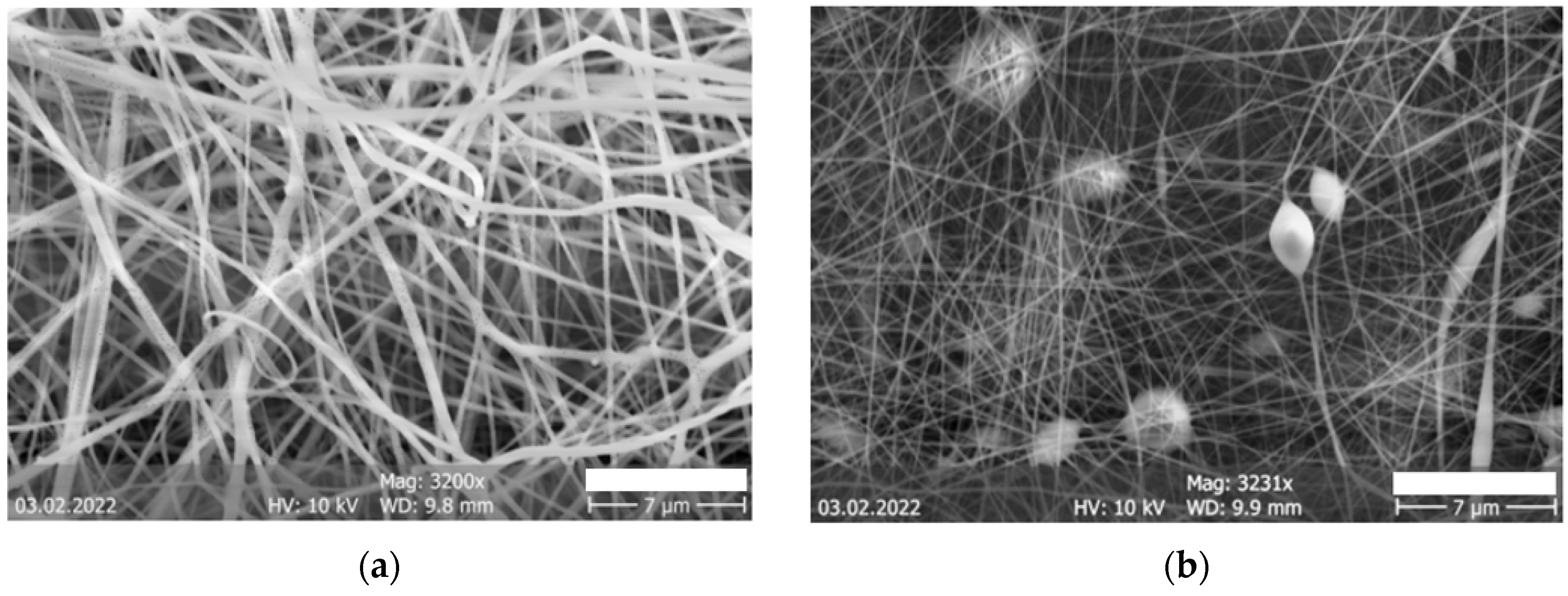
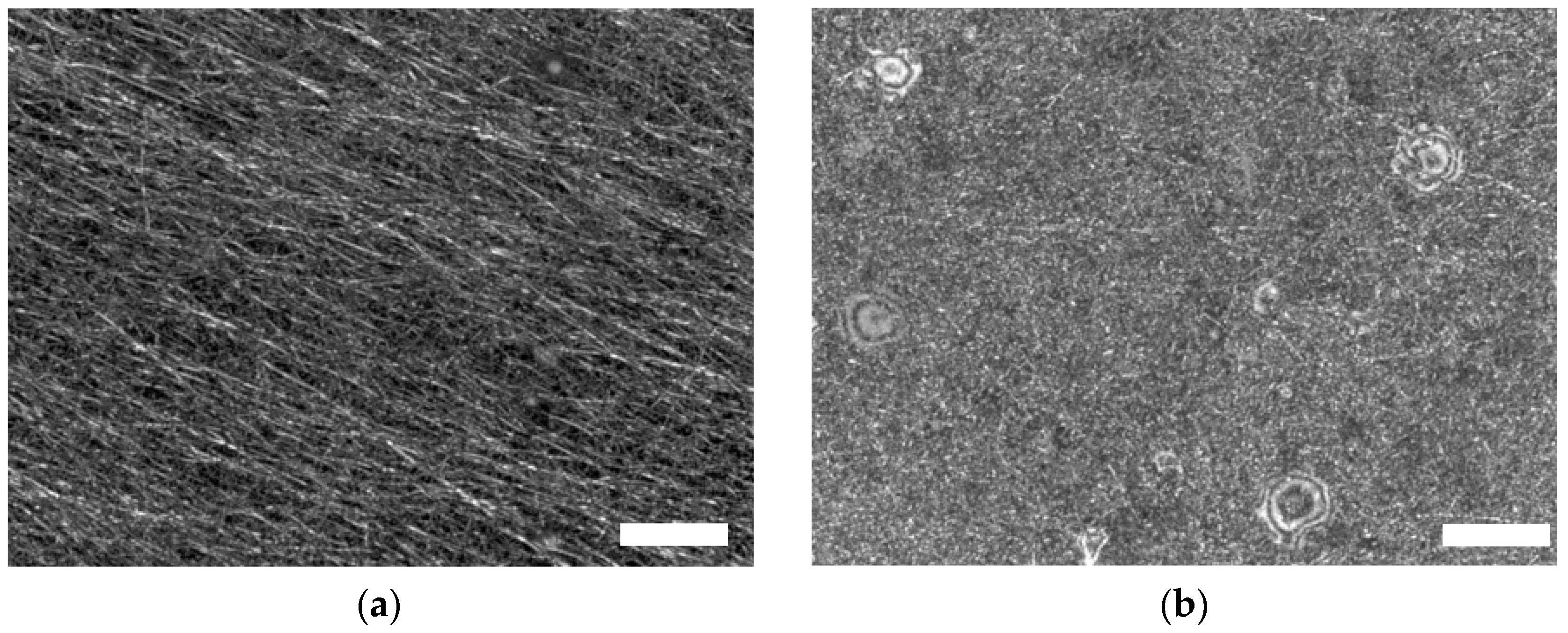
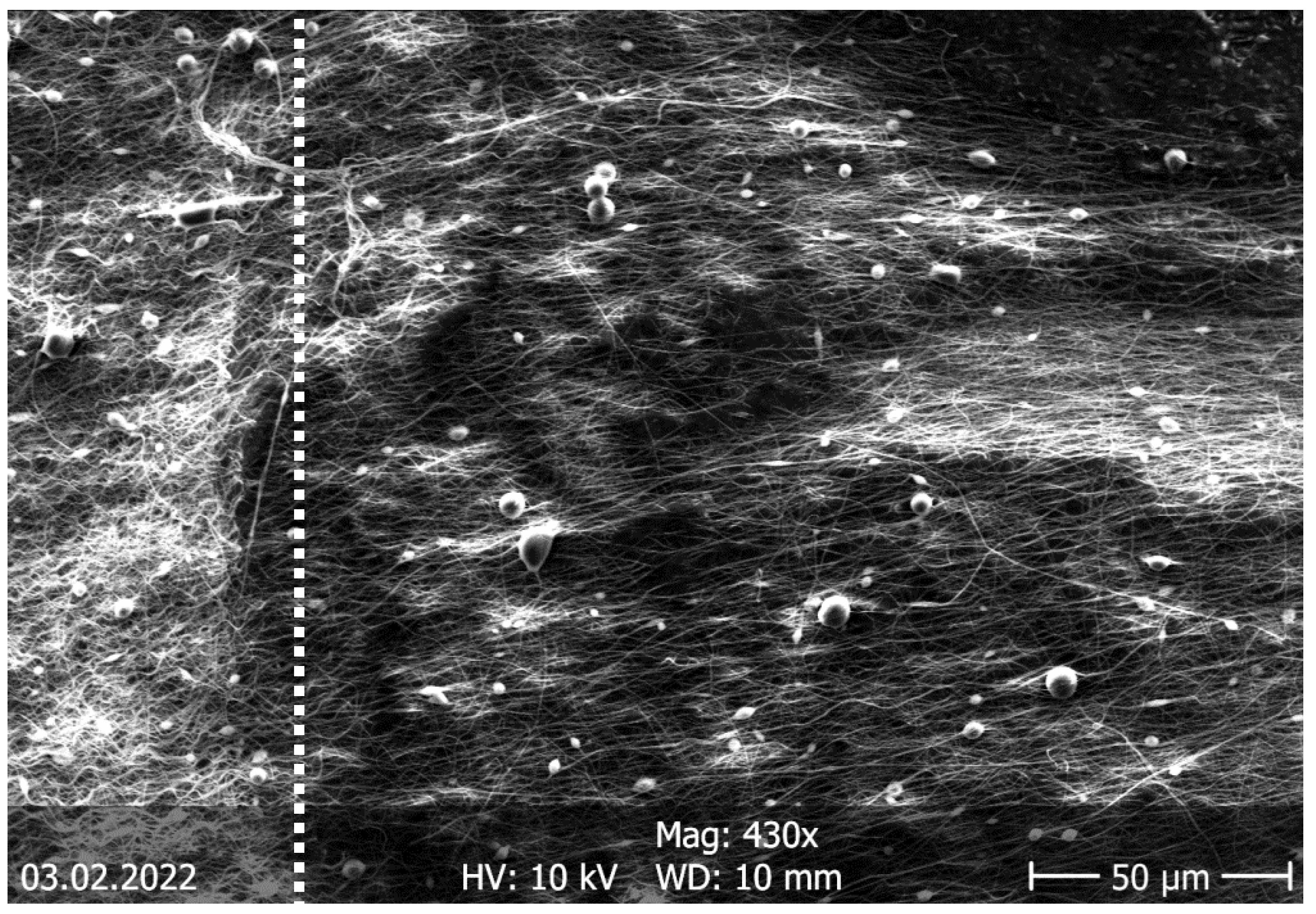
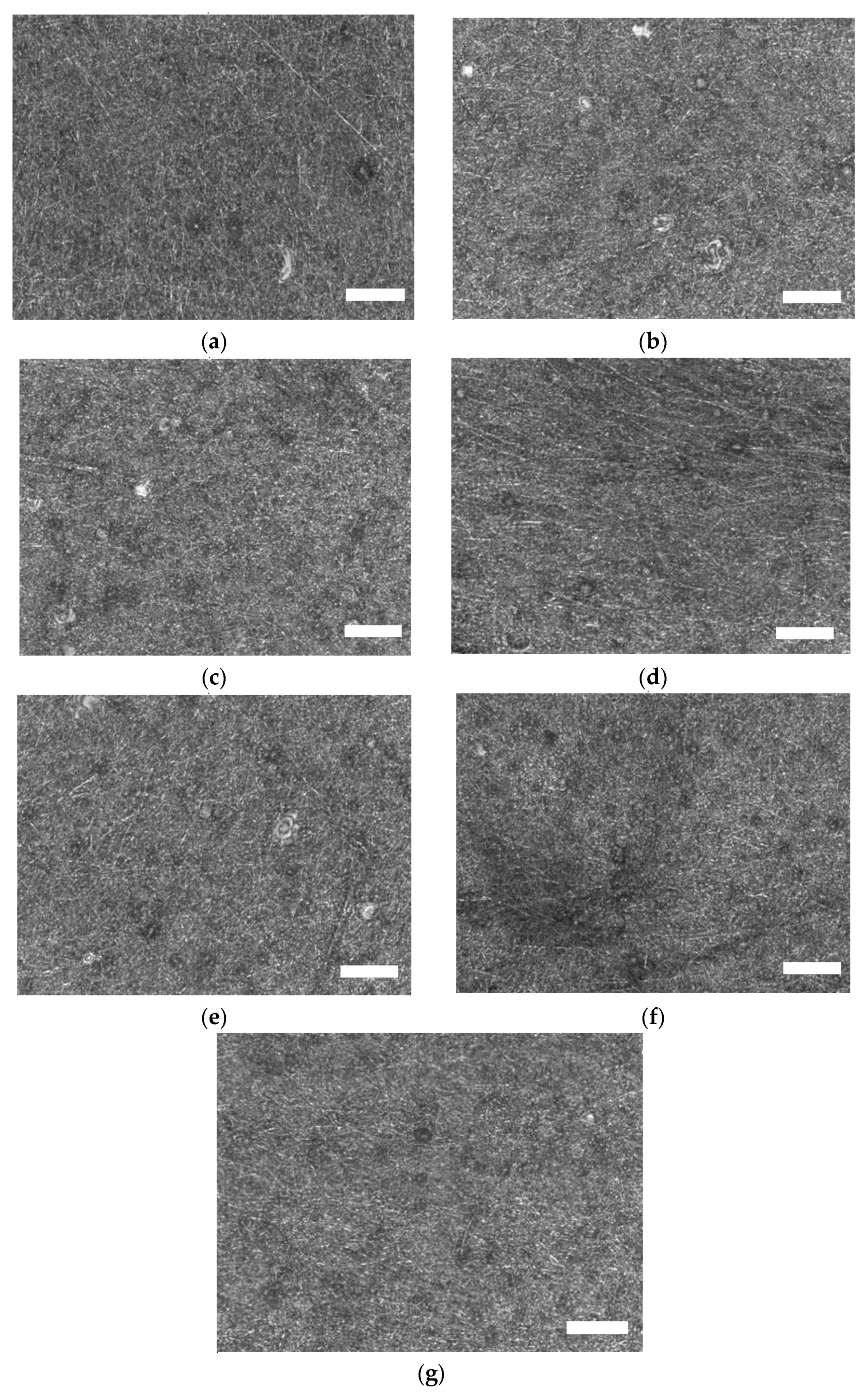
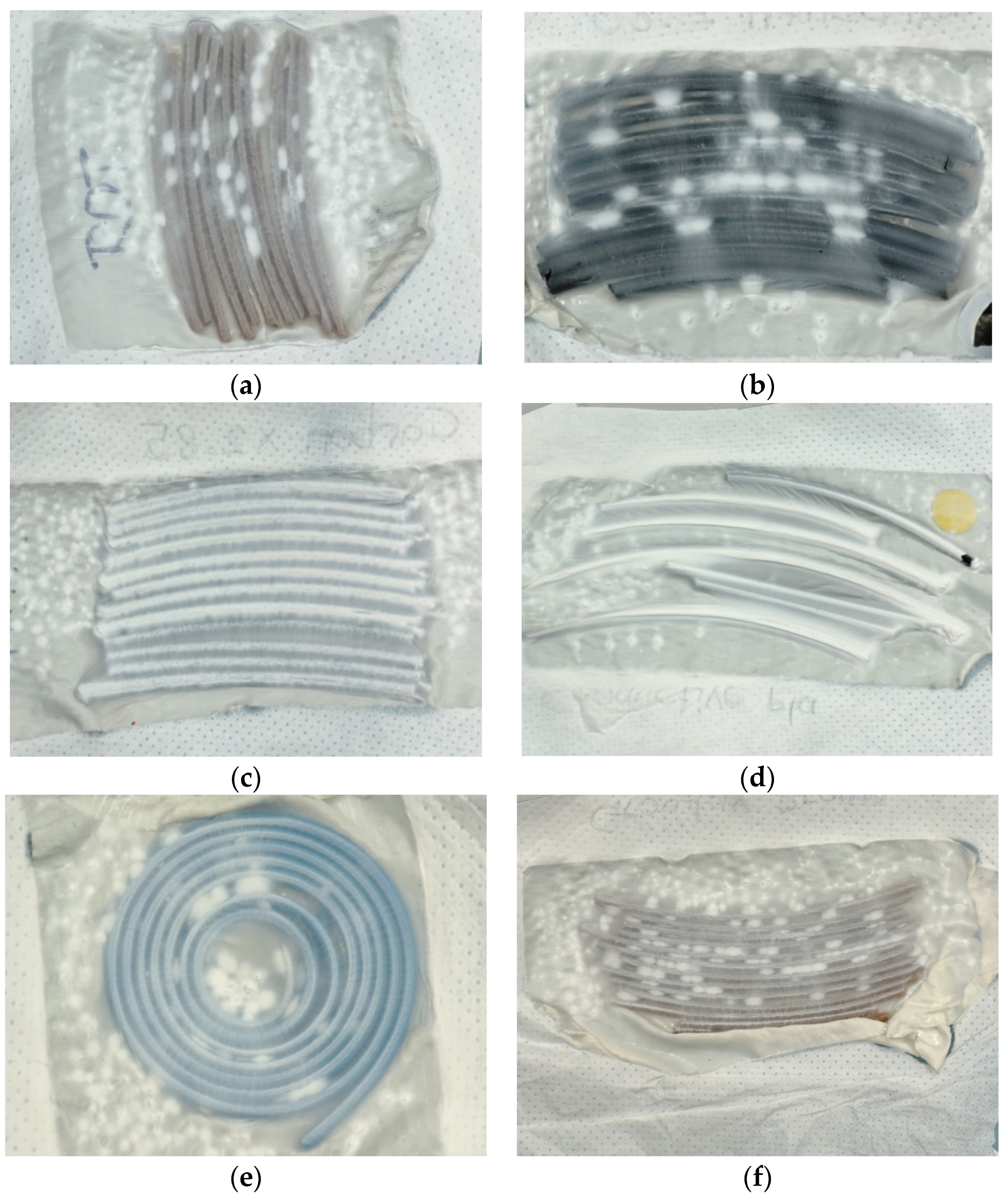
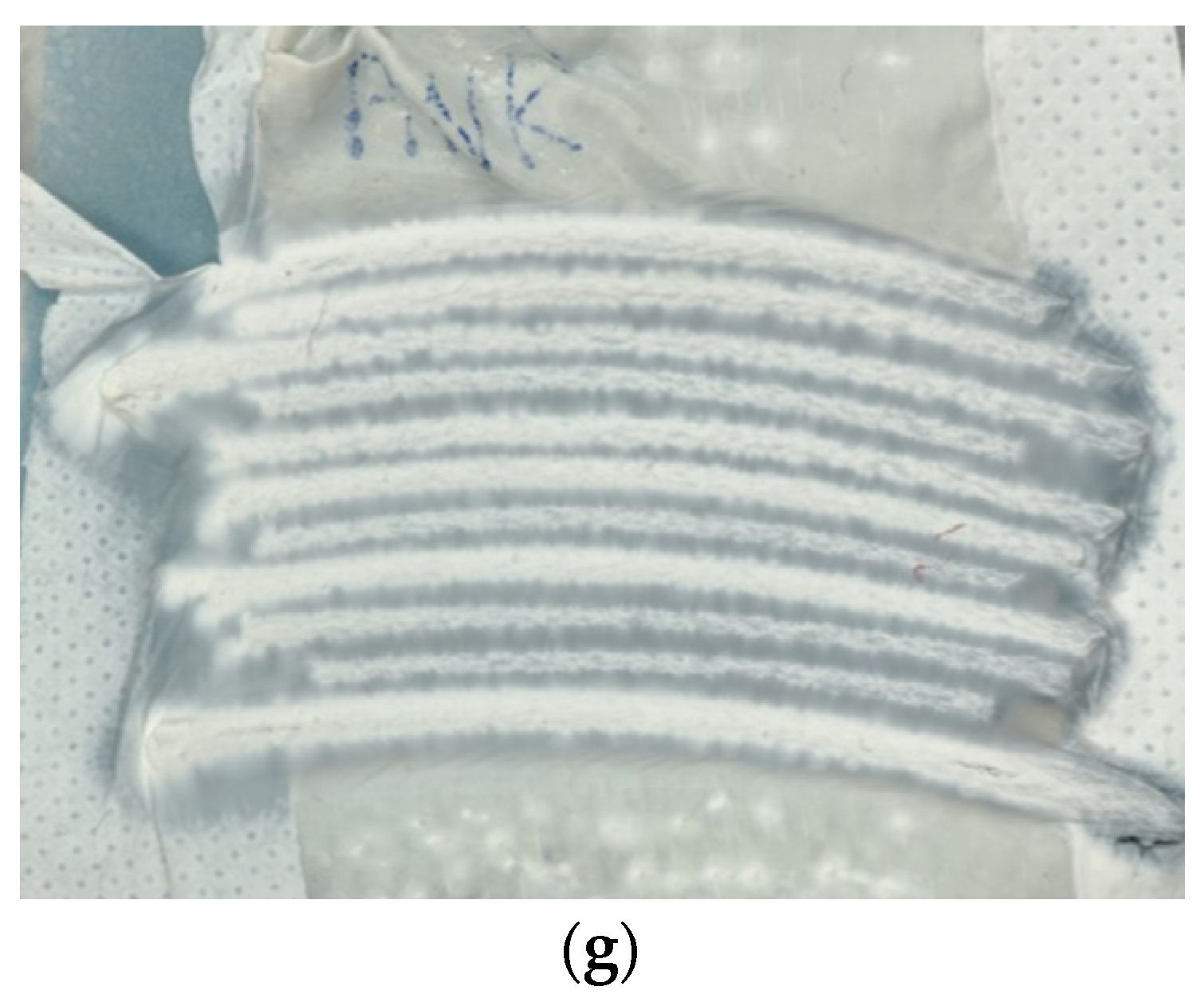

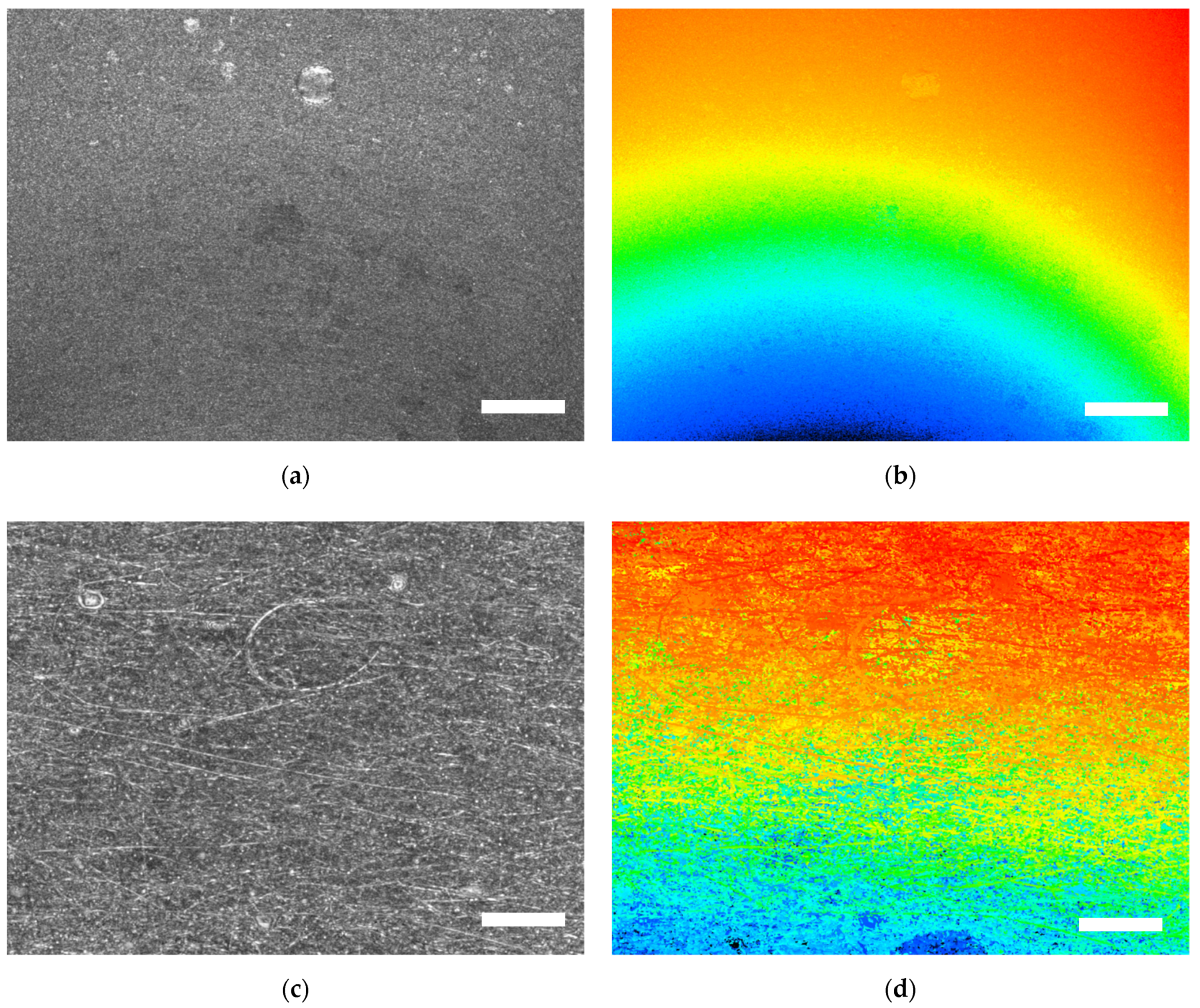
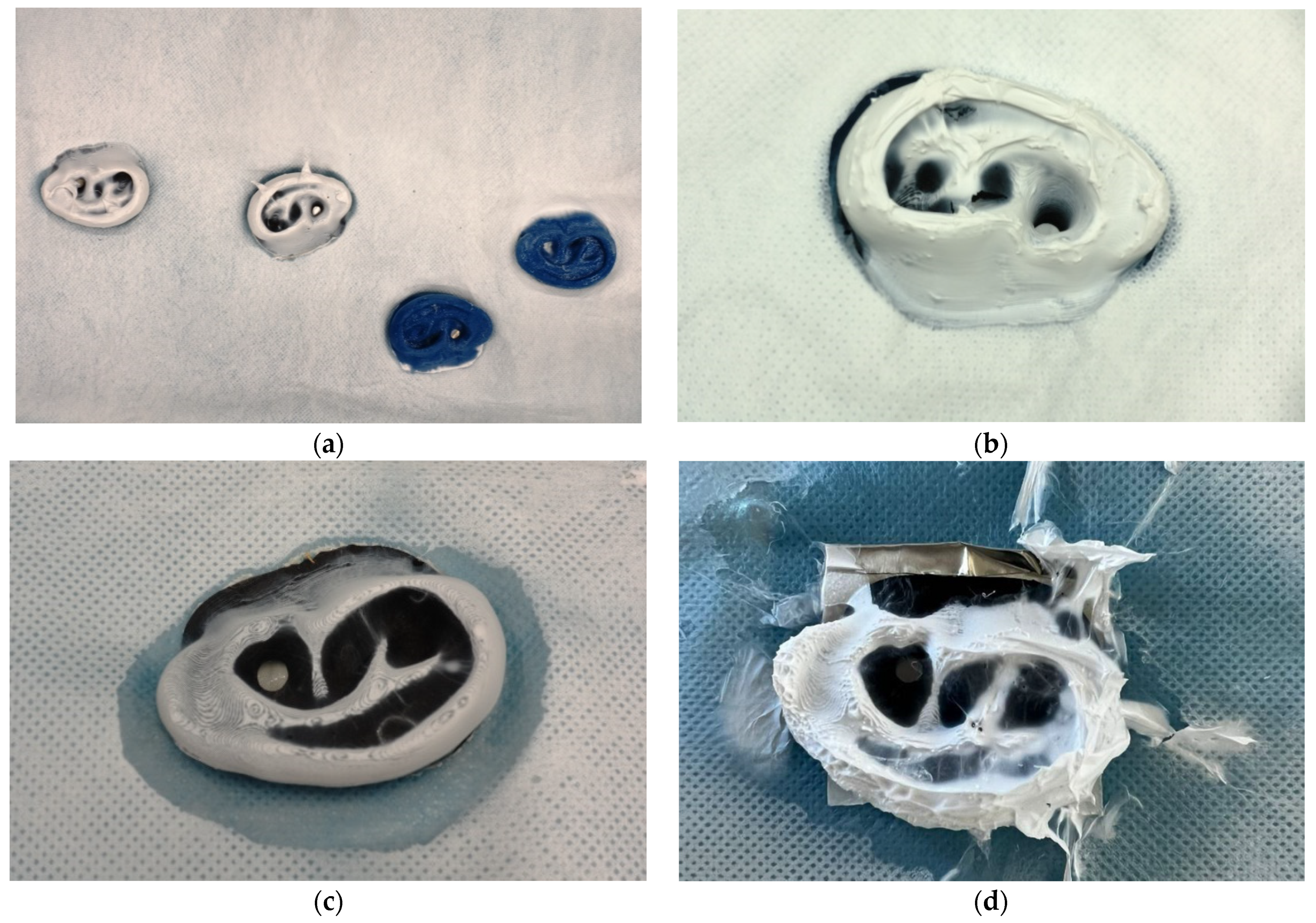
| Description | 3D Printed Part | Spinning Solution | Voltage | Current | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1 | None | 16% PAN | 80 kV | 0.116 mA | 30 min |
| V2 | None | 16% PAN | 80 kV | 0.08 mA | 30 min |
| V3 | None | 16% PAN | 80 kV | 0.08 mA | 30 min |
| V4 | None | 16% PAN + 5% dextran | 80 kV | 0.04 mA | 31 min |
| V5 | None | 14% PAN | 80 kV | 0.04 mA | 45 min |
| V6 | Various 3D parts | 14% PAN | 81 kV | 0.032 mA | 30 min |
| V6-1 | Various 3D parts | 14% PAN | 81 kV | 0.032 mA | 30 min |
| V6-2 | Various 3D parts | 14% PAN | 81 kV | 0.032 mA | 30 min |
| V7 | Aluminum foil | 14% PAN | 81 kV | 0.032 mA | 30 min |
| V9-2 | 3D filaments | 14% PAN | 80 kV | 0.03 mA | 30 min |
| V10 | 3D printed ear | 12% PAN + 2% dextran | 80 kV | 0.03 mA | 17 min |
| V11 | 3D printed ears from different filaments | 13% PAN | 80 kV | 0.03 mA | 25 min |
| V12-1 | 3D printed funnel in profile | 13% PAN | 82 kV | 0.03 mA | 16 min |
| V12-2 | 3D printed ears (partly grounded) | 13% PAN | 50 kV | 0.016 mA | 30 min |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bauer, L.; Brandstäter, L.; Letmate, M.; Palachandran, M.; Wadehn, F.O.; Wolfschmidt, C.; Grothe, T.; Güth, U.; Ehrmann, A. Electrospinning for the Modification of 3D Objects for the Potential Use in Tissue Engineering. Technologies 2022, 10, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies10030066
Bauer L, Brandstäter L, Letmate M, Palachandran M, Wadehn FO, Wolfschmidt C, Grothe T, Güth U, Ehrmann A. Electrospinning for the Modification of 3D Objects for the Potential Use in Tissue Engineering. Technologies. 2022; 10(3):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies10030066
Chicago/Turabian StyleBauer, Laura, Lisa Brandstäter, Mika Letmate, Manasi Palachandran, Fynn Ole Wadehn, Carlotta Wolfschmidt, Timo Grothe, Uwe Güth, and Andrea Ehrmann. 2022. "Electrospinning for the Modification of 3D Objects for the Potential Use in Tissue Engineering" Technologies 10, no. 3: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies10030066
APA StyleBauer, L., Brandstäter, L., Letmate, M., Palachandran, M., Wadehn, F. O., Wolfschmidt, C., Grothe, T., Güth, U., & Ehrmann, A. (2022). Electrospinning for the Modification of 3D Objects for the Potential Use in Tissue Engineering. Technologies, 10(3), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies10030066








