A Study on the Pass-Through Rate of the Exchange Rate on the Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) Import Price in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Previous Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Unit Root and Cointegration Test Method
3.2. TVR-VAR Model
3.3. Impulse Response Function
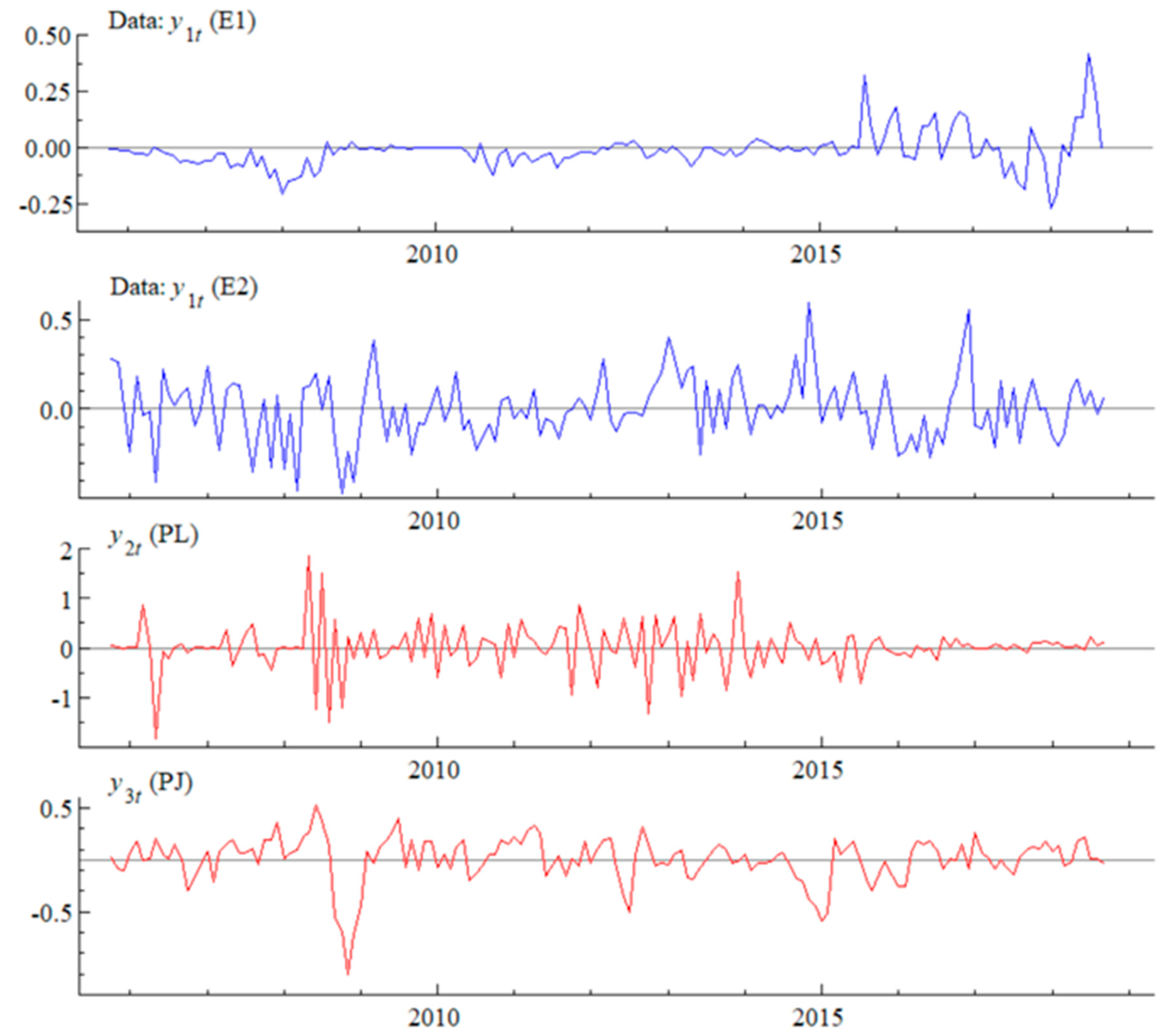
3.4. Data
4. Results
4.1. Unit Root and Cointegration Tests
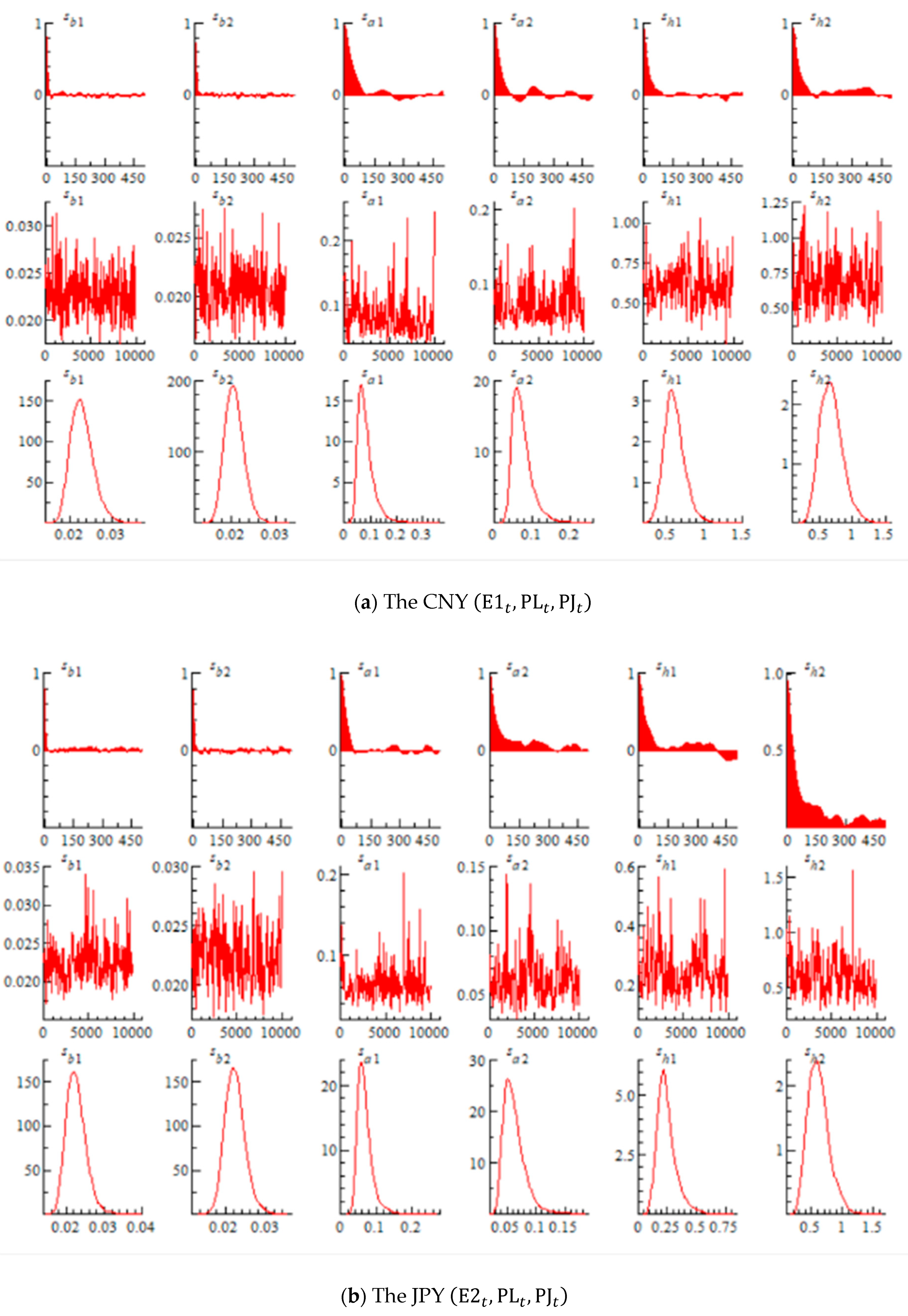
4.2. MCMC Estimation Results
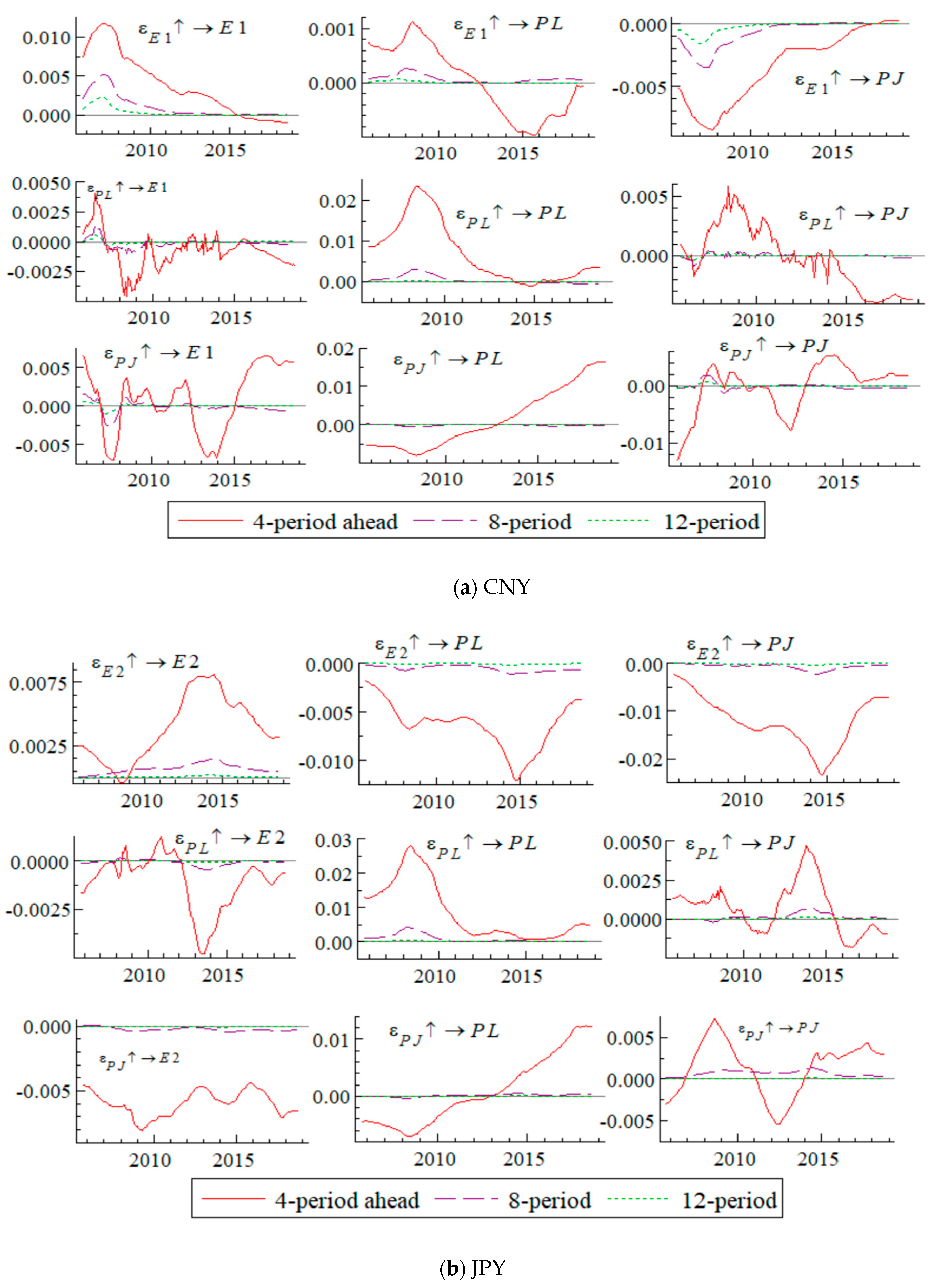
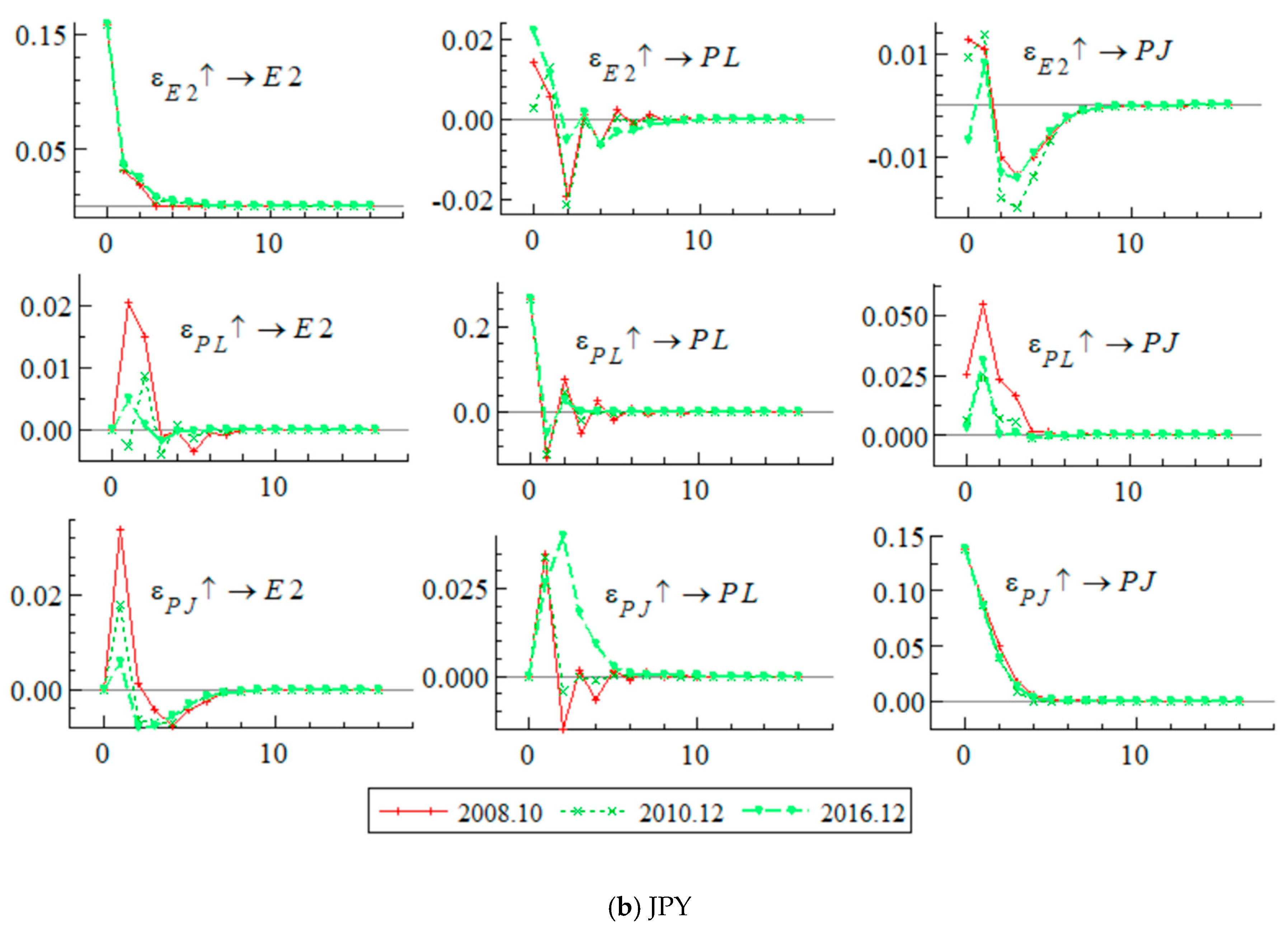
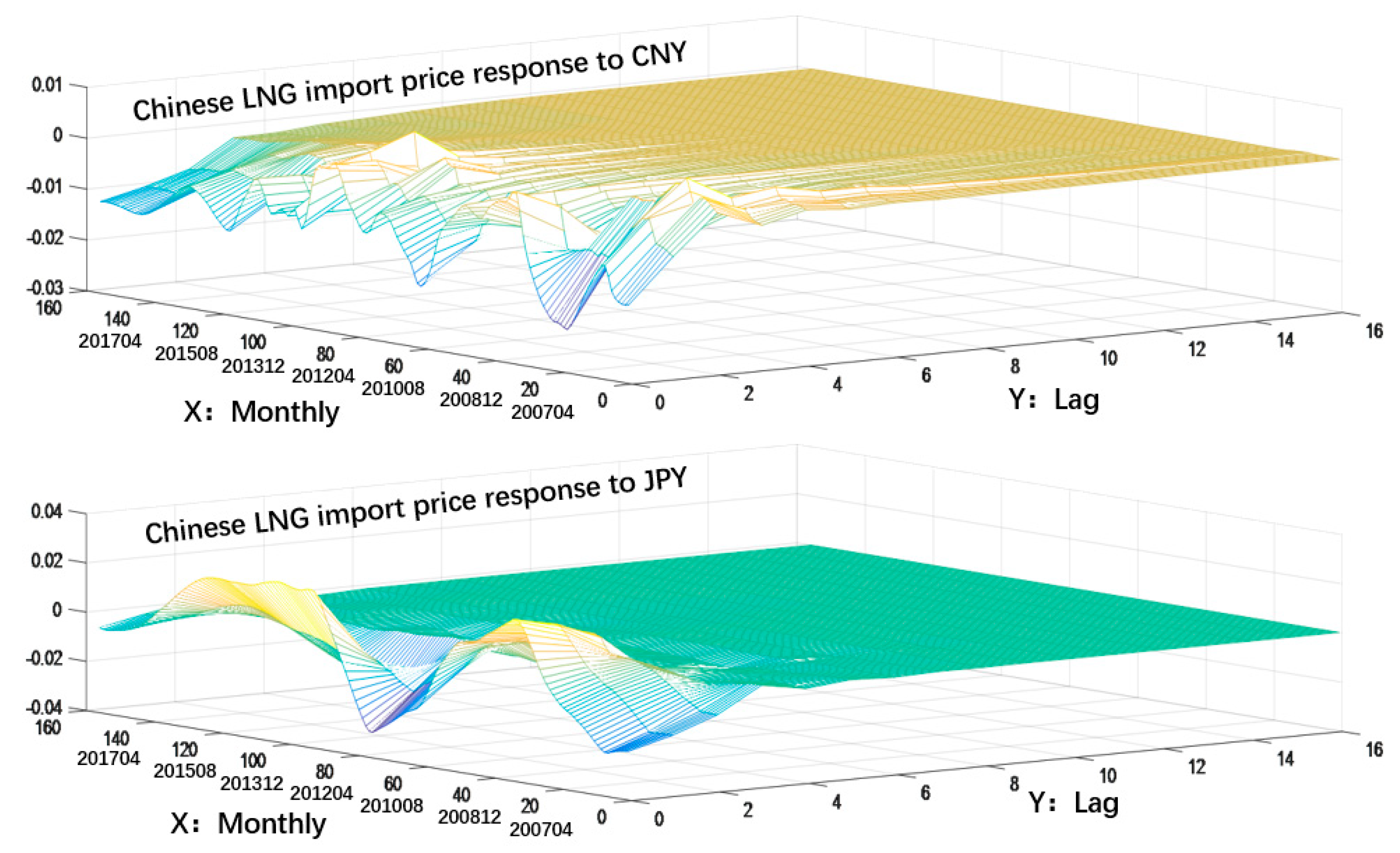
4.3. Results of the Impulse Response Analysis
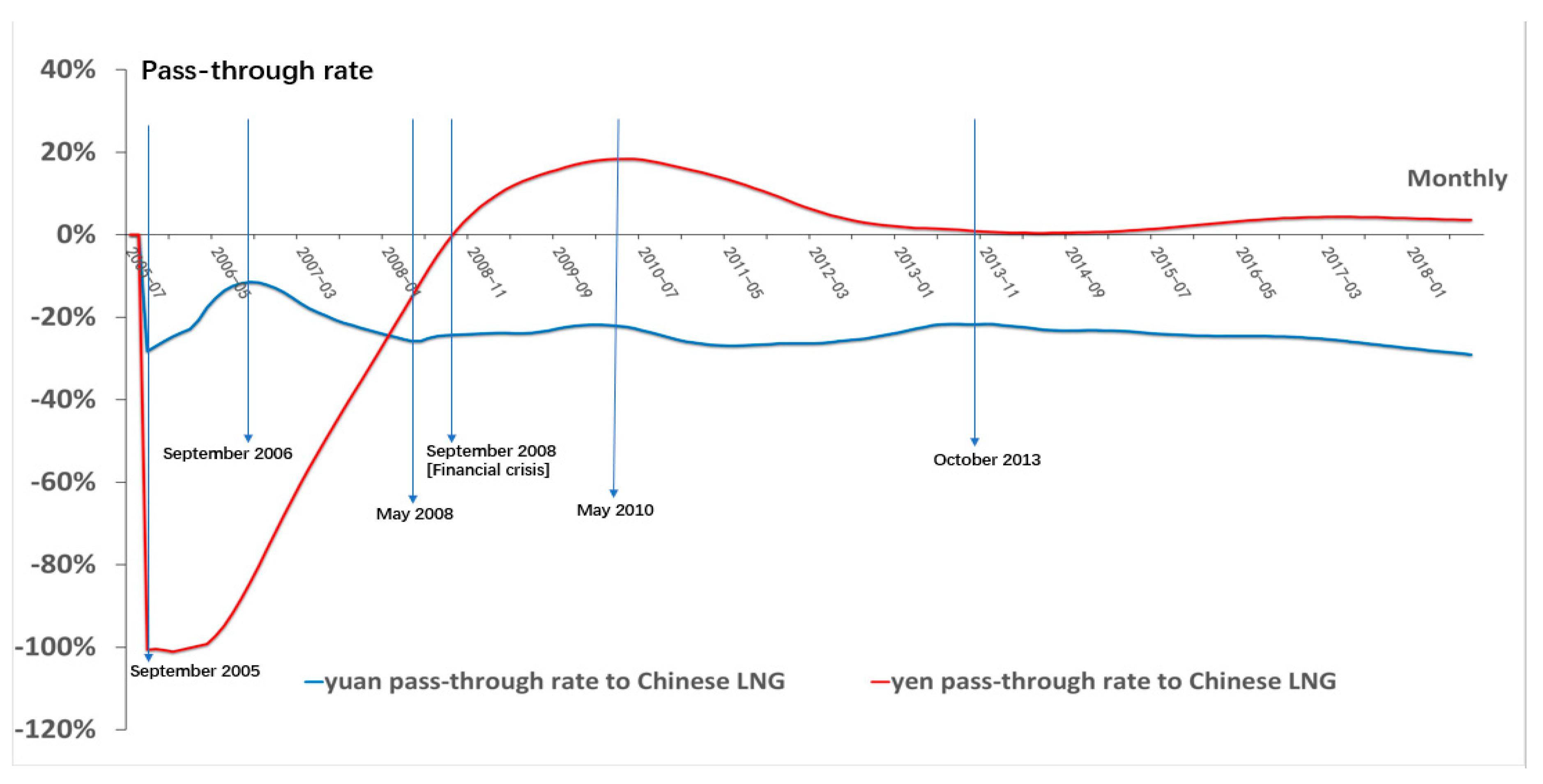
4.4. Pass-Through Rate Results
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- British Petroleum (BP). 2014. Statistical Review of World Energy. Available online: http://large.stanford.edu/courses/2014/ph240/milic1/docs/bpreview.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2019).
- British Petroleum (BP). 2015. Statistical Review of World Energy. Available online: http://large.stanford.edu/courses/2015/ph240/zerkalov2/docs/bp2015.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2019).
- British Petroleum (BP). 2019. Statistical Review of World Energy. pp. 20–29. Available online: https://www.bp.com/content/dam/bp/business-sites/en/global/corporate/pdfs/energy-economics/statistical-review/bp-stats-review-2019-full-report.pdf (accessed on 5 December 2019).
- Ceglowski, Janet. 2010. Exchange rate pass-through to bilateral import prices. Journal of International Money and Finance 29: 1637–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Gobong, and Eunnyeong Heo. 2017. Estimating the price premium of LNG in Korea and Japan: The price formula approach. Energy Policy 109: 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhria, Ehsan U., and Dalia S. Hakura. 2015. The exchange rate pass-through to import and export prices: The role of nominal rigidities and monetary choice. Journal of International Money and Finance 51: 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geweke, John. 1991. Evaluating the Accuracy of Sampling-Based Approaches to the Calculation of Posterior Moments. Staff Report 148. Minneapolis: Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, Xiao-feng, Yu-hua Wang, and Guang-sen Zhang. 2013. An Empirical Study on the result of the Passthrough of Exchange Rate into Domestic Price Based on VAR Model. Journal of Industrial Engineering/Engineering Management 27: 72–73. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- John, Eatwell, Murray Milgate, and Peter Newman. 1992. The New Palgrave Dictionary of Money and Finance. London: Palgrave Macmillan, vol. 3, pp. 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- Jose, Manuel Campa, and Linda S. Goldberg. 2006. Exchange Rate Pass-Through into Import Prices. Review of Economics and Statistics 87: 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto, Kaoru, and Kenji Tsuzaki. 2007. Market valuation of LNG price formulas. Journal of Japan Society of Energy and Resources 29: 1–7. (In Japanese). [Google Scholar]
- Kosumi, Hideo. 2016. Bayesian Computational Statistics, 4th ed. Tokyo: Asakura Bookstore, pp. 68–100. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtović, Safet, Siljković Boris, Denić Nebojsa, Petković Dalibor, Mladenović Svetlana Sokolov, Igor Mladenovic, and Milovancevic Milos. 2018. Exchange rate pass-through and Southeast European economies. Physica A 503: 400–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Hai Yue, and Xiao Lan Chen. 2017. The imported price, inflation and exchange rate pass-through in China. Cogent Economics & Finance 5: 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Marazzi, Mario, Sheets Nathan, Vigfusson Robert, Faust Jon, Gagnon Joseph, Jaime R. Marquez, Martin Rovert, Reeve Trevor, and Rogers John. 2005. Exchange Rate Passthrough to US Import Prices: Some New Evidence. Discussion Paper. Washington, DC: International Finance, vol. 833. [Google Scholar]
- Martono, Jeremia Dwi, and Kentaka Aruga. 2018. Investing the price linkage between Asian LNG spot and East Asian LNG prices and its implications. International Journal of Global Energy Issues 41: 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Economy. 2015. 2014 Annual Report on Energy (Energy White Paper 2015), Chapter 3, Section 1. Available online: https://www.enecho.meti.go.jp/about/whitepaper/2015html/1-3-1.html (accessed on 8 December 2019).
- Ministry of Economy. 2016. 2015 Annual Report on Energy (Energy White Paper 2016), Chapter 1, Section 3. Available online: https://www.enecho.meti.go.jp/about/whitepaper/2016html/1-1-3.html (accessed on 8 December 2019).
- Nakajima, Jouchi. 2011. Time-Varying Parameter VAR Model with Stochastic Volatility: An Overview of Methodology and Empirical Applications. Institute for Monetary and Economic Studies Bank of Japan E-9: 107–42. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima, Jouchi, and Toshiaki Watanabe. 2012. Time-Varying Vector Autoregressive Model-Survey and Application to Japanese Macro Data. Kunitachi: Institute of Economic Research, Hitotsubashi University, vol. 62, pp. 193–208. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- National Energy Board (NEB). 2016. The 13th Five-Year Plan for Energy Development. Available online: http://www.nea.gov.cn/2017-01/17/c_135989417.htm (accessed on 15 August 2019). (In Chinese)
- Pennings, Steven. 2017. Pass-through of competitors’ exchange rates to US import and producer prices. Journal of International Economics 105: 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primiceri, Giorgio E. 2005. Time-varying structural vector autoregressions and monetary policy. The Review of Economic Studies 72: 821–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Yuri. 2019. Pass-through effect in which exchange rates are reflected in prices-Is pass-through of Japanese imports declining? Ministry of Finance, Policy Research Institute, Ministry of Finance, Financial Review 136: 118–43. (In Japanese). [Google Scholar]
- Sekine, Toshitaka. 2006. Time-varying Exchange Rate Pass-through: Experiences of Some Industrial Countries. BIS Working Paper. Basel: Bank for International Settlements, vol. 202, pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Xunpeng, and Malamakkavu Padinjare Variam Hari. 2016. Gas and LNG trading hubs, hub indexation and destination flexibility in East Asia. Energy Policy 96: 587–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinkai, Junichi. 2011. Examination of Pass-through Effect of Exchange Rates in the Pacific Region. Osaka University Economics 61: 37–47. (In Japanese). [Google Scholar]
- Shioji, Etsuro. 2010. Transition of Exchange Rate Pass-Through Rate-Re-Examination with Time-Varying Coefficient VAR. Tokyo: Research Institute of Economy, Trade & Industry, vol. 10, pp. 1–24. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Shioji, Etsuro, and Taisuke Uchino. 2009. Is the Pass-Through of Exchange Rate and Oil Price Fluctuation Changed? Bank of Japan Working Paper Series; Tokyo: Bank of Japan, vol. 9, p. 1. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Xiaoguang, Jiong Zheng, and Bo Fang. 2014. Strategic analysis on establishing a natural gas trading hub in China. Natural Gas Industry B1: 210–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wind. 2019. Wind Is a Paid Network That Collects Global Economic and Other Data. Available online: https://www.wind.com.cn/en/Default.html (accessed on 5 December 2019).

| Steps | Detail of Steps |
|---|---|
| 1 | Set the initial value of . |
| 2 | Sampling from . |
| 3 | Sampling from . |
| 4 | Sampling from . |
| 5 | Sampling from . |
| 6 | Sampling from . |
| 7 | Sampling from . |
| 8 | Back to step 2. |
| Variables | Level Data (t-Value) | First Difference Data | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADF | PP | KPSS | ADF | PP | KPSS | |
| E1 | −1.29 | −2.43 | 0.63 | |||
| E2 | −0.16 | −1.34 | 0.18 | |||
| PL | −0.34 | −2.45 | 0.09 | |||
| PJ | −0.46 | −2.19 | 0.07 | |||
| Rank Number | Trace Test Statistic | 0.01 Critical Value | p-Value | Maximum Eigenvalue Test Statistic | 0.01 Critical Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | 35.46 | 25.86 | ||||
| At most 1 | 19.94 | 18.52 | ||||
| At most 2 | 6.63 | 6.63 |
| Rank Number | Trace Test Statistic | 0.01 Critical Value | p-Value | Maximum Eigenvalue Test Statistic | 0.01 Critical Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | 35.46 | 12.04 | 25.86 | |||
| At most 1 | 19.94 | 7.29 | 18.52 | |||
| At most 2 | 6.63 | 6.63 |
| Parameter | Average | Standard Deviation | 95%Credit Section | CD | Inefficiency Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.023 | 0.003 | [0.018, 0.029] | 9.160 | ||
| 0.021 | 0.002 | [0.017, 0.025] | 6.650 | ||
| 0.082 | 0.032 | [0.043, 0.163] | 70.690 | ||
| 0.074 | 0.026 | [0.040, 0.140] | 51.010 | ||
| 0.610 | 0.132 | [0.385, 0.901] | 41.910 | ||
| 0.686 | 0.168 | [0.397, 1.063] | 56.460 |
| Parameter | Average | Standard Deviation | 95%Credit Section | CD | Inefficiency Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.023 | 0.003 | [0.018, 0.028] | 9.360 | ||
| 0.022 | 0.002 | [0.018, 0.028] | 5.170 | ||
| 0.068 | 0.022 | [0.039, 0.125] | 41.420 | ||
| 0.063 | 0.019 | [0.038, 0.124] | 78.930 | ||
| 0.246 | 0.084 | [0.124, 0.458] | 72.560 | ||
| 0.613 | 0.171 | [0.331, 1.001] | 89.370 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, C.; Aruga, K. A Study on the Pass-Through Rate of the Exchange Rate on the Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) Import Price in China. Int. J. Financial Stud. 2020, 8, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs8040070
Tang C, Aruga K. A Study on the Pass-Through Rate of the Exchange Rate on the Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) Import Price in China. International Journal of Financial Studies. 2020; 8(4):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs8040070
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Chaofeng, and Kentaka Aruga. 2020. "A Study on the Pass-Through Rate of the Exchange Rate on the Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) Import Price in China" International Journal of Financial Studies 8, no. 4: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs8040070
APA StyleTang, C., & Aruga, K. (2020). A Study on the Pass-Through Rate of the Exchange Rate on the Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) Import Price in China. International Journal of Financial Studies, 8(4), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs8040070






