Comparison of Students’ Self-Assessment and Simulated Patient Assessment in a Patient Counseling Evaluation and Perceived Importance of Communication Skills
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
3.2. Comparison of Students’ Self-Assessment and Simulated Patient Assessment
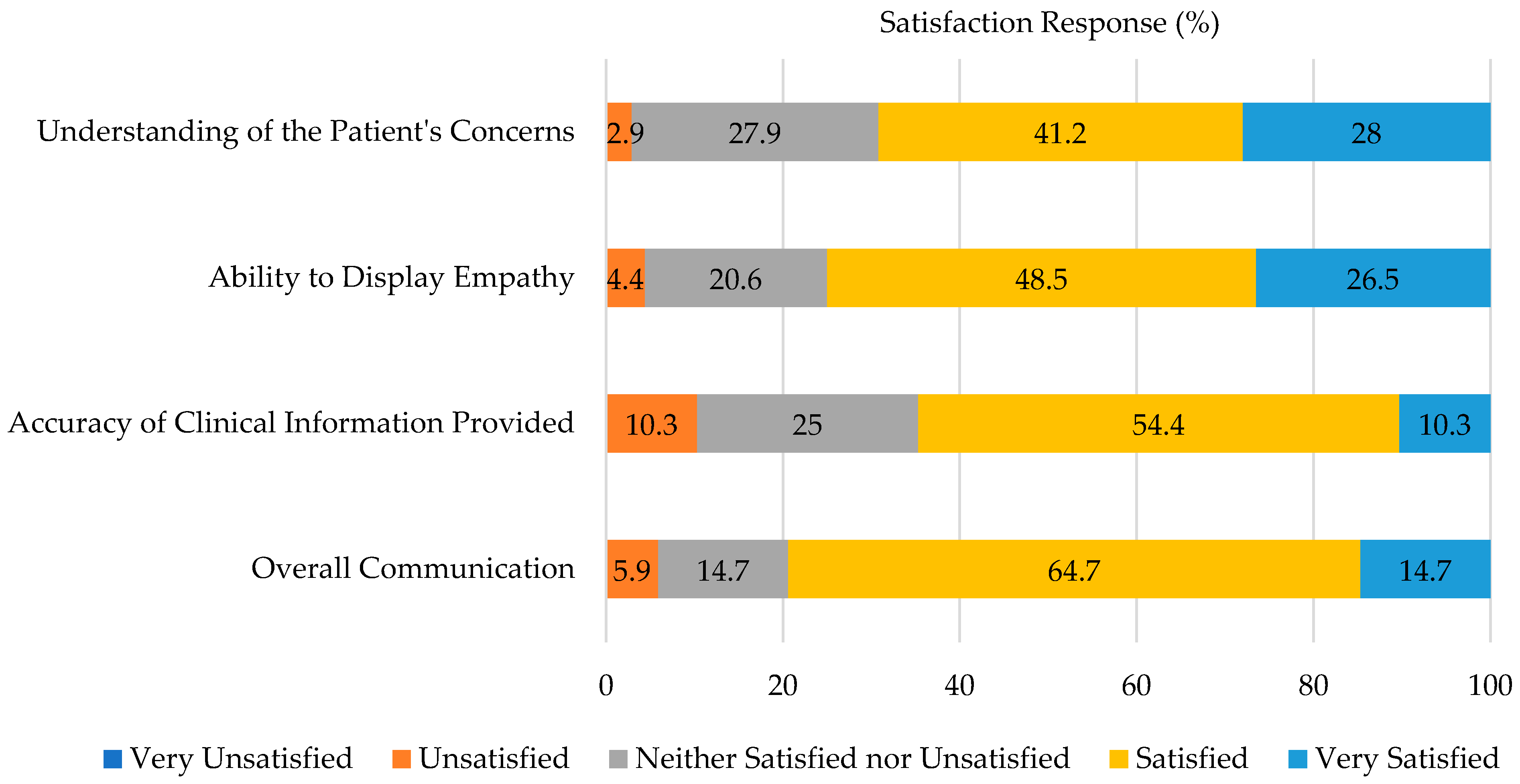
3.3. Evaluation Performance Satisfaction
3.4. Perceptions of Communication Skills
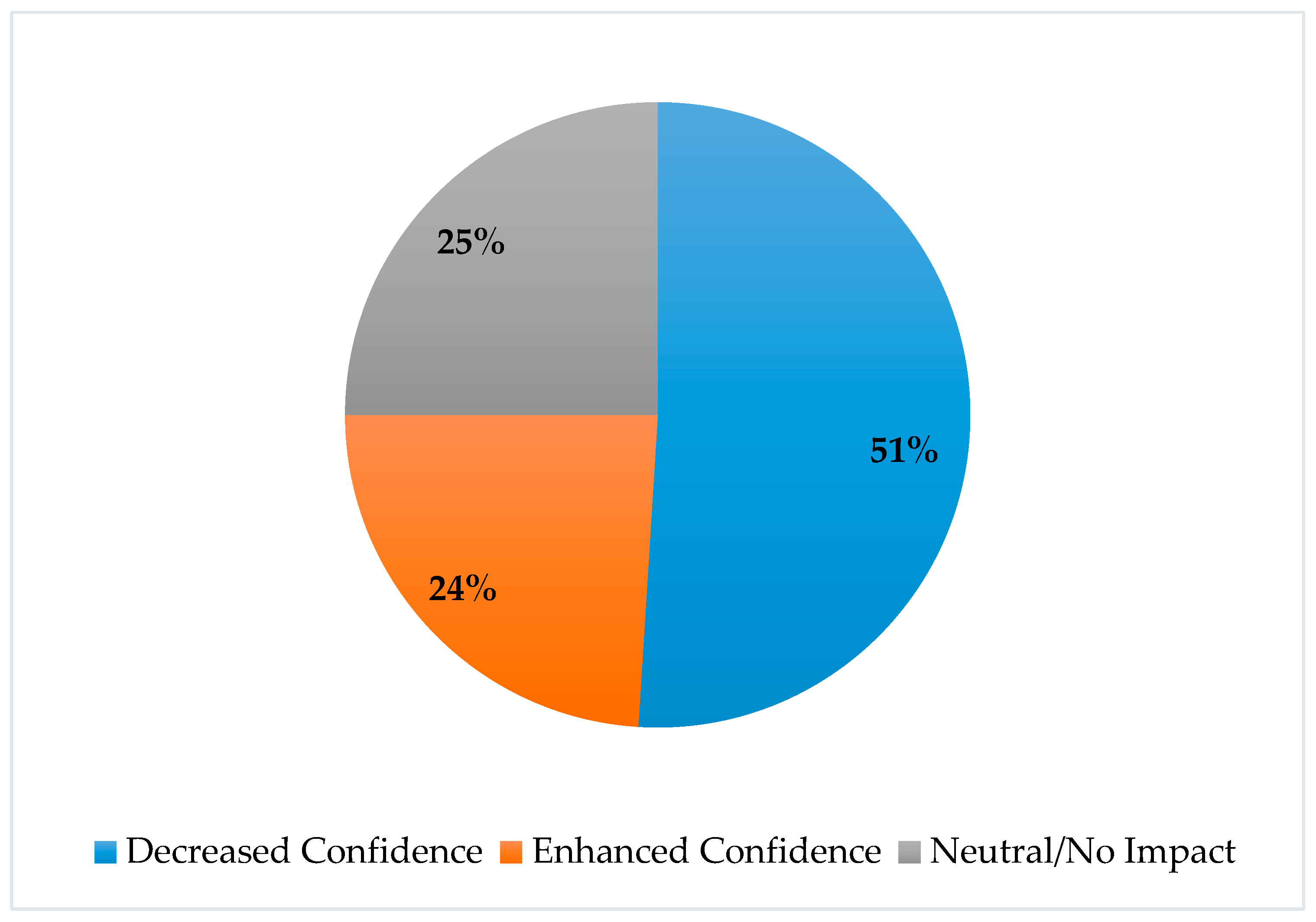
3.5. Perceptions of Virtual Evaluation Format
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liebrecht, C.; Montenery, S. Use of simulated psychosocial role-playing to enhance nursing students’ development of soft skills. Creat. Nurs. 2016, 22, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartzman, E.; Chung, E.P.; Sakharkar, P.; Law, A.V. Instruction and assessment of student communication skills in US and Canadian pharmacy curricula. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2013, 5, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACPE Standards. Accreditation Standards and Key Elements for the Professional Program in Pharmacy Leadings to the Doctor of Pharmacy Degree; Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education: Chicago, IL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- AACP Curriculum Outcomes and Entrustable Professional Activities (COEPA) 2022. American Association of Colleges of Pharmacy. Available online: https://www.aacp.org/sites/default/files/2022-11/coepa-document-final.pdf (accessed on 2 December 2022).
- Ammentorp, J.; Thomsen, J.L.; Jarbøl, D.E.; Holst, R.; Øvrehus, A.L.; Kofoed, P.E. Comparison of the medical students’ perceived self-efficacy and the evaluation of the observers and patients. BMC Med. Educ. 2013, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hache, C.; Honoré, S.; Hache, G. Implementation of a patient-teaching workshop to improve pharmacy students’ competencies in patient-centered communication: A case report. BMC Med. Educ. 2022, 22, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gülpınar, G.; Özçelikay, G. Development of a Structured Communication and Counseling Skills Course for Pharmacy Students: A Simulation-based Approach. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 18, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, H.; Weil, J.; Mukherji, P. Set Up and Execution of an Effective Standardized Patient Program in Medical Simulation. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Smithson, J.; Bellingan, M.; Glass, B.; Mills, J. Standardized patients in pharmacy education: An integrative literature review. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2015, 7, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickles, N.M.; Tieu, P.; Myers, L.; Galal, S.; Chung, V. The impact of a standardized patient program on student learning of communication skills. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2009, 73, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford-Hemming, T.; Alfes, C.M.; Breymier, T.L. A systematic review of the use of standardized patients as a simulation modality in nursing education. Nurs. Educ. Perspect. 2019, 40, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.L.; Bohnert, C.A.; Gammon, W.L.; Hölzer, H.; Lyman, L.; Smith, C.; Thompson, T.M.; Wallace, A.; Gliva-McConvey, G. The Association of Standardized Patient Educators (ASPE) Standards of Best Practice (SOBP). Adv. Simul. 2017, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElGeed, H.; El Hajj, M.S.; Ali, R.; Awaisu, A. The utilization of simulated patients for teaching and learning in the pharmacy curriculum: Exploring pharmacy students’ and recent alumni’s perceptions using mixed-methods approach. BMC Med. Educ. 2021, 21, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawluk, S.A.; Zolezzi, M.; Rainkie, D. Comparing student self-assessments of global communication with trained faculty and standardized patient assessments. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2018, 10, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanch-Hartigan, D. Medical students’ self-assessment of performance: Results from three meta-analyses. Patient Educ. Couns. 2011, 84, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lempicki, K.A.; Mazan, J.L.; D’Souza, J.J.; Harpe, S.E. Analysis of pharmacy student communication self-evaluation skills during standardized patient encounters. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2021, 13, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murry, L.T.; Reist, J.C.; Fravel, M.A.; Knockel, L.E.; Witry, M.J. An exploratory mixed methods study of standardized patient comments on empathy and student communication scores. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2022, 86, ajpe8642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, C.M.; Metcalfe, A.; Spivey, C.; Renfro, C.P.; Schoelles, J. Comparison of student performance in therapeutics and communications courses to outcomes of objective structured clinical examinations: A retrospective analysis. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2022, 14, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, L.M.; Shogbon, A.O.; Momary, K.M.; Rogers, H.K. A comparison of students’ self-assessments with faculty evaluations of their communication skills. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2013, 77, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mort, J.R.; Hansen, D.J. First-year pharmacy students’ self-assessment of communication skills and the impact of video review. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2010, 74, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchouse, C.; McCafferty, C. Standardized Patients Versus Simulated Patients: Is There a Difference? Clin. Simul. Nurs. 2012, 8, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harackiewicz, J.M.; Smith, J.L.; Priniski, S.J. Interest matters: The importance of promoting interest in education. Policy Insights Behav. Brain Sci. 2016, 3, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.; Bolliger, D.U. Engagement matters: Student perceptions on the importance of engagement strategies in the online learning environment. Online Learn. 2018, 22, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoular, S.; Huntsberry, A.; Patel, T.; Wettergreen, S.; Brunner, J.M. Transitioning competency-based communication assessments to the online platform: Examples and student outcomes. Pharmacy 2021, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanLangen, K.M.; Sahr, M.J.; Salvati, L.A.; Meny, L.M.; Bright, D.R.; Sohn, M. Viability of virtual skills-based assessments focused on communication. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2021, 85, 8378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillette, C.; Rudolph, M.; Rockich-Winston, N.; Stanton, R.; Anderson, H.G., Jr. Improving pharmacy student communication outcomes using standardized patients. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2017, 81, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.C.; Wallace, T.D.; Yu, F.S. Pharmacy faculty and students’ perceptions of standardized patients for objective structured clinical examinations. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2019, 11, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garling, K.A. Revitalization of a communication pharmacy course: The journey of reframing student perceptions. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2022, 14, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, C.E.; Stafford, R.; Franks, A.M. Establishment of a patient-centered communication course to address curricular gaps. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2018, 10, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, J.M.; McNair, C.D.; Linnebur, S.A.; Valdez, C.; Trujillo, T.C. The impact of a standalone, patient-centered communication course series on student achievement, preparedness, and attitudes. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2016, 80, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
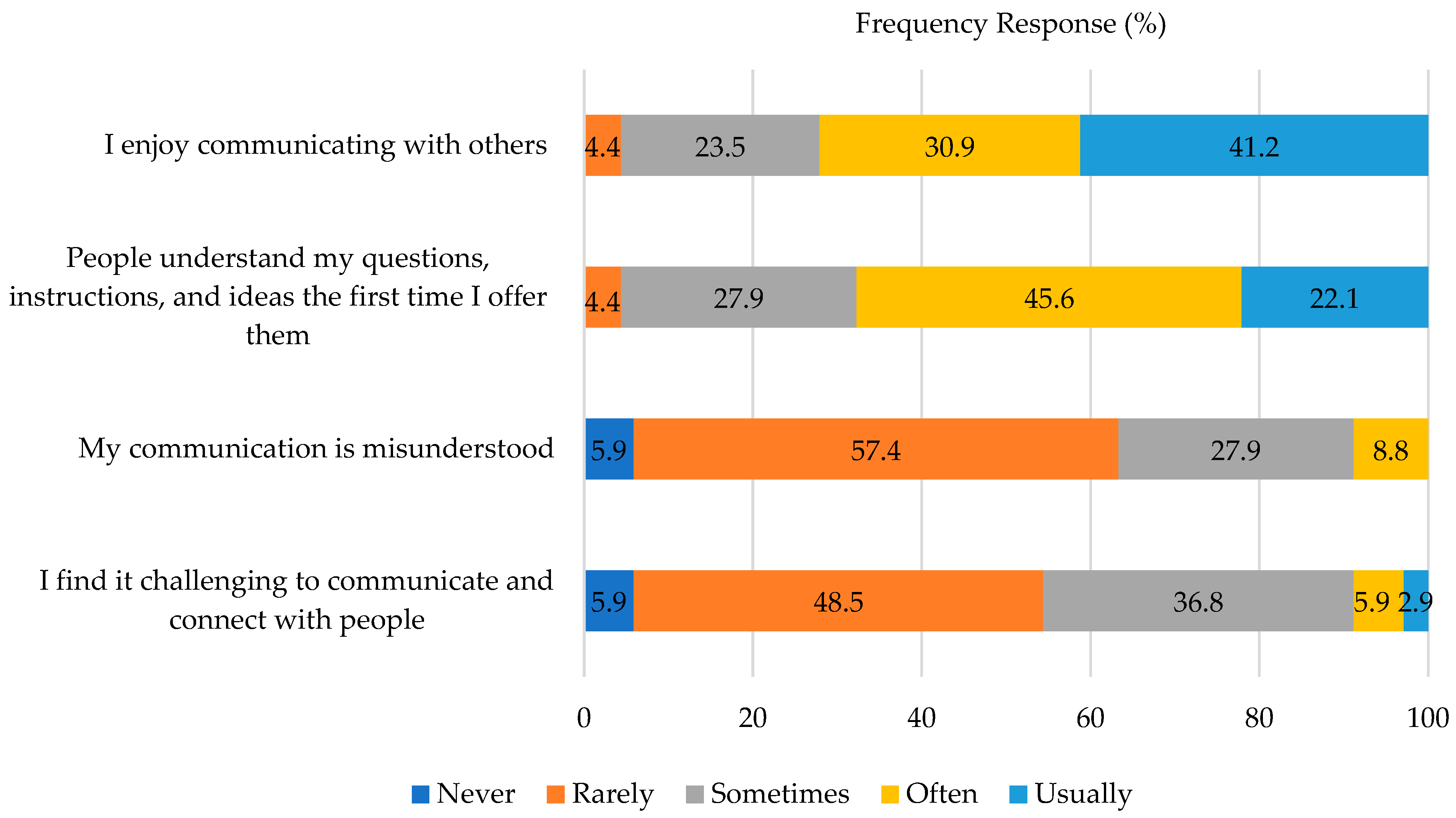
| Age (mean, SD) | 26 years ± 5.03 |
| Gender (Female; n, %) | 47 (69.12) |
| Race | |
| Asian | 20 (29.41) |
| Asian and White or Caucasian | 2 (2.94) |
| Black or African American | 1 (1.47) |
| White or Caucasian | 40 (58.82) |
| Other | 3 (4.41) |
| Prefer not to answer | 2 (2.94) |
| Ethnicity | |
| Hispanic/Latino | 11 (16.18) |
| Non-Hispanic/Latino | 52 (76.47) |
| Prefer not to answer | 5 (7.35) |
| Patient Counseling Component | SP Rating (n, %) | Self-Assessment Rating (n, %) | SP Versus Self-Assessment (p-Value) a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Completed Chunks and Checks | 1.0 | ||
| Yes | 64 (94.1) | 62 (91.2) | |
| No | 9 (5.9) | 6 (8.8) | |
| Demonstrated Empathy | 0.17 | ||
| Yes | 41 (60.3) | 41 (60.3) | |
| Partially | 21 (30.9) | 26 (38.2) | |
| No | 6 (8.8) | 1 (1.5) | |
| Non-Verbal Communication | 0.57 | ||
| Yes | 51 (75) | 38 (55.9) | |
| Partially | 17 (25) | 30 (44.1) | |
| No | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Used Patient-Friendly Language | 0.22 | ||
| Yes | 56 (82.4) | 57 (83.8) | |
| Partially | 11 (16.2) | 11 (16.2) | |
| No | 1 (1.5) | 0 (0) |
| Statement | Rating, n (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strongly Disagree | Somewhat Disagree | Neither Agree nor Disagree | Somewhat Agree | Strongly Agree | |
| I believe that the development of soft skills, such as empathy, is an important aspect of being a pharmacist. | 0 | 1 (1.5) | 4 (5.9) | 7 (10.3) | 56 (82.4) |
| I recognize the importance of communication skills to my future practice as a pharmacist. | 0 | 0 | 2 (2.9) | 4 (5.9) | 62 (91.2) |
| I feel that communication is important to developing patient rapport and trust as a healthcare professional. | 0 | 0 | 3 (4.4) | 4 (5.9) | 61 (89.7) |
| Impact of the Virtual Format of the Evaluation on Your Ability to… | Rating, n (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hindered My Ability | Neutral/No Impact | Enhanced My Ability | |
| Provide Empathy | 28 (41.2) | 34 (50) | 6 (8.9) |
| Develop a Trusting Relationship with the Patient | 31 (45.6) | 34 (50) | 3 (4.4) |
| Demonstrate Non-Verbal Communication | 41 (60.3) | 21 (30.9) | 6 (8.9) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wettergreen, S.A.; Pearson, M.J.; Scoular, S.K. Comparison of Students’ Self-Assessment and Simulated Patient Assessment in a Patient Counseling Evaluation and Perceived Importance of Communication Skills. Pharmacy 2022, 10, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy10060177
Wettergreen SA, Pearson MJ, Scoular SK. Comparison of Students’ Self-Assessment and Simulated Patient Assessment in a Patient Counseling Evaluation and Perceived Importance of Communication Skills. Pharmacy. 2022; 10(6):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy10060177
Chicago/Turabian StyleWettergreen, Sara A., Maria J. Pearson, and Sarah K. Scoular. 2022. "Comparison of Students’ Self-Assessment and Simulated Patient Assessment in a Patient Counseling Evaluation and Perceived Importance of Communication Skills" Pharmacy 10, no. 6: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy10060177
APA StyleWettergreen, S. A., Pearson, M. J., & Scoular, S. K. (2022). Comparison of Students’ Self-Assessment and Simulated Patient Assessment in a Patient Counseling Evaluation and Perceived Importance of Communication Skills. Pharmacy, 10(6), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy10060177






