Enhancing the Solubility of Curcumin Using a Solid Dispersion System with Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Prepared by Grinding, Freeze-Drying, and Common Solvent Evaporation Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Quantification of CUR
2.3. Phase Solubility Analysis
2.4. Method of Preparation of SDs
2.4.1. Grinding Method
2.4.2. Freeze-Drying (FD) Method
2.4.3. Common Solvent Evaporation (CSE) Method
2.5. Characteristic Evaluation Methods
2.5.1. Solubility
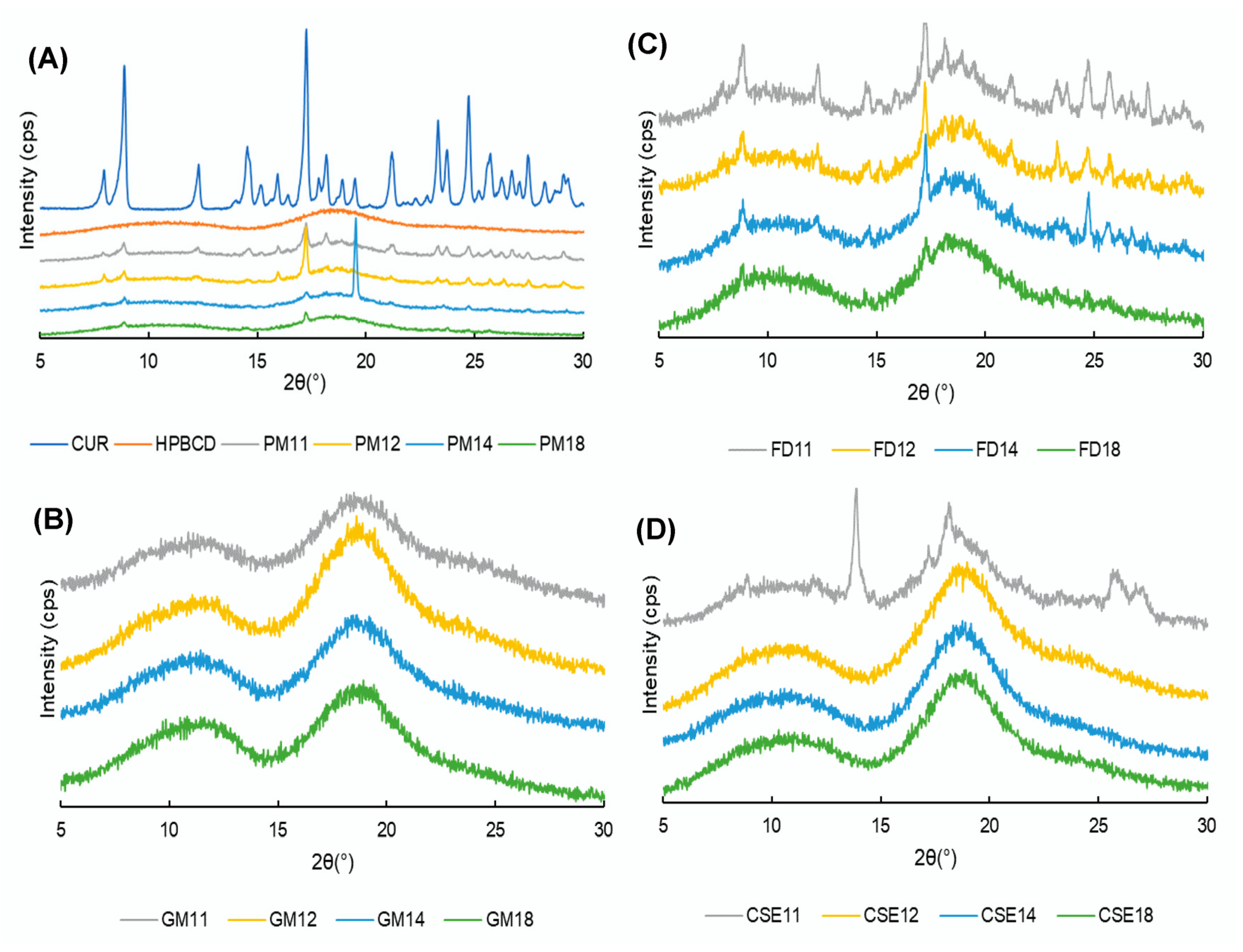
2.5.2. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD)
2.5.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
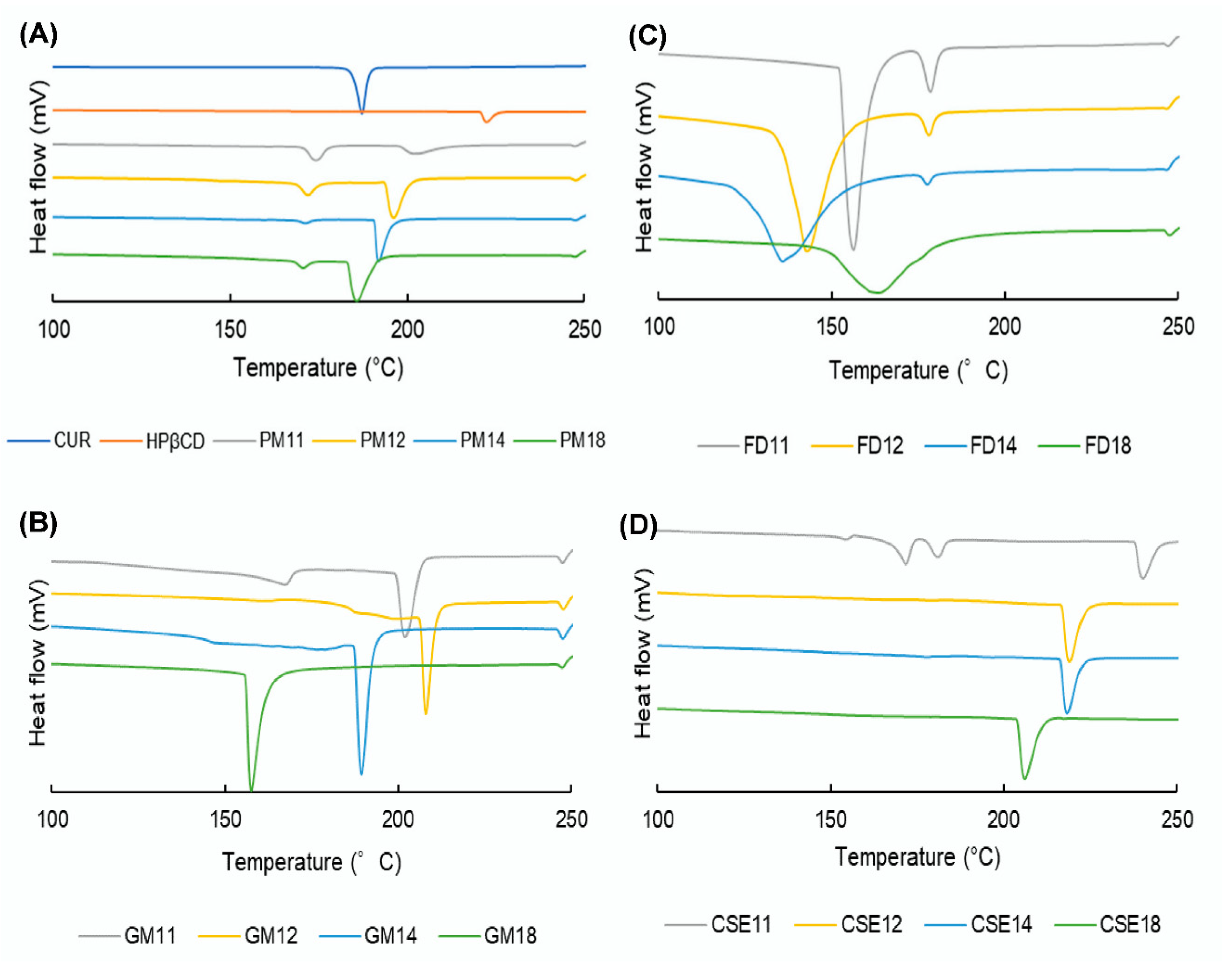
2.5.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
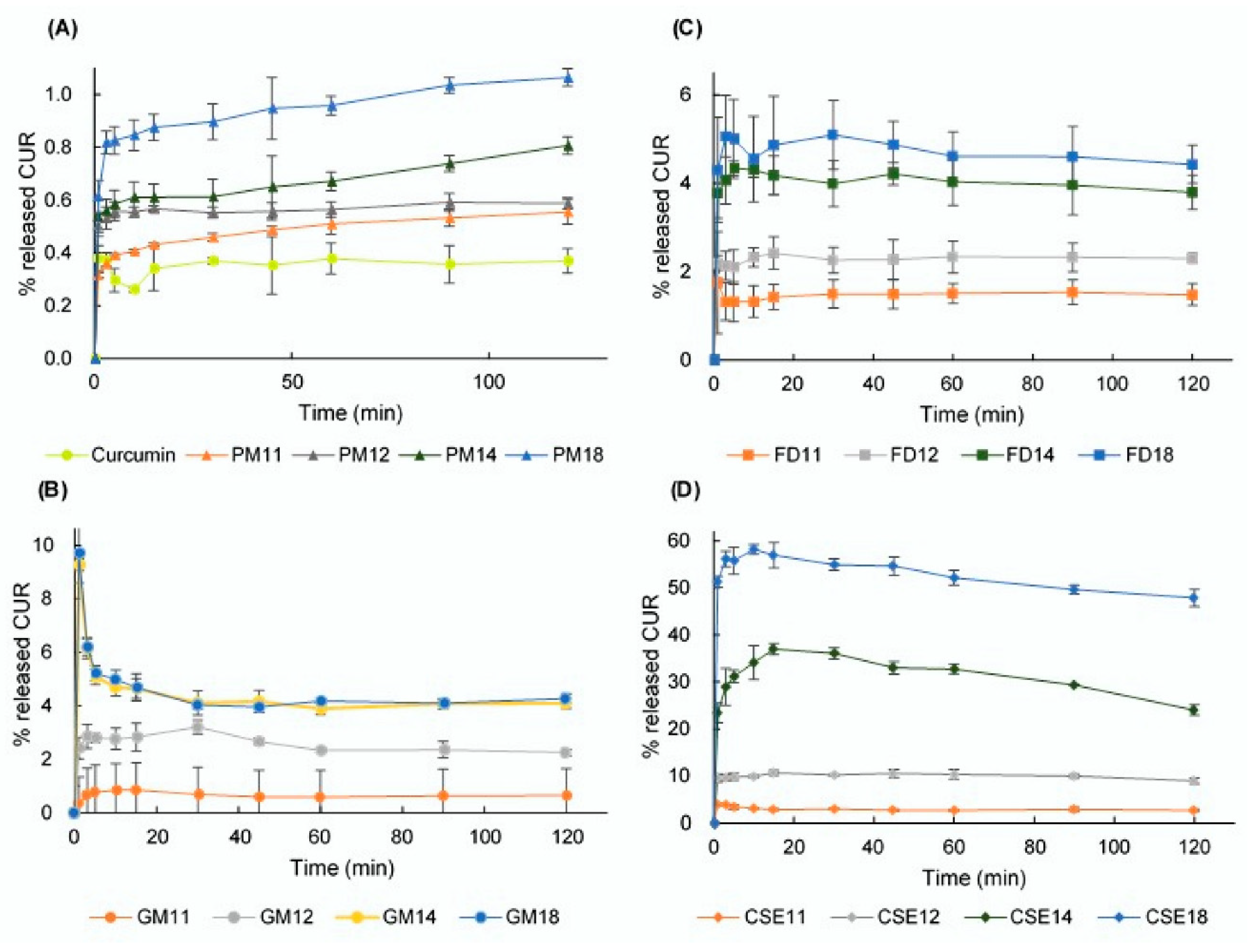
2.5.5. Dissolution Studies
2.5.6. Dissolution Efficiency (DE)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Quantification of CUR
3.2. Phase Solubility Analysis
3.3. Solubility Study
3.4. PXRD Patterns
3.5. FTIR Spectroscopy
3.6. DSC
3.7. Dissolution Study
3.8. DE
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amidon, G.L.; Lennernäs, H.; Shah, V.P.; Crison, J.R. A theoretical basis for a biopharmaceutic drug classification: The correlation of in vitro drug product dissolution and in vivo bioavailability. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rams-Baron, M.; Jachowicz, R.; Boldyreva, E.; Zhou, D.; Jamroz, W.; Paluch, M. Amorphous drug solubility and absorption enhancement. In Amorphous Drugs, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 41–68. [Google Scholar]
- Braig, V.; Konnerth, C.; Peukert, W.; Lee, G. Enhanced dissolution of naproxen from pure-drug, crystalline nanoparticles: A case study formulated into spray-dried granules and compressed tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 554, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Farajtabar, A.; Zhao, H.; Han, G. Solubility modelling and thermodynamic aspect of d-aspartic acid in aqueous co-solvent mixtures of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, N,N-dimethylformamide, dimethyl sulfoxide and 1,4-dioxane. J. Chem. Therm. 2019, 138, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, B.; Silvetsre, A.J.D.; Pinto, P.C.R.; Freire, C.S.R.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Hydrotrophy and cosolvency in lignin solubilization with deep eutectic solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 12485–12493. [Google Scholar]
- Zi, P.; Zhang, C.; Ju, C.; Su, Z.; Bao, Y.; Gao, J.; Sun, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, C. Solubility and bioavailability enhancement study of lopinavir solid dispersion matrixed with a polymeric surfactant—Soluplus. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 134, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.; Pyo, Y.C.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.E.; Kim, J.K.; Park, J.S. Overview of the manufacturing methods of solid dispersion technology for improving the solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs and application to anticancer drugs. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xie, X.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Cai, C.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, Z.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, M.; et al. Effect of plasticizers on manufacturing ritonavir/copovidone solid dispersions via hot-melt extrusion: Preformulation, physicochemical characterization, and pharmacokinetics in rats. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 127, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Shinde, V.V.; Jeong, D.; Choi, Y.; Jung, S. Solubility enhancement of atrazine by complexation with cyclosophoraose isolated from Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii TA-1. Polymers 2019, 11, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konan, K.V.; Le, T.C.; Mateescu, M.A. Enhanced solubility of alkaloid by complexation with polycarboxylic materials for controlled release formulations: Case of Peschiera fuchsiaefolia. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, G.D. Extensive diminution of particle size and amorphization of a crystalline drug attained by eminent technology of solid dispersion: A comparative study. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 1770–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshafiee, M.; Aljammal, M.K.; Markl, D.; Ward, A.; Walton, K.; Blunt, L.; Korde, S.; Pagire, S.K.; Kelly, A.L.; Paradkar, A.; et al. Hot-melt extrusion process impact on polymer choice of glyburide solid dispersion: The effect of wettability and dissolution. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 559, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sammour, O.A.; Hammad, M.A.; Megrab, N.A.; Zidan, A.S. Formulation and optimization of mouth dissolve tablets containing rofecoxib solid dispersion. AAPS PharmSciTech 2006, 7, E167–E175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivino, A.; Gumireddy, A.; Meng, F.; Prasad, D.; Chauhan, H. Drug–polymer miscibility, interactions, and precipitation inhibition studies for the development of amorphous solid dispersions for the poorly soluble anticancer drug flutamide. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 1277–1291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Solanki, N.G.; Lam, K.; Tahsin, M.; Gumaste, S.G.; Shah, A.V.; Serajuddin, A.T.M. Effects of surfactants on itraconazole-HPMCAS solid dispersion prepared by hot-melt extrusion I: Miscibility and drug release. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1453–1465. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Y.; Xu, M.; Ohm, J.B.; Chen, B.; Rao, J. Solid dispersion-based spray-drying improves solubility and mitigates beany flavour of pea protein isolate. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asare-Addo, K.; Alshafiee, M.; Walton, K.; Ward, A.; Totea, A.M.; Taheri, S.; Mawla, N.; Adebisi, A.O.; Elawad, S.; Diza, C.; et al. Effect of preparation method on the surface properties and UV imaging of indomethacin solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 137, 148–163. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, W.; Hu, H.; Ni, X.; Ni, S.; Xu, Y.; Yang, L.; Xu, D. Co-precipitation of calcium carbonate and curcumin in an ethanol medium as a novel approach for curcumin dissolution enhancement. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 51, 397–402. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanacharyulu, R.; Krishna, S.C.; Mudit, D. Design and development of sustained release tablets using solid dispersion of beclomethasone dipropionate. Res. Rev. J. Drug Formul. Dev. Prod. 2015, 2, 30–41. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Di, L. Application of the combination of ball milling and hot-melt extrusion in the development of an amorphous solid dispersion of a poorly water-soluble drug with high melting point. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 22263–22273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, R.E.; Maria, L.A.; Katarina, B.; Howard, D.P.; David, S.K. Cyclodextrin inclusion complexes: Studies of the variation in the size of alicyclic guests. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 6765–6772. [Google Scholar]
- Swati, R.; Sanjay, K. Solubility enhancement of celecoxib using b-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 57, 263–267. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Zhu, S. Preparation and characterization of inclusion complexes of prazosin hydrochloride with β-cyclodextrin and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Tan, F.; Jing, Z.; Liu, Z. Preparation and study the 1:2 inclusion complex of carvedilol with β-cyclodextrin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2004, 34, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karathanos, V.T.; Mourtzinos, I.; Yannakopoulou, K.; Andrikopoulos, N.K. Study of the solubility, antioxidant activity and structure of inclusion complex of vanillin with β-cyclodextrin. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambasevam, K.P.; Mohamad, S.; Sarih, N.M.; Ismail, N.A. Synthesis and characterization of the inclusion complex of β-cyclodextrin and azomethine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 3671–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, P.P.; Serafini, M.R.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J.; Silva, G.F.; Olivera, J.F.; Carvalho, F.M.S.; Souza, J.C.C.; Matos, J.R.; Alves, P.B.; Matos, I.L.; et al. Inclusion complex of (−)-linalool and β-cyclodextrin. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 115, 2429–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; Zhu, D.H.; Feng, K.; Liu, F.J.; Lou, W.Y.; Li, N.; Zong, M.H.; Wu, H. Fabrication of electrospun polylactic acid nanofilm incorporating cinnamon essential oil/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex for antimicrobial packaging. Food Chem. 2015, 196, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Másson, M.; Brewster, M.E. Self-association of cyclodextrins and cyclodextrin complexes. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Loftsson, T.; Magnúsdóttir, A.; Másson, M.; Sigurjónsdóttir, J.F. Self-association and cyclodextrin solubilization of drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 2307–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, H.K.; Peh, K.K. Comparative curcumin solubility enhancement study of β-cyclodextrin and its derivative hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2013, 32, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Martín, L.; León, A.; Olives, A.I.; Castillo, B.; Martín, M.A. Spectrofluorimetric determination of stoichiometry and association constants of the complexes of harmane and harmine with β-cyclodextrin and chemically modified β-cyclodextrins. Talanta 2020, 60, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbik, D.; Ghadiri, M.; Chrzanowski, W.; Rohadizadeh, R. Curcumin as a wound healing agent. Life Sci. 2014, 116, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Available online: https://www.applichem.com/en/shop/product-detail/as/2-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin/ (accessed on 4 June 2020).
- Zhang, Q.; Ren, W.; Dushkin, A.V.; Su, W. Preparation, characterization, in vitro and in vivo studies of olmesartan medoxomil in a ternary solid dispersion with N-methyl-D-glucamine and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 101546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantarat, C.; Sirathanarun, P.; Ratanapongsai, S.; Watcharakan, P.; Sunyapong, S.; Wadu, A. Curcumin-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex preparation methods: Effect of common solvent evaporation, freeze drying, and pH shift on Solubility and stability of curcumin. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Du, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Jin, Y.; Qian, X. Transdermal delivery of the in situ hydrogels of curcumin and its inclusion complexes of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin for melanoma treatment. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 469, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, N.; Wu, T.; Qiu, C.; Wang, X.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, T.; Wei, C.; Wang, T. Preparation of curcumin-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex by cosolvency-lyophilization procedure to enhance oral bioavailability of the drug. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 1966–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaught, A.D.; Wilkinson, A. Compendium of Chemical Terminology, The Gold Book, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Science Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi, T.; Connors, K.A. Phase solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 1965, 4, 117–212. [Google Scholar]
- Dhanoa, M.S.; Lister, S.J.; Sanderson, R.; Barnes, R.J. The link between multiplicative scatter correction (MSC) and standard normal variate (SNV) transformations of NIR spectra. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 1994, 2, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Dissolution test. In The Japanese Pharmacopeia, 17th ed.; Yakuji Nippo Ltd.: Chiyoda-ku, Japan, 2016; pp. 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, K.A.; Rhodes, C.T. Effect of compaction pressure on the dissolution efficiency of some direct compression systems. Pharm. Acta Helv. 1972, 47, 594–700. [Google Scholar]
- Jahed, V.; Zarrabi, A.; Bordbar, A.; Hafezi, M.S. NMR (1H, ROESY) spectroscopic and molecular modelling investigations of supramolecular complex of β-cyclodextrin and curcumin. Food Chem. 2014, 165, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, T.M.; Velcheva, E.A.; Stamboliyska, B.A.; Spiteller, M. DFT and experimental studies of the structure and vibrational spectra of curcumin. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2005, 102, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, E. The melting point of impure organic compounds. J. Chem. Educ. 1942, 19, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
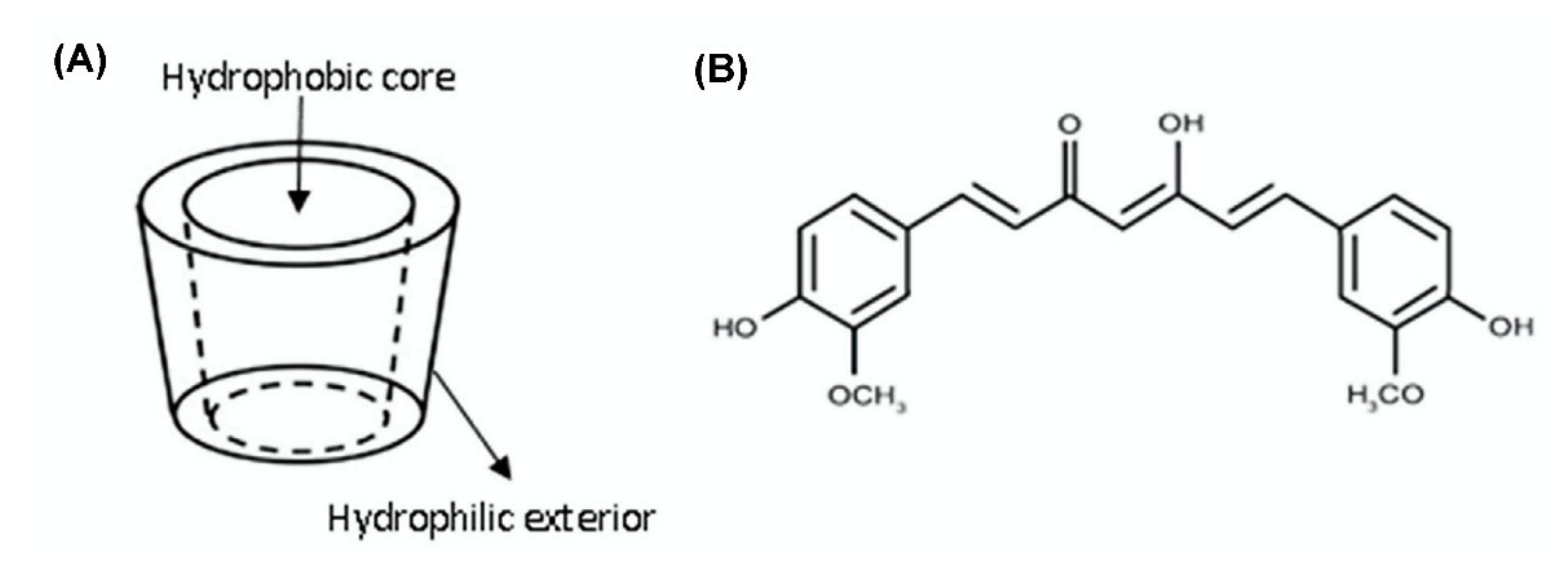
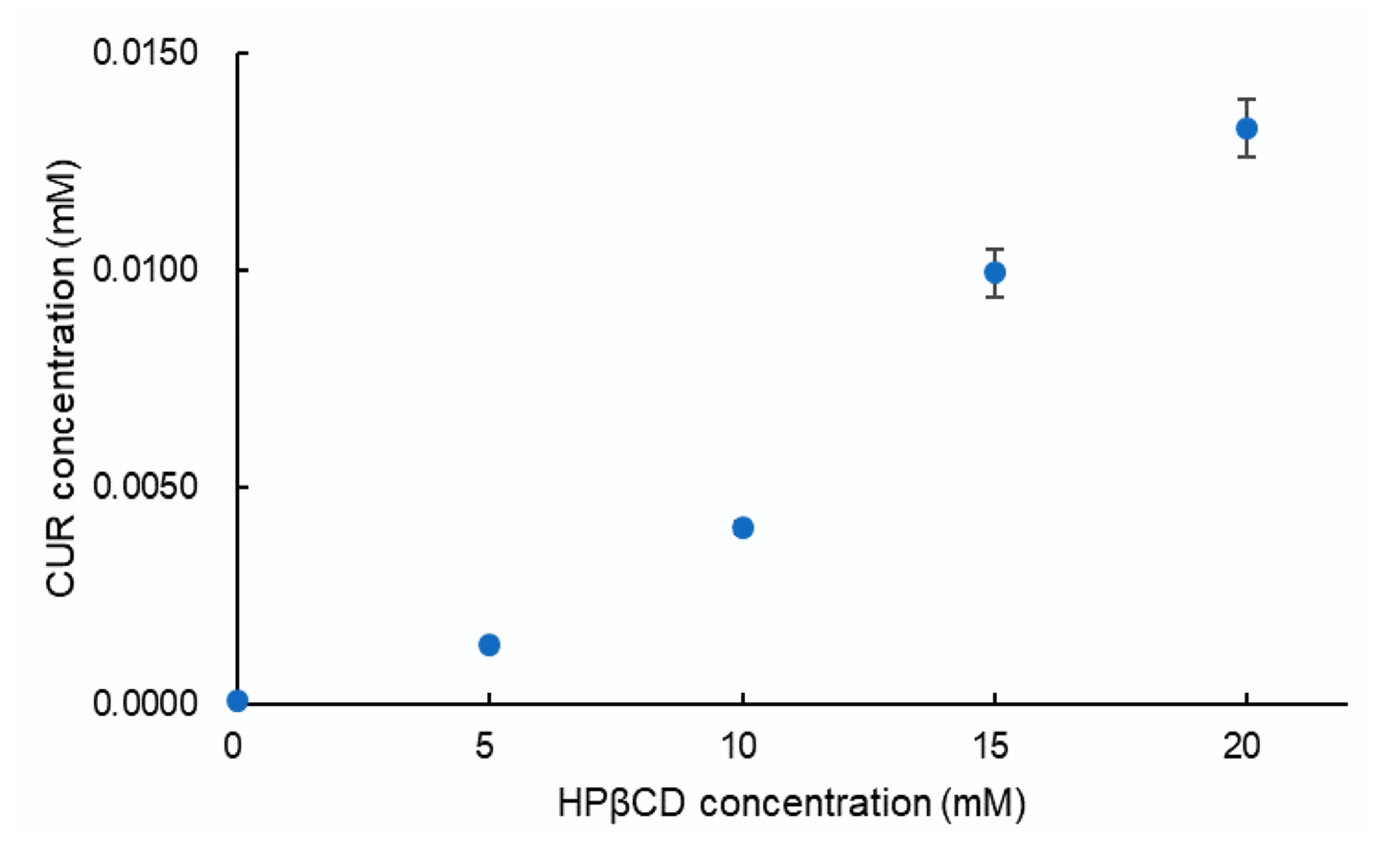
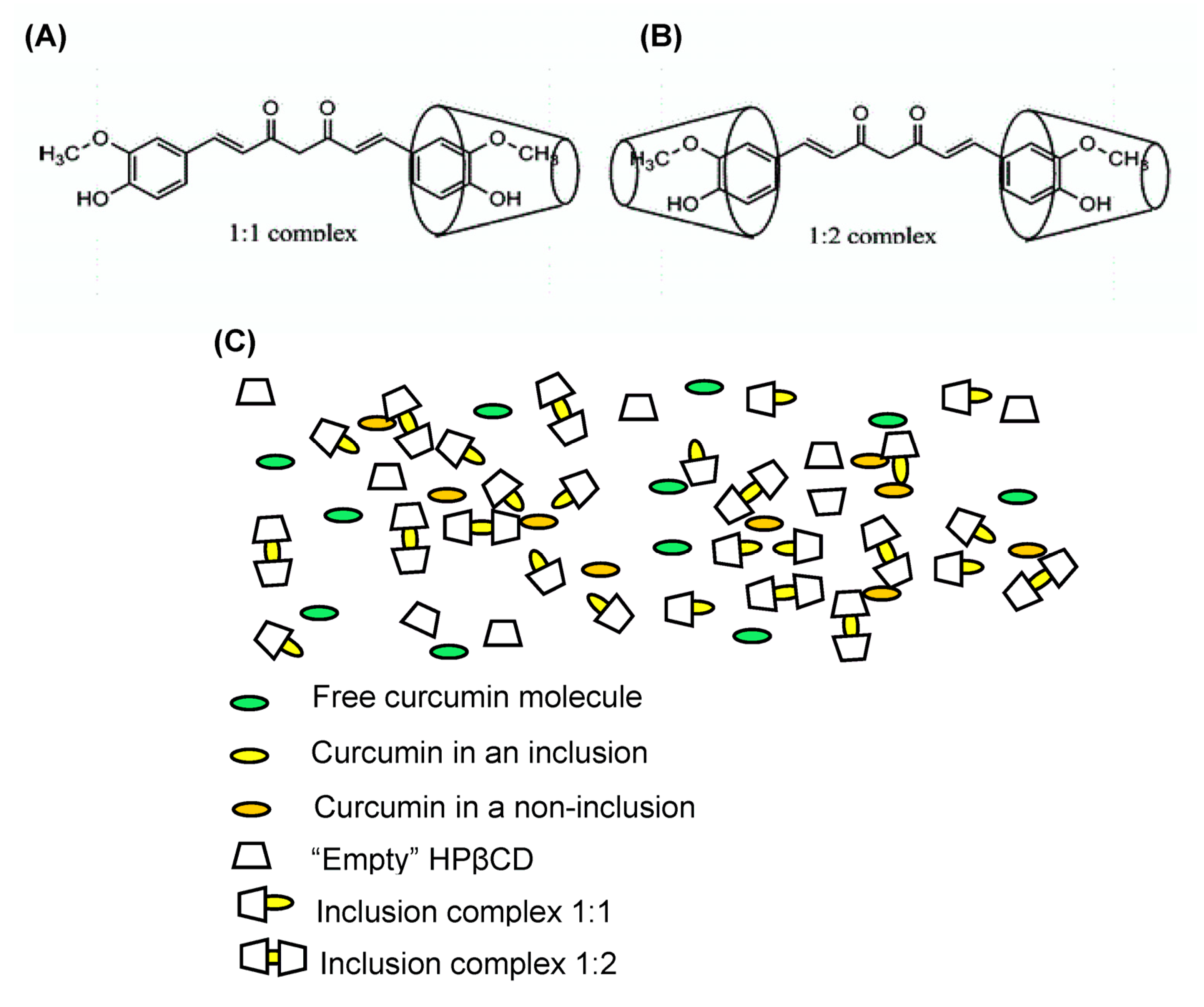

| Sample | CUR:HPβCD Ratio (mol:mol) | Solubility (µg/mL) | DE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CUR | - | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.36 ± 0.02 |
| GM11 | 1:1 | 0.89 ± 0.17 | 0.66 ± 0.12 |
| GM12 | 1:2 | 1.25 ± 0.25 | 2.55 ± 0.13 |
| GM14 | 1:4 | 2.55 ± 0.24 | 4.17 ± 0.26 |
| GM18 | 1:8 | 6.61 ± 0.15 | 4.31 ± 0.10 |
| FD11 | 1:1 | 0.27 ± 0.02 | 1.48 ± 0.27 |
| FD12 | 1:2 | 0.54 ± 0.01 | 2.30 ± 0.31 |
| FD14 | 1:4 | 1.61 ± 0.13 | 4.02 ± 0.46 |
| FD18 | 1:8 | 5.23 ± 0.18 | 4.69 ± 0.60 |
| CSE11 | 1:1 | 2.64 ± 0.11 | 2.82 ± 0.18 |
| CSE12 | 1:2 | 3.08 ± 0.19 | 10.00 ± 0.45 |
| CSE14 | 1:4 | 4.70 ± 0.29 | 31.27 ± 0.31 |
| CSE18 | 1:8 | 14.16 ± 1.27 | 52.21 ± 0.75 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mai, N.N.S.; Nakai, R.; Kawano, Y.; Hanawa, T. Enhancing the Solubility of Curcumin Using a Solid Dispersion System with Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Prepared by Grinding, Freeze-Drying, and Common Solvent Evaporation Methods. Pharmacy 2020, 8, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy8040203
Mai NNS, Nakai R, Kawano Y, Hanawa T. Enhancing the Solubility of Curcumin Using a Solid Dispersion System with Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Prepared by Grinding, Freeze-Drying, and Common Solvent Evaporation Methods. Pharmacy. 2020; 8(4):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy8040203
Chicago/Turabian StyleMai, Nguyen Ngoc Sao, Riko Nakai, Yayoi Kawano, and Takehisa Hanawa. 2020. "Enhancing the Solubility of Curcumin Using a Solid Dispersion System with Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Prepared by Grinding, Freeze-Drying, and Common Solvent Evaporation Methods" Pharmacy 8, no. 4: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy8040203
APA StyleMai, N. N. S., Nakai, R., Kawano, Y., & Hanawa, T. (2020). Enhancing the Solubility of Curcumin Using a Solid Dispersion System with Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Prepared by Grinding, Freeze-Drying, and Common Solvent Evaporation Methods. Pharmacy, 8(4), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy8040203